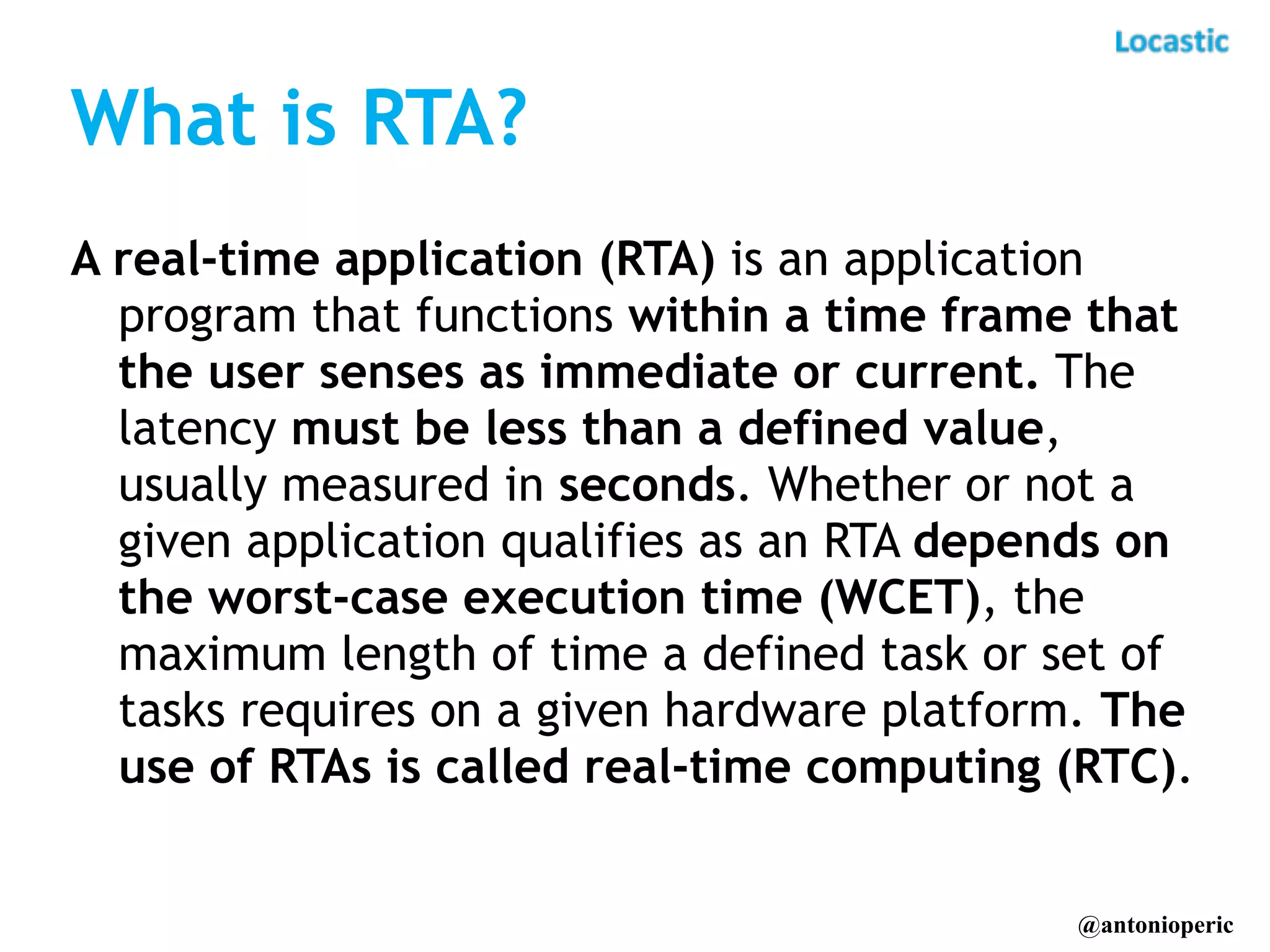
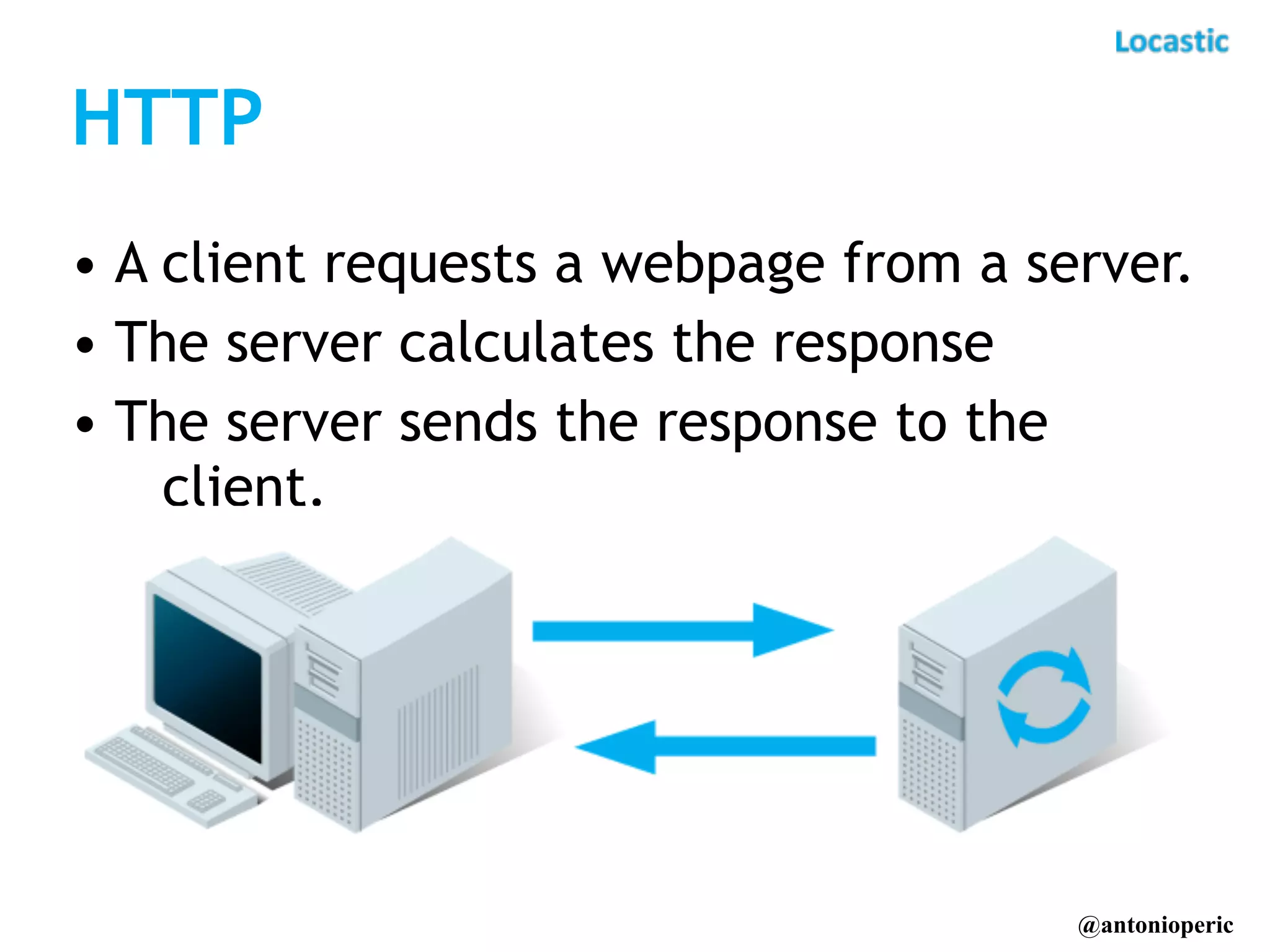
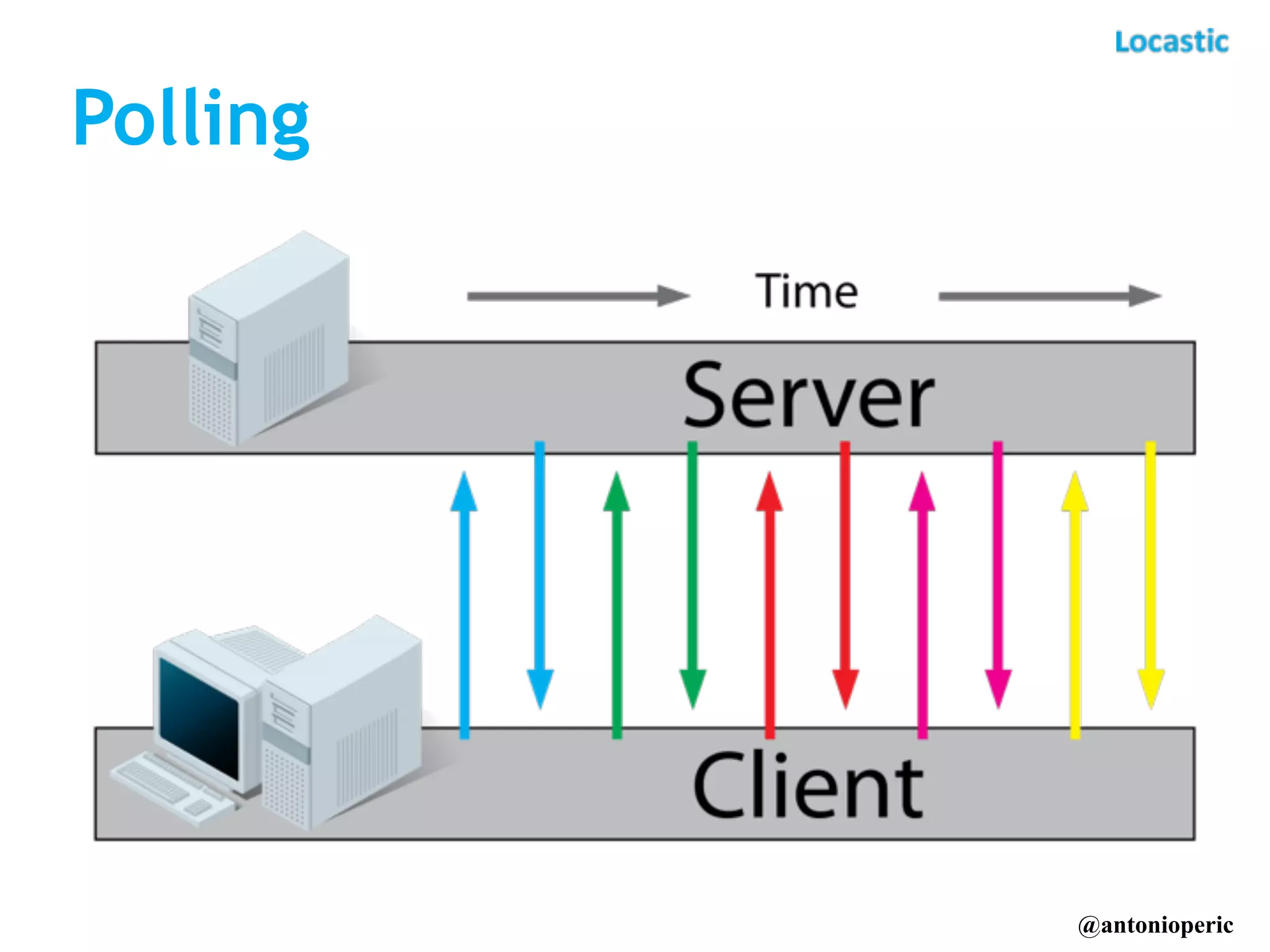
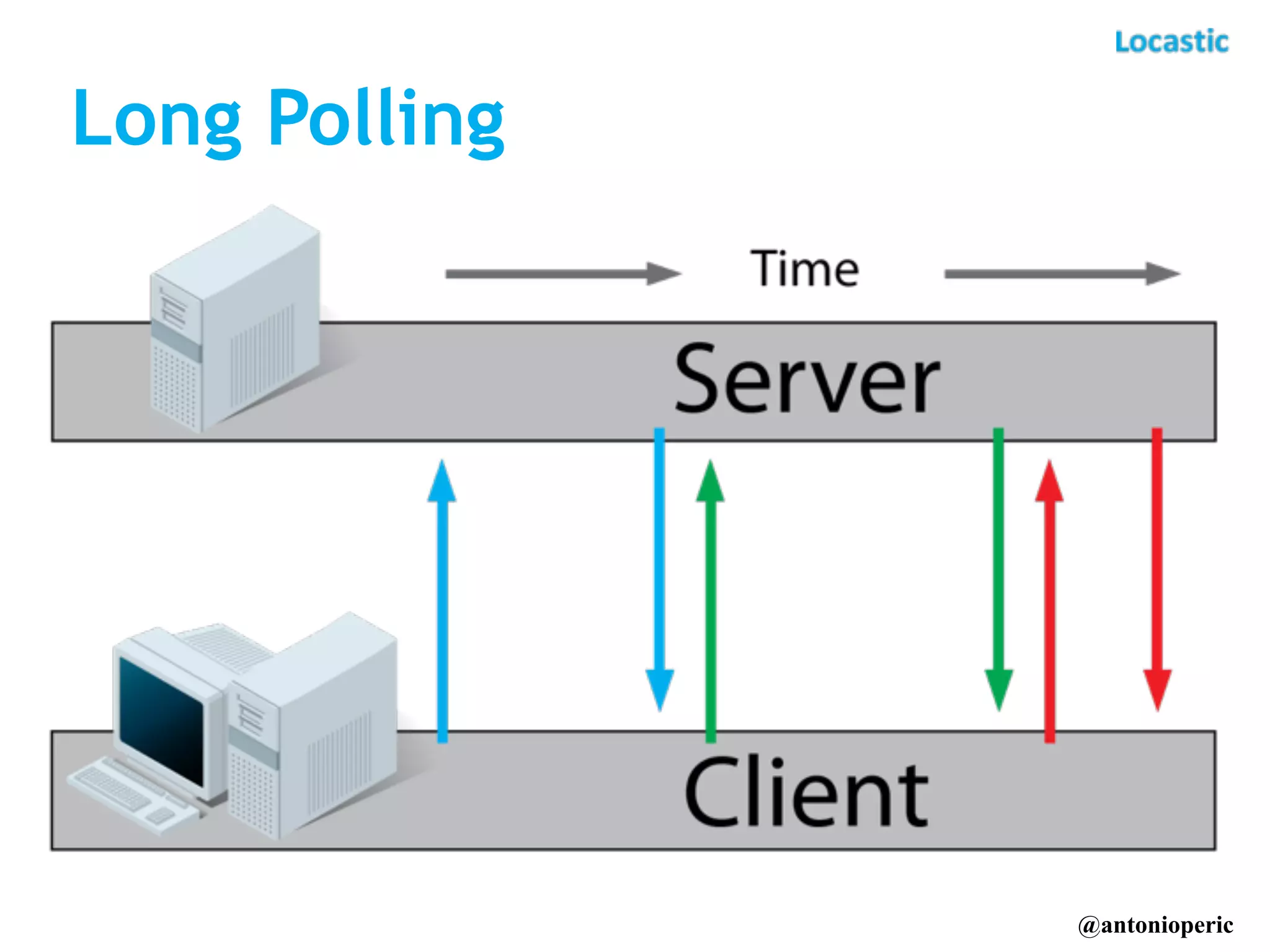
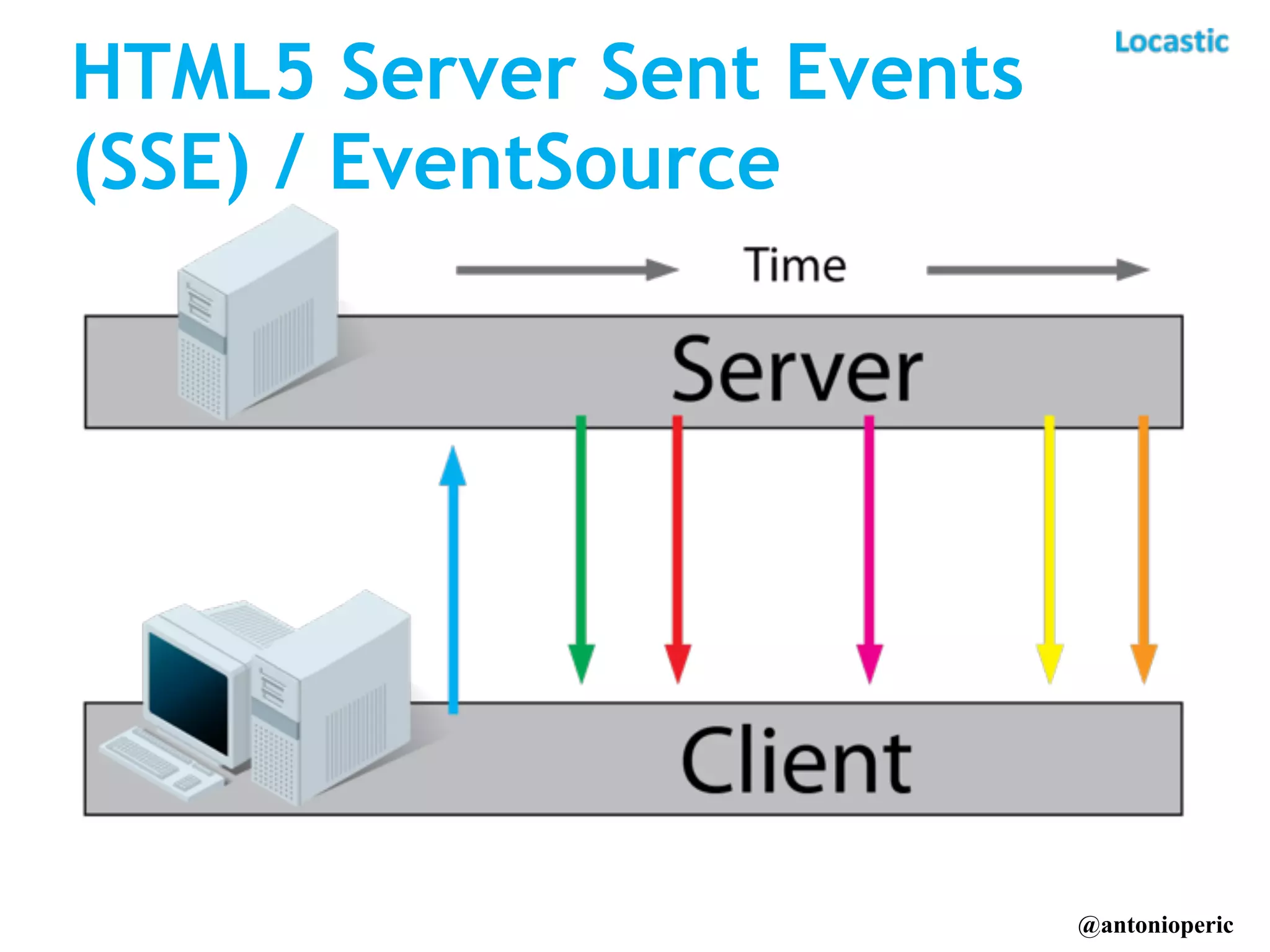
The document discusses building real-time applications with Symfony2. It begins by introducing the speaker and their company Locastic. It then defines what a real-time application is and provides examples of common use cases. The document goes on to explain various technologies that can be used to build real-time functionality, such as polling, long polling, server-sent events, websockets, and streaming. It also discusses different communication patterns and factors to consider when choosing a technology. Finally, it provides an example of a real-time dashboard that was built with Symfony2, AngularJS, and RabbitMQ and describes hosted solutions like Pusher that can be used.