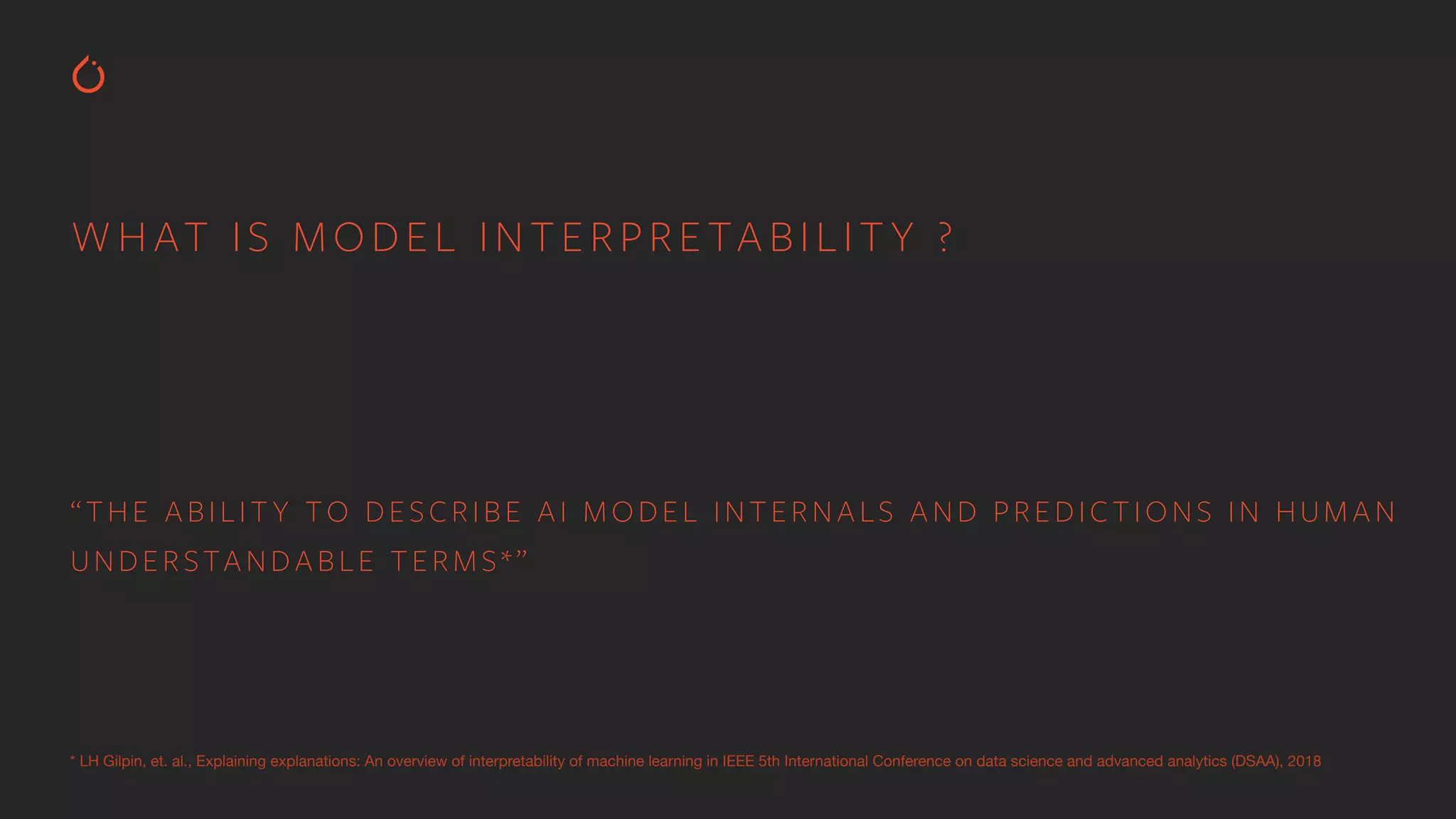
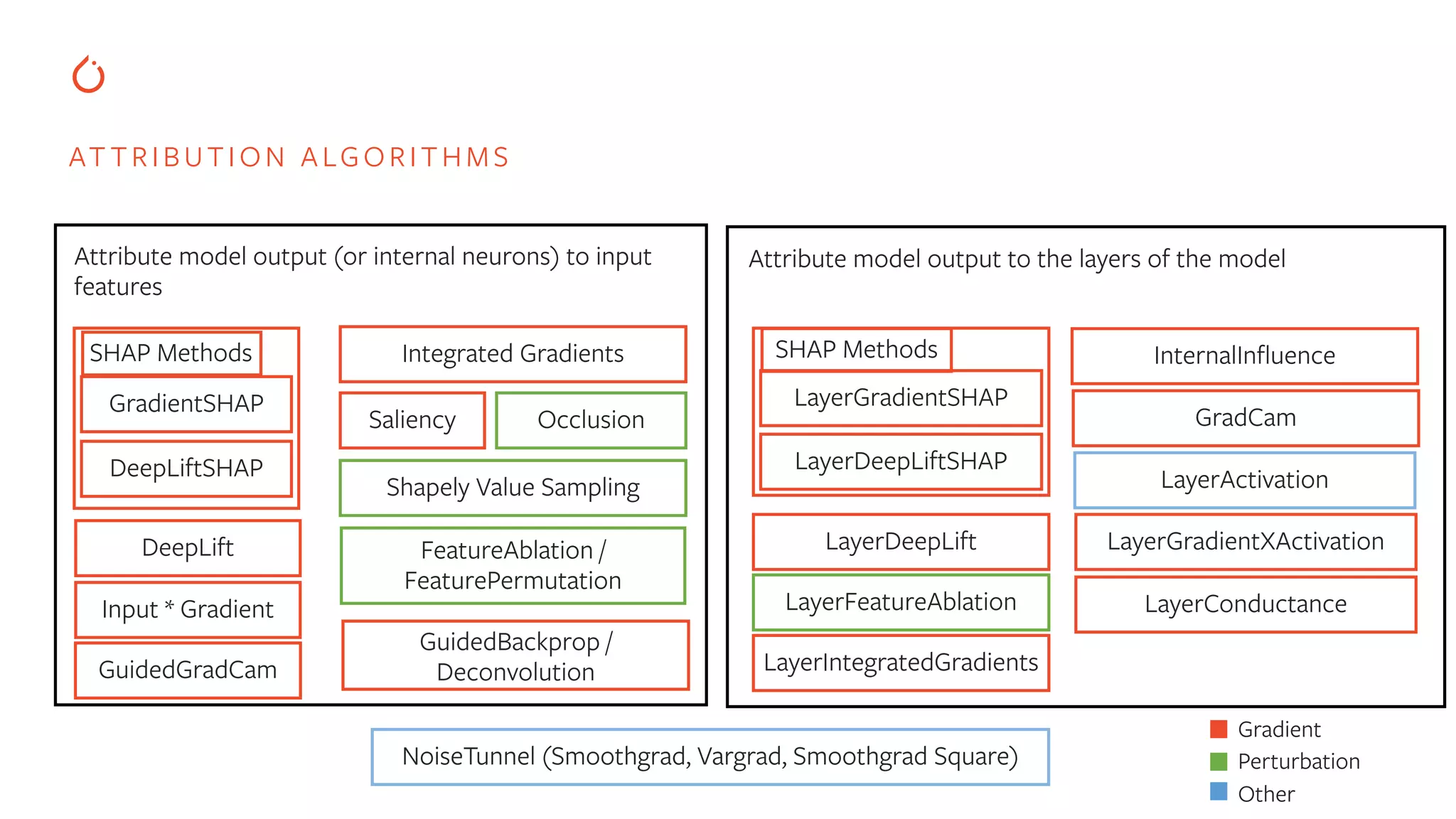
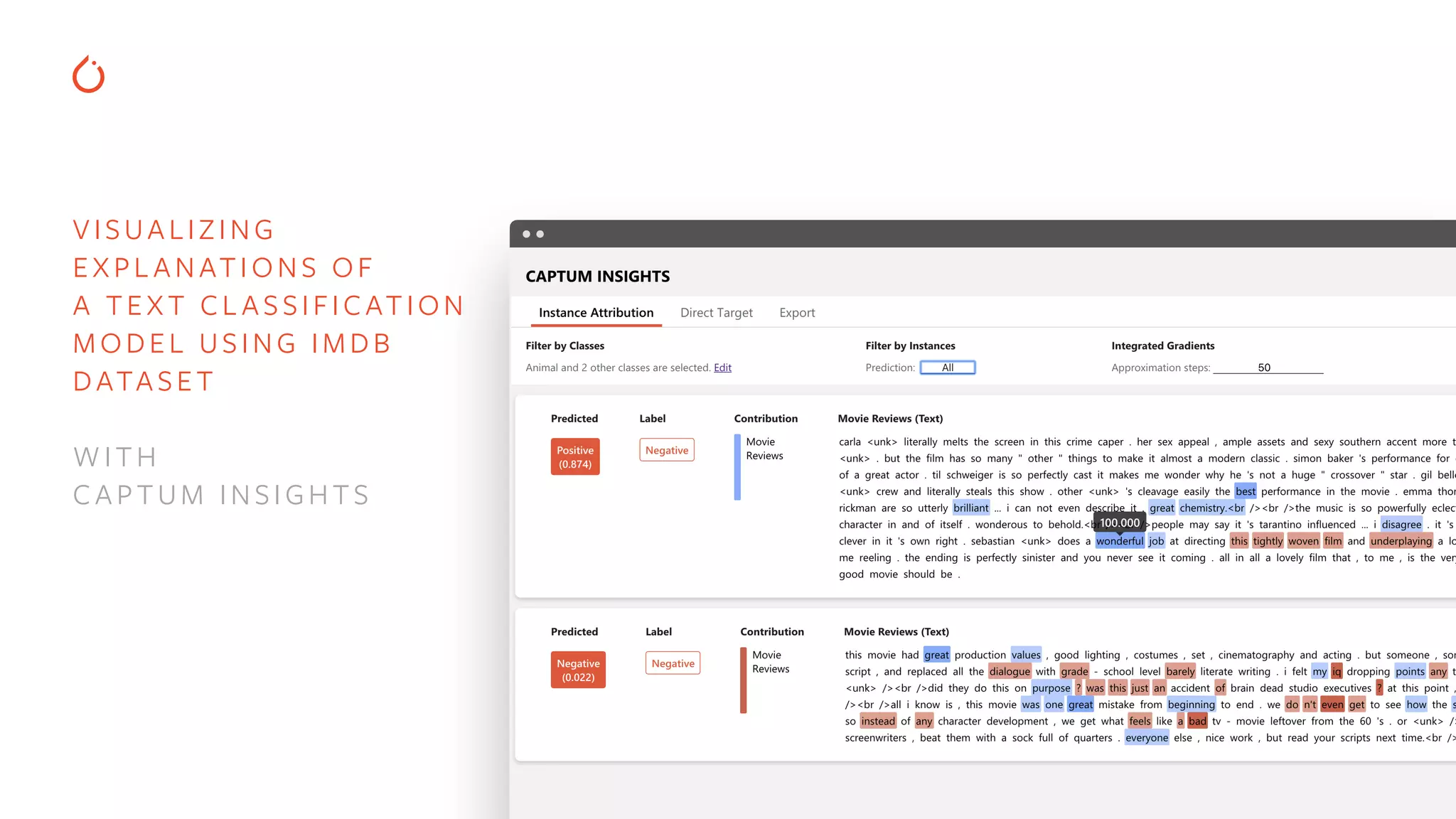
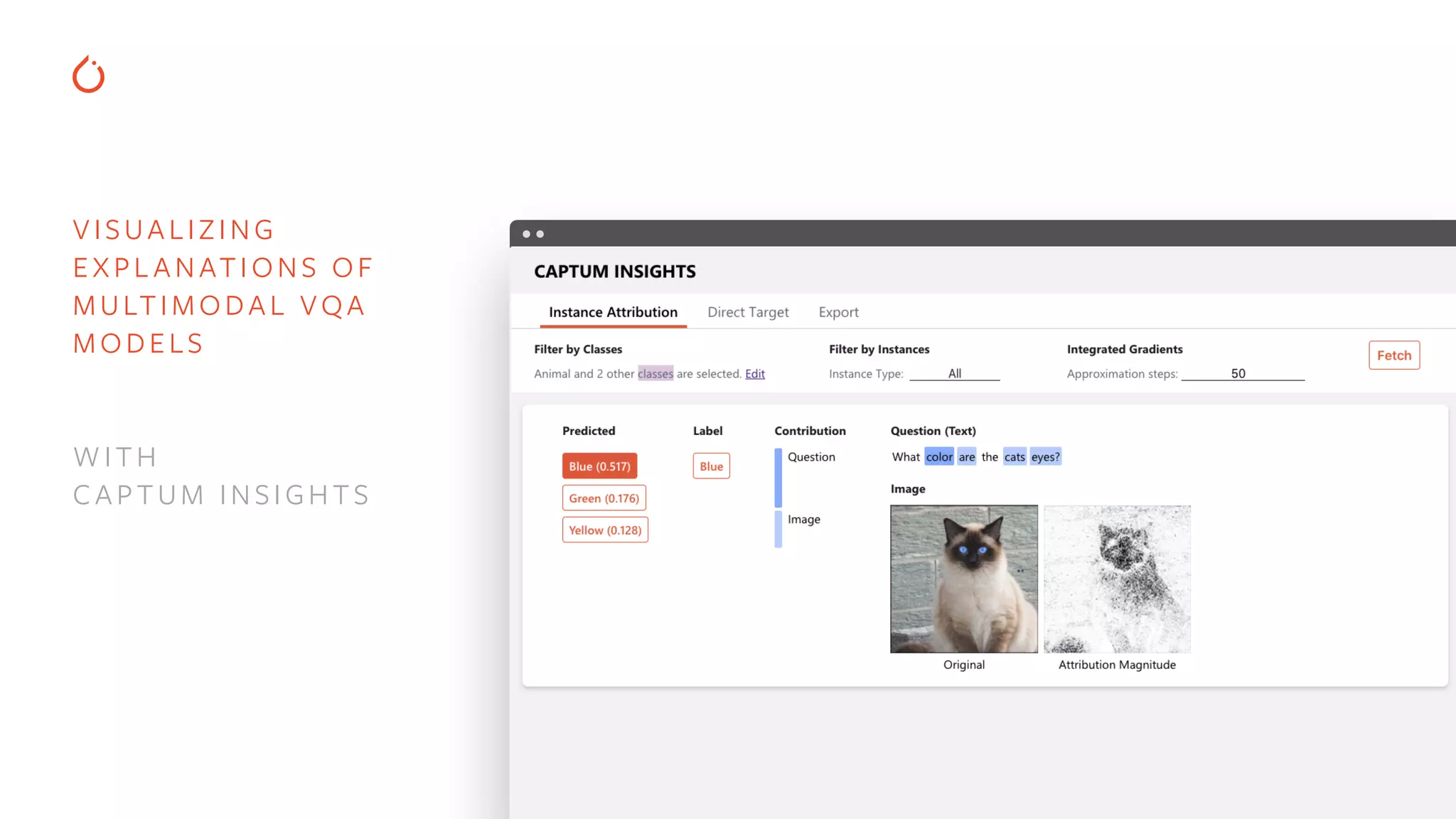
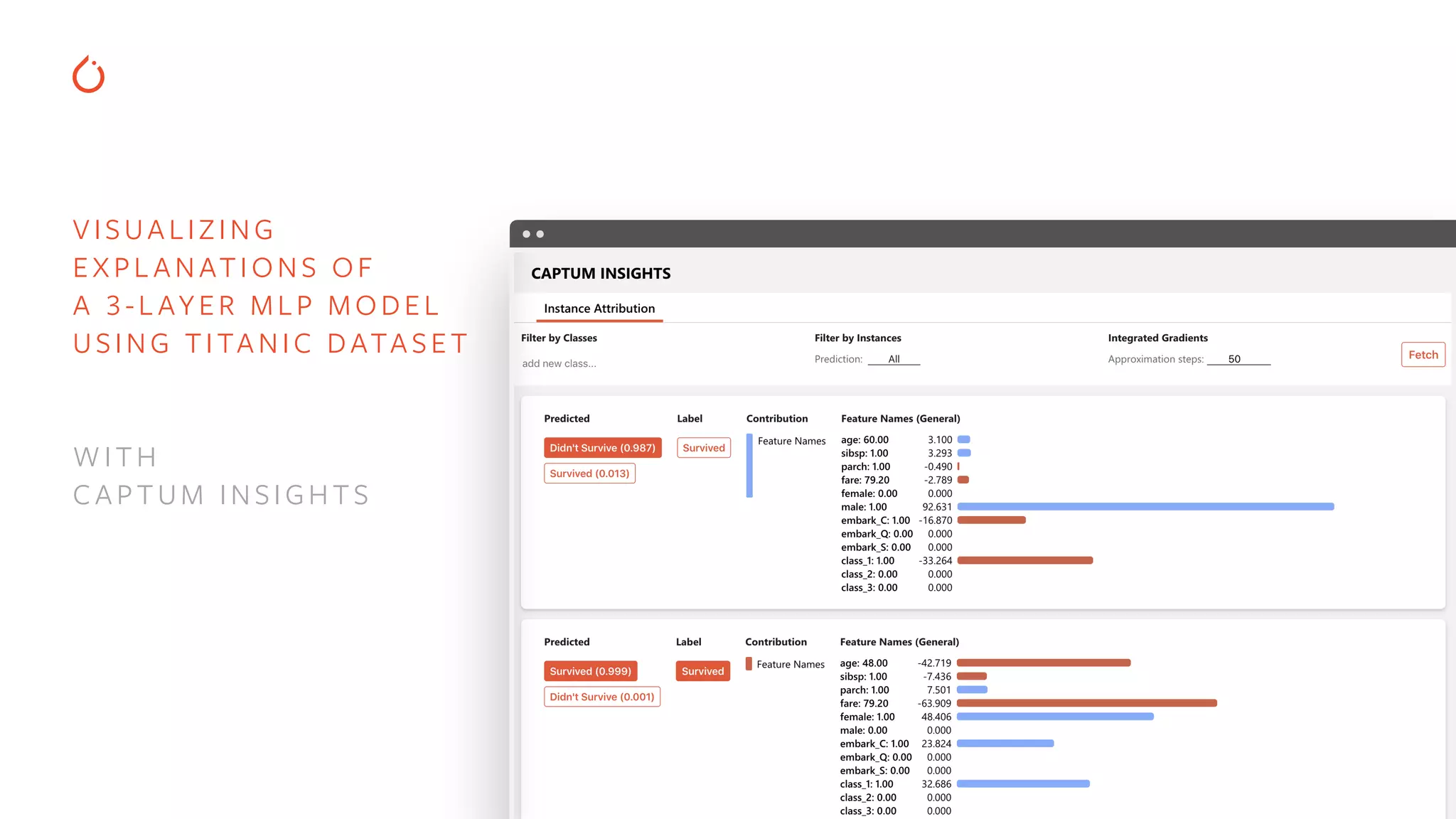
The document discusses building interpretable and secure AI systems using PyTorch, focusing on model interpretability, various attribution techniques, and privacy-preserving AI methods. It covers tools such as Captum for model explanation and Crypten for secure multi-party computation, emphasizing their applications in sensitive data scenarios. Additionally, references and resources for further learning in these areas are provided.




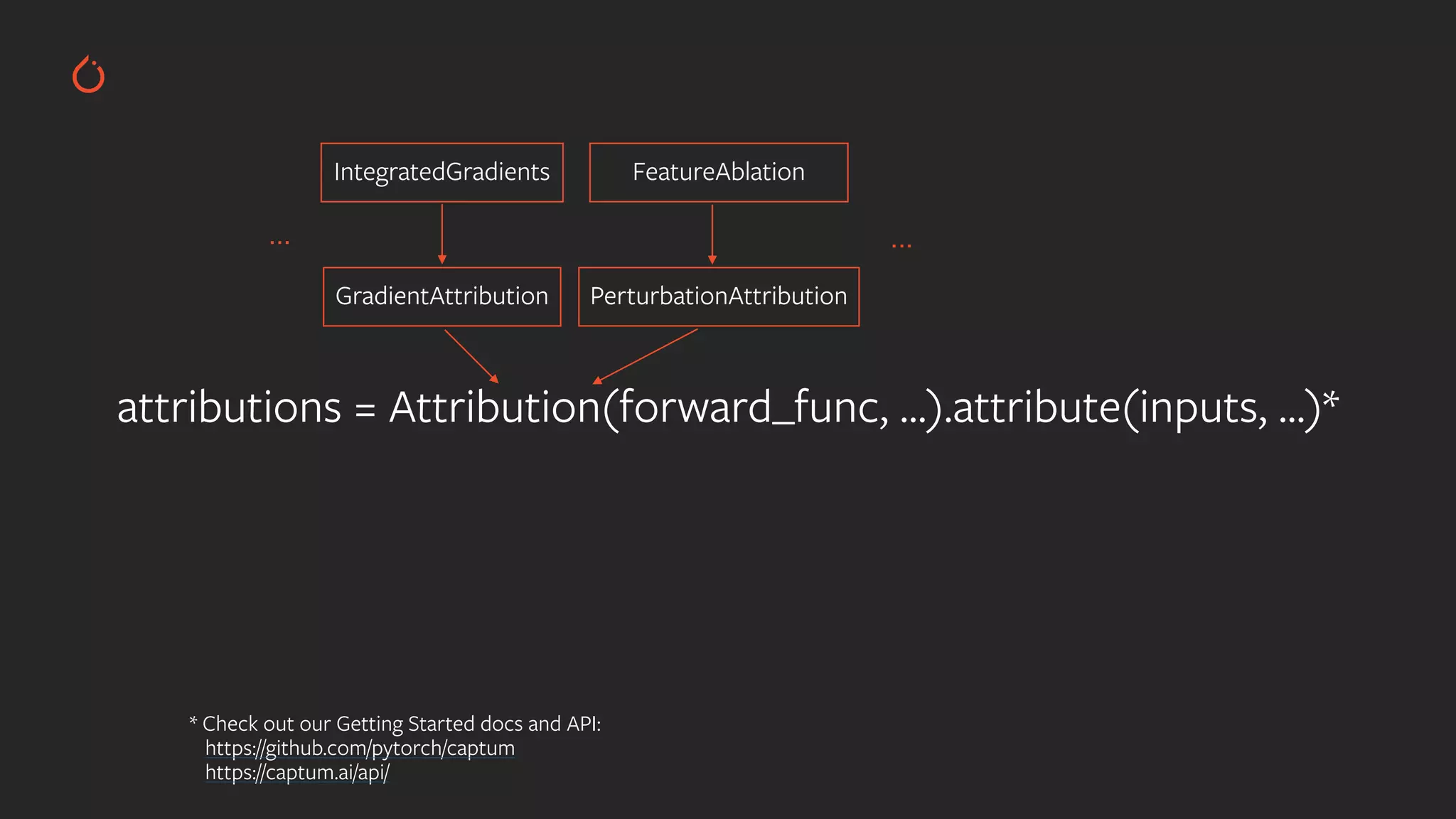

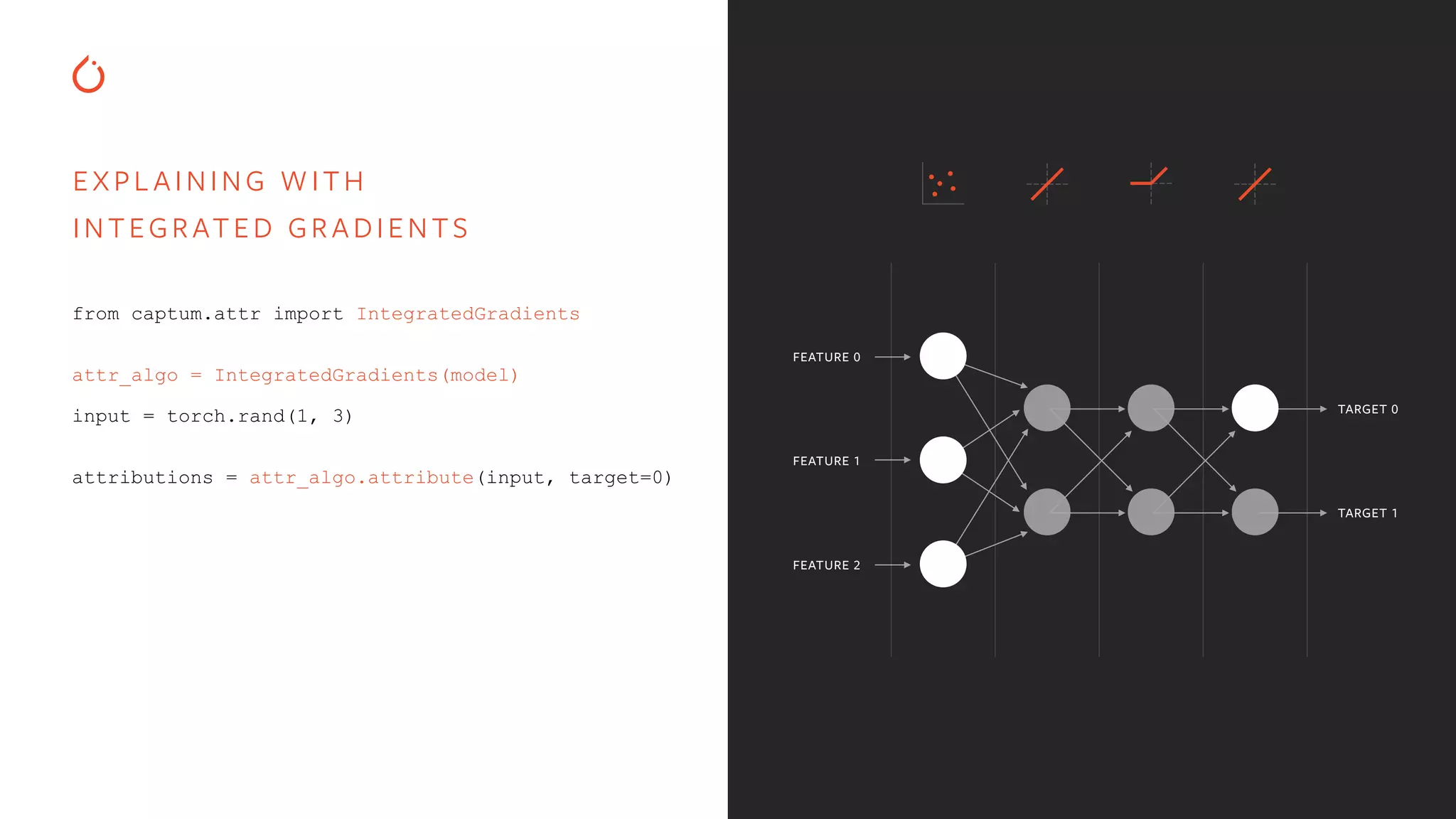
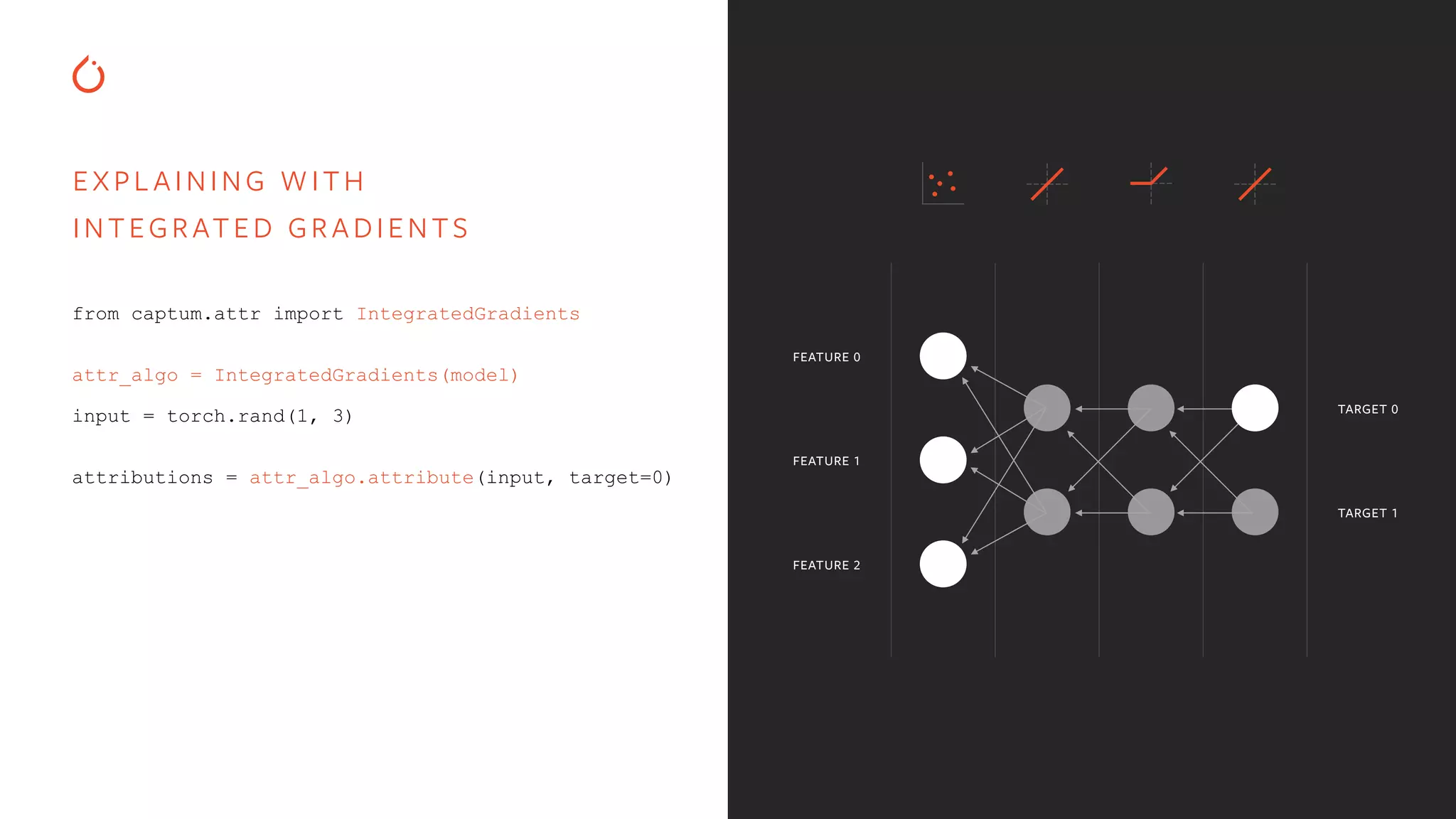
![EXPL AINING WITH INTEGRATED GRADIENTS from captum.attr import IntegratedGradients attr_algo = IntegratedGradients(model) input = torch.rand(1, 3) attributions = attr_algo.attribute(input, target=0) FEATURE 0 FEATURE 1 FEATURE 2 TARGET 0 TARGET 1 OUTPUT attributions: tensor([[-0.41, 0.54, 0.88]])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildinginterpretablesecureaiusingpytorch-200606110801/75/Building-Interpretable-Secure-AI-Systems-using-PyTorch-12-2048.jpg)
![EXPL AINING WITH INTEGRATED GRADIENTS from captum.attr import IntegratedGradients attr_algo = IntegratedGradients(model) input = torch.rand(1, 3) attributions, delta = attr_algo.attribute(input, target=0, return_convergence_delta=True) FEATURE 0 FEATURE 1 FEATURE 2 TARGET 0 TARGET 1 OUTPUT attributions: tensor([[-0.41, 0.54, 0.88]]) delta: 0.0190](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildinginterpretablesecureaiusingpytorch-200606110801/75/Building-Interpretable-Secure-AI-Systems-using-PyTorch-13-2048.jpg)
![EXPL AINING WITH INTEGRATED GRADIENTS from captum.attr import IntegratedGradients attr_algo = IntegratedGradients(model) input = torch.rand(1, 3) baseline = torch.rand(1, 3) attributions, delta = attr_algo.attribute(input, target=0, return_convergence_delta=True, n_steps=5000, baselines=baselines) FEATURE 0 FEATURE 1 FEATURE 2 TARGET 0 TARGET 1 OUTPUT attributions: tensor([[0.0, 0.88, -2.45]]) convergence delta: 1.5497e-06](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildinginterpretablesecureaiusingpytorch-200606110801/75/Building-Interpretable-Secure-AI-Systems-using-PyTorch-14-2048.jpg)


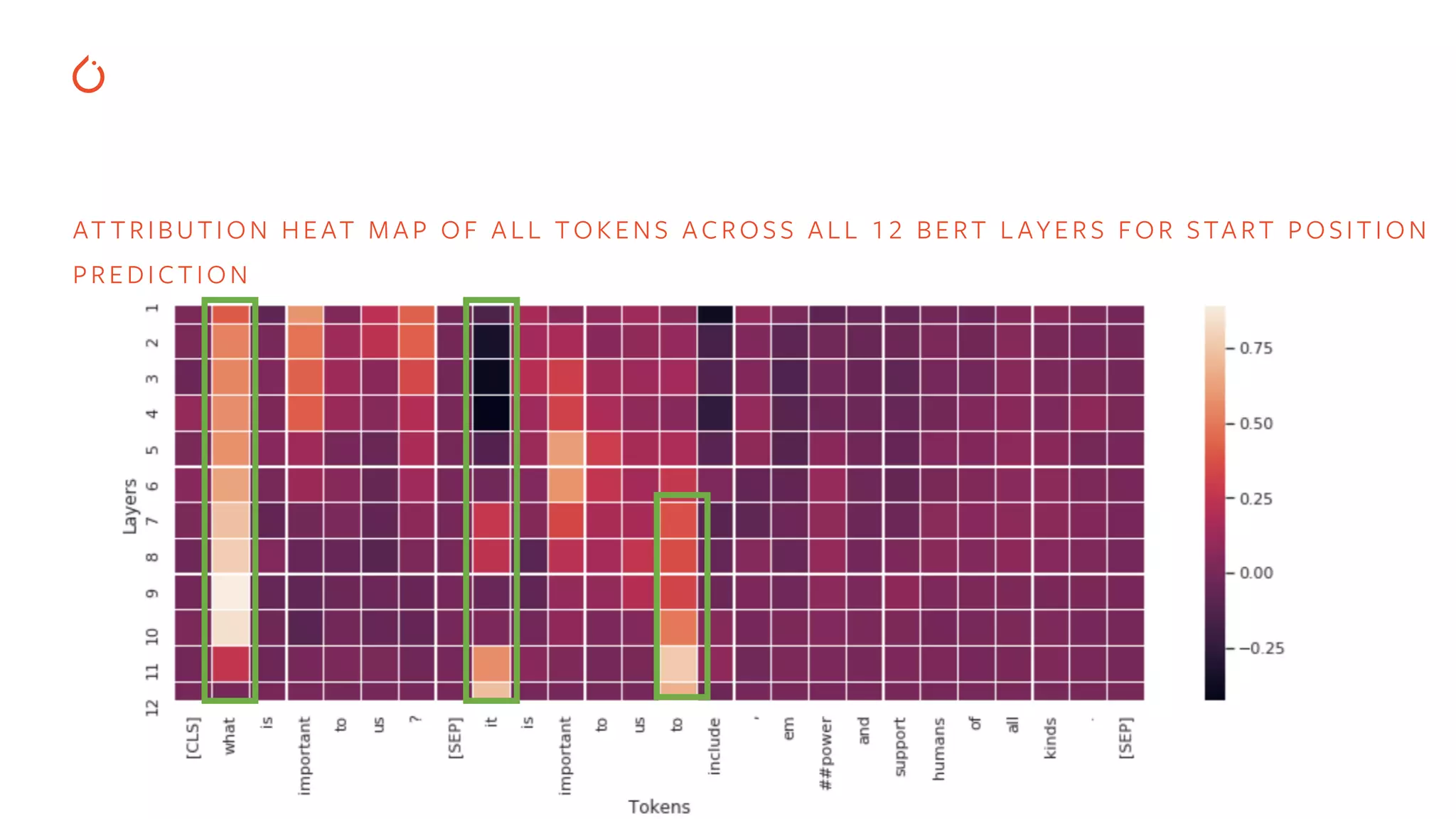
![EXPL AINING BERT MODELS FOR QUESTION ANSWERING text = 'It is important to us to include, empower and support humans of all kinds.' question = 'What is important to us?' [CLS] tokens what [SEP]to isimportant ?is us it important to us to include em, and support humans of all kinds .##power P(Start Position) = 0.72 P(End Position) = 0.73 [SEP]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildinginterpretablesecureaiusingpytorch-200606110801/75/Building-Interpretable-Secure-AI-Systems-using-PyTorch-21-2048.jpg)
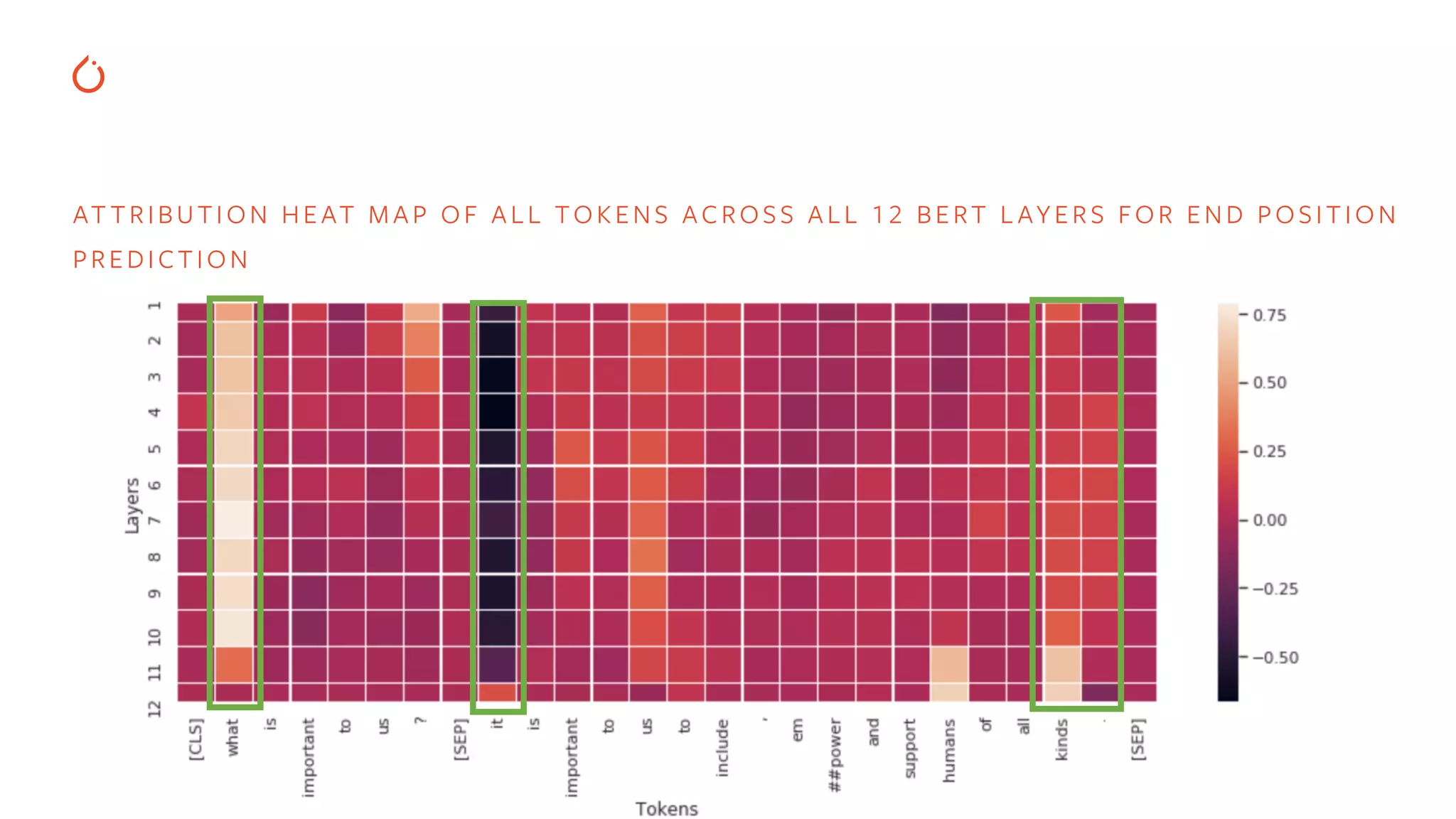
![# explaining layers for i in range(model.config.num_hidden_layers): lc = LayerConductance(squad_pos_forward_func, model.bert.encoder.layer[i]) layer_attributions_start = lc.attribute( input_embed, baselines=ref_emb, ..., 0)) layer_attributions_end = lc.attribute( input_embed, baselines=ref_emb, ..., 1)) EXPL AINING BERT MODELS FOR QUESTION ANSWERING](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildinginterpretablesecureaiusingpytorch-200606110801/75/Building-Interpretable-Secure-AI-Systems-using-PyTorch-22-2048.jpg)









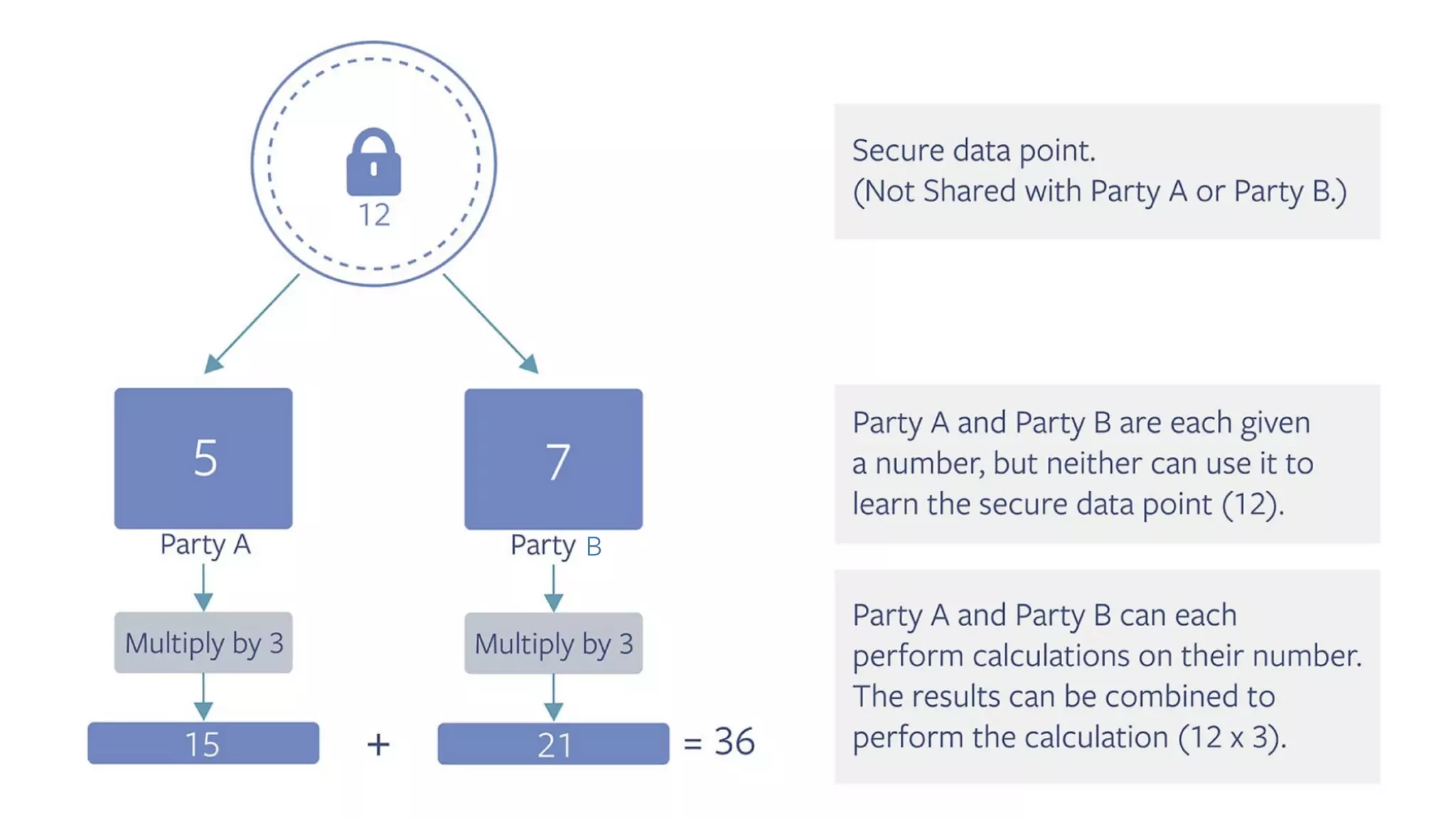
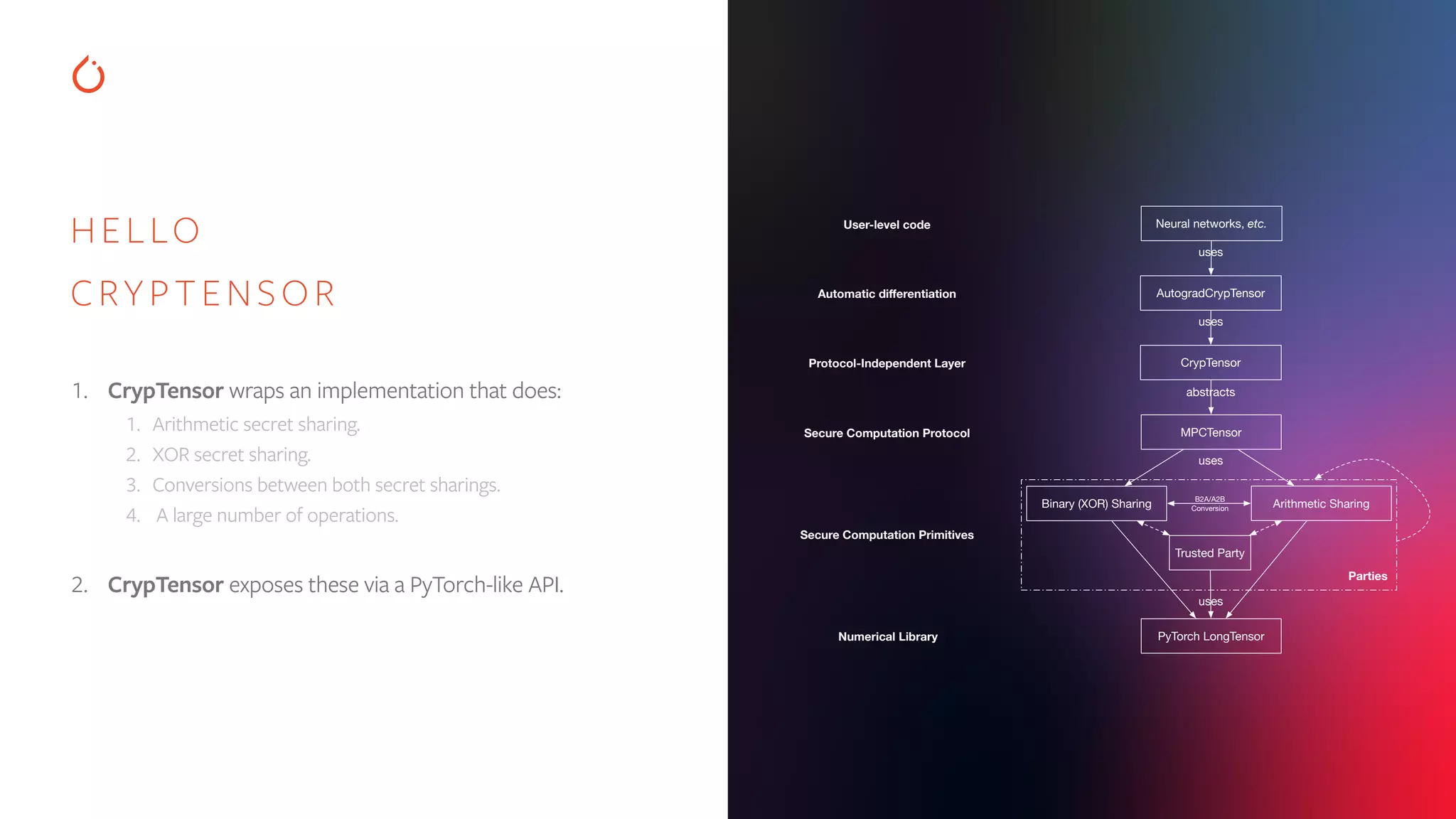
![CRYPTEN import crypten import torch crypten.init() # sets up communication x = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 3.0]) x_enc = crypten.cryptensor(x) # encrypts tensor x_dec = x_enc.get_plain_text() # decrypts tensor assert torch.all_close(x_dec, x) # this passes! y_enc = crypten.cryptensor([2.0, 3.0, 4.0]) xy_enc = x_enc + y_enc # adds encrypted tensors xy_dec = xy_enc.get_plain_text() assert torch.all_close(xy_dec, x + y) # this passes! z = torch.tensor([4.0, 5.0, 6.0]) xz_enc = x_enc + z # adds FloatTensor to CrypTensor xz_dec = xz_enc.get_plain_text() assert torch.all_close(xz_dec, x + z) # this passes! K E Y F E AT U R E S : • Tensors and CrypTensors coexist and can be mixed and matched • Uses standard eager execution — No compilers! Easy debugging and learning • Support for Secure multi-party computation (MPC) A platform for research in machine learning using secure-computation techniques](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildinginterpretablesecureaiusingpytorch-200606110801/75/Building-Interpretable-Secure-AI-Systems-using-PyTorch-35-2048.jpg)

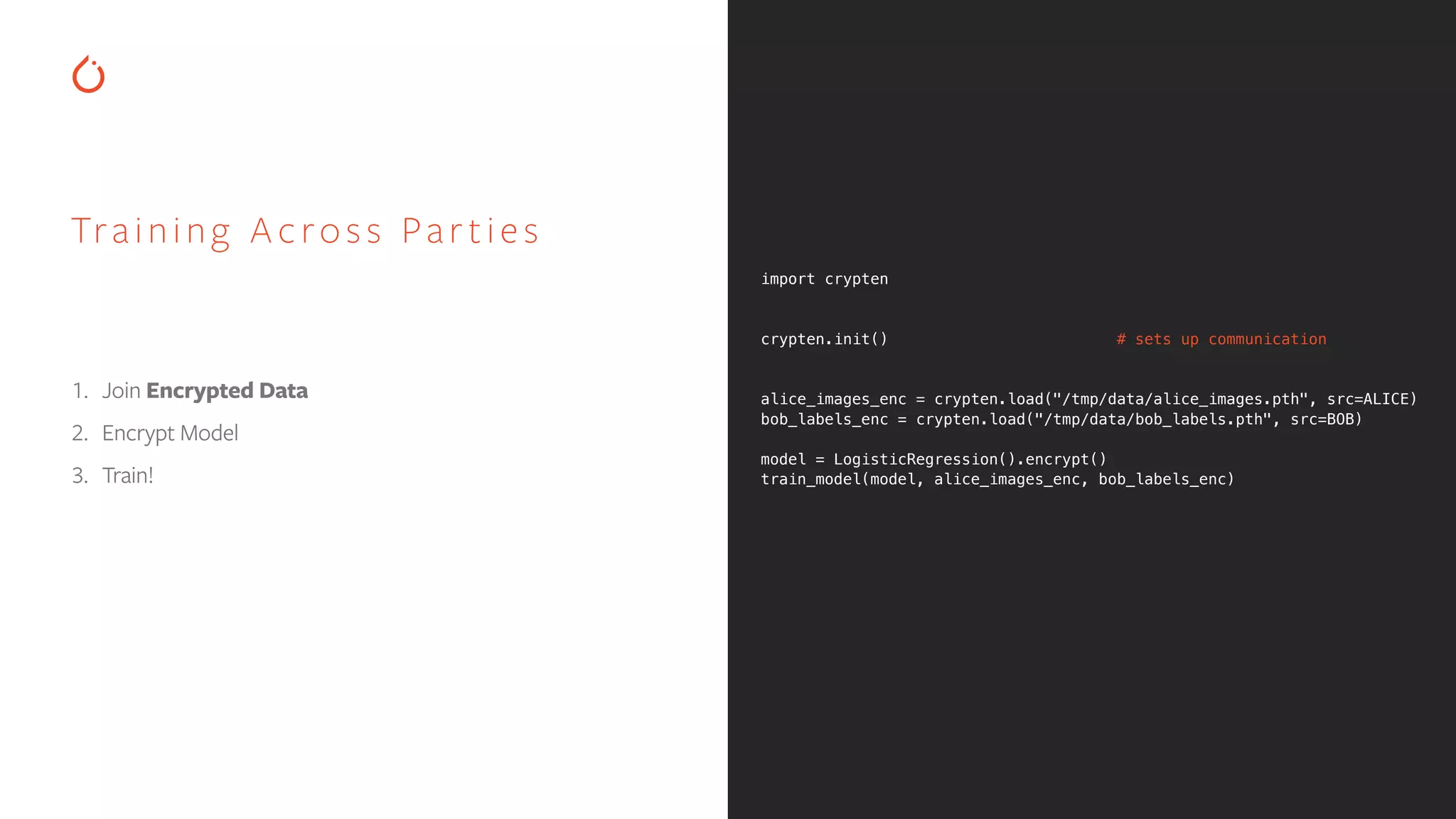
![1. Create a PyTorch or ONNX model. 2. Import model into CrypTen. 3. All computations are now encrypted. PY TORCH / ONNX INTEGRATION import torchvision.datasets as datasets import torchvision.models as models # download and set up ImageNet dataset: transform = transforms.ToTensor() dataset = datasets.ImageNet( imagenet_folder, transform=transform, ) # download pre-trained ResNet-18 model and encrypt it: model = models.resnet18(pretrained=True) encrypted_model = crypten.nn.from_pytorch( model, dataset[0], ) # do inference on encrypted images with encrypted model: encrypted_image = crypten.cryptensor(dataset[1]) encrypted_output = encrypted_model(encrypted_image) output = encrypted_output.get_plain_text() # this works](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildinginterpretablesecureaiusingpytorch-200606110801/75/Building-Interpretable-Secure-AI-Systems-using-PyTorch-40-2048.jpg)