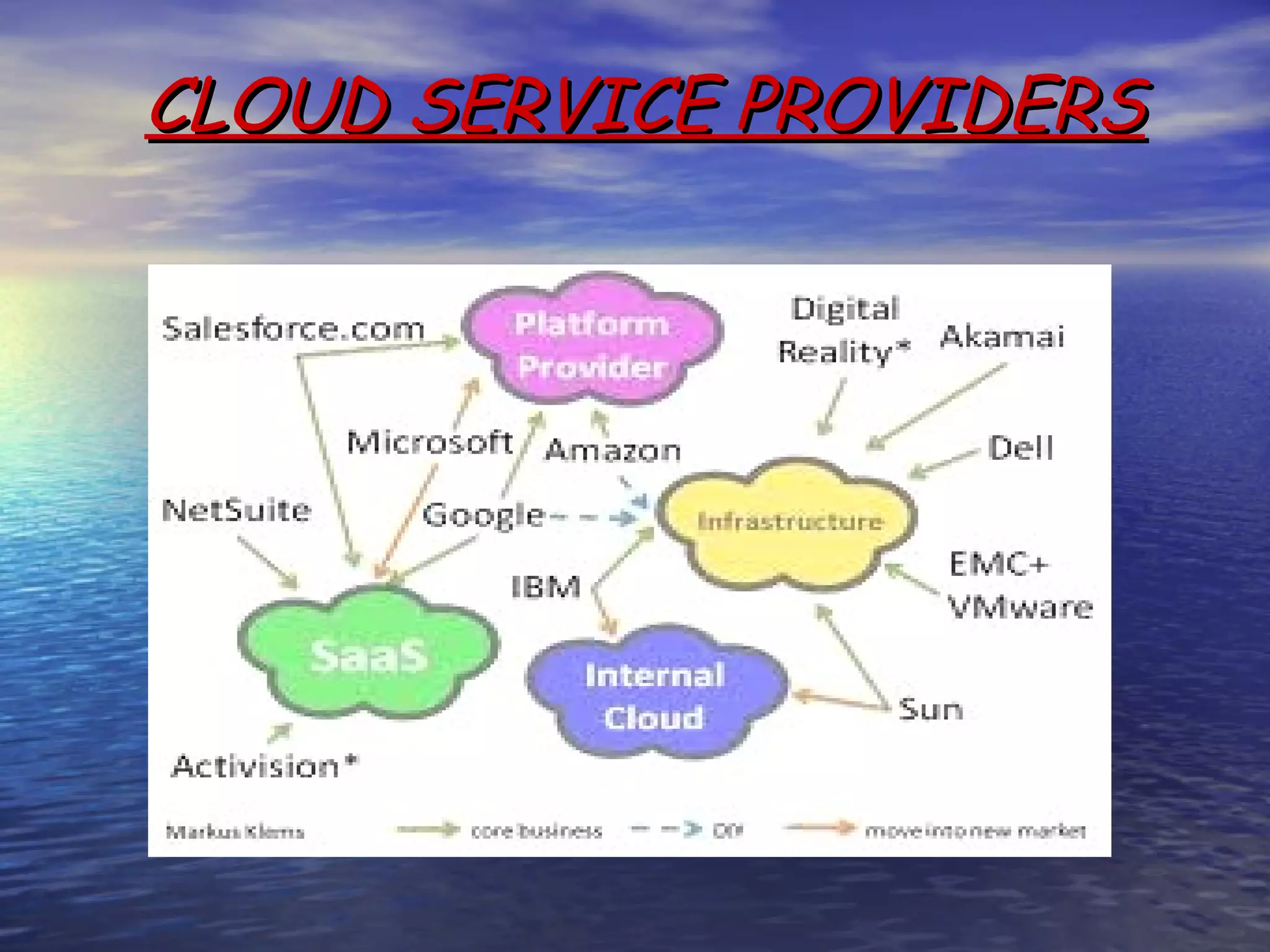
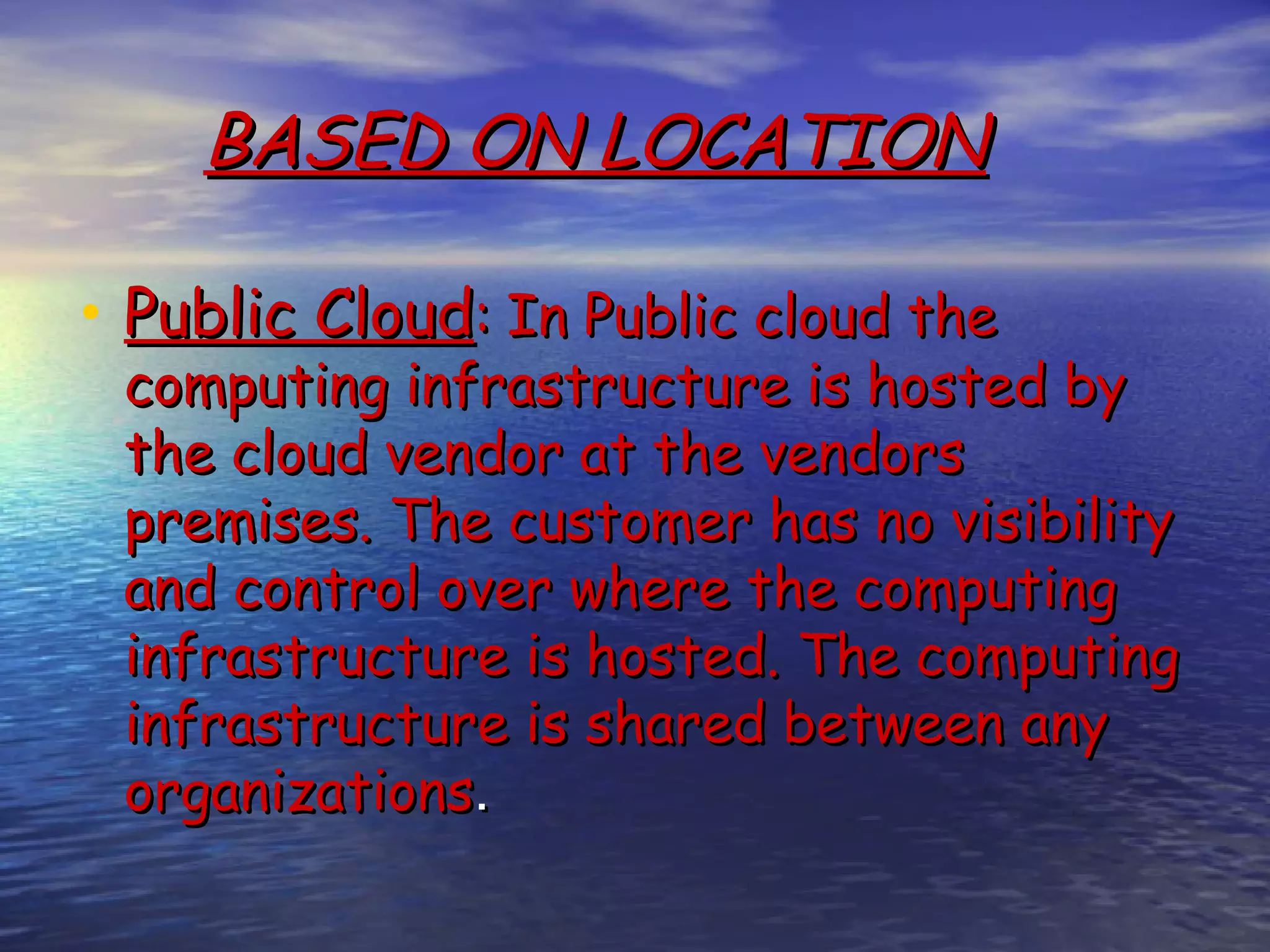
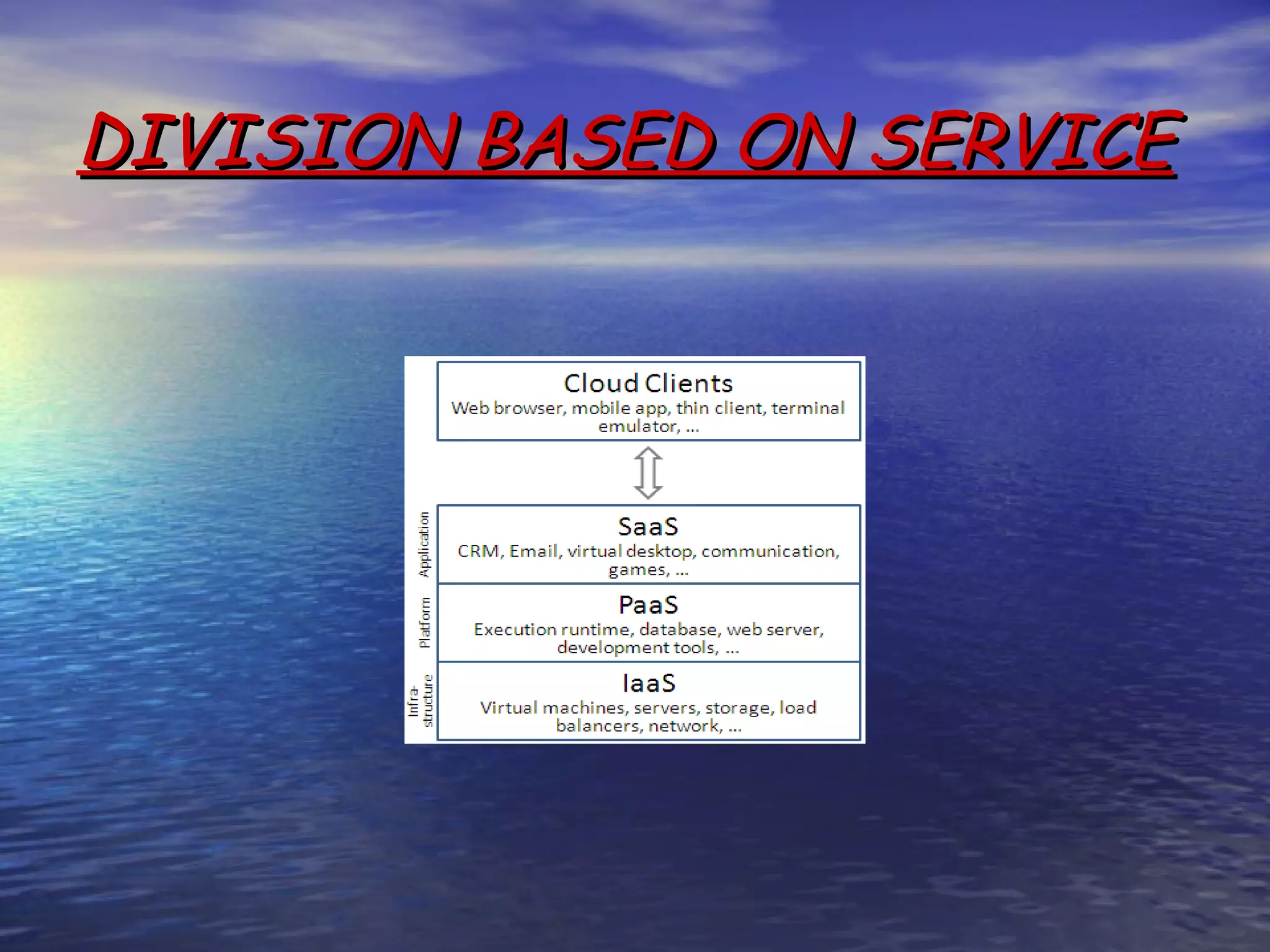
Cloud computing allows users to access scalable IT resources and applications online without direct active management. It provides benefits like reduced costs, increased scalability and accessibility of resources. However, some concerns include data security, reliability of service and lack of transparency about data locations. For businesses, cloud computing can help lower costs especially for startups, while also providing green benefits from reduced energy usage compared to maintaining private servers. Firms must evaluate their individual needs to determine if migrating workloads to the cloud is appropriate.

































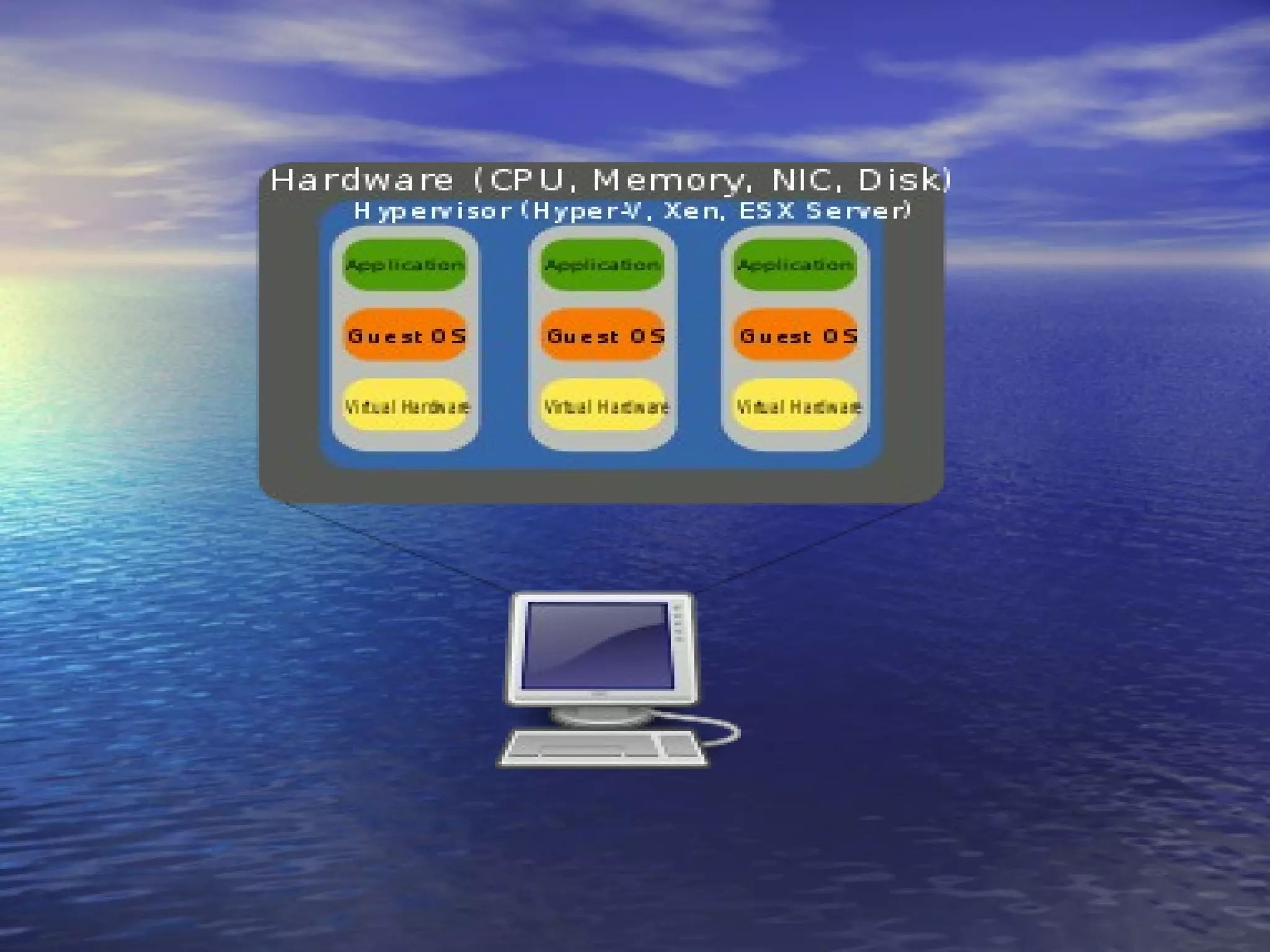
![REASONS FOR VIRTUALISATION • n the case of server consolidation, many small physical servers are replaced by one larger physical server to increase the utilization of costly hardware resources such as CPU. Although hardware is consolidated, typically OSes are not. Instead, each OS running on a physical server becomes converted to a distinct OS running inside a virtual machine. The large server can "host" many such "guest" virtual machines. This is known as Physical-to- Virtual (P2V) transformation. • Consolidating servers can also have the added benefit of reducing energy consumption. A typical server runs at 425W[3] and VMware estimates an average server consolidation ratio of 10:1. [4] • A virtual machine can be more easily controlled and inspected from outside than a physical one, and its configuration is more flexible. This is very useful in kernel development and for teaching operating system courses. [5] • A new virtual machine can be provisioned as needed without the need for an up-front hardware purchase. • A virtual machine can easily be relocated from one physical machine to another as needed. For example, a salesperson going to a customer can copy a virtual machine with the demonstration software to his laptop, without the need to transport the physical computer. Likewise, an error inside a virtual machine does not harm the host system, so there is no risk of breaking down the OS on the laptop.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sapthagiricloud-120918022450-phpapp01/75/cloud-computing-Introduction-40-2048.jpg)