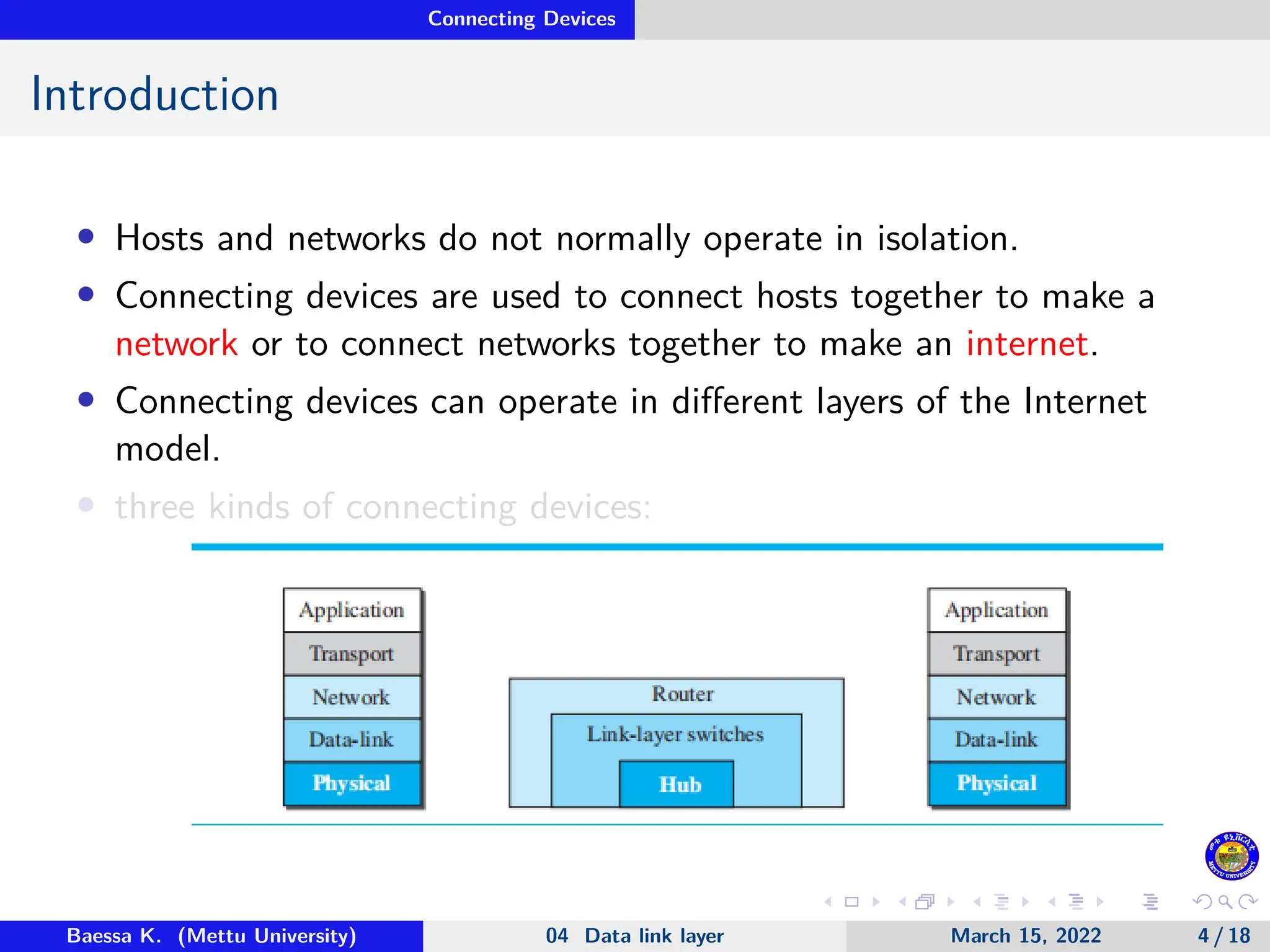
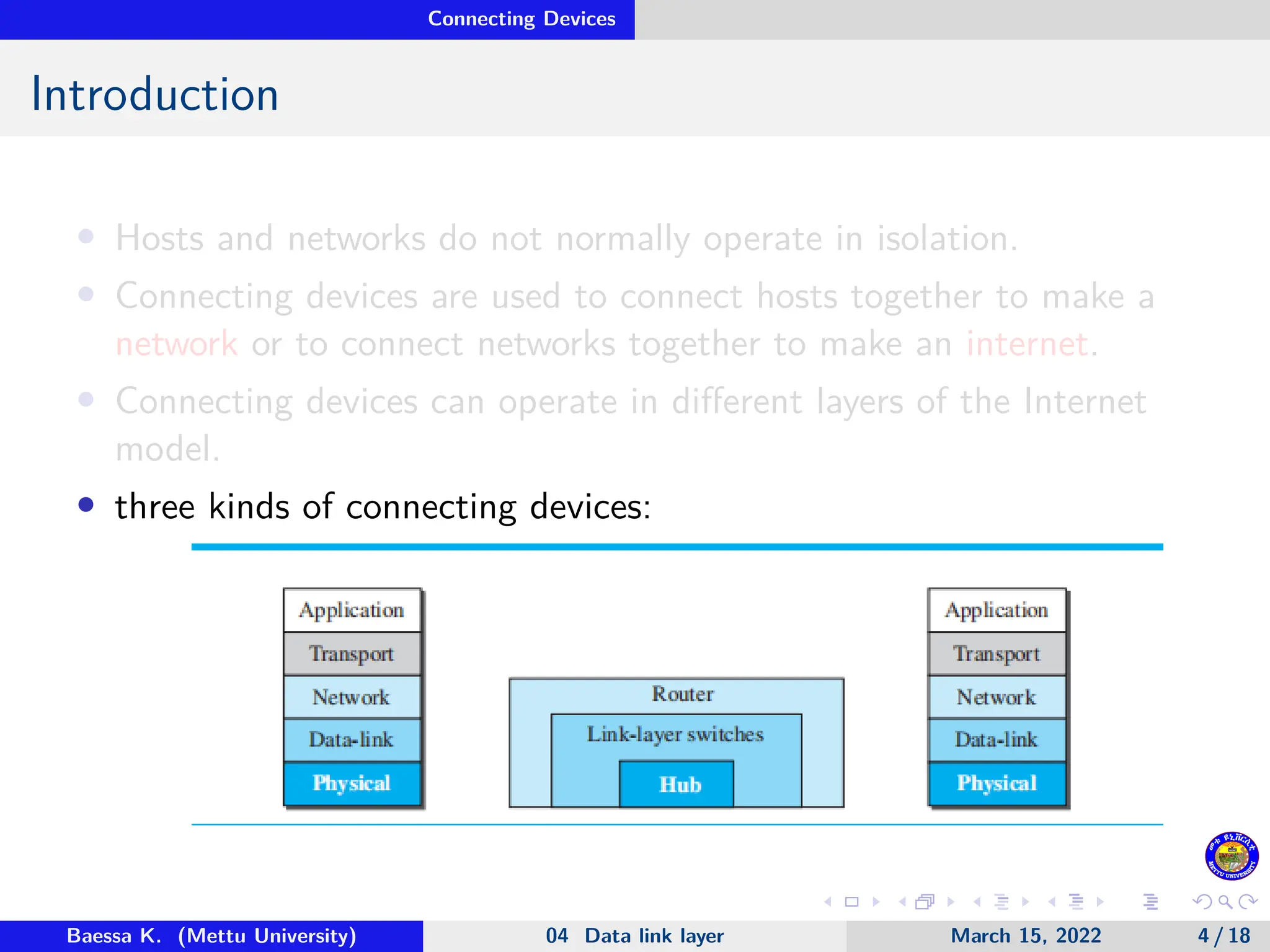
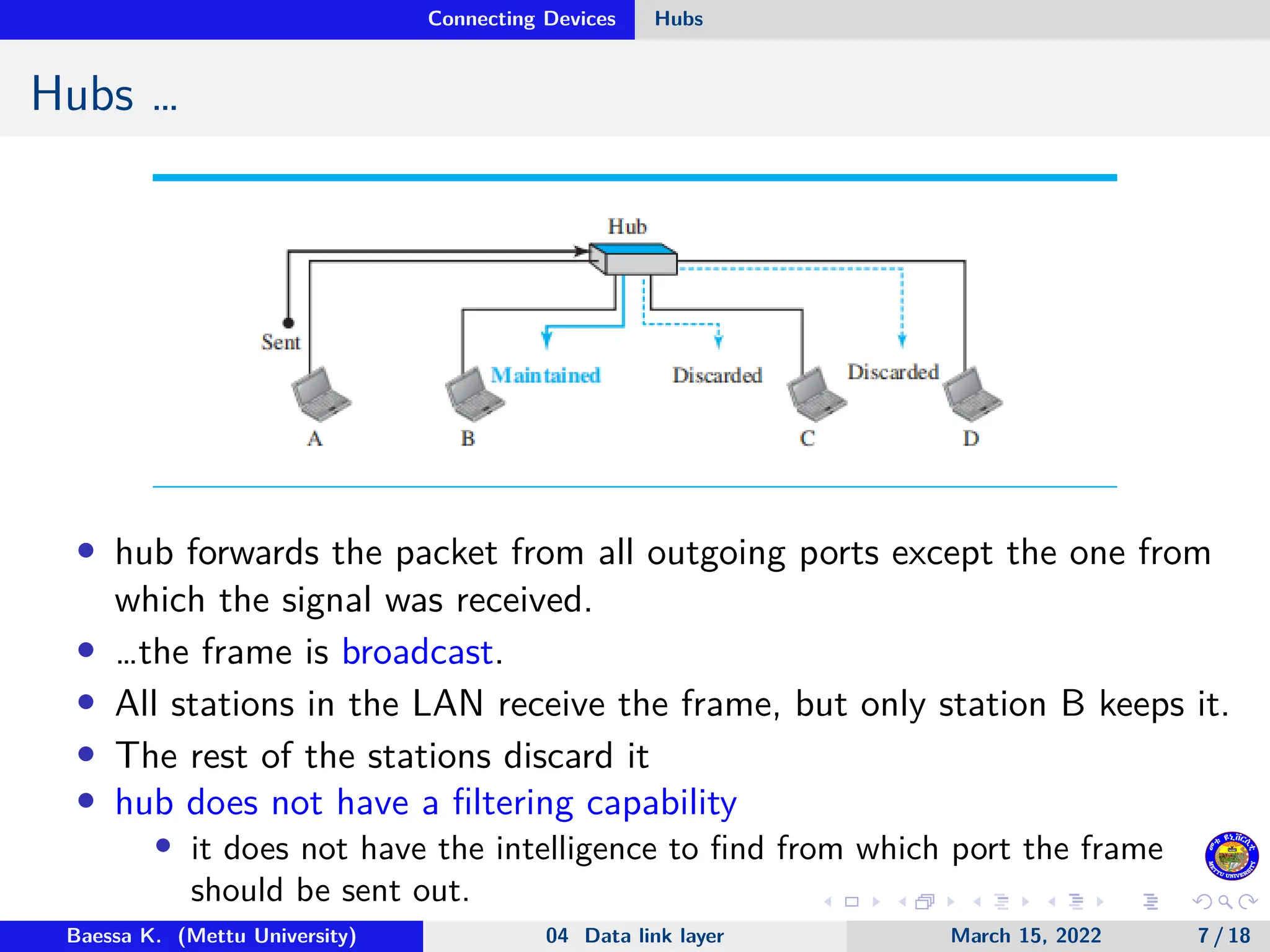
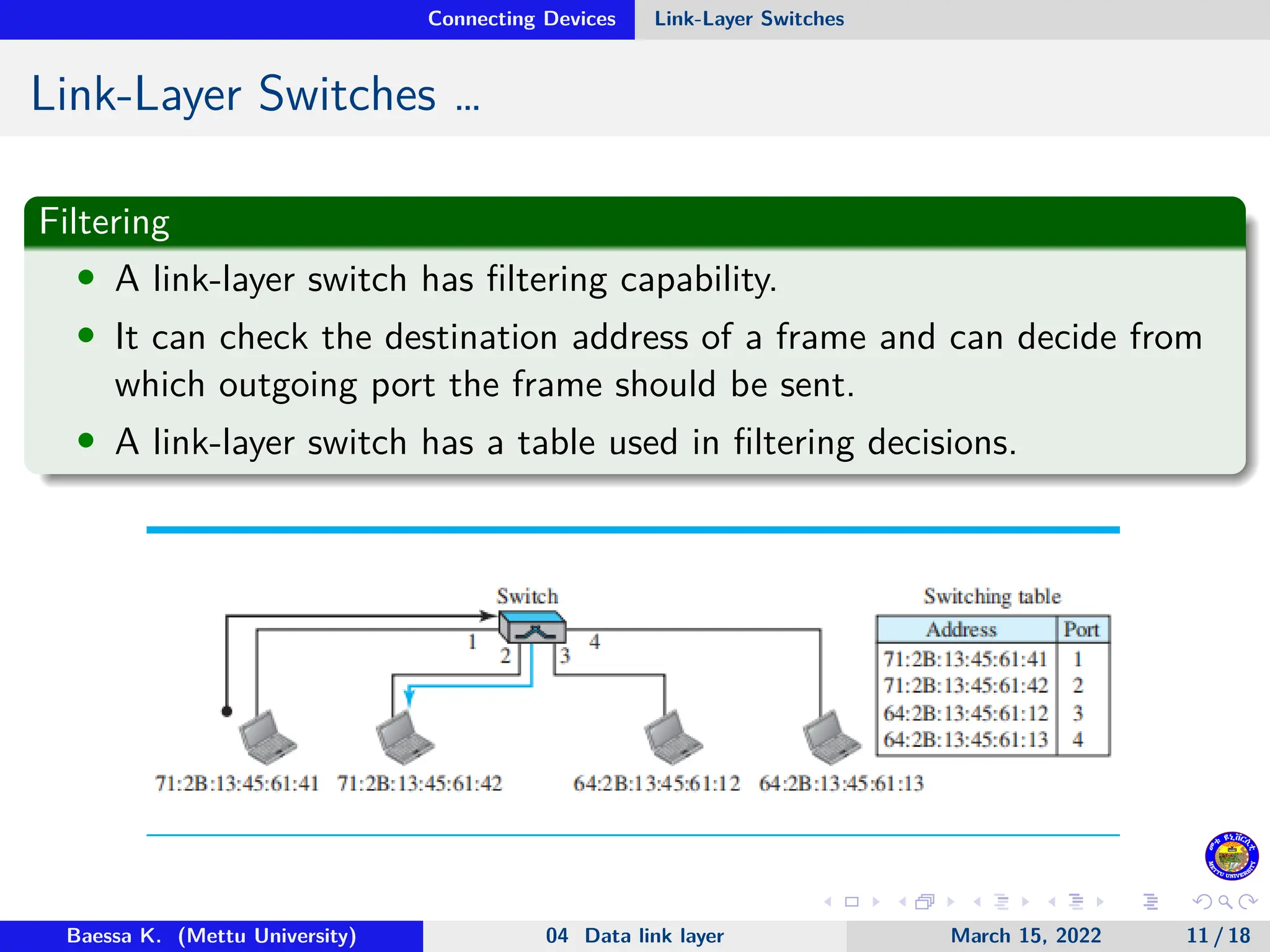
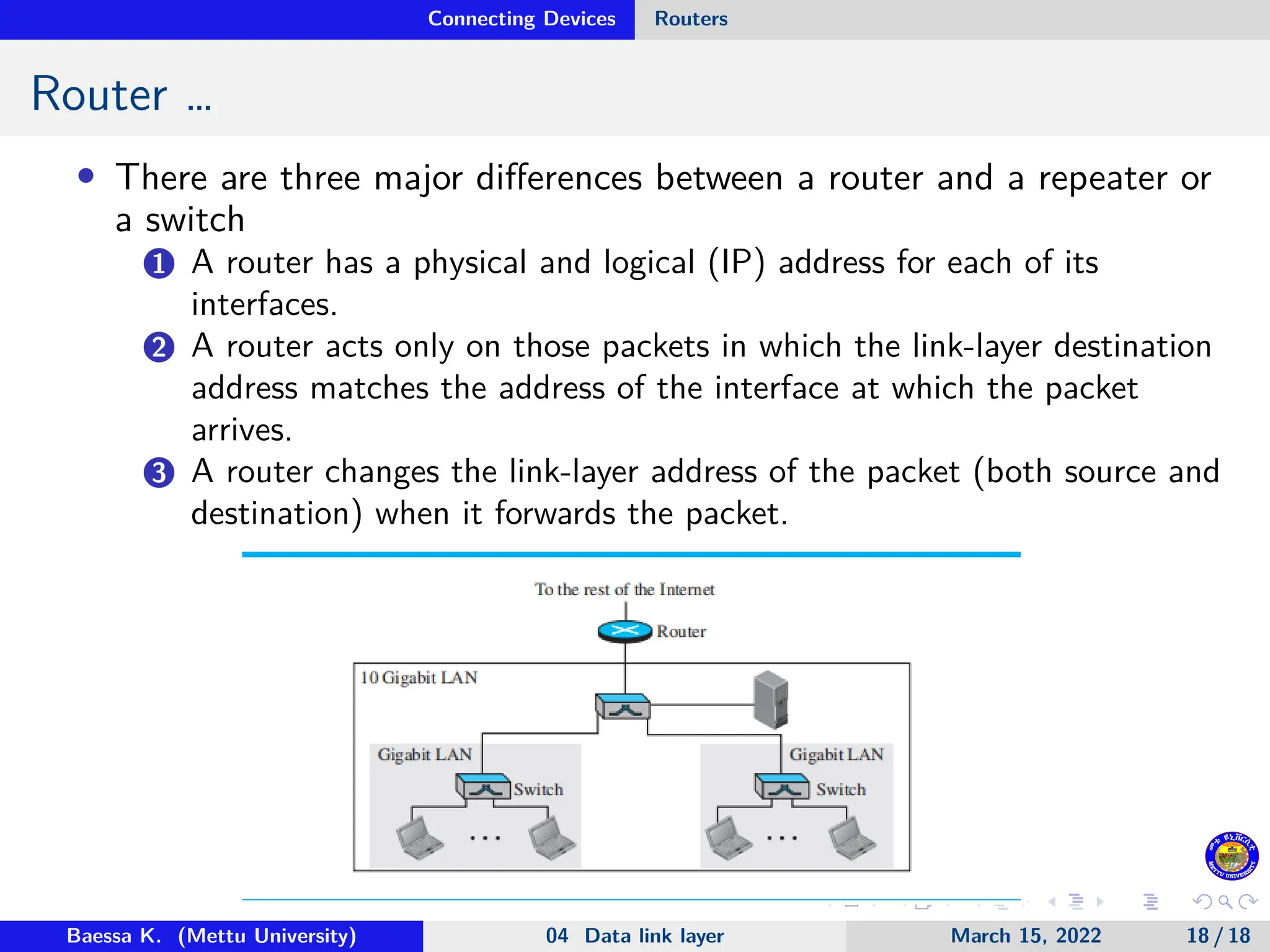
The document discusses connecting devices in data communications, specifically focusing on hubs, link-layer switches, and routers. Hubs operate at the physical layer and simply forward signals without filtering, while link-layer switches add filtering capabilities and can check MAC addresses to reduce collisions. Routers function at multiple layers, connecting different networks while managing both link-layer and network-layer addresses, thus enabling internetwork communication.