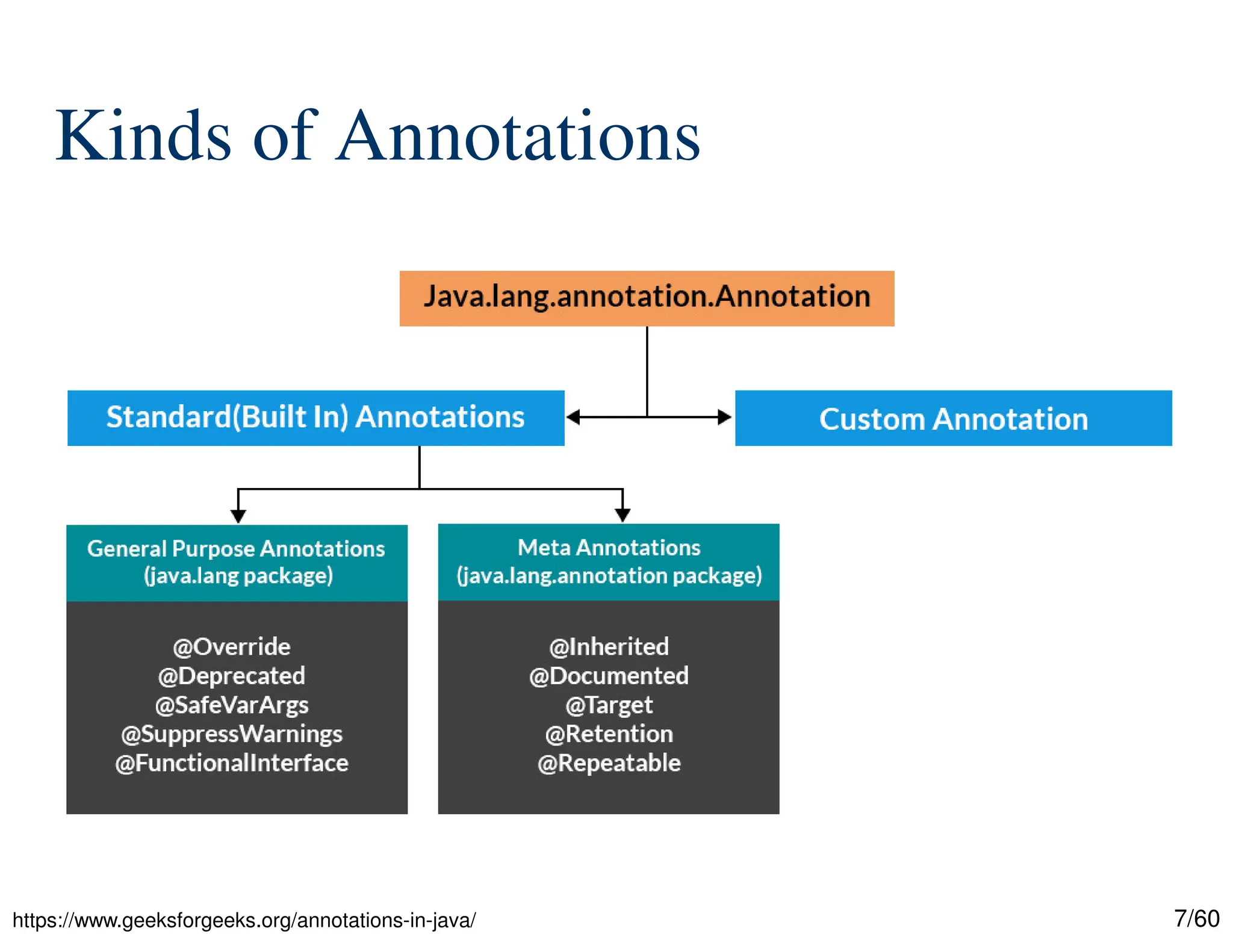
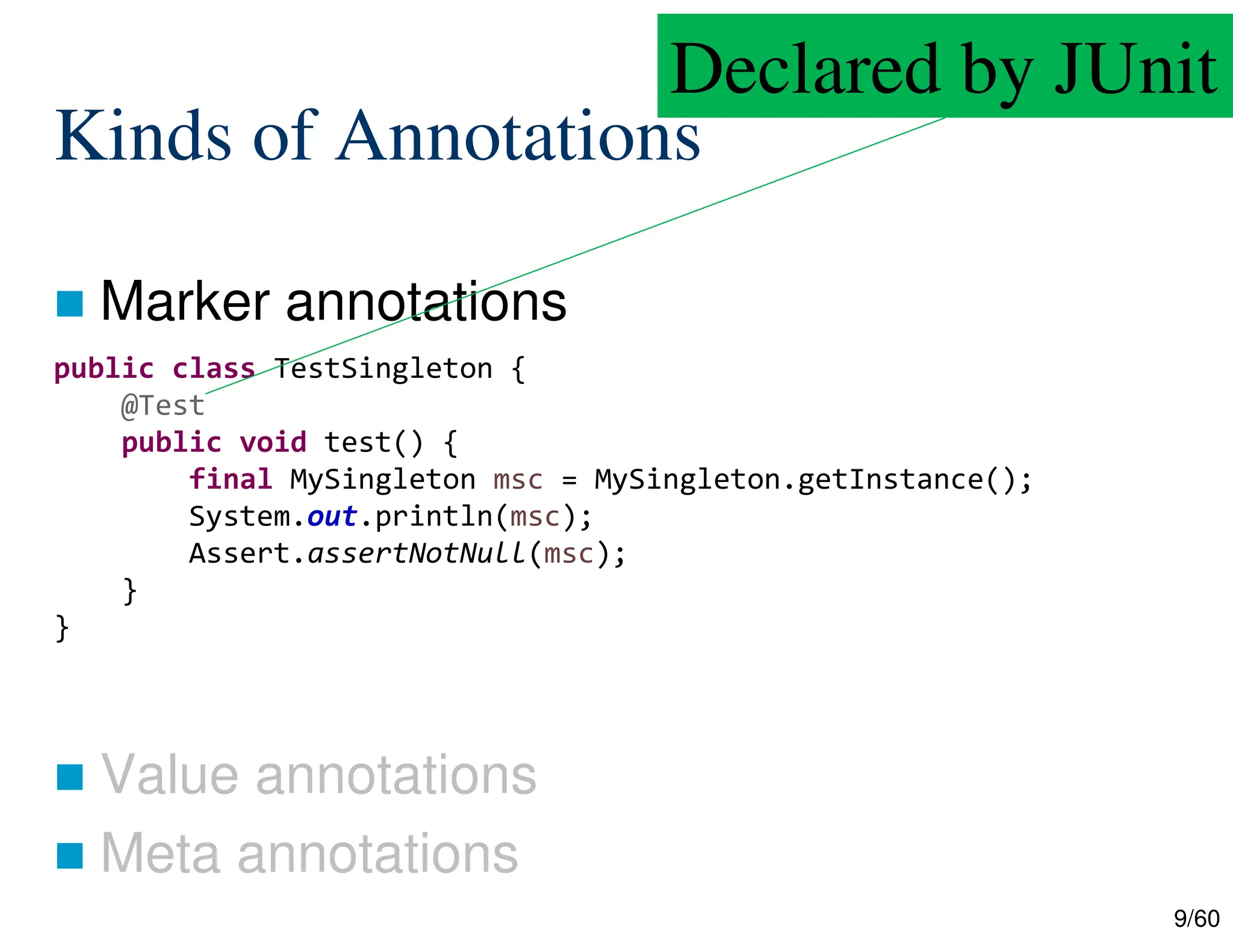
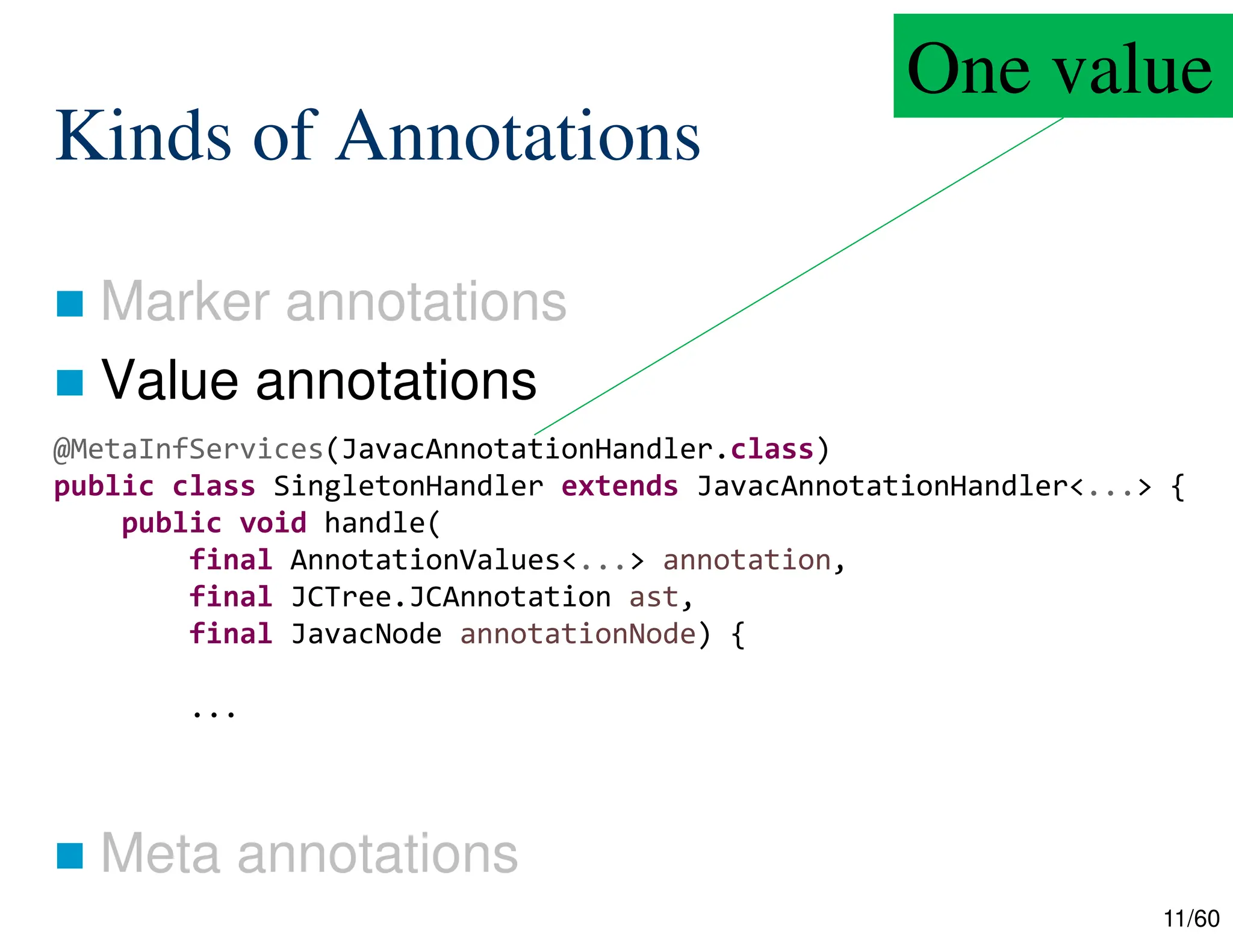
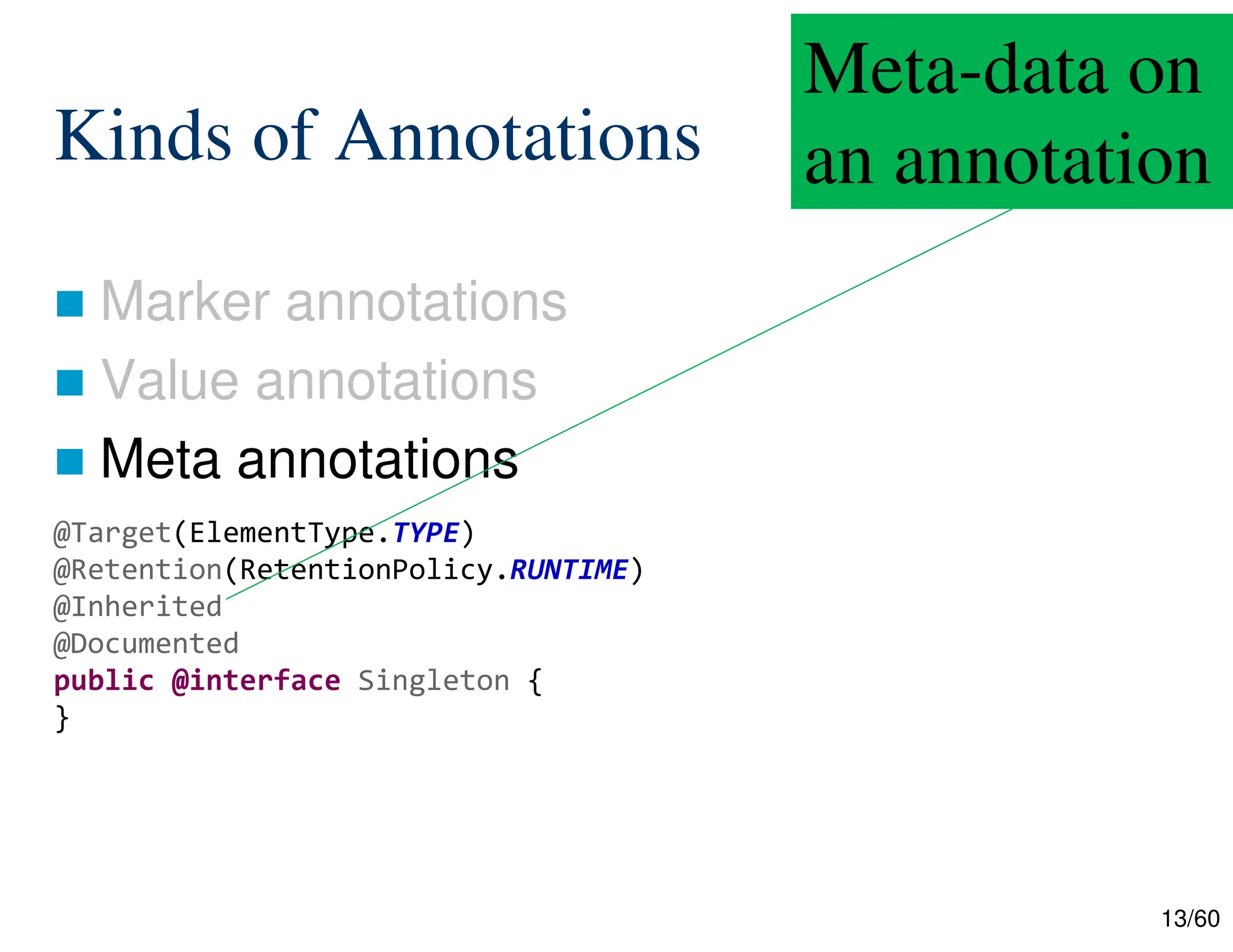
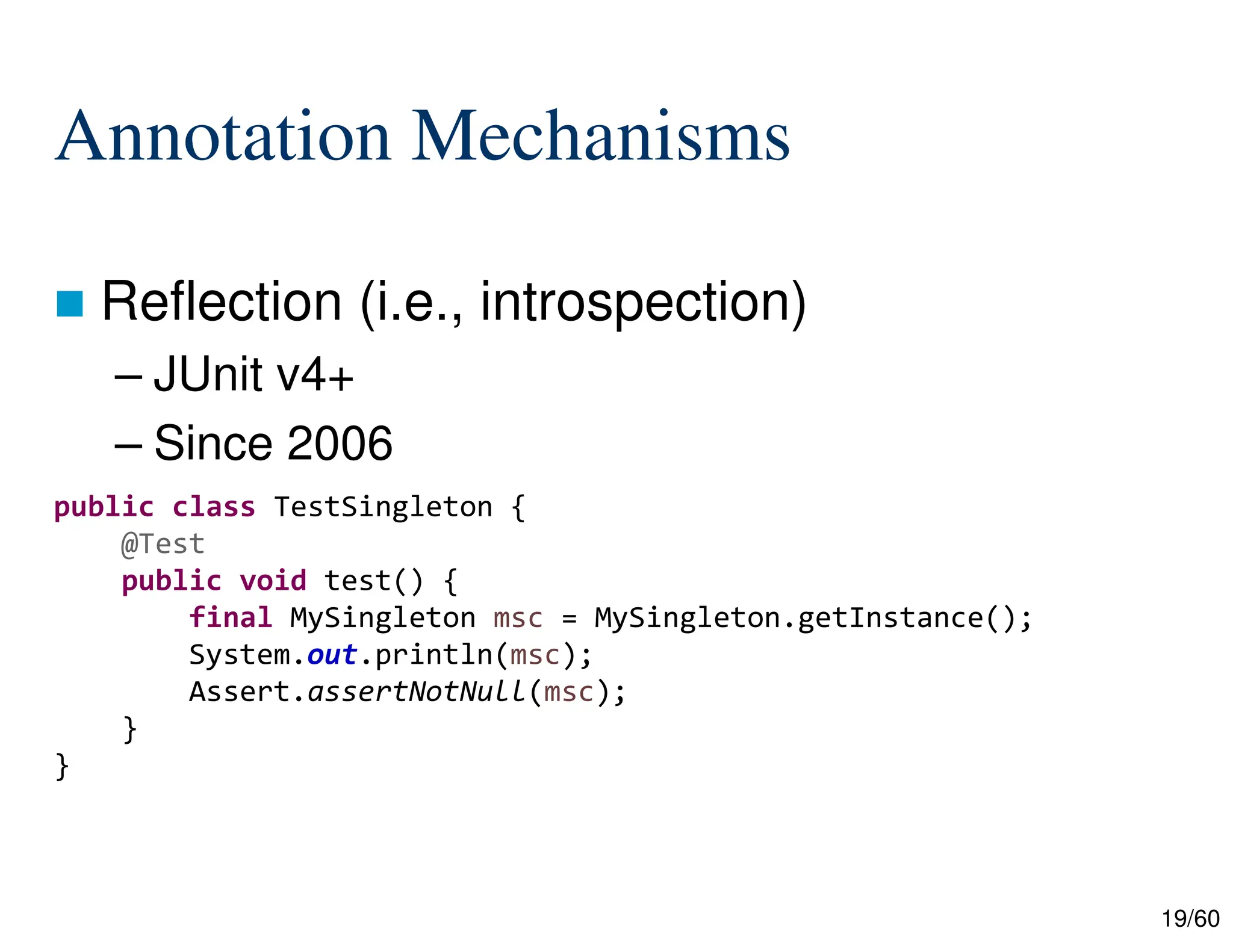
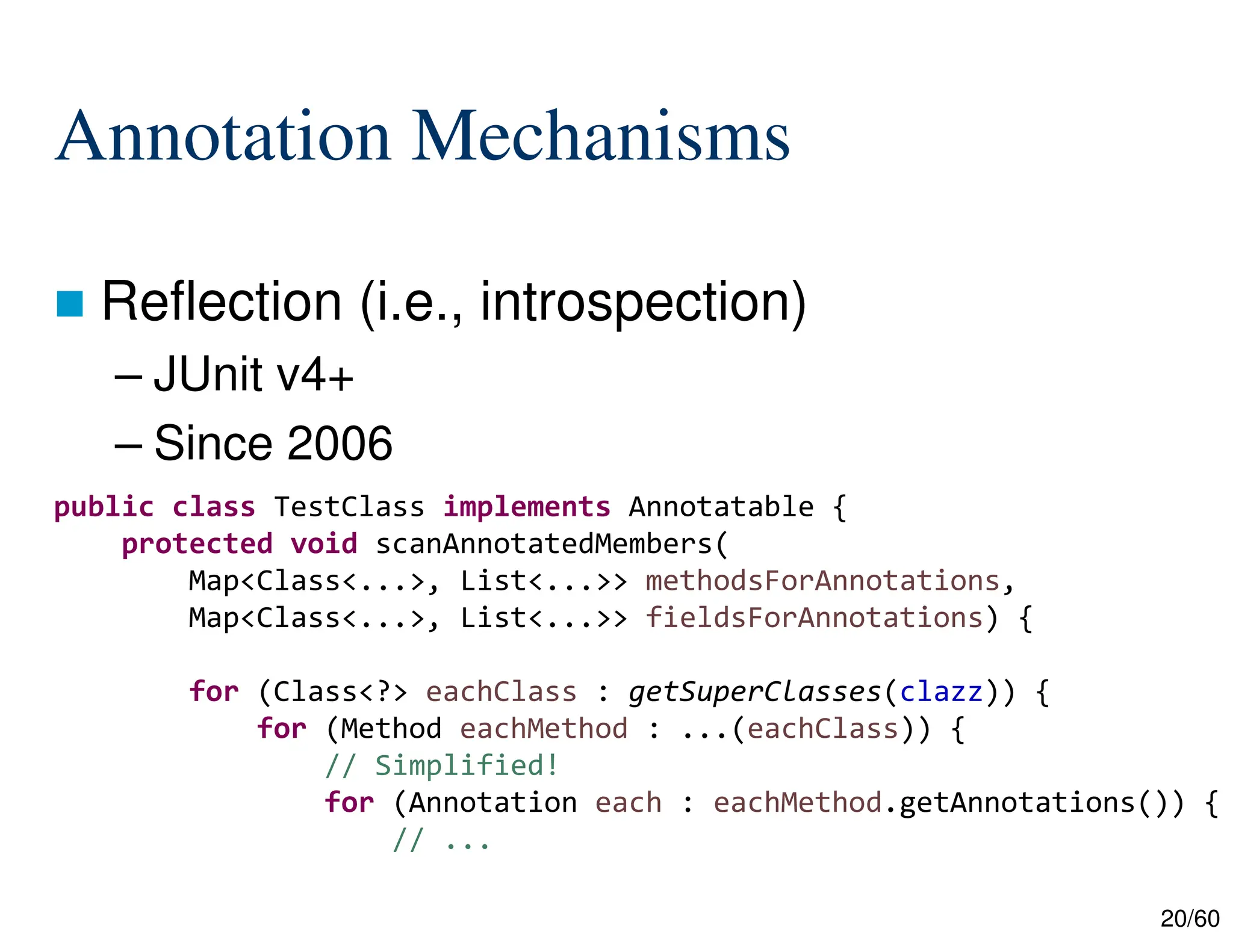
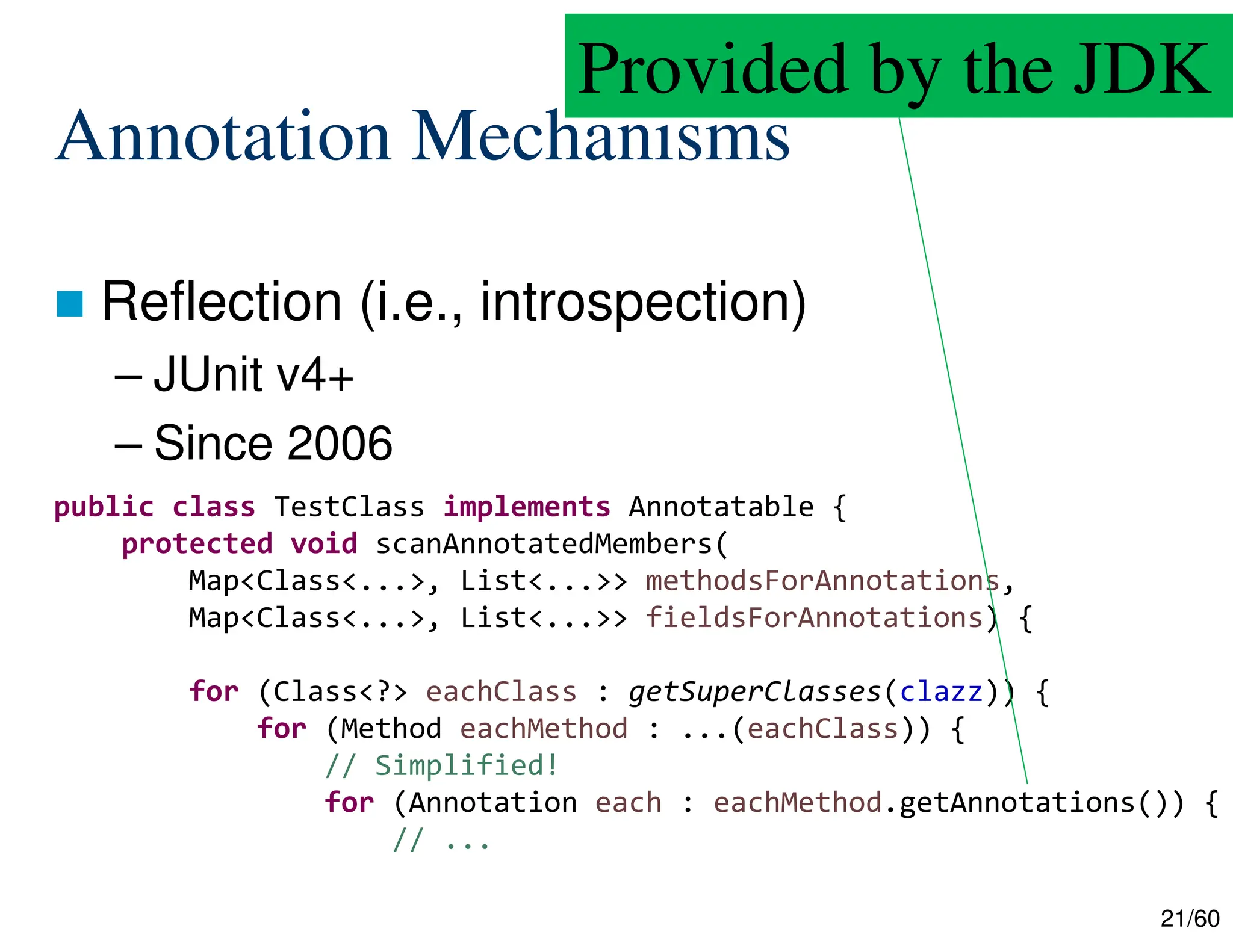
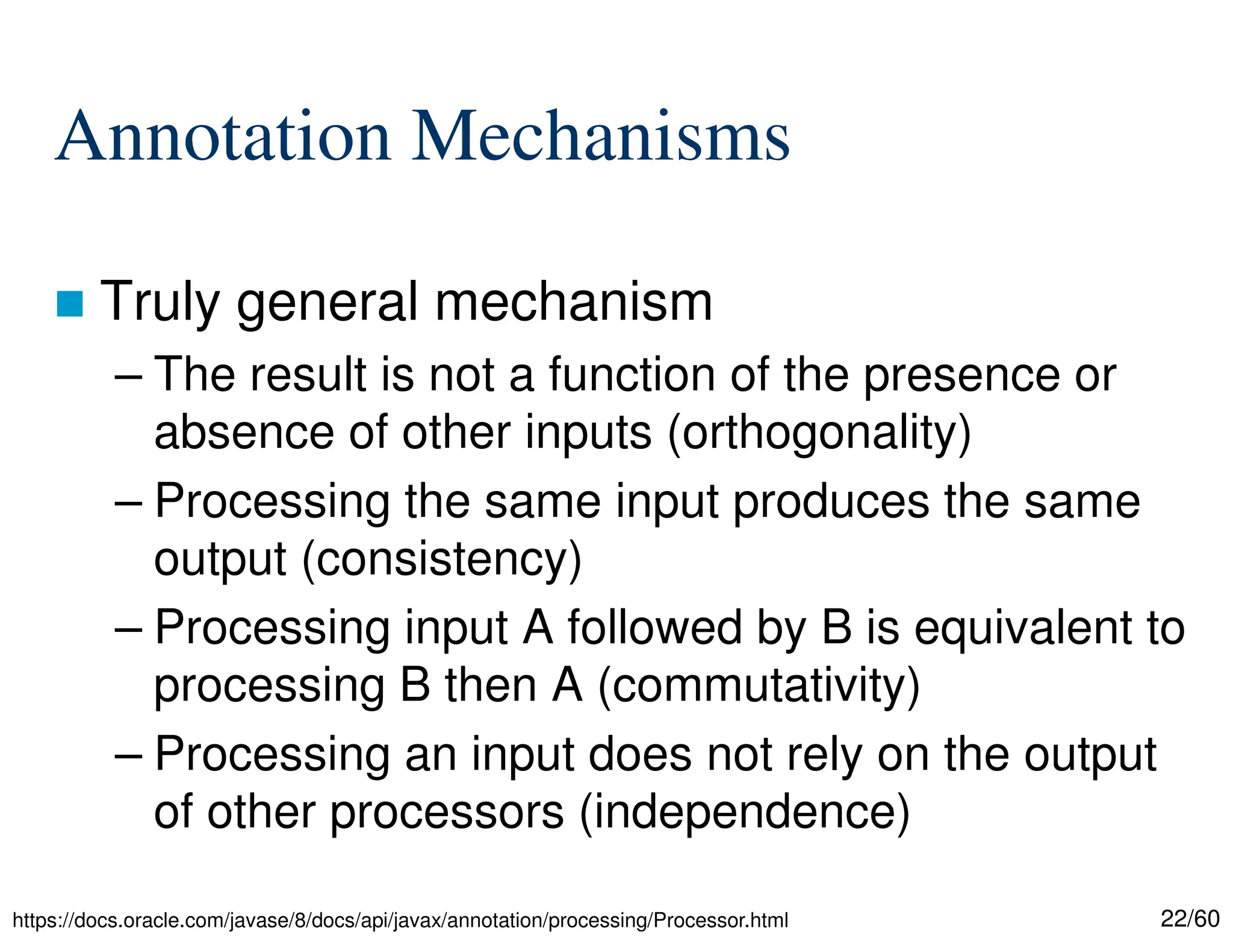
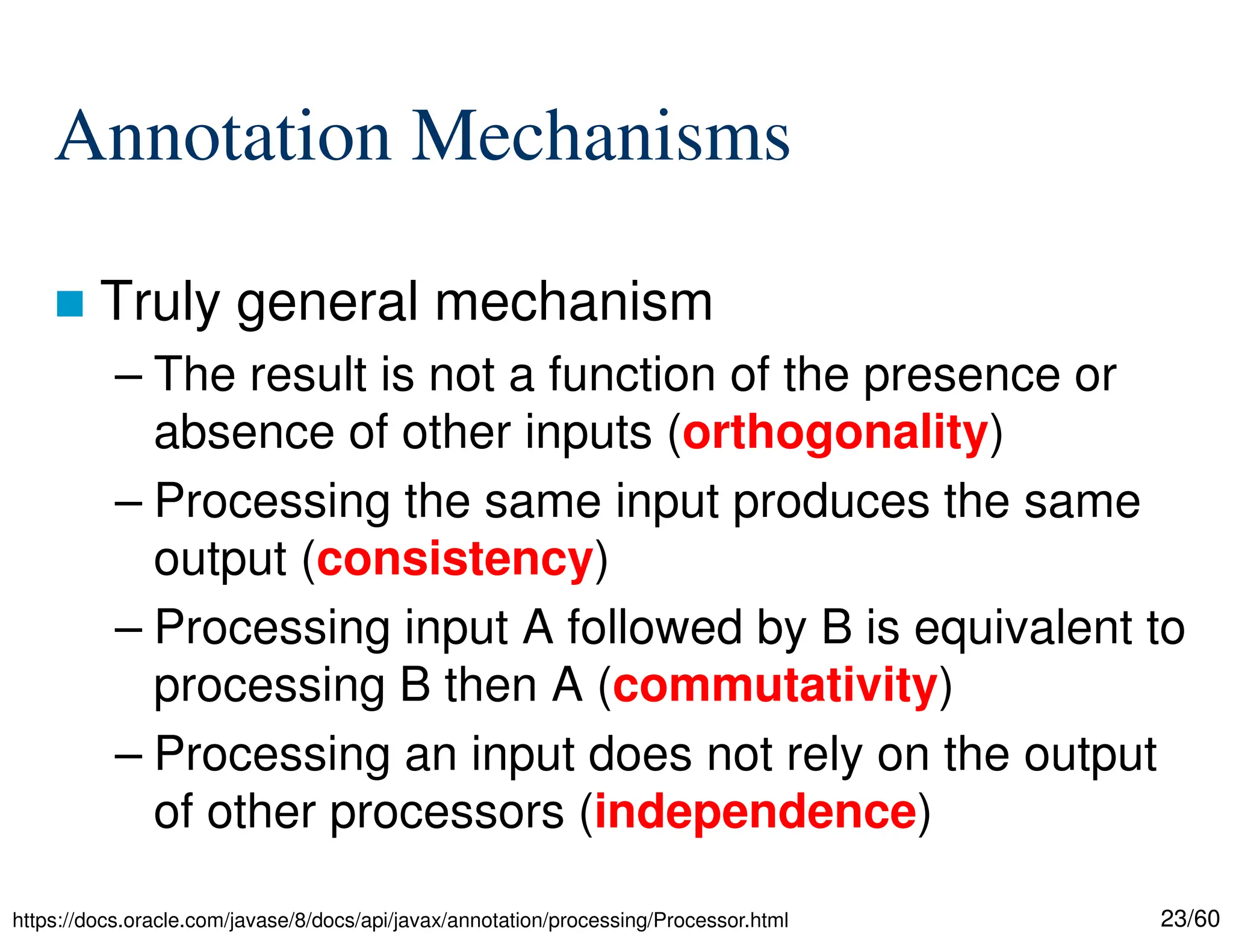
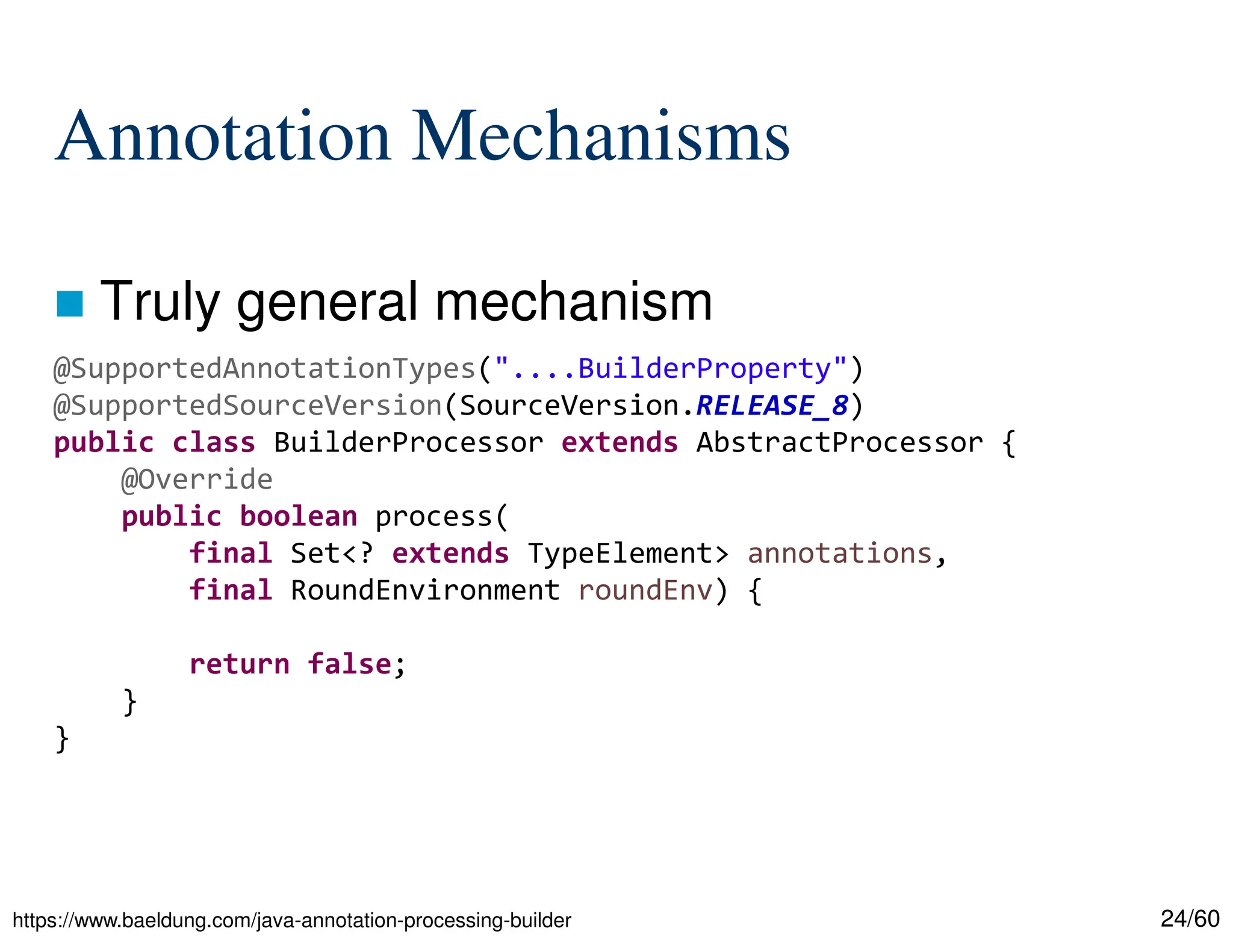
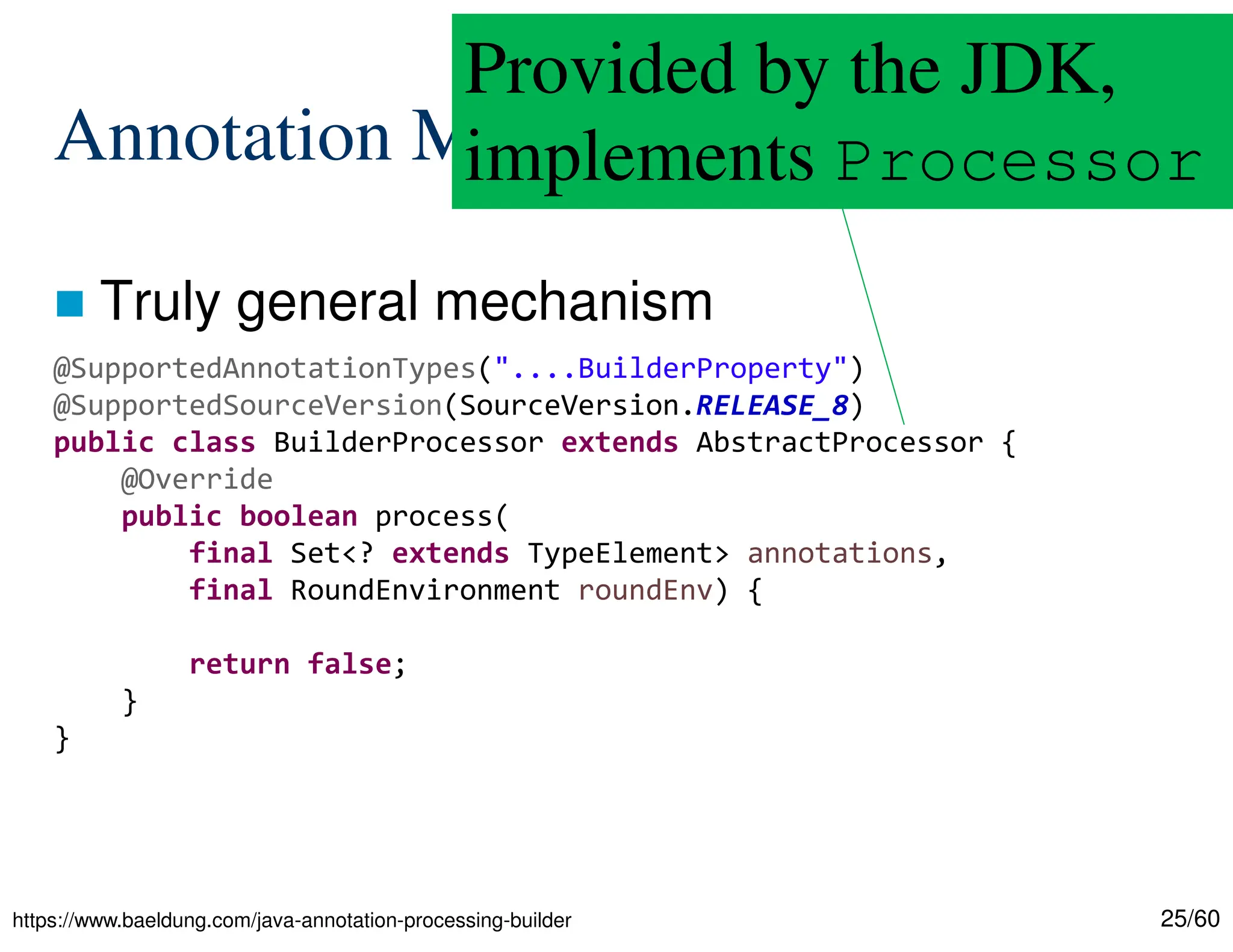
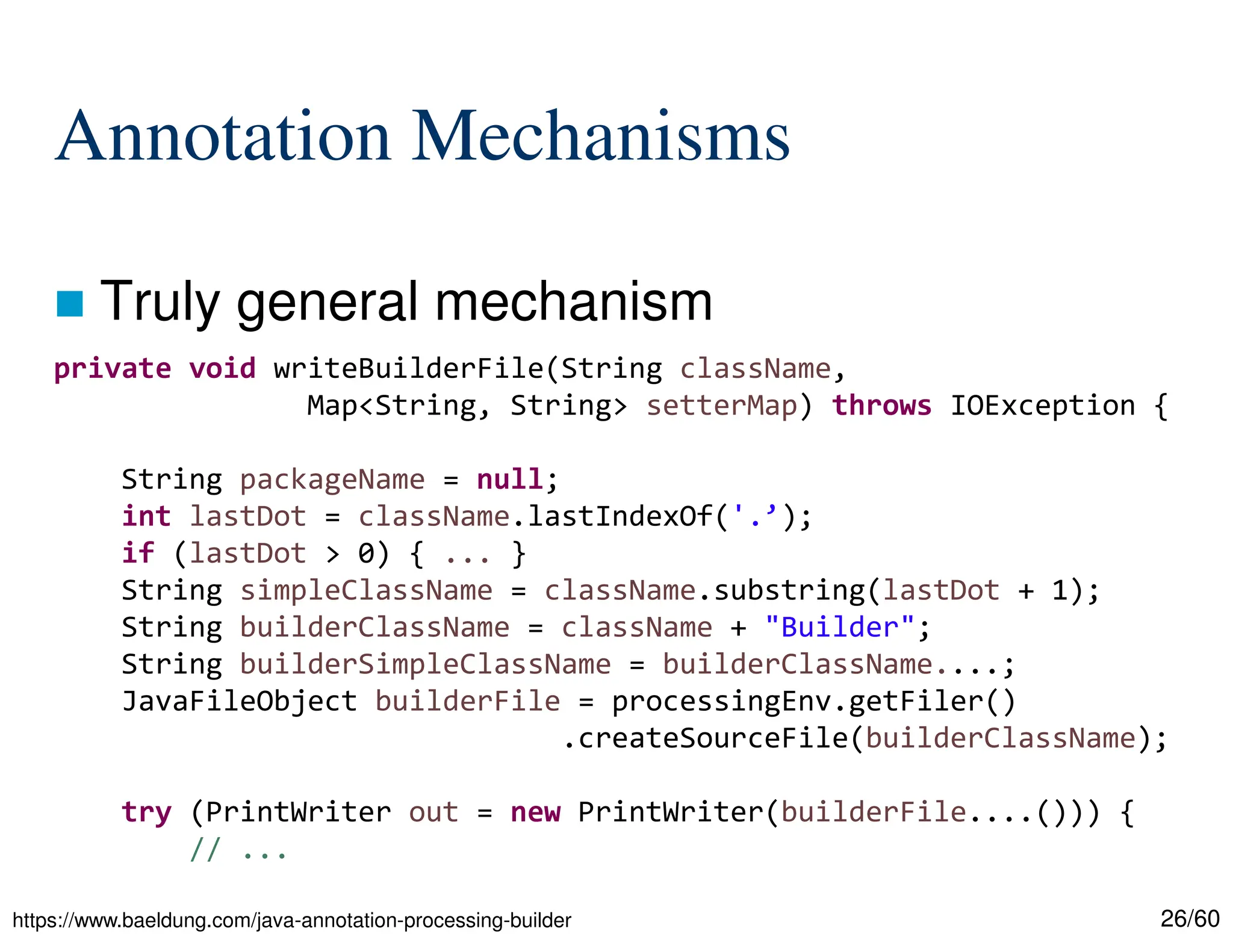
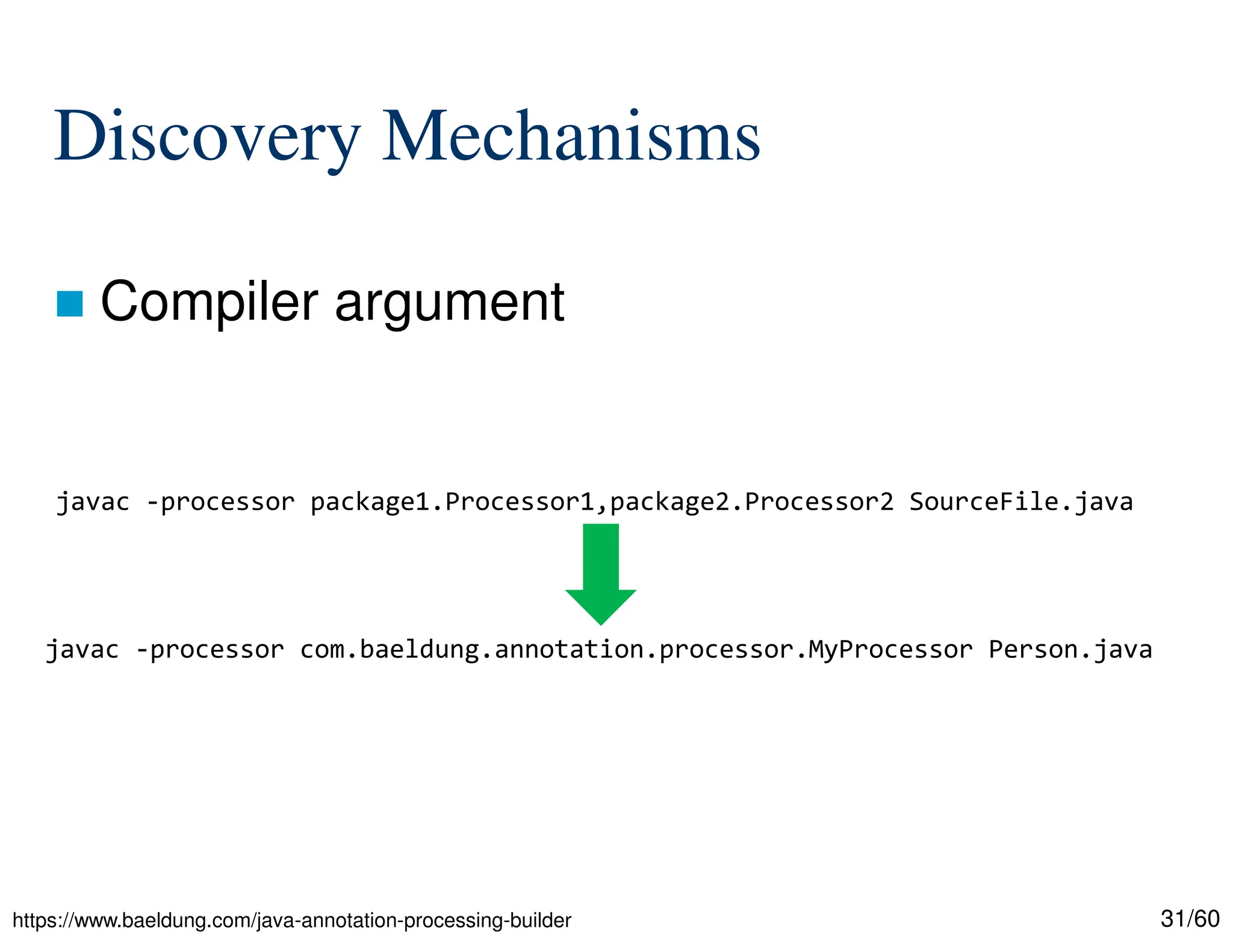
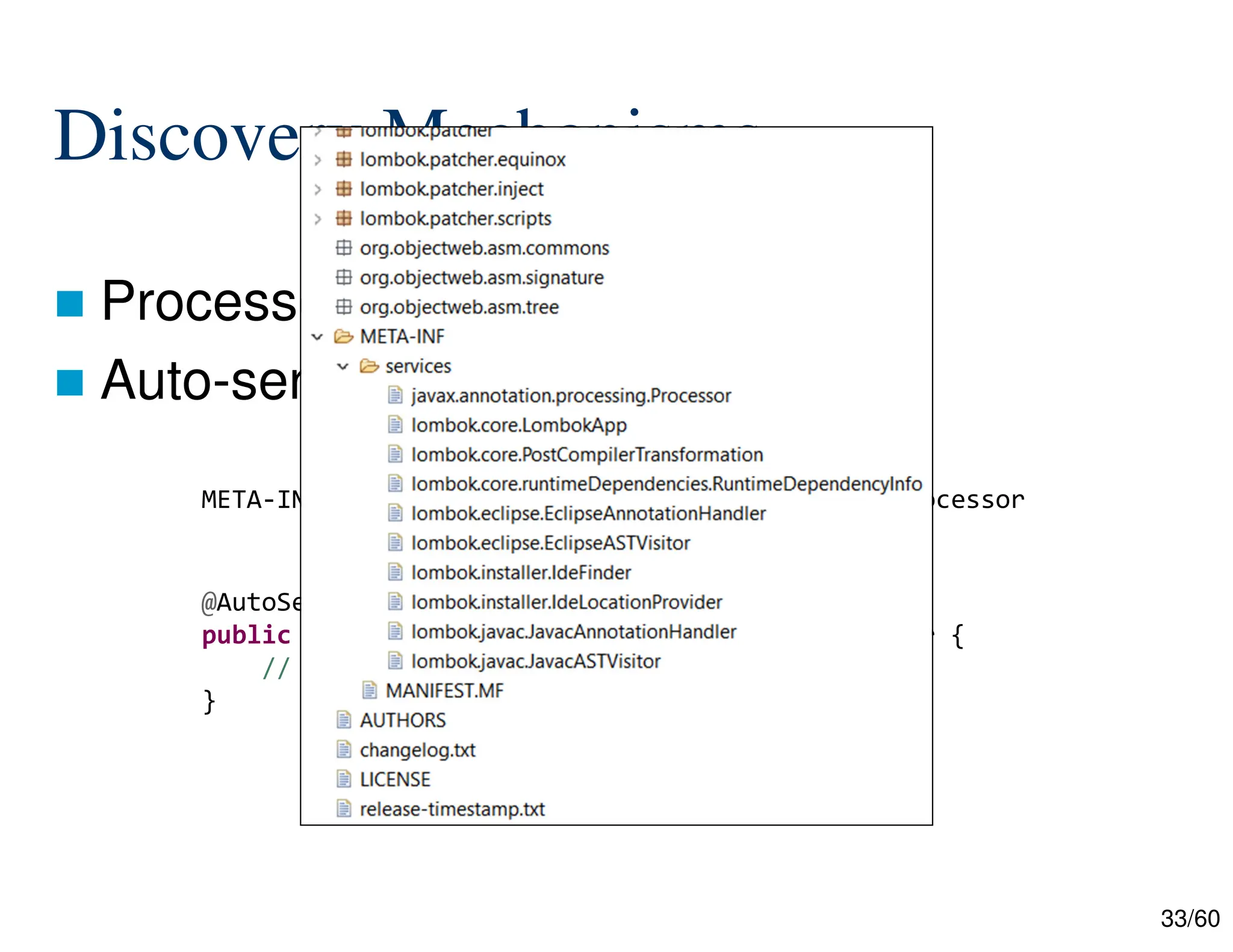
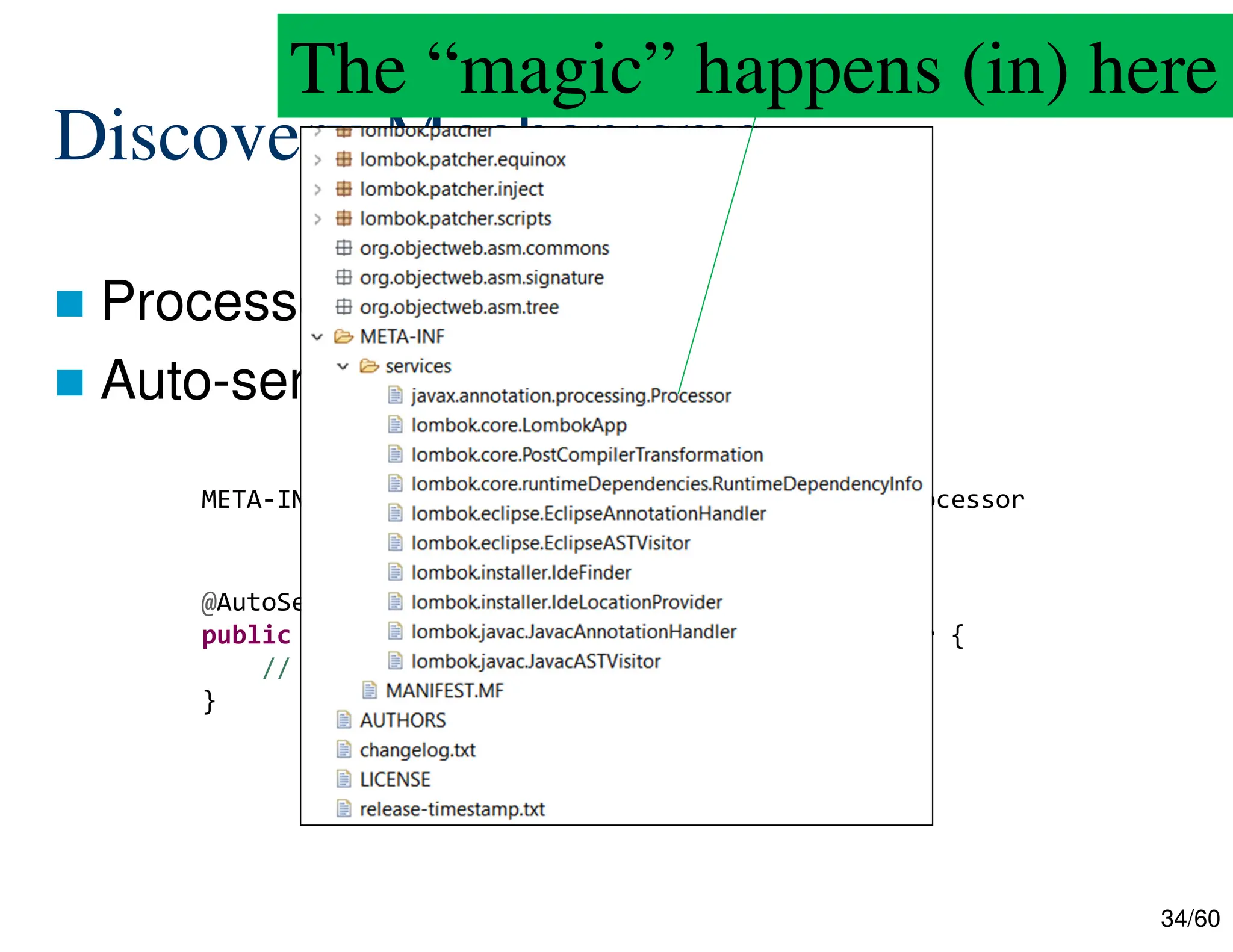
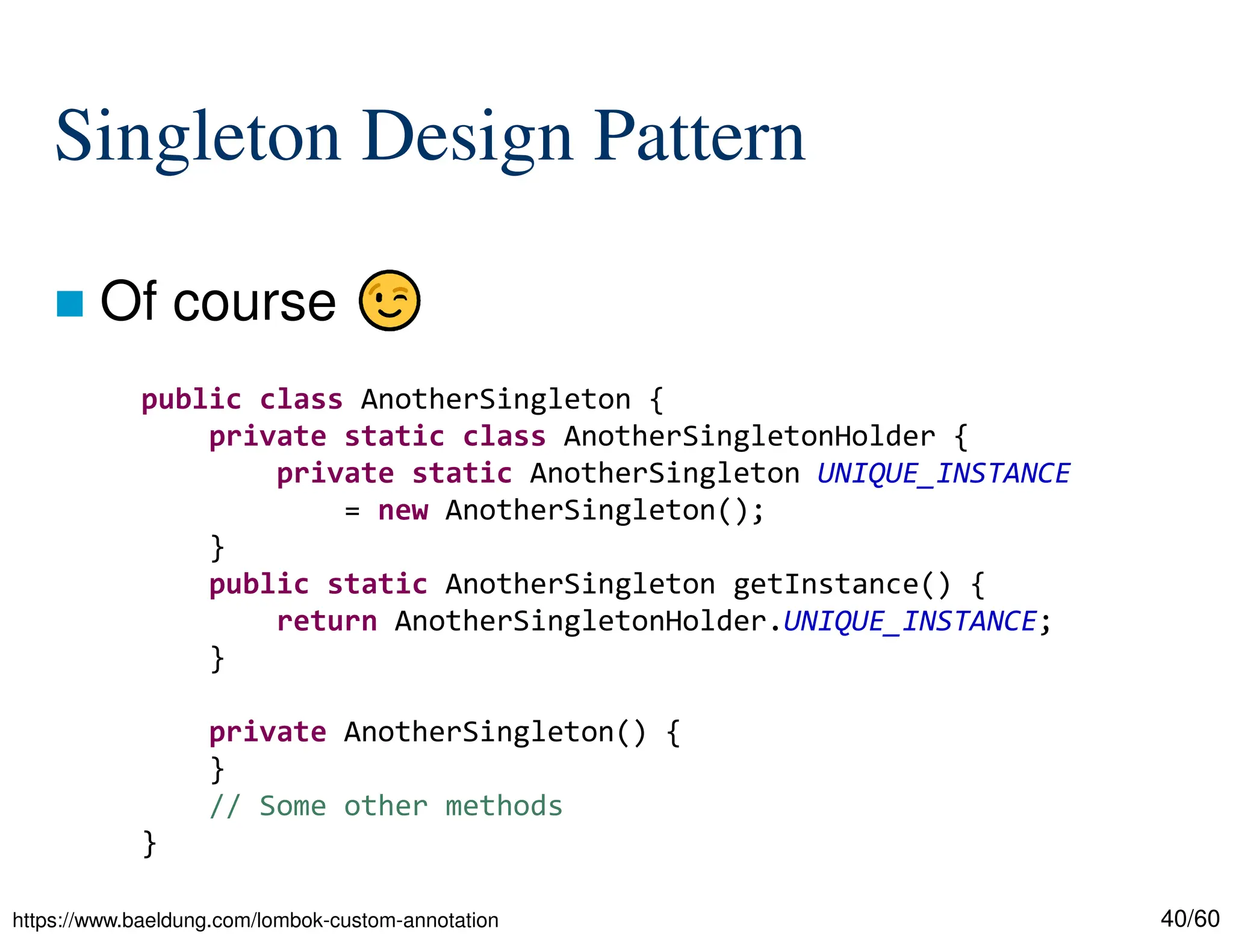
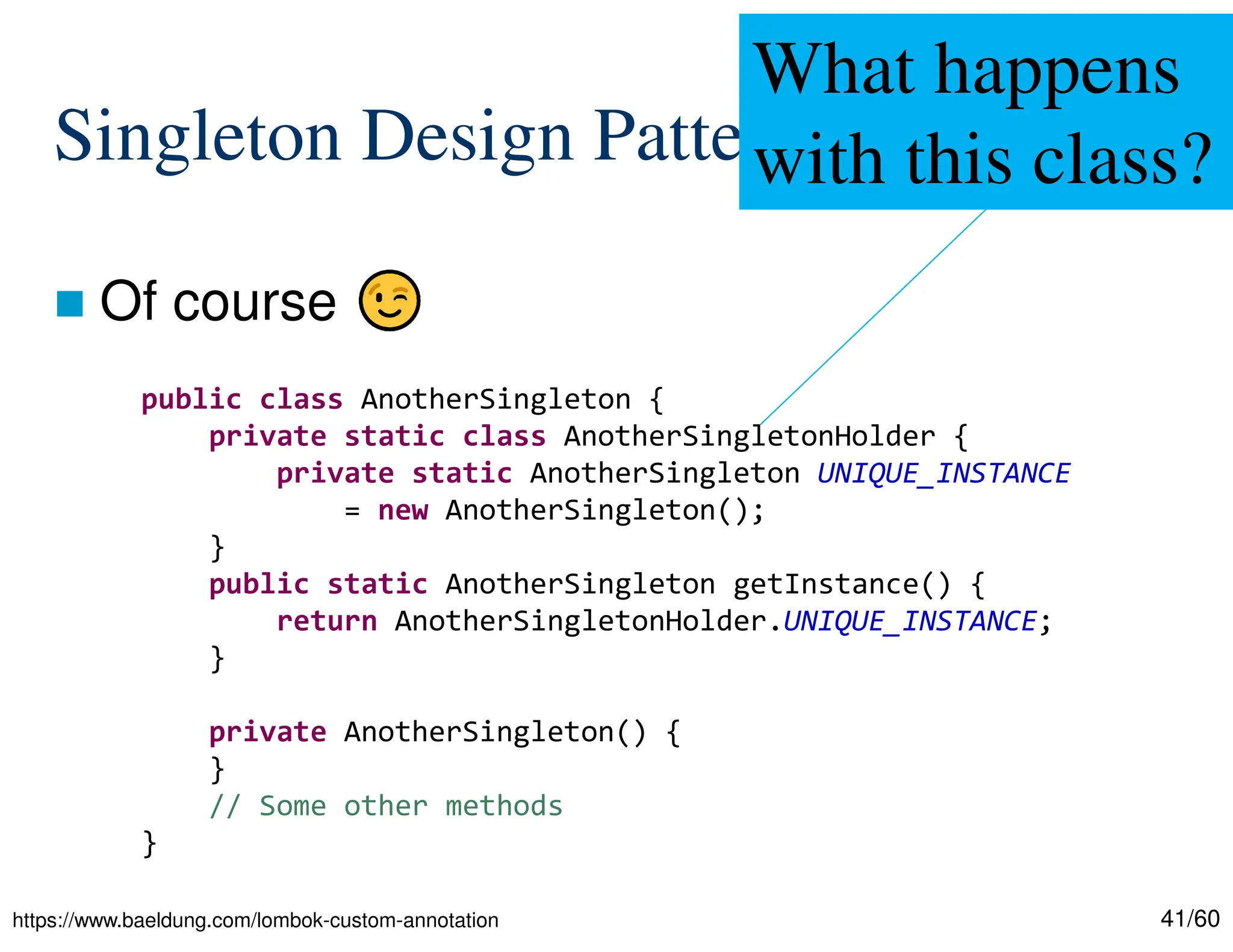
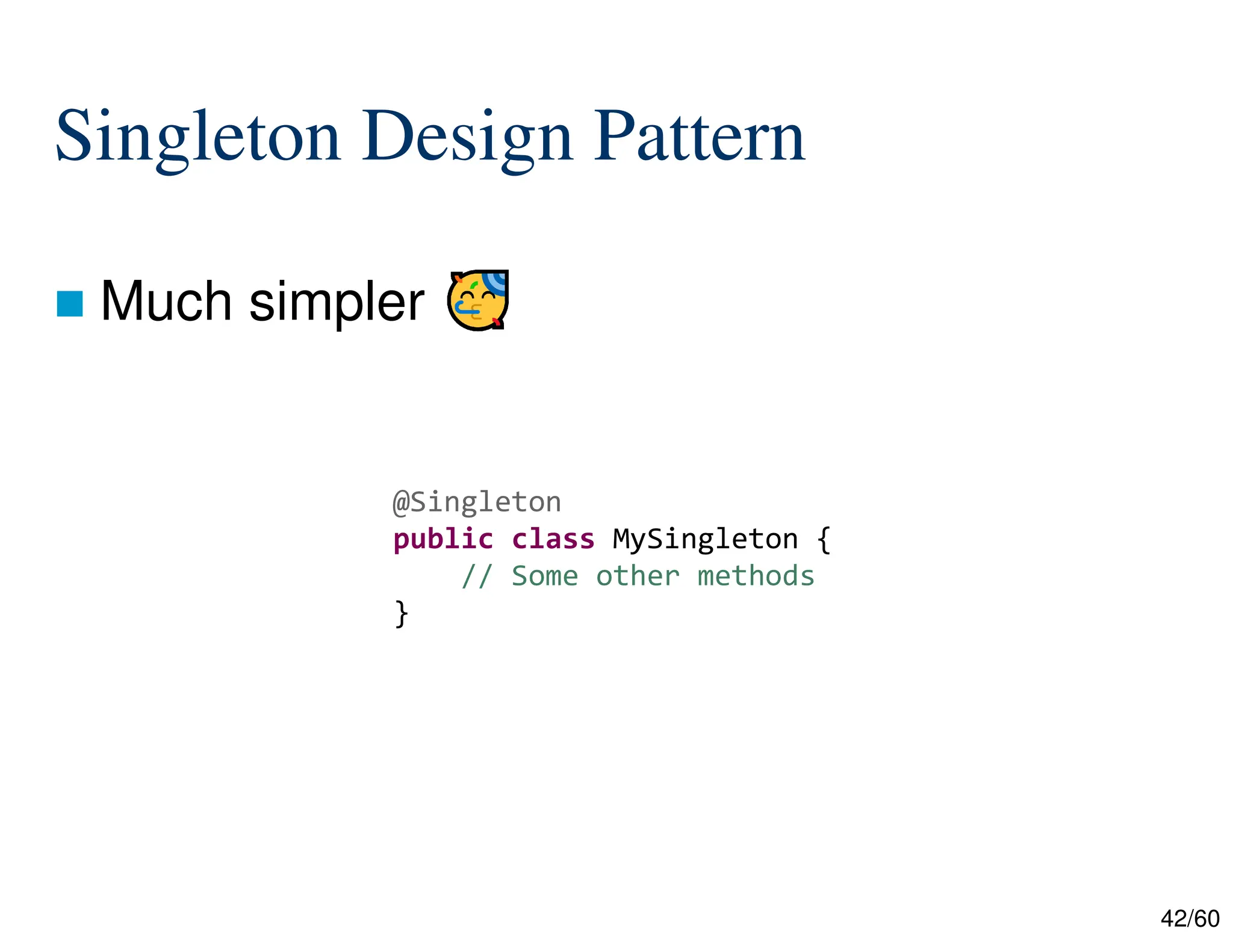
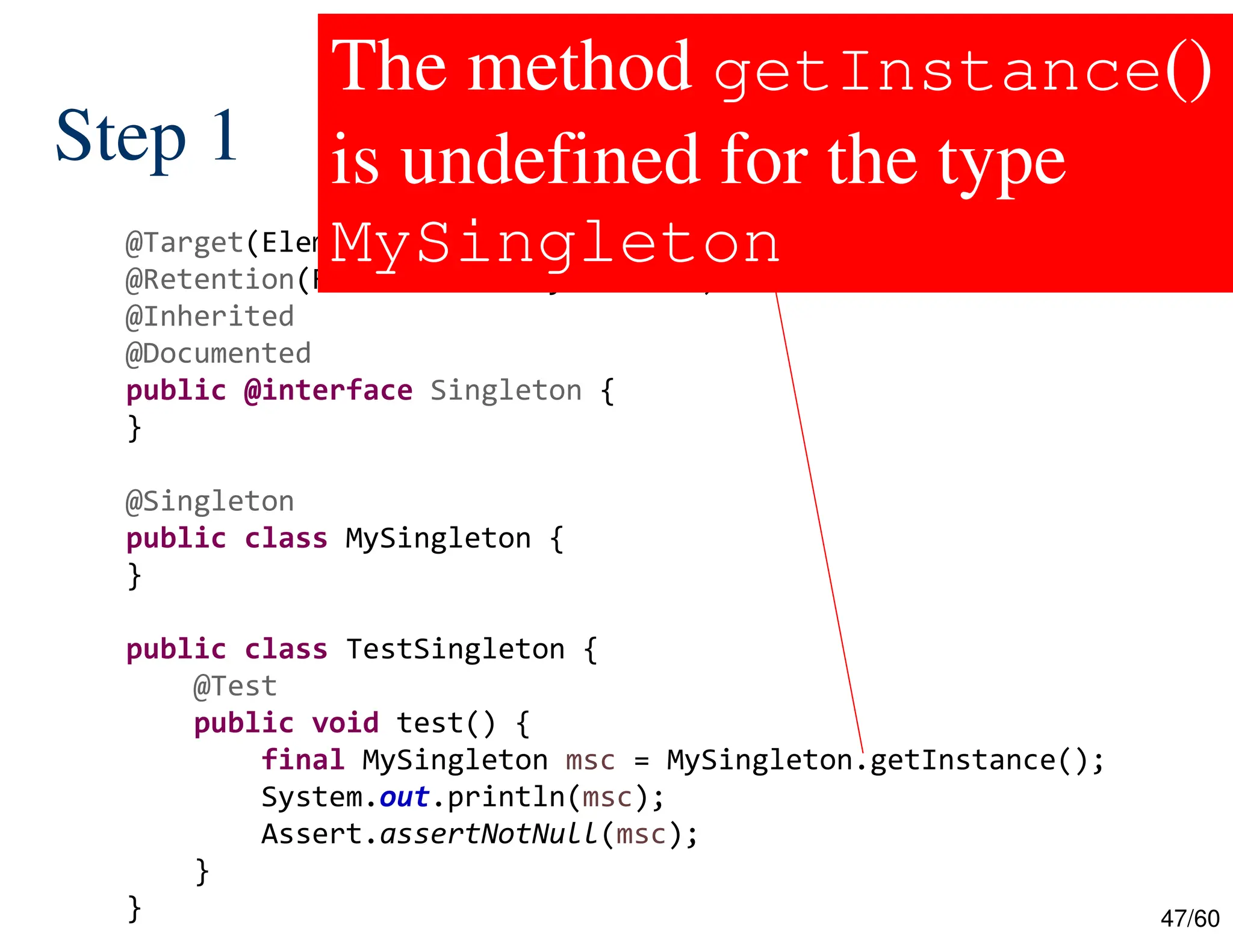
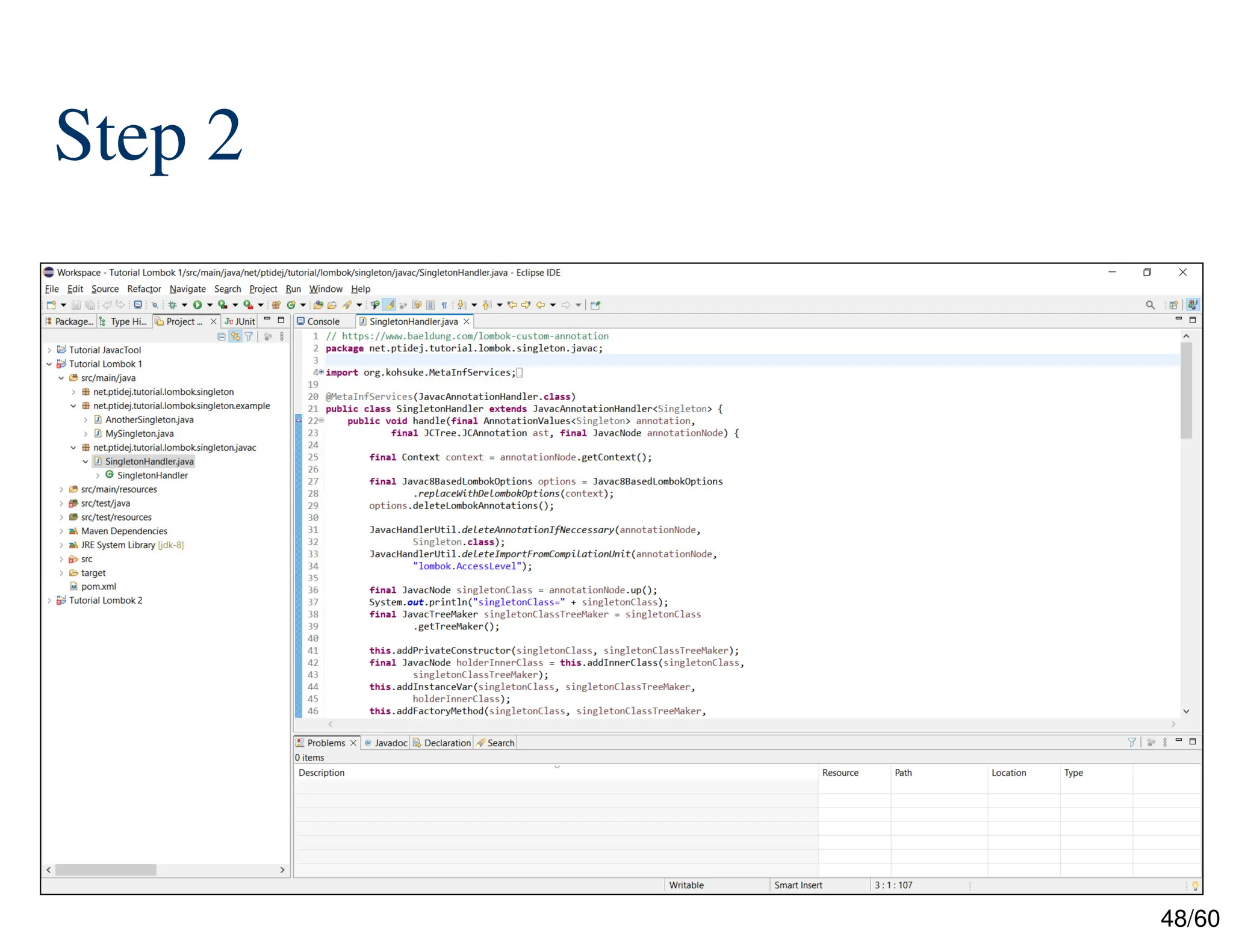
The document discusses creating custom annotations in Java using Project Lombok, focusing on how to guide code compilation and execution with ad-hoc annotations. It covers different types of annotations, annotation mechanisms such as reflection, and explains the singleton design pattern with Lombok annotations. The document concludes with considerations on code generation, transformation, and future work in aspect-oriented programming and Spring Boot.