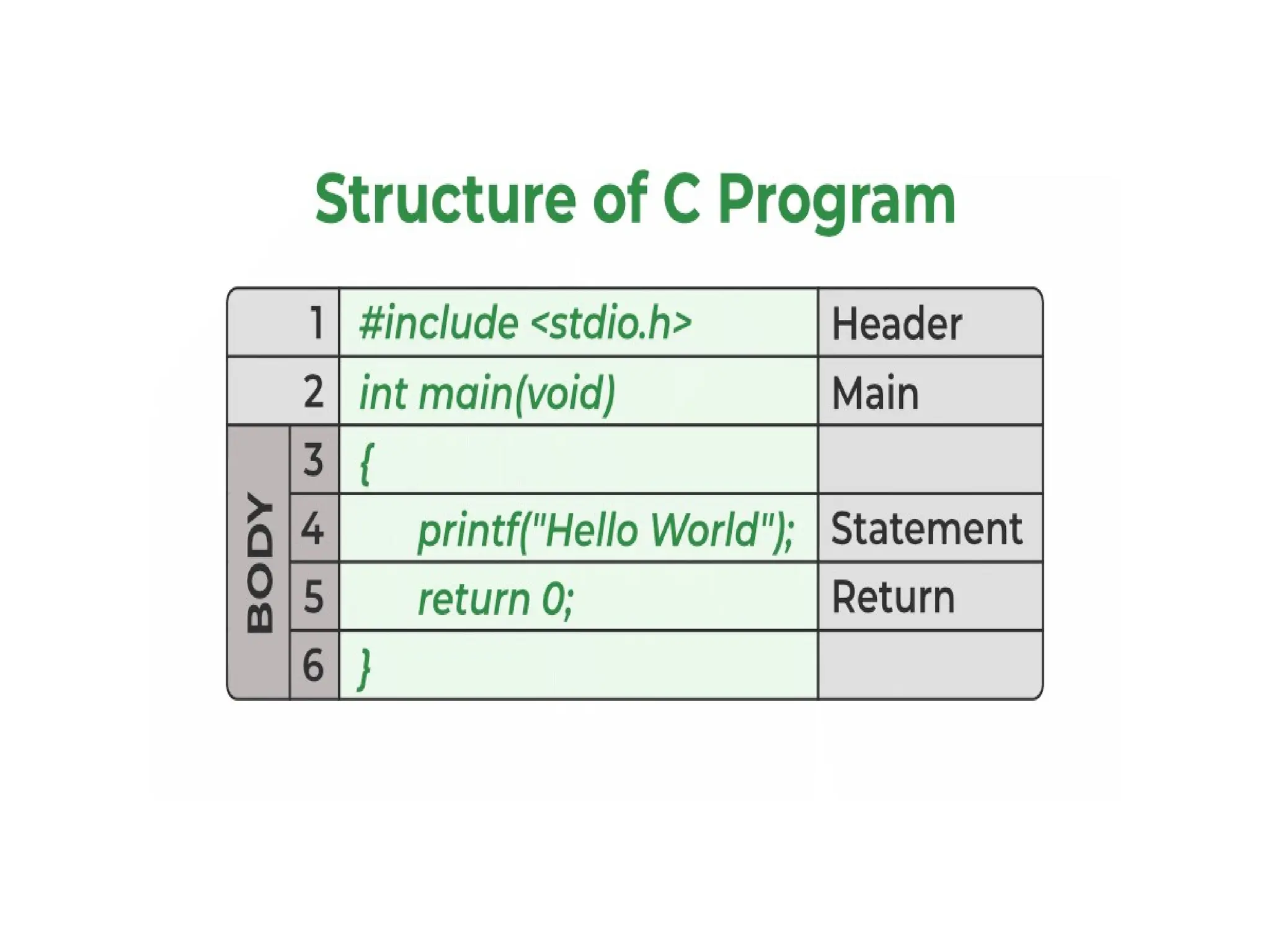
The document is a presentation on C programming by Mrs. B. Dhivya, covering the fundamentals of the C language, its history, features, and structure. It discusses various components such as standard input/output functions, tokens, keywords, constants, and operators, along with programming examples and exercises. Additionally, it explains common errors and outputs in C programming, along with assessments to test understanding.





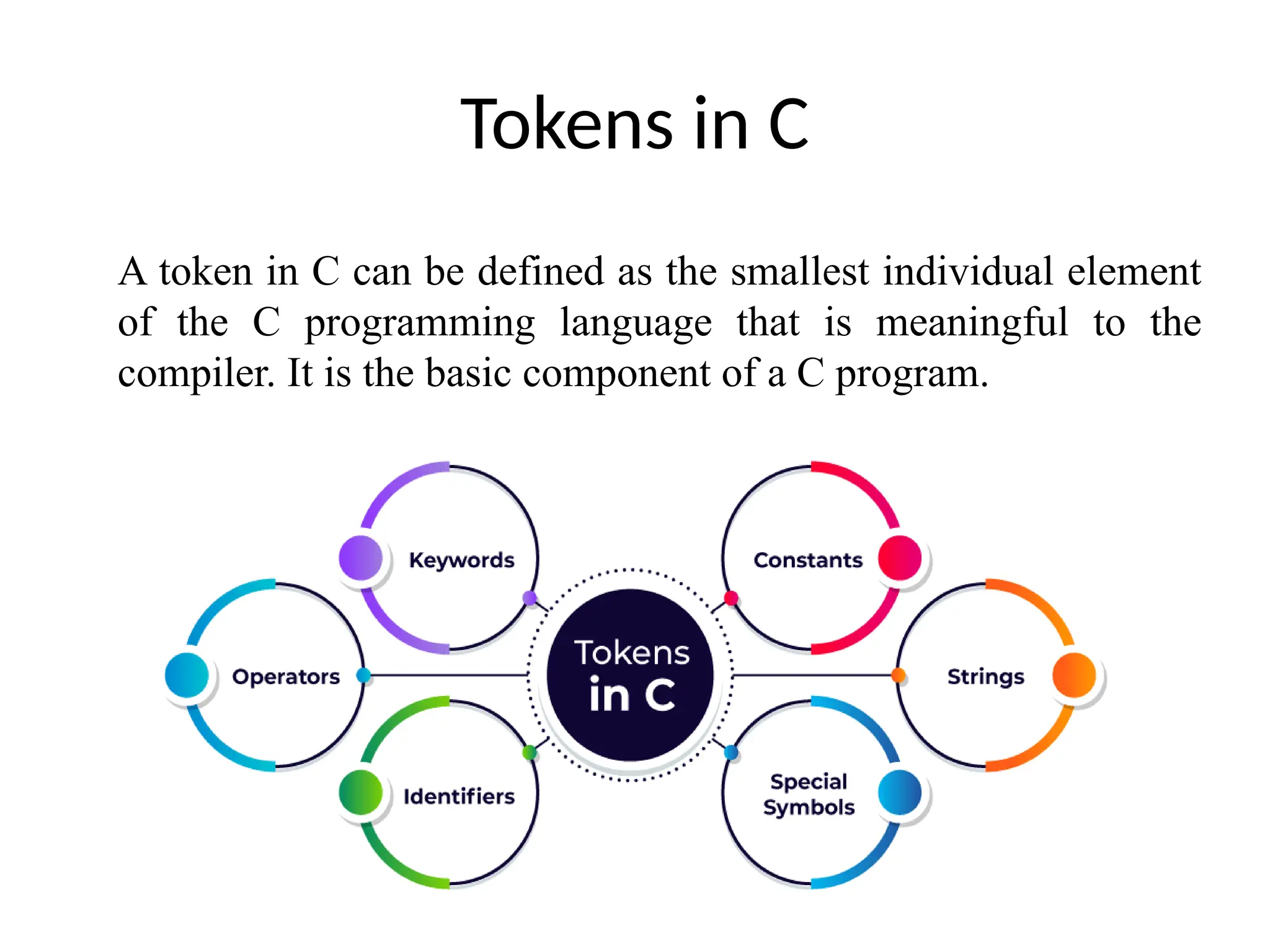



![Strings Strings are nothing but an array of characters ended with a null character (‘0’). This null character indicates the end of the string. Strings are always enclosed in double quotes. Whereas, a character is enclosed in single quotes in C. Examples of String char str[20] = {‘g’, ’e’, ‘e’, ‘k’, ‘s’, ‘f’, ‘o’, ‘r’, ‘g’, ’e’, ‘e’, ‘k’, ‘s’, ‘0’}; char str[20] = “geeksforgeeks”; Char s1[] = “geeksforgeeks”;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasics-250206051204-4b1e93db/75/C-Programming-Basics-of-c-history-of-c-13-2048.jpg)
![Special Symbols Special symbols are used in C having some special meaning and thus, cannot be used for some other purpose. Brackets[]: Opening and closing brackets are used as array element references. These indicate single and multidimensional subscripts. Parentheses(): These special symbols are used to indicate function calls and function parameters. Braces{}: These opening and ending curly braces mark the start and end of a block of code containing more than one executable statement. Comma (, ): It is used to separate more than one statement like for separating parameters in function calls. Colon(:): It is an operator that essentially invokes something called an initialization list. Semicolon(;): It is known as a statement terminator. It indicates the end of one logical entity. That’s why each individual statement must be ended with a semicolon. Asterisk (*): It is used to create a pointer variable and for the multiplication of variables. Assignment operator(=): It is used to assign values and for logical operation validation. Pre-processor (#): The preprocessor is a macro processor that is used automatically by the compiler to transform your program before actual compilation. Period (.): Used to access members of a structure or union. Tilde(~): Used as a destructor to free some space from memory.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasics-250206051204-4b1e93db/75/C-Programming-Basics-of-c-history-of-c-14-2048.jpg)