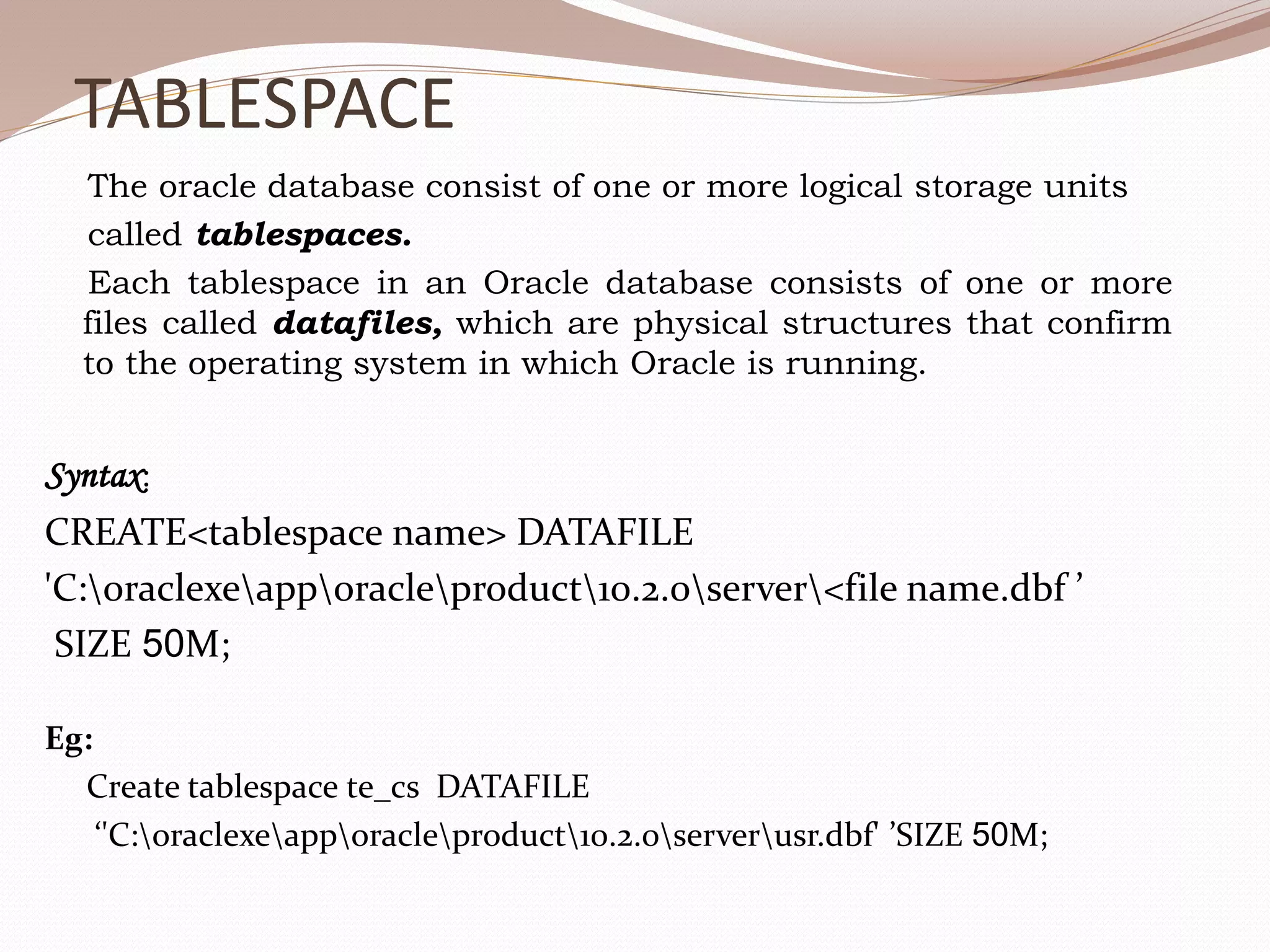
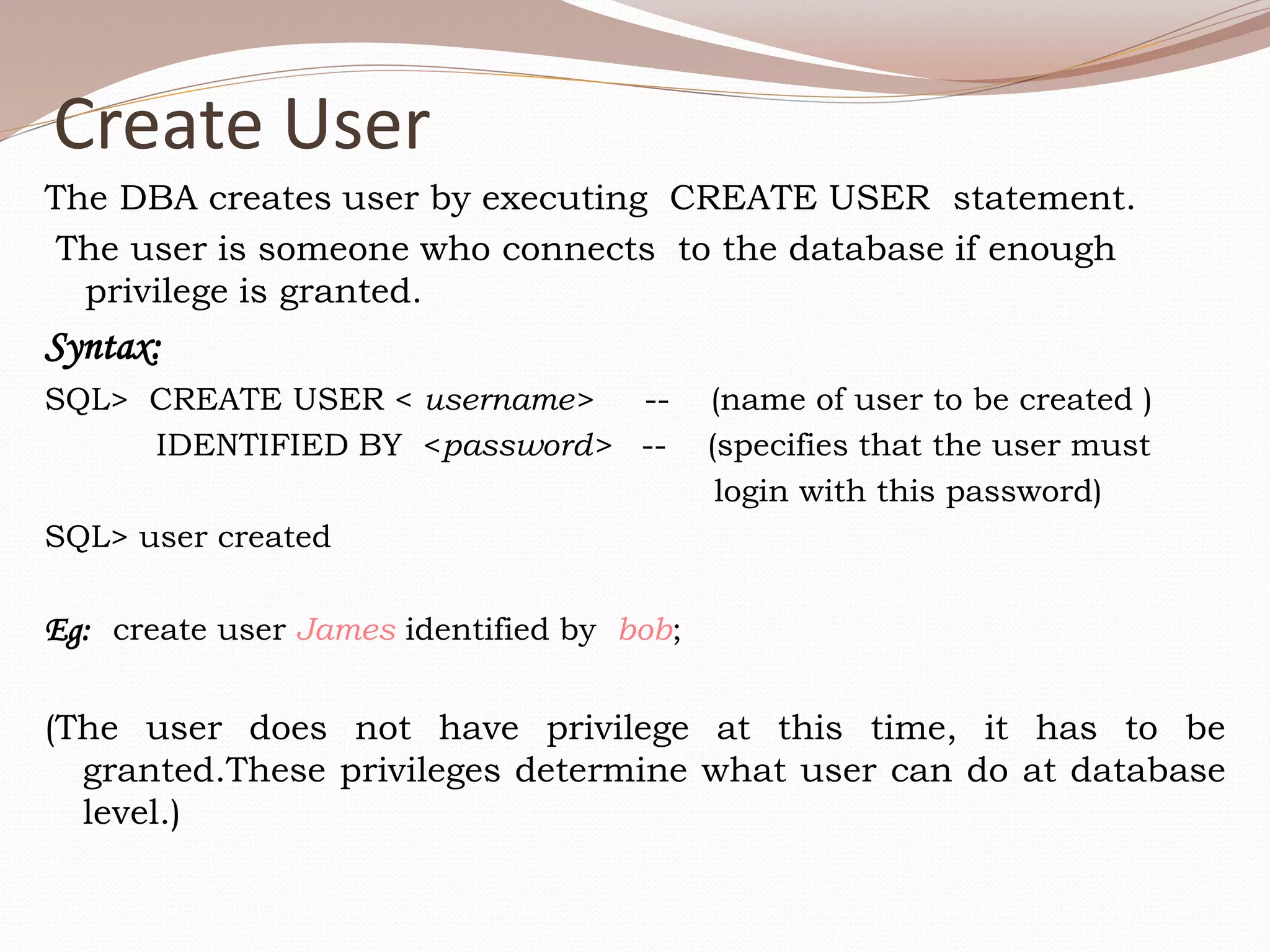
This document provides an overview of database administration tasks in Oracle including creating databases and tablespaces, managing users, granting and revoking privileges, managing passwords, and using roles. The key points covered are: - How to create databases and tablespaces using the CREATE statements. - How to create users with the CREATE USER statement and initialize passwords. - The types of privileges (system and object) and how to grant privileges to users using the GRANT statement. - How to change user passwords using the ALTER USER statement. - How to group related privileges as roles and grant roles to users. - How to revoke privileges from users using the REVOKE statement.





![GRANT : The DBA uses the GRANT statement to allocate system privileges to other user. Syntax: SQL> GRANT privilege [privilege…. … ] TO USER ; SQL> Grant succeeded Eg: Grant create session, create table, create view to James;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/databaseadministrationppt-151018193258-lva1-app6892/75/Database-administration-commands-8-2048.jpg)
![Object privileges vary from object to object.An owner has all privilege or specific privileges on object. SQL> GRANT object_priv [(column)] ON object TO user; SQL>GRANT select, insert ON emp TO James; SQL>GRANT select ,update (e_name,e_address) ON emp TO James;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/databaseadministrationppt-151018193258-lva1-app6892/75/Database-administration-commands-9-2048.jpg)


![REVOKE REVOKE statement is used to remove privileges granted to other users.The privileges you specify are revoked from the users. Syntax: REVOKE [privilege.. …] ON object FROM user Eg: REVOKE create session,create table from James; REVOKE select ,insert ON emp FROM James](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/databaseadministrationppt-151018193258-lva1-app6892/75/Database-administration-commands-12-2048.jpg)
