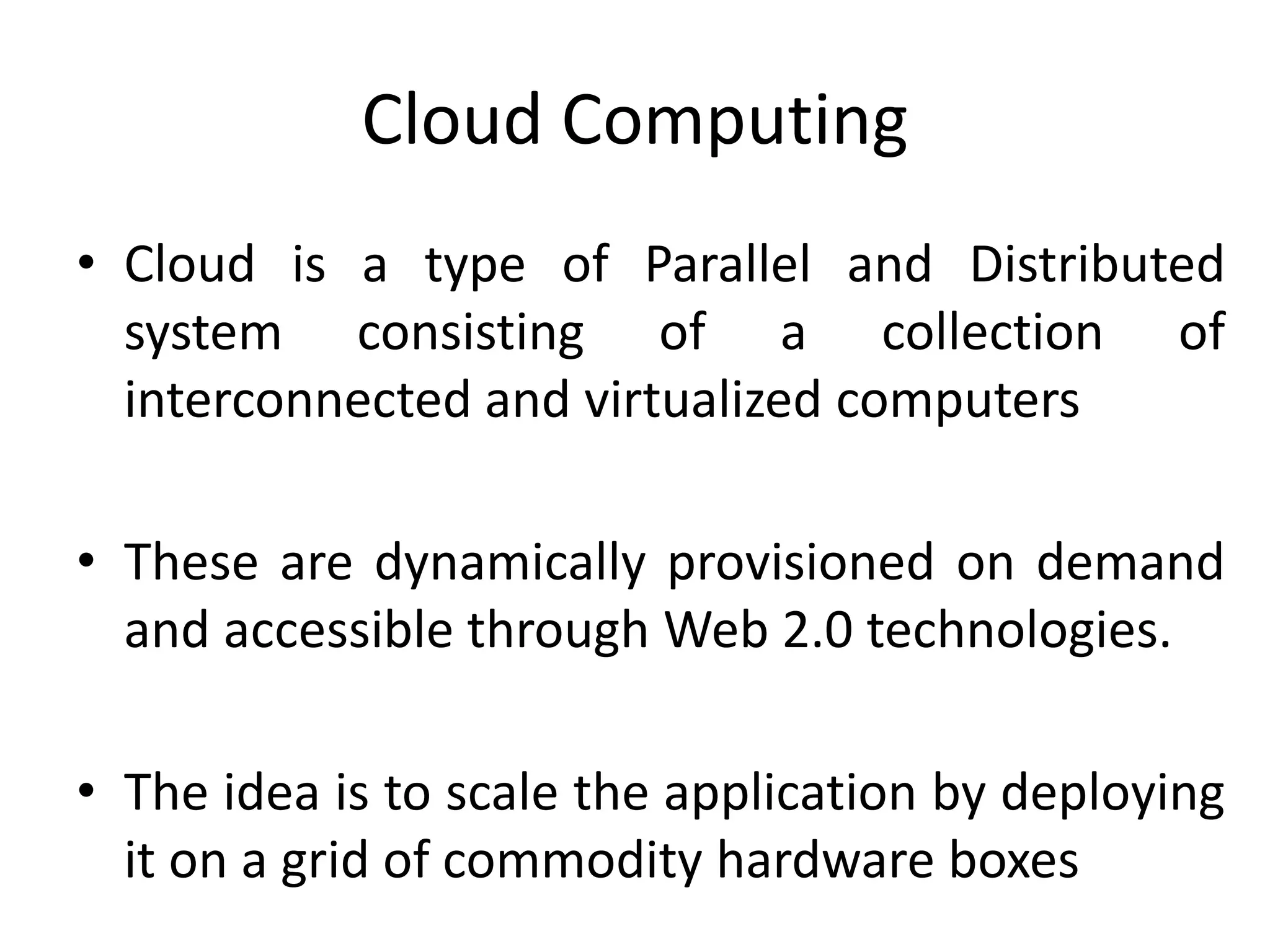
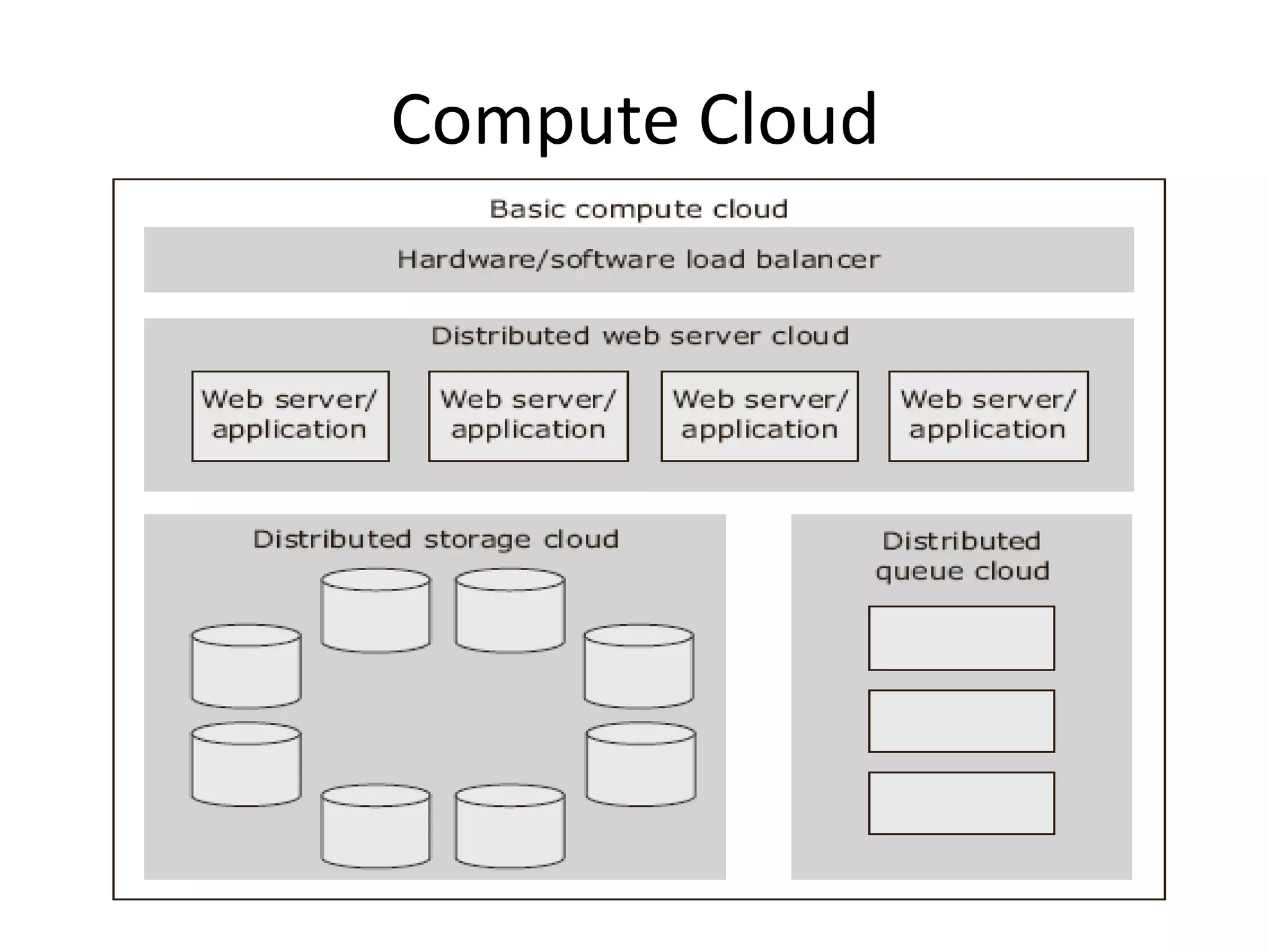
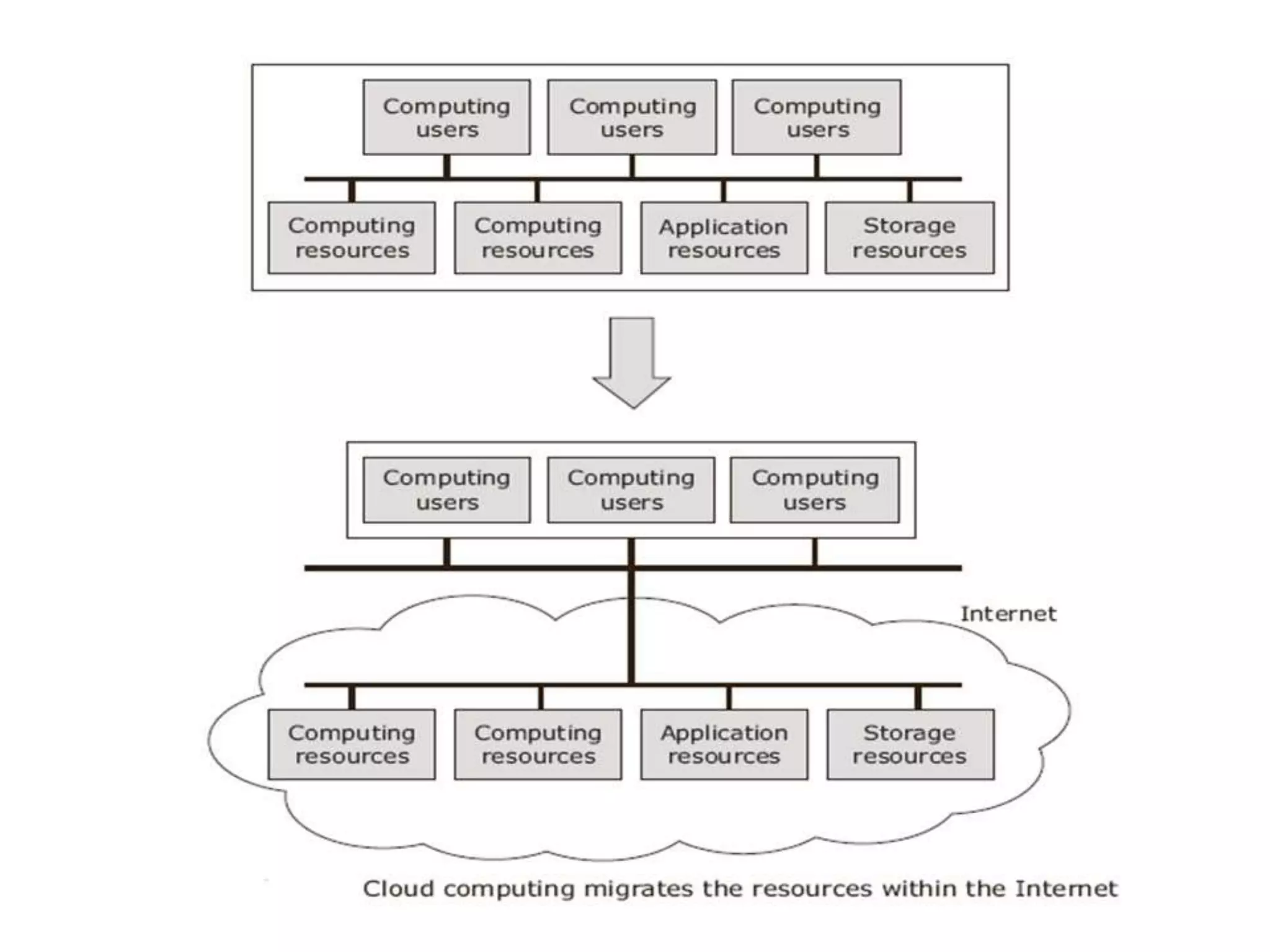
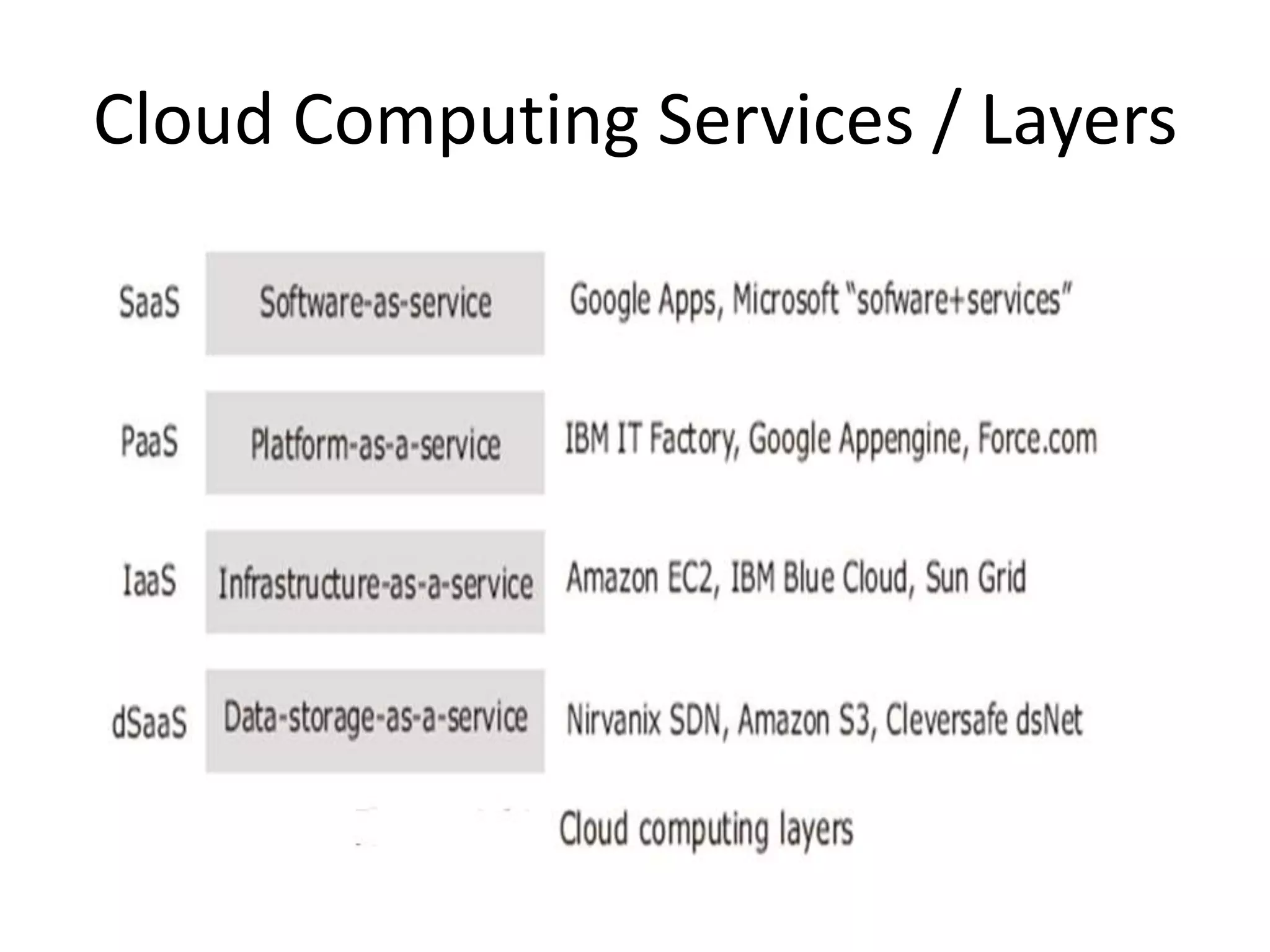
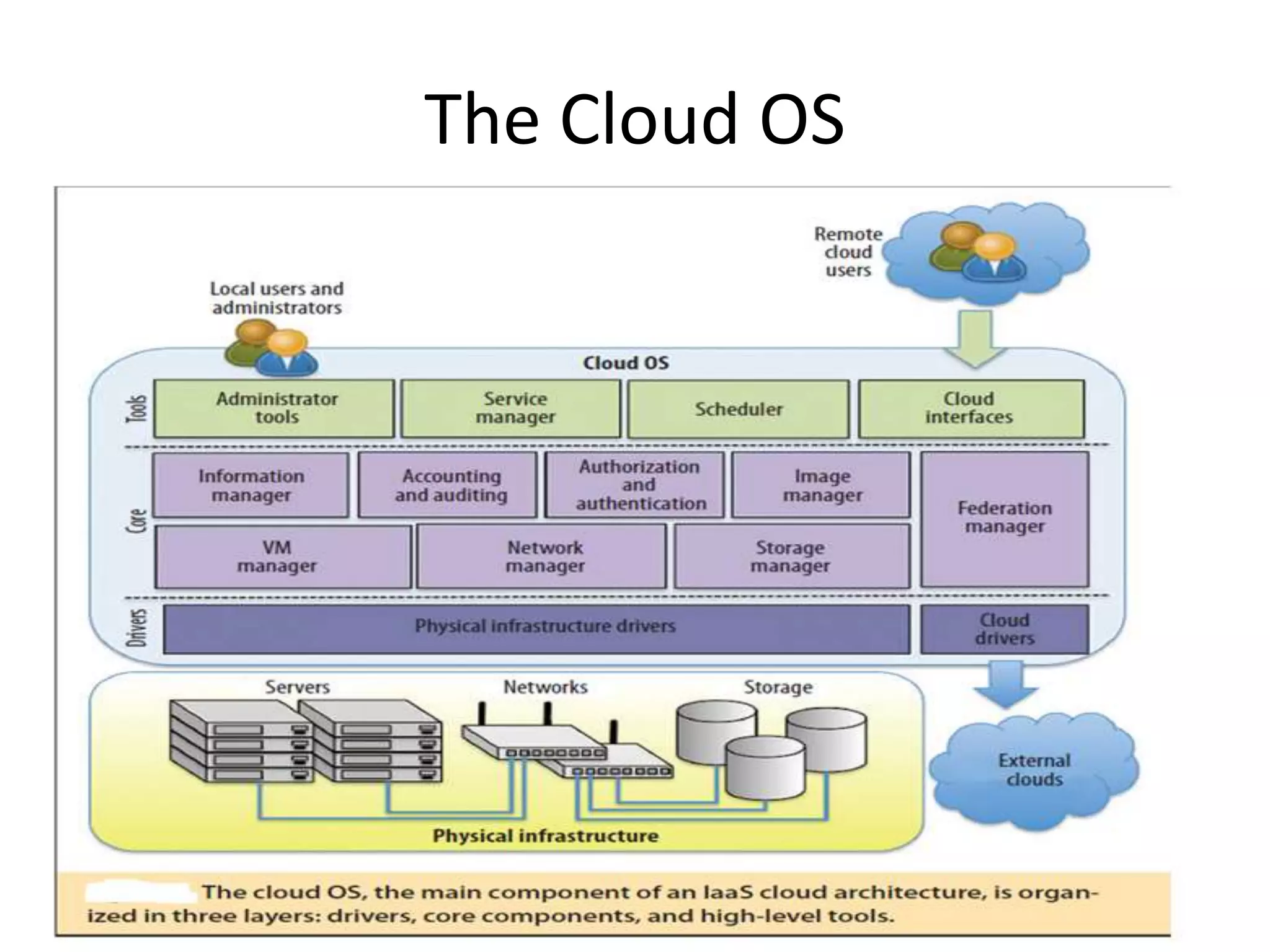
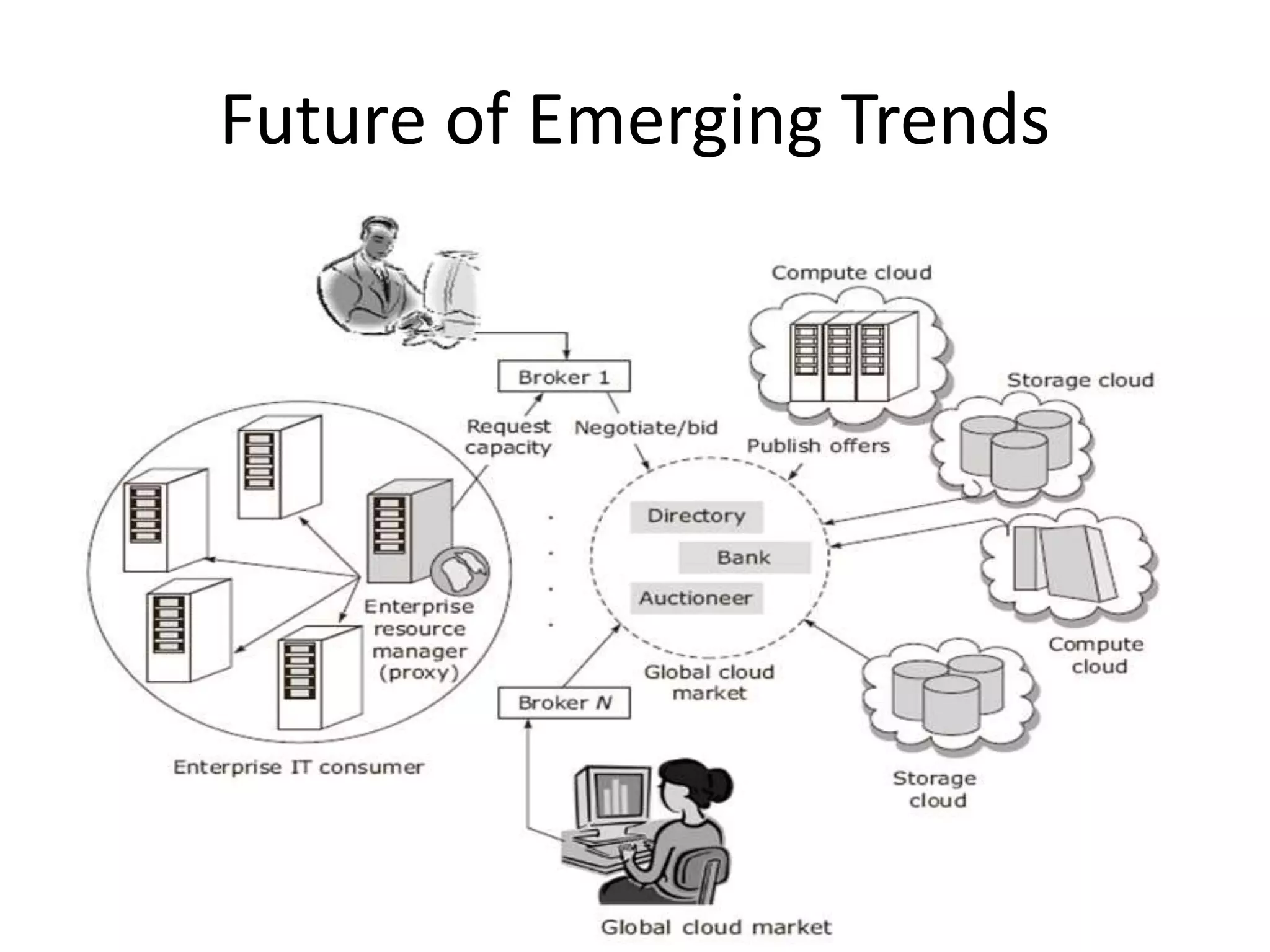
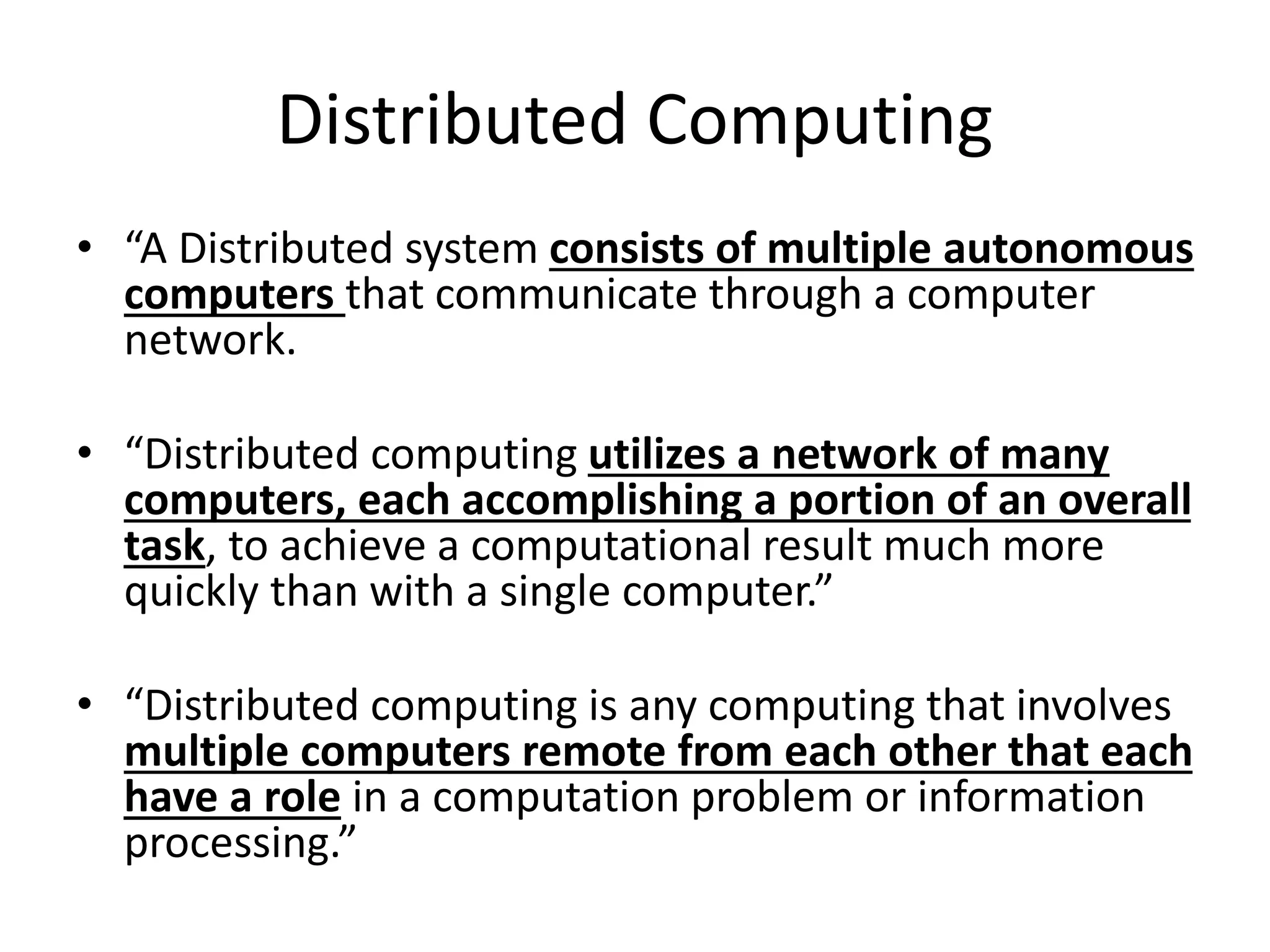
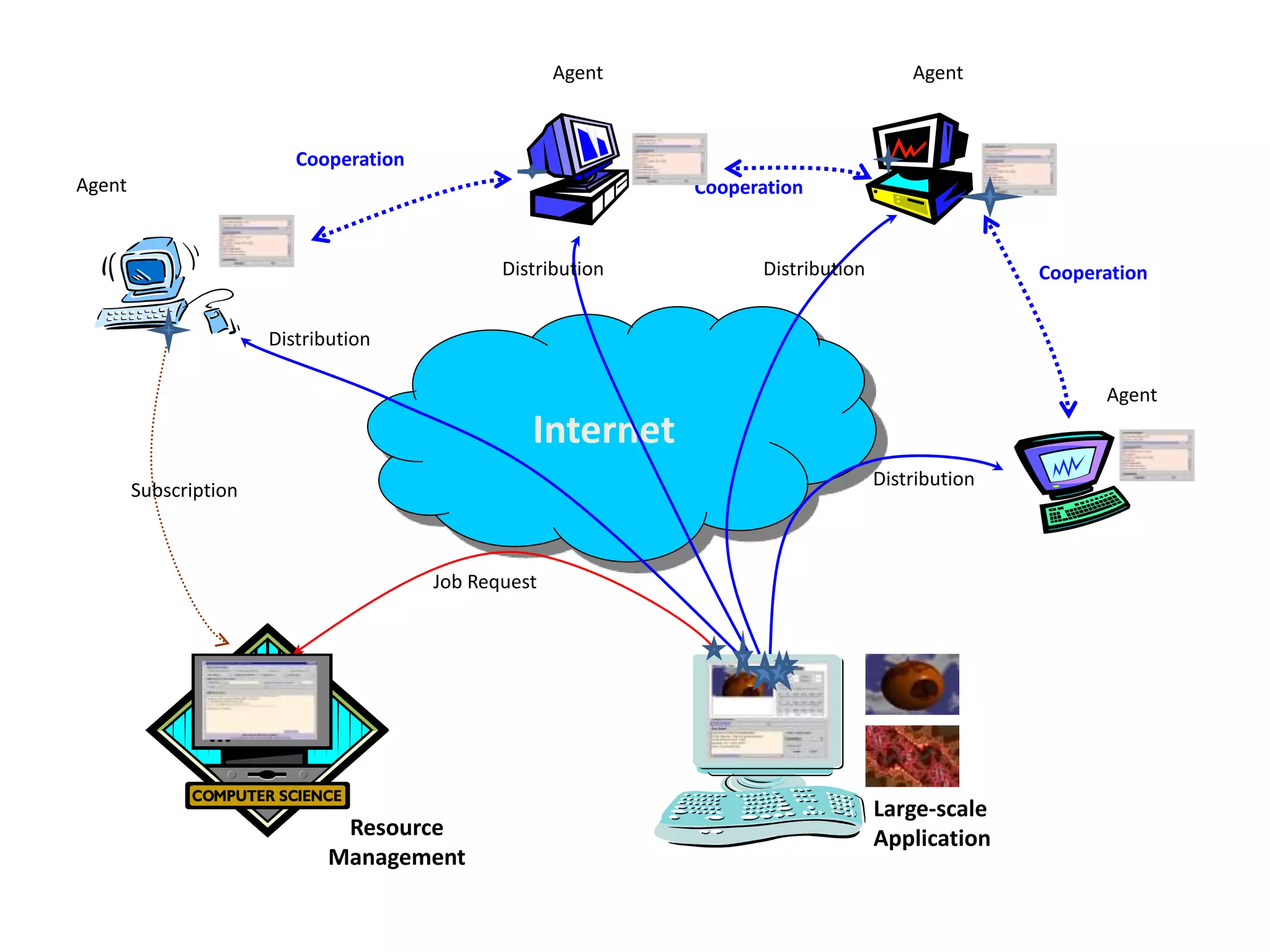
The document discusses cloud computing and distributed computing. It defines cloud computing as a type of parallel and distributed system consisting of interconnected and virtualized computers that are dynamically provisioned on demand through web technologies. Distributed computing is defined as utilizing a network of autonomous computers communicating over a network to accomplish a task more quickly than a single computer. The document then covers the history, characteristics, applications, advantages, and disadvantages of distributed computing and cloud computing.











![Dr. Kamal Gulati Associate Professor | University Quality Support Head | Mentoring Programme Coordinator [Ph. D., M.Sc. (Computer Science), M.C.A., M.B.A] Professional Certifications: • Certified Microsoft Innovative Educator • Data Science 101 Certification from Big Data University • R Language 101 Certification from Big Data University • SQL Certification from SOLOLEARN.com • Certified IBM Big Data 101 from Big Data University • R Program & Python Certified from DataCamp • Wiley Certified Big Data Analyst [WCBDA] • Certification on DBMS from IIT Mumbai • Certified Cisco Certified Network Associate [CCNA] • Certified Microsoft Certified Professional [MCP] • Certified Brainbench in Computer Fundamentals, Microsoft Access, MySQL 5.7 Administration & Microsoft Project](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputingdistributedcomputing-1712080505031-221117173718-66060c58/75/cloudcomputingdistributedcomputing-171208050503-1-pdf-28-2048.jpg)




