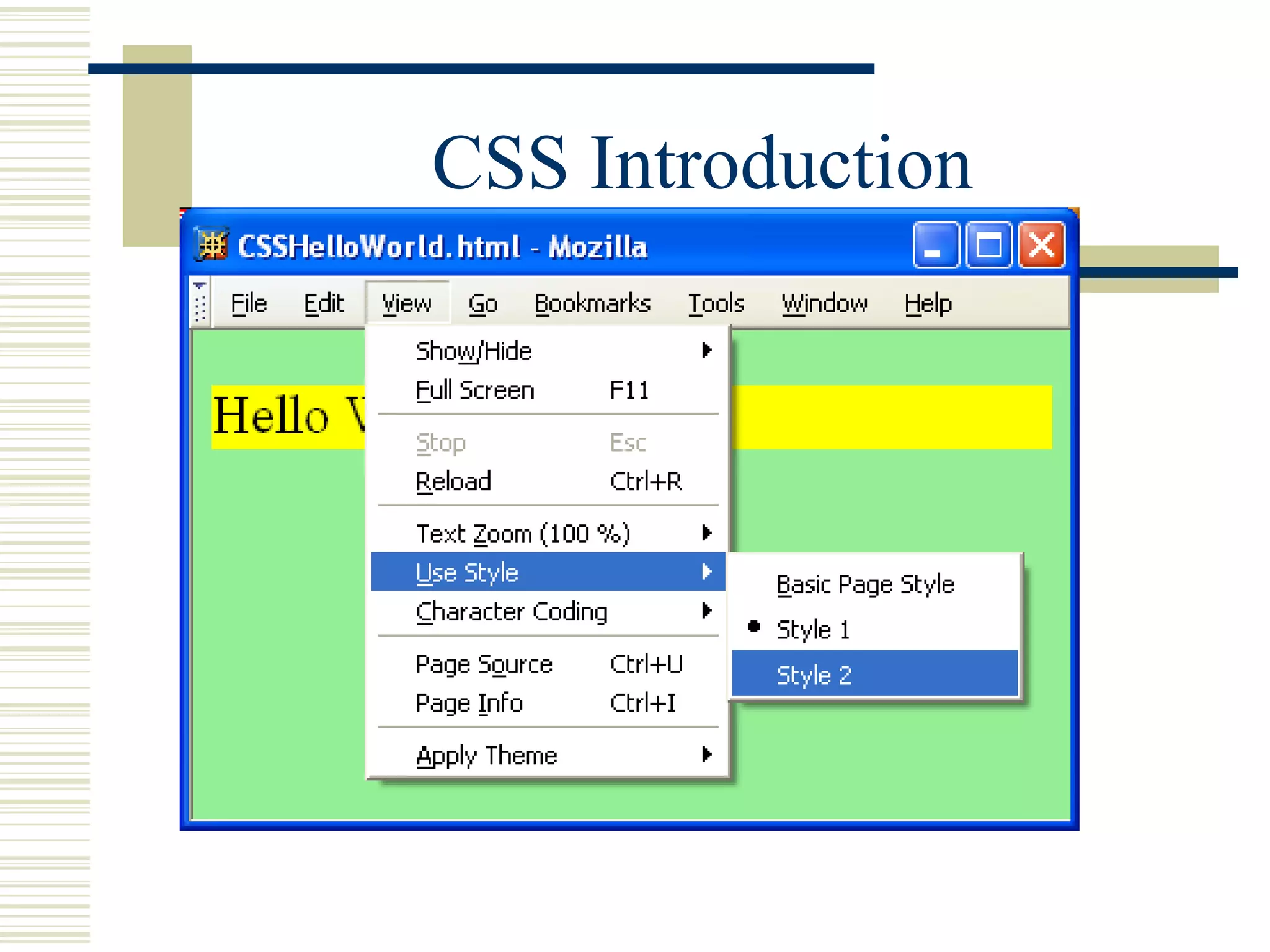
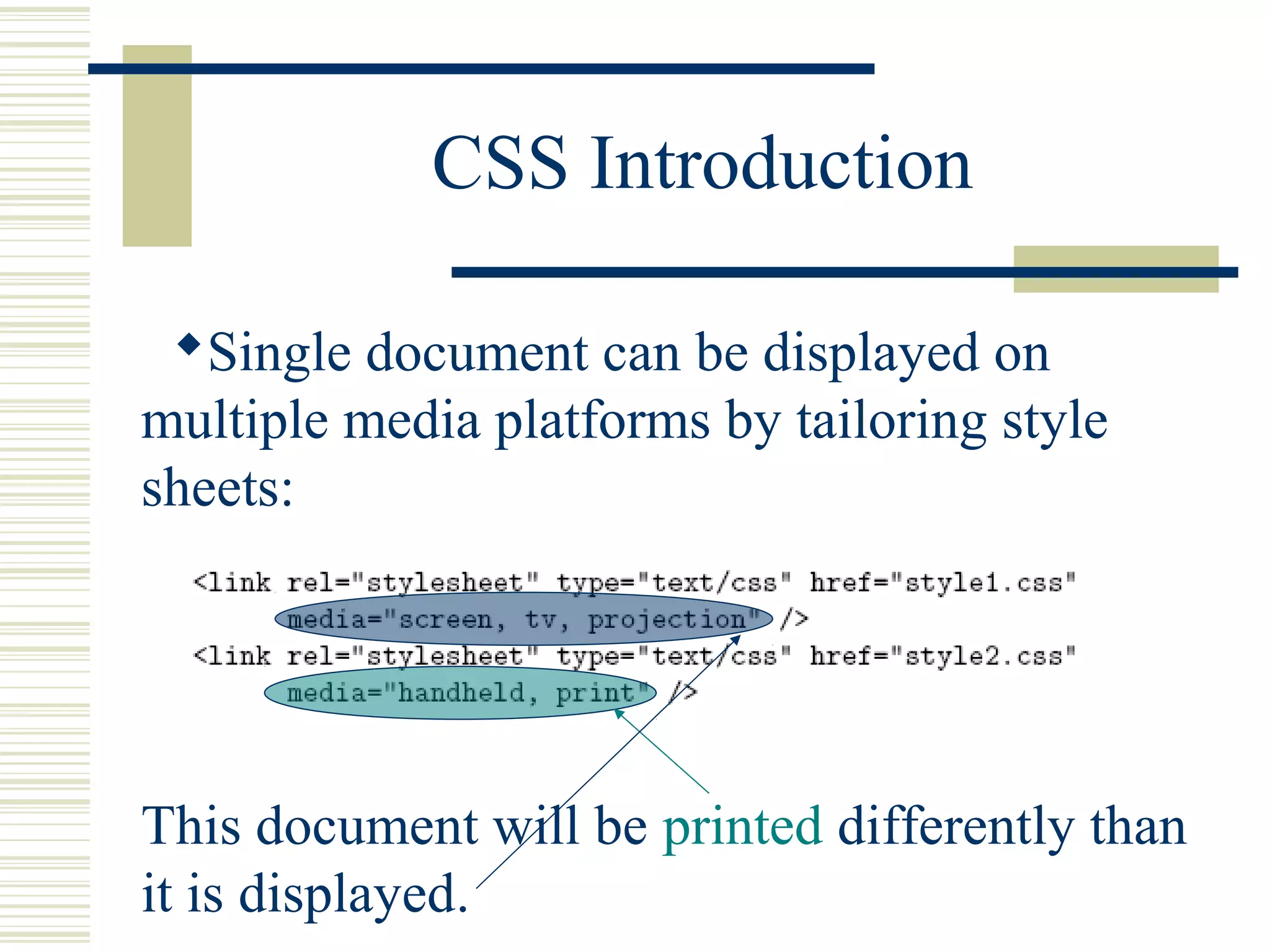
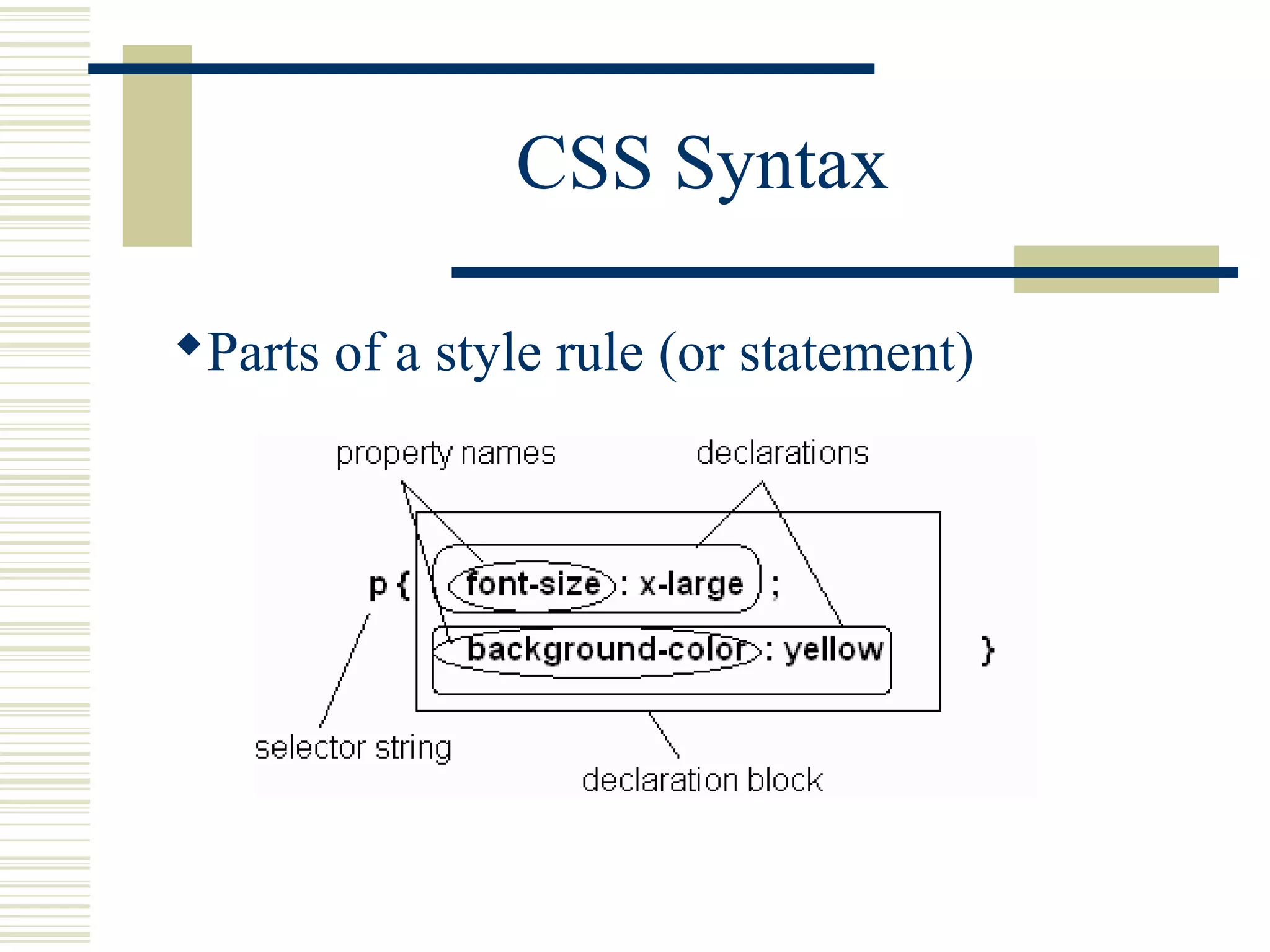
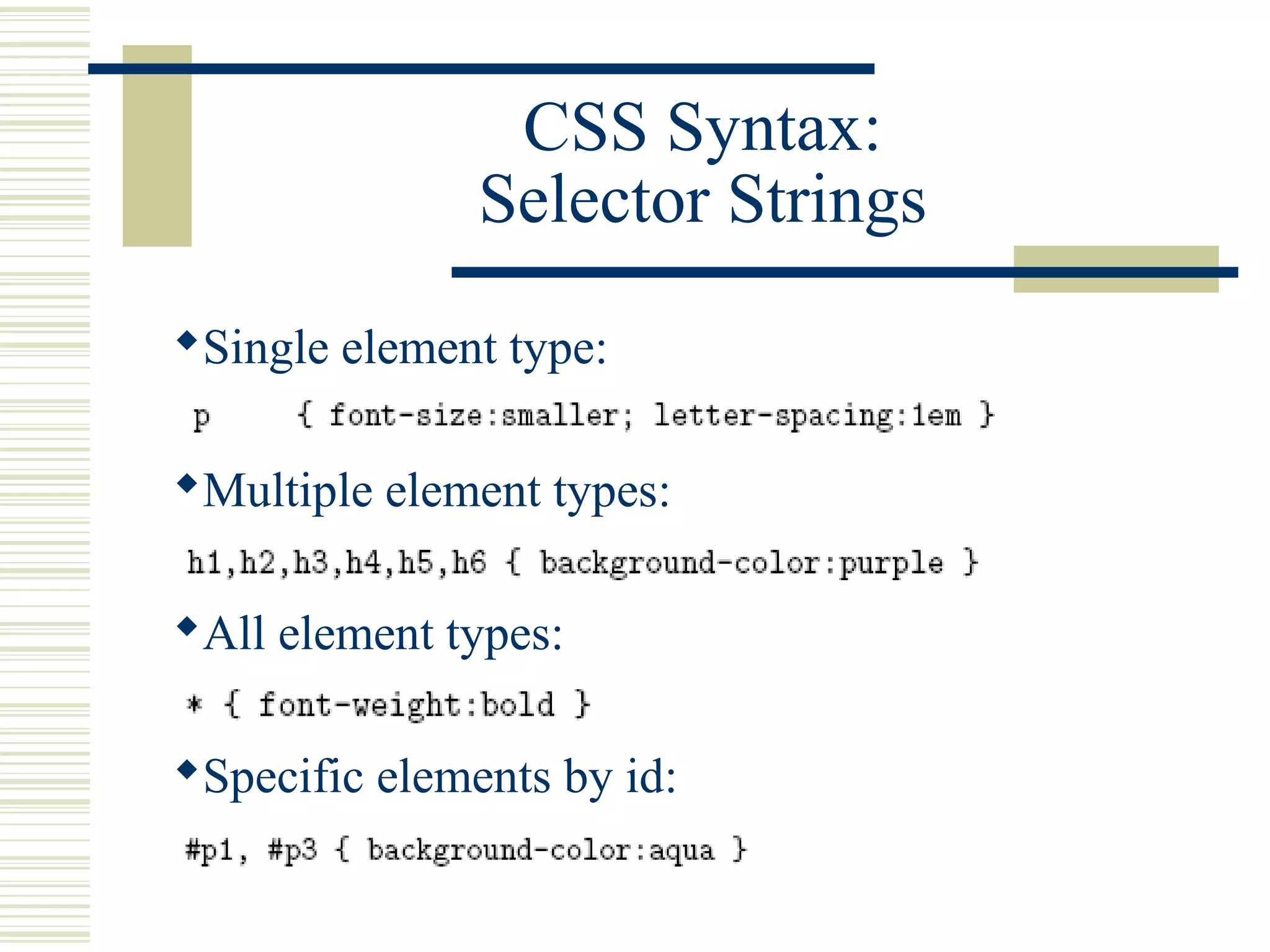
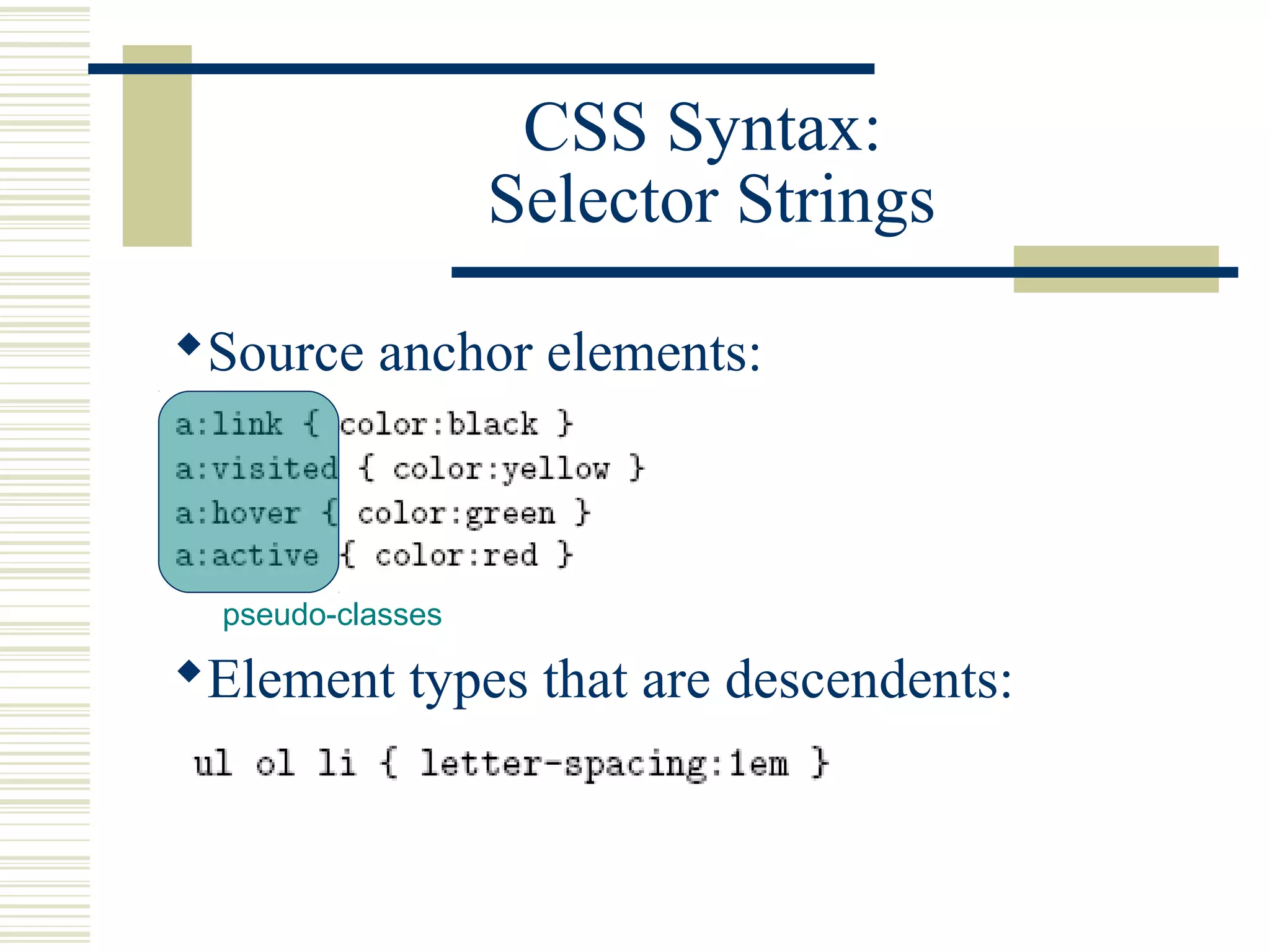
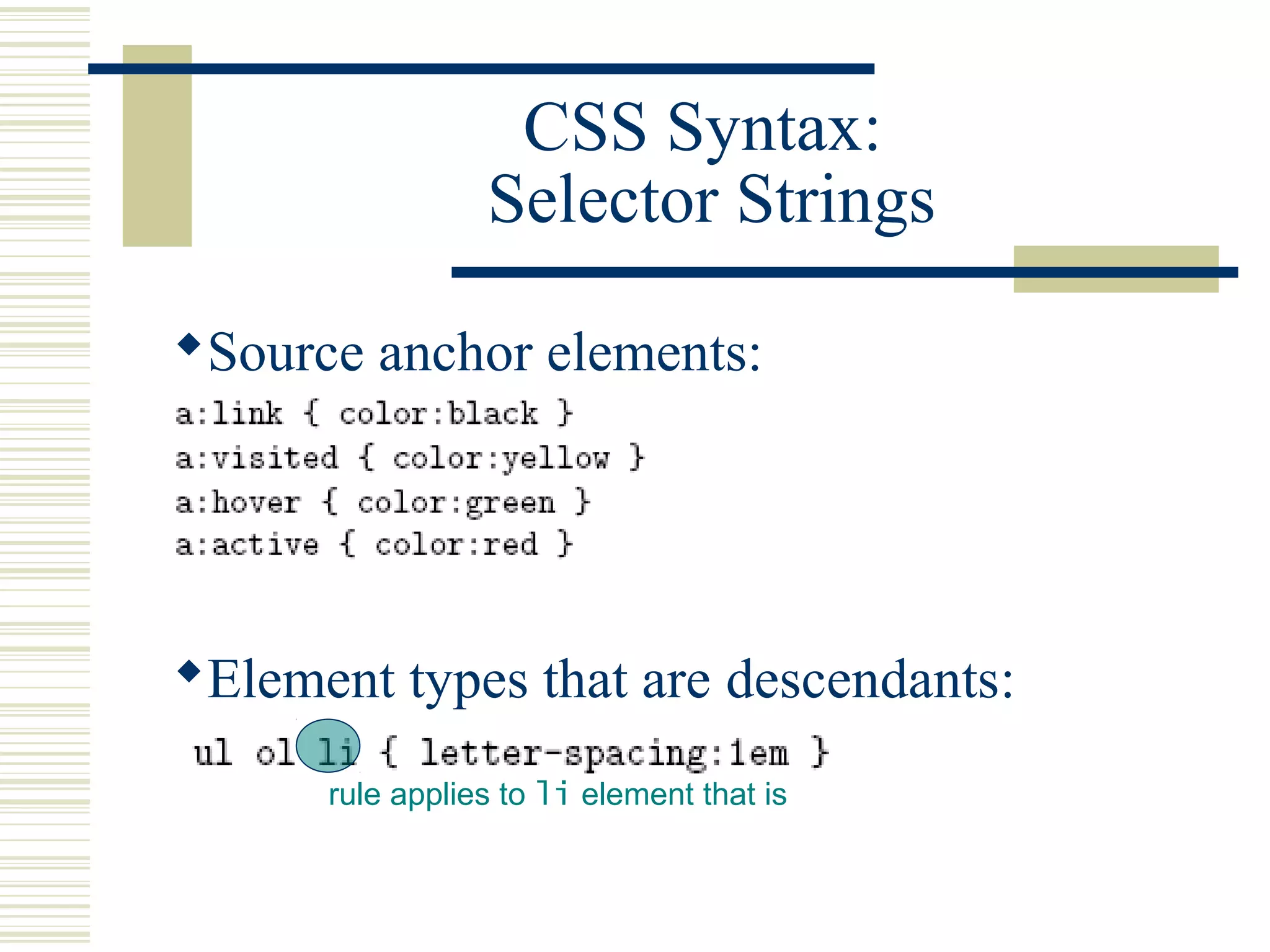
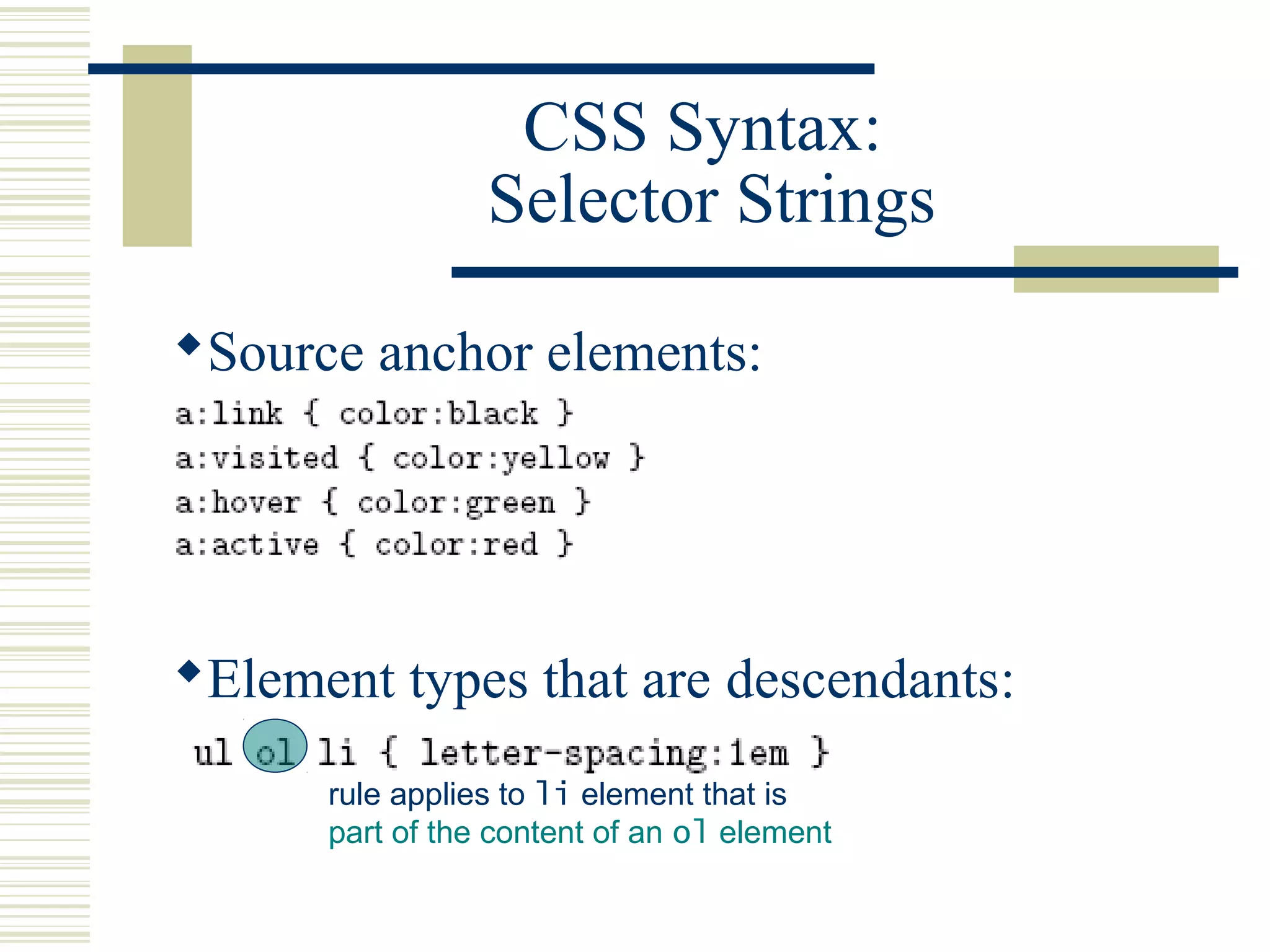
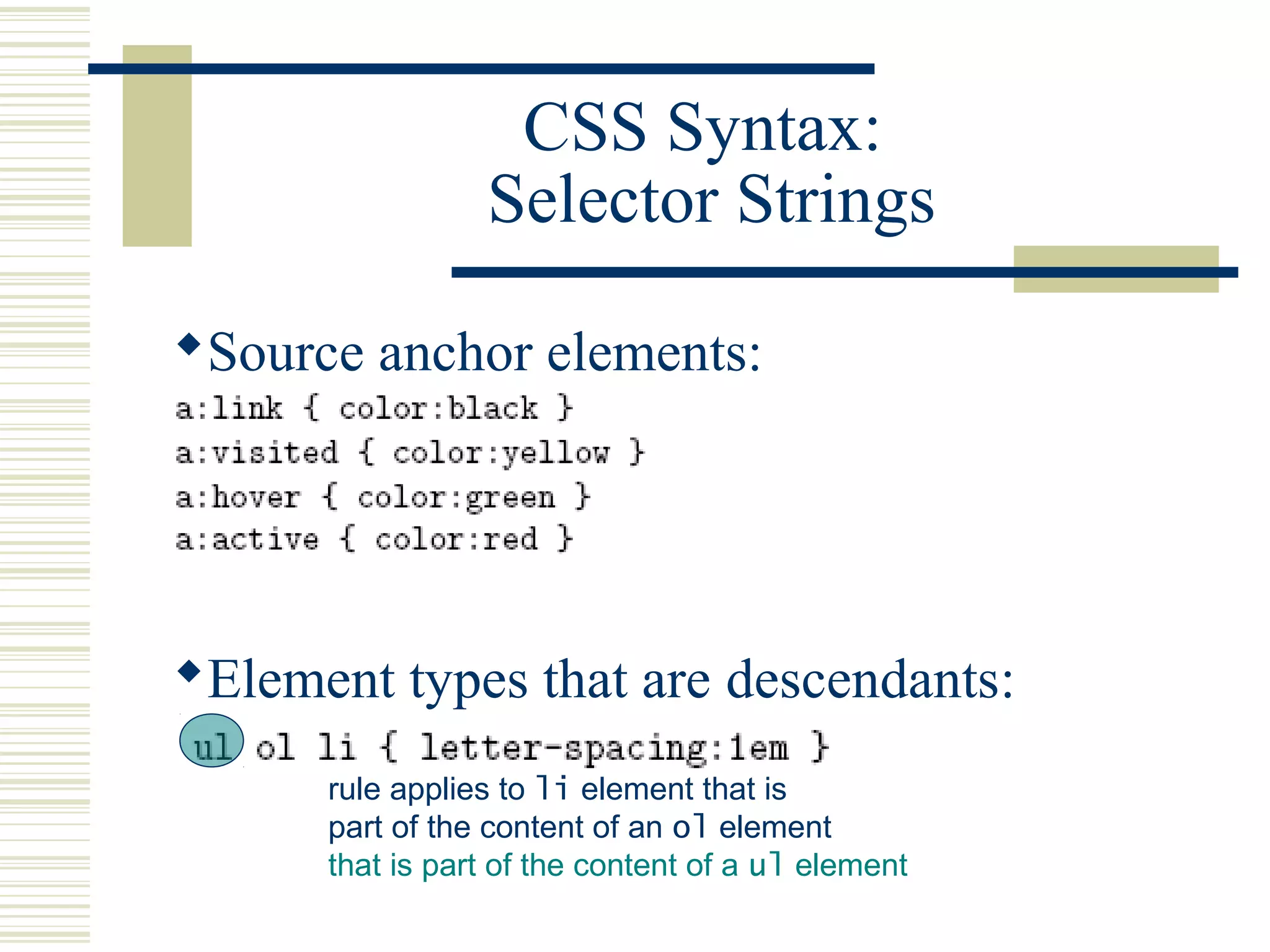
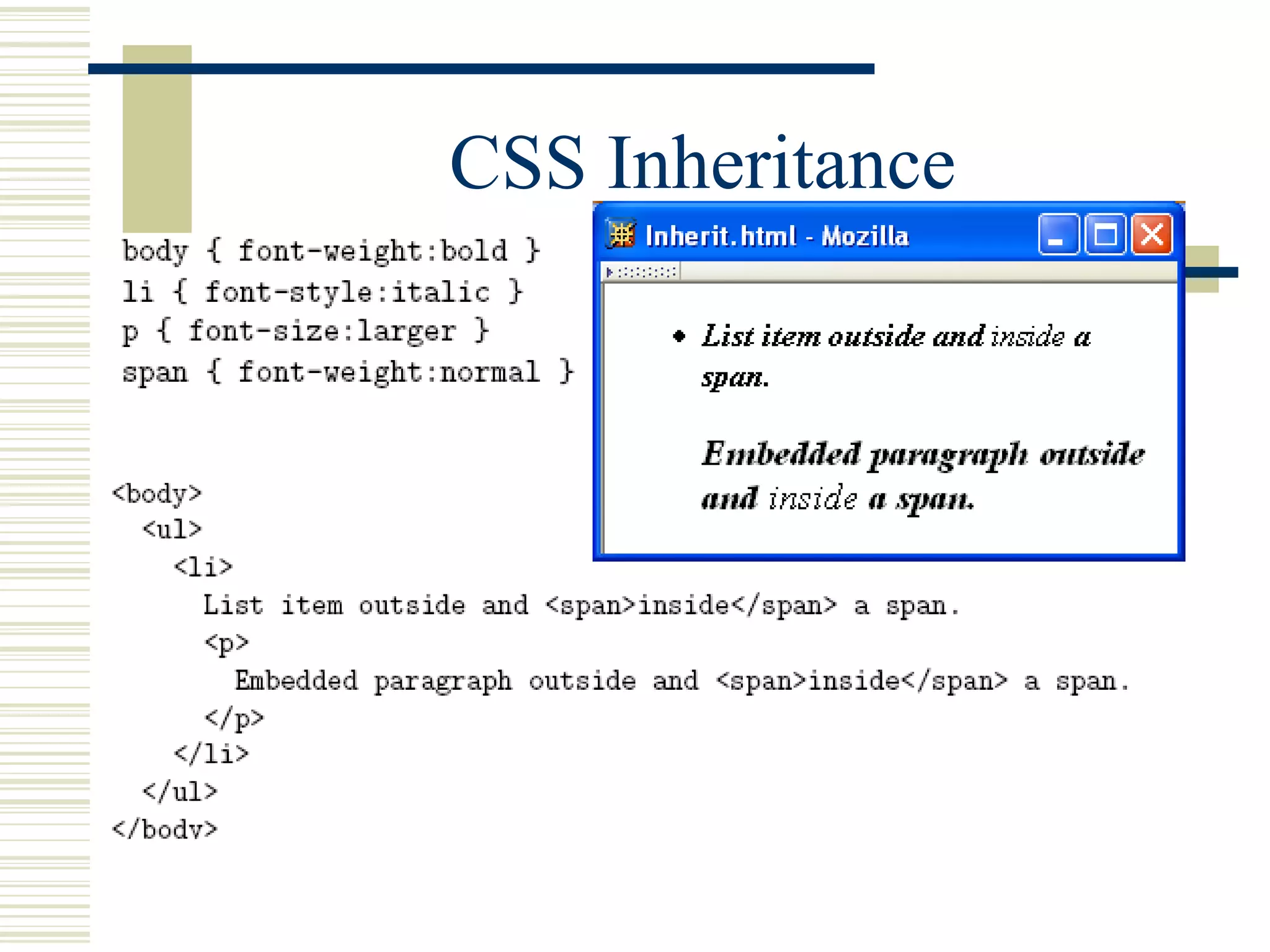
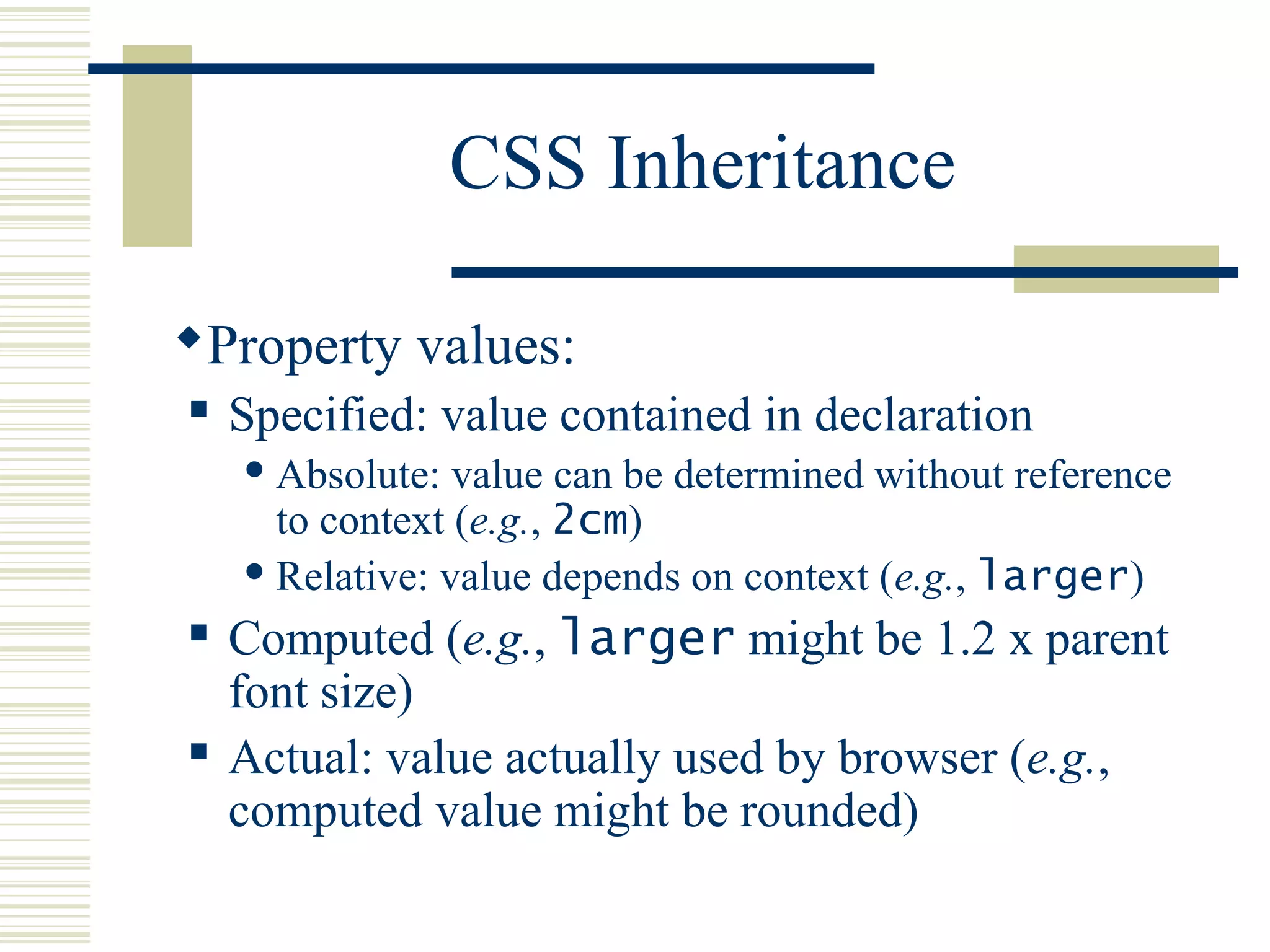
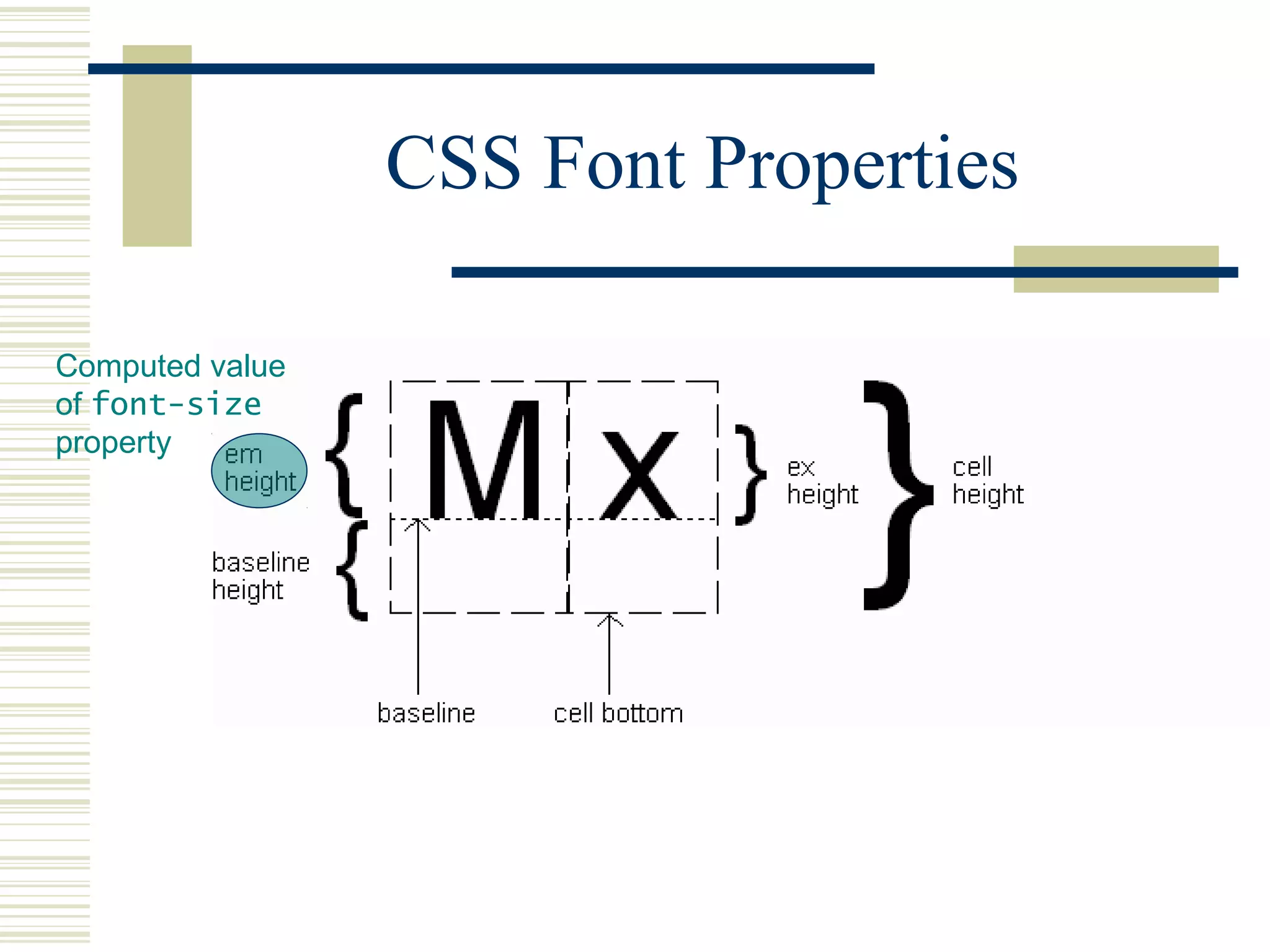
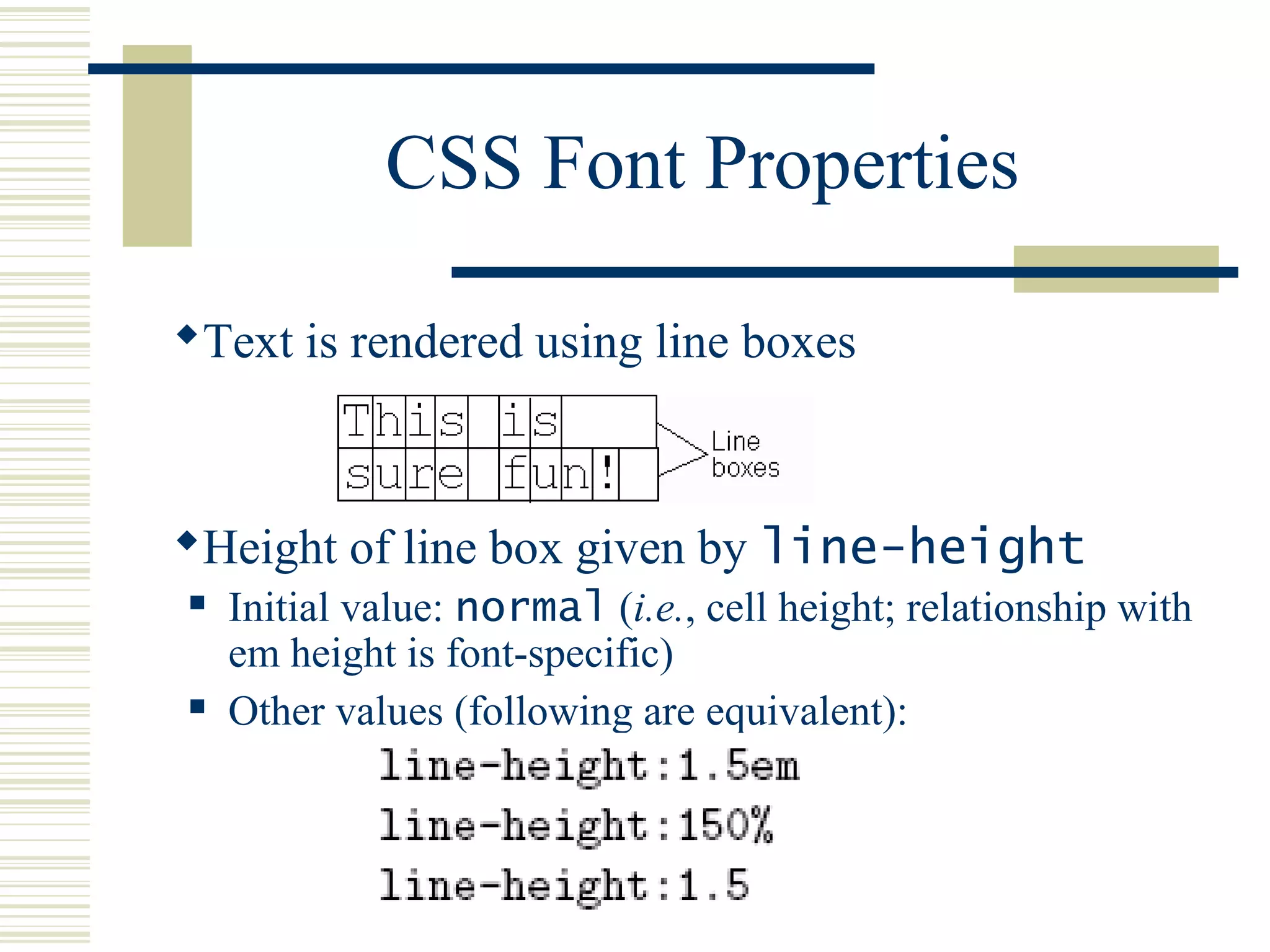
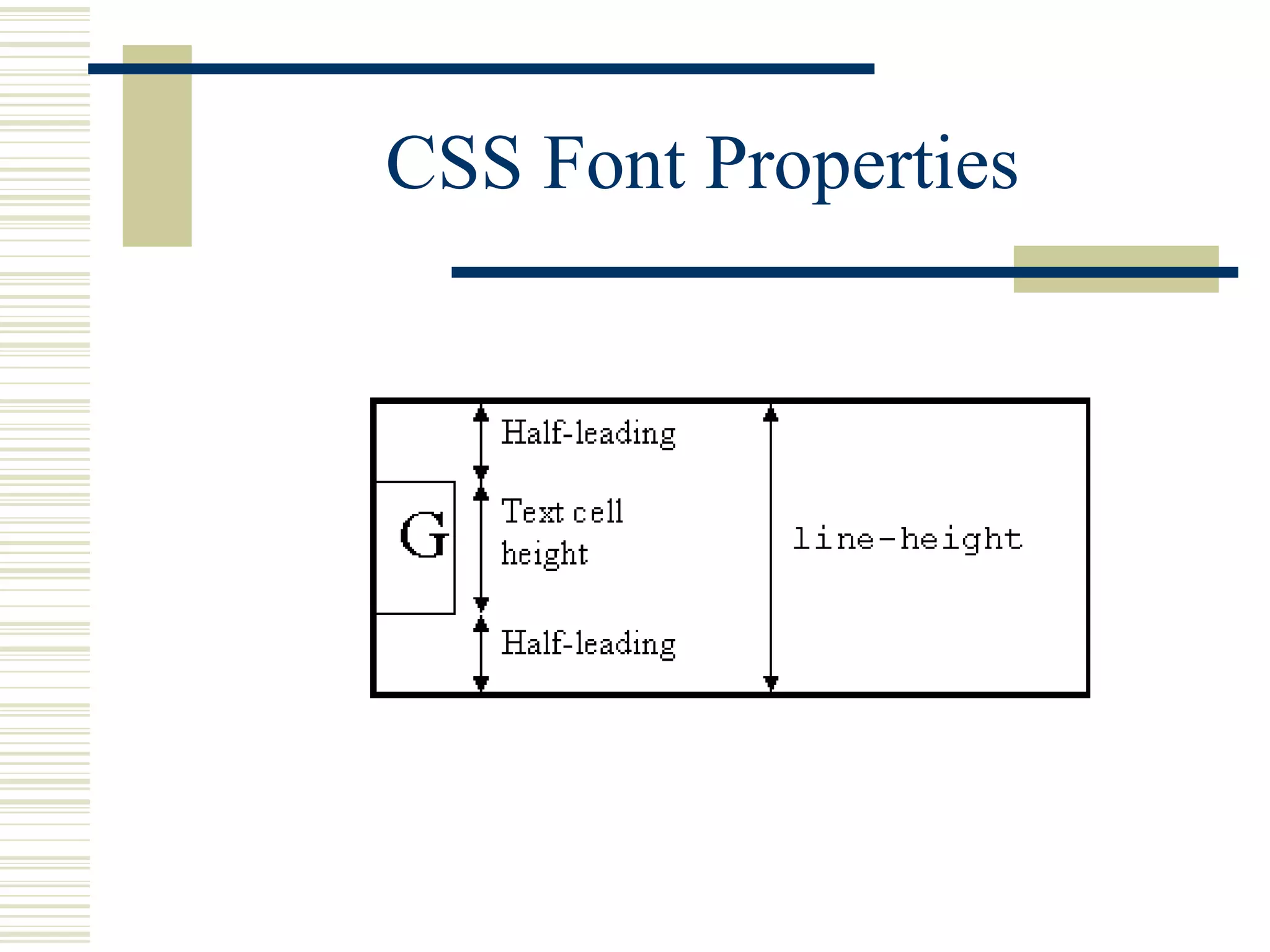
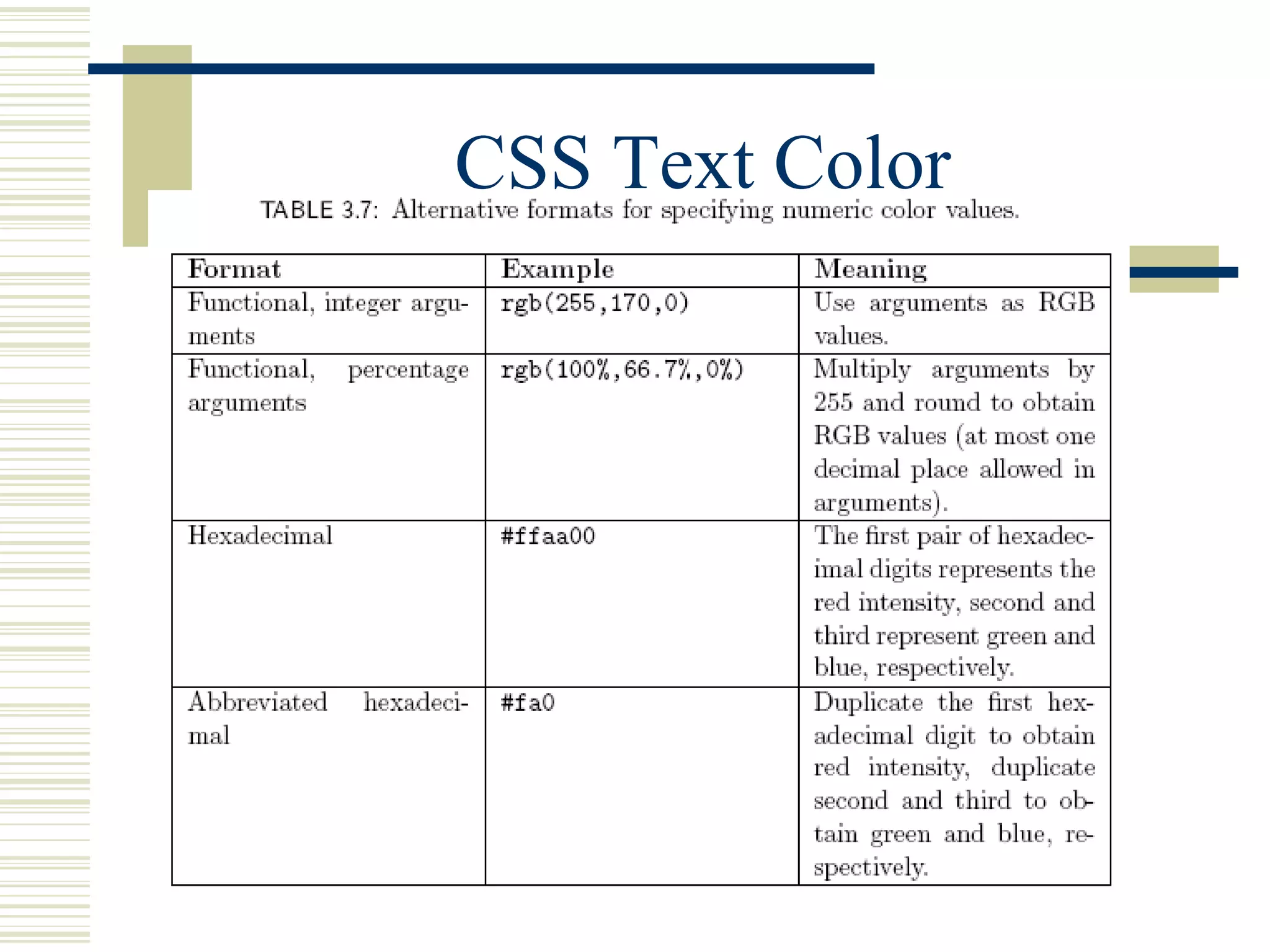
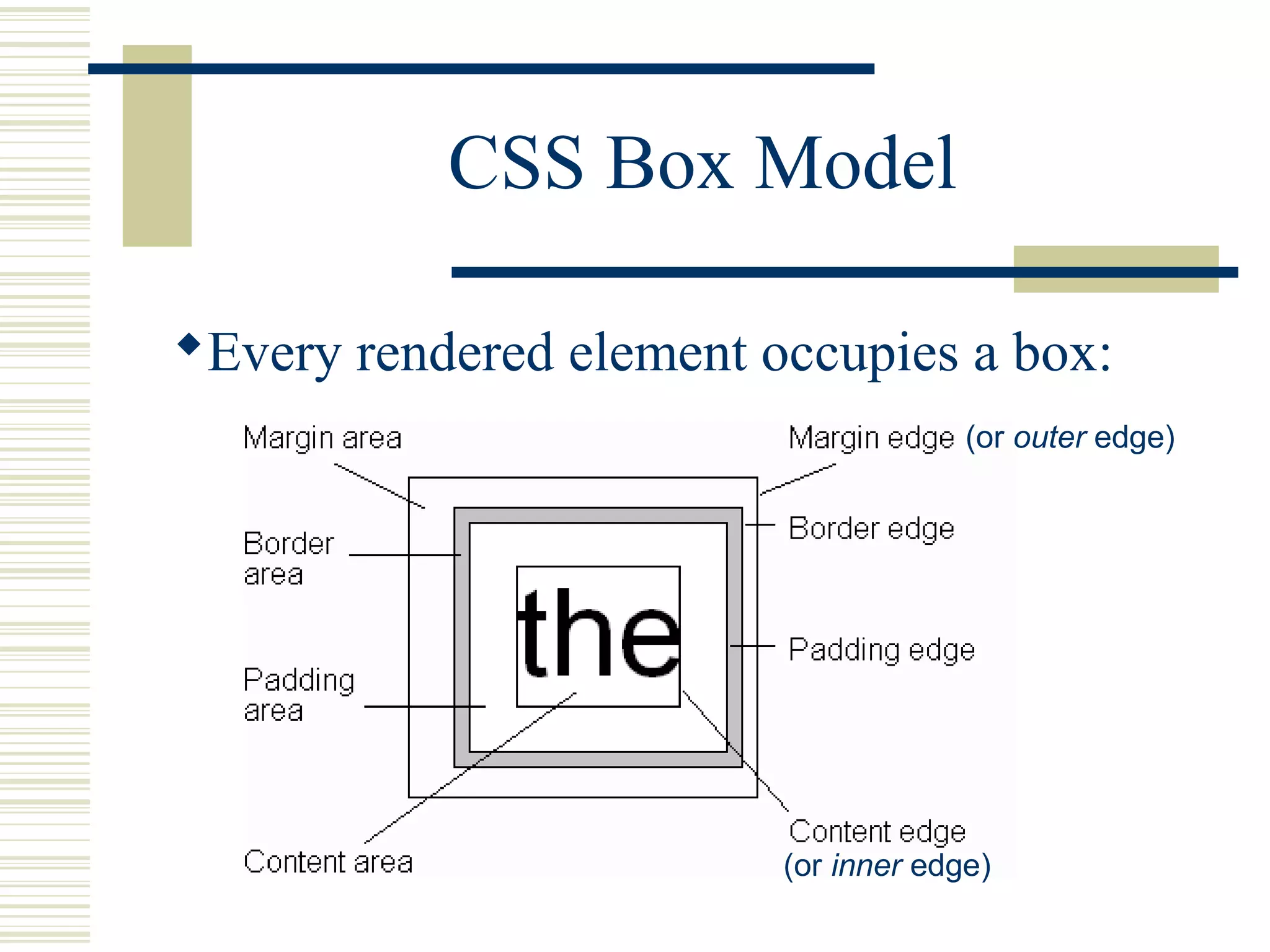
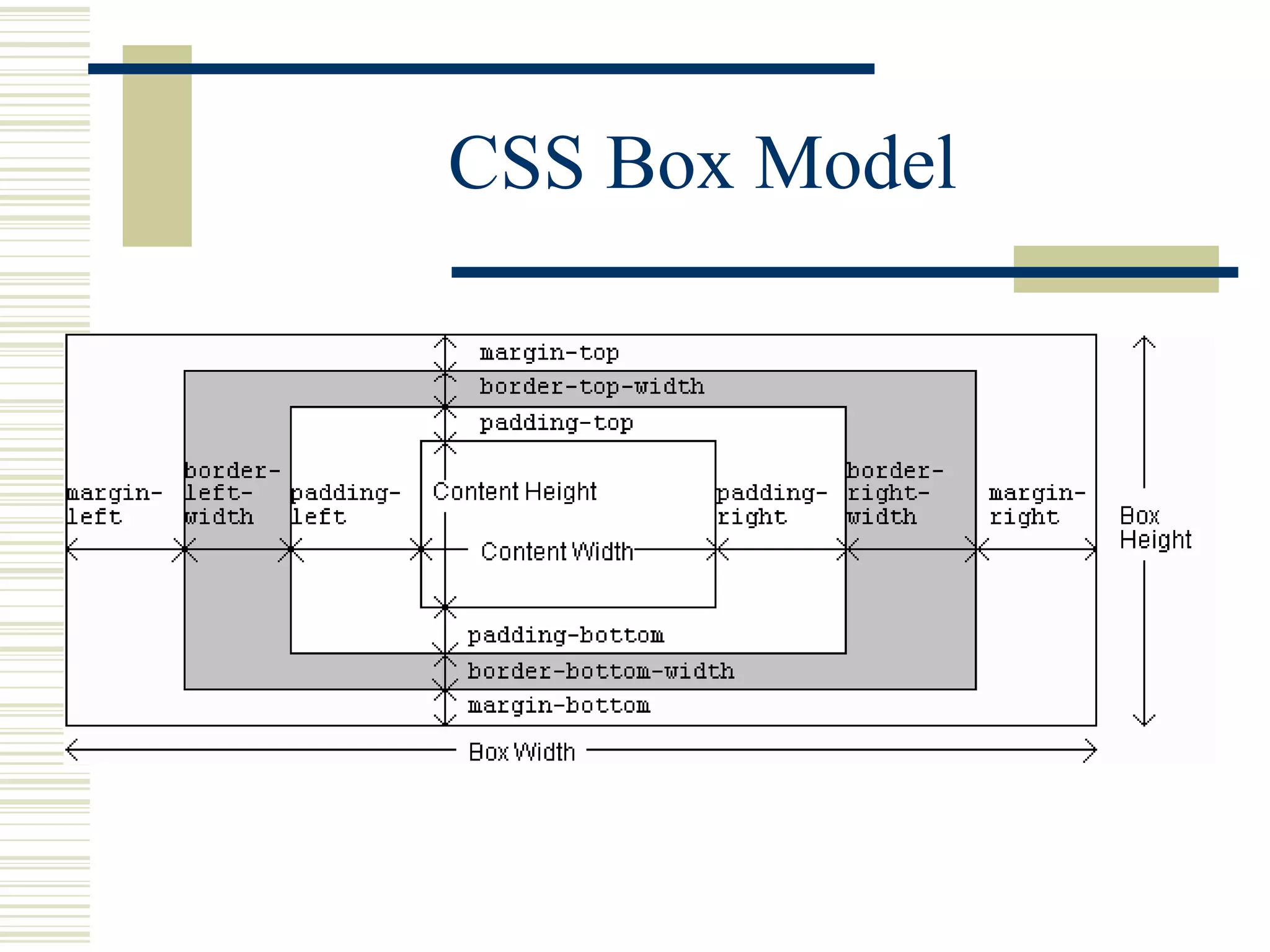
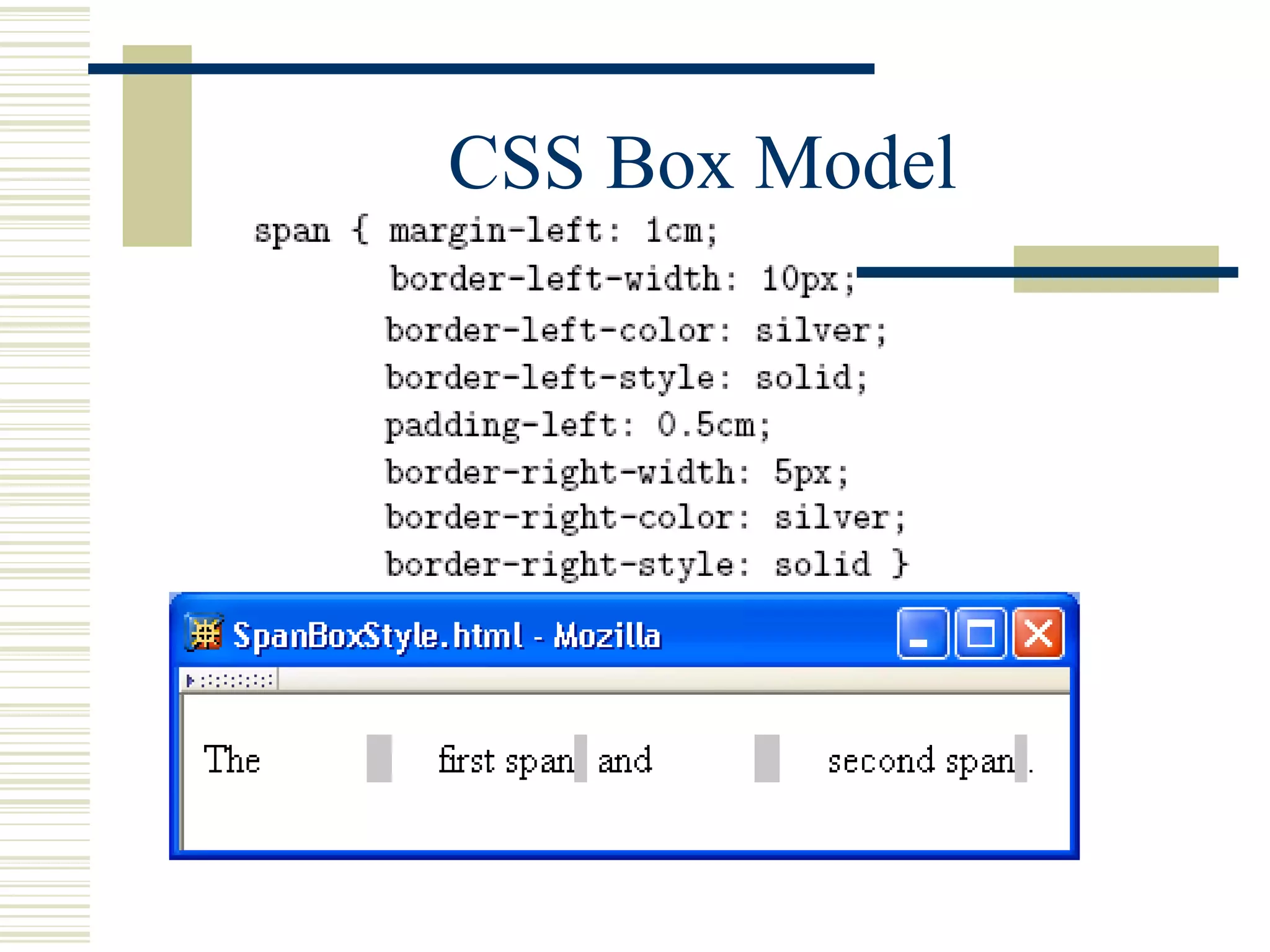
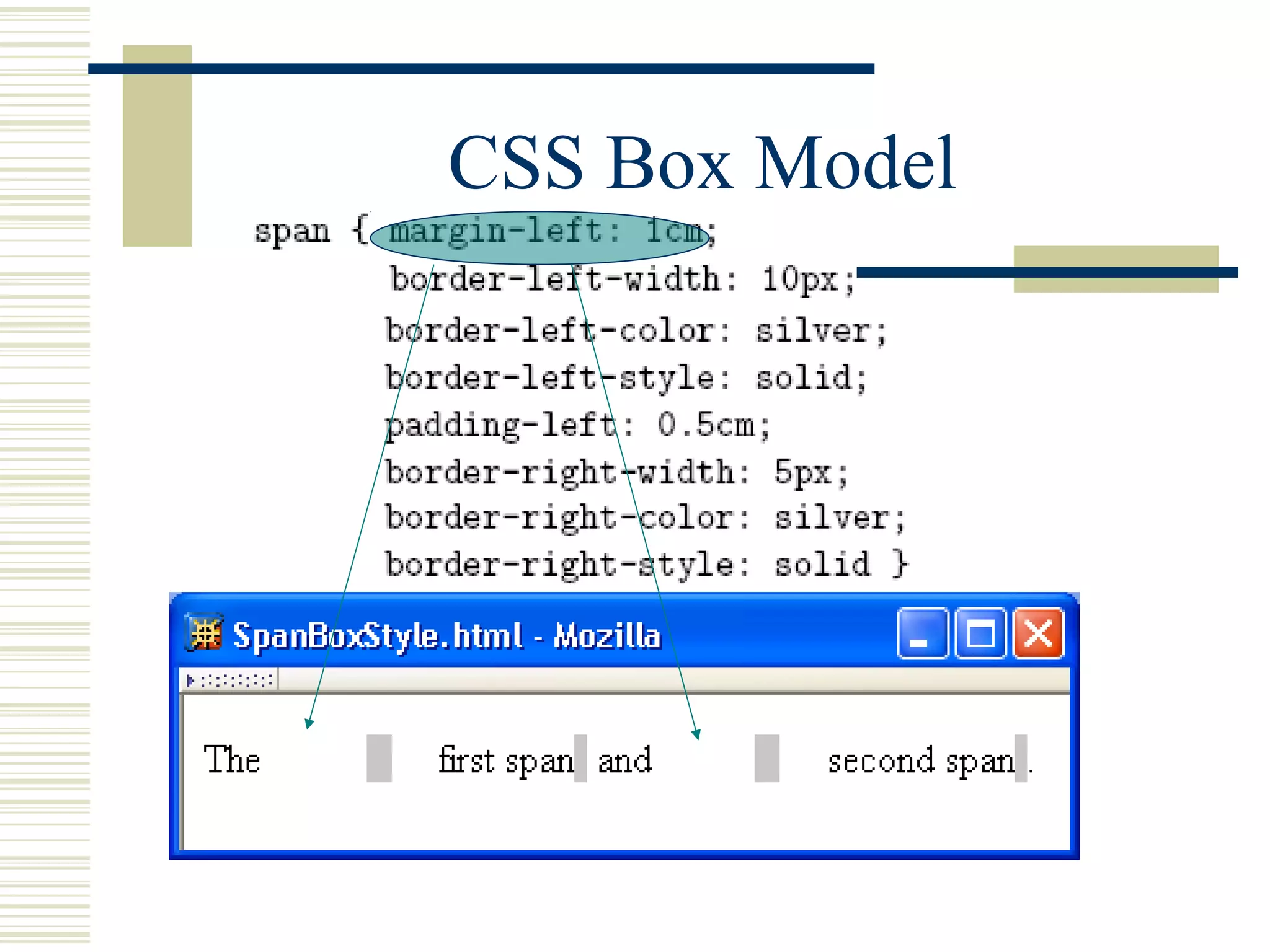
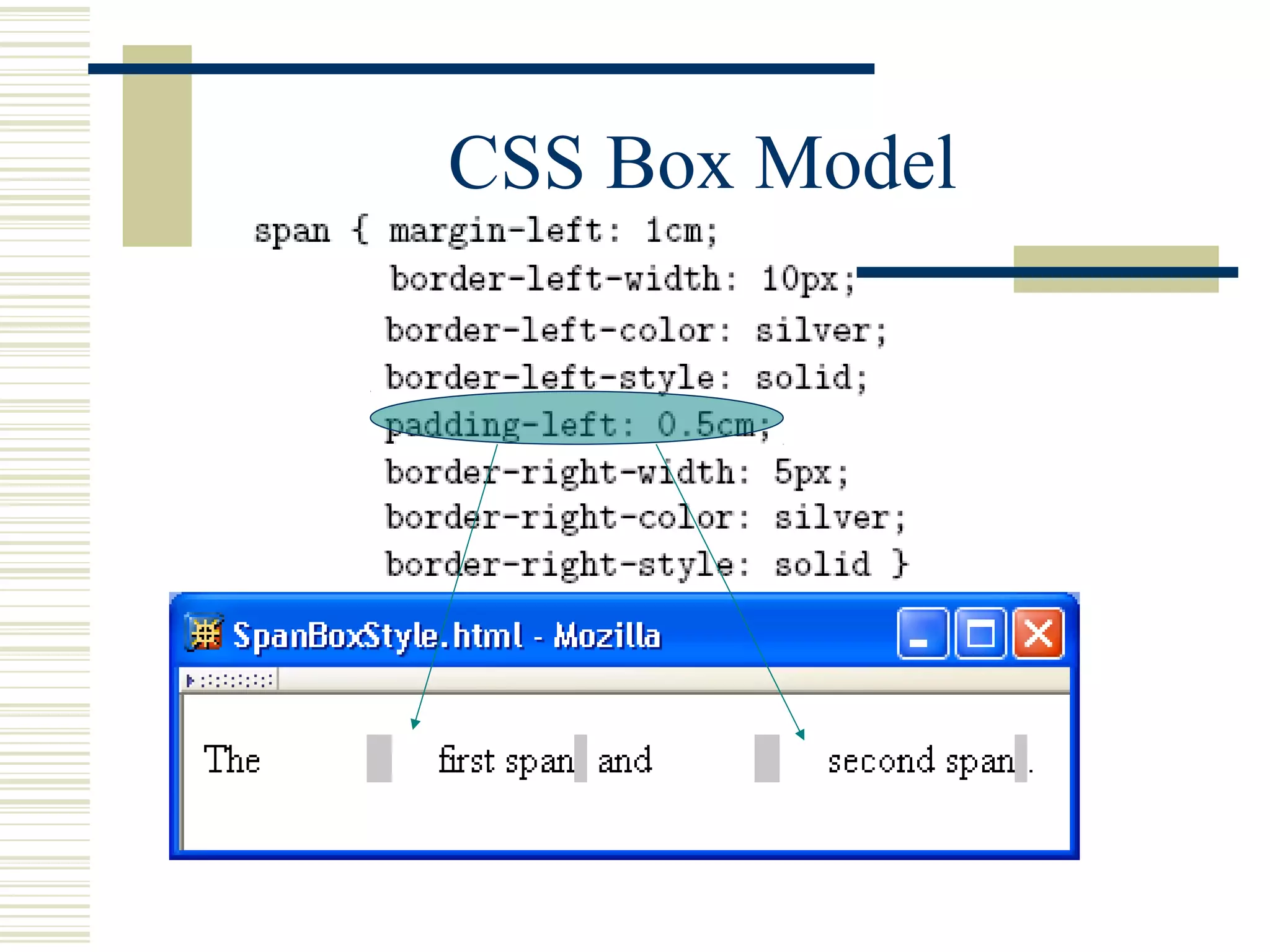
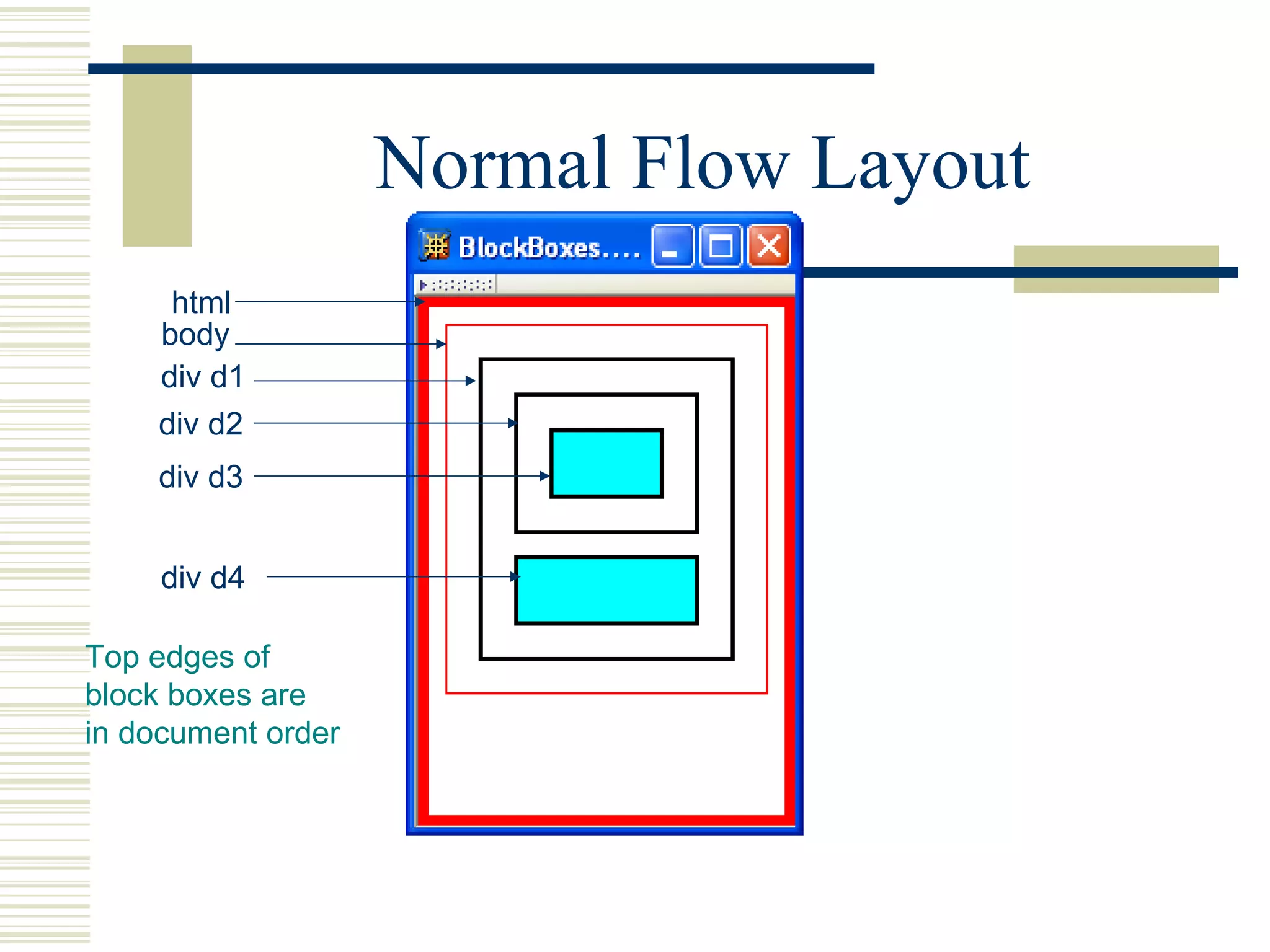
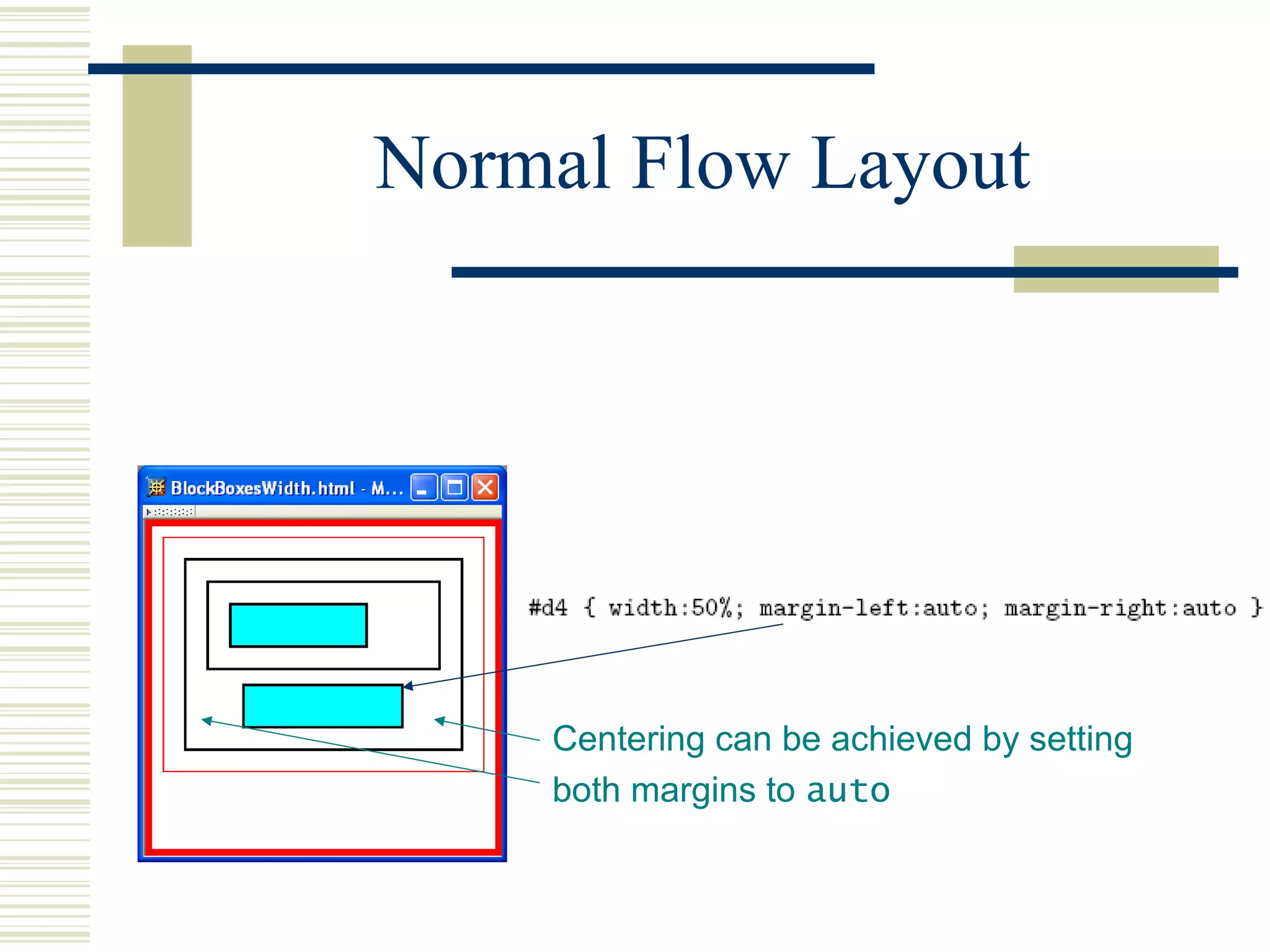
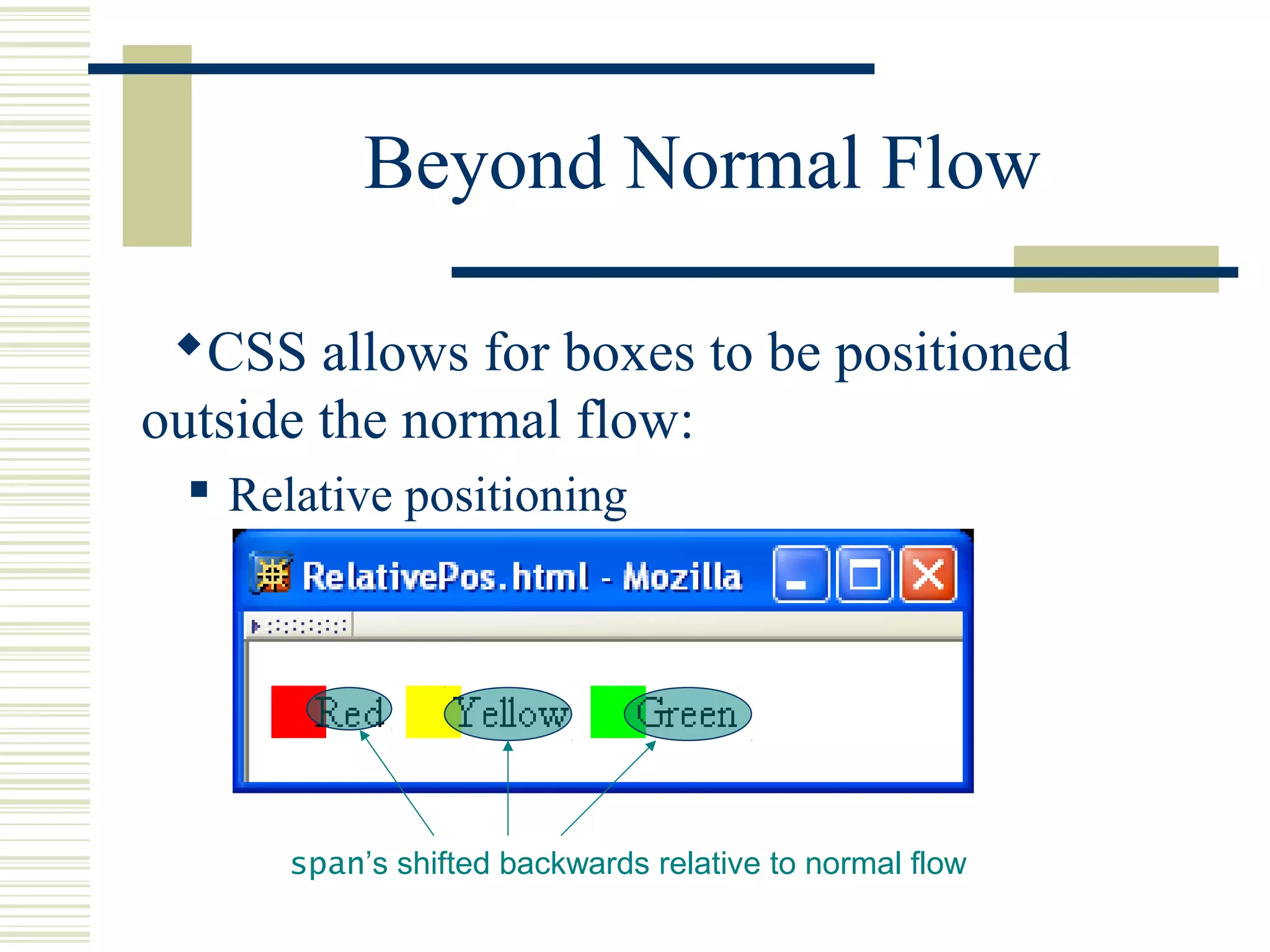
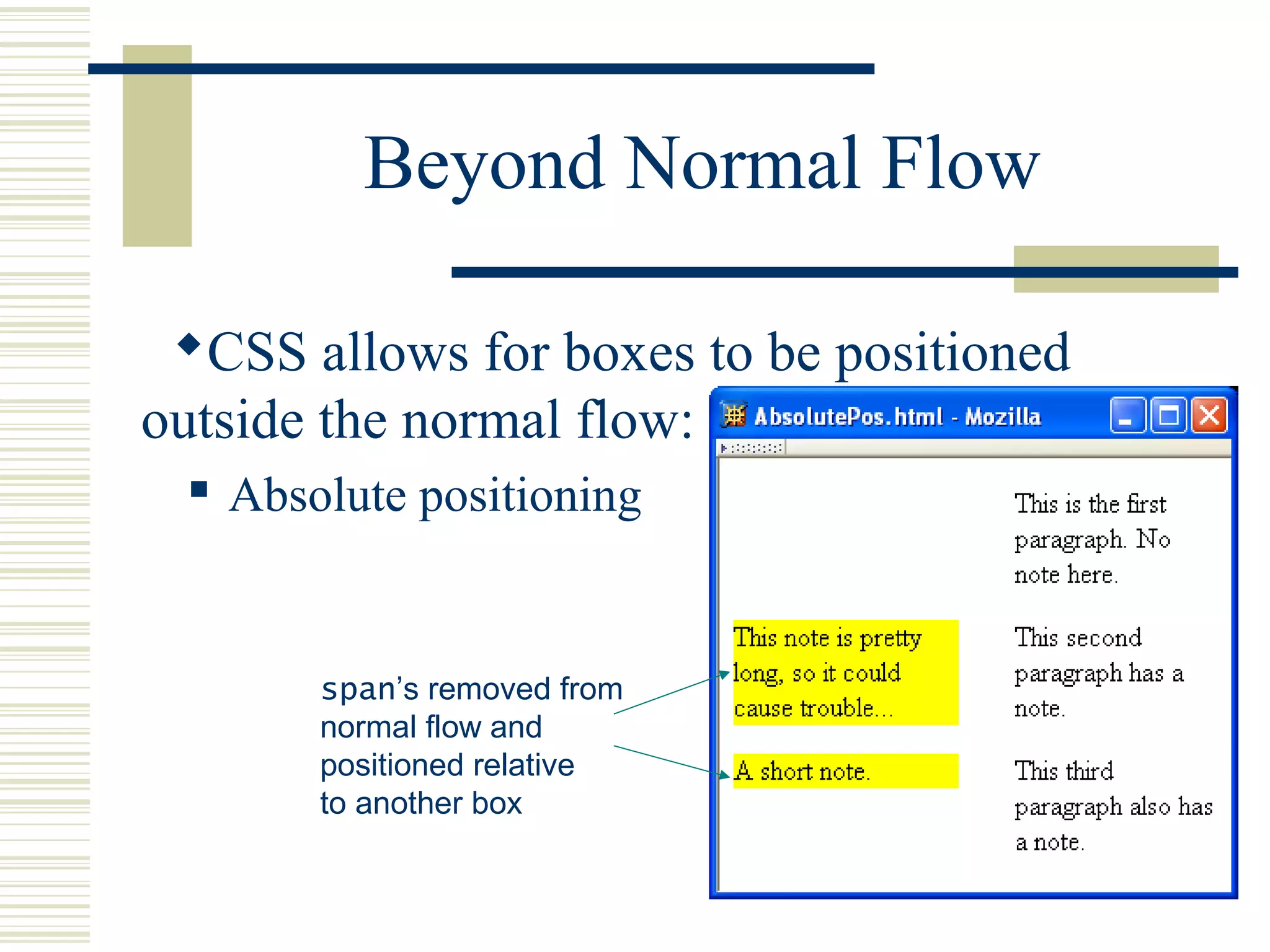
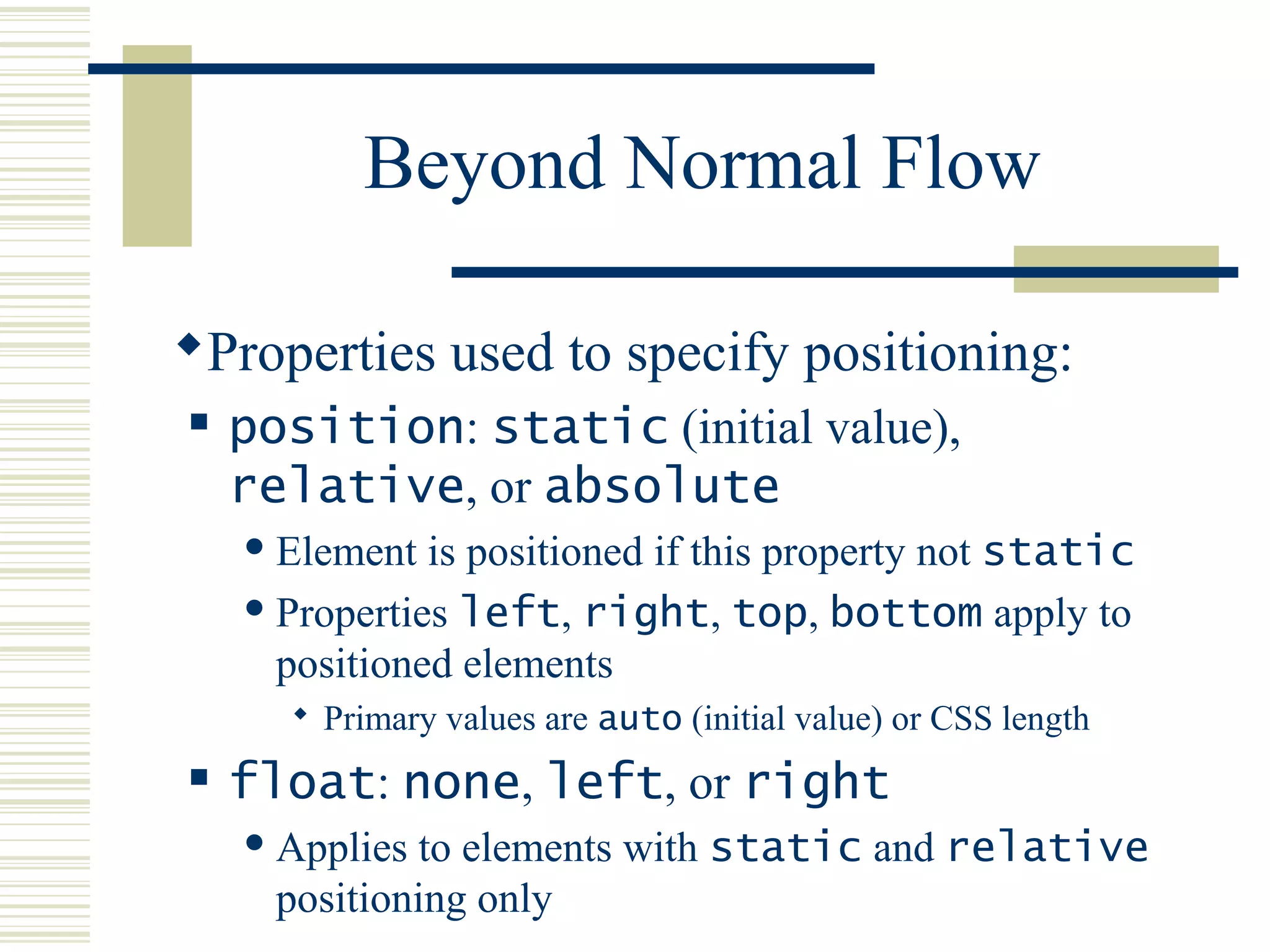
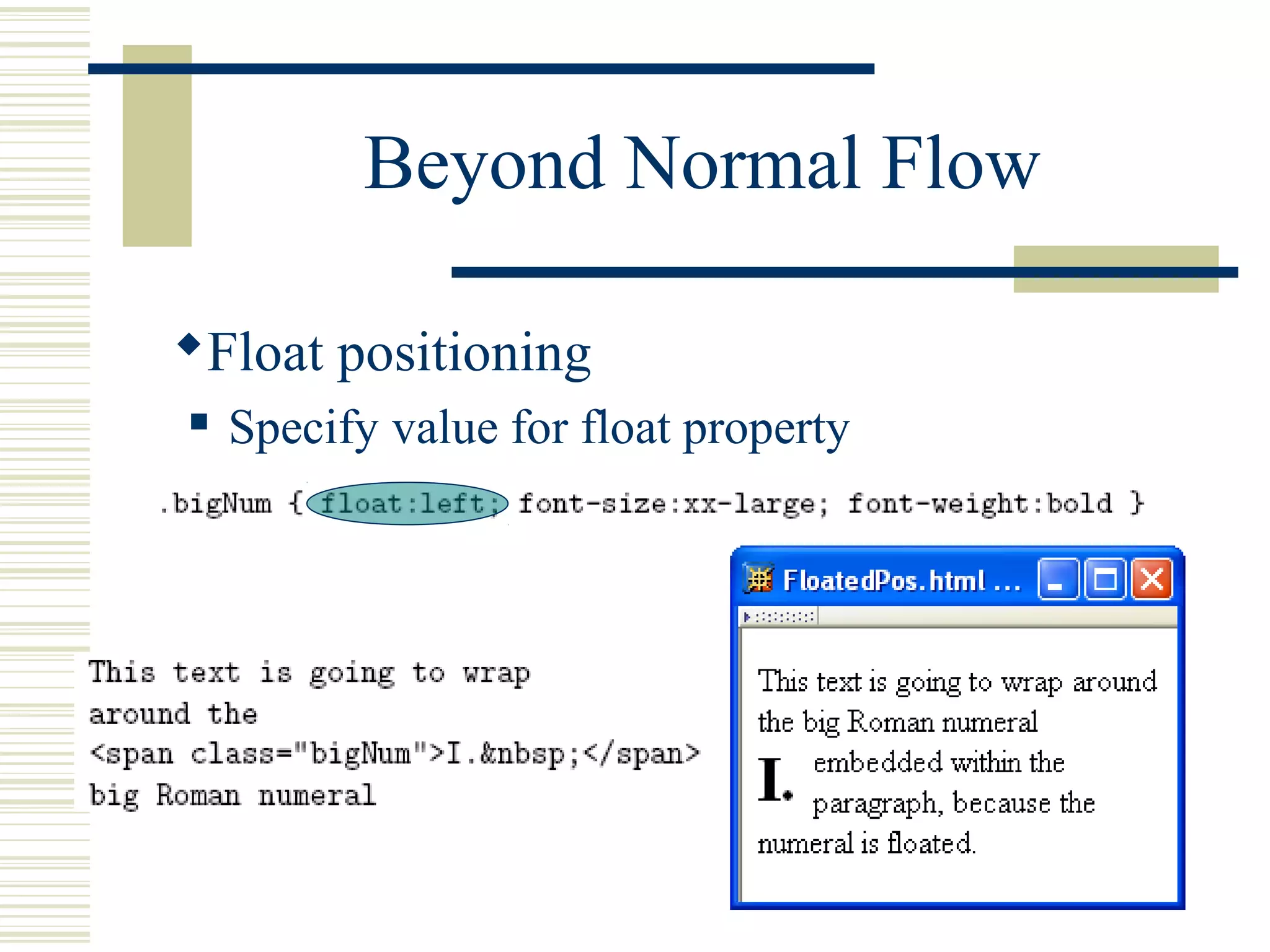
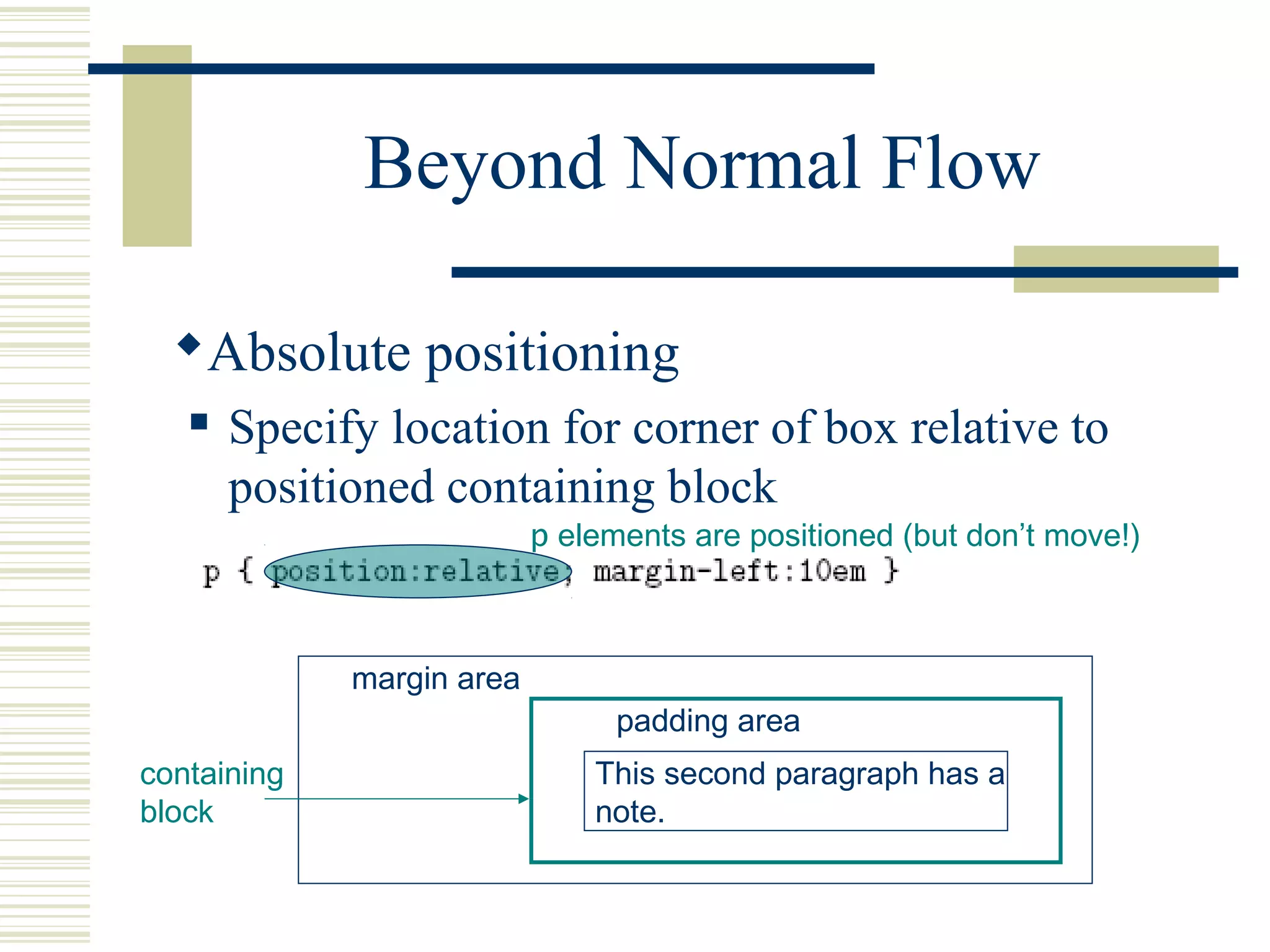
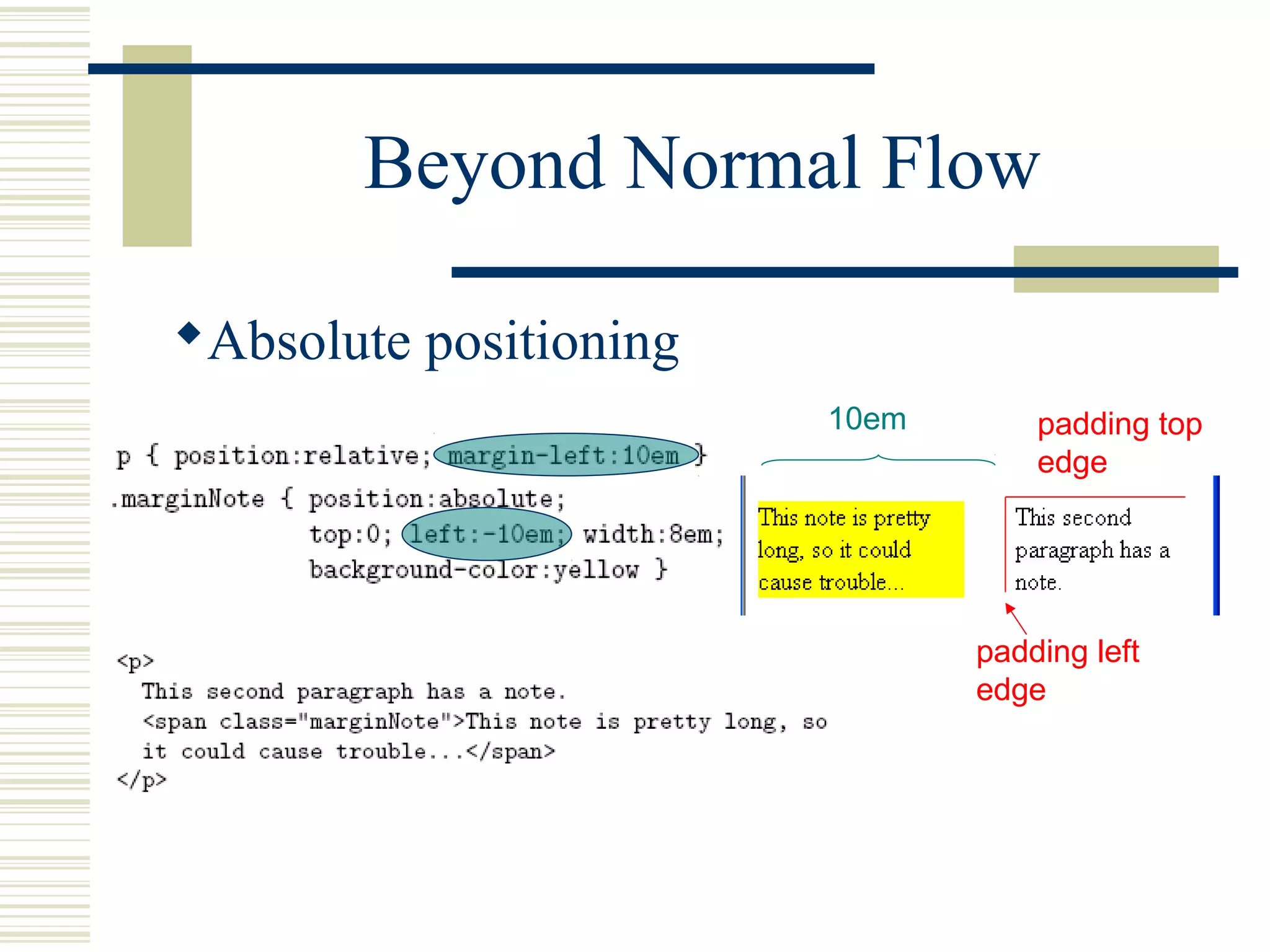
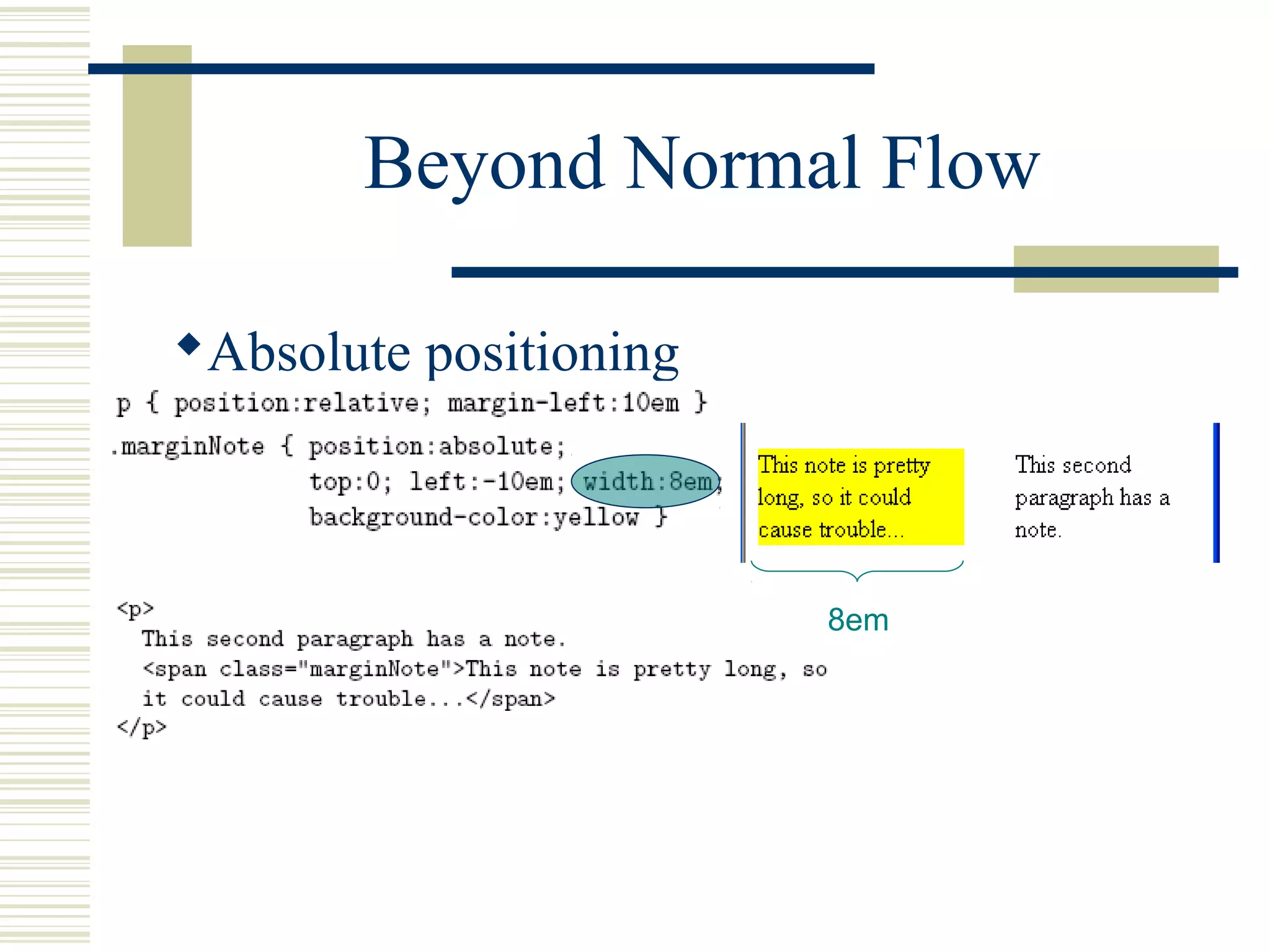
This document discusses Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and how they can be used to control the style and layout of web documents. CSS allows for a consistent look across multiple platforms, division of labor between design and coding teams, and user control over formatting. CSS rules use selectors to target specific elements and properties to set styles like colors, fonts, sizes, and positioning. CSS handles inheritance of styles and prioritizes rules based on specificity. Styles can position elements outside of normal flow using relative, float, and absolute positioning.