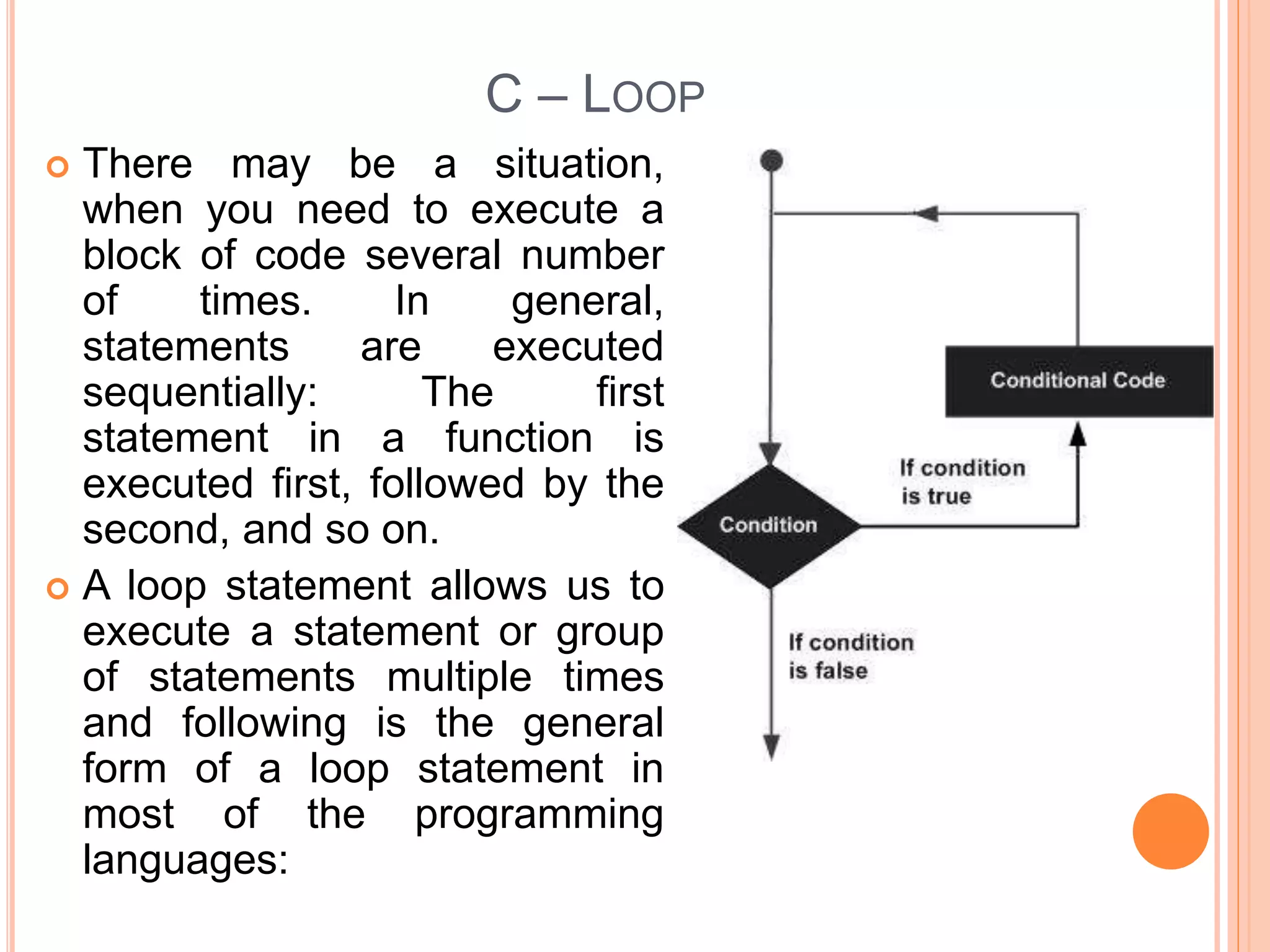
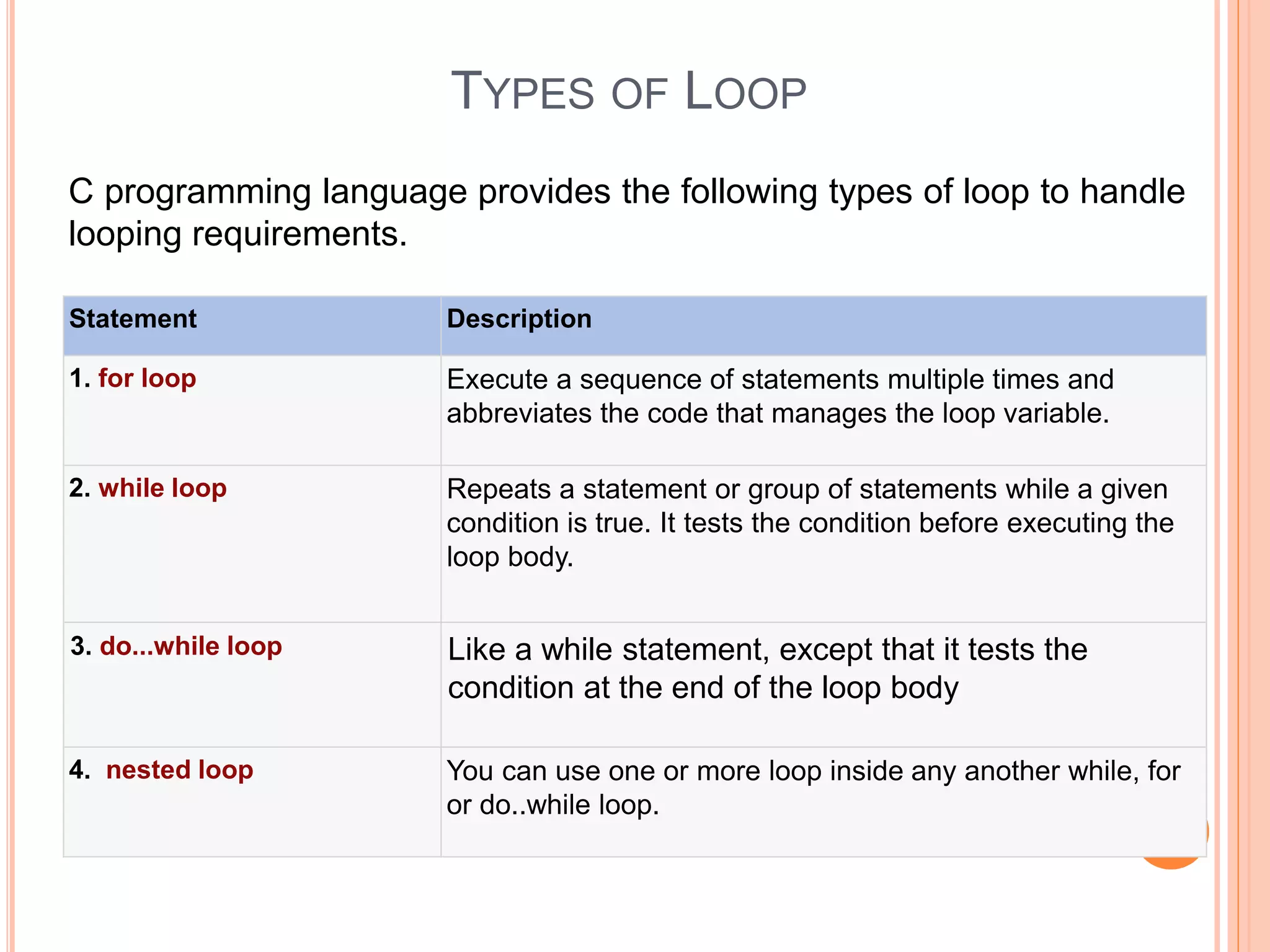
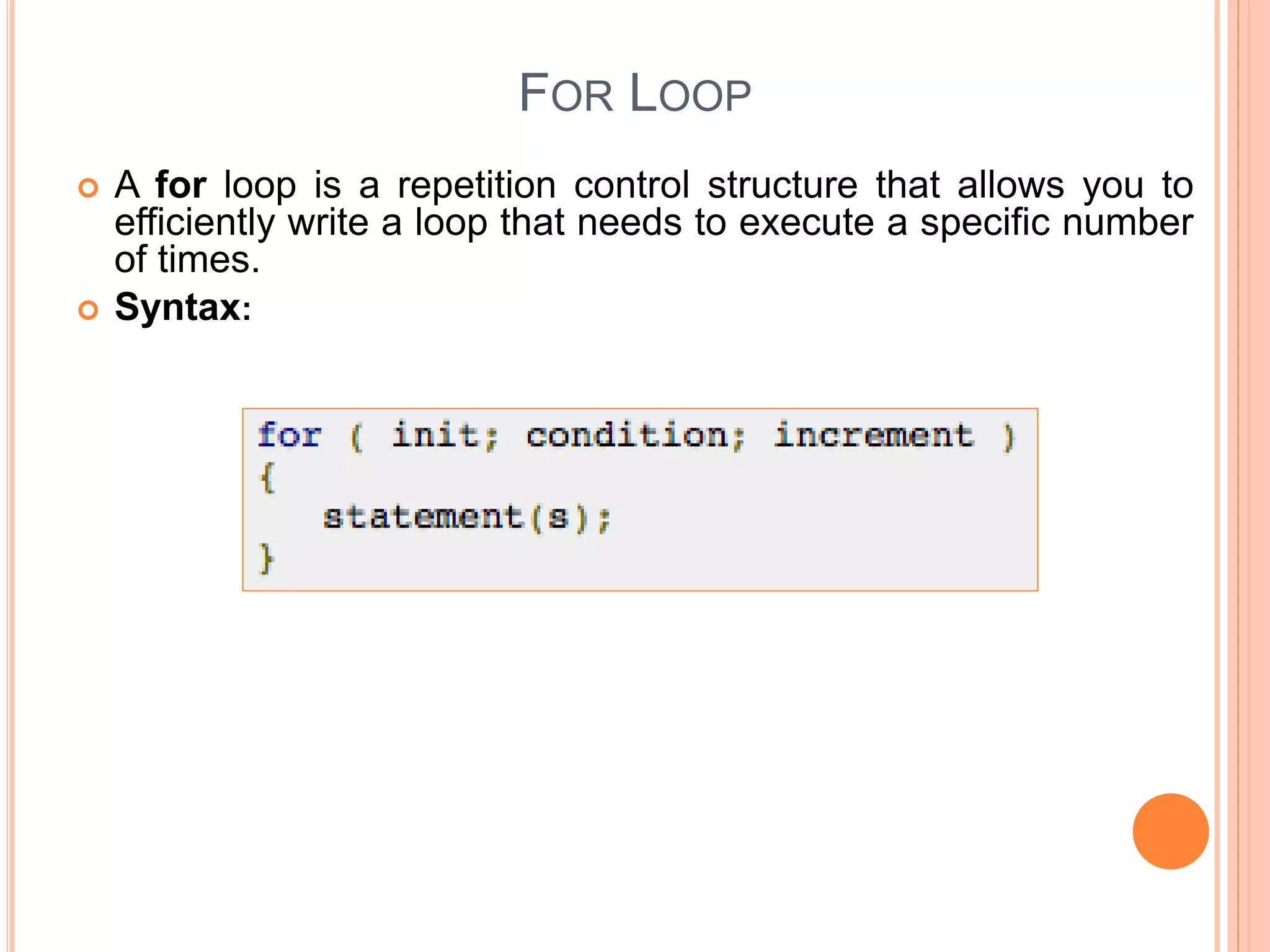
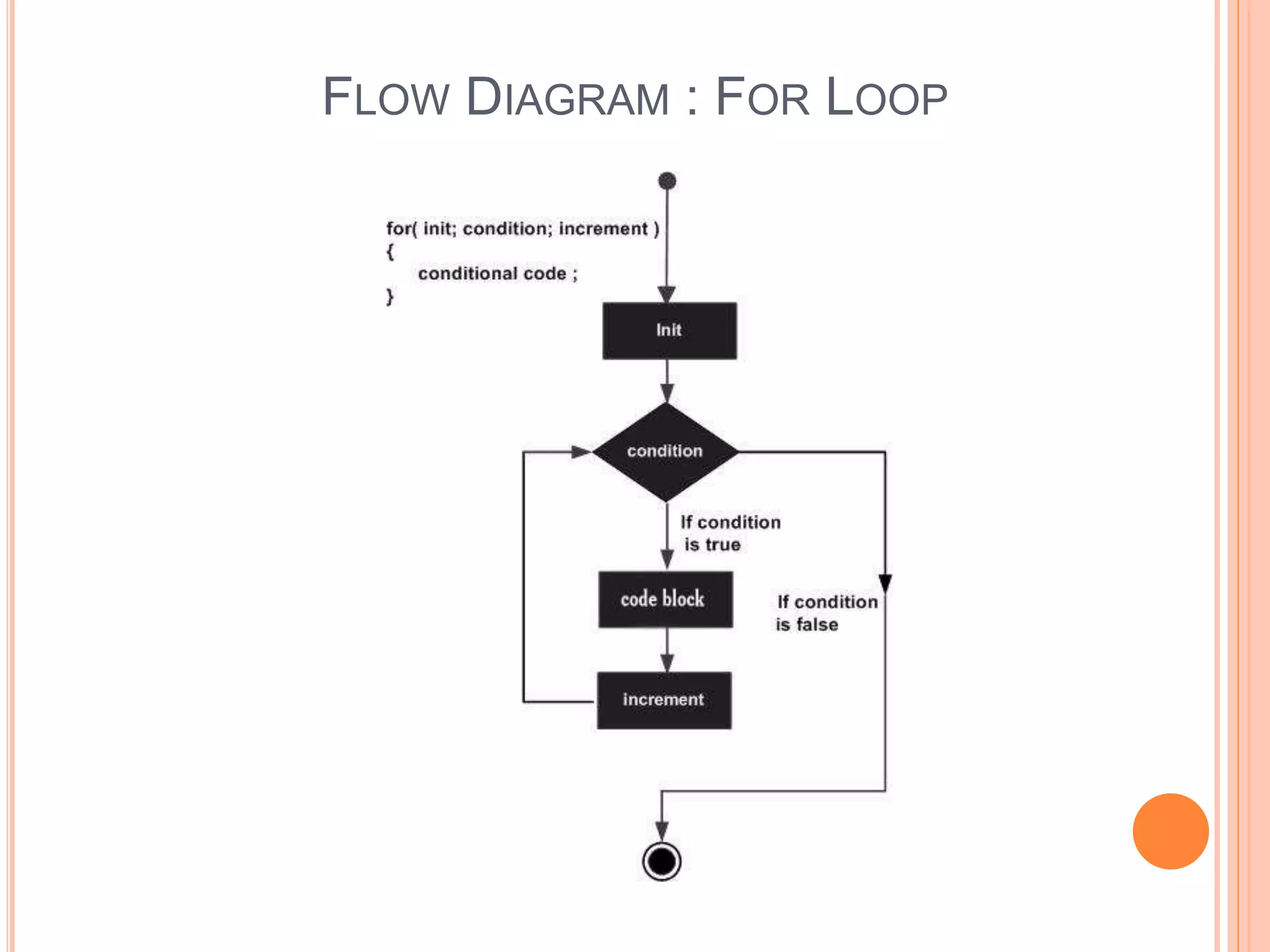
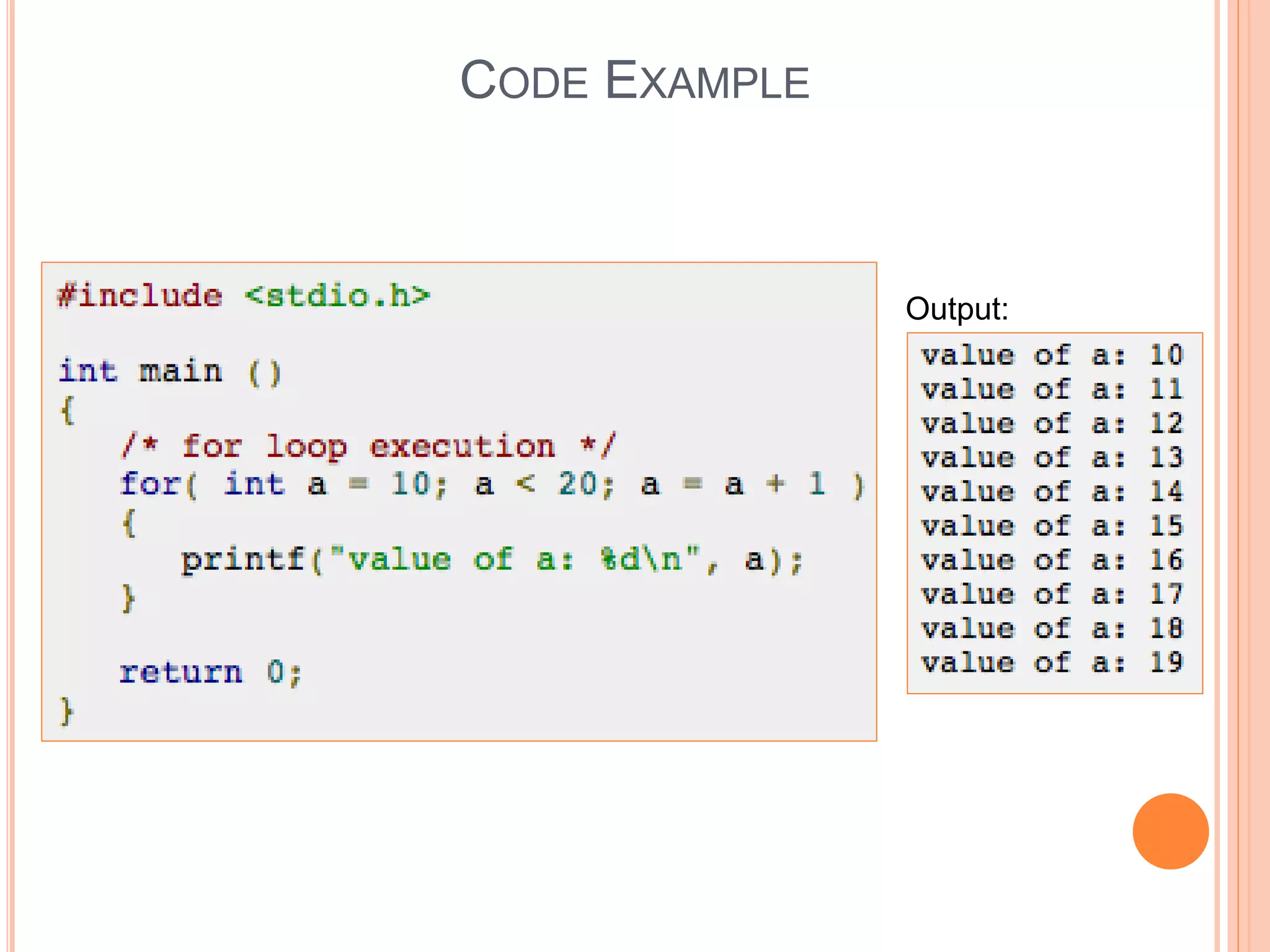
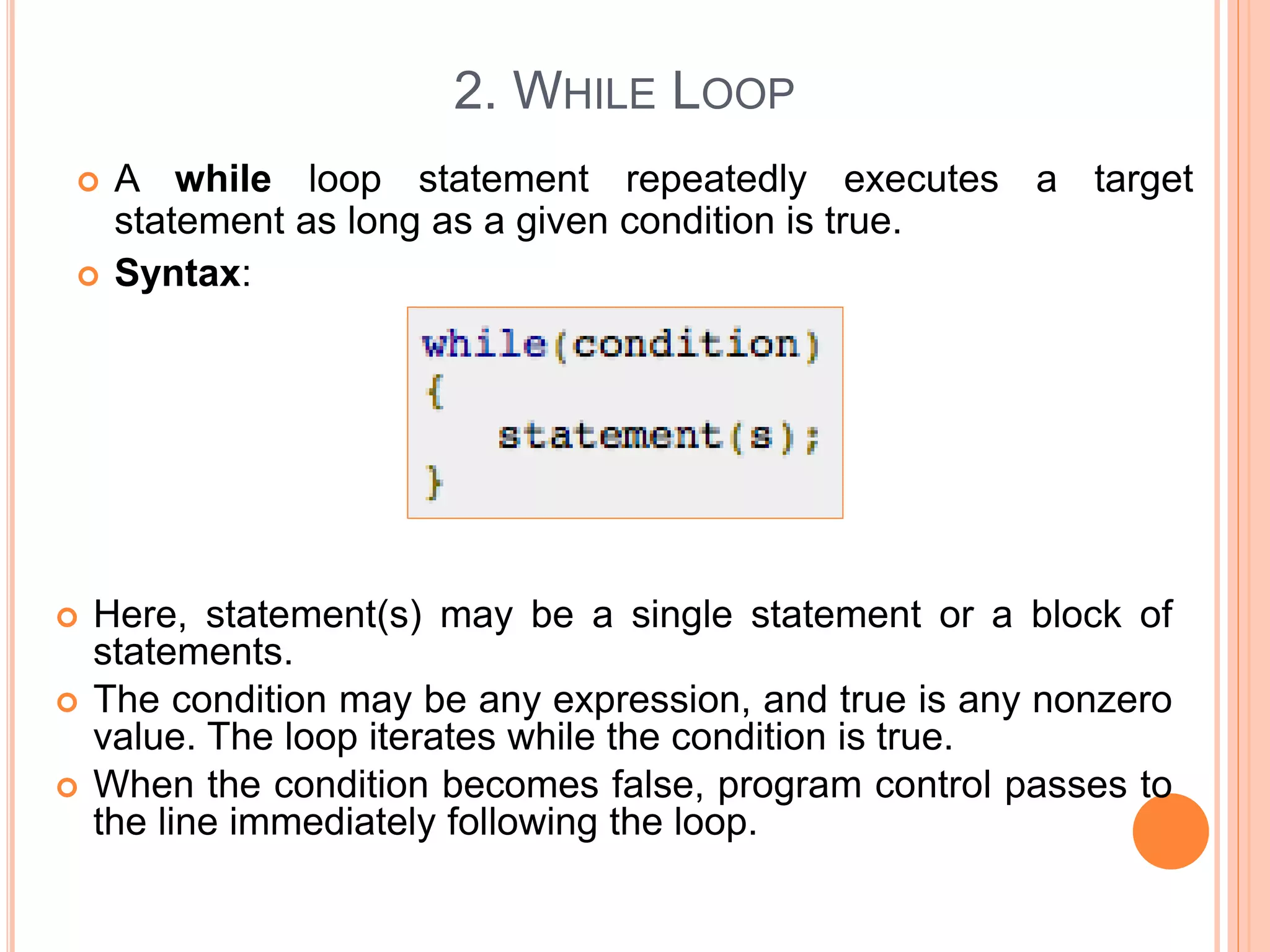
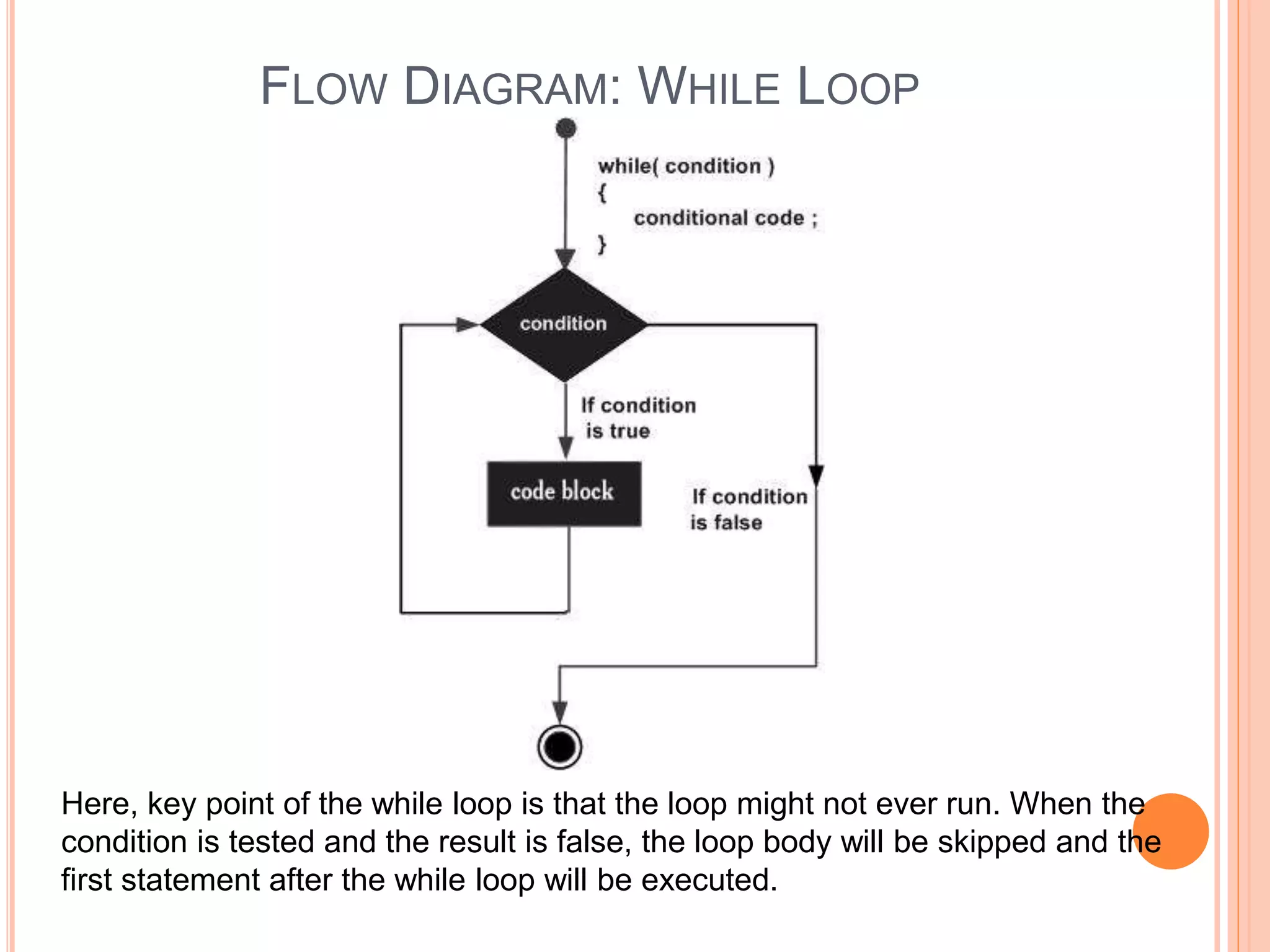
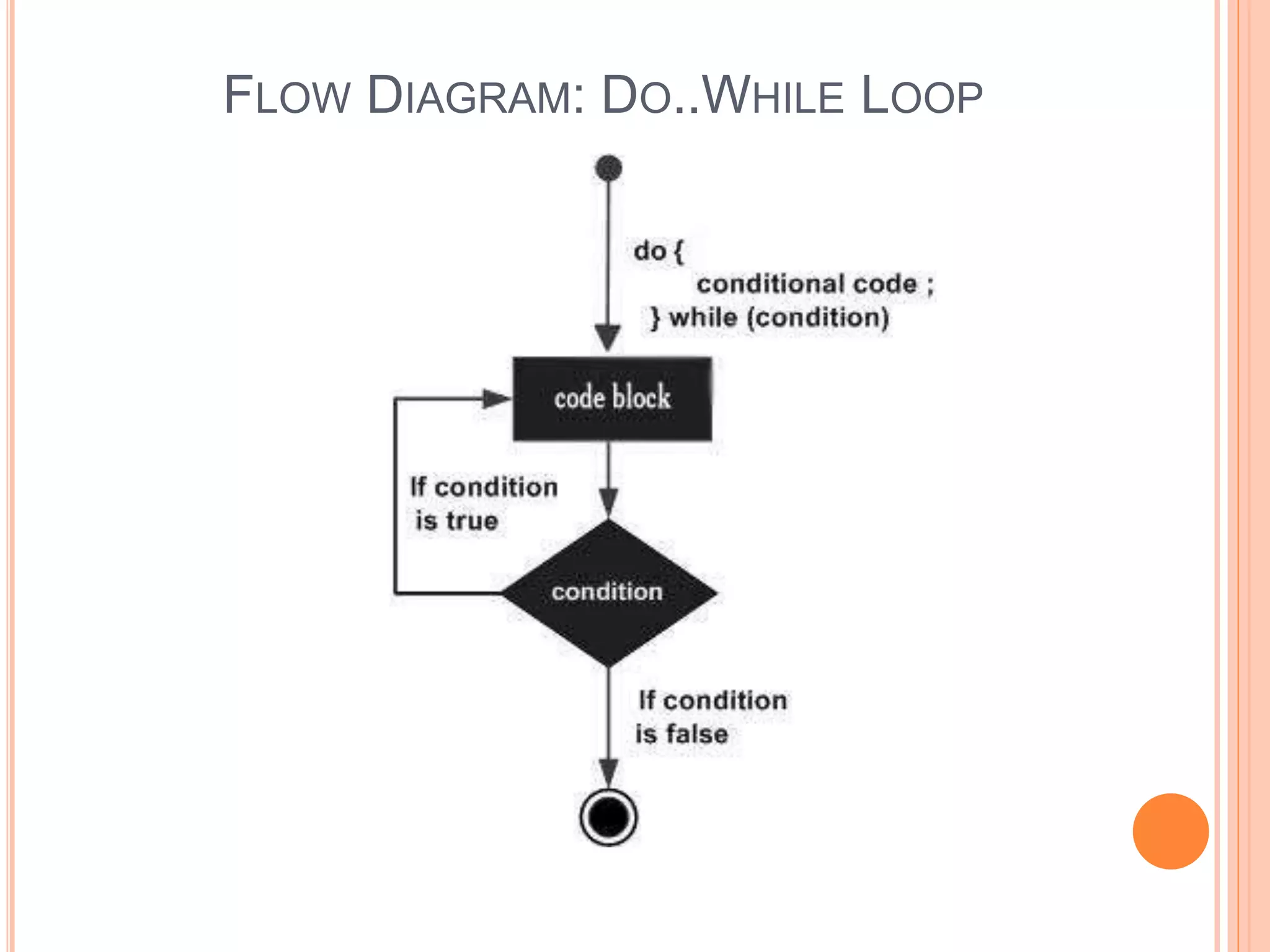
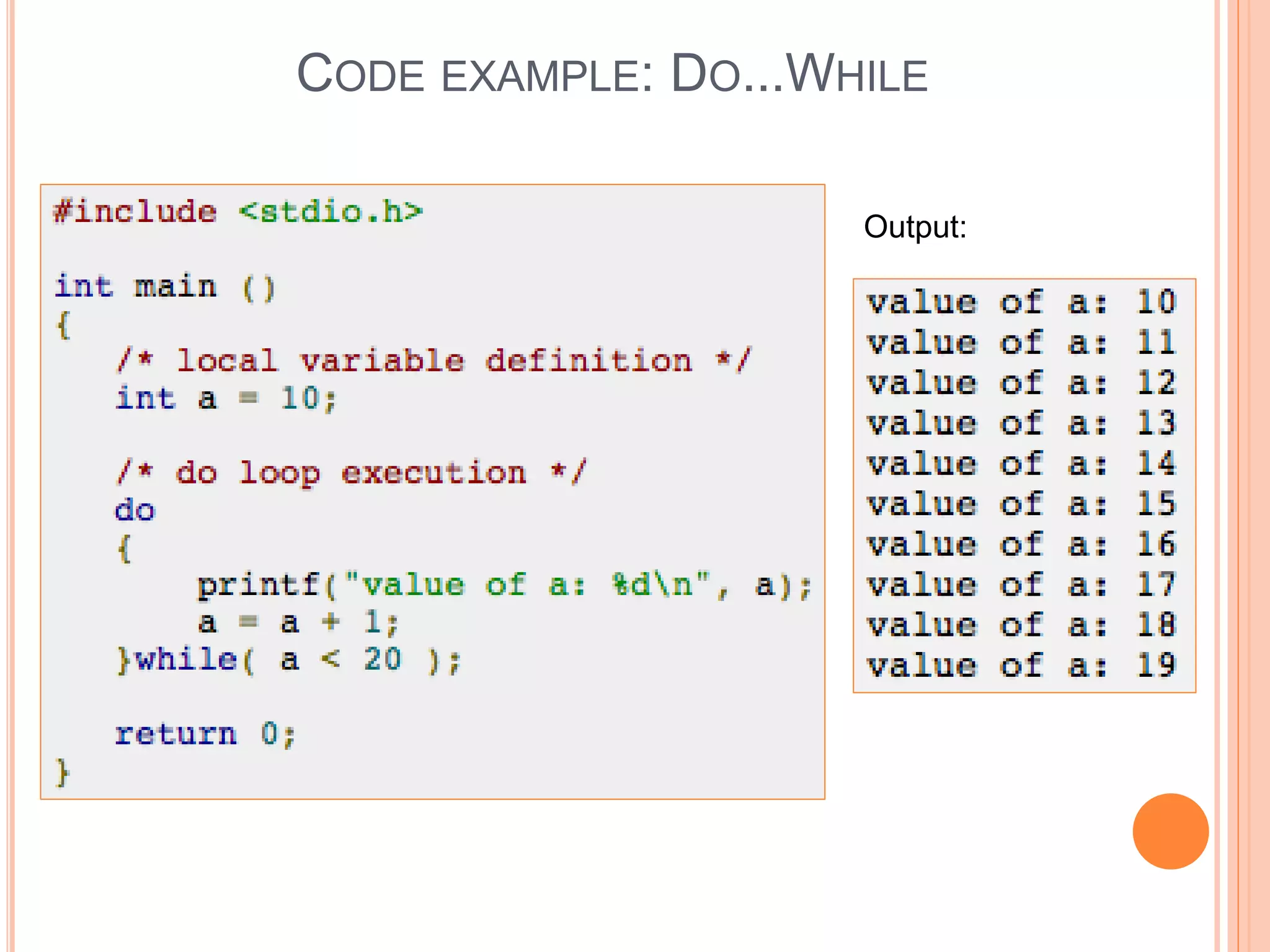
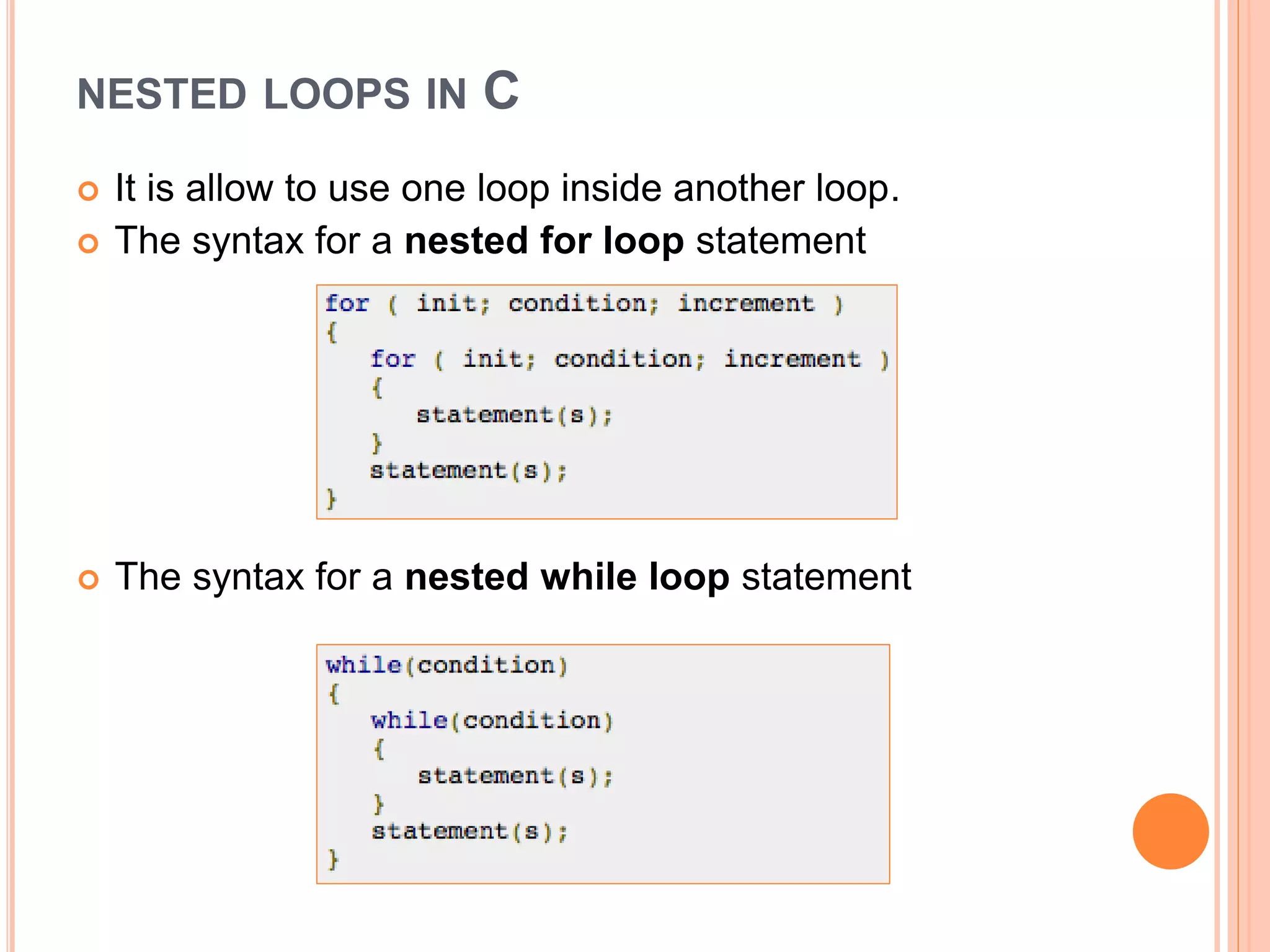
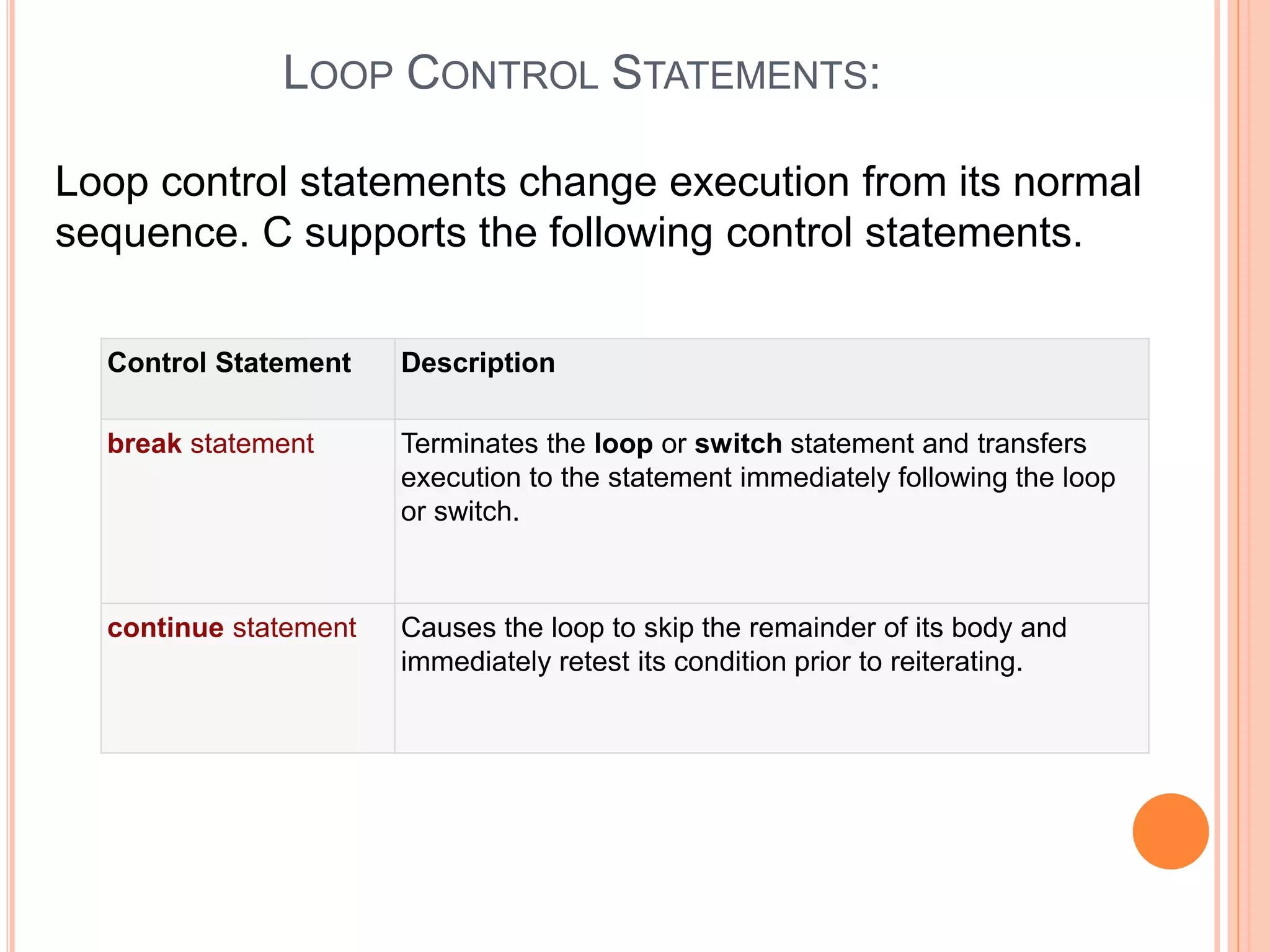
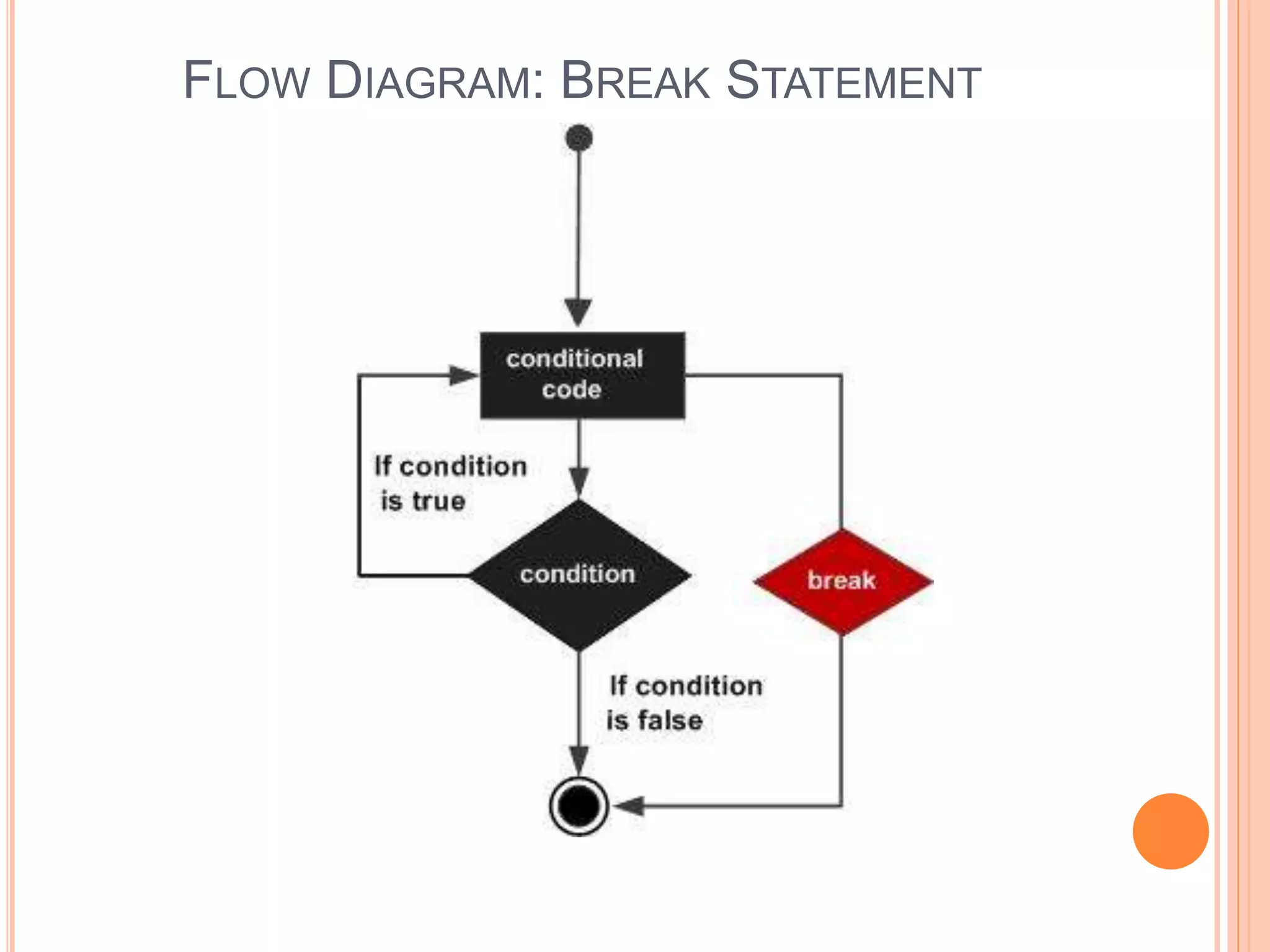
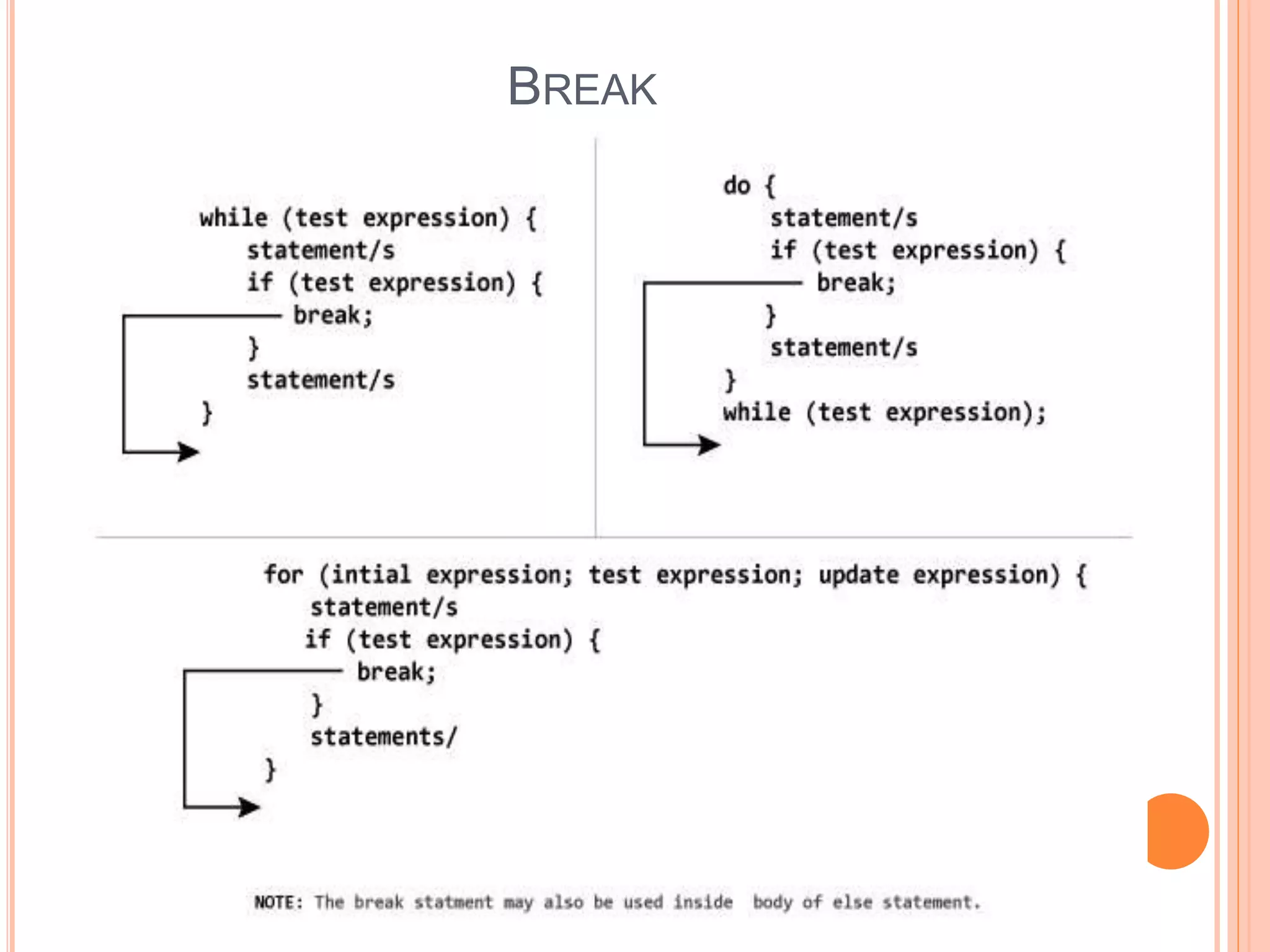
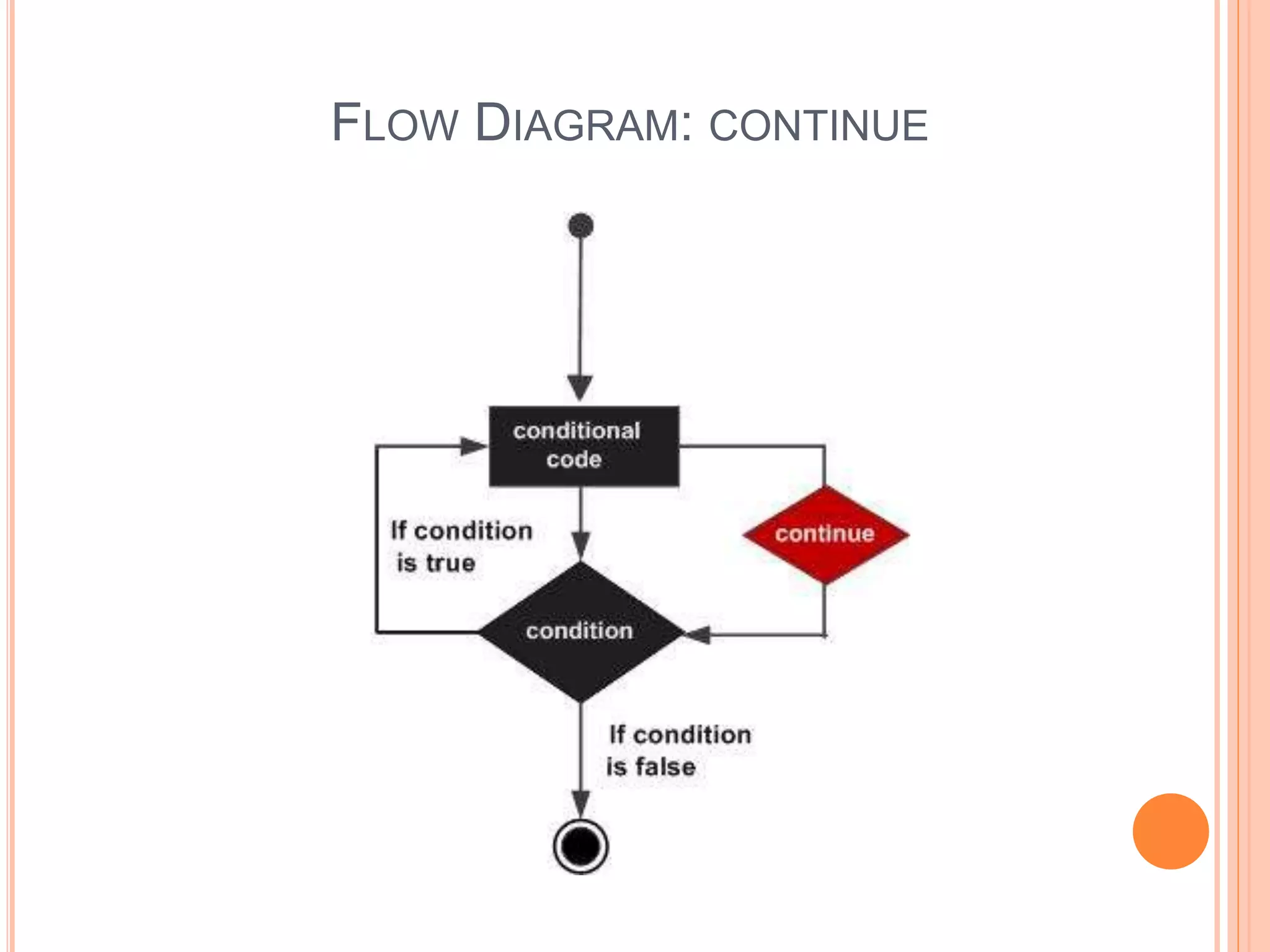
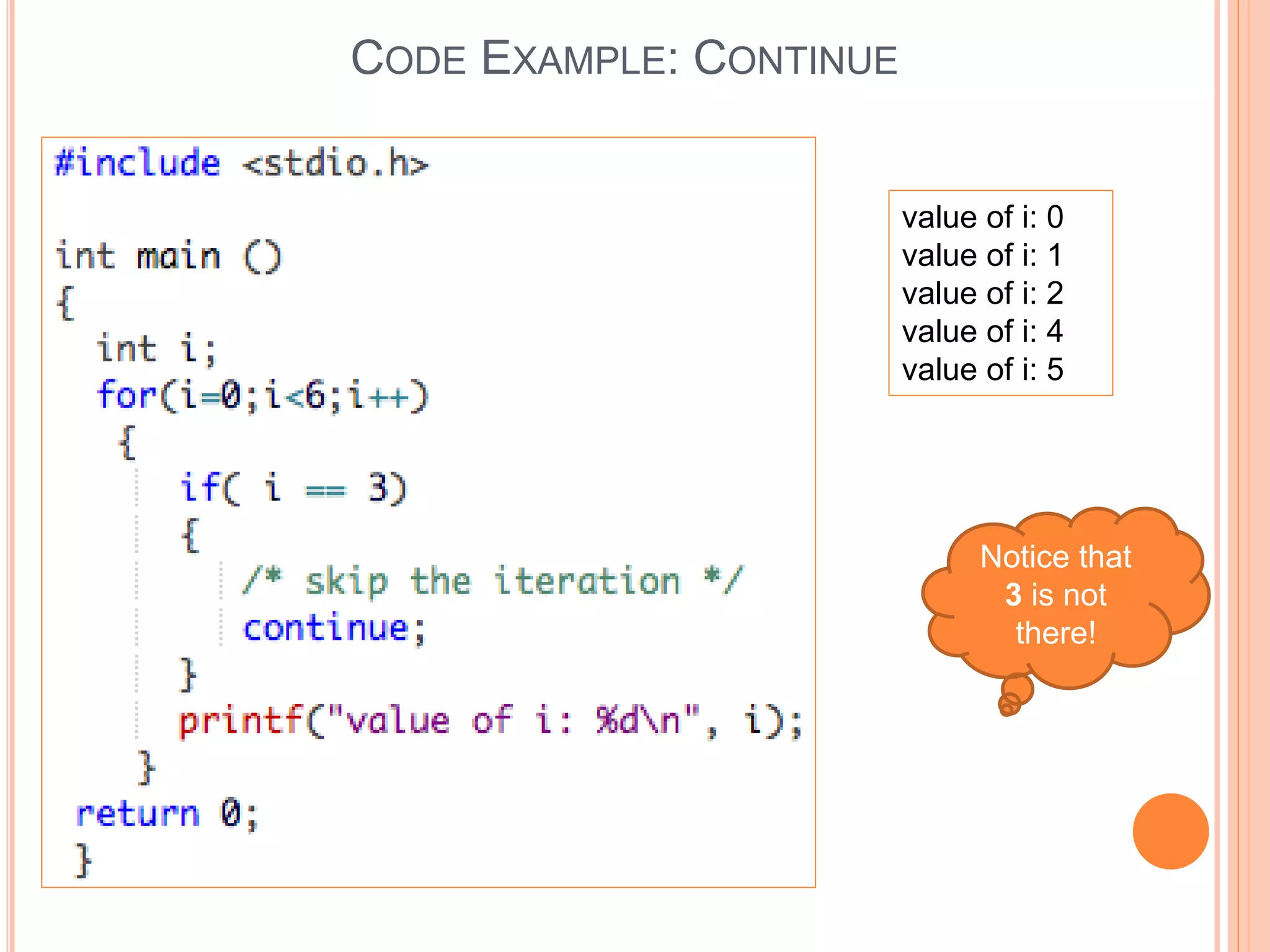
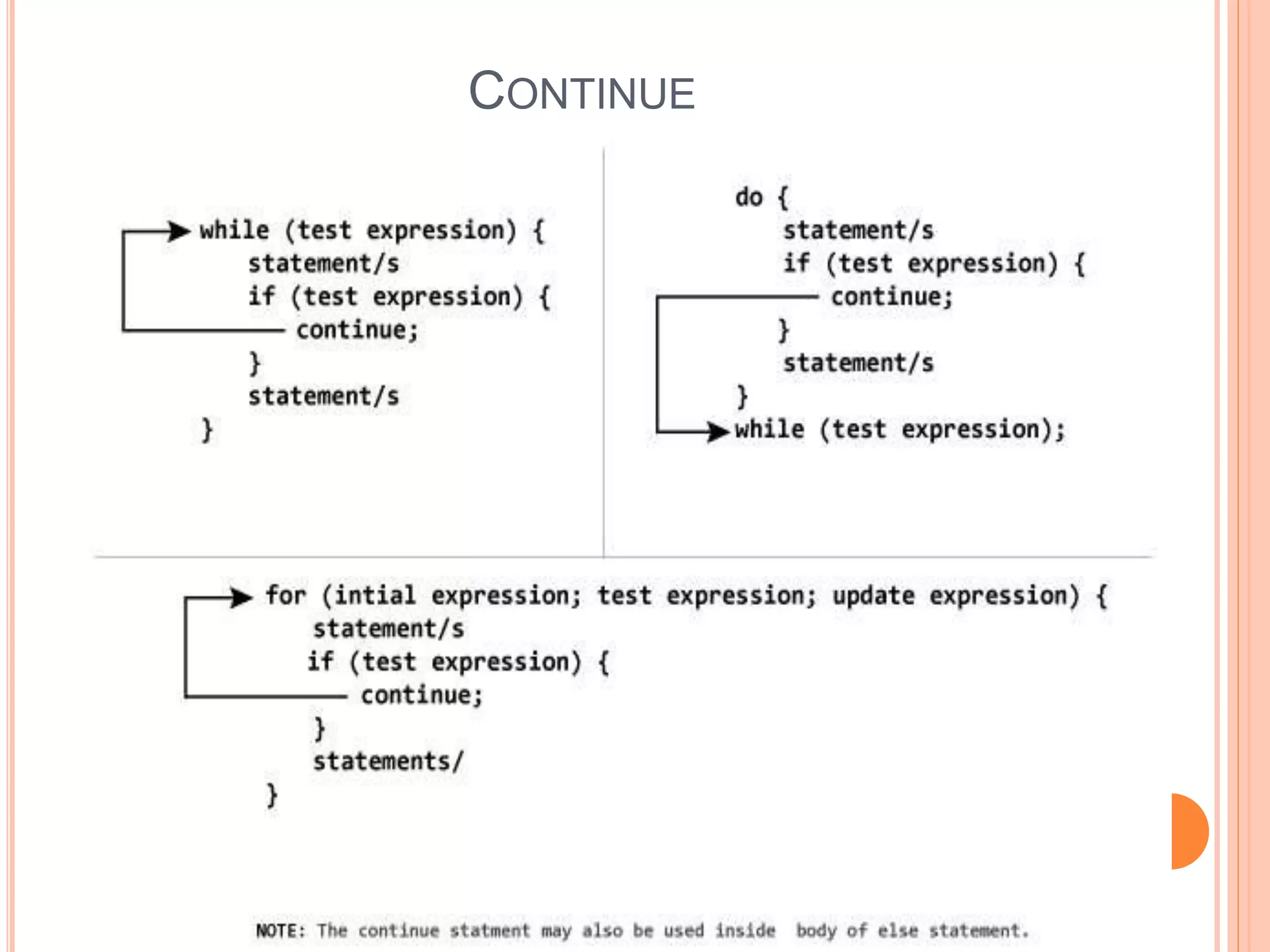
The document explains different types of loop statements in programming, specifically in C, including for loops, while loops, do...while loops, and nested loops. It describes the syntax and behavior of each loop type, including their control structures and how to utilize loop control statements like break and continue. The document emphasizes the execution flow and conditions for each loop type to manage repetitive tasks efficiently.