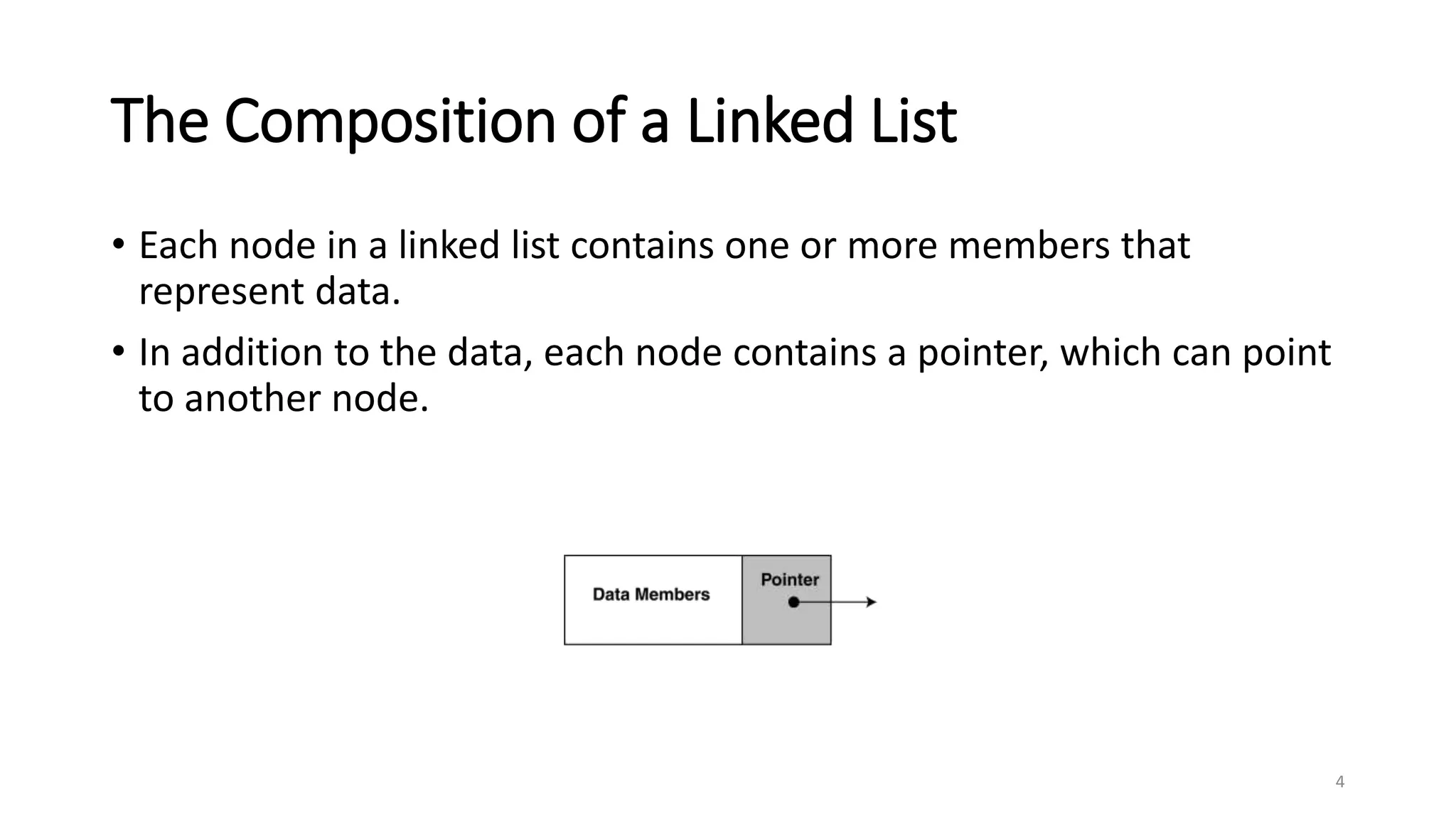
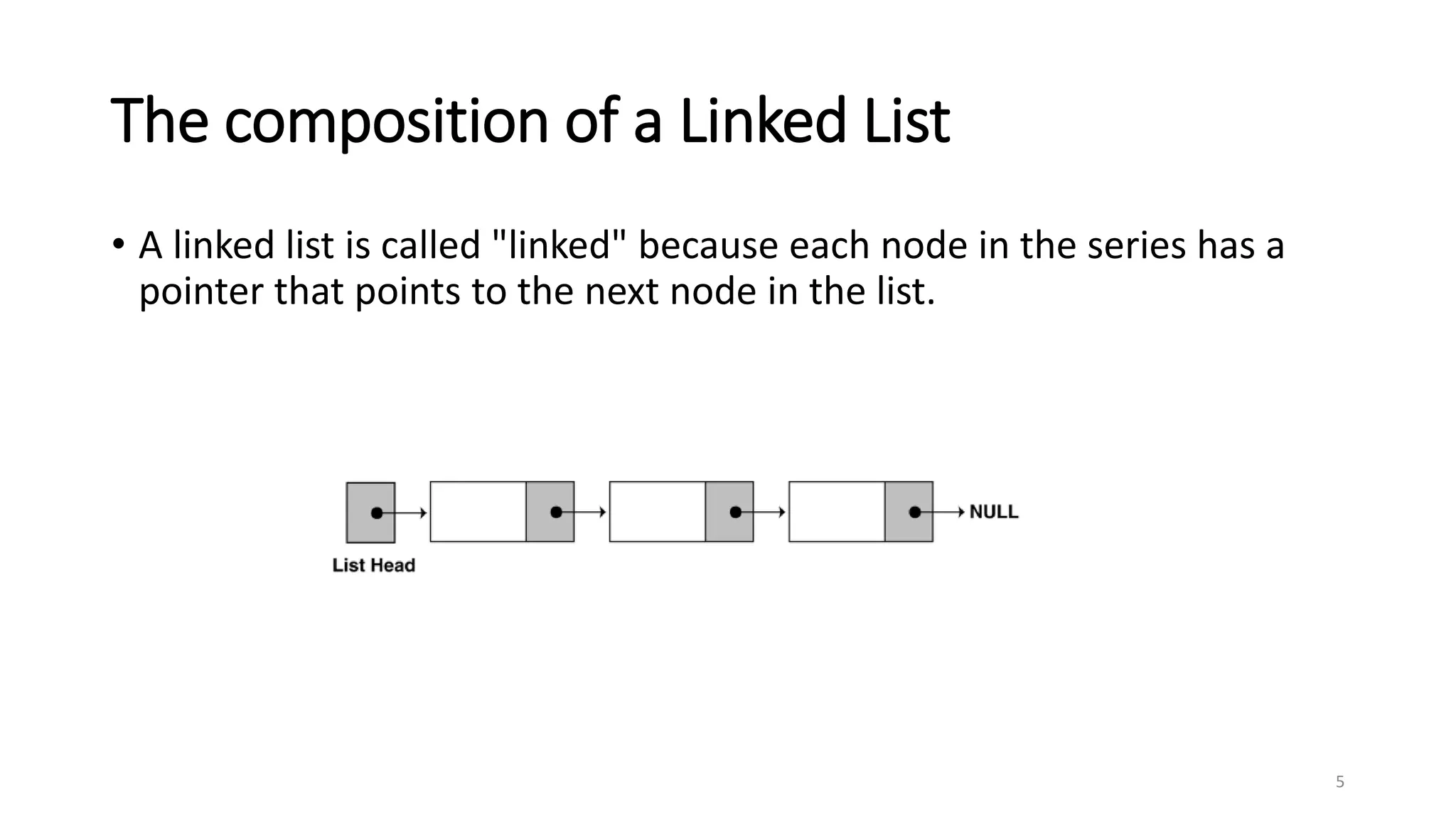
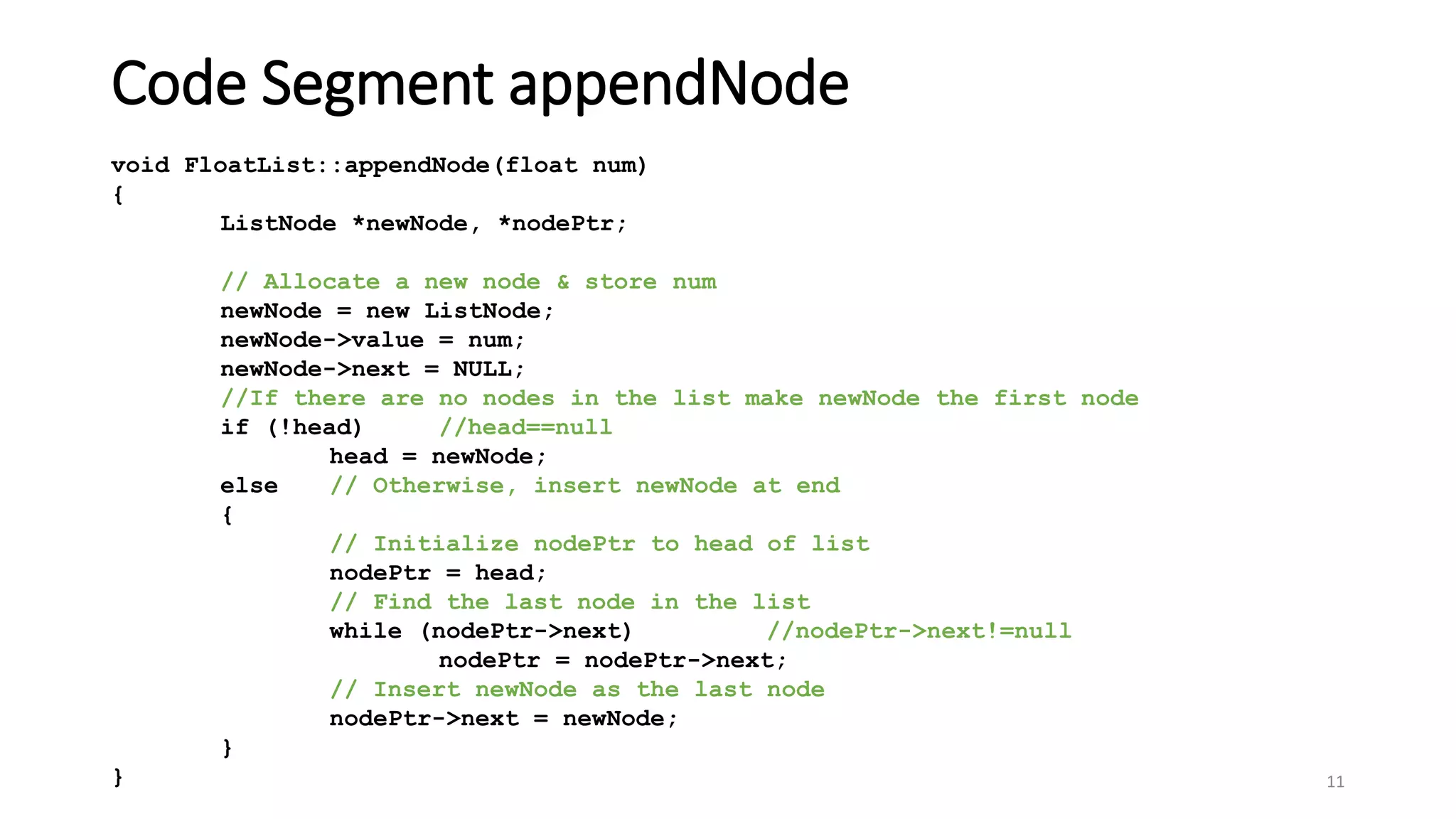
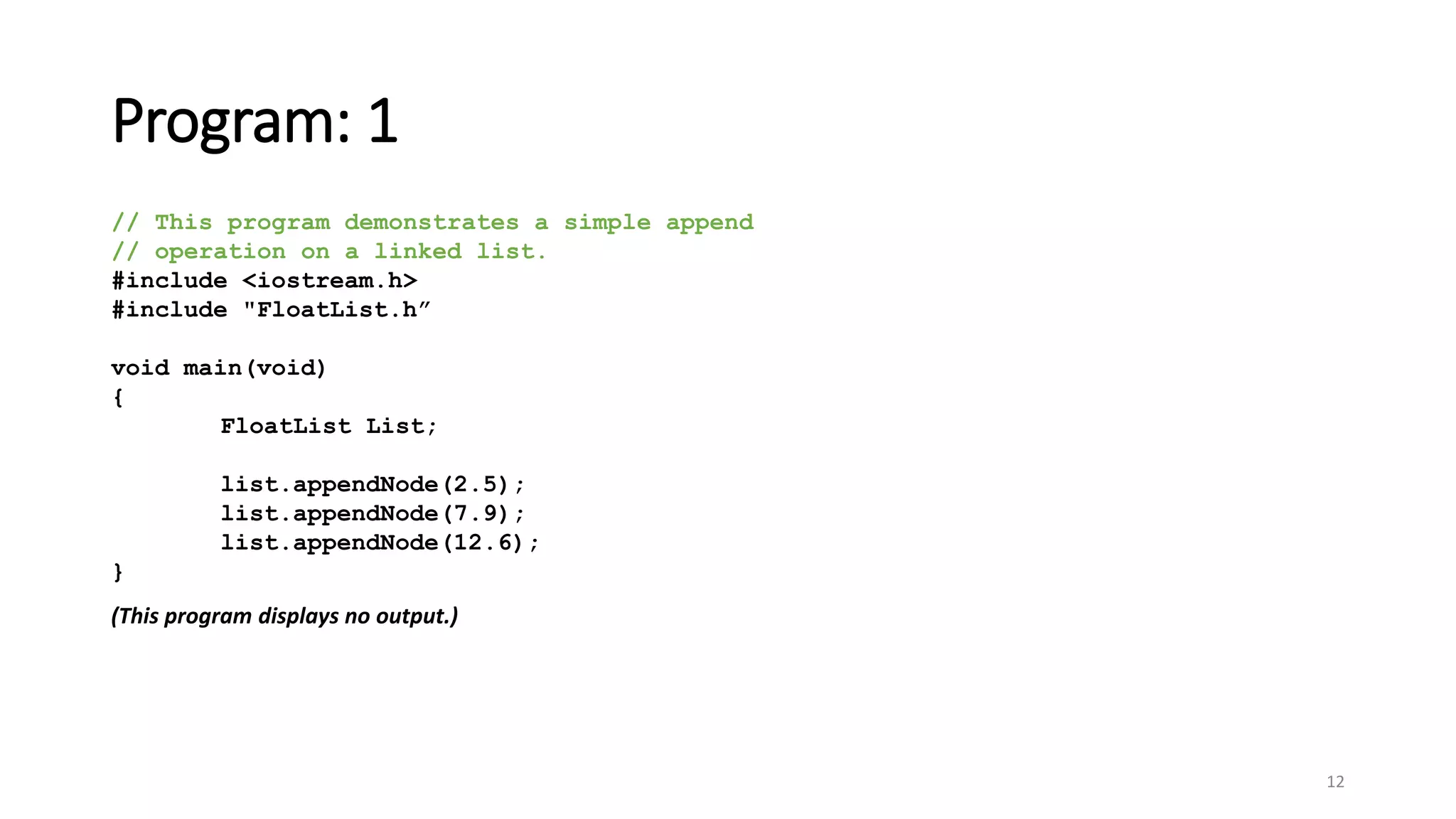
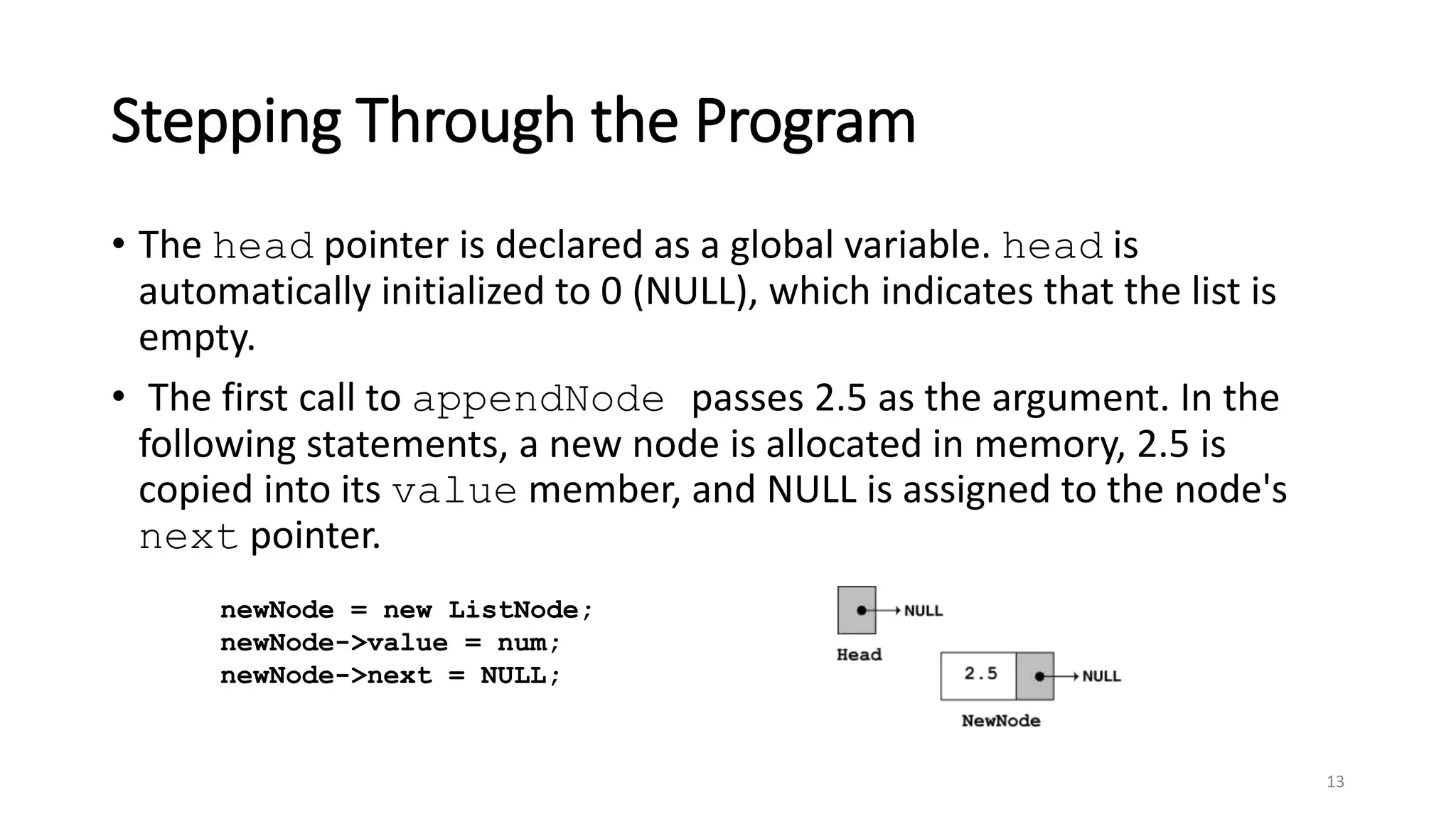
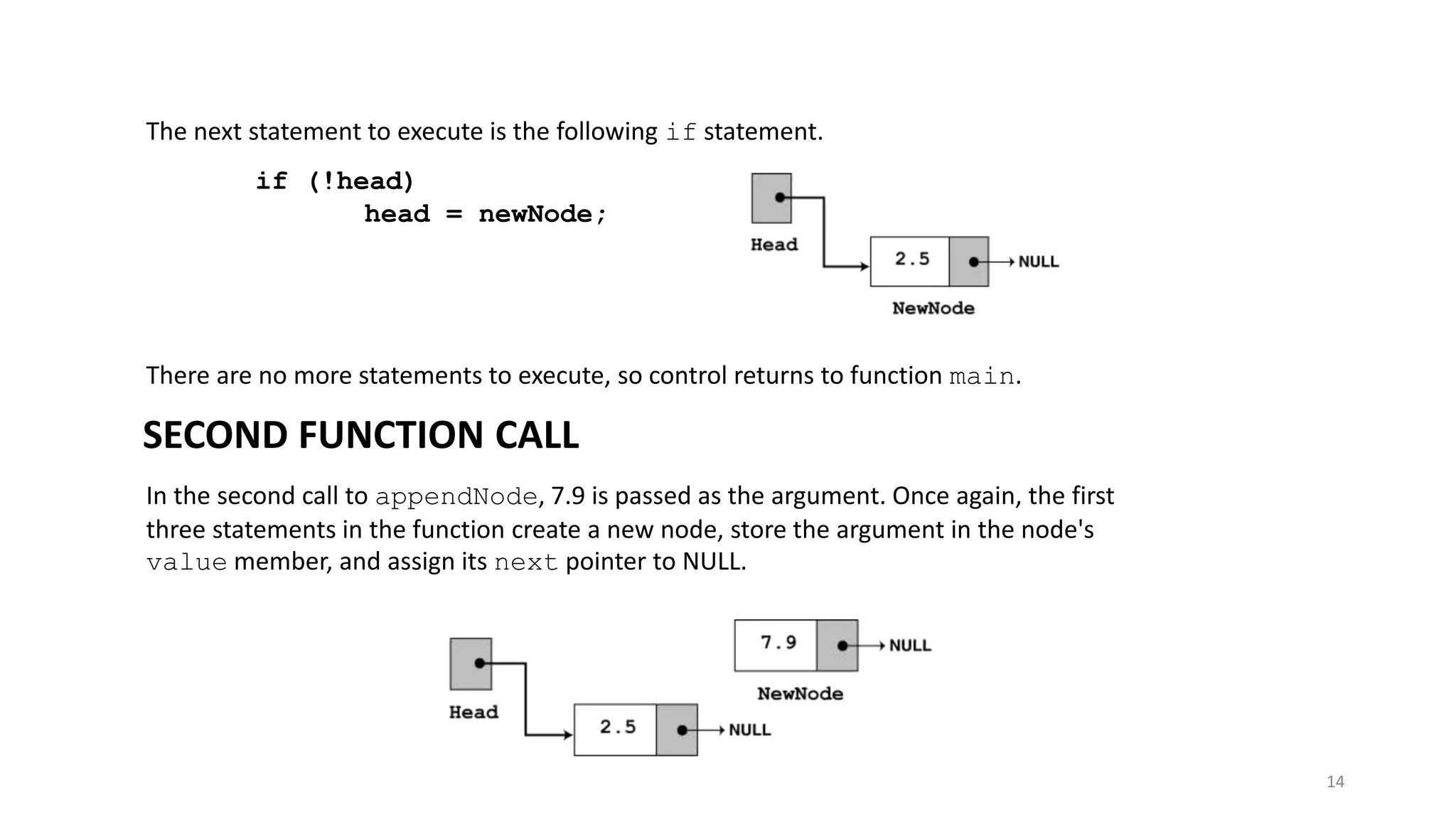
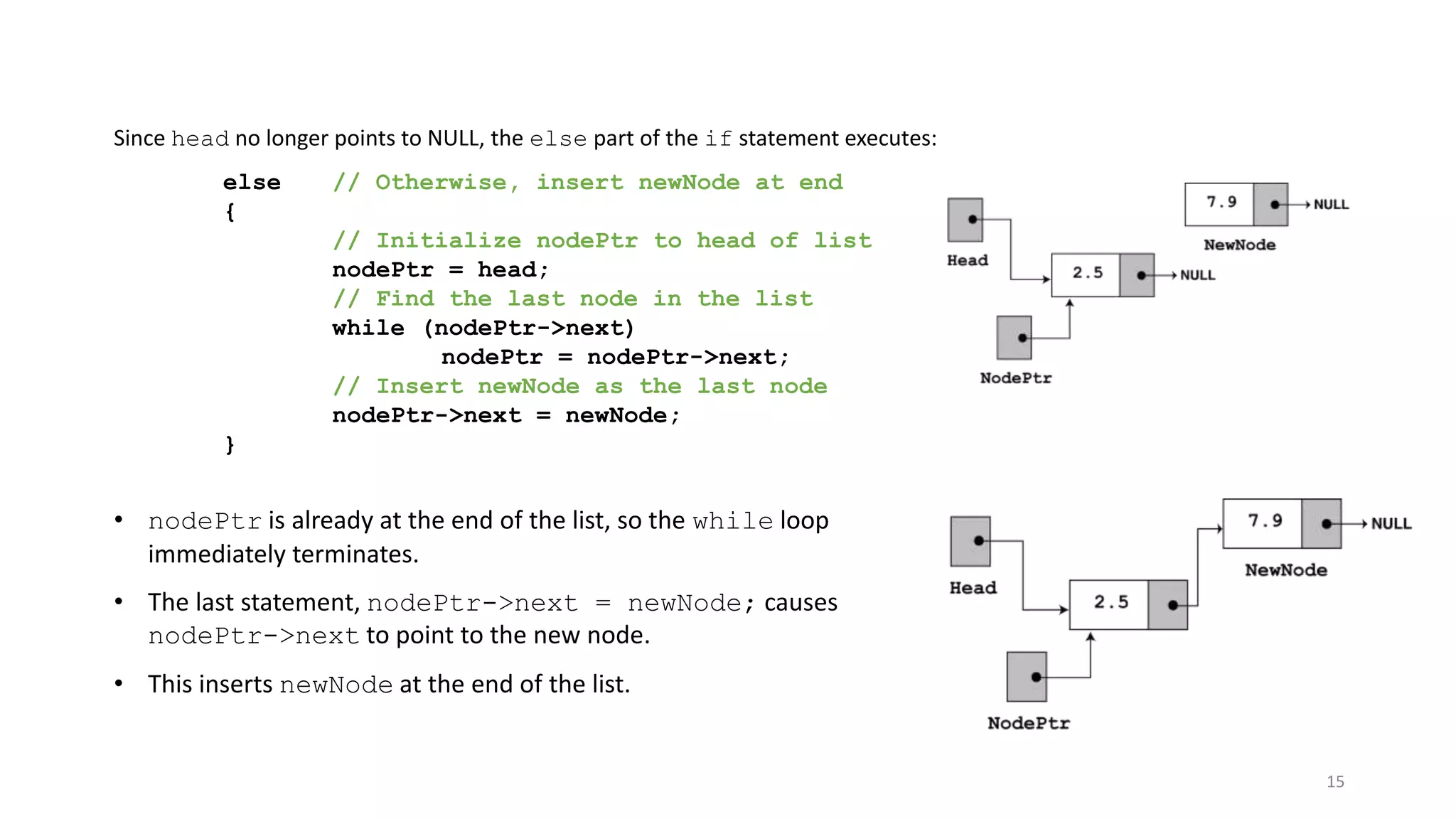
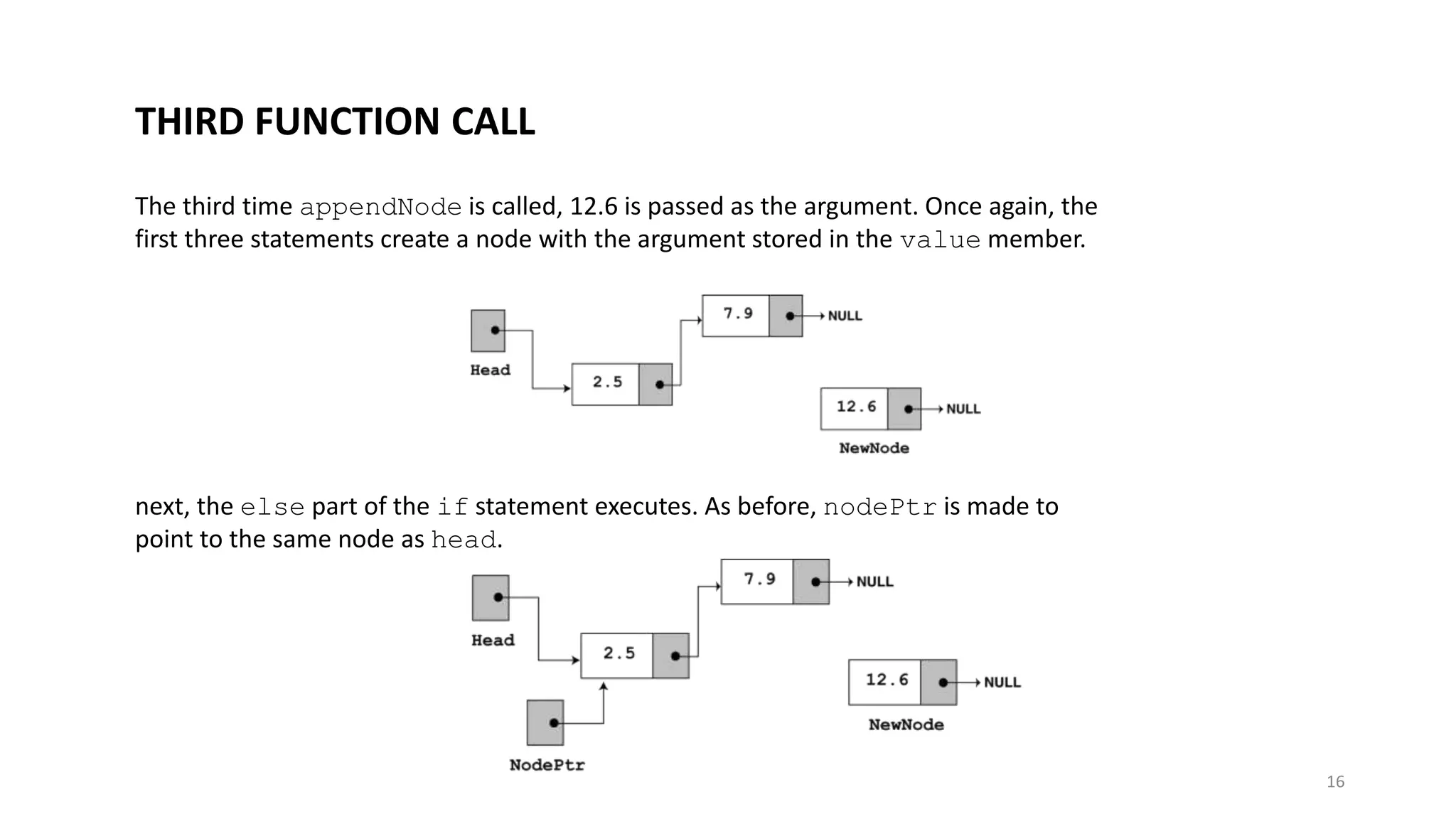
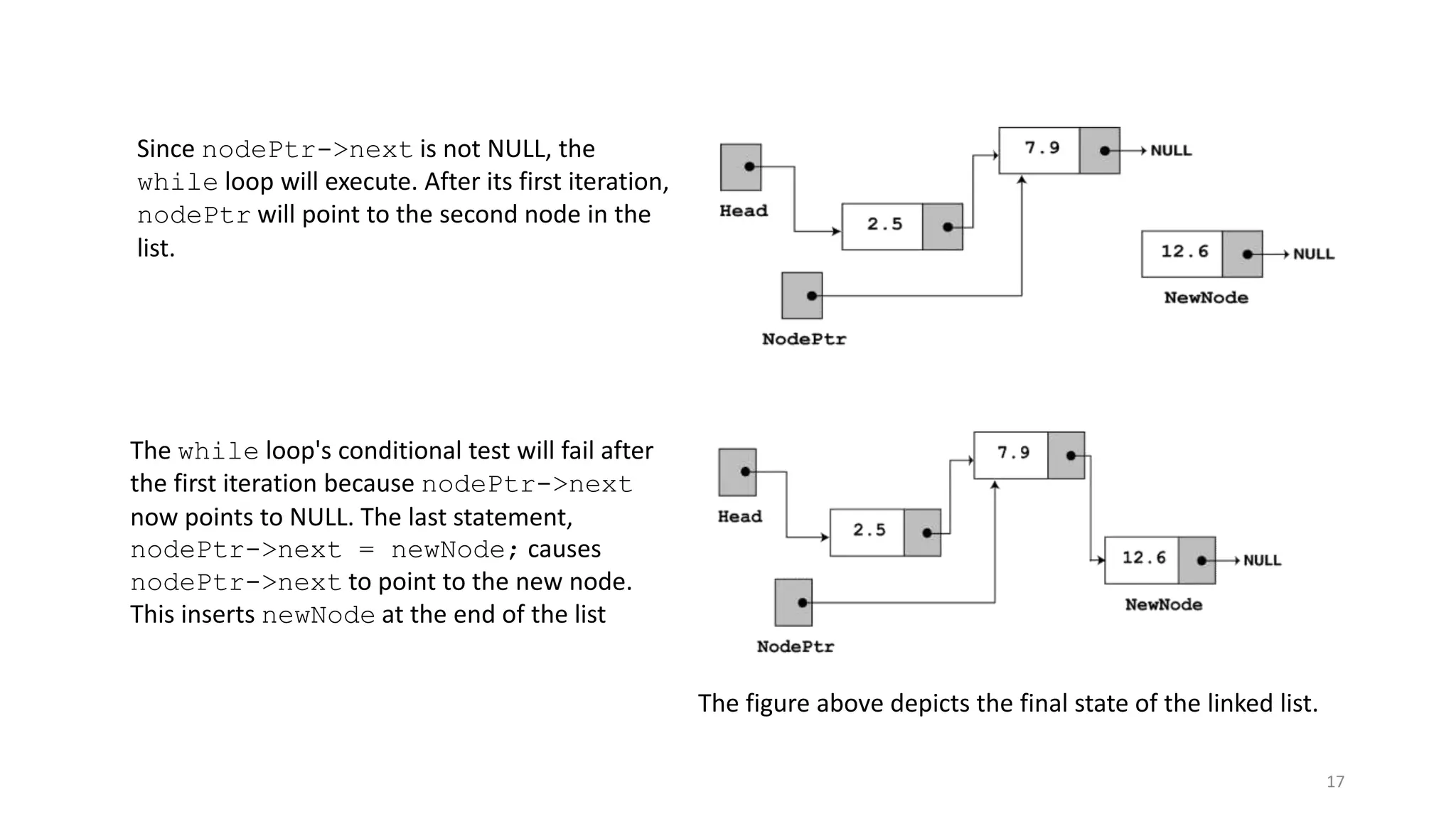
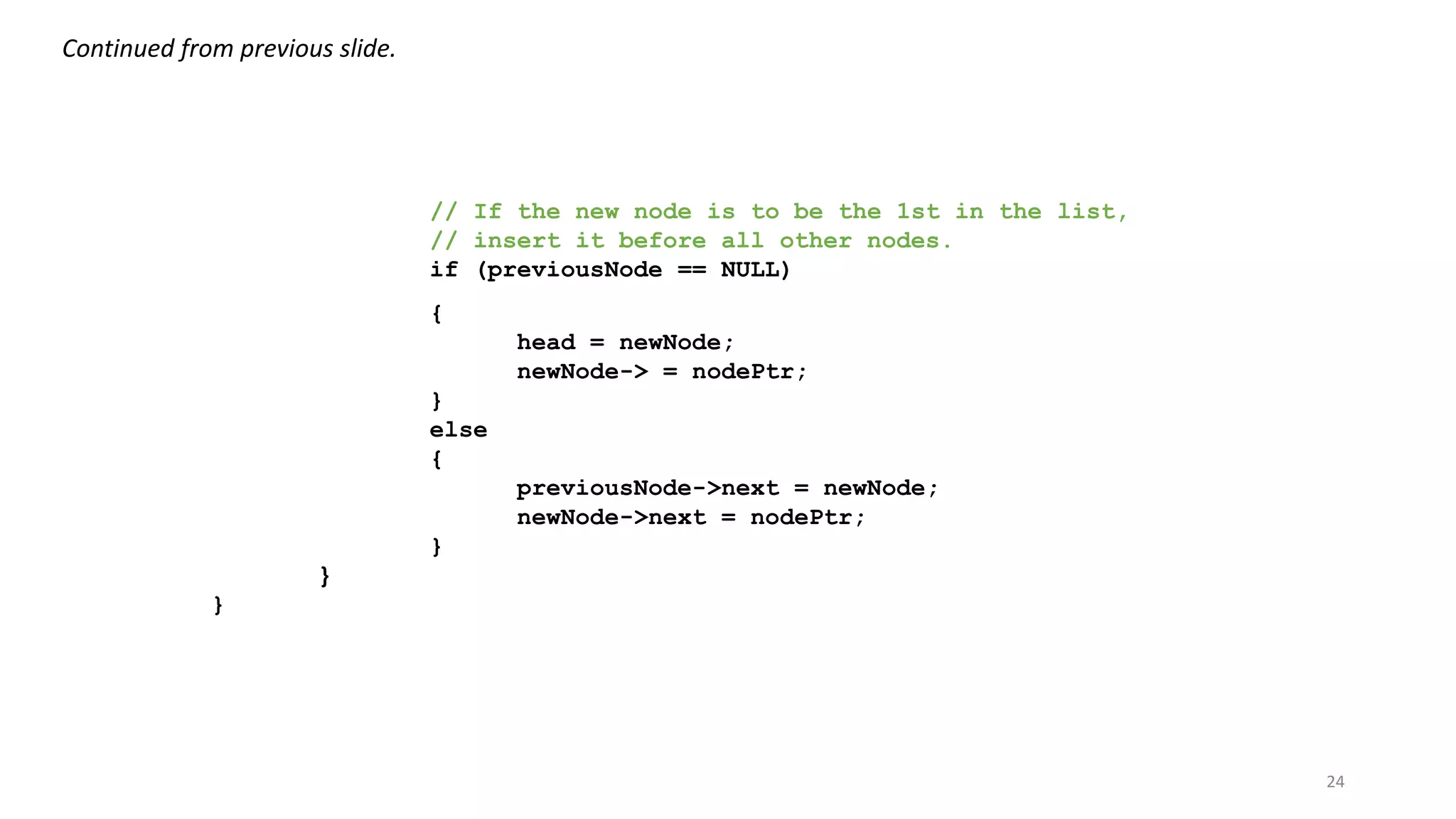
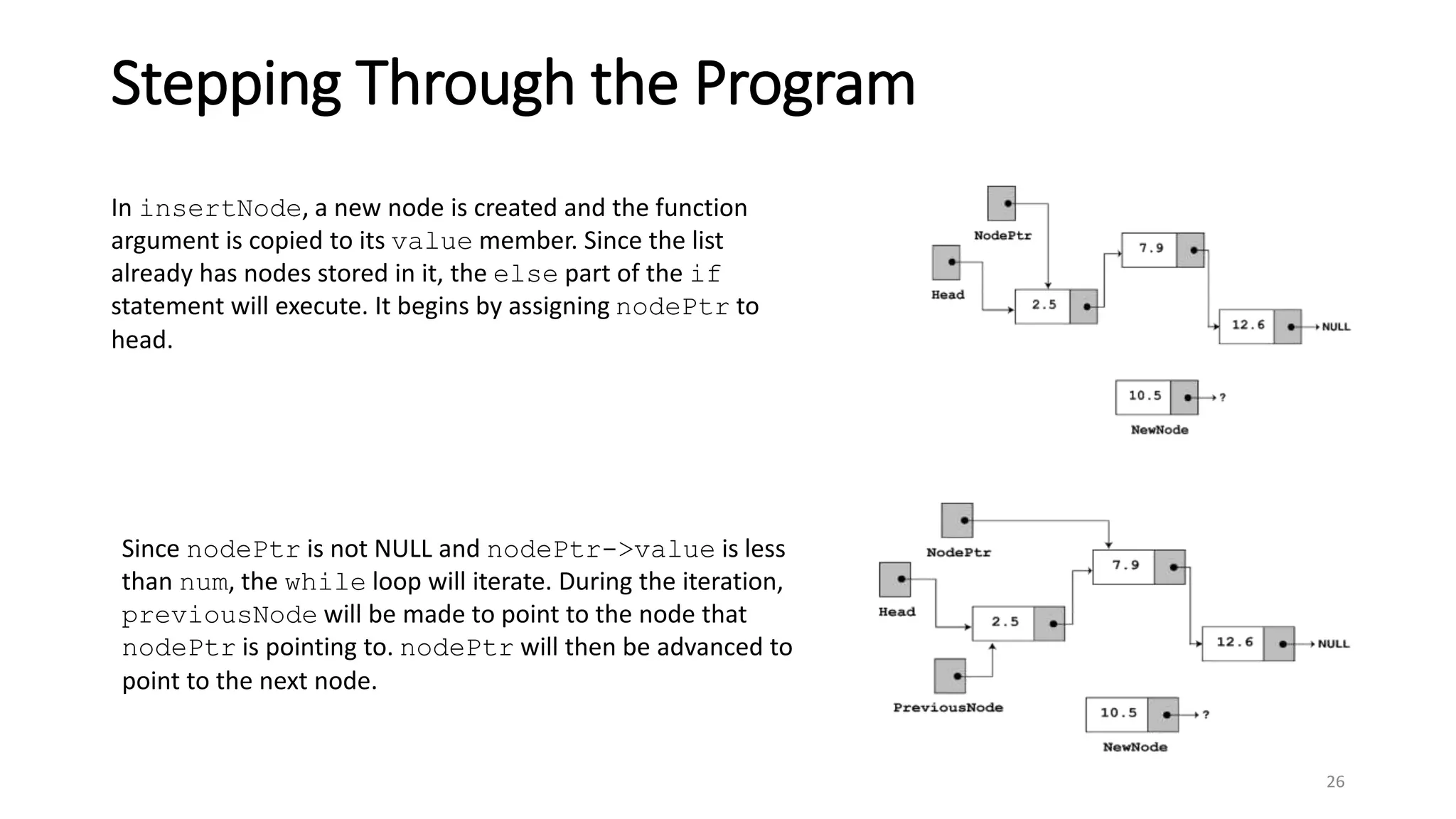
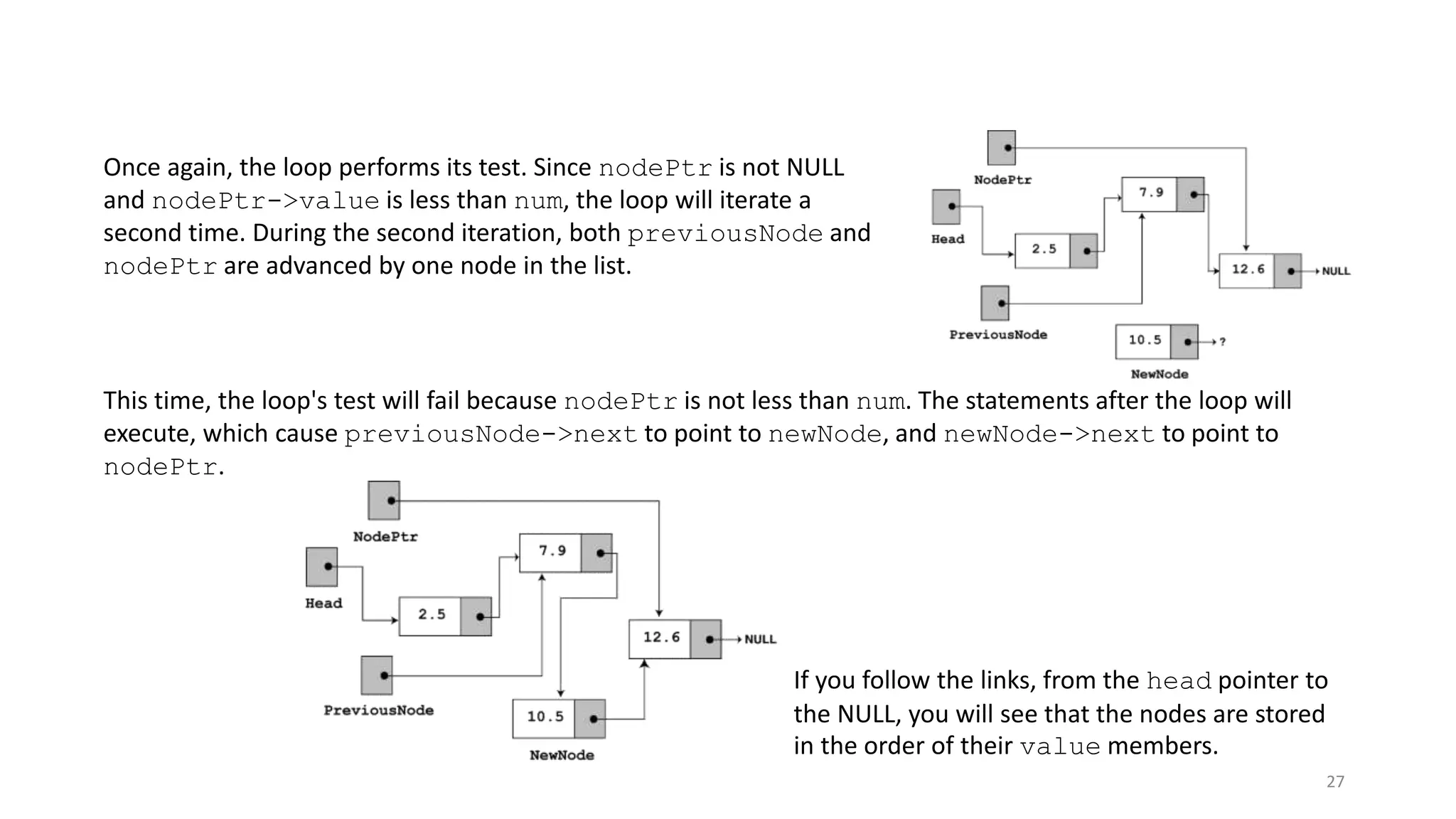
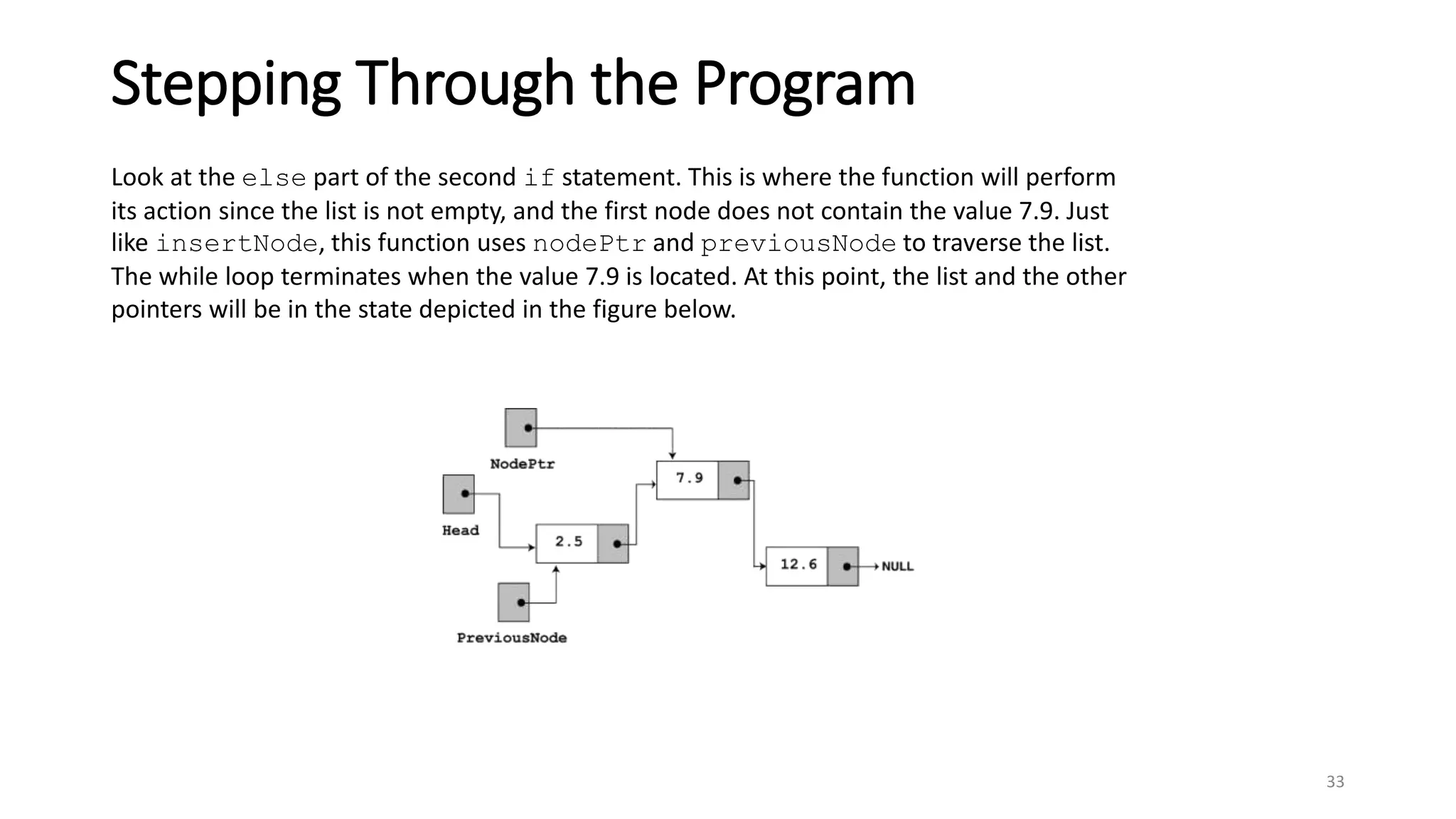
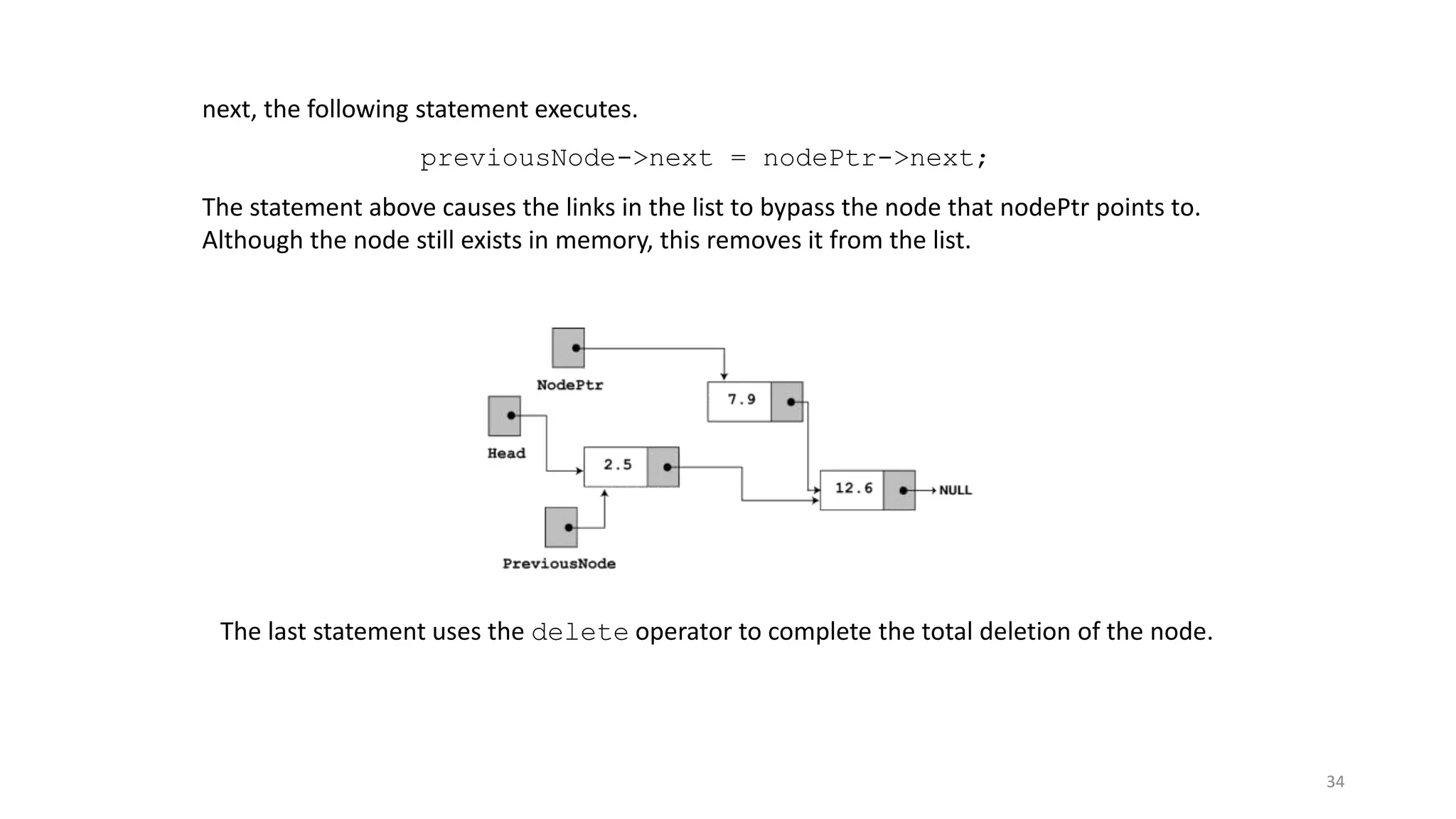
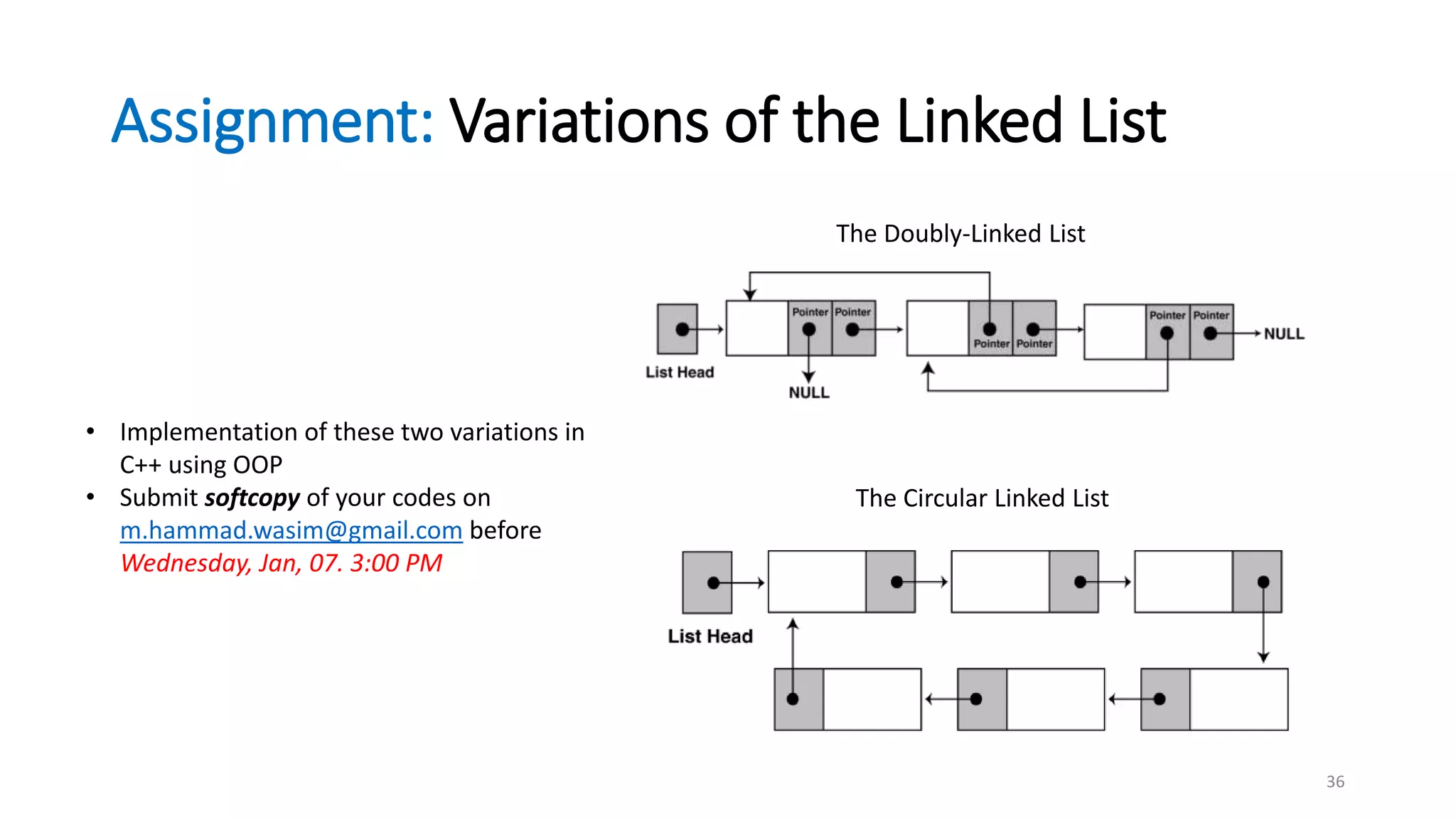
- A linked list is a data structure where each node contains a data field and a pointer to the next node. - It allows dynamic size and efficient insertion/deletion compared to arrays. - A doubly linked list adds a pointer to the previous node, allowing traversal in both directions. - A circular linked list connects the last node back to the first node, making it a continuous loop. - Variations require changes to the node structure and functions like append/delete to handle the added previous/next pointers.