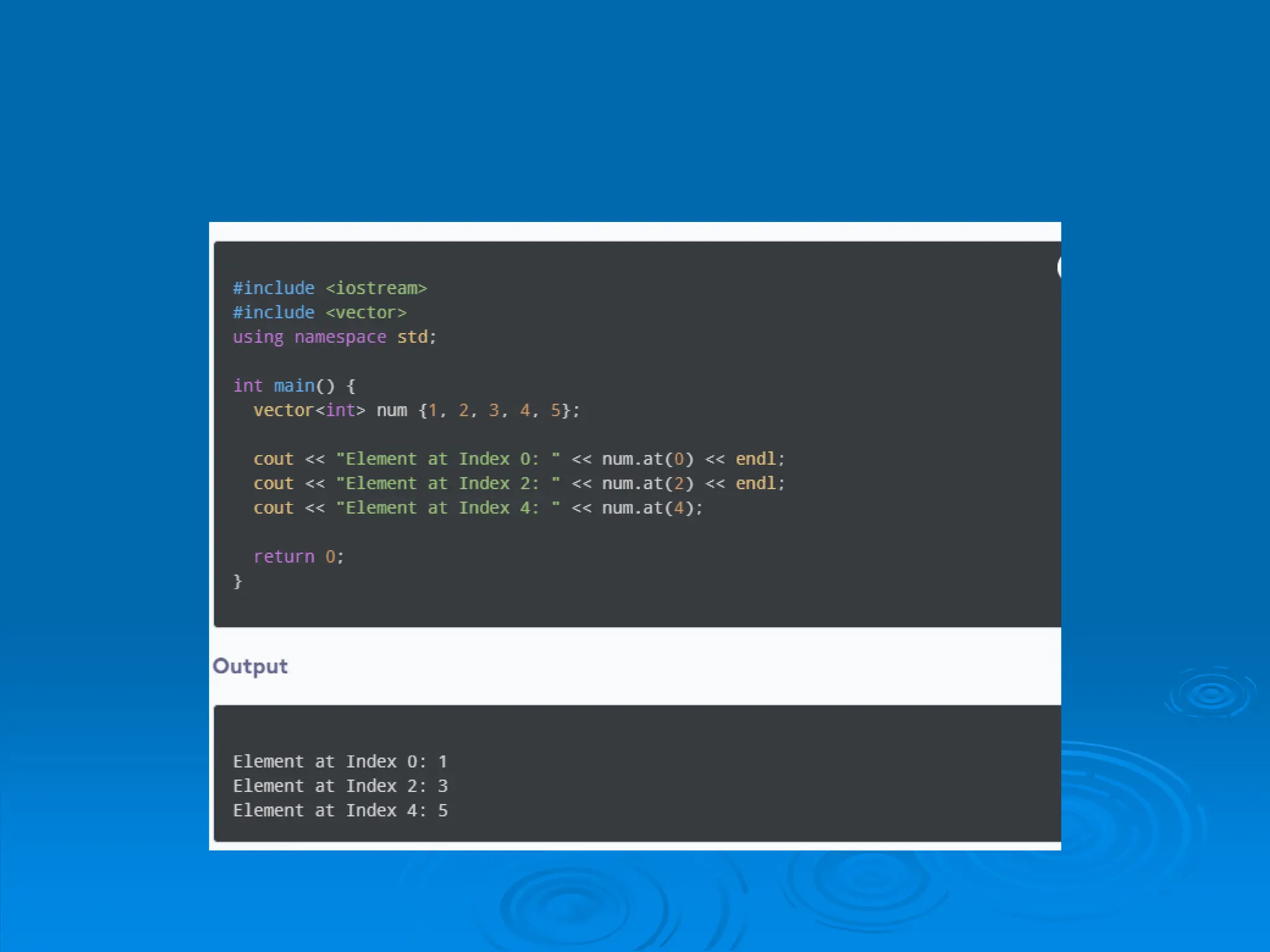
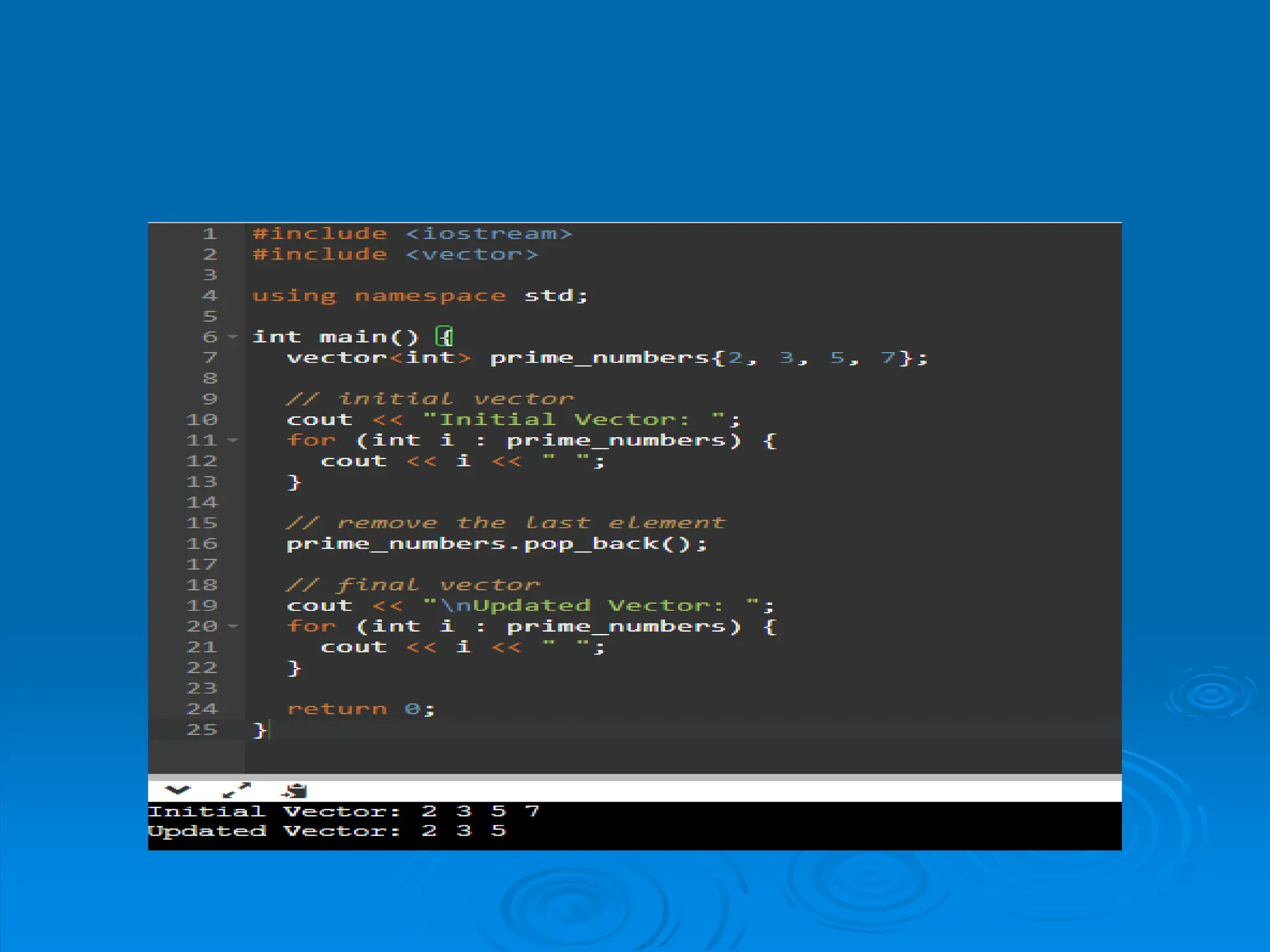
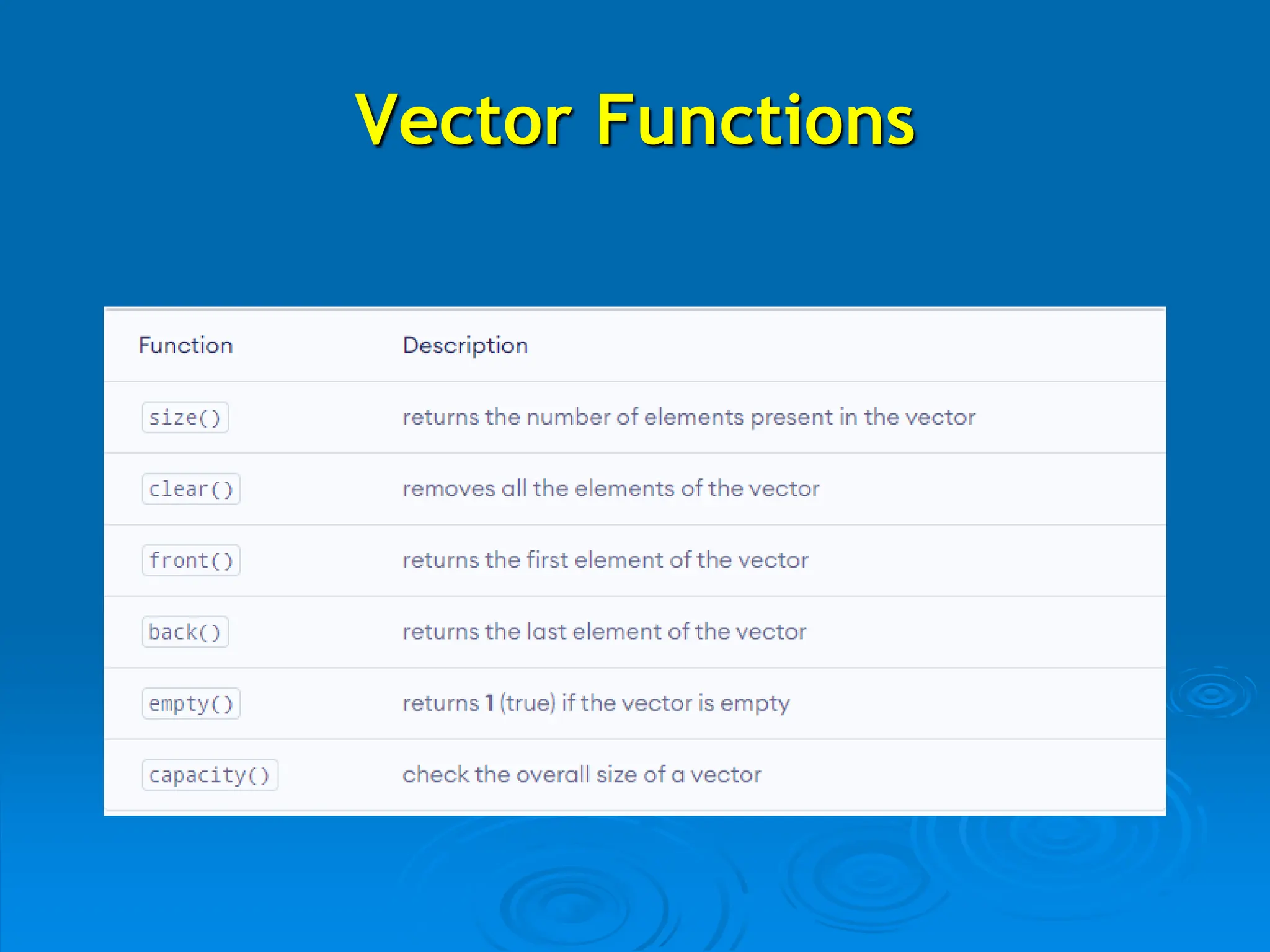
The document introduces vectors in C++, explaining their dynamic size capability and how to declare and initialize them. It covers different initialization methods, basic operations like adding, accessing, updating, and deleting elements, along with relevant functions such as push_back(), at(), and pop_back(). The content provides a foundational understanding of vector usage and operations in C++ programming.