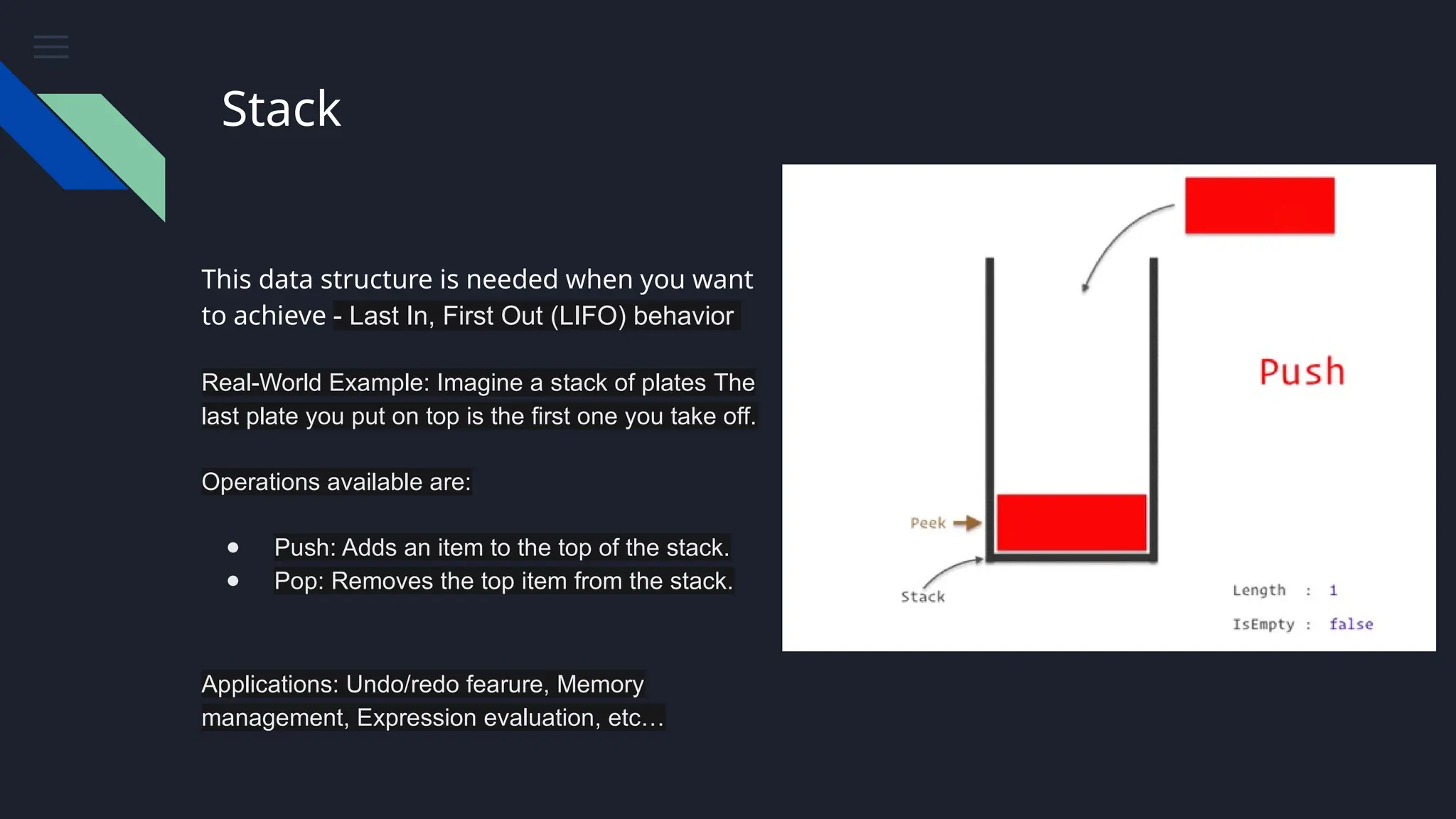
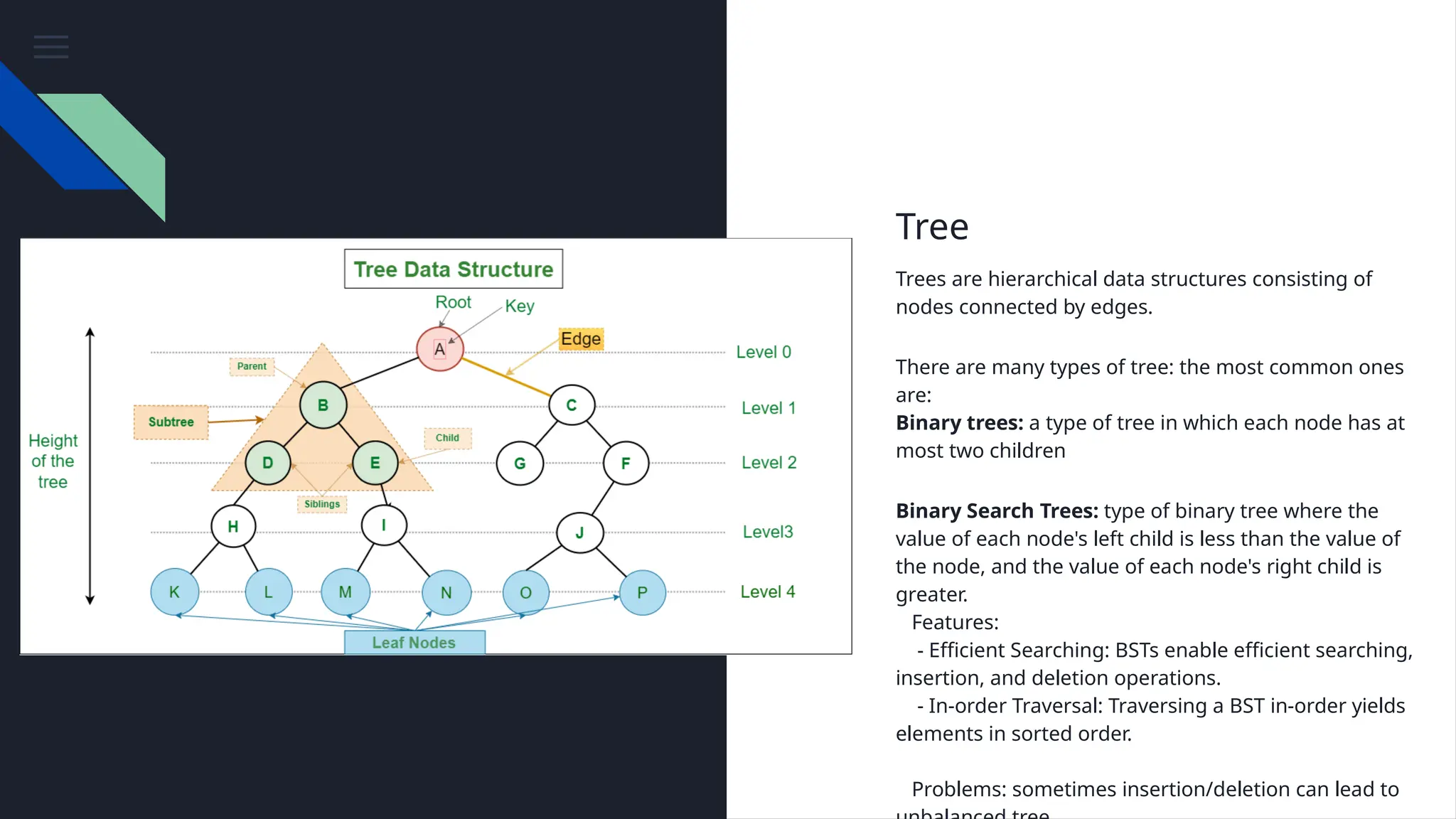
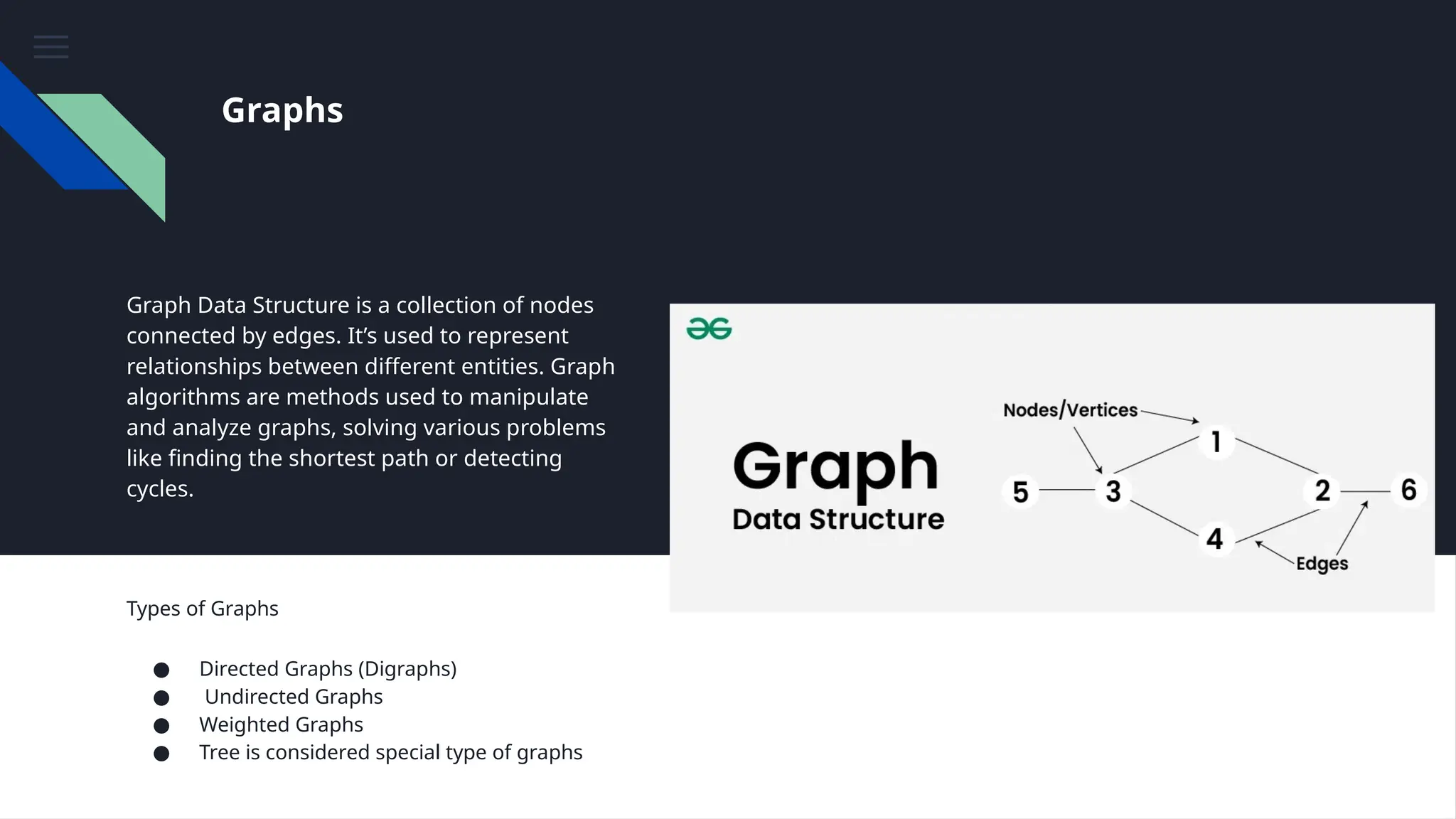
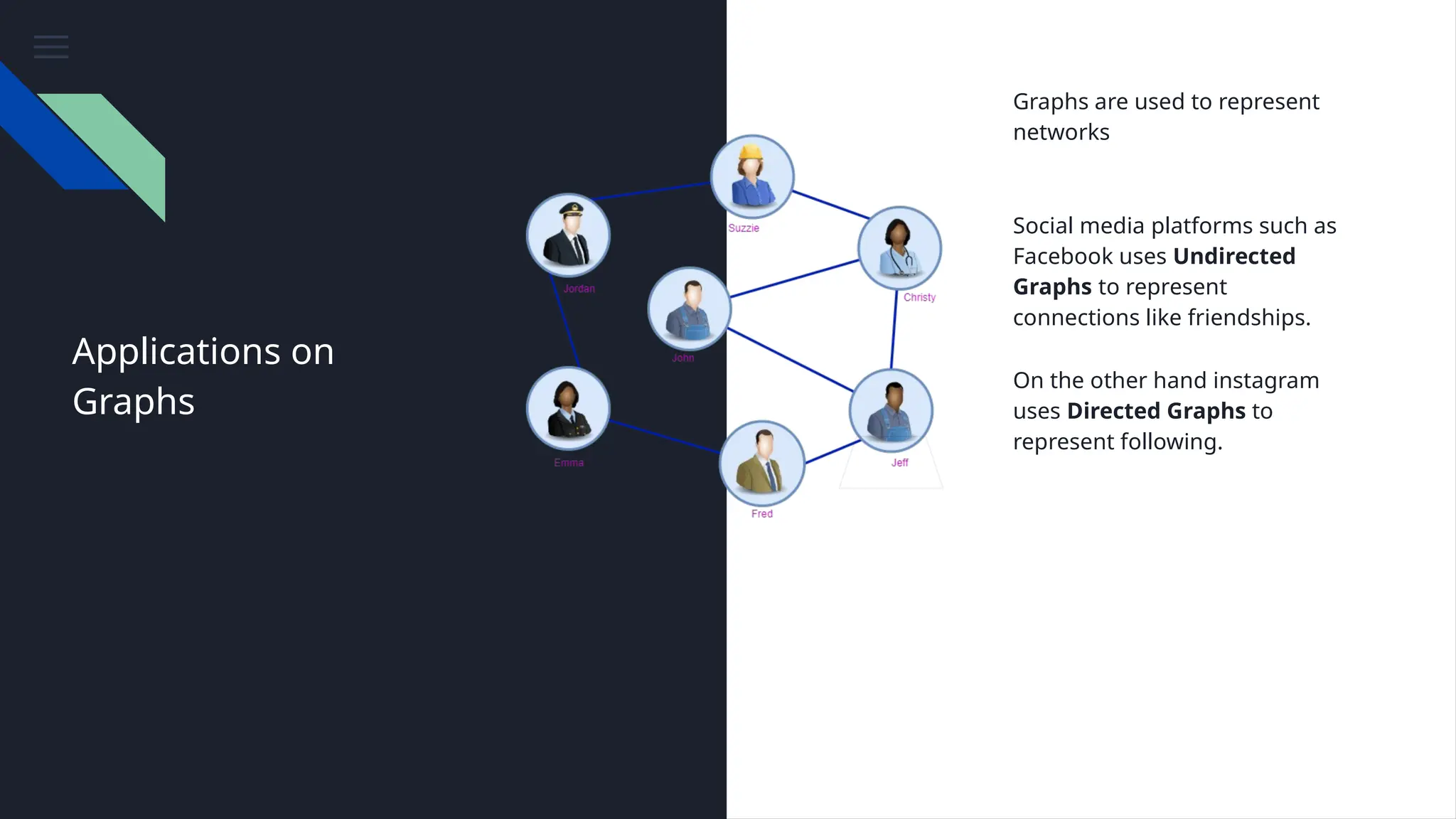
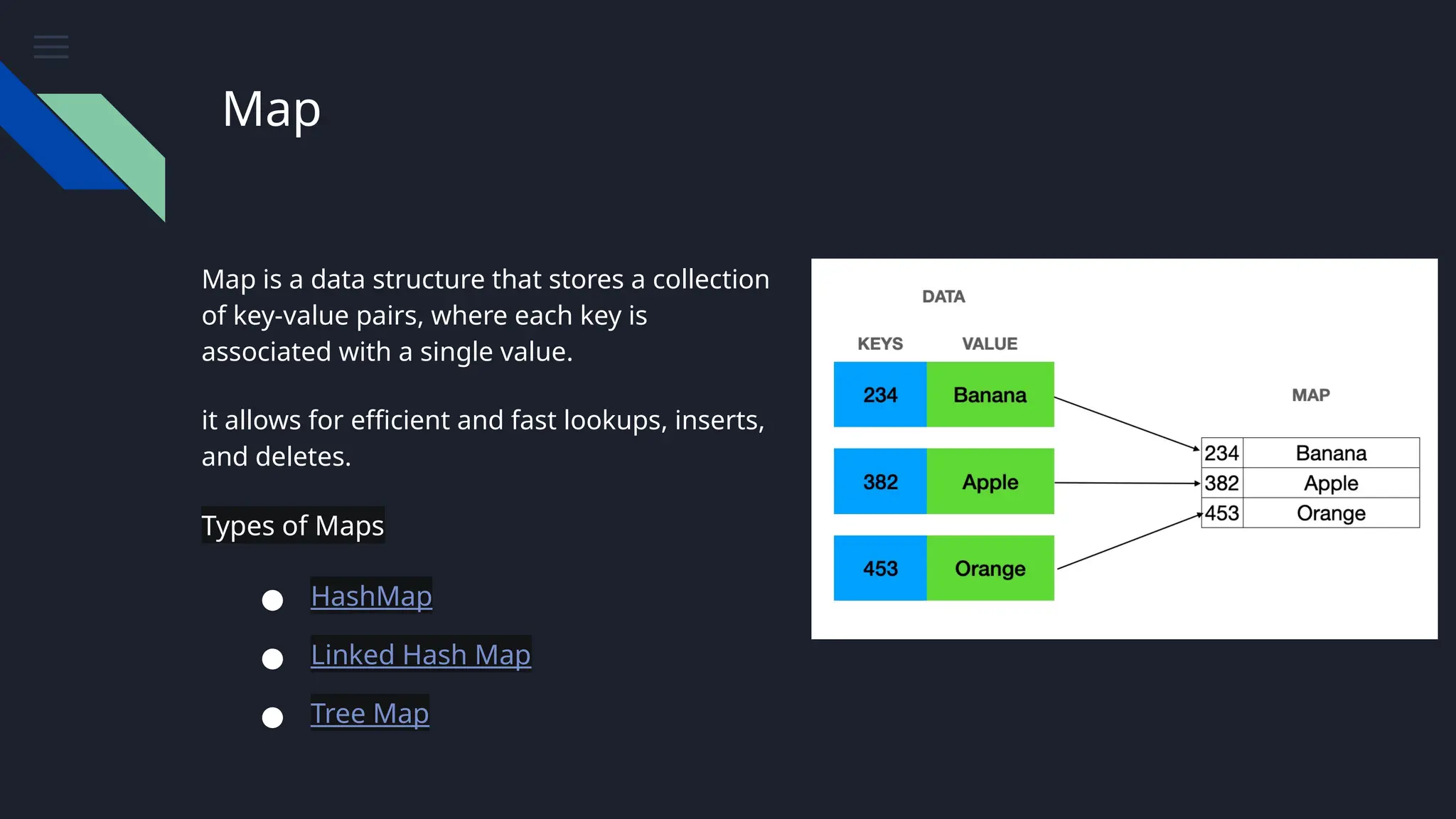
The document provides an overview of data structures, emphasizing their importance in organizing and managing data efficiently to optimize algorithm performance. It discusses various types of data structures such as arrays, lists, stacks, queues, trees, and graphs, along with their characteristics and applications. Understanding these structures leads to improved software performance through better resource management and faster algorithms.