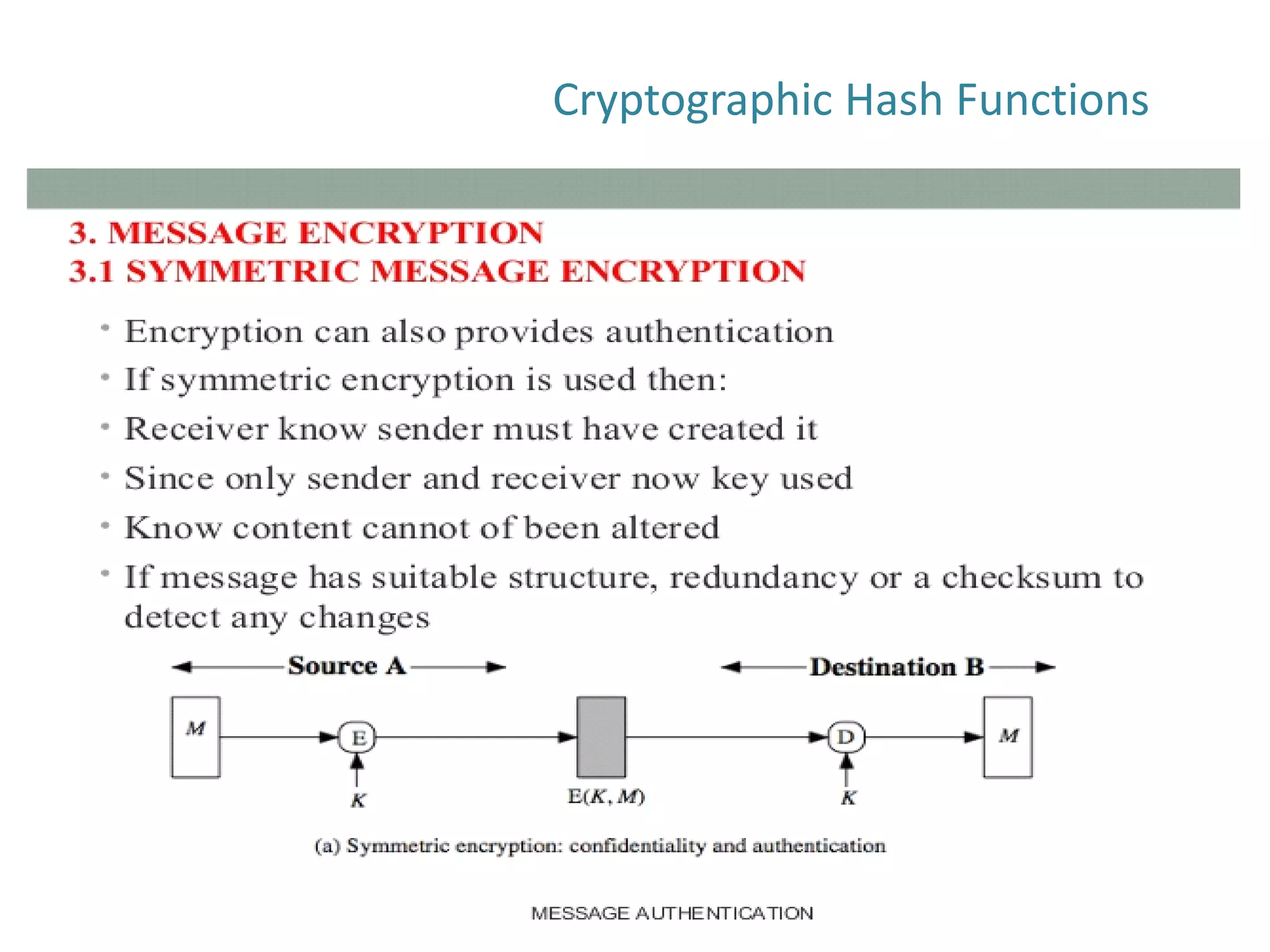
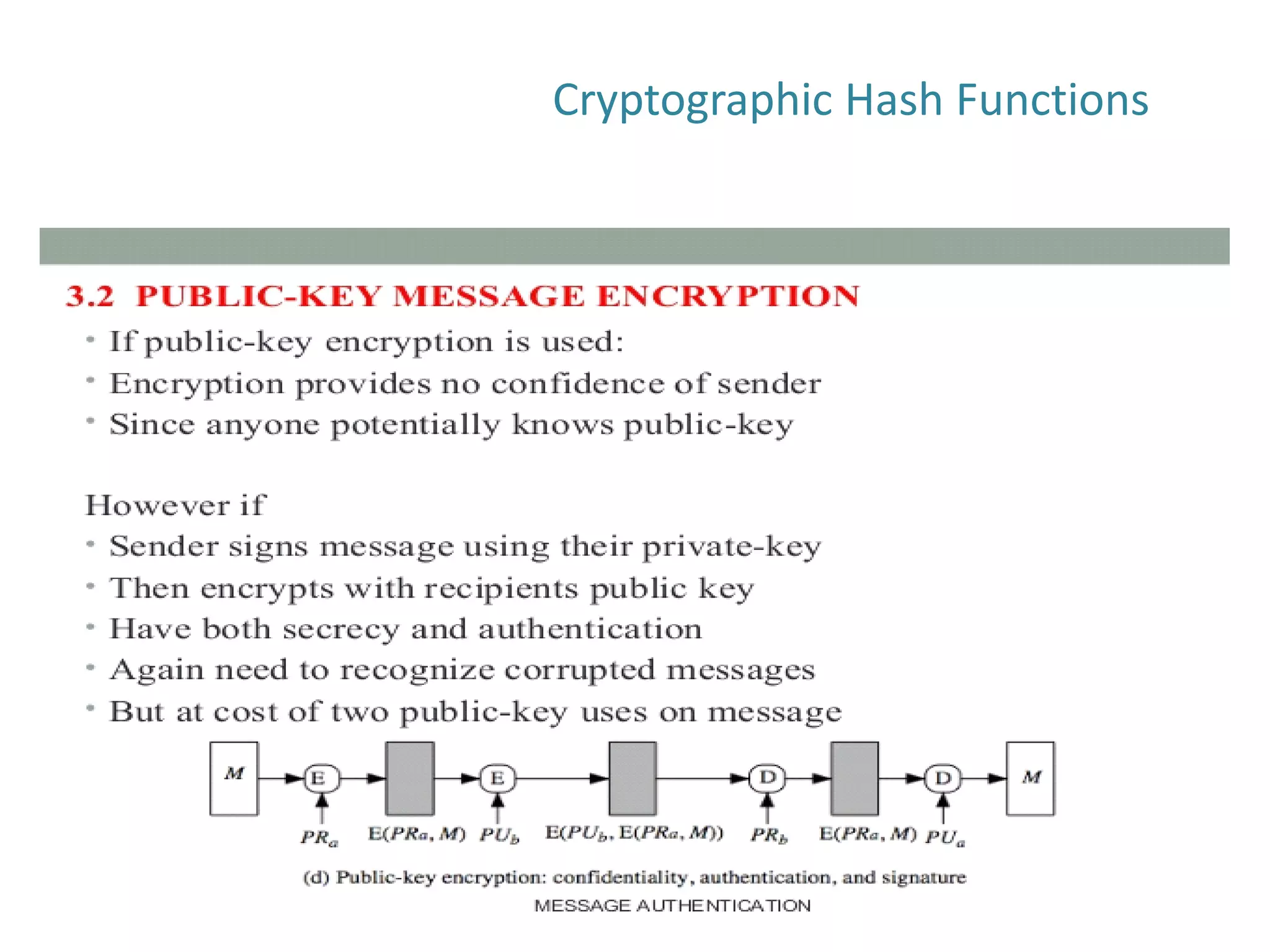
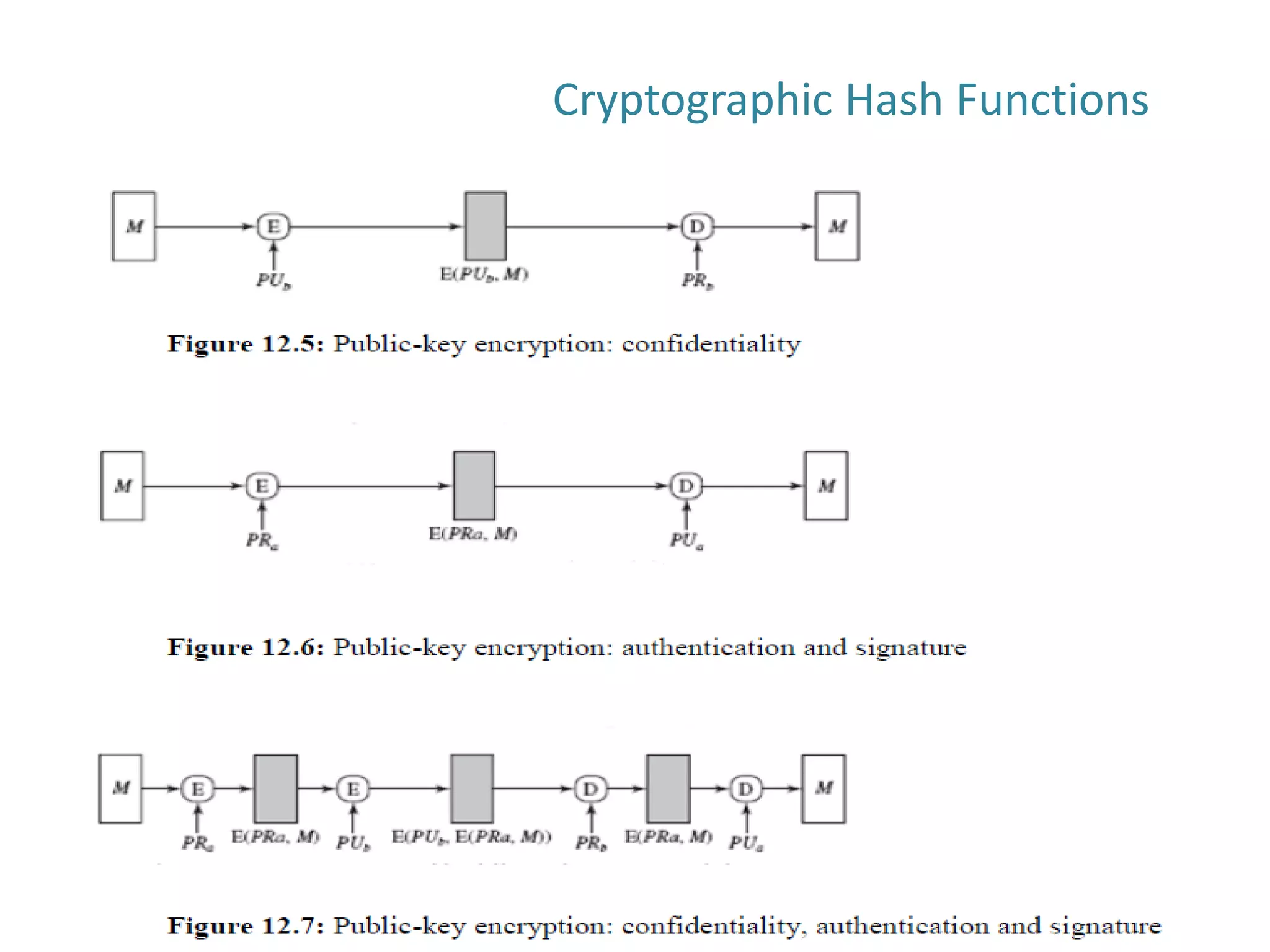
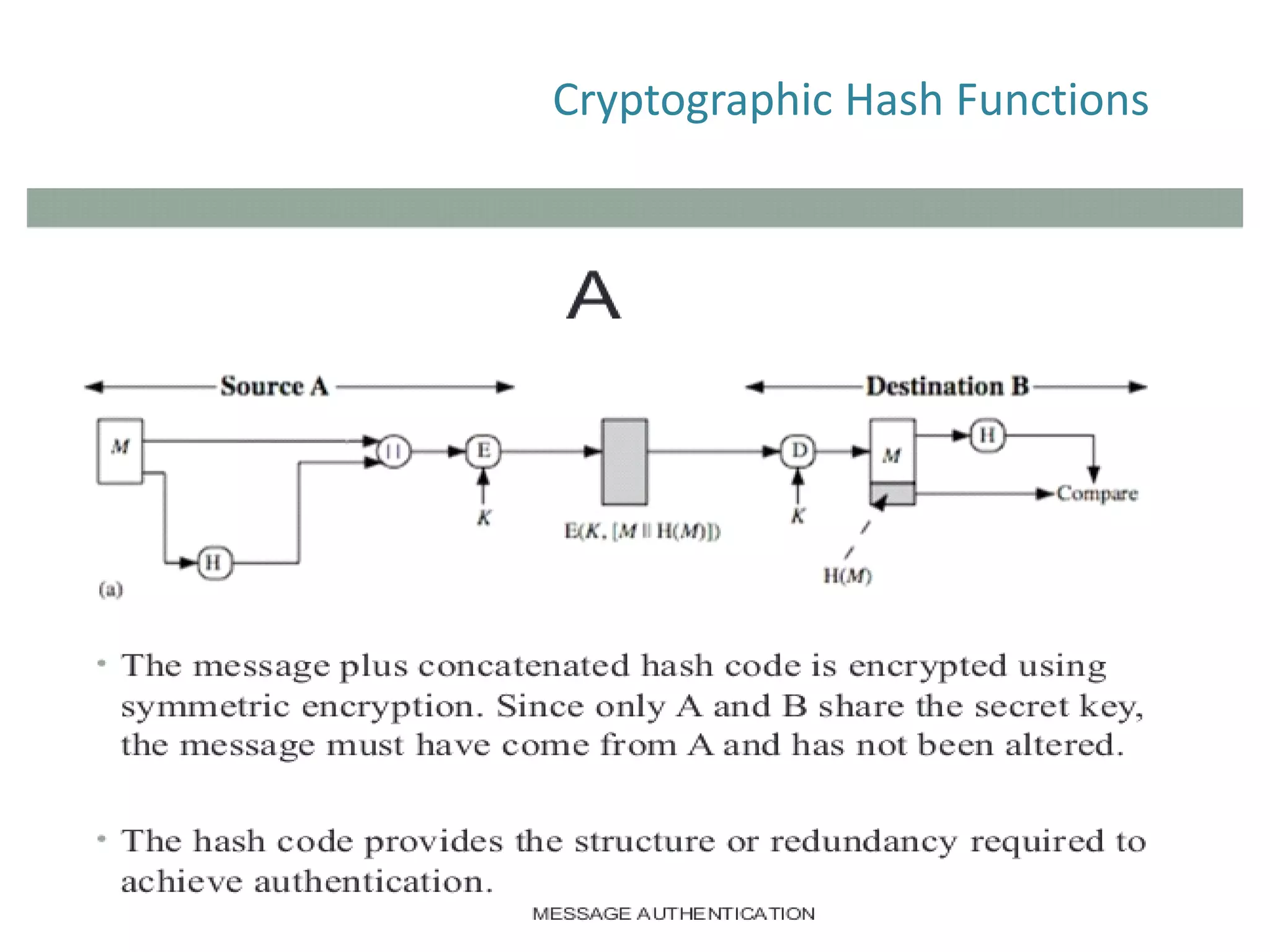
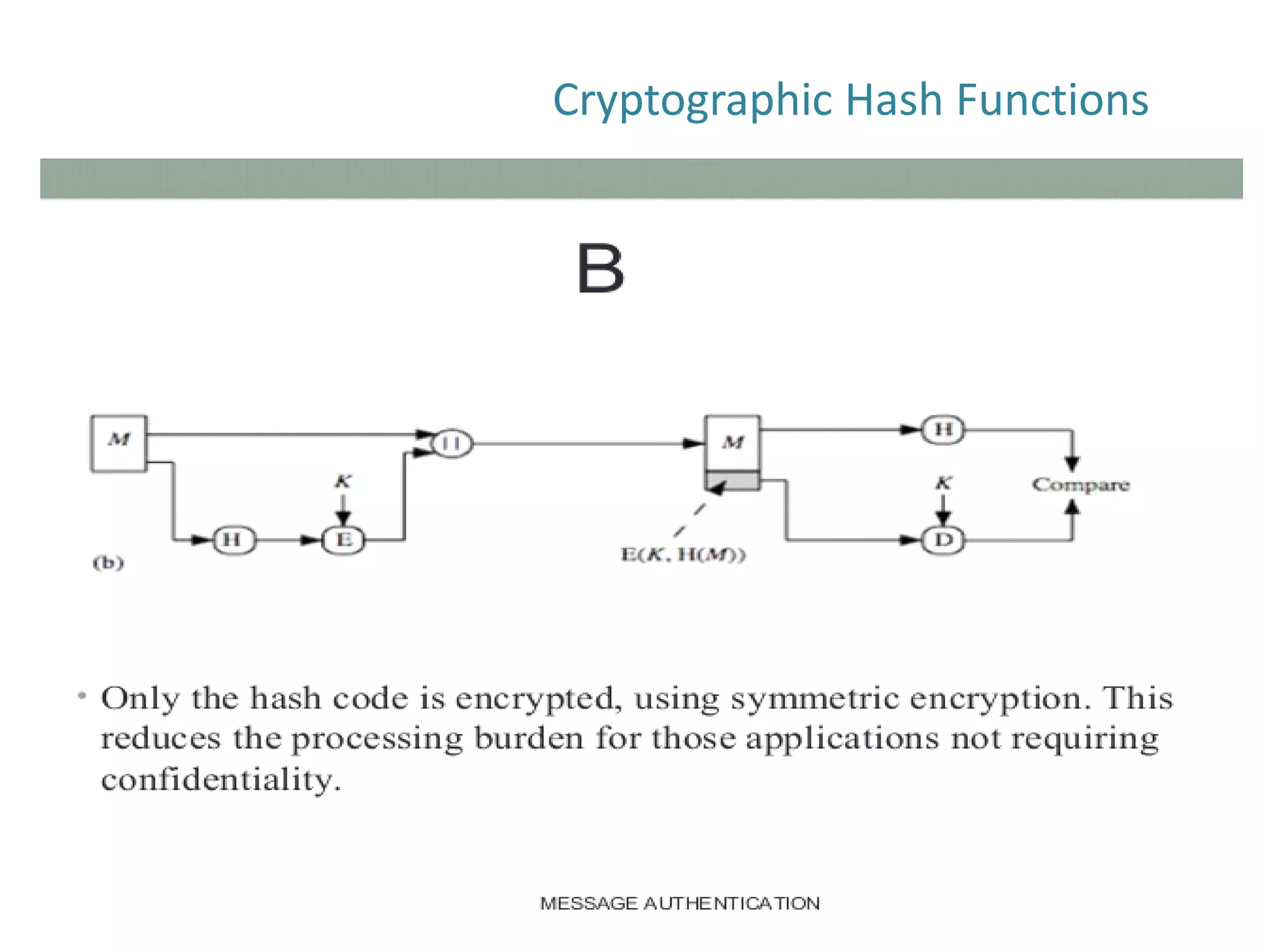
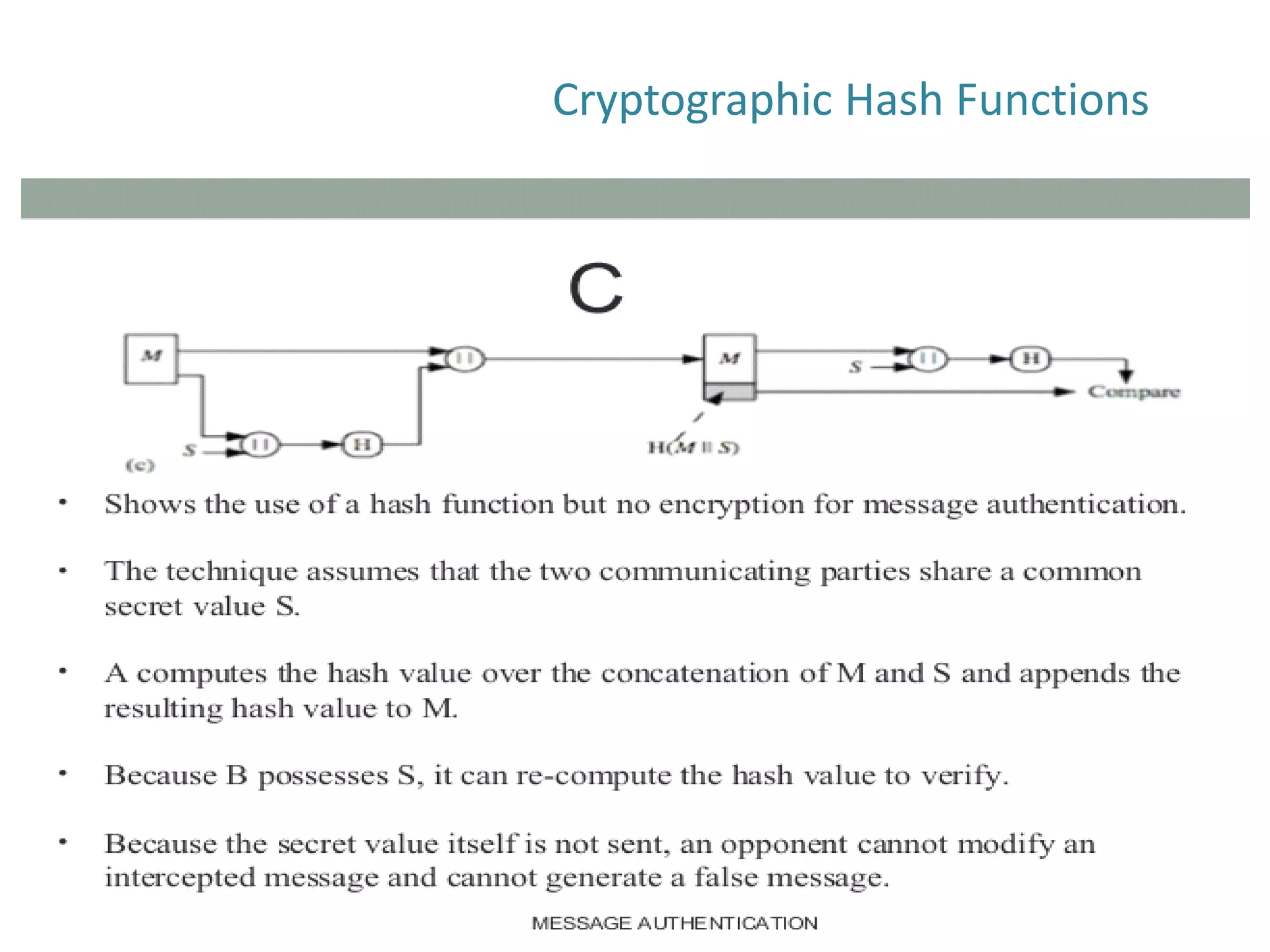
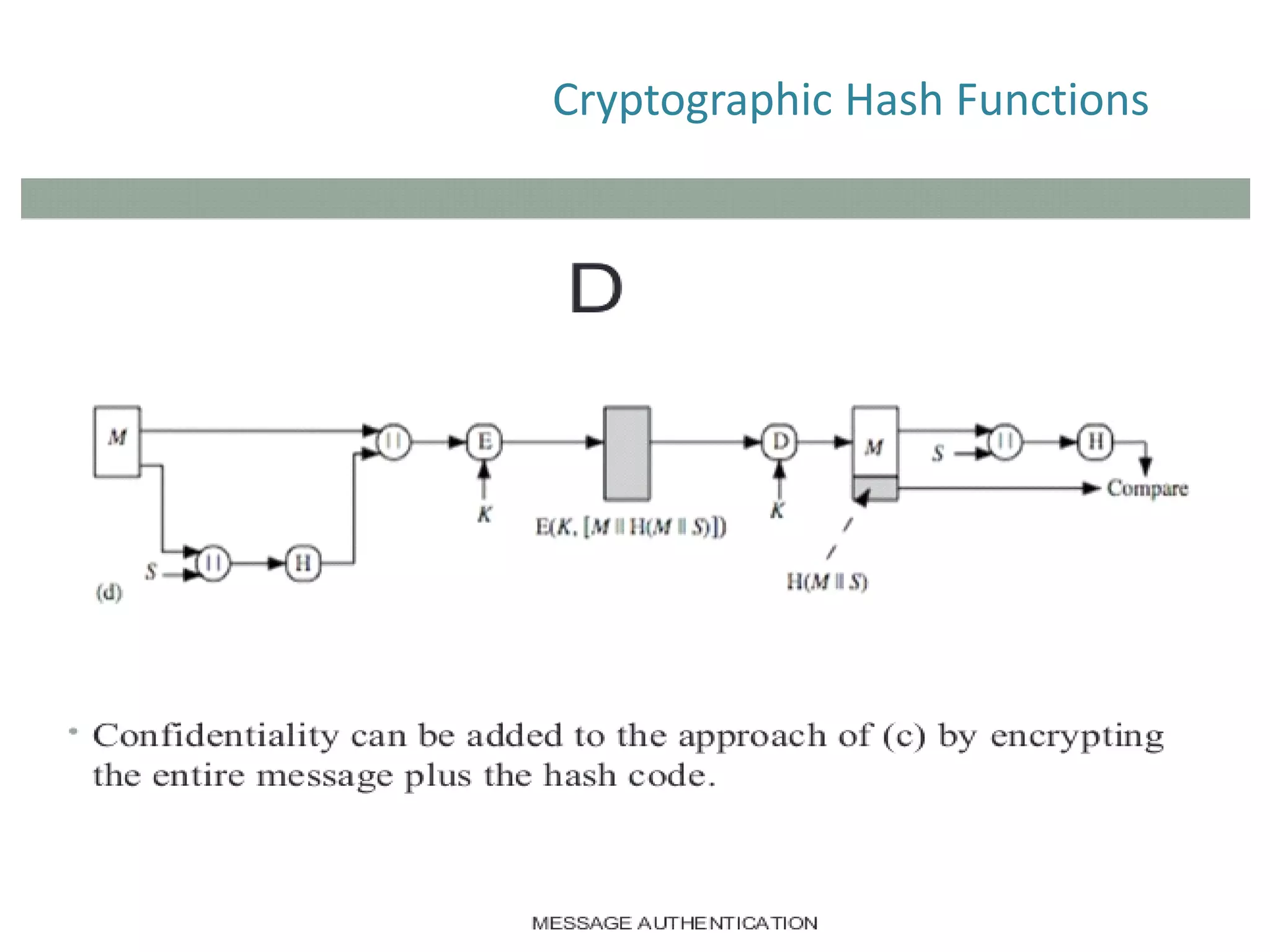
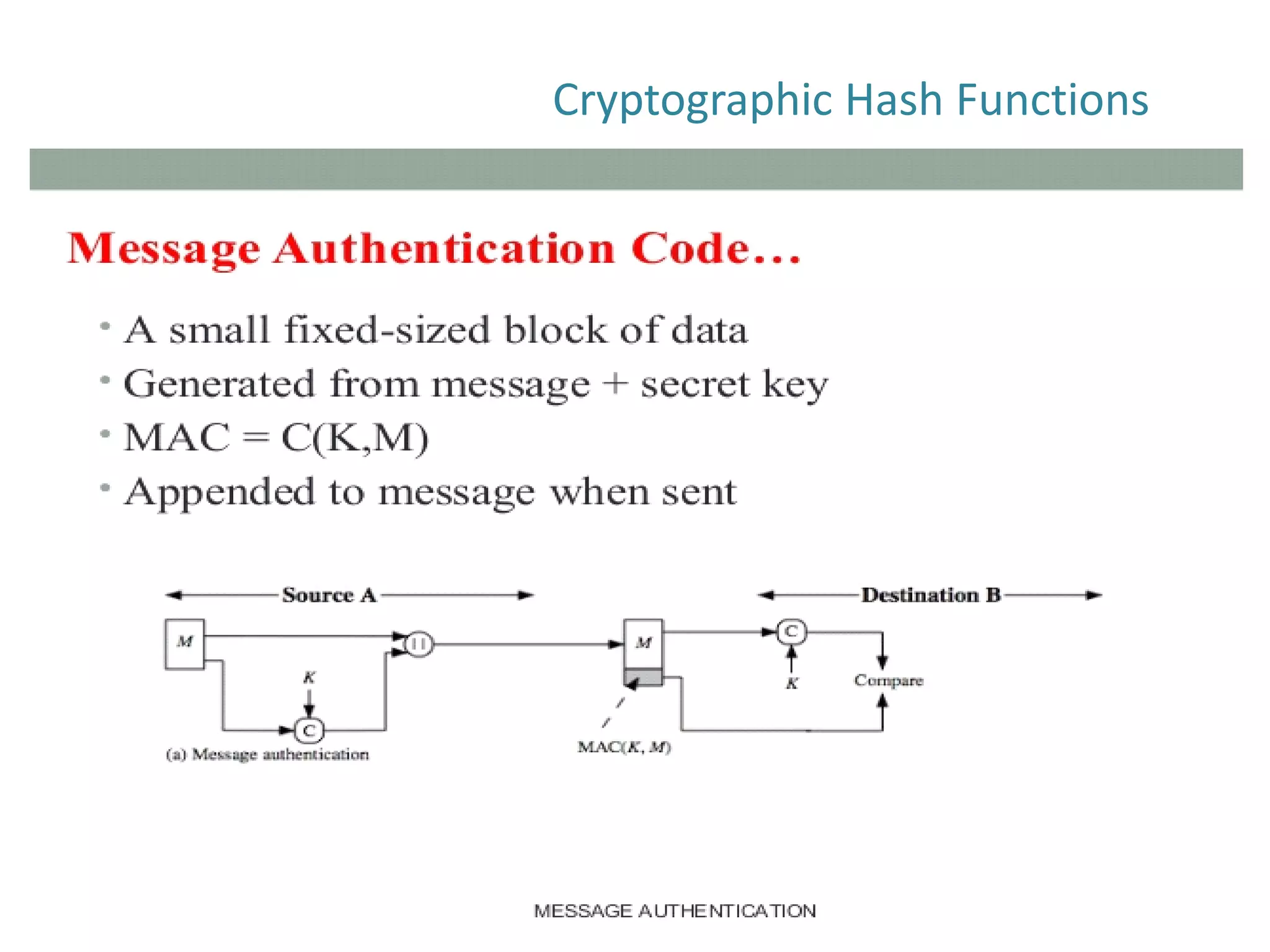
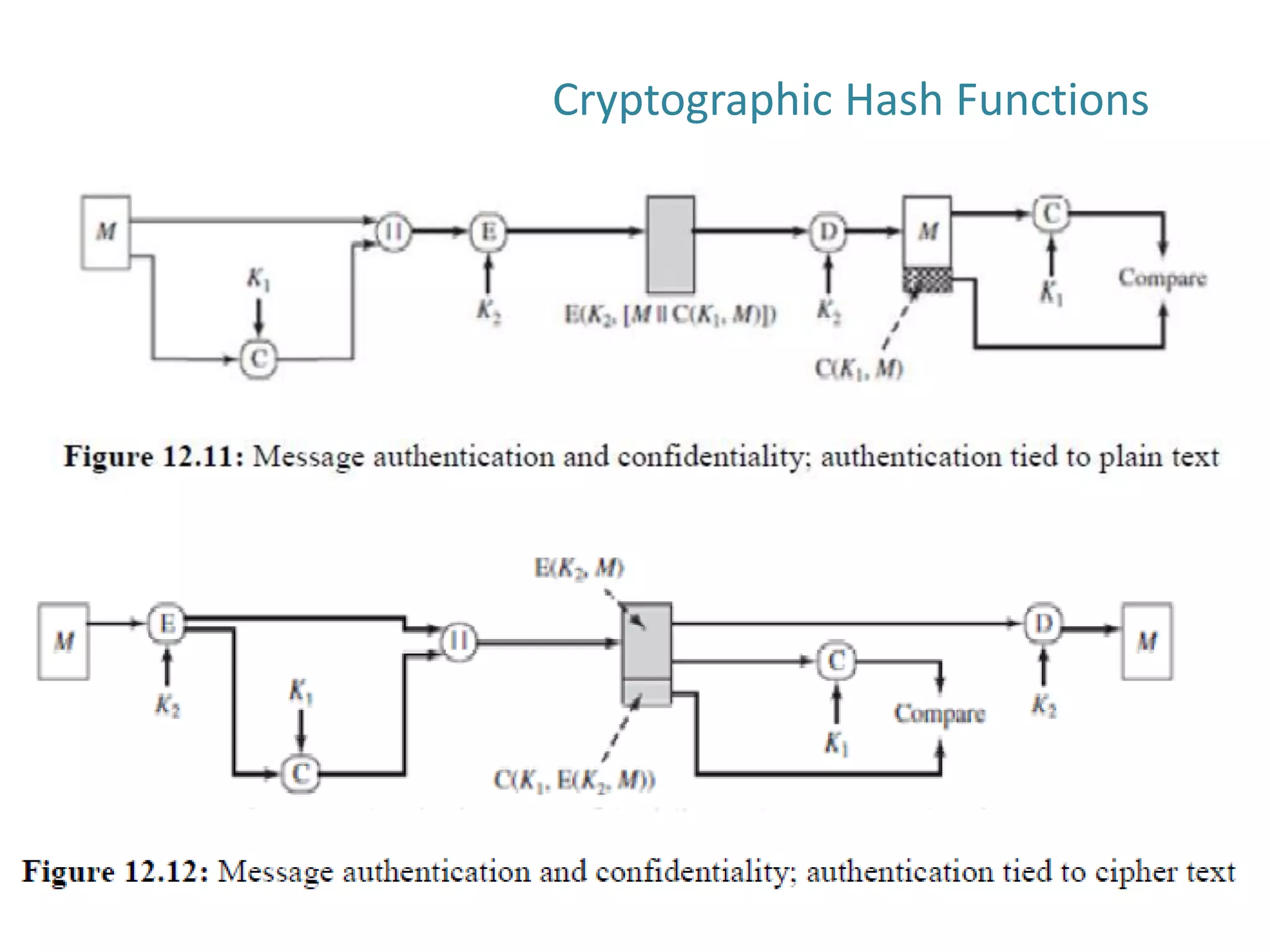
The document discusses cryptographic hash functions and their applications in internet security, focusing on message authentication methods and key management techniques. It covers the principles of cryptographic hash functions, including their types and functionalities, as well as topics related to digital signatures and public key infrastructure. Additionally, it offers resources for further learning and addresses common security challenges businesses face.