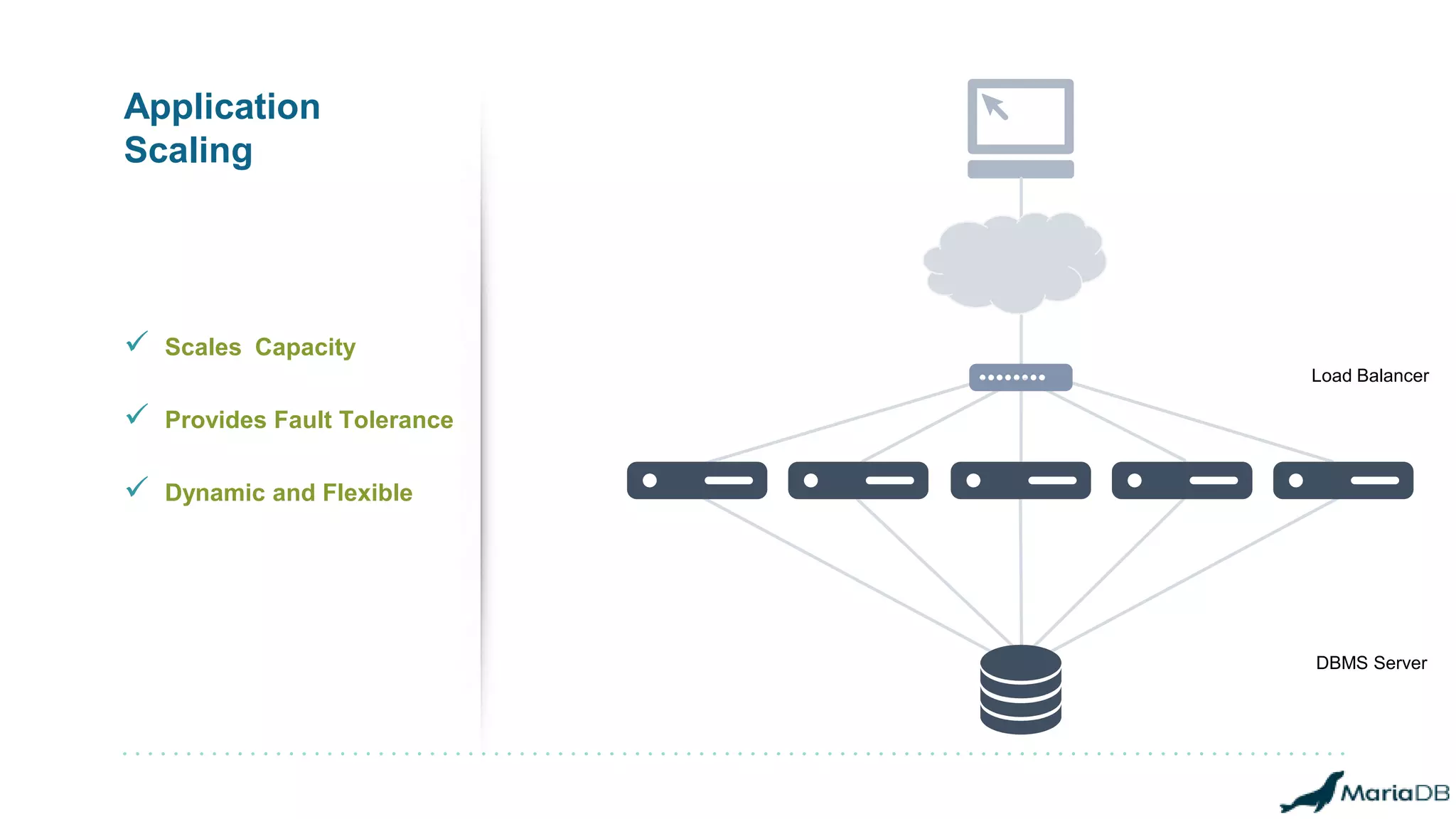
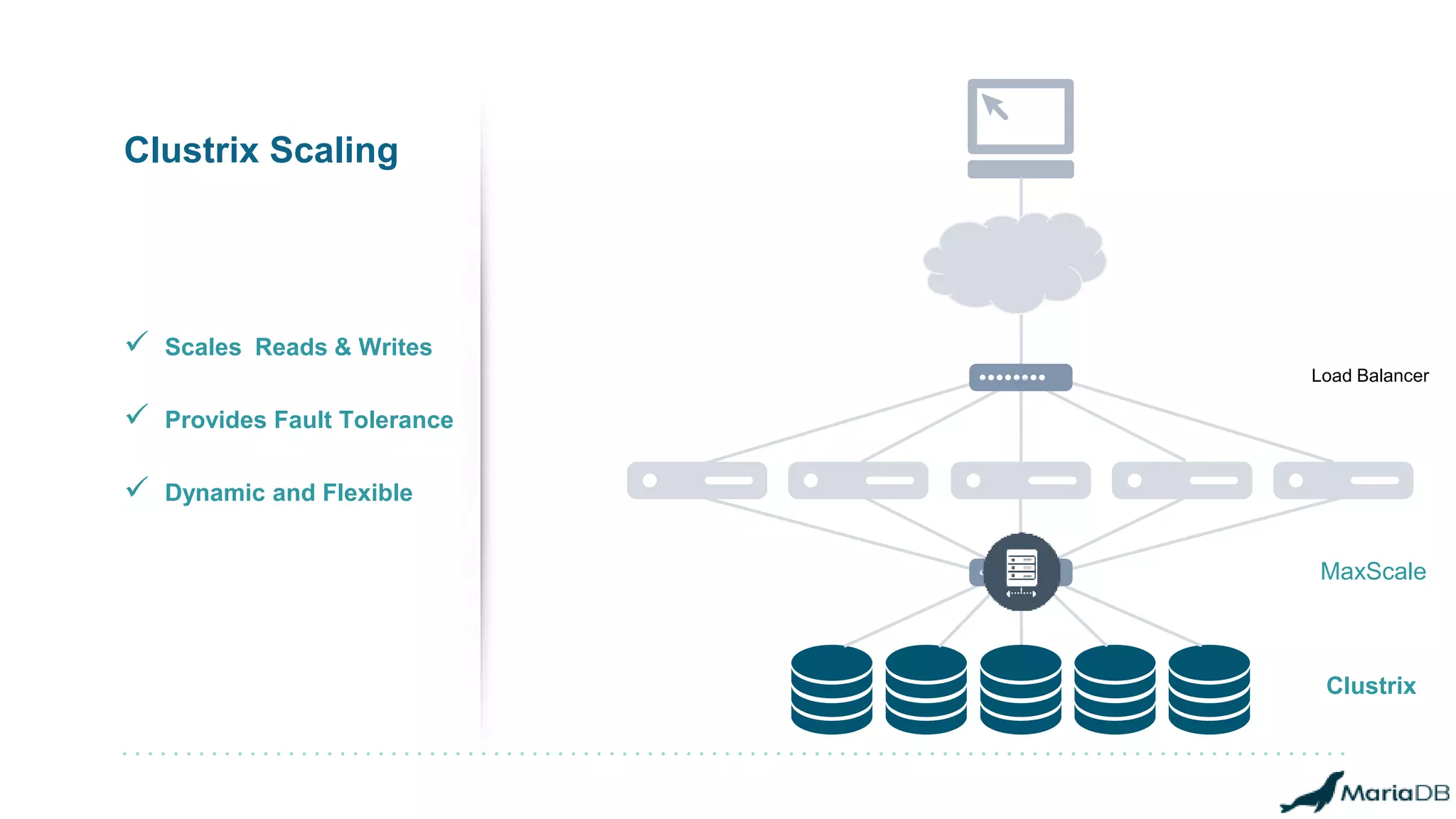
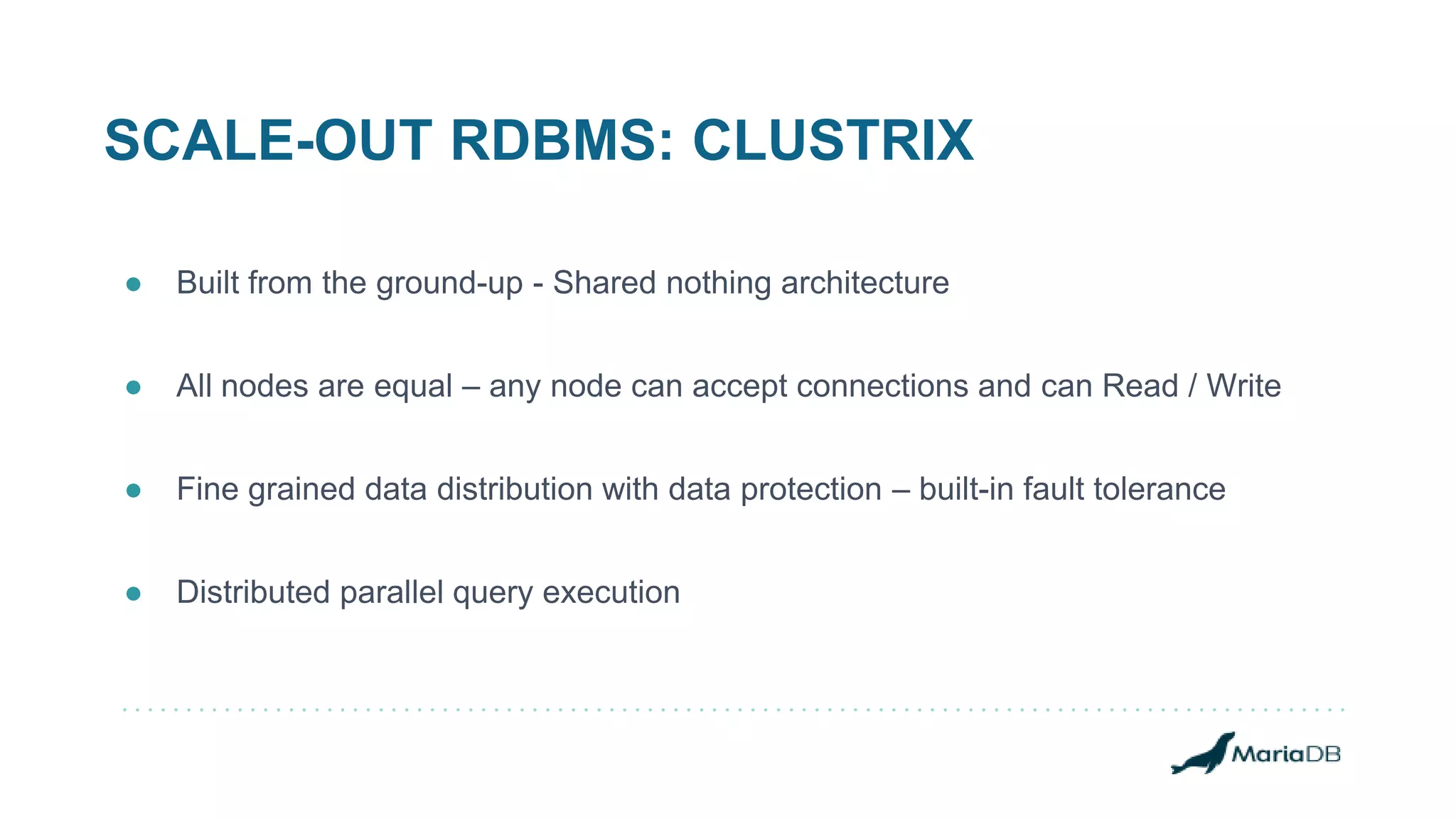
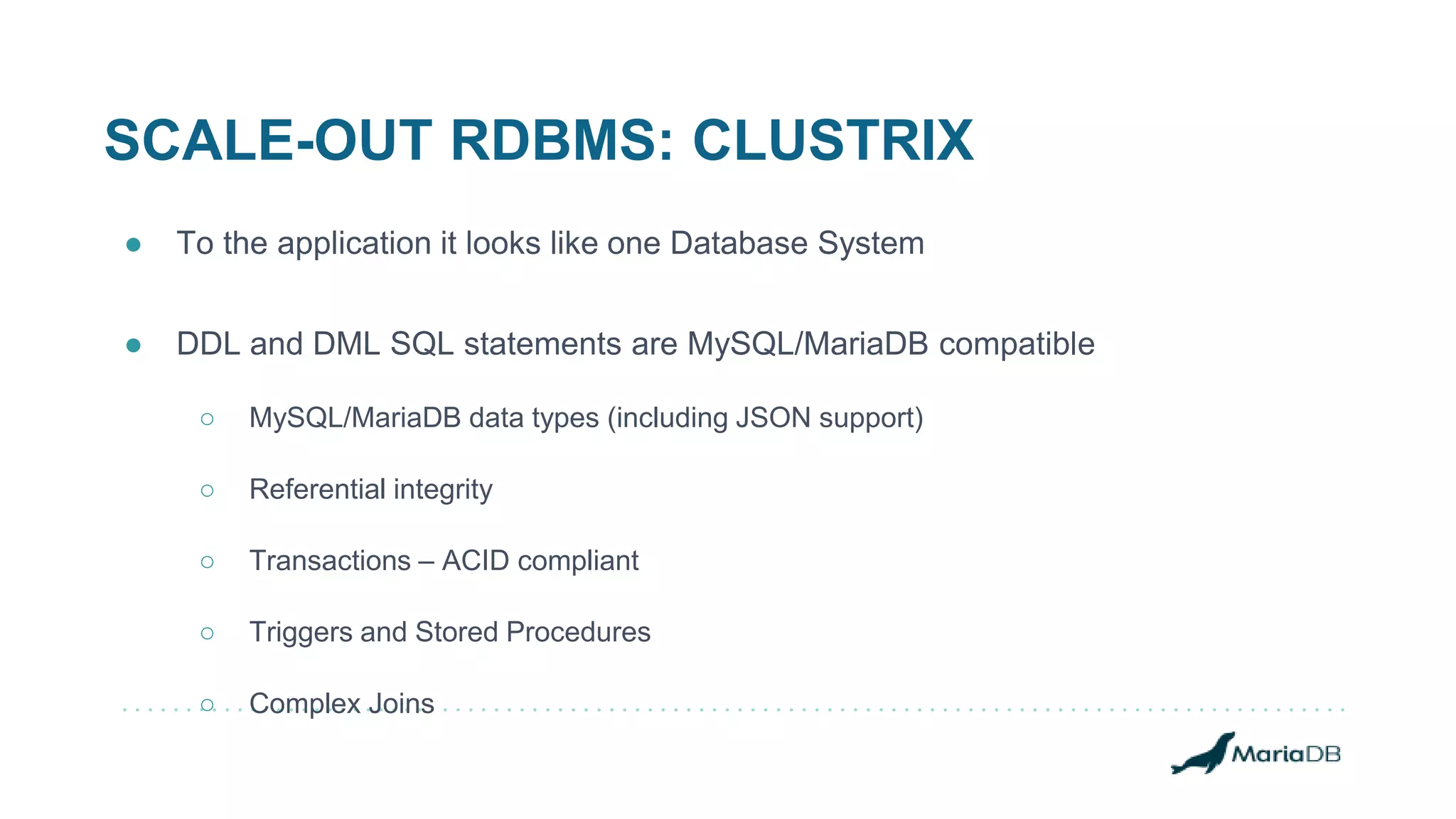
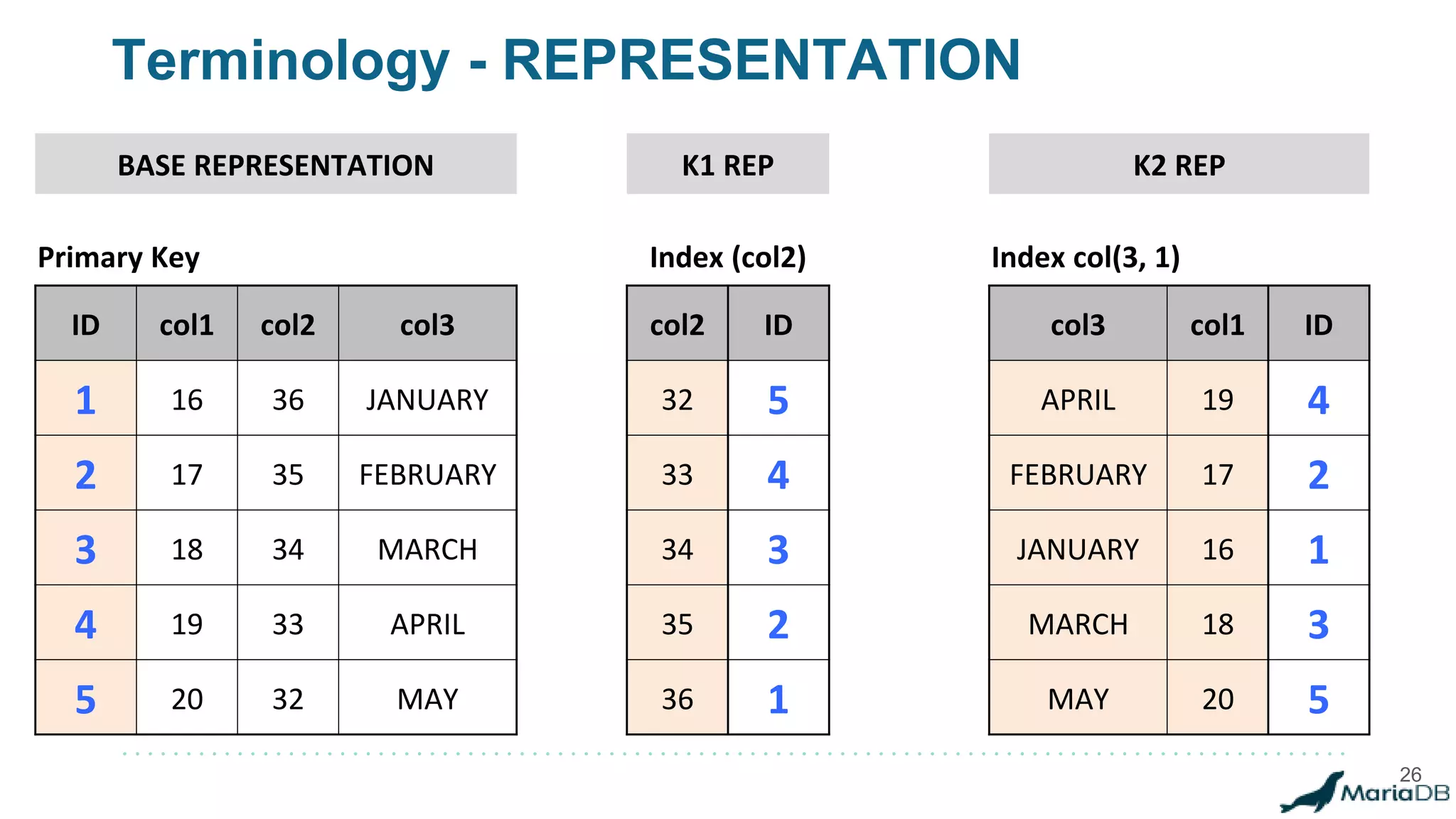
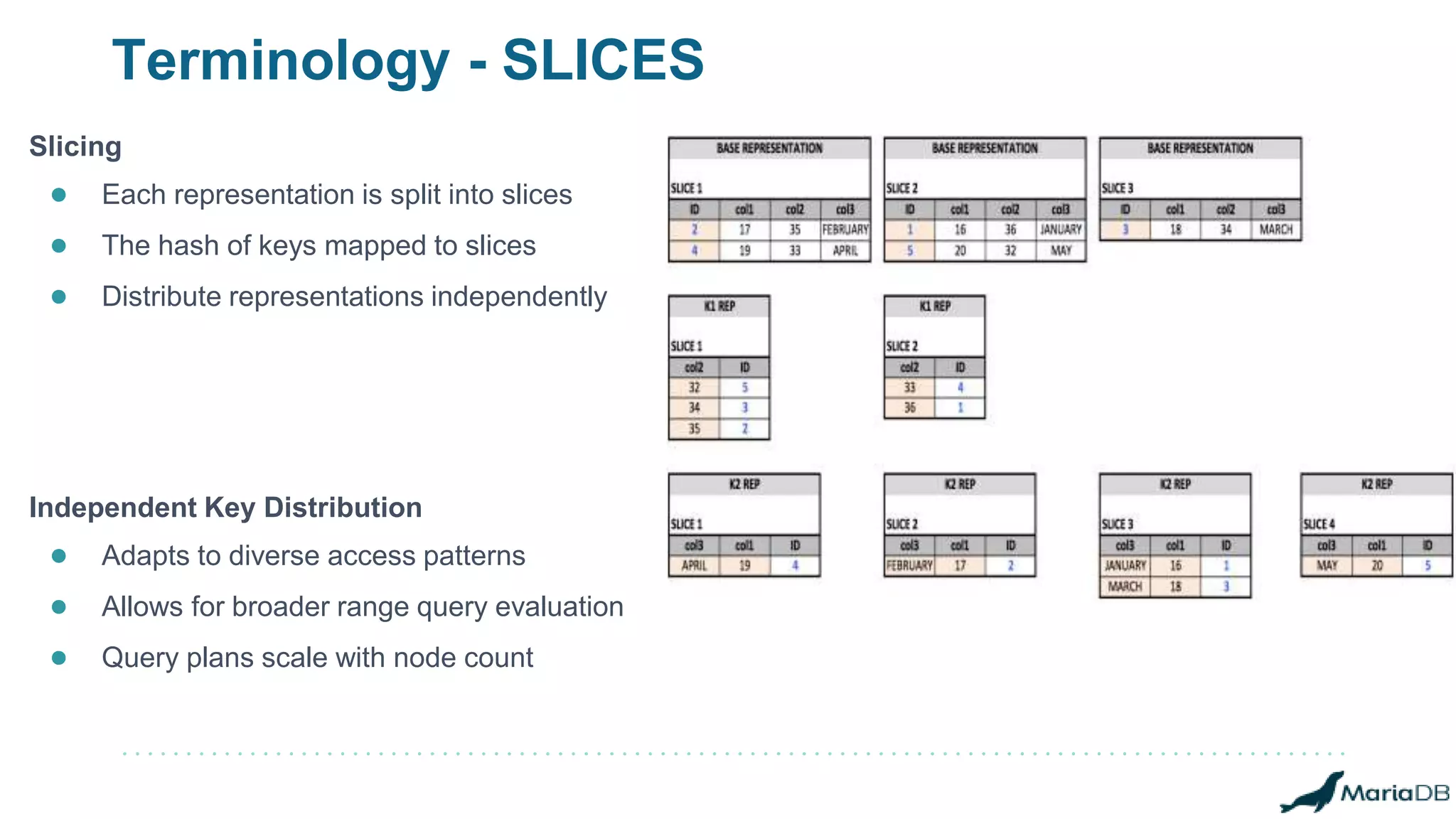
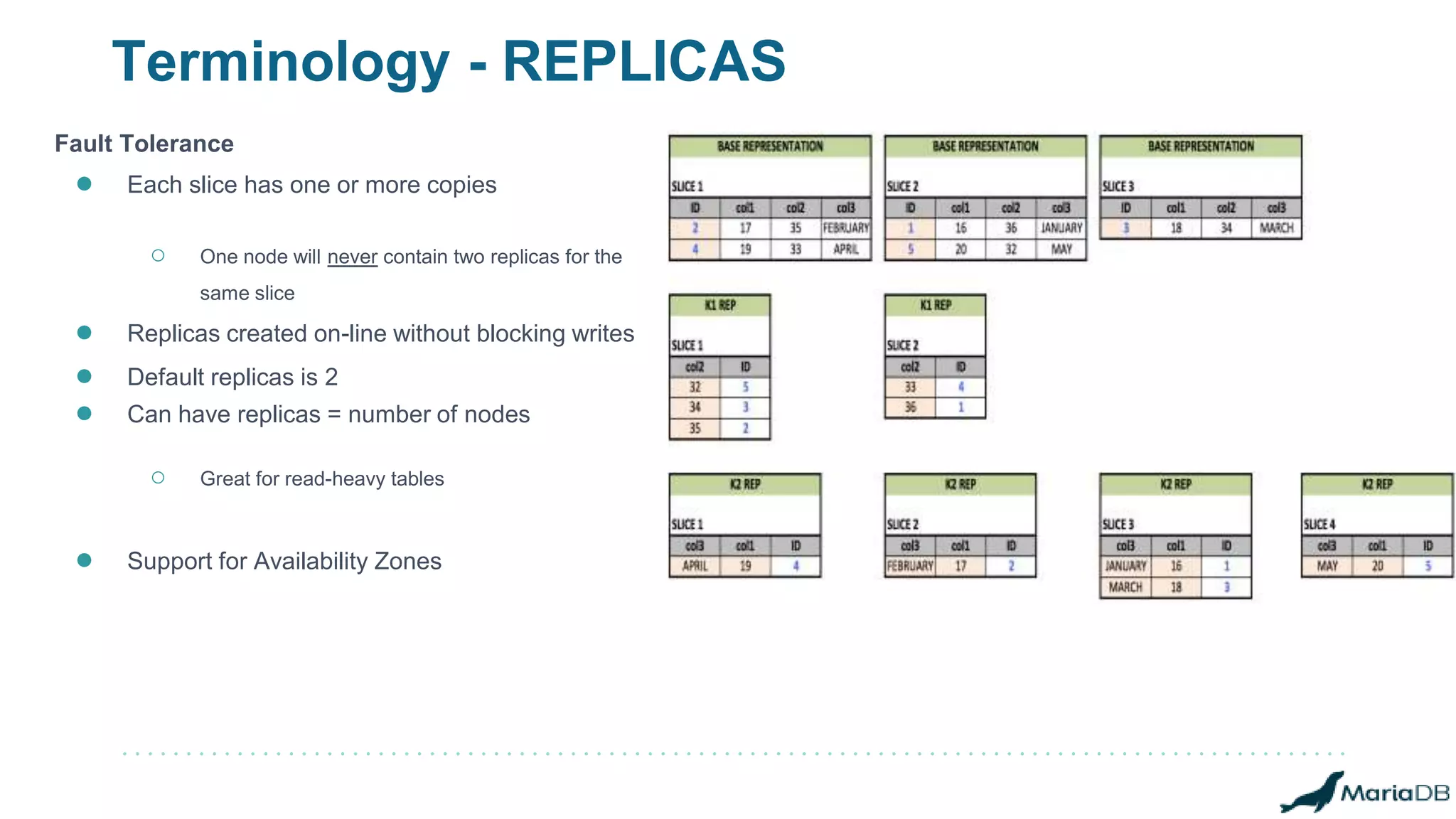
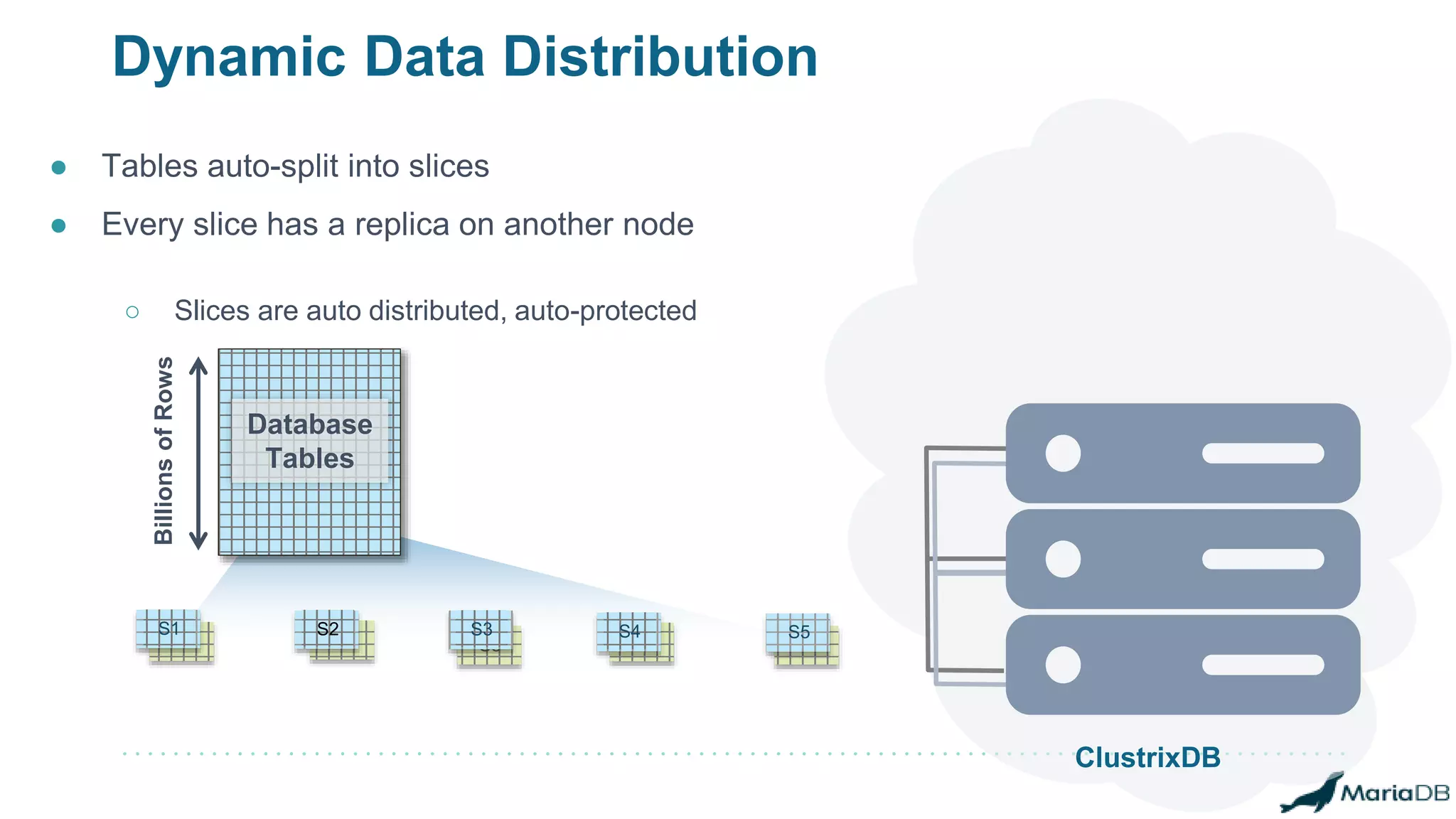
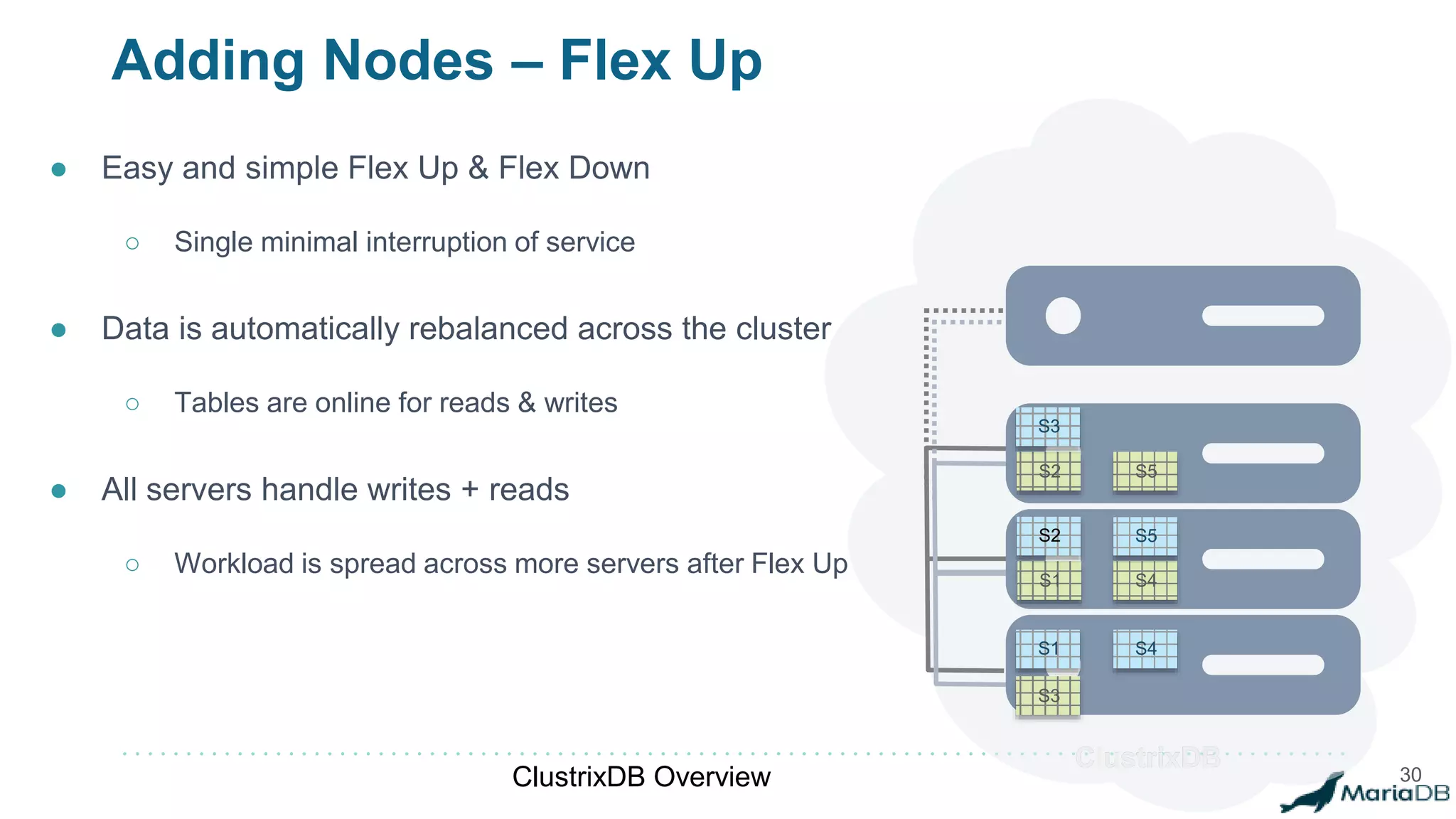
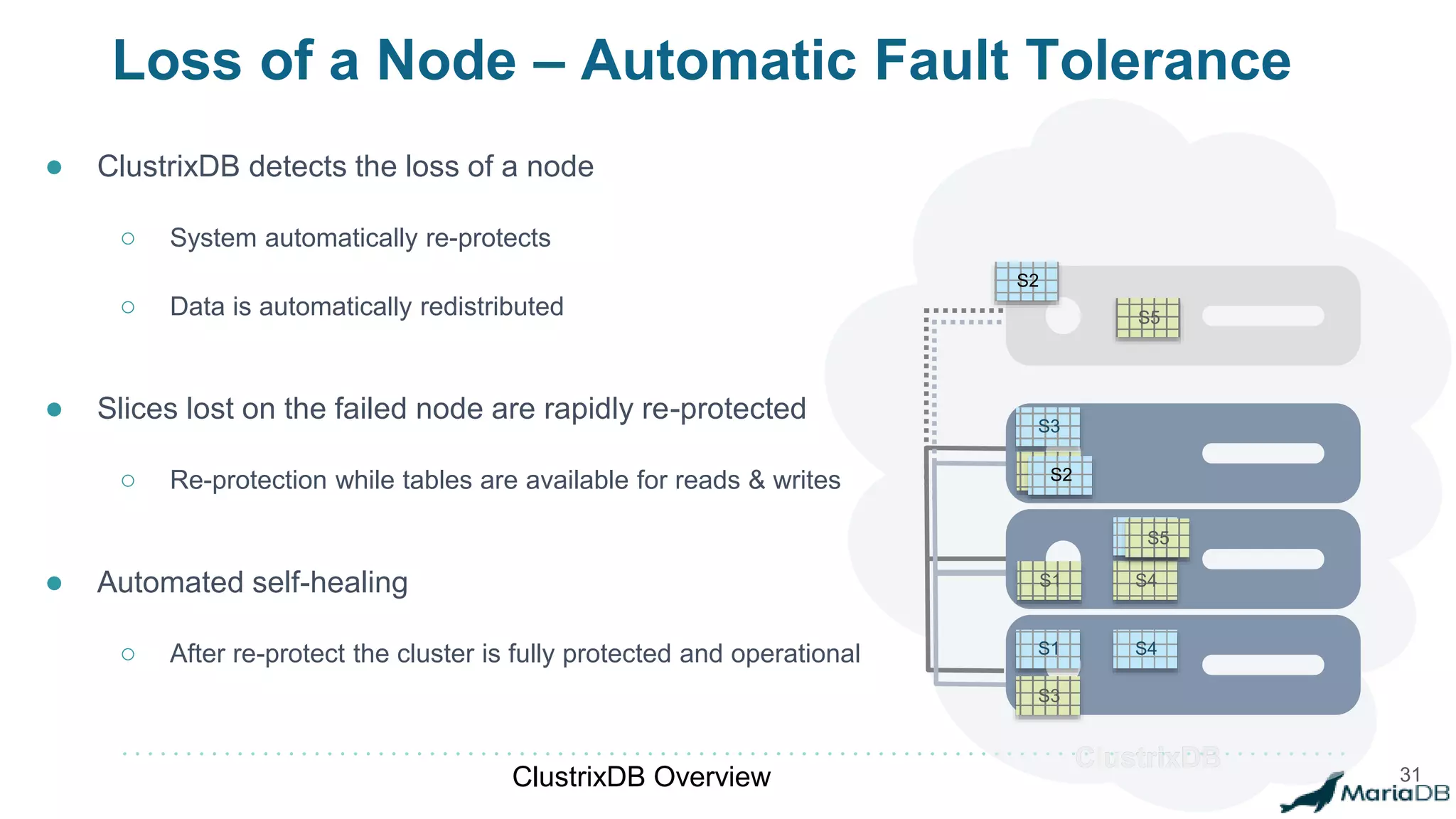
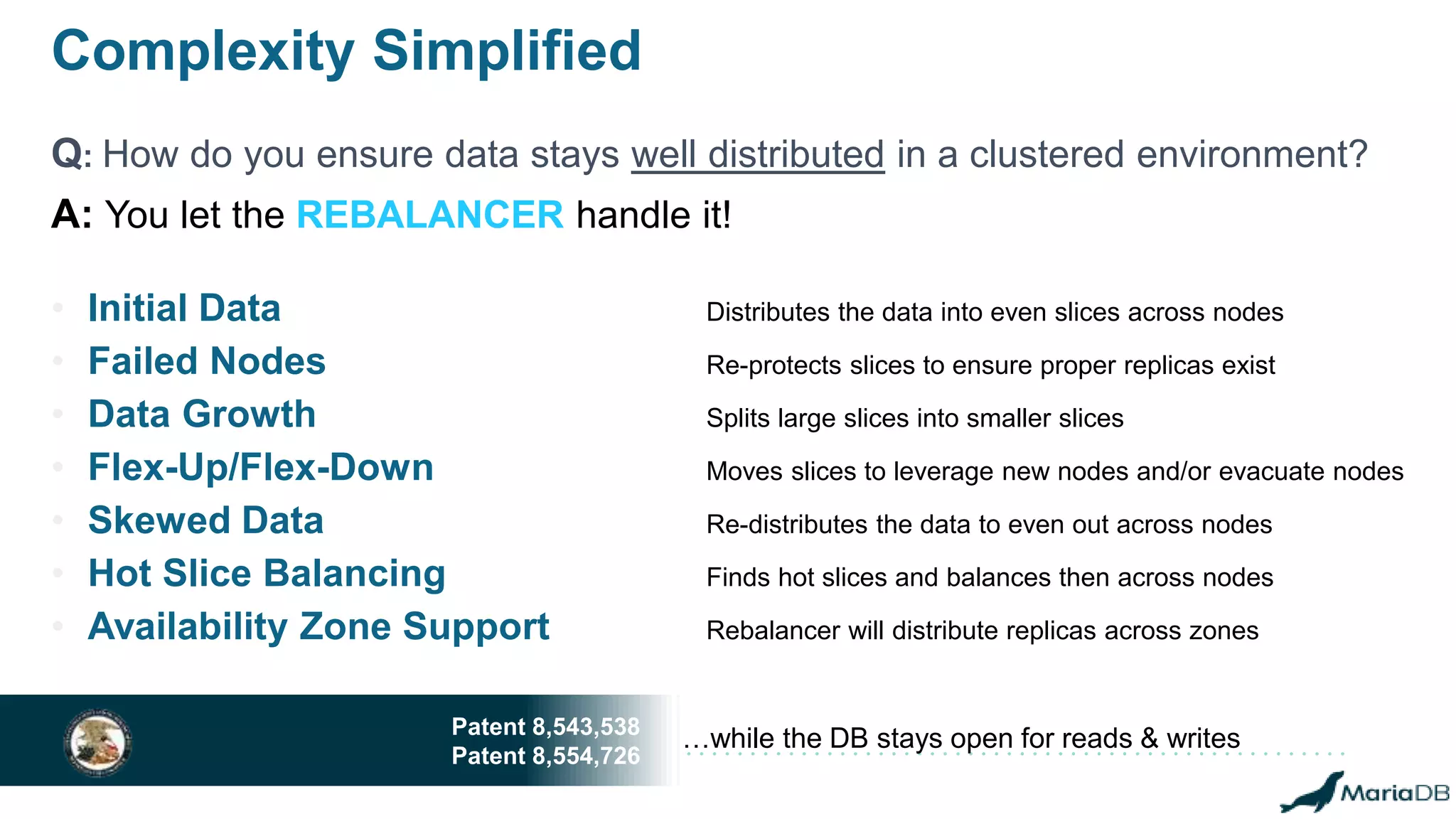
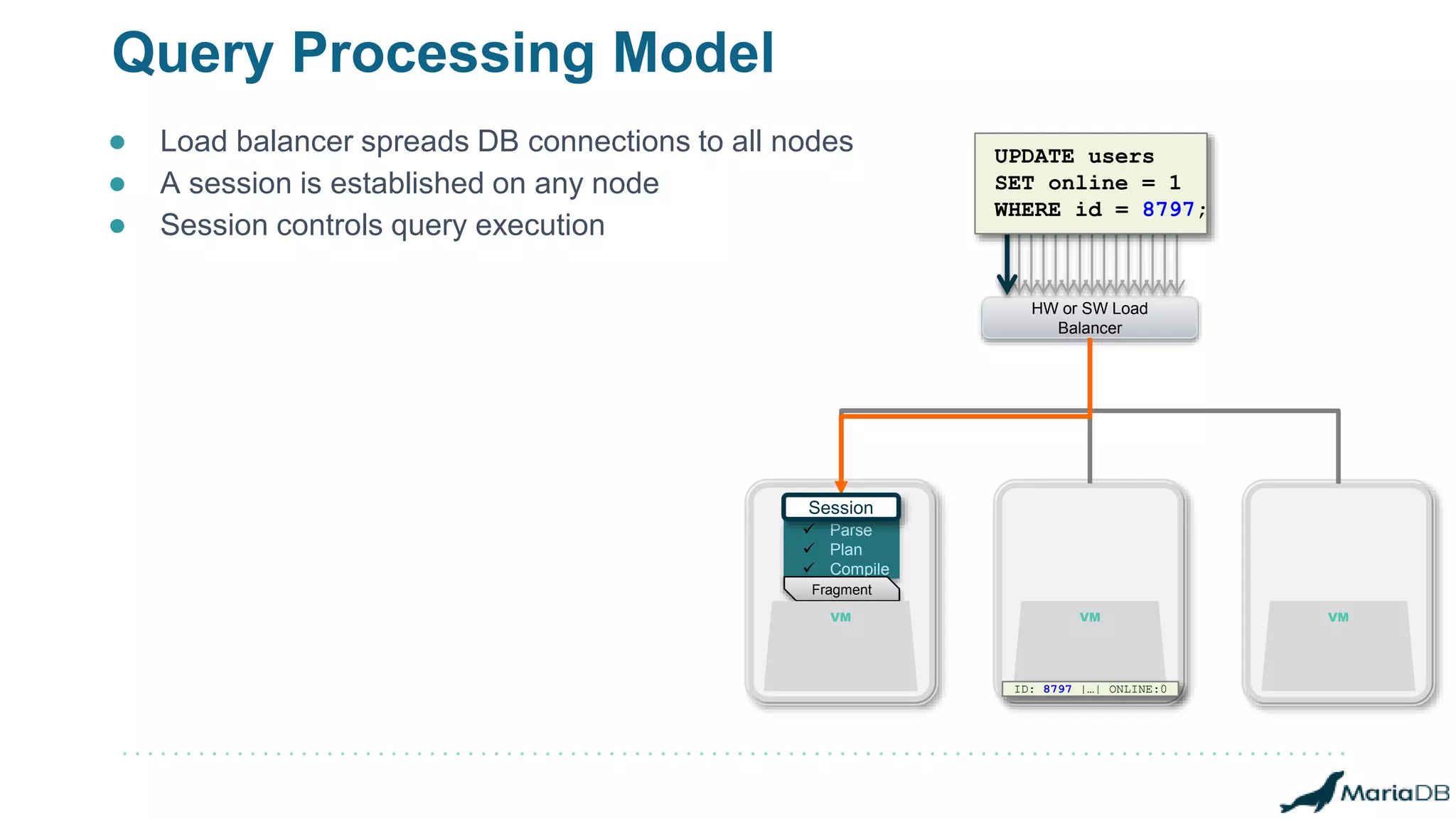
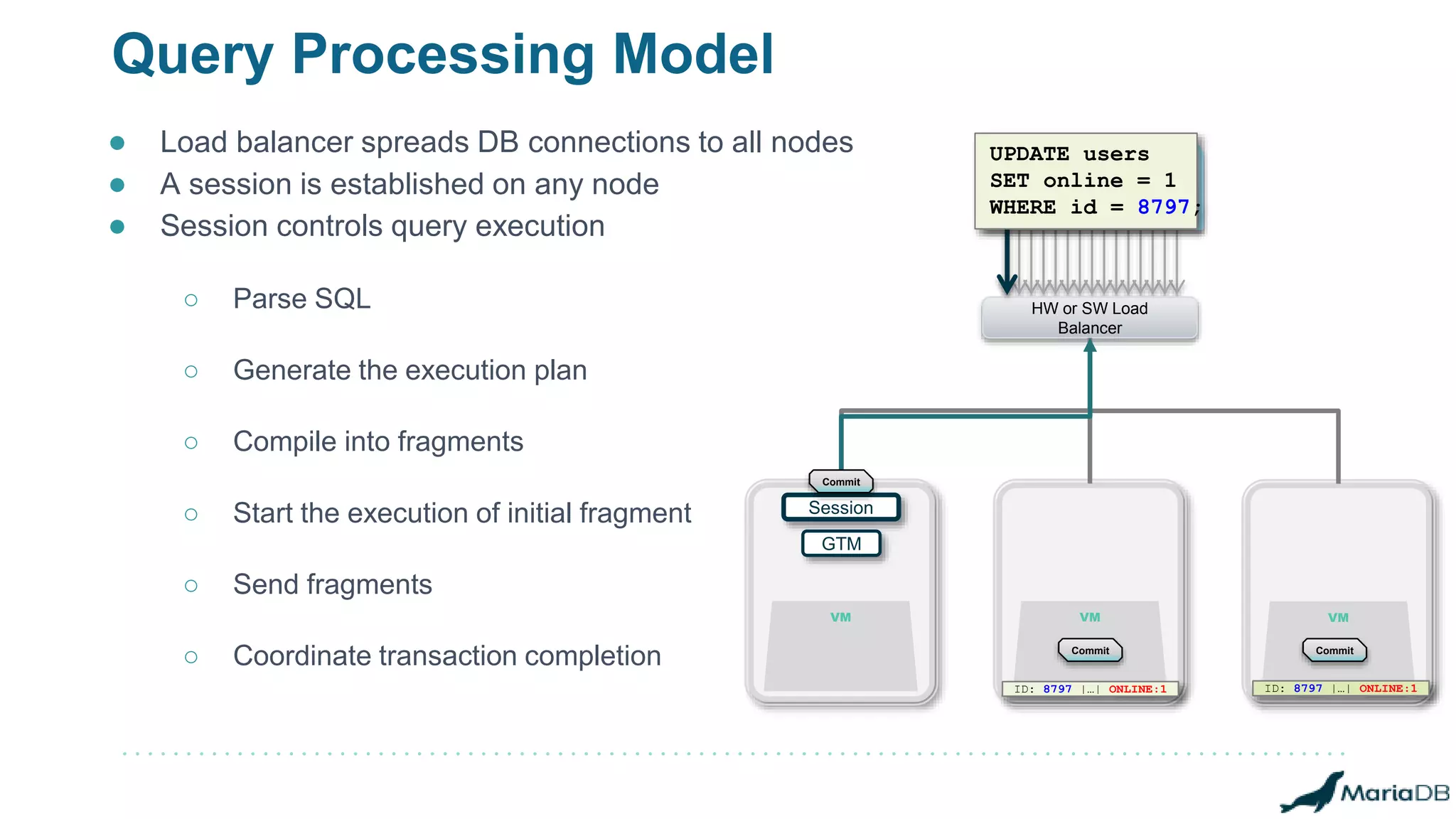
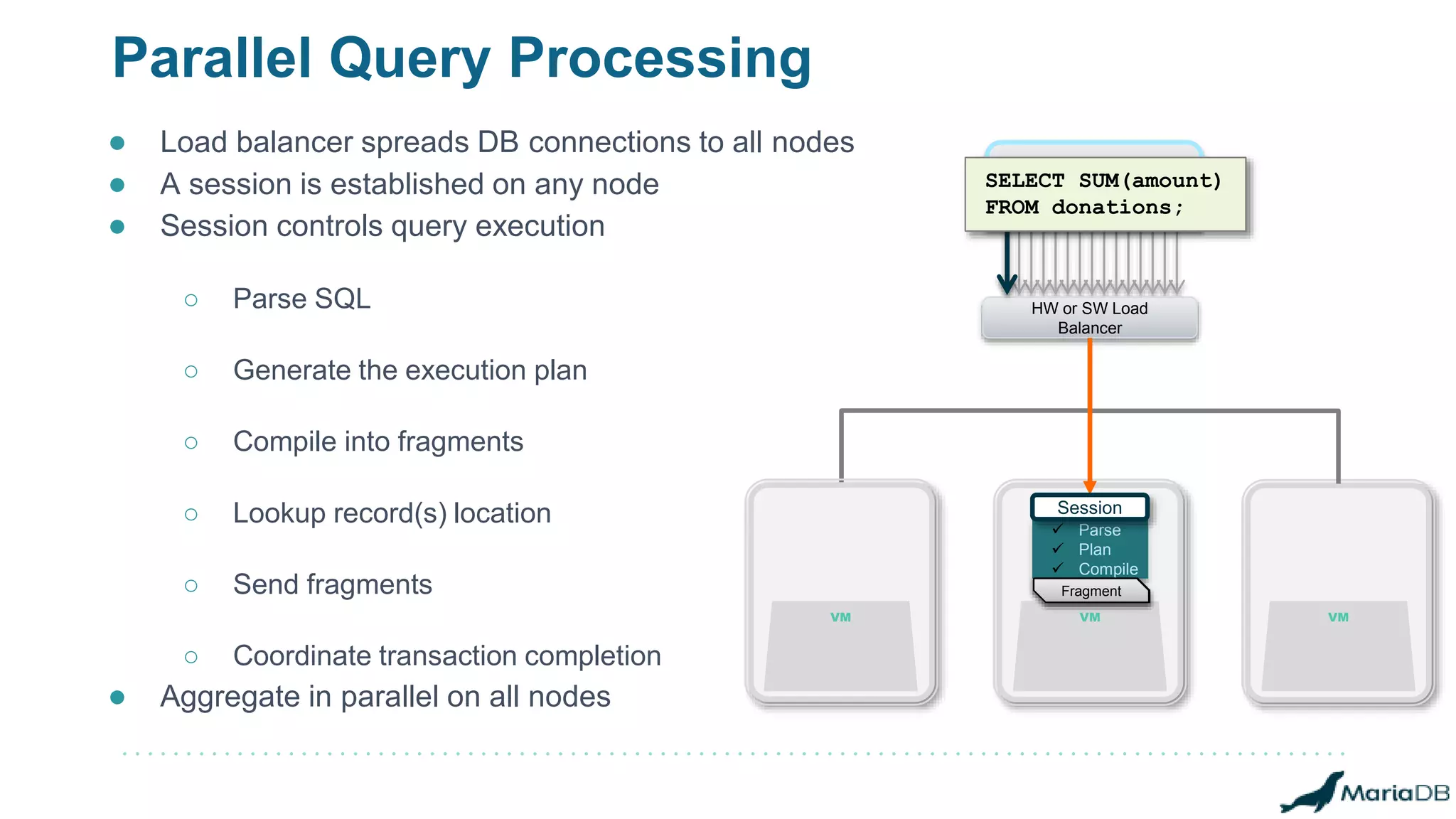
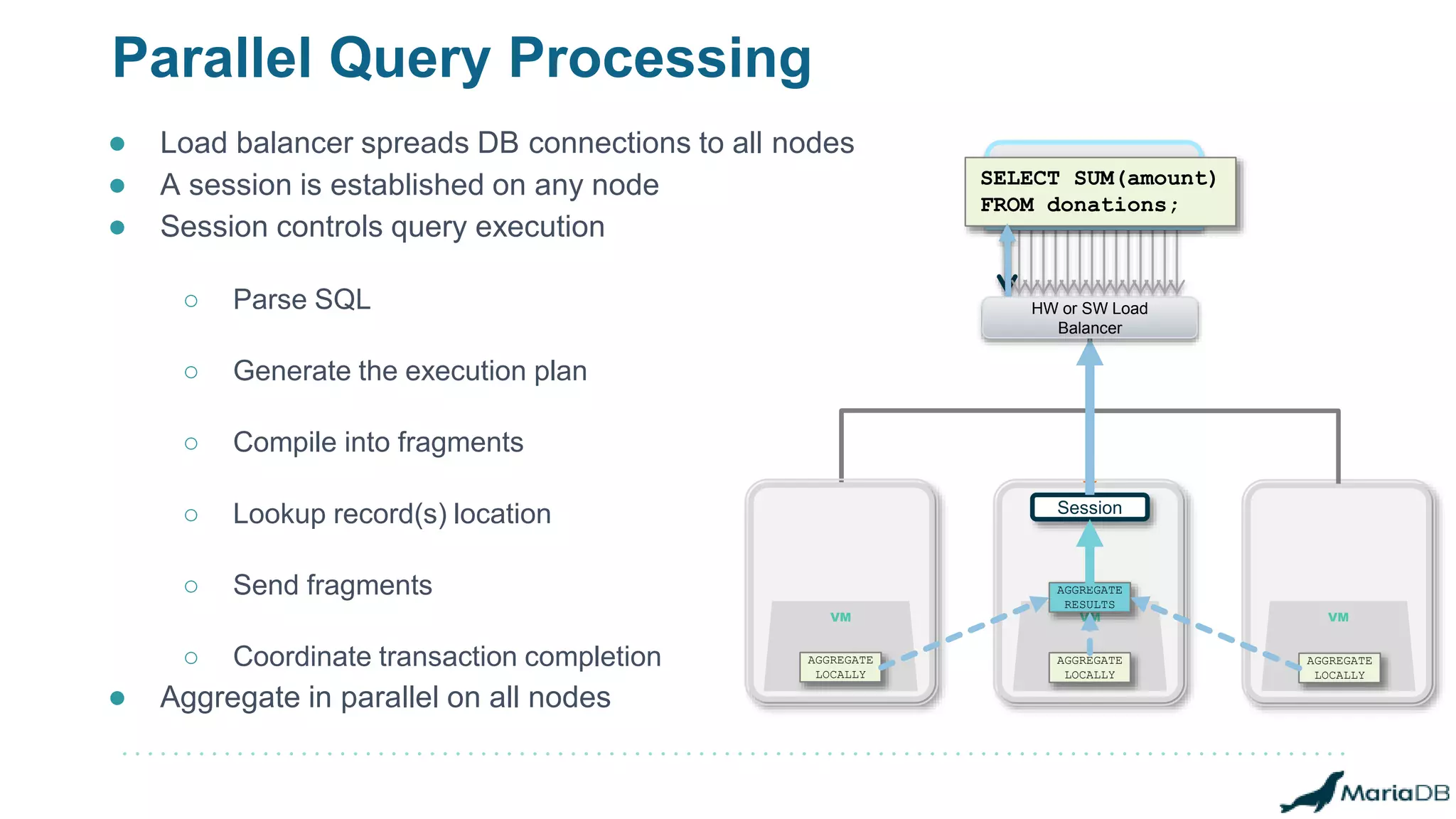
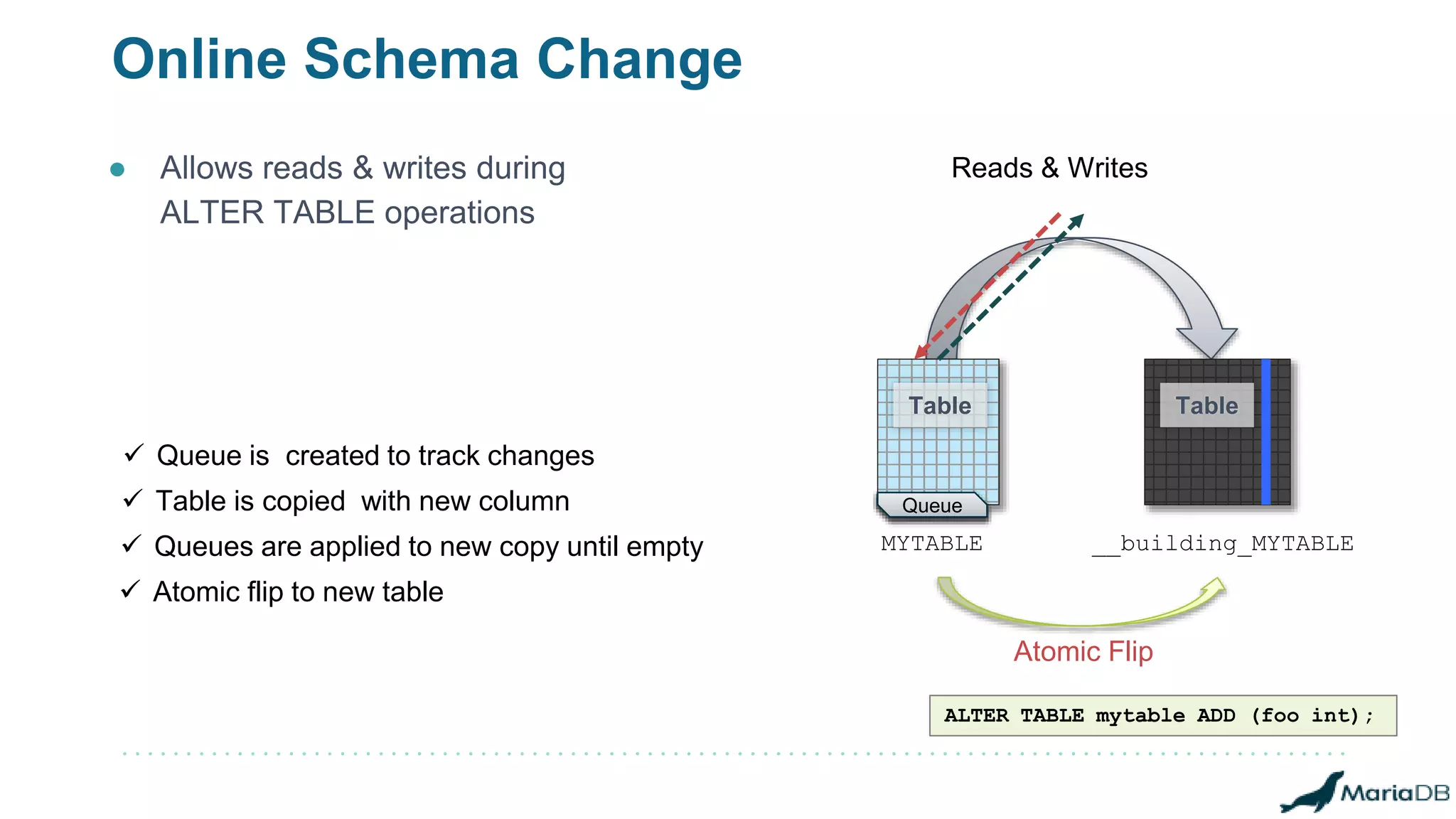
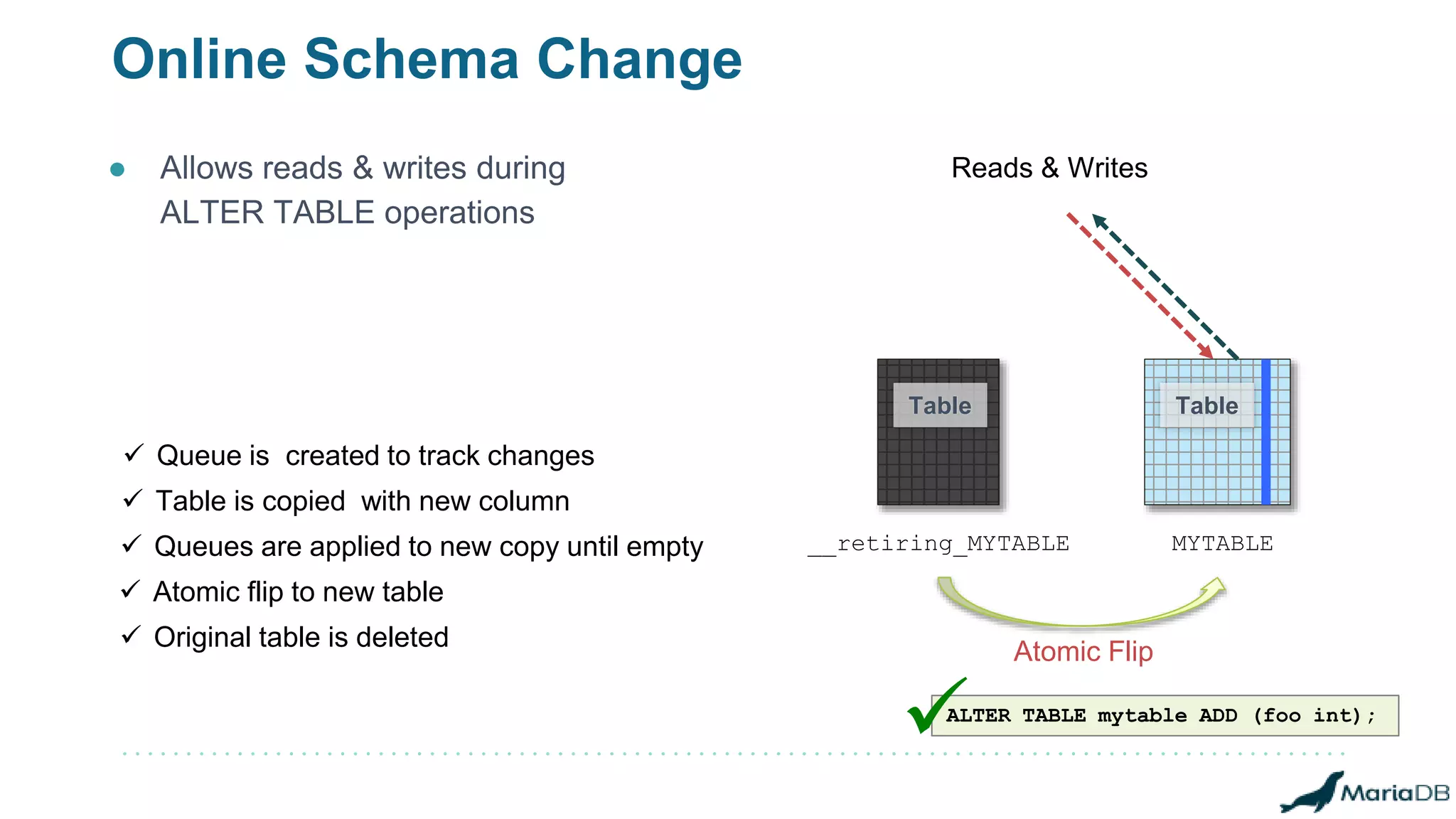
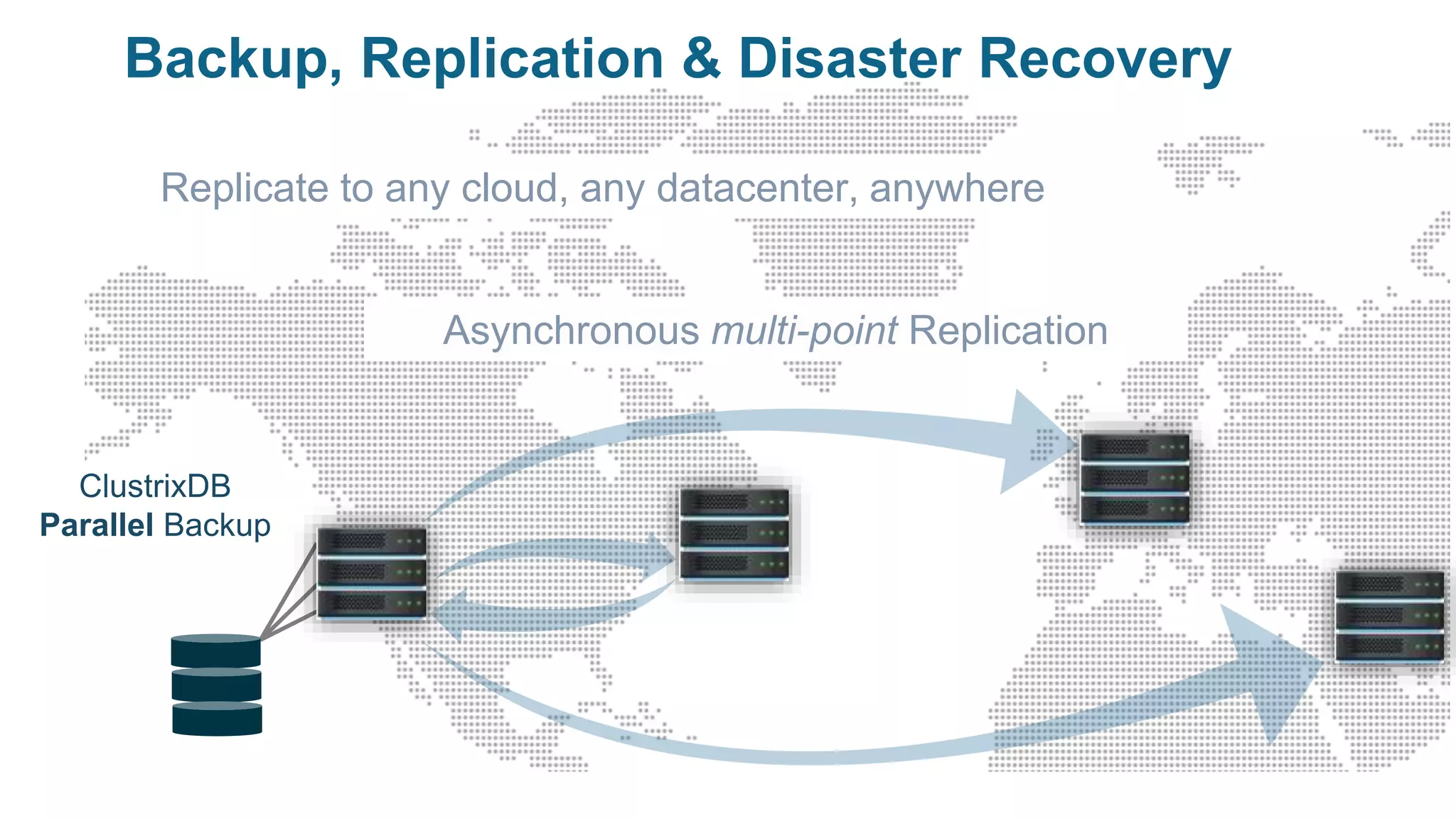
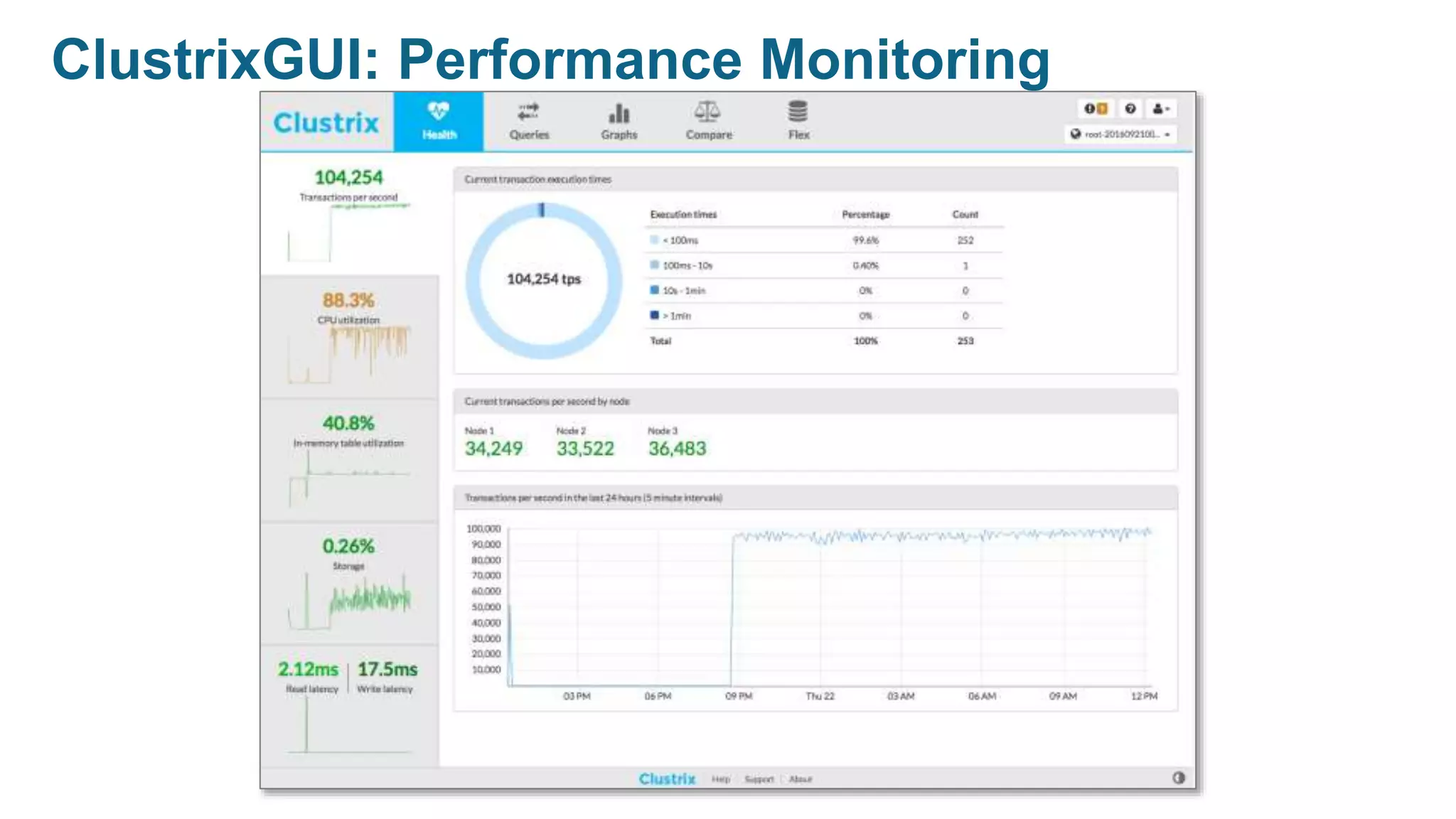
The document provides an overview of MariaDB Clustrix, highlighting its shared-nothing architecture and features like scalability, fault tolerance, and dynamic data distribution. It emphasizes key functionalities such as online schema changes, replication, and parallel query processing, ensuring the system remains operational even during failures. Clustrix also supports various administration features, including automated data rebalancing and self-healing capabilities to maintain performance and availability.