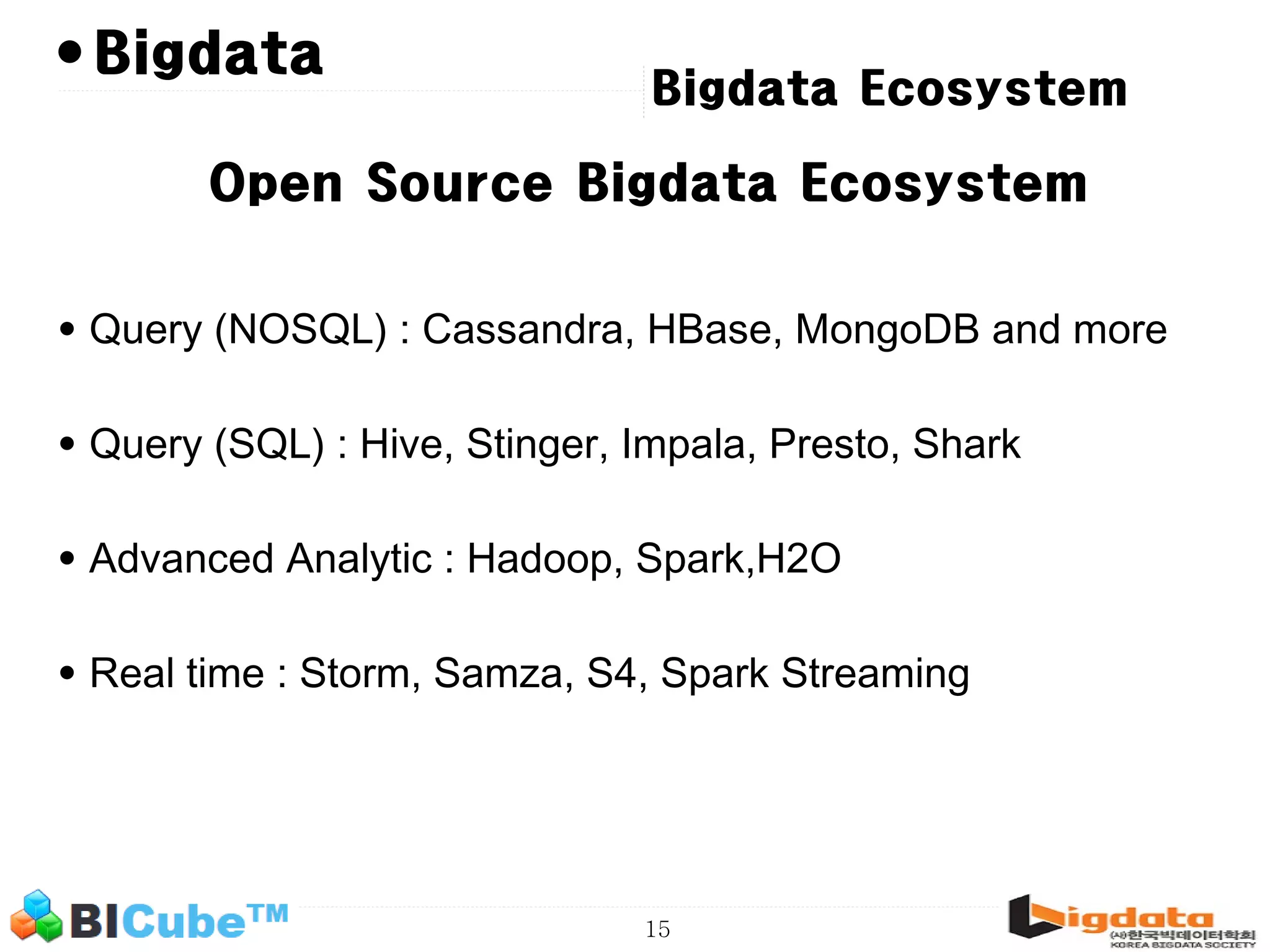
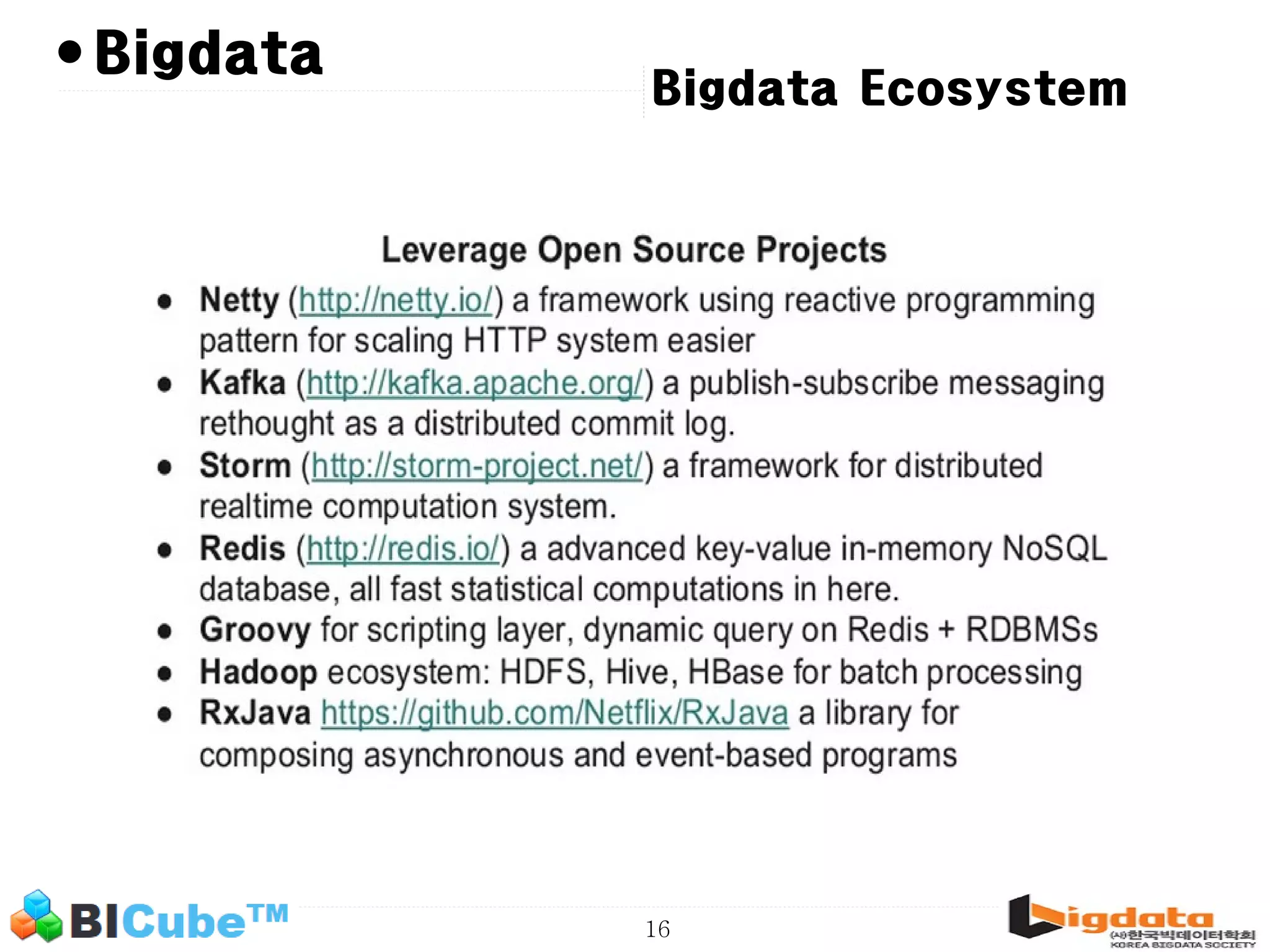
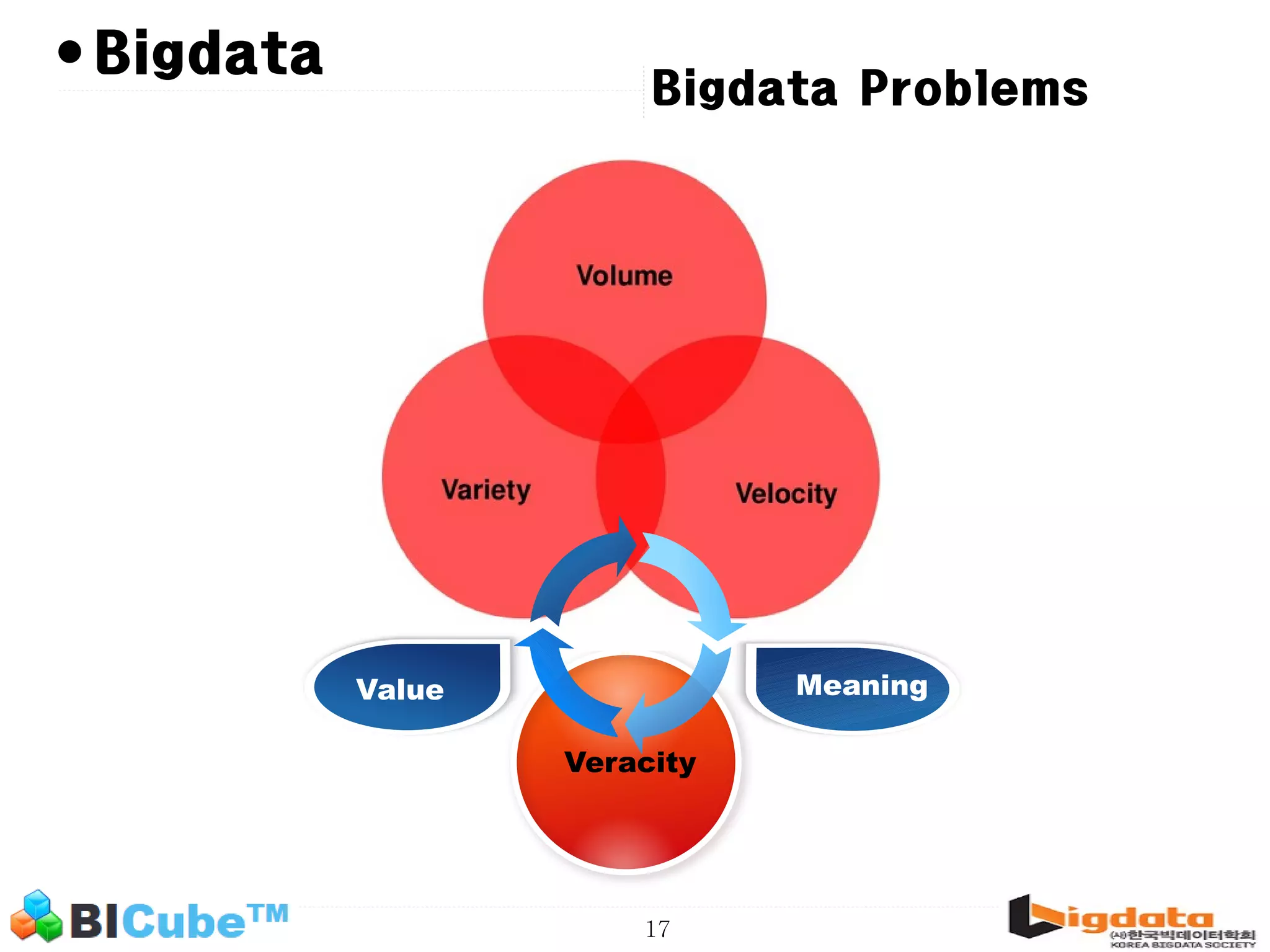
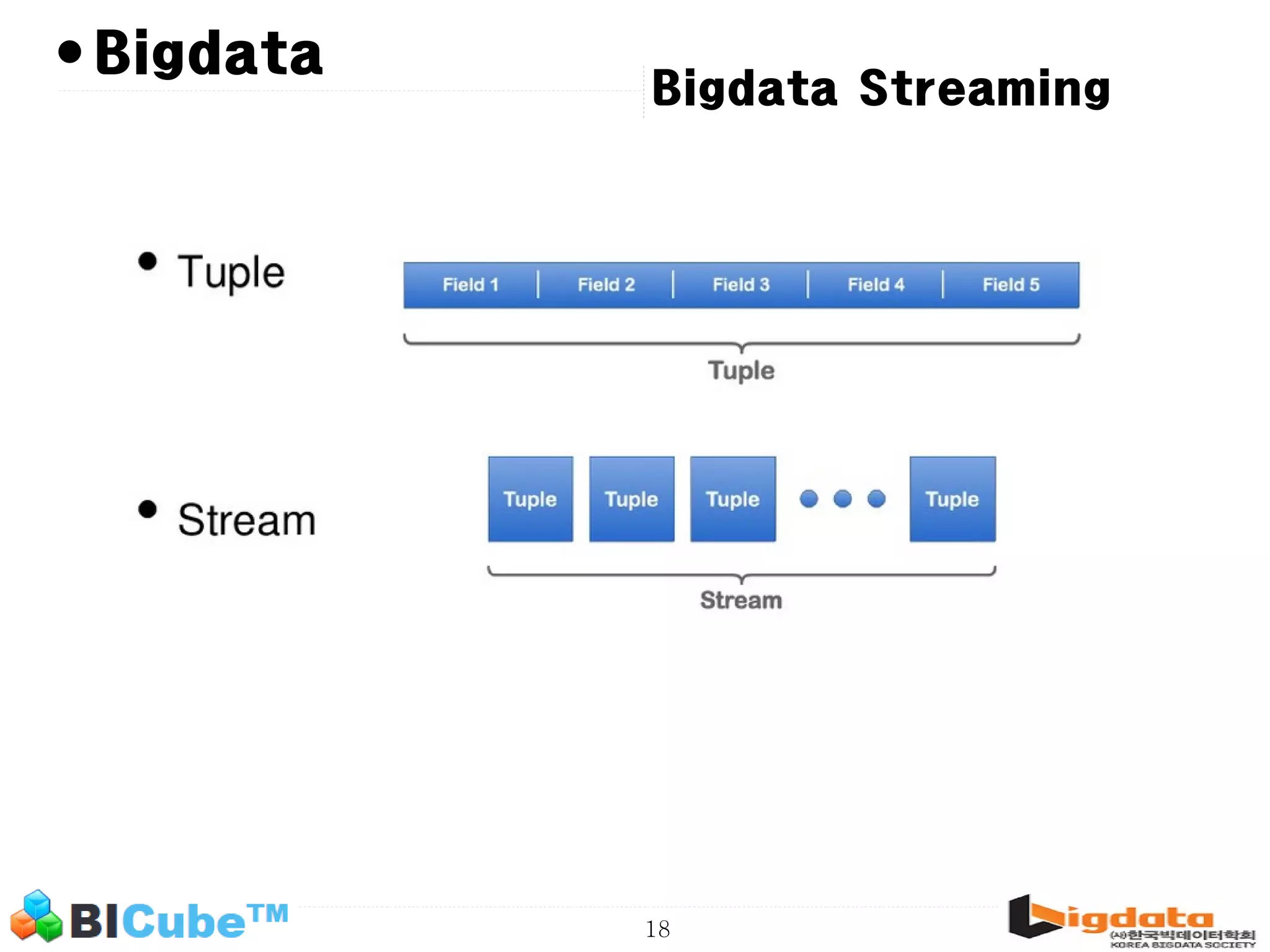
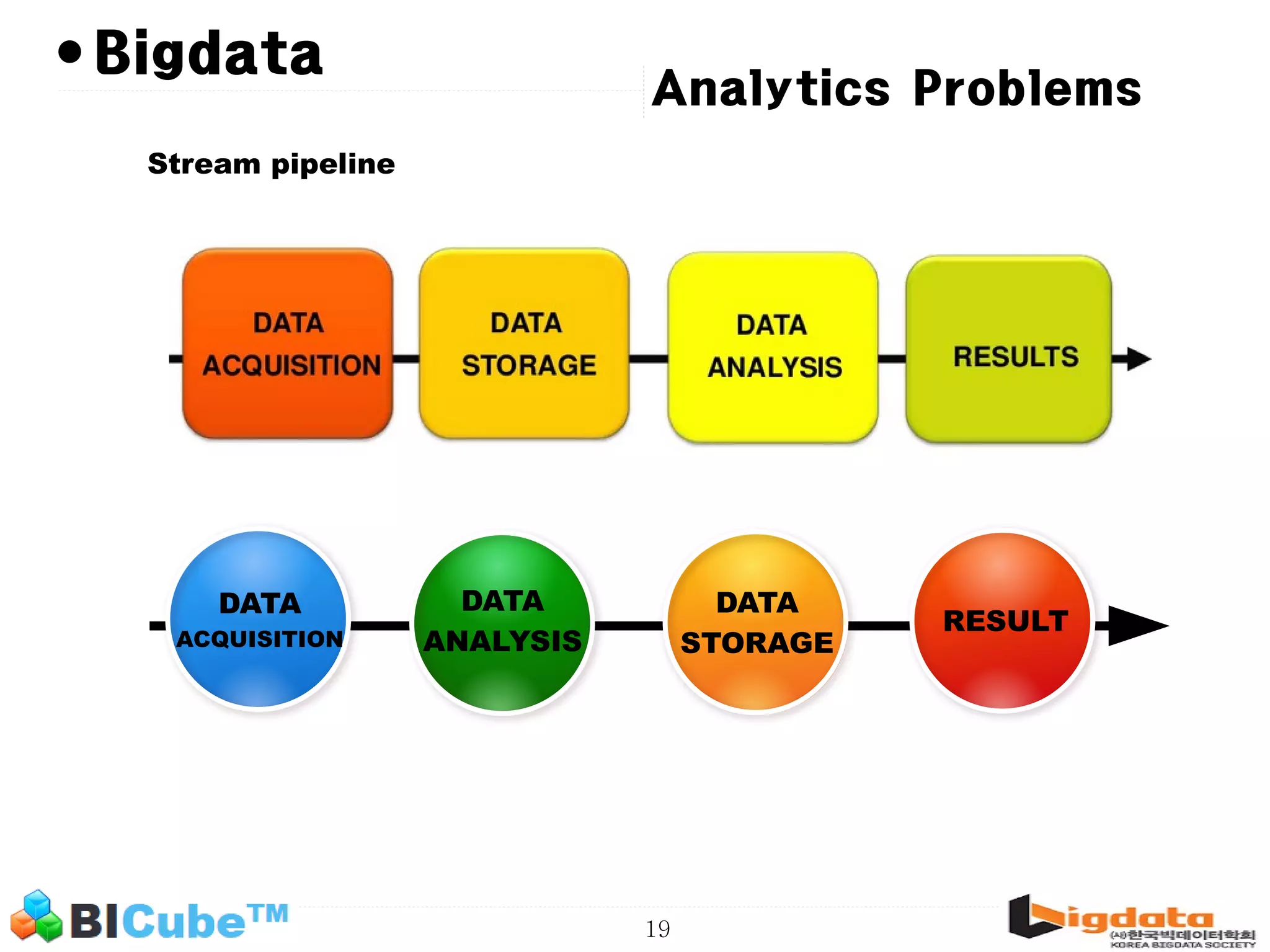
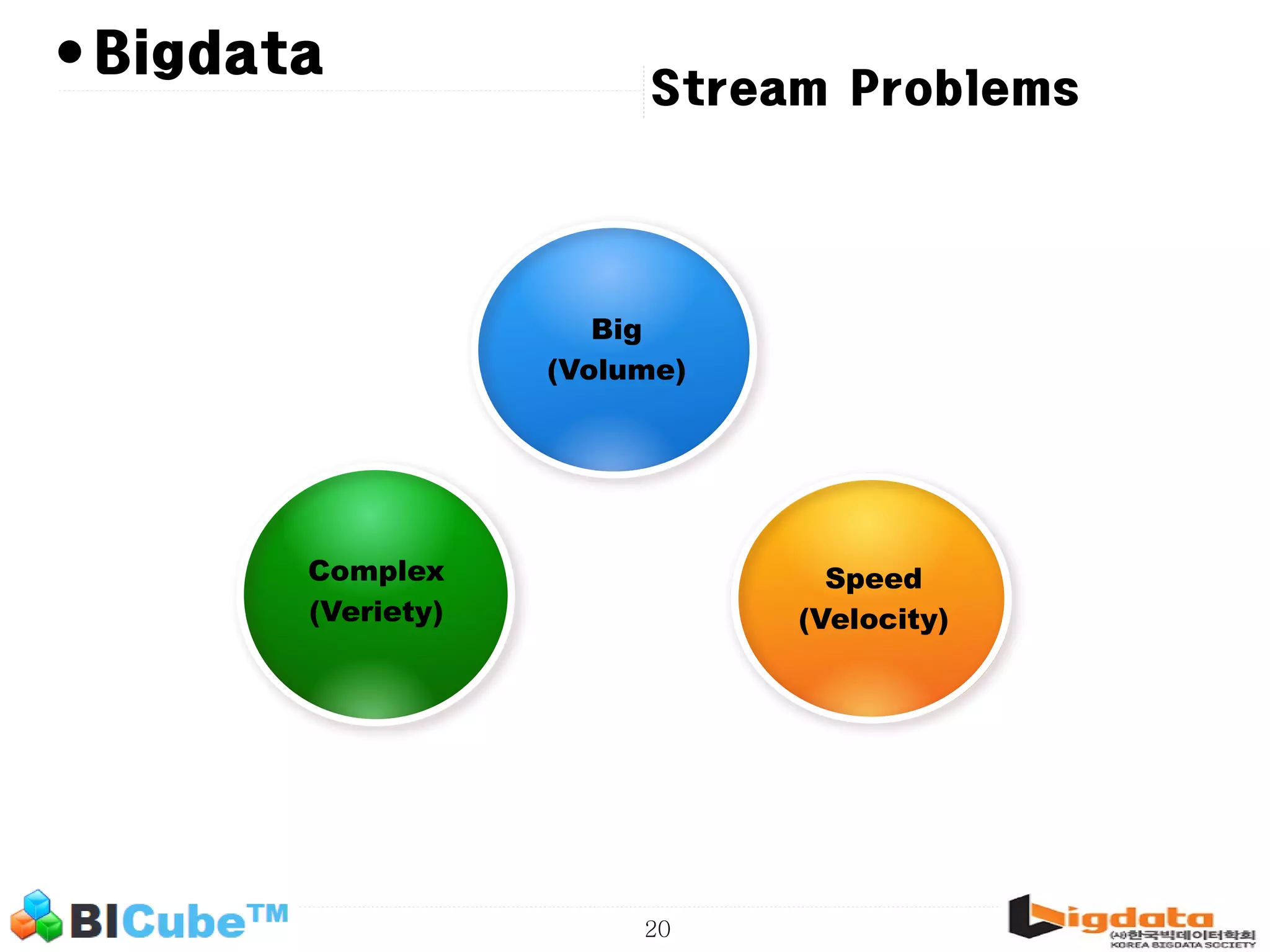
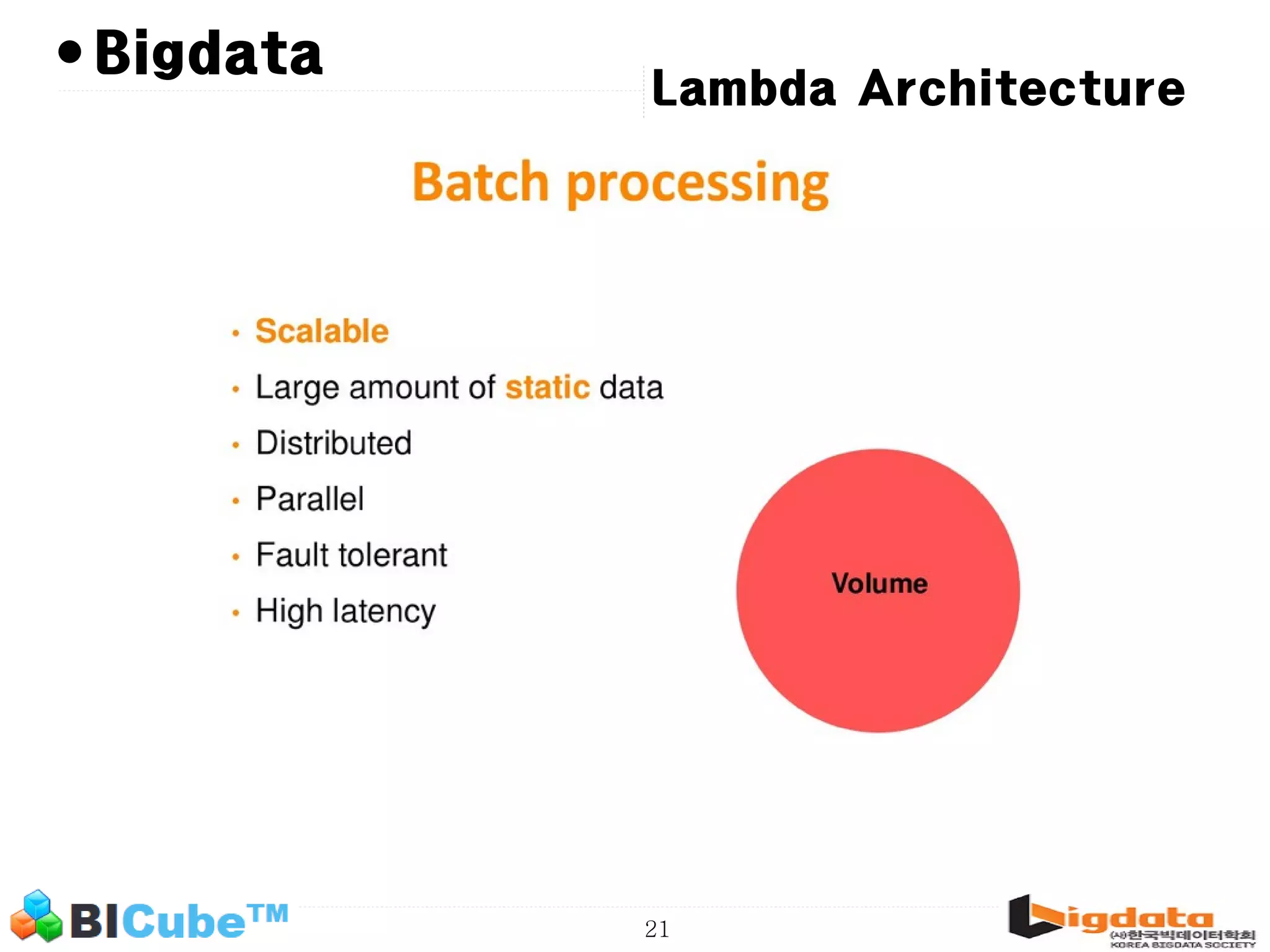
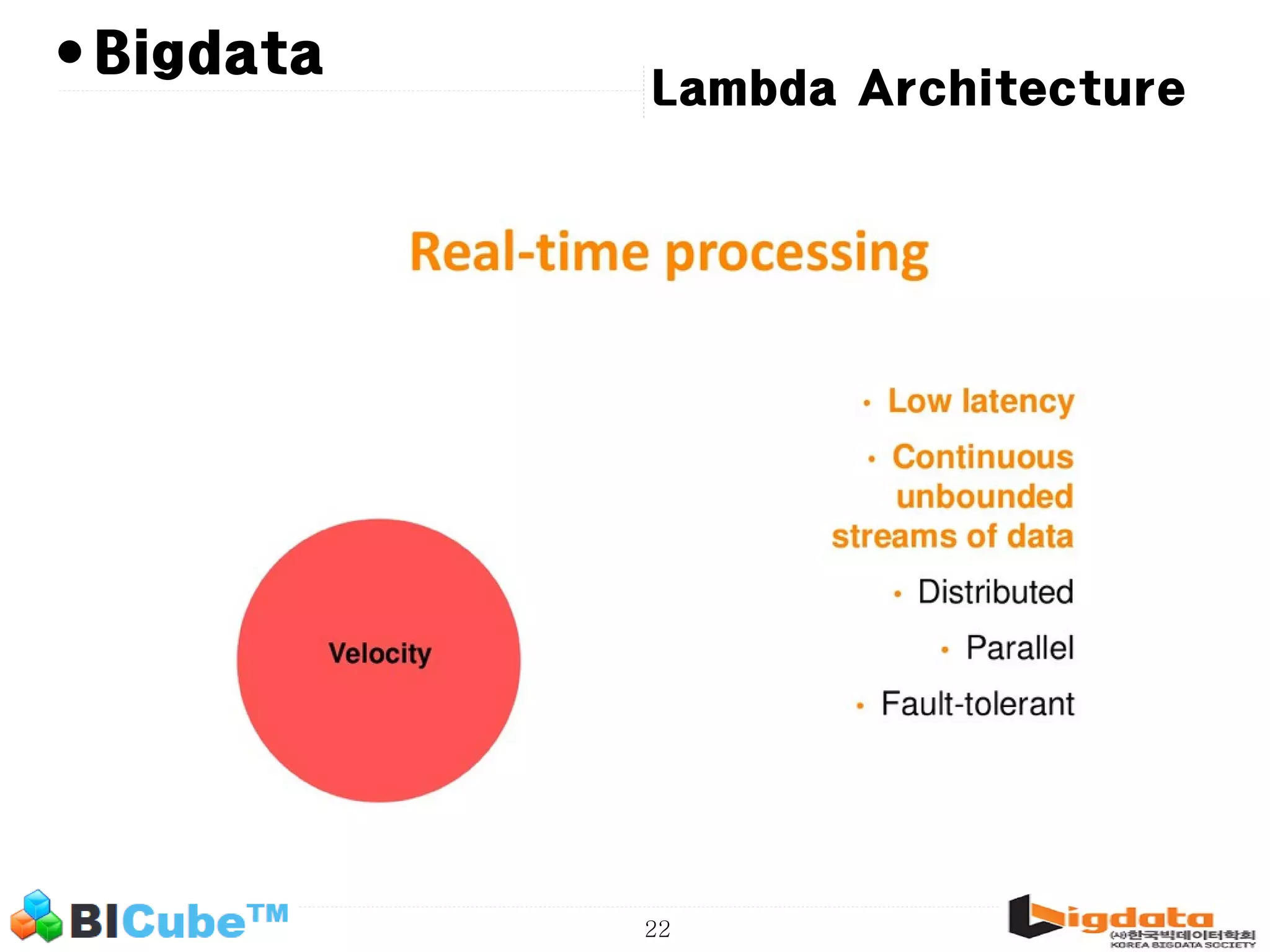
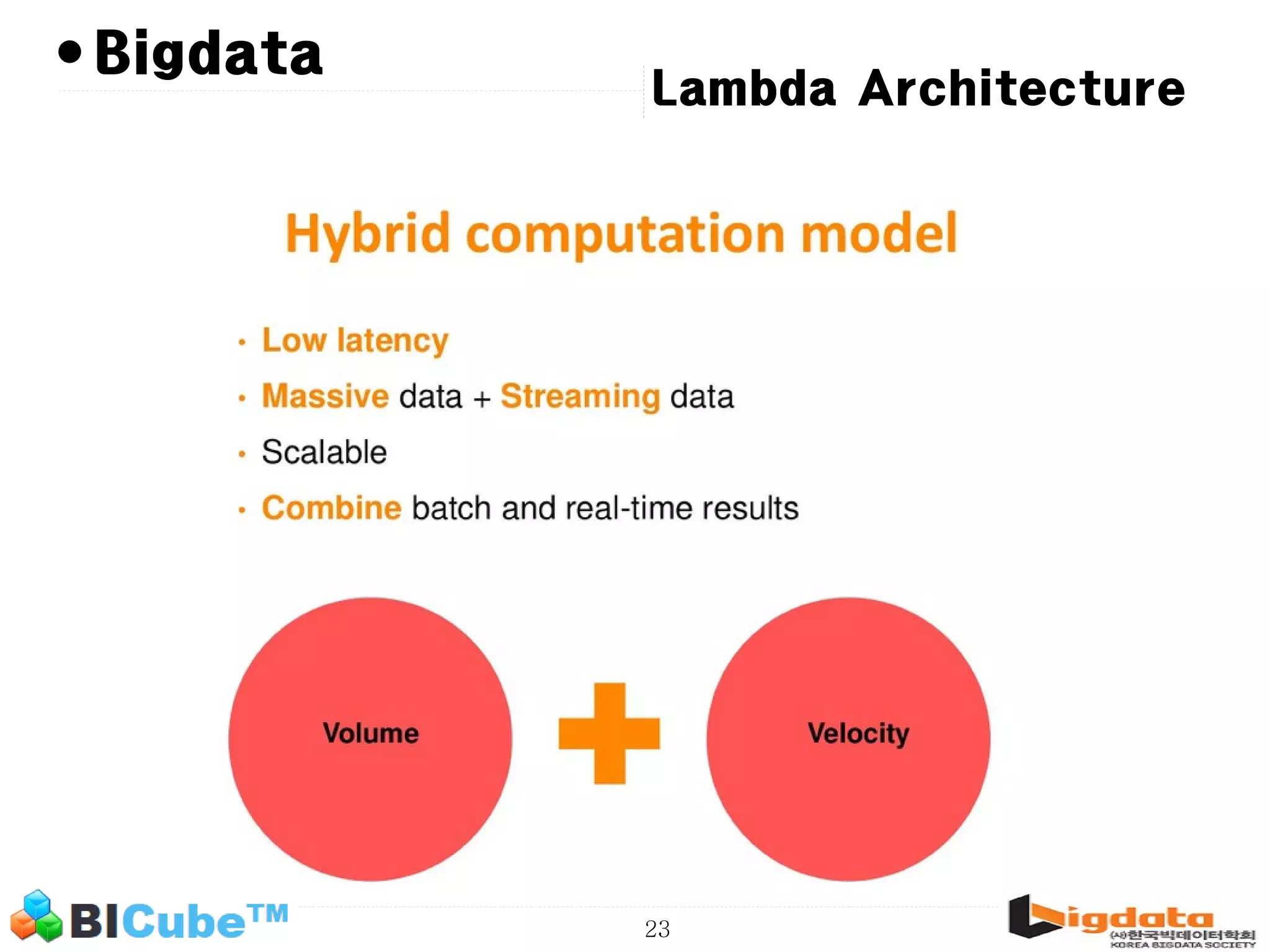
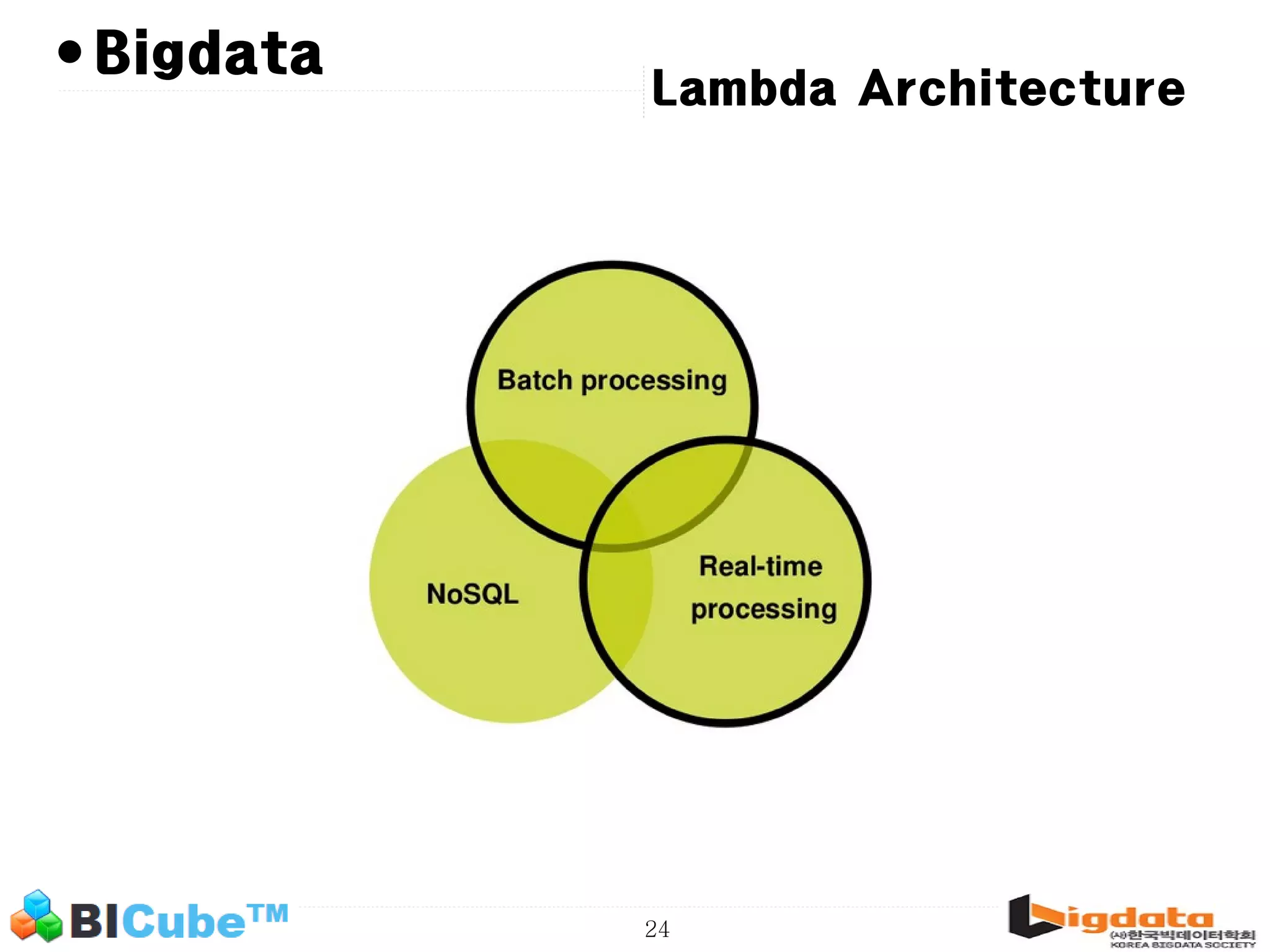
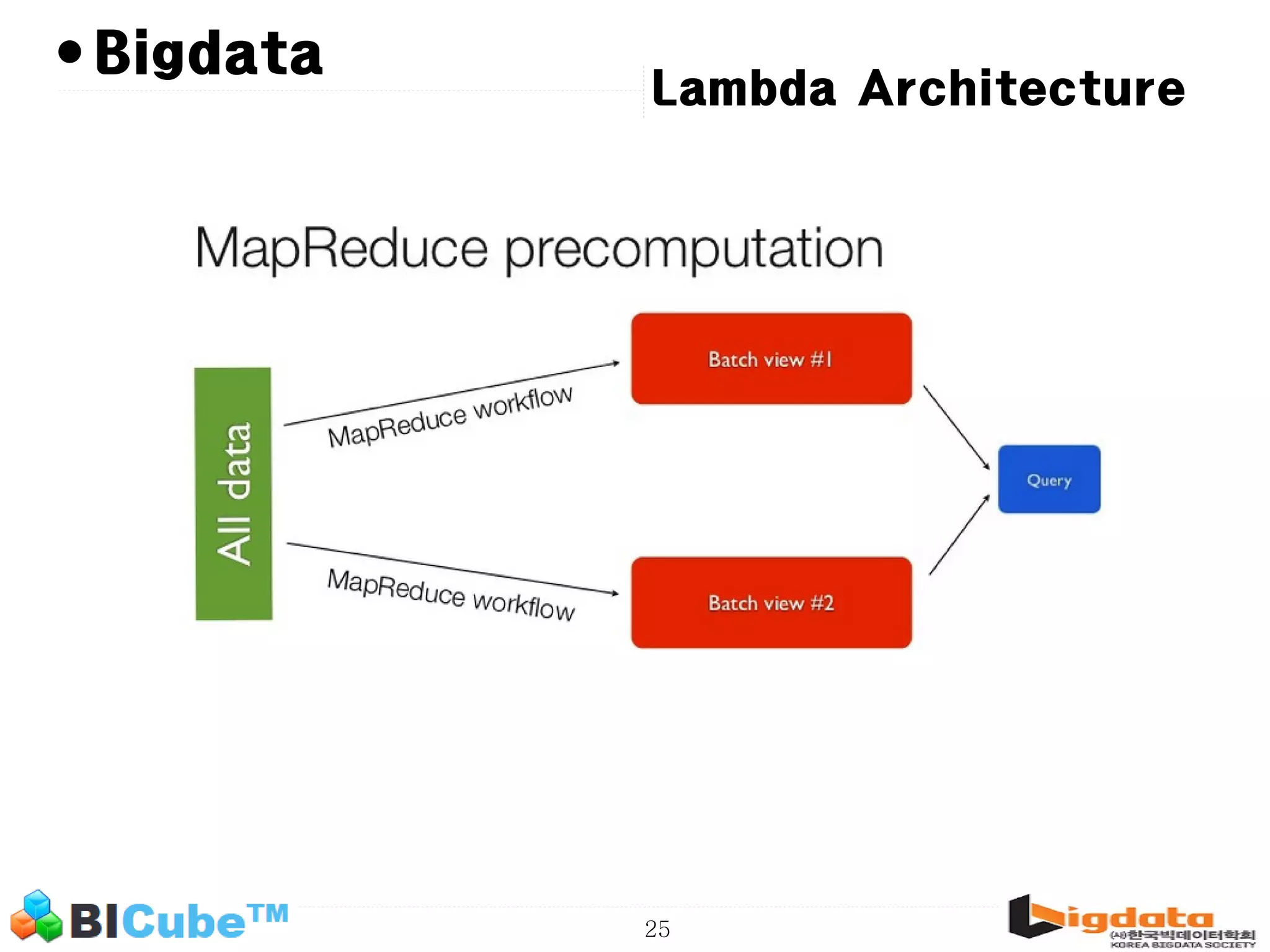
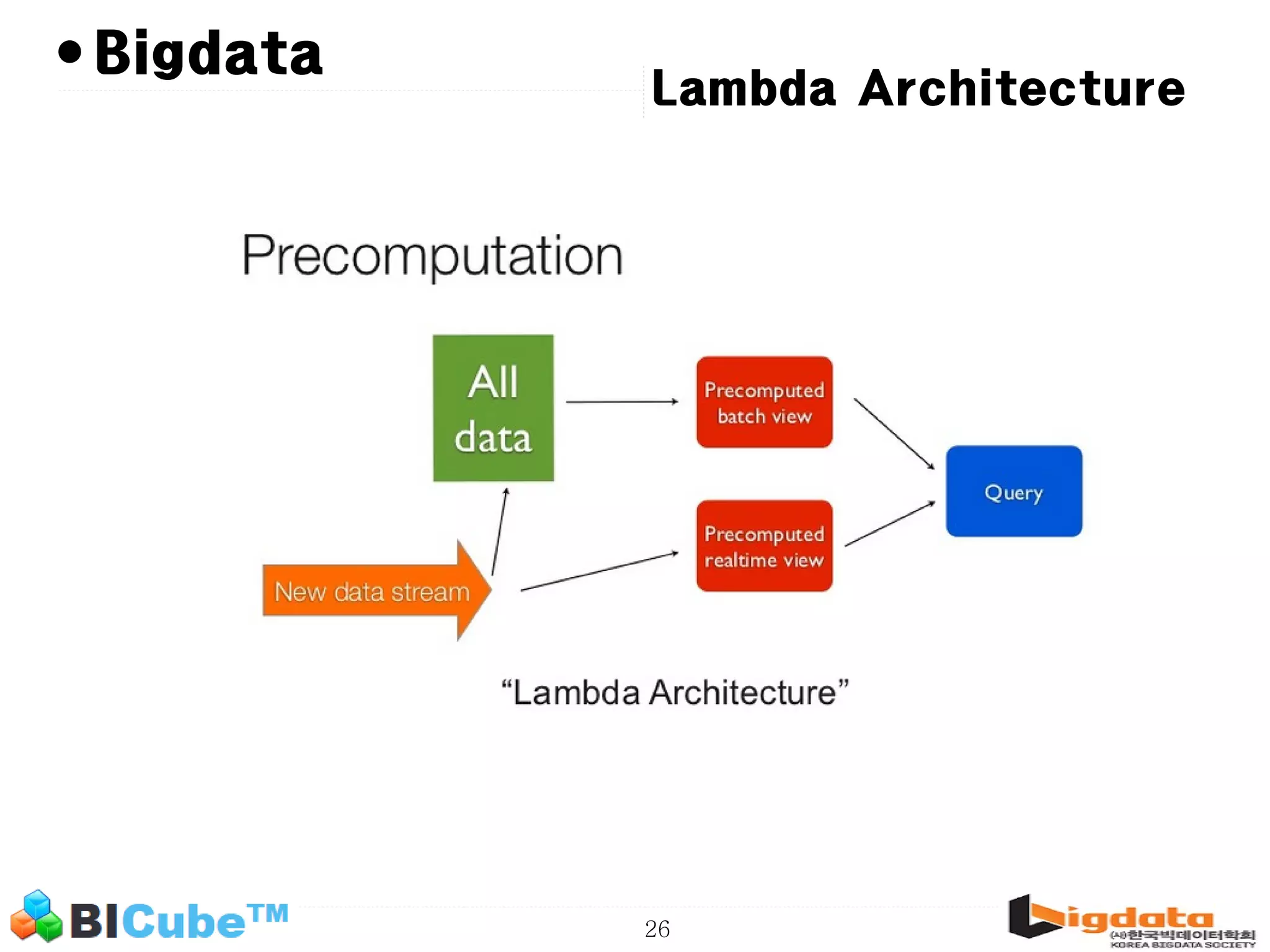
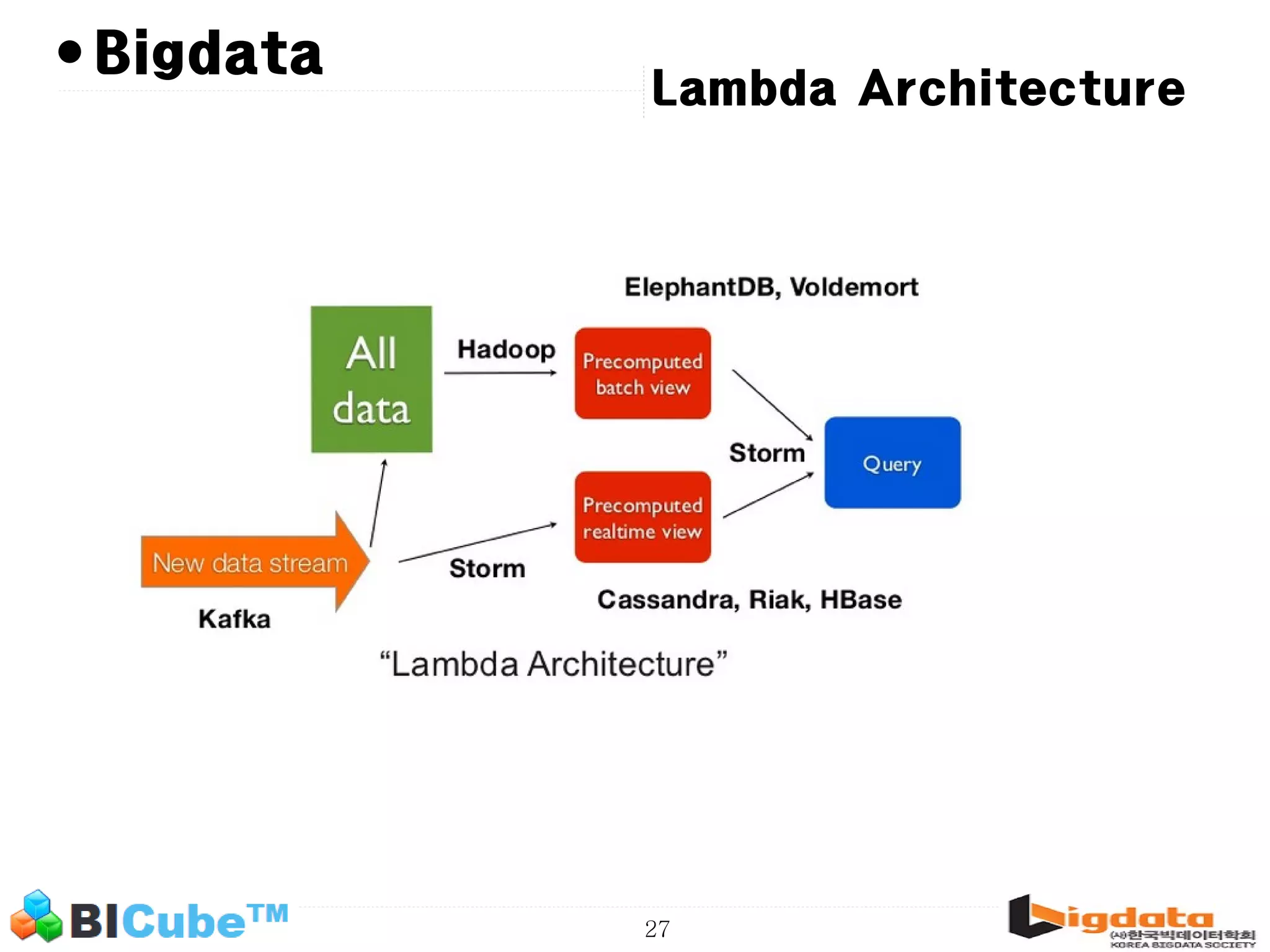
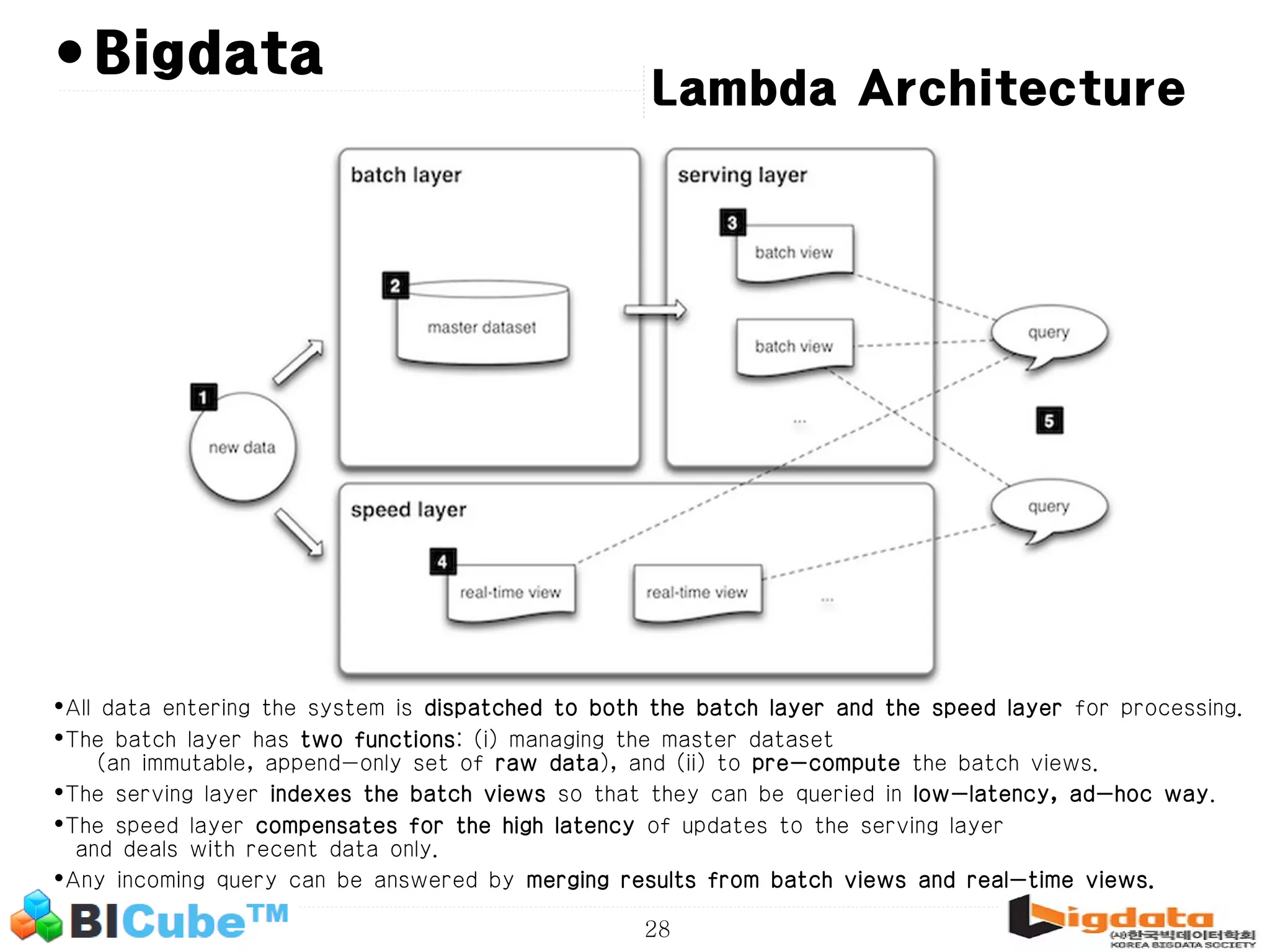
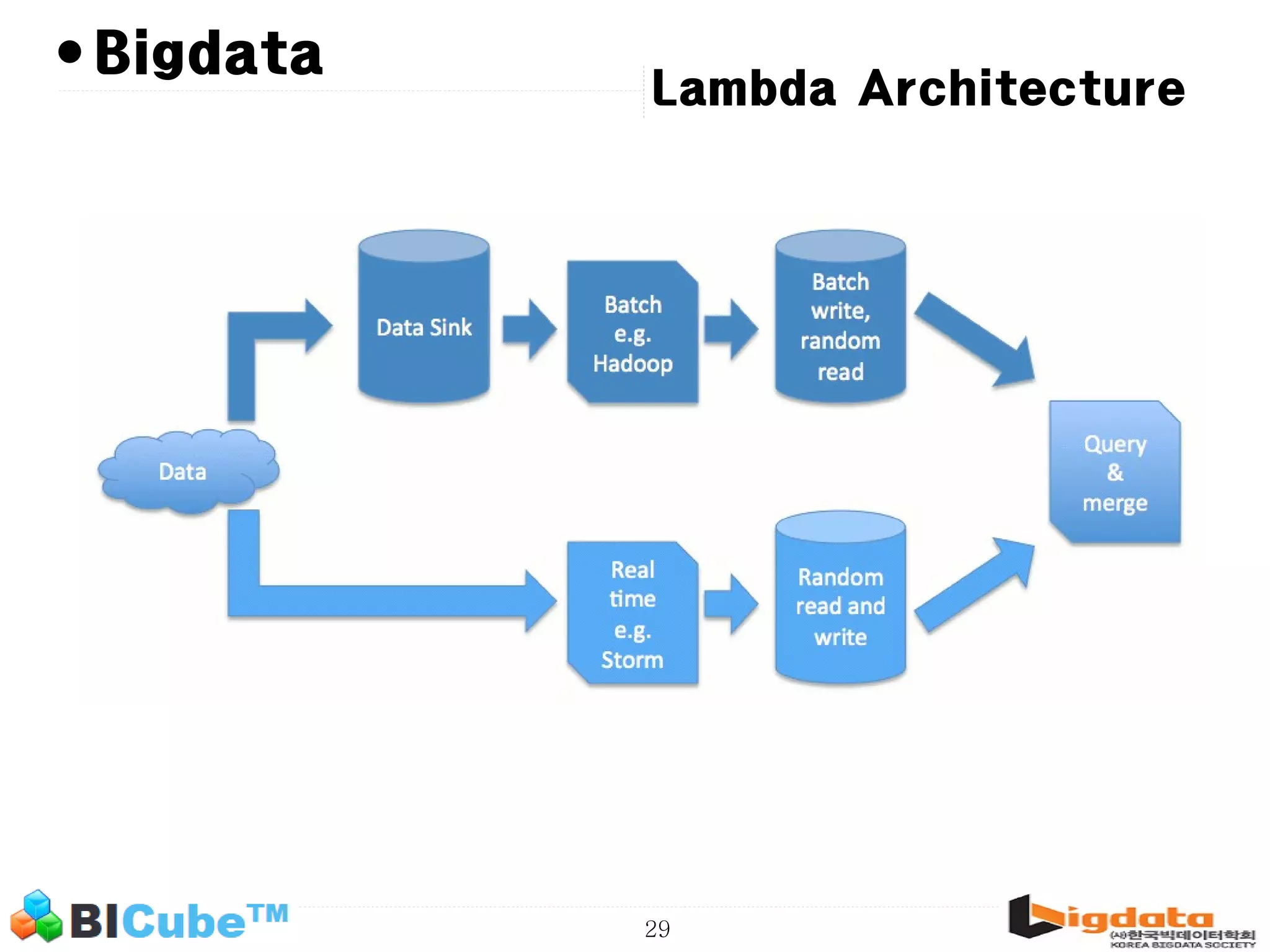
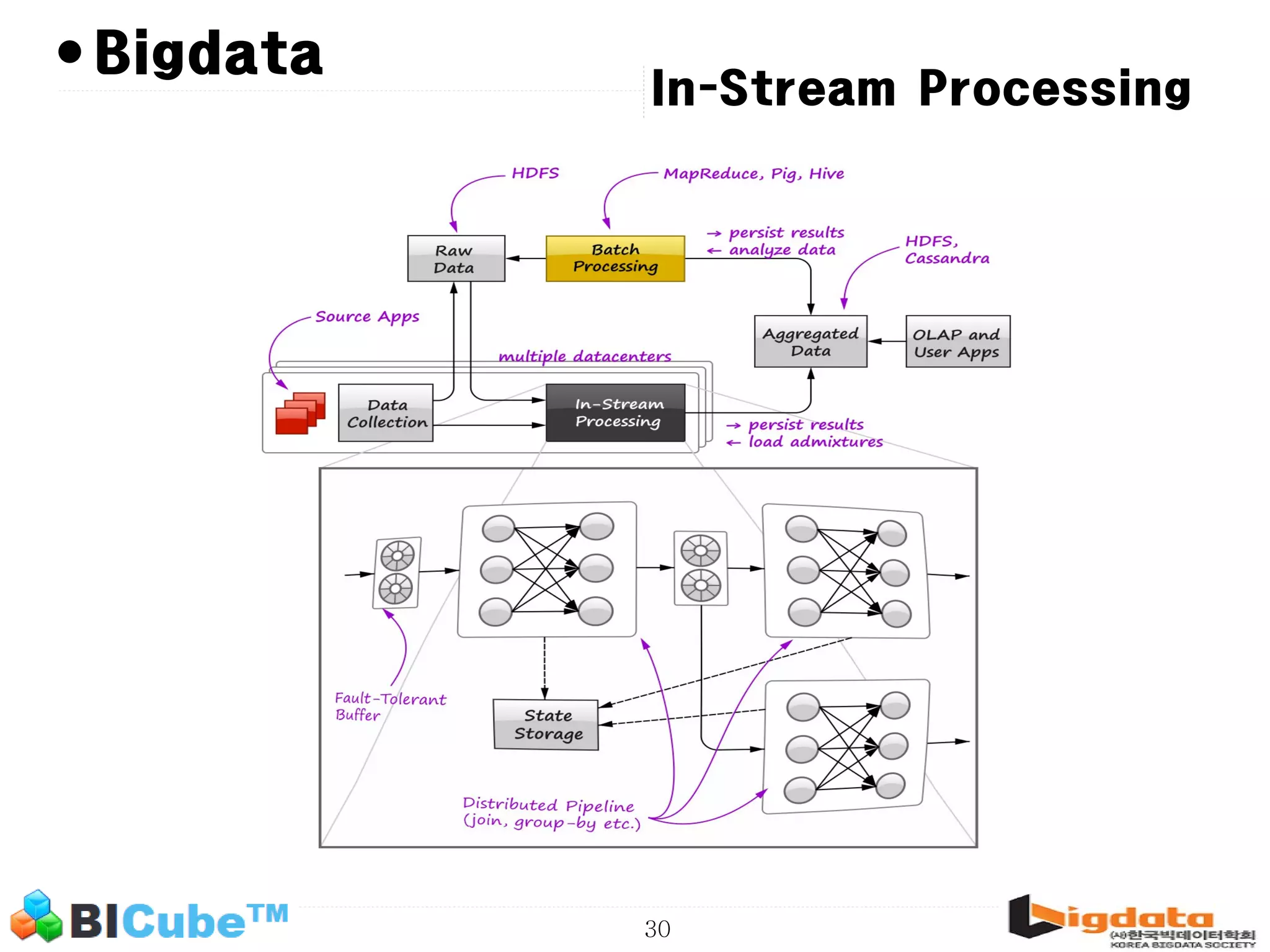
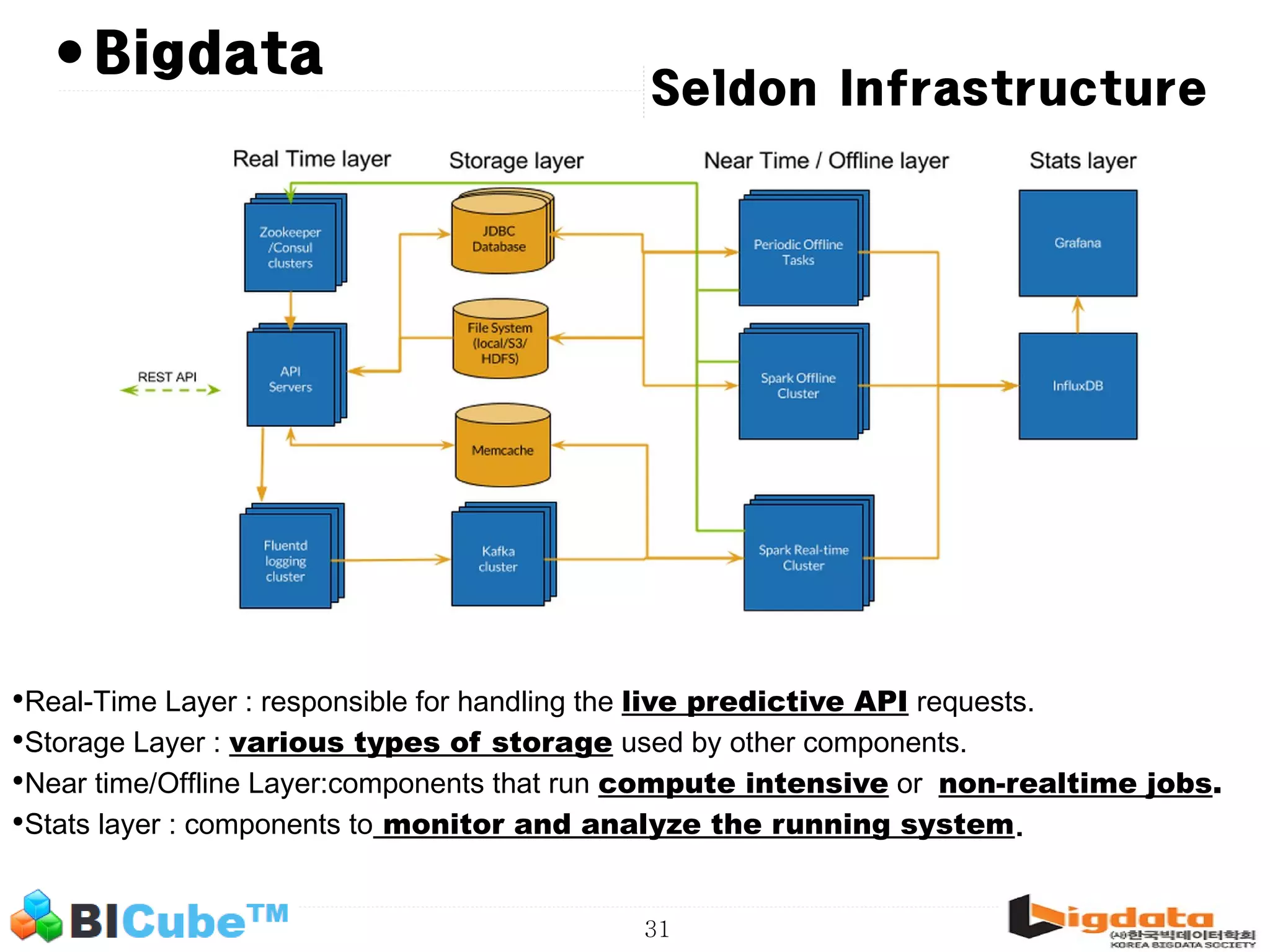
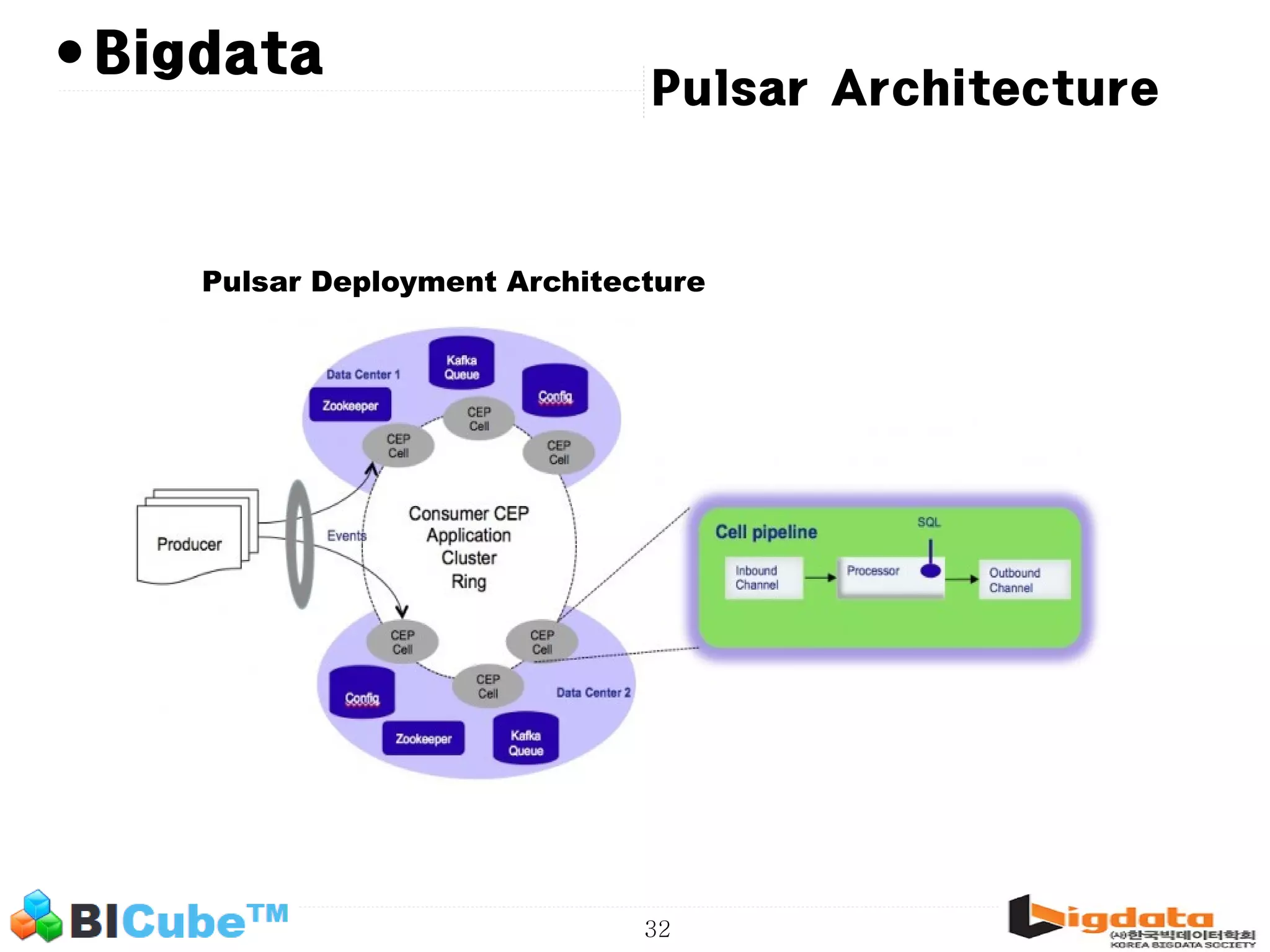
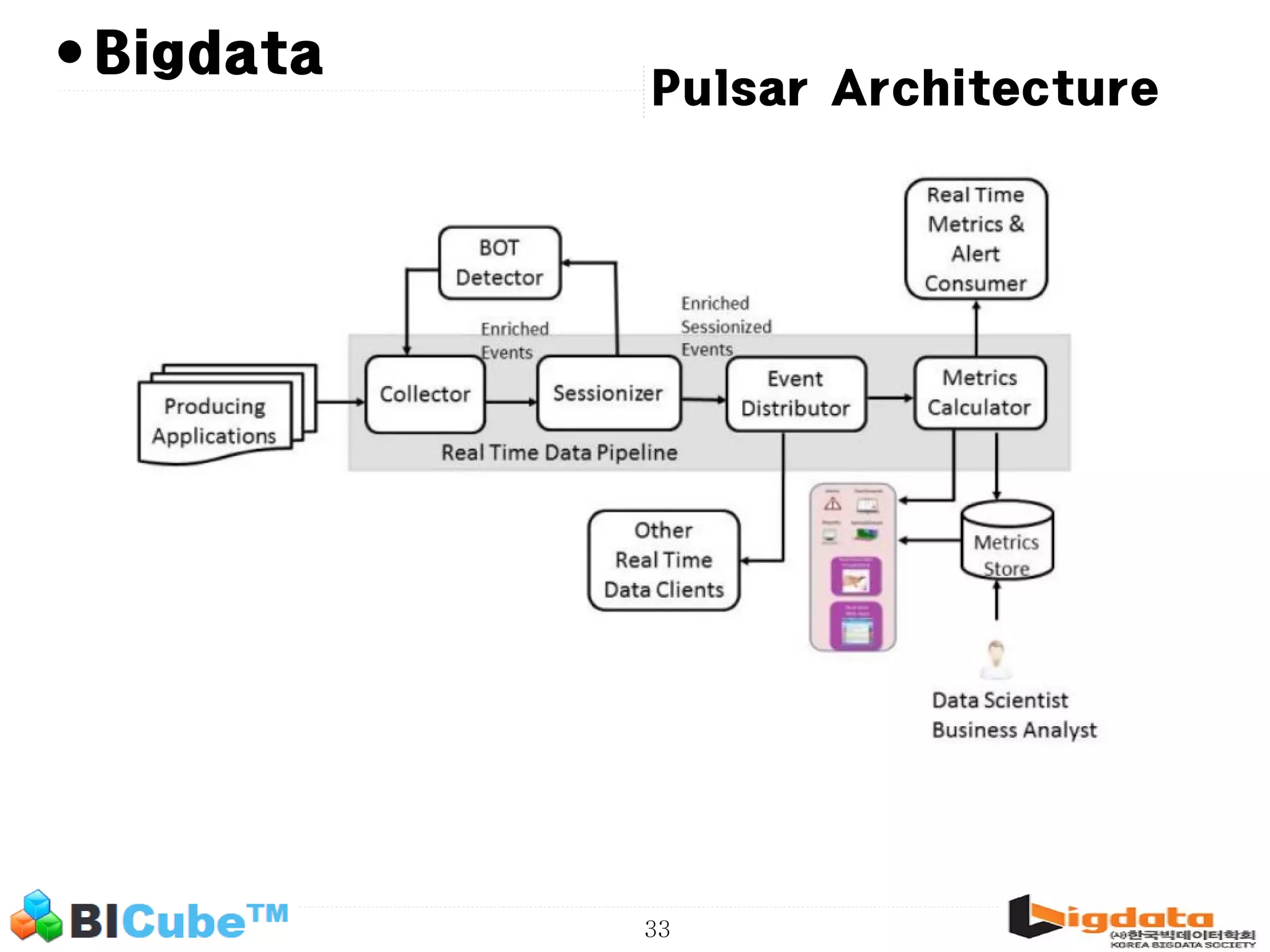
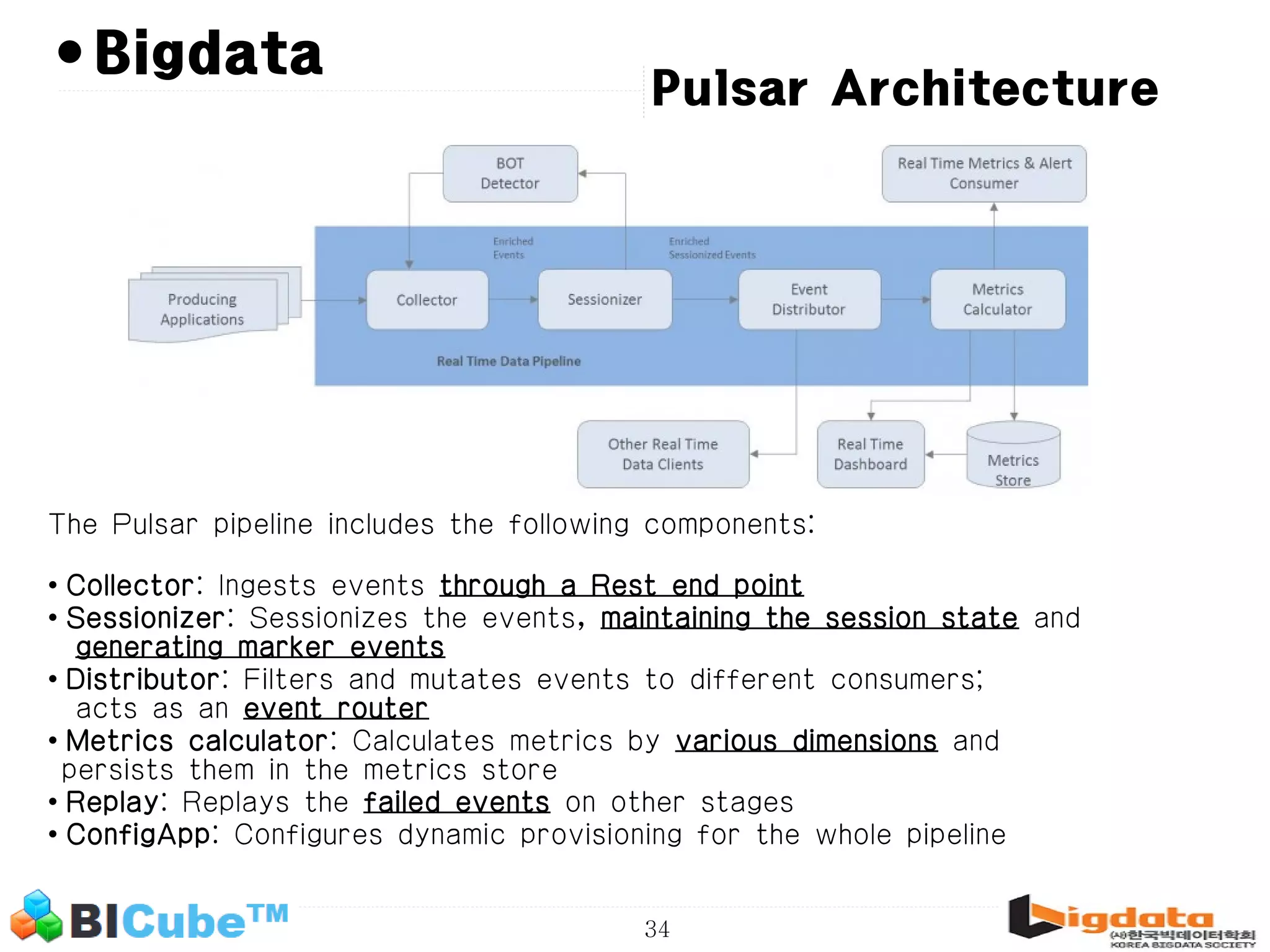
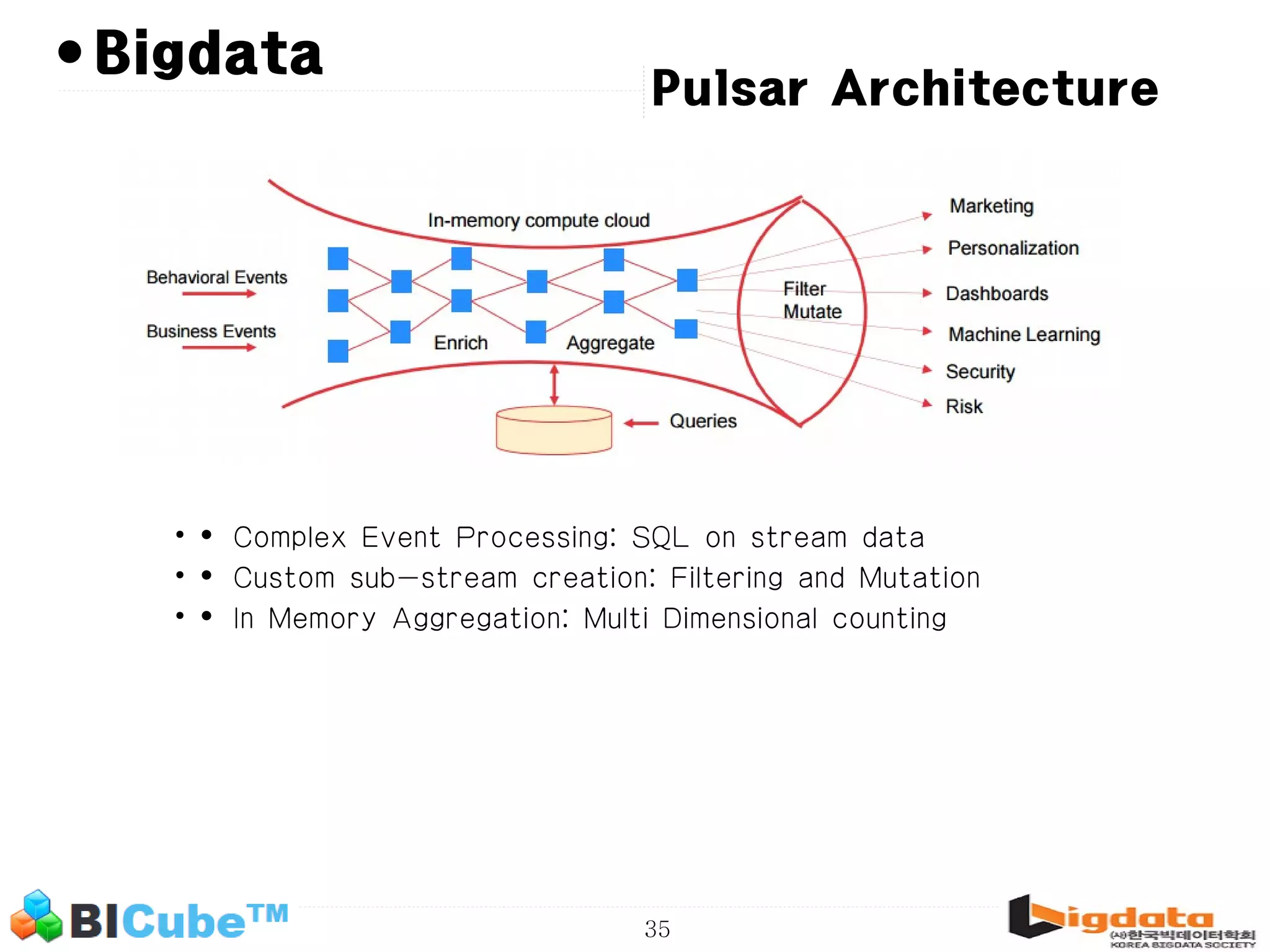
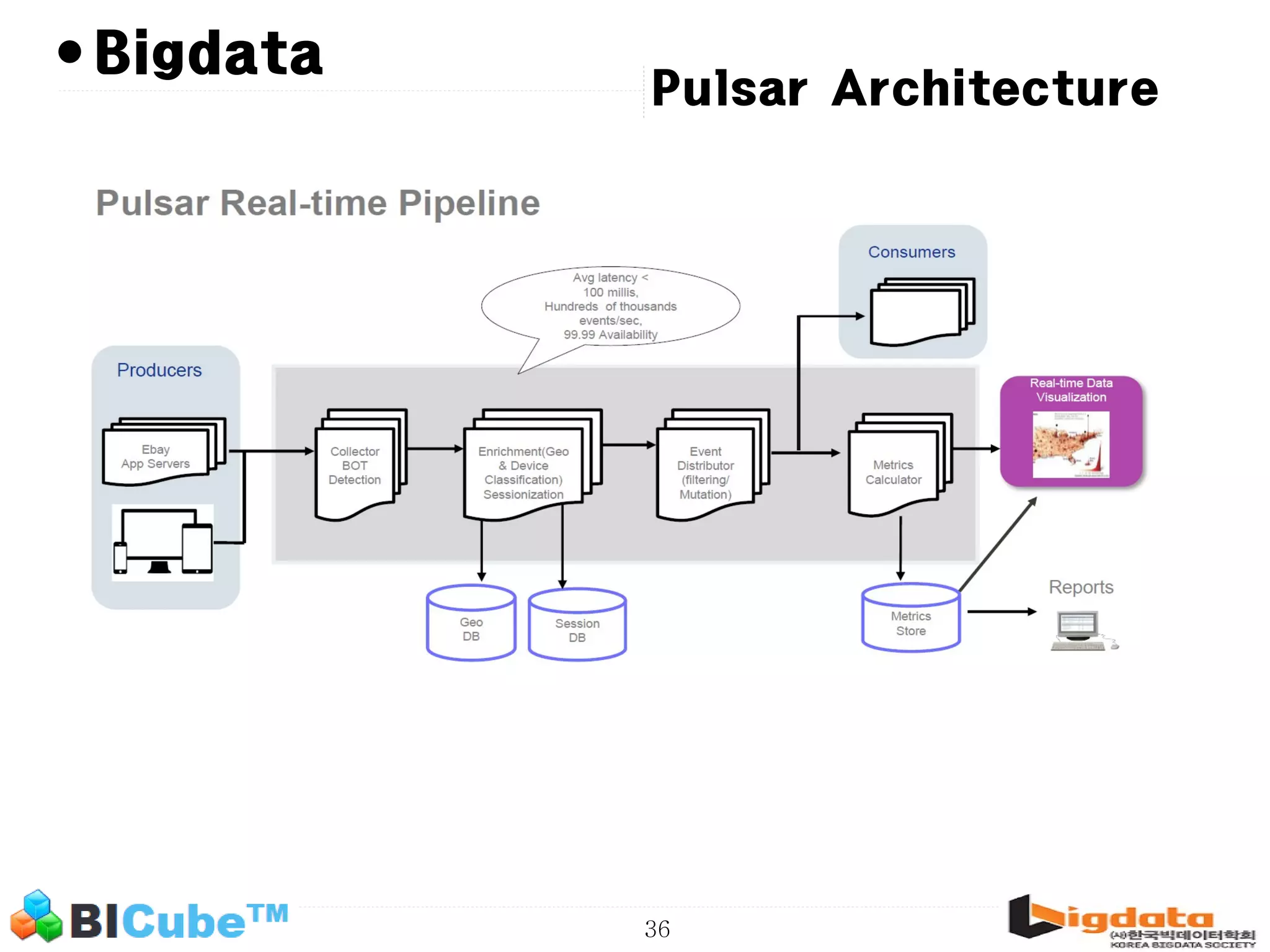
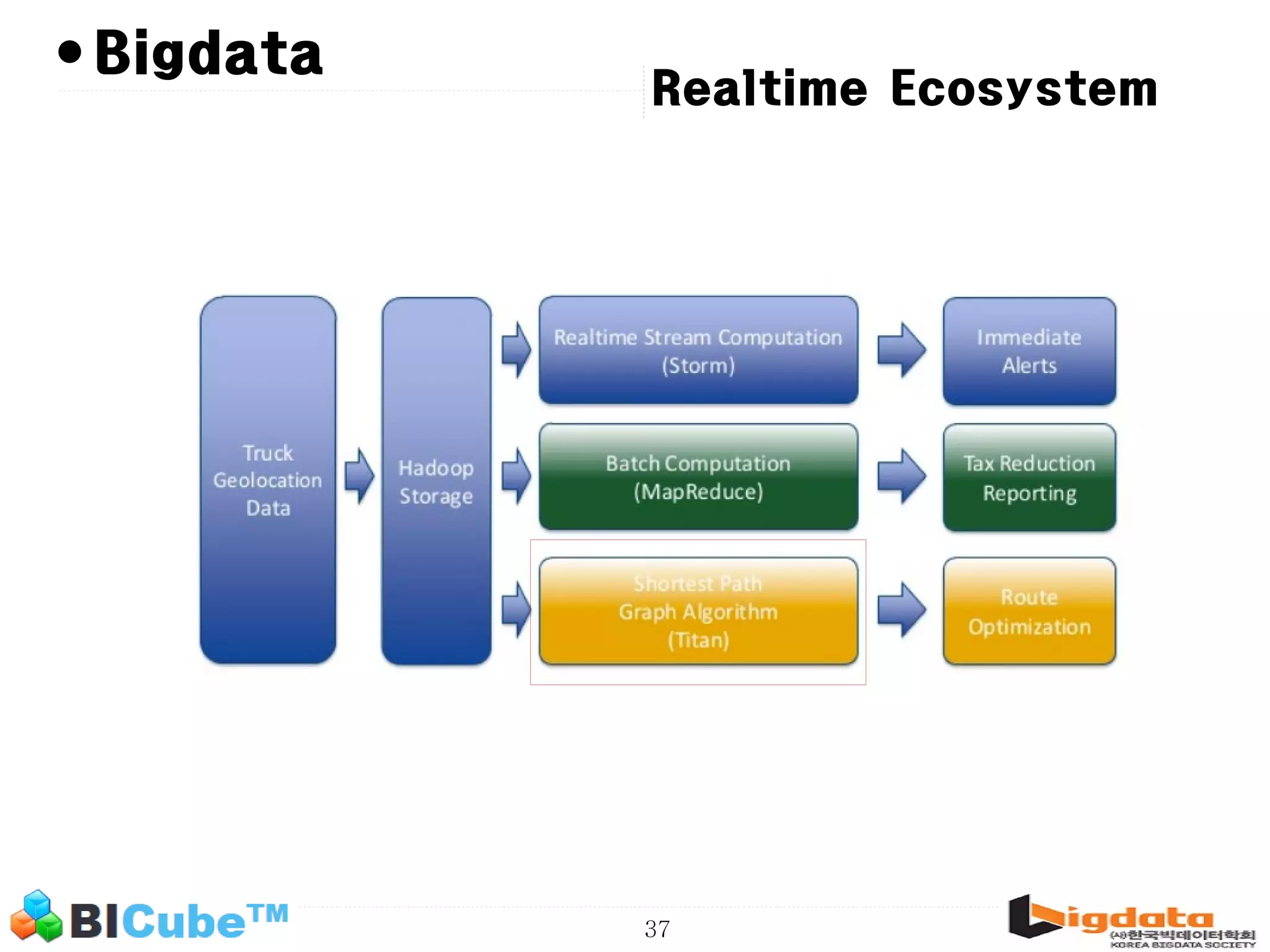
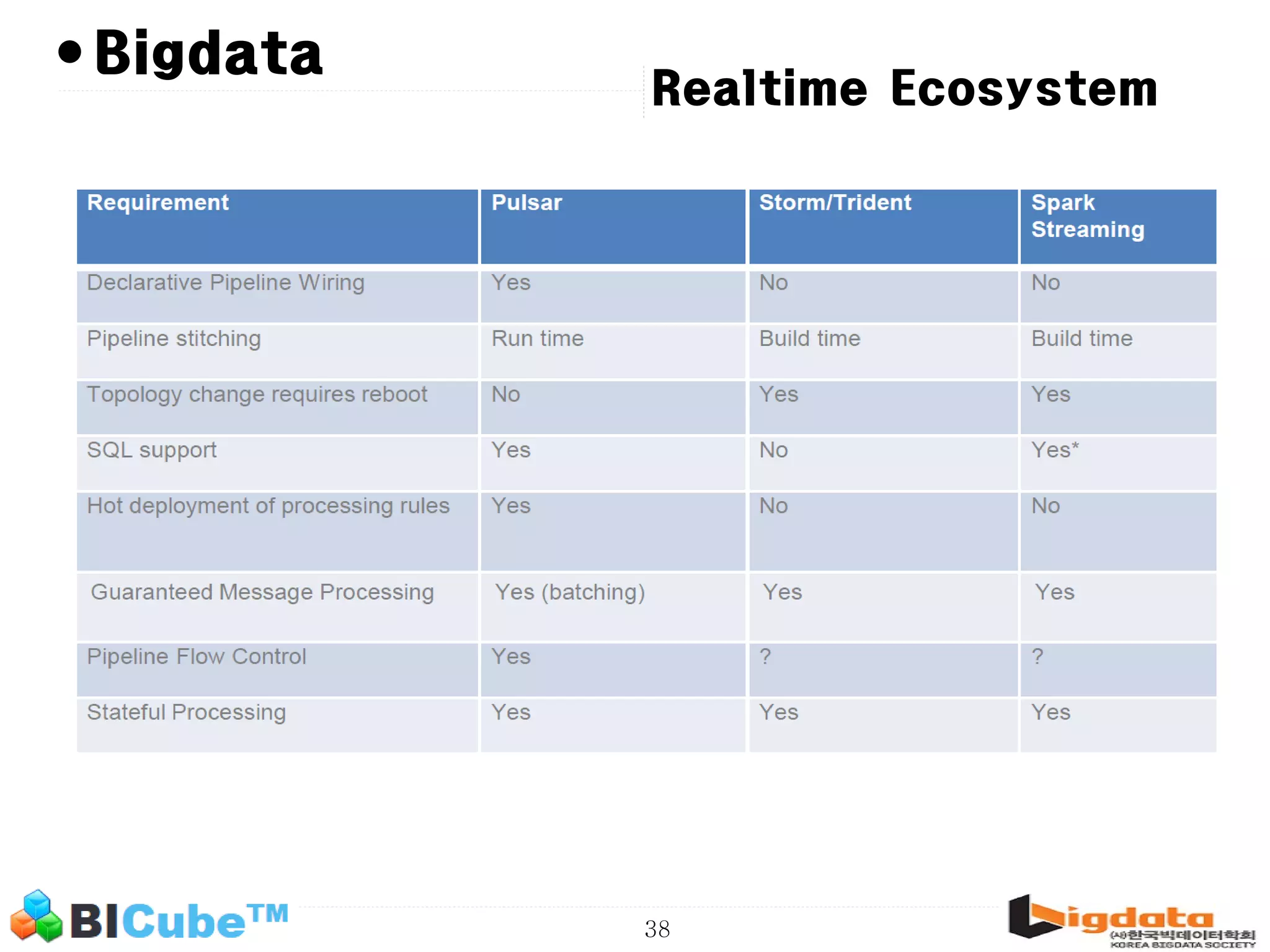
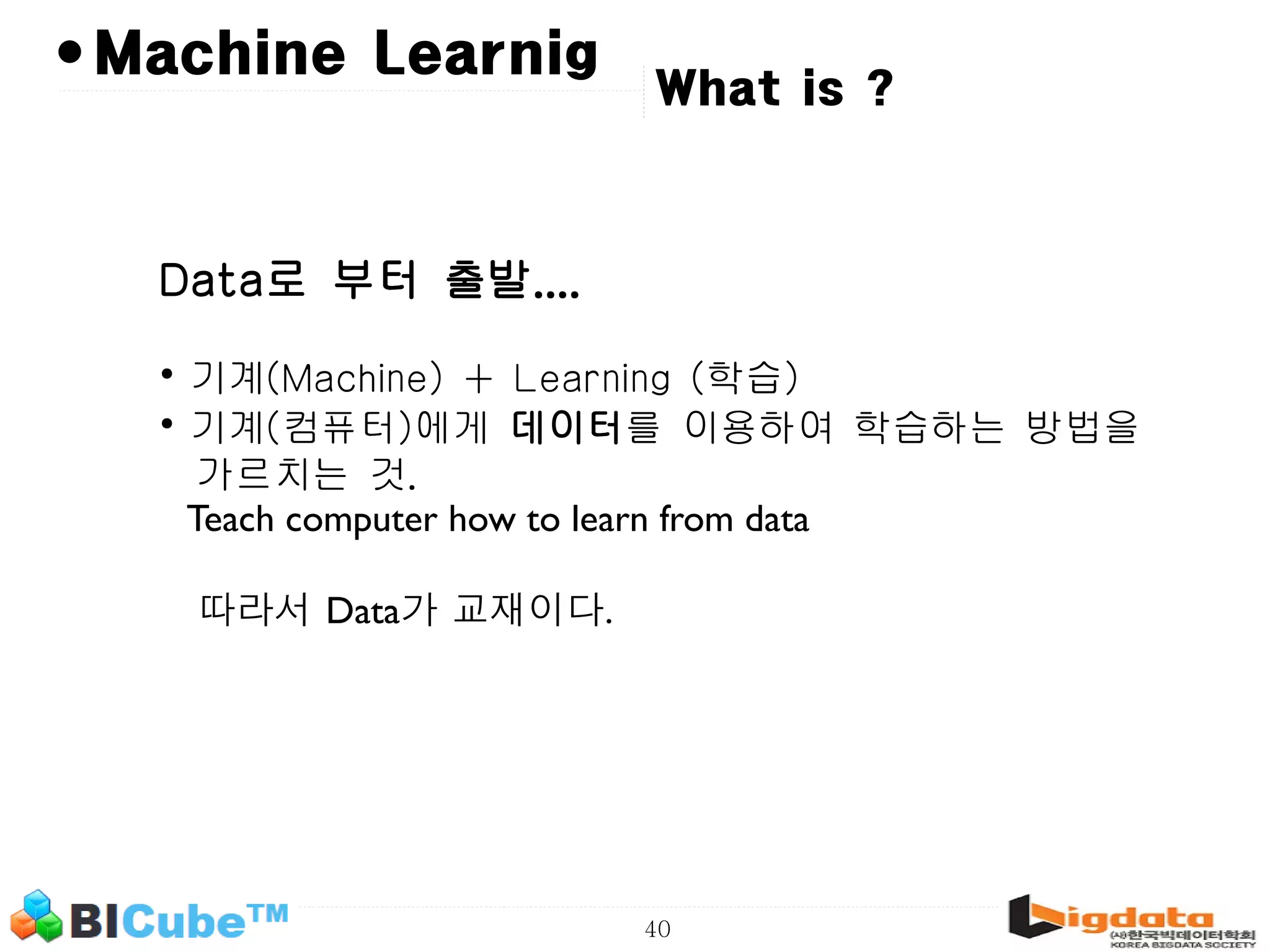
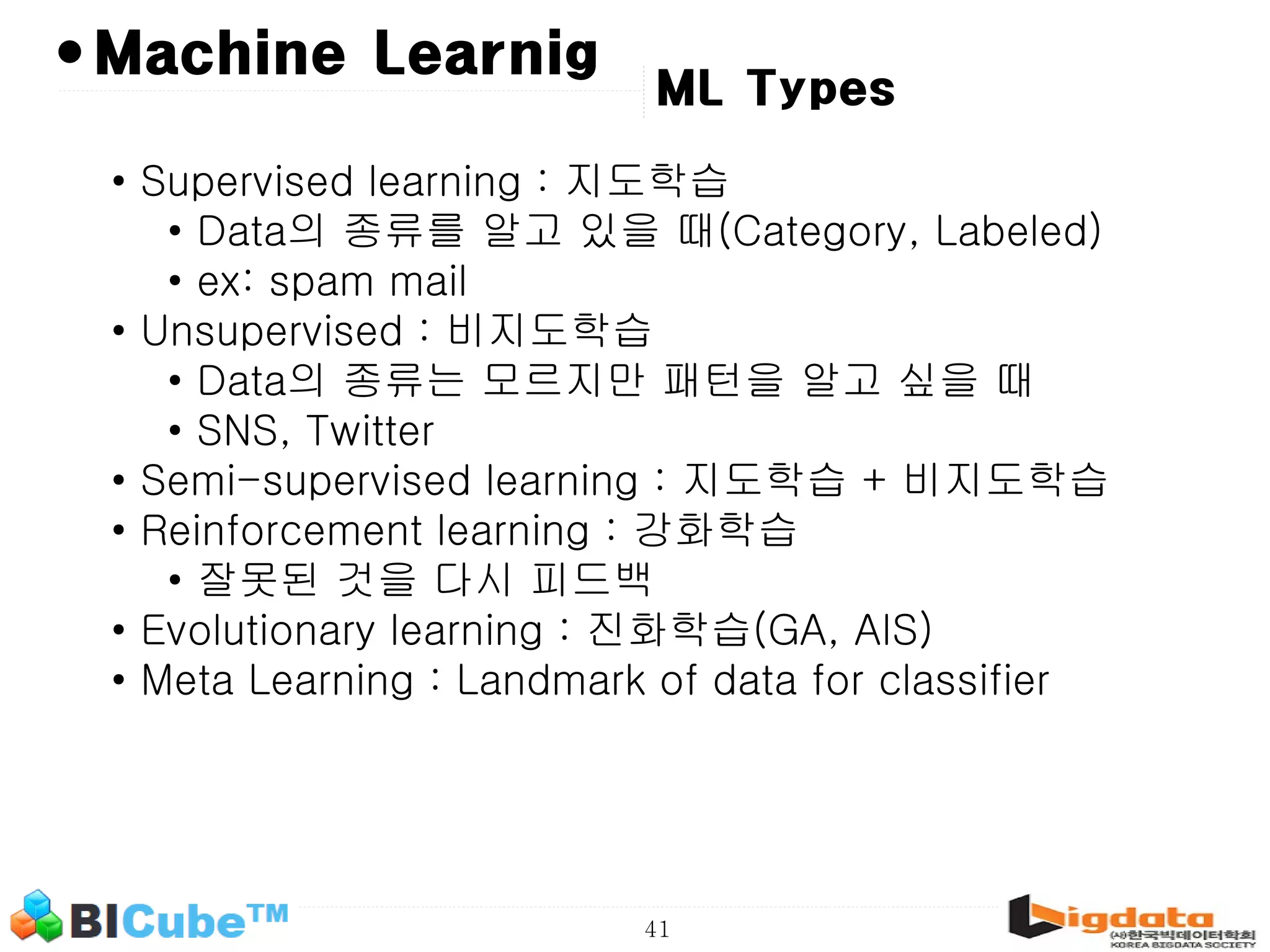
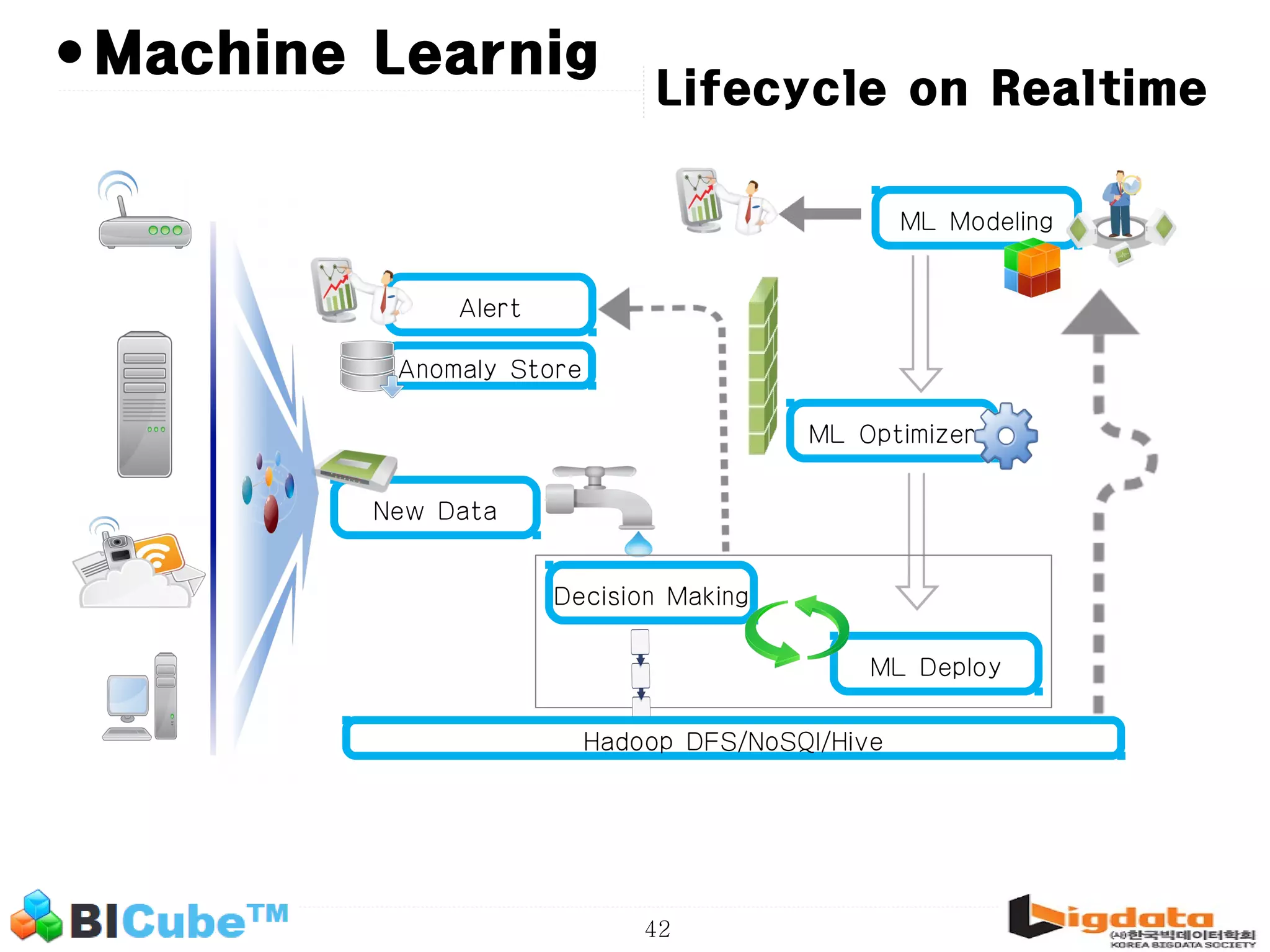
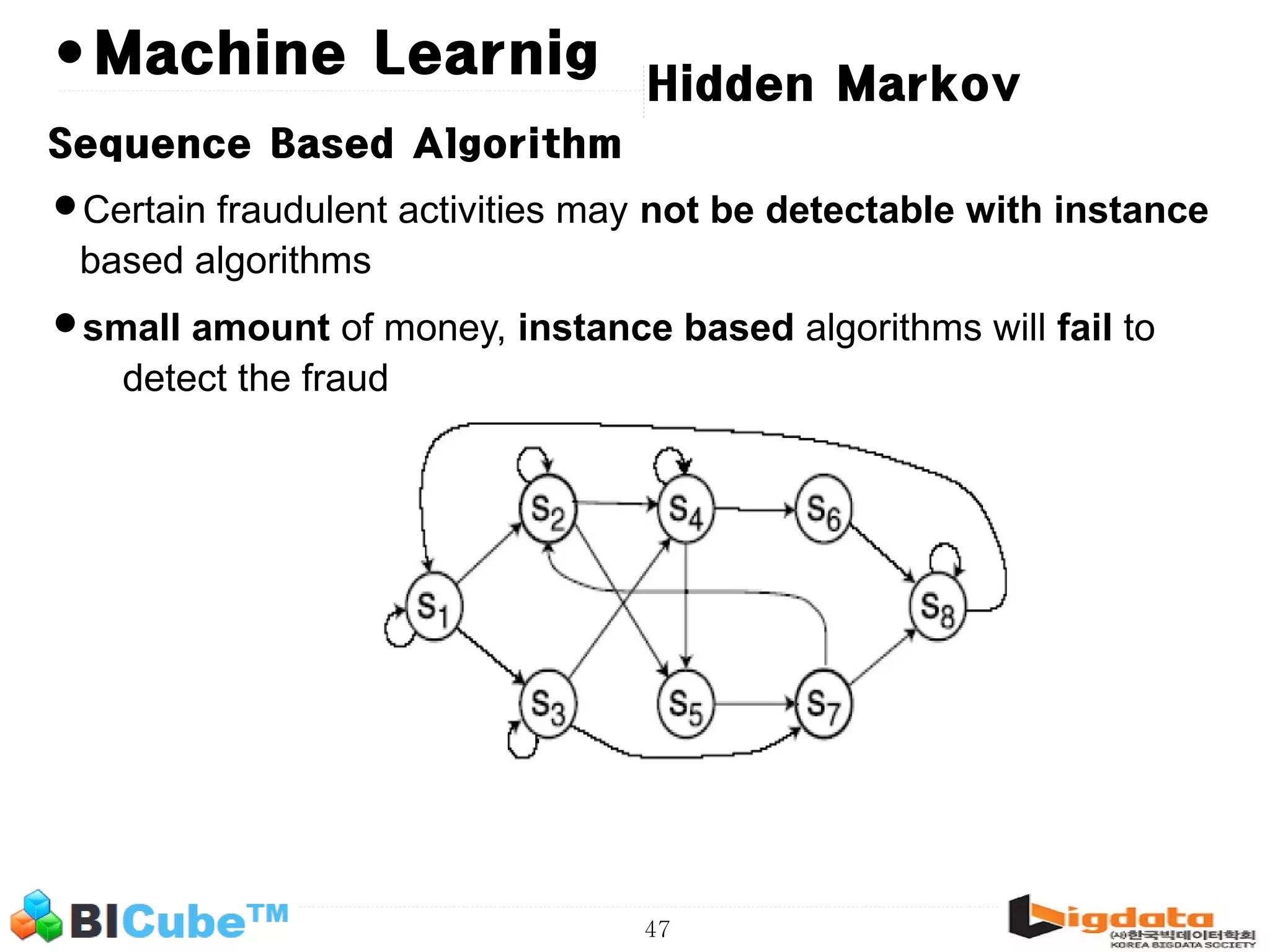
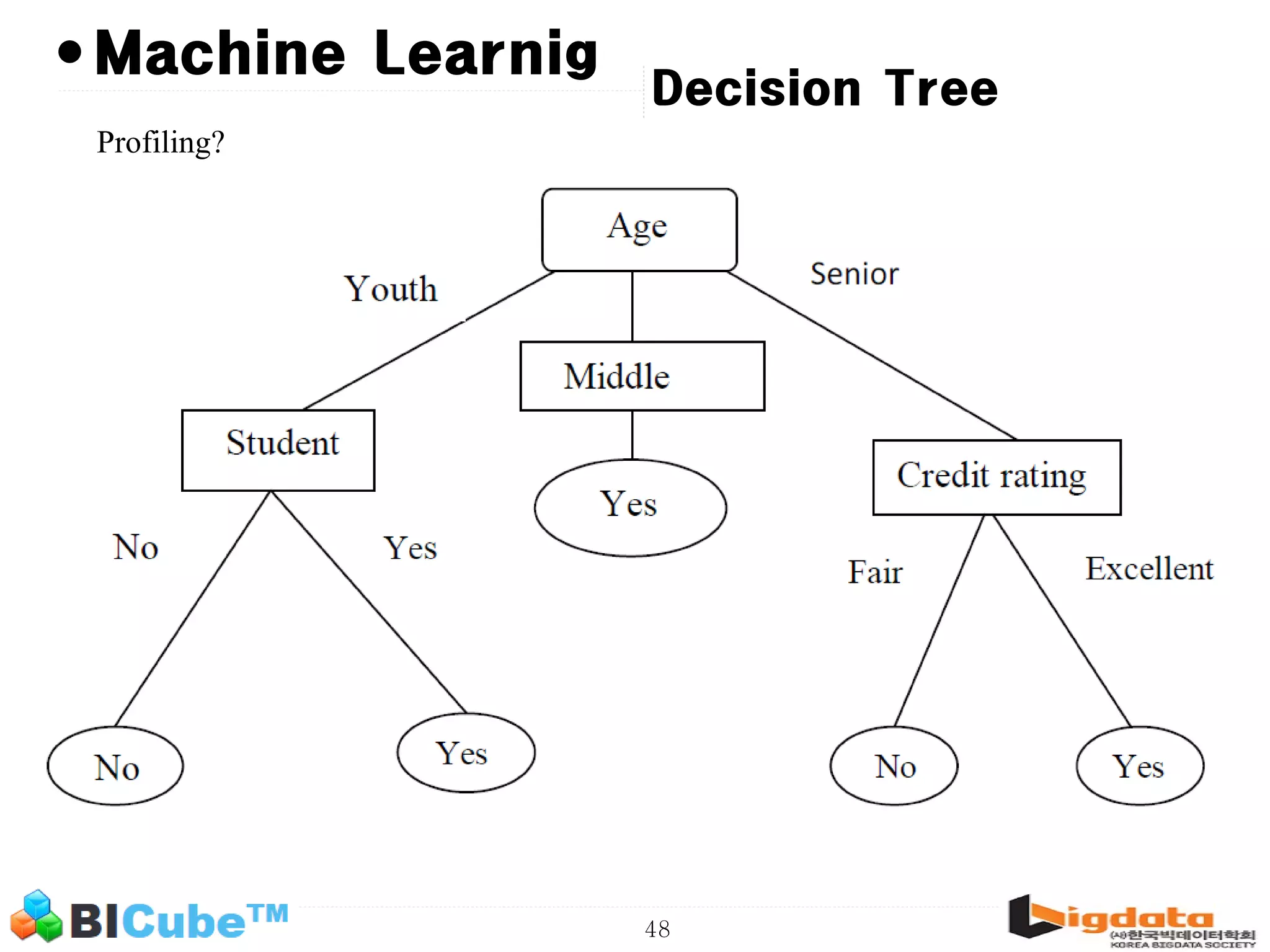
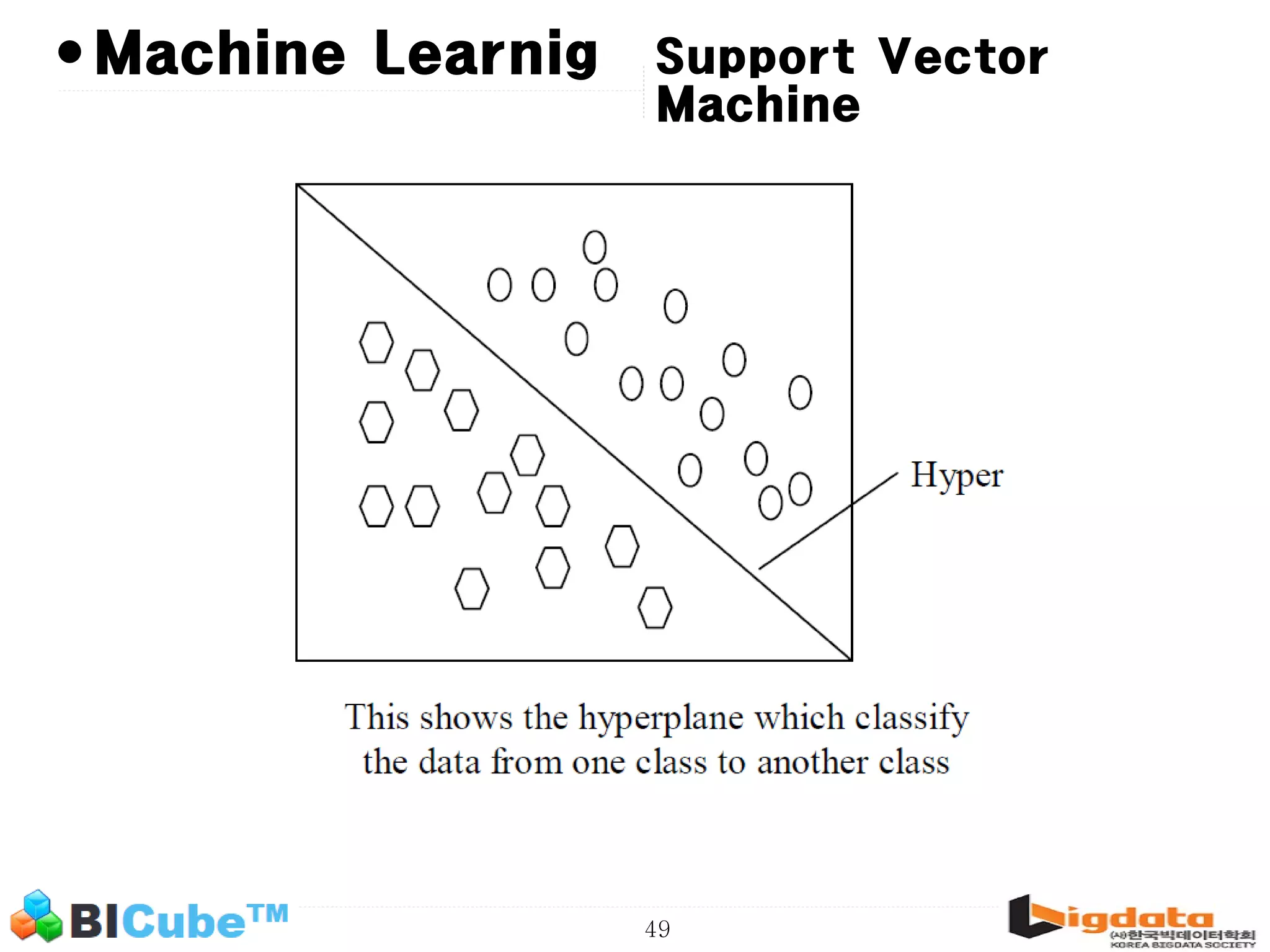
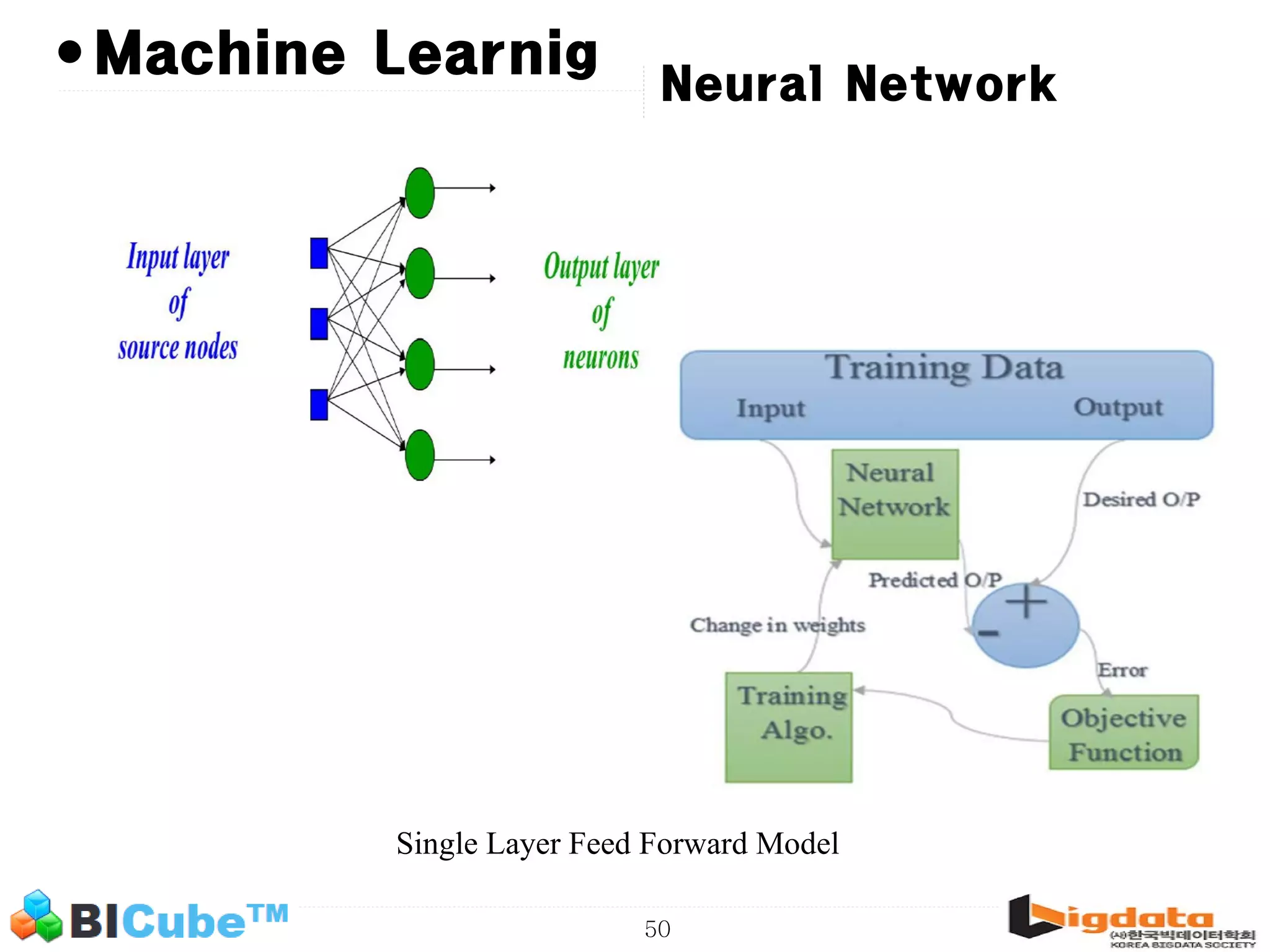
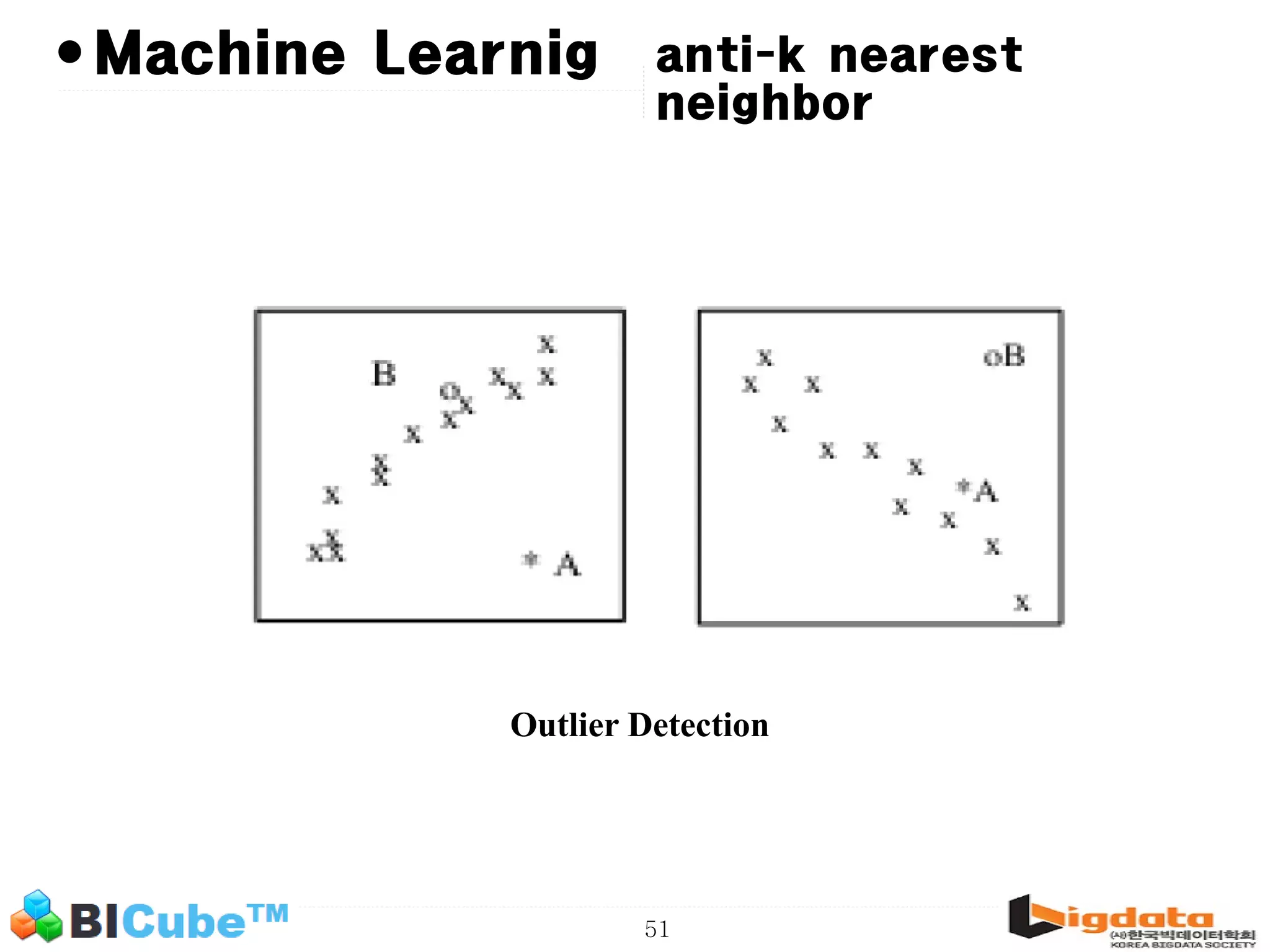
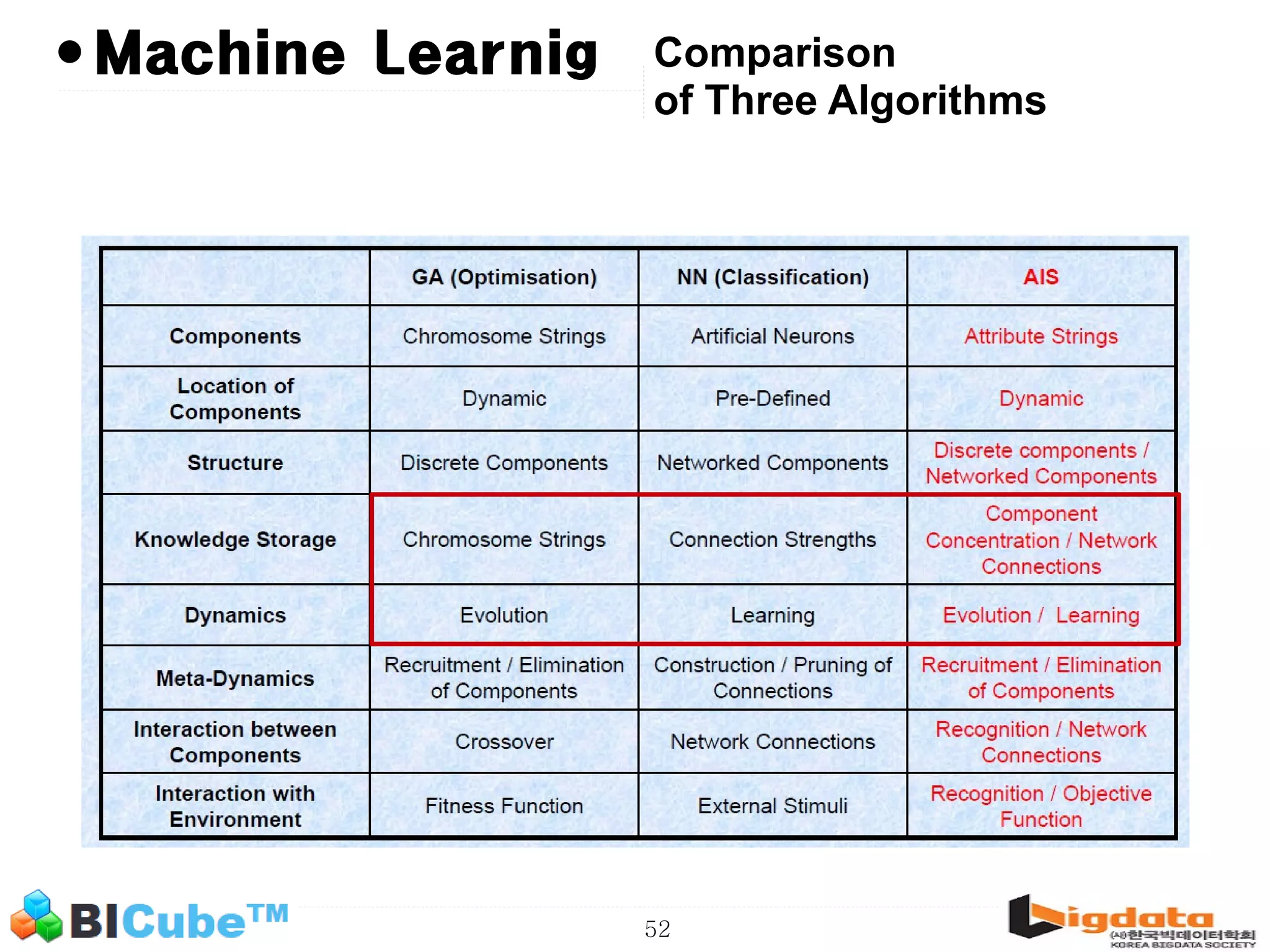
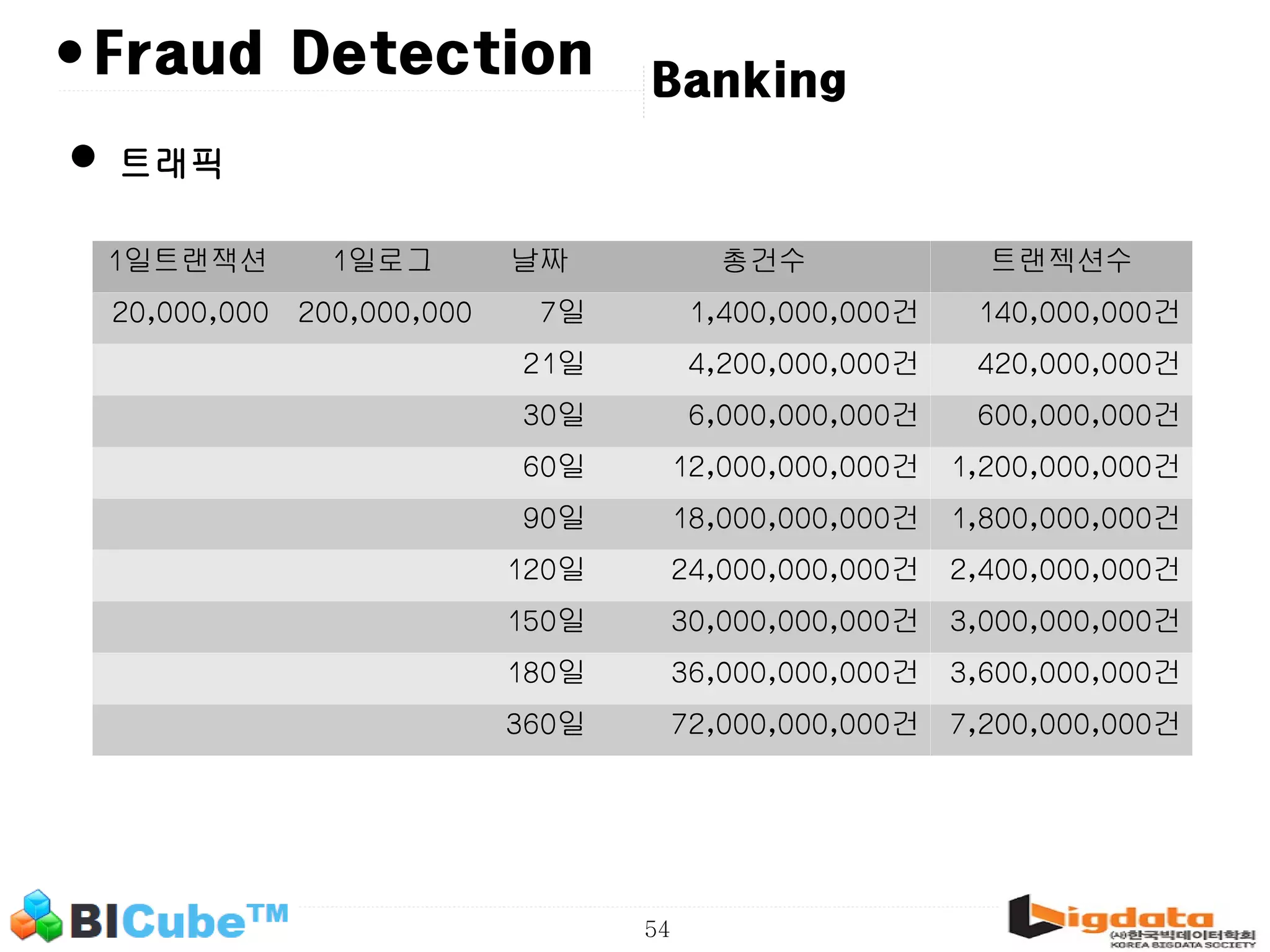
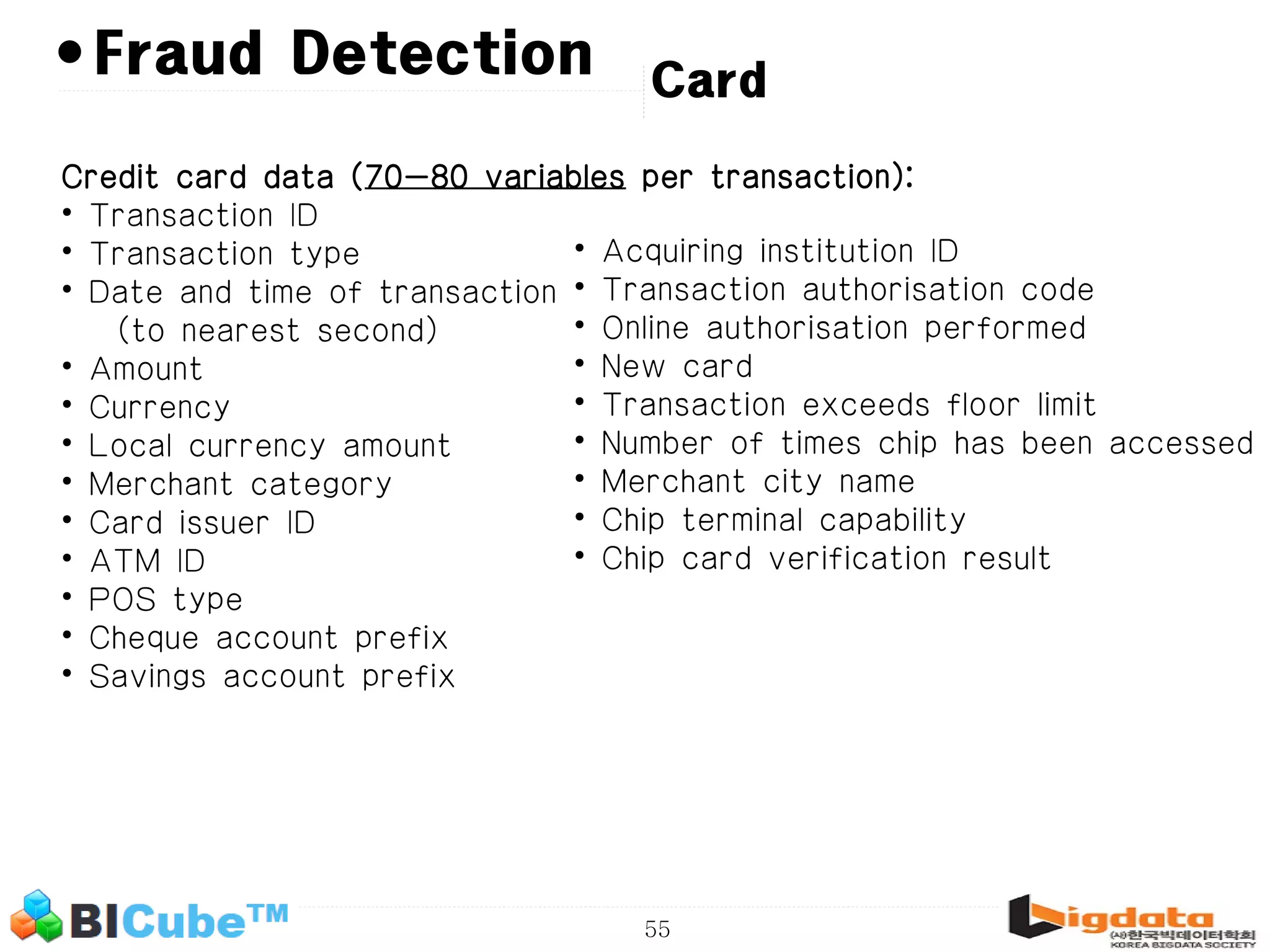
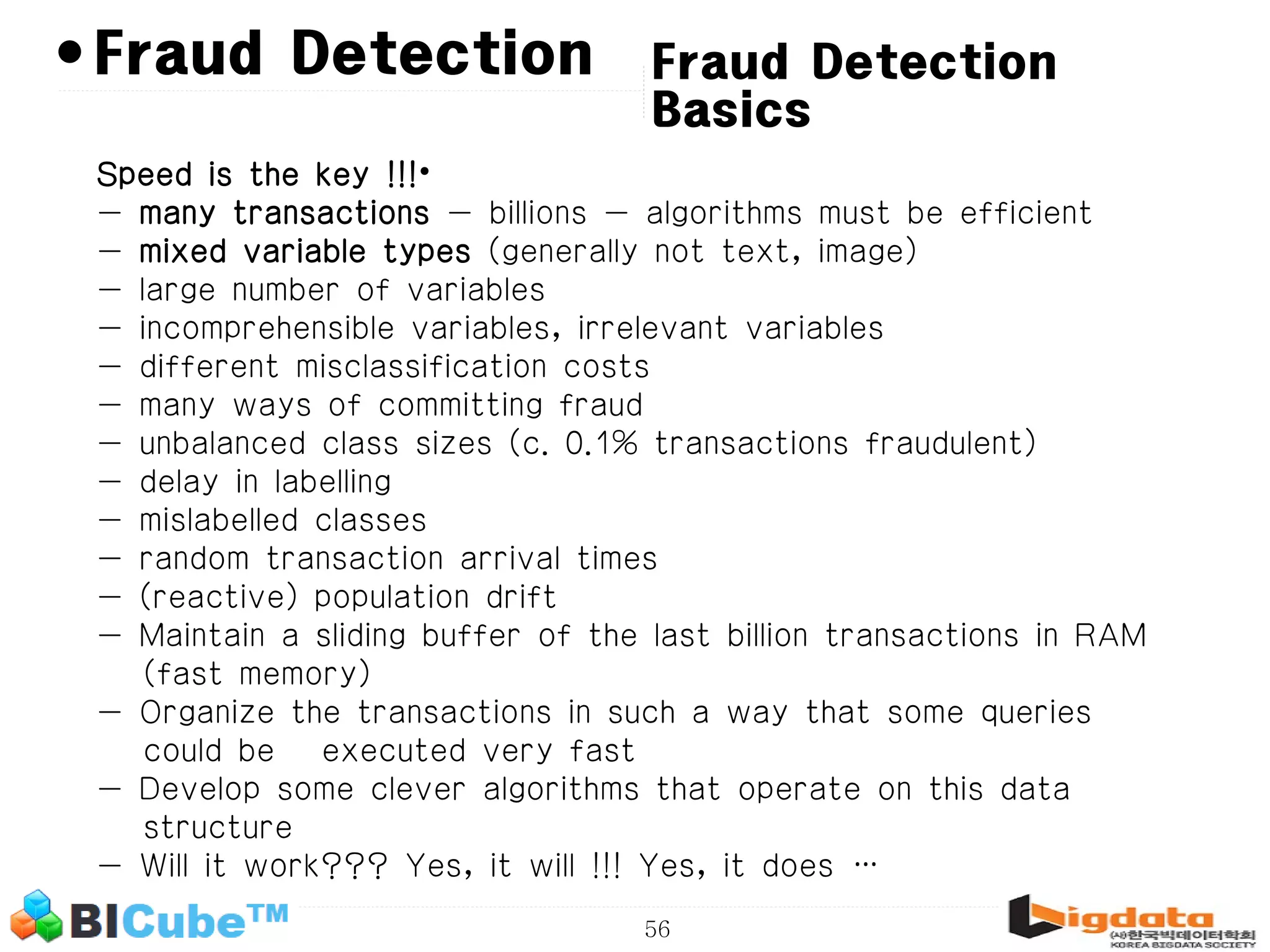
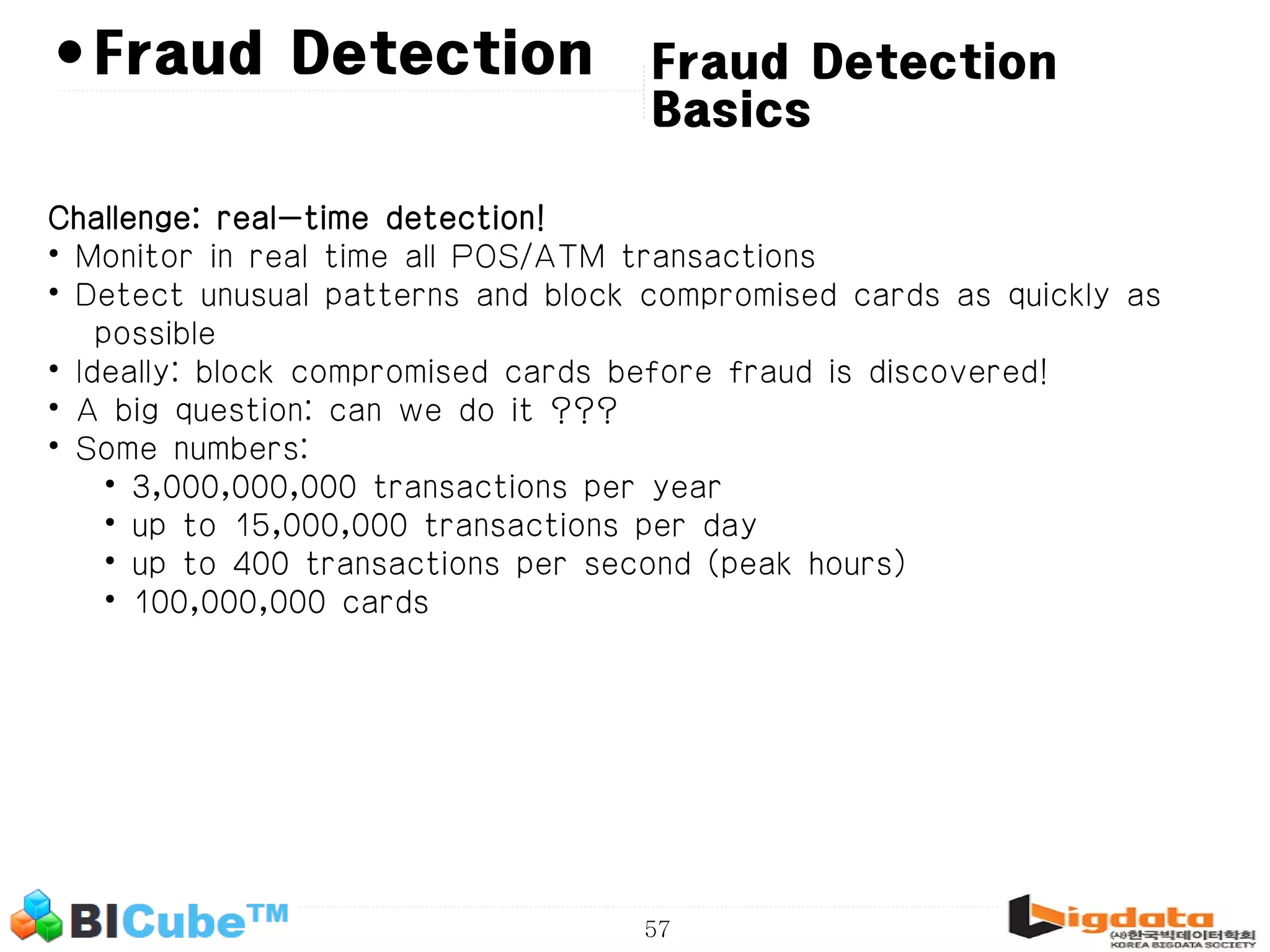
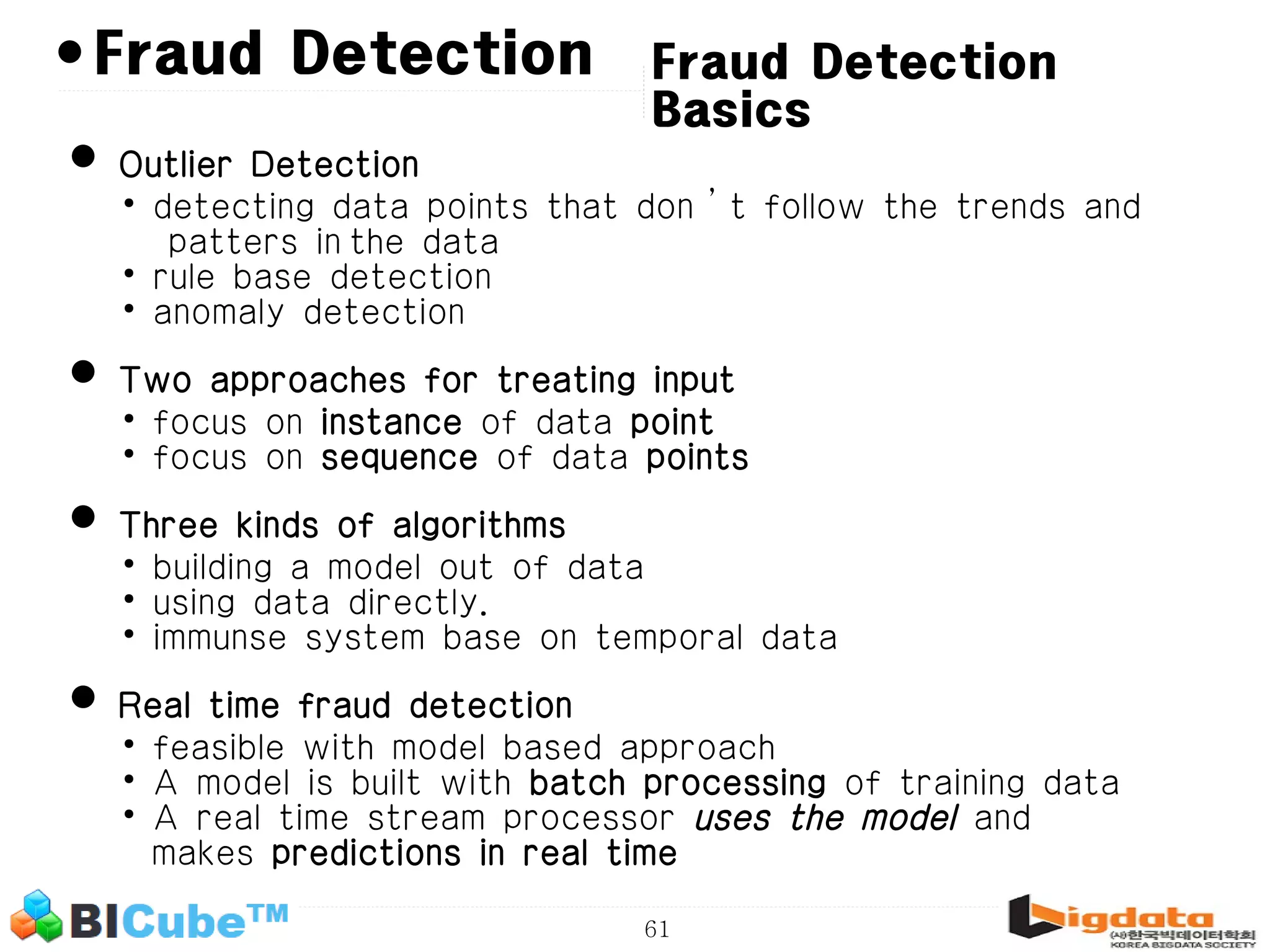
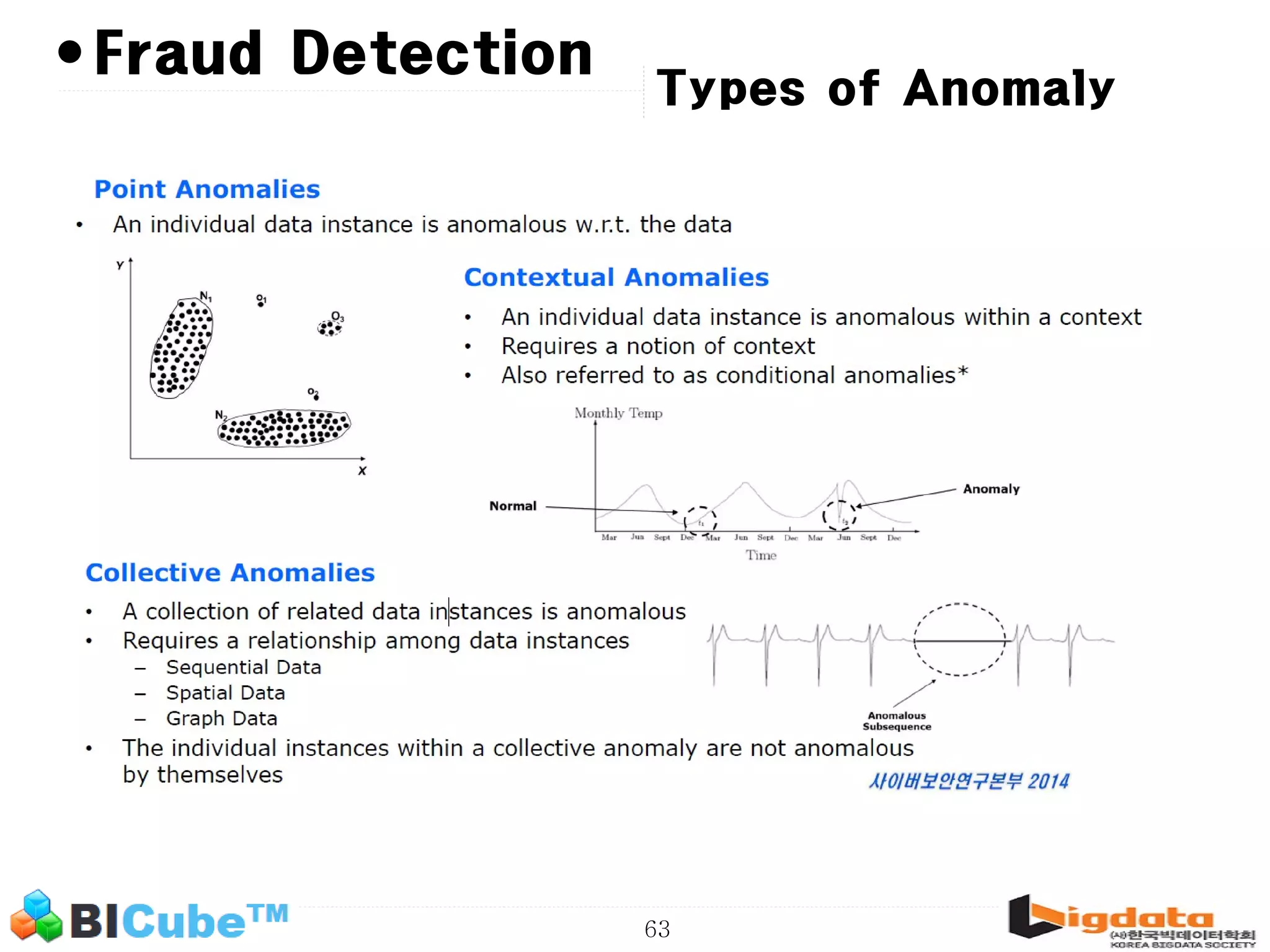
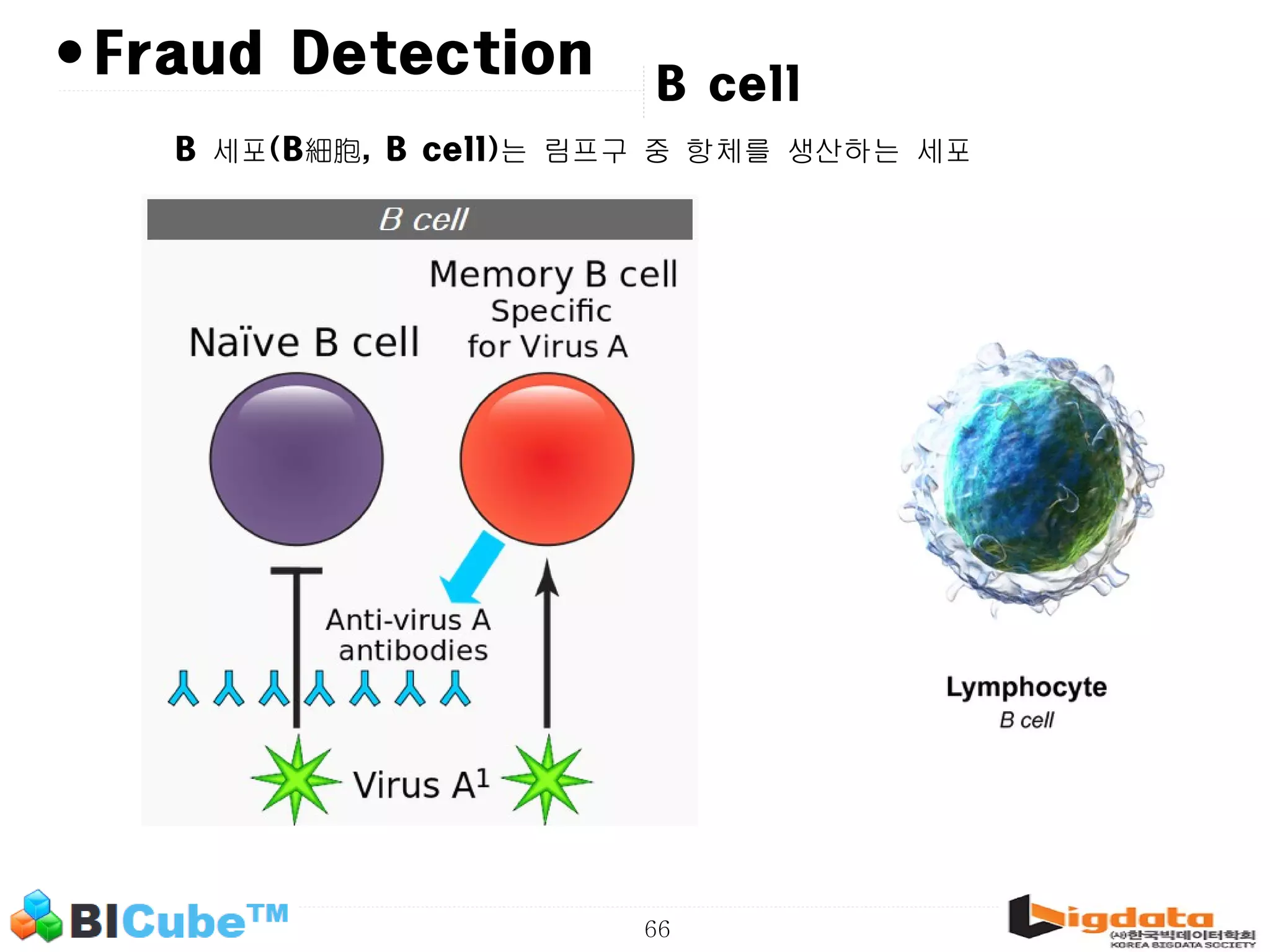
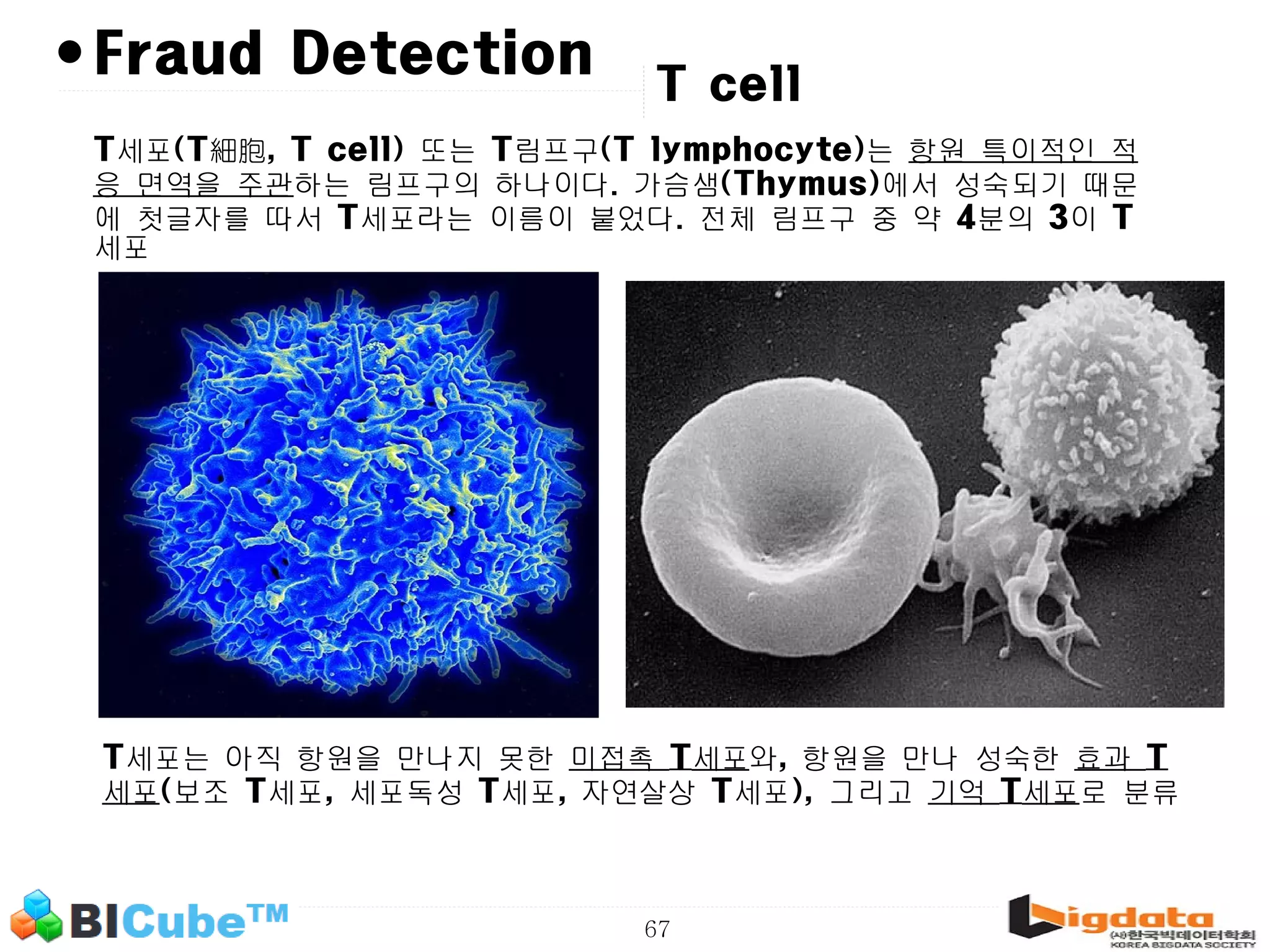
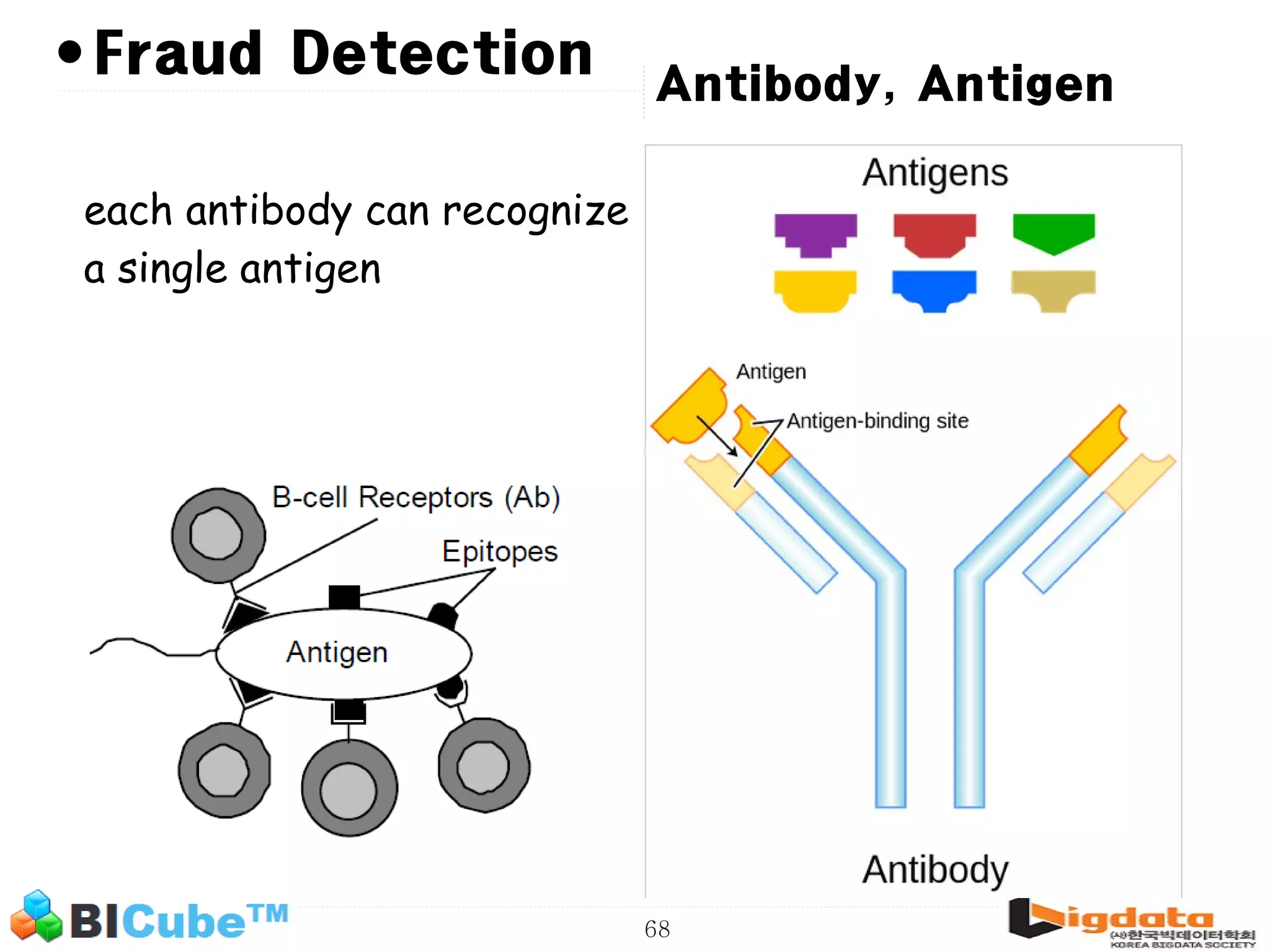
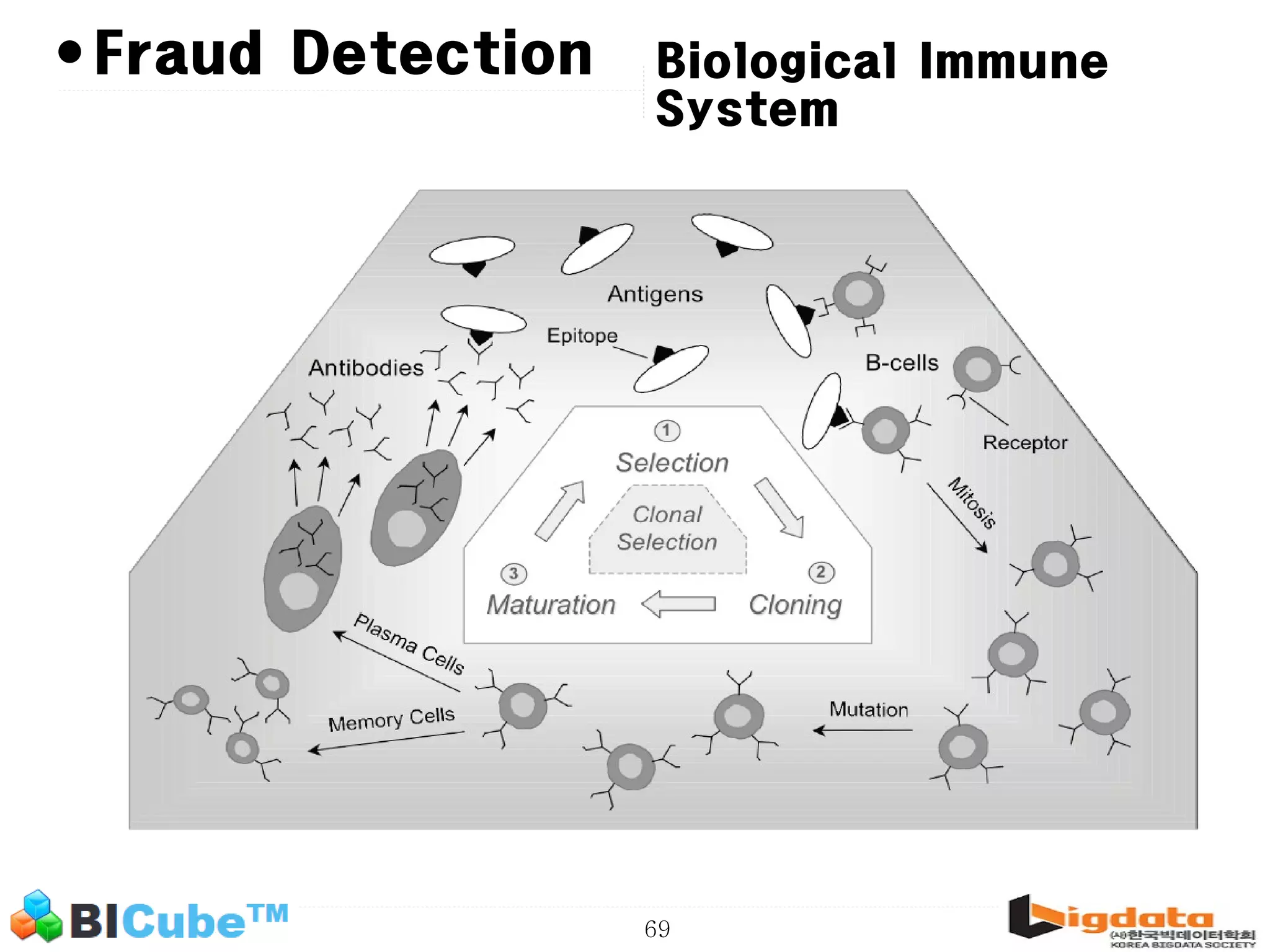
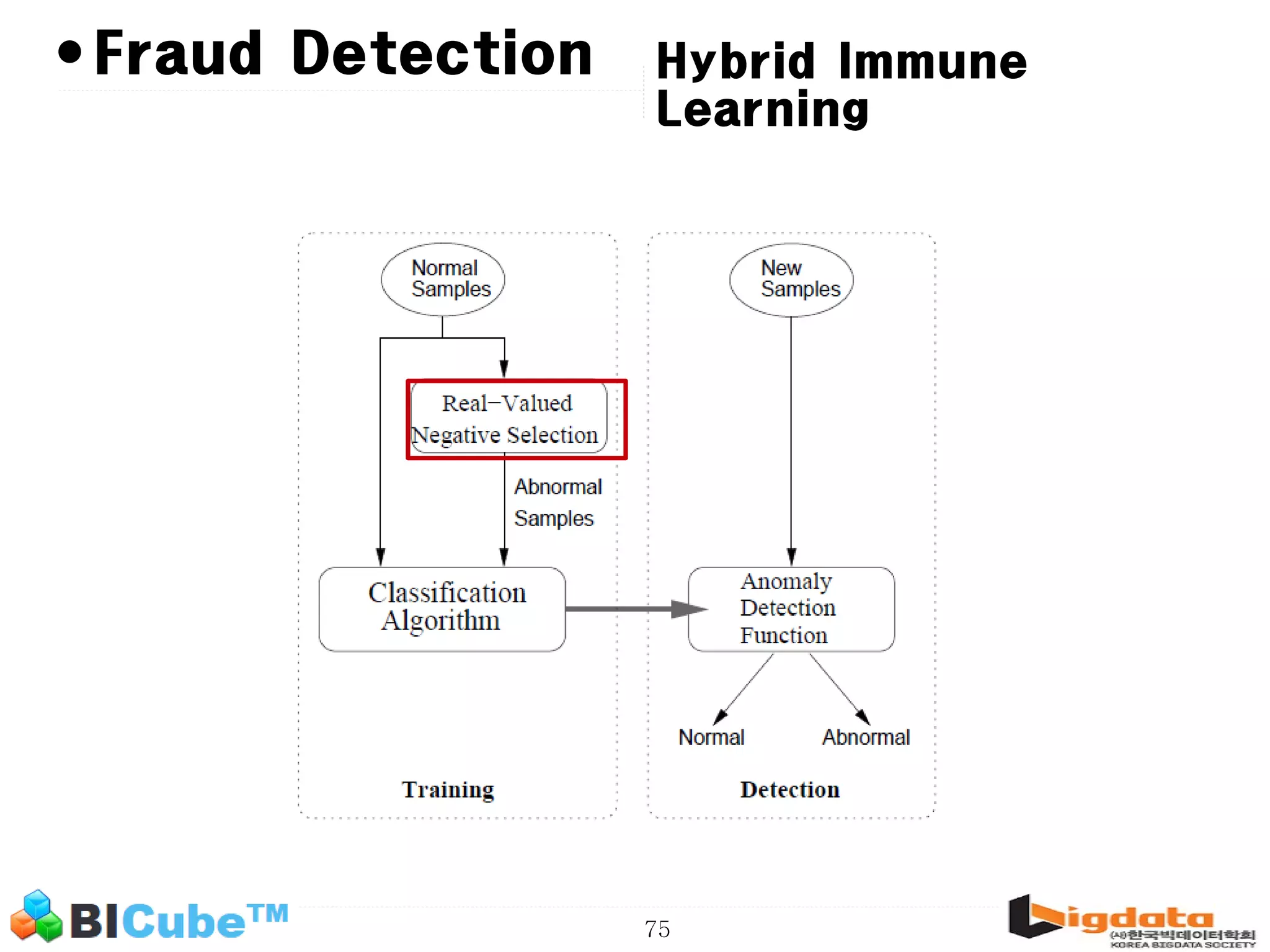
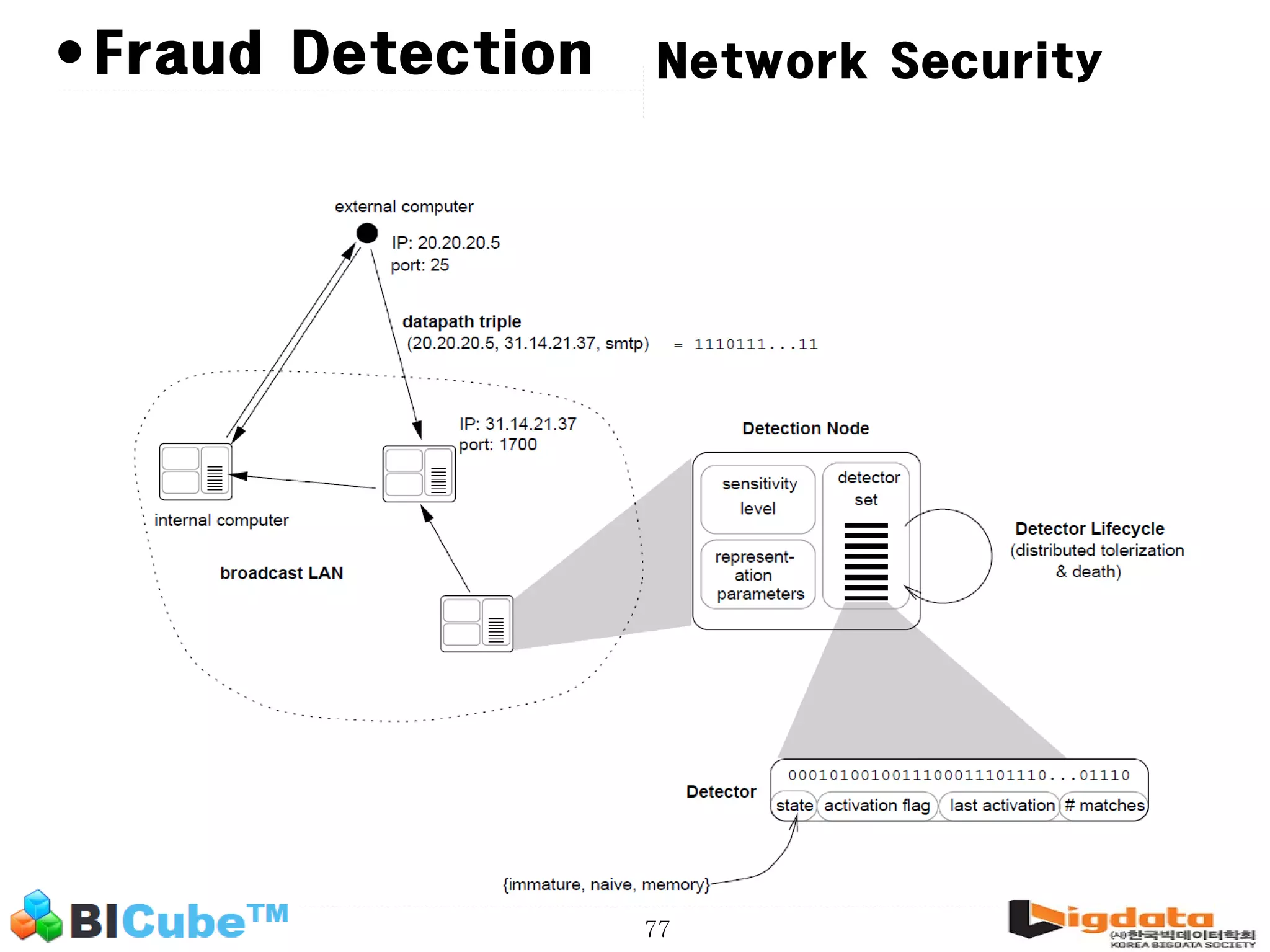
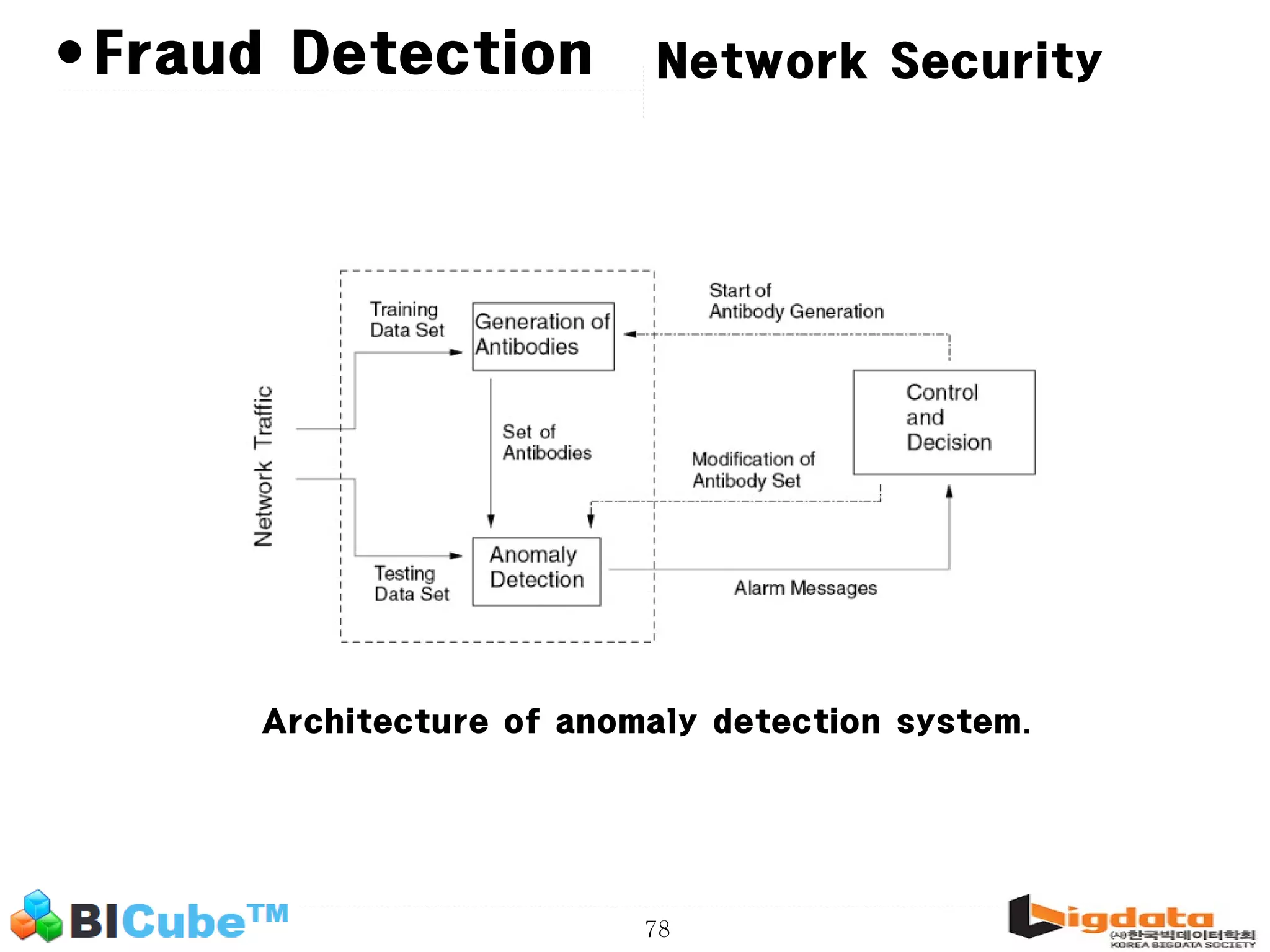
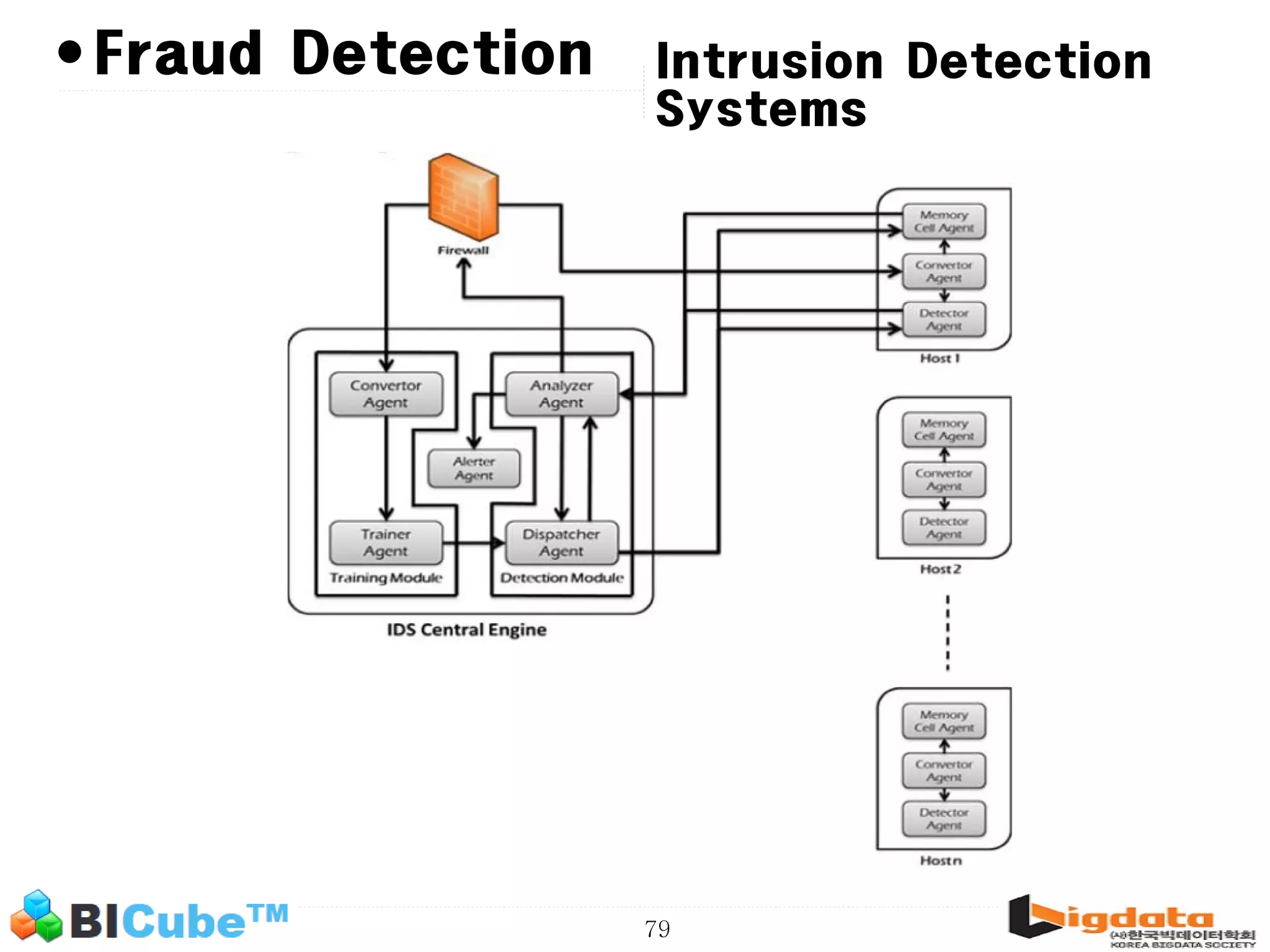
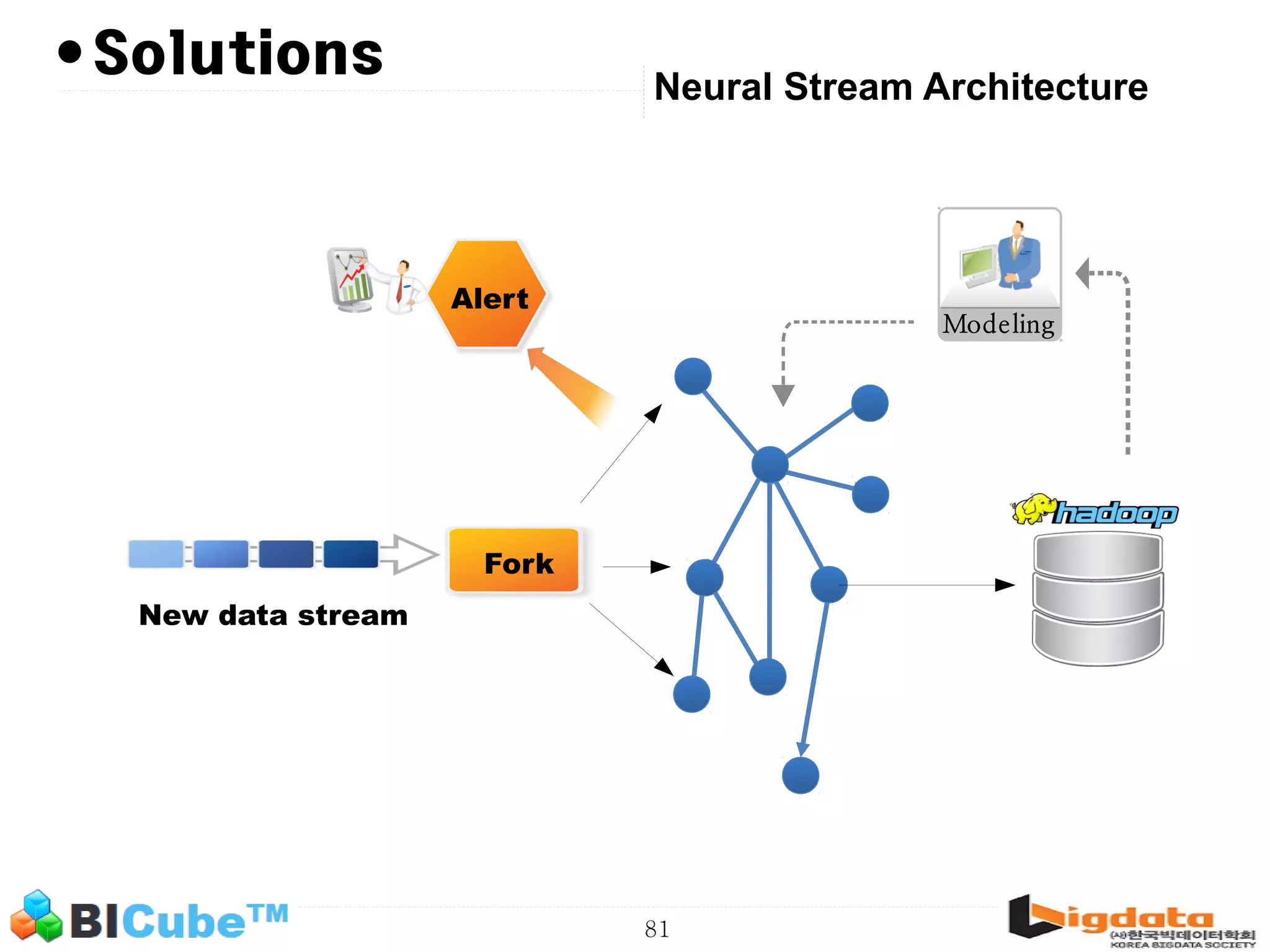
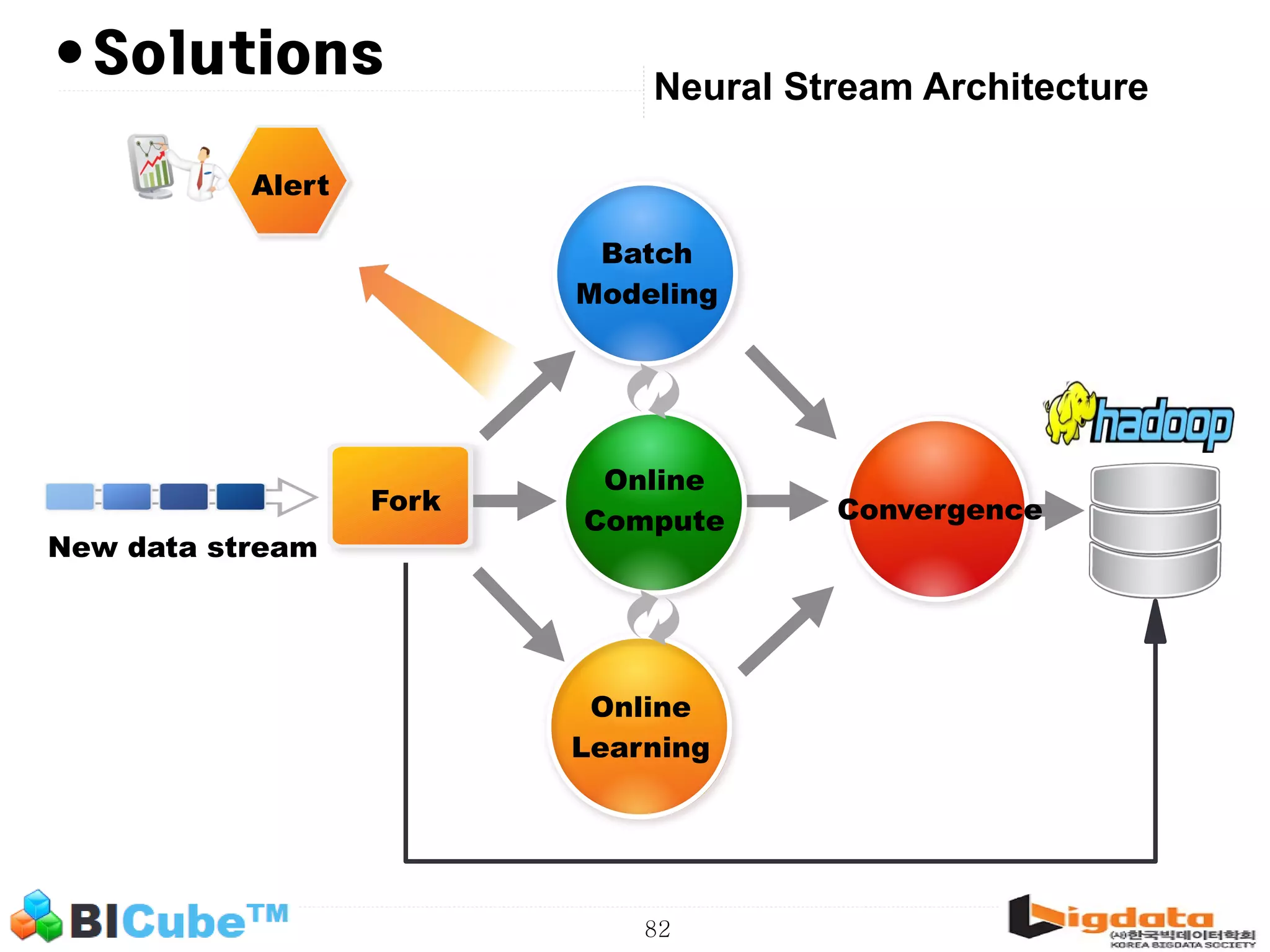
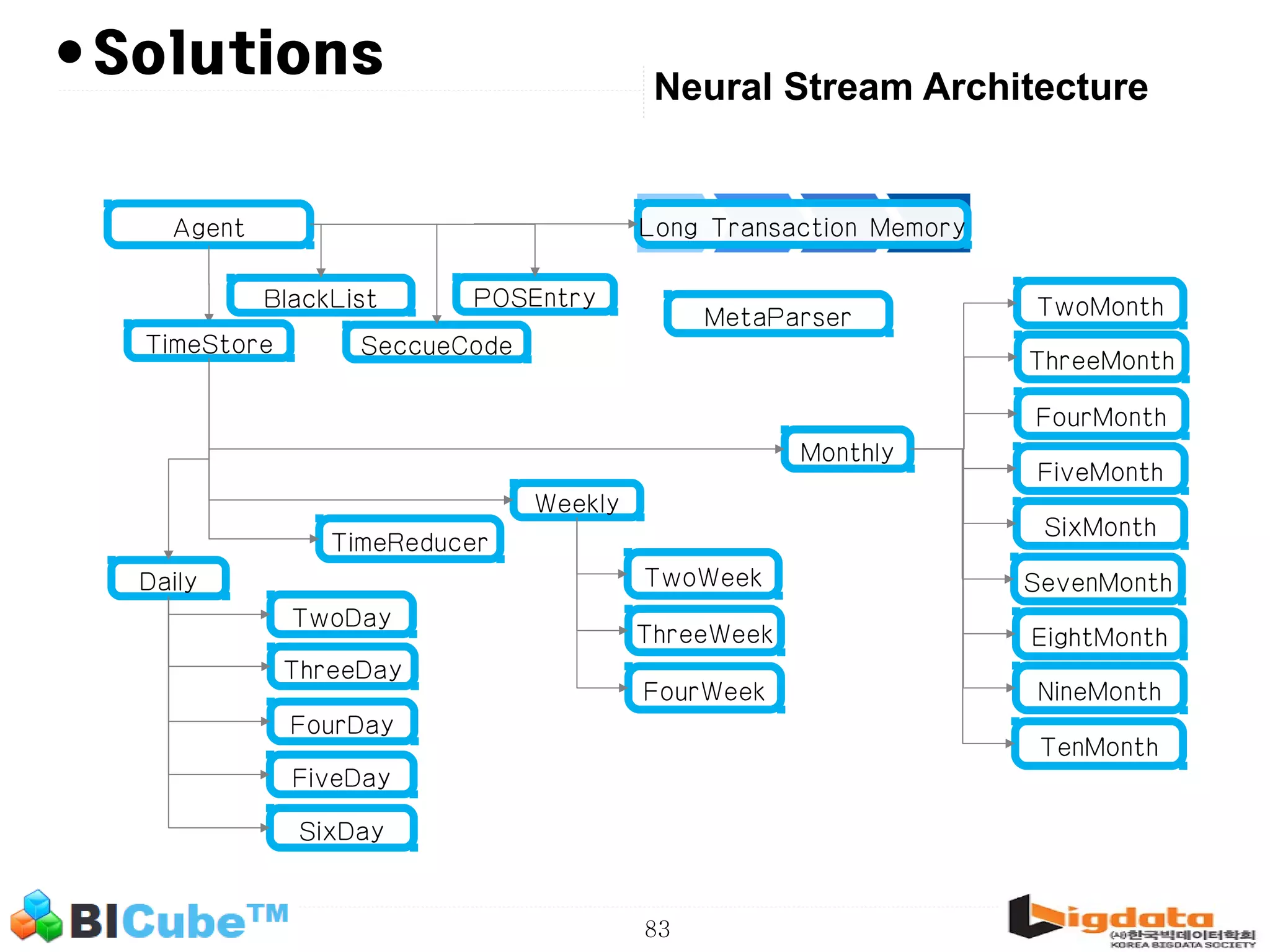
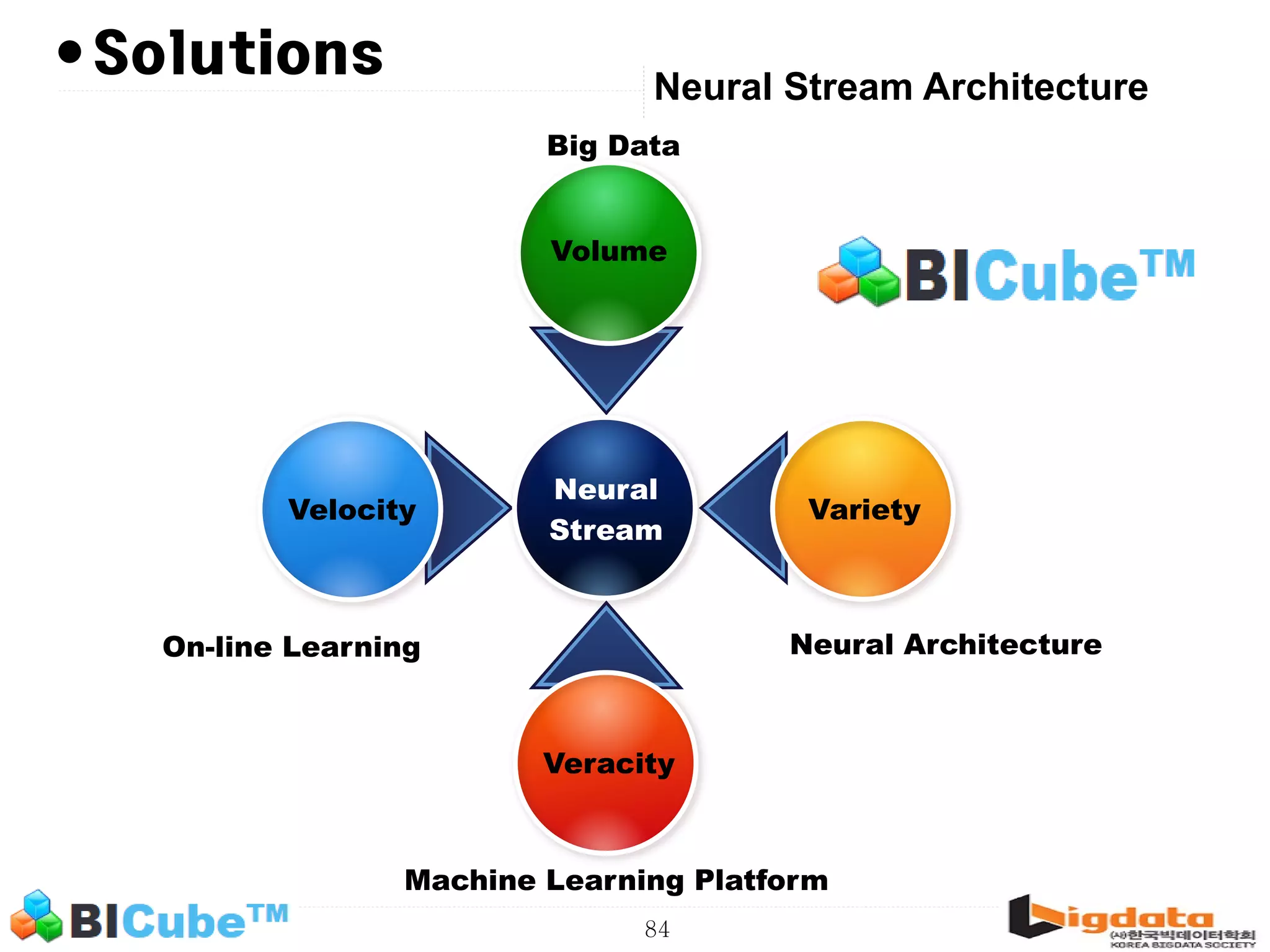
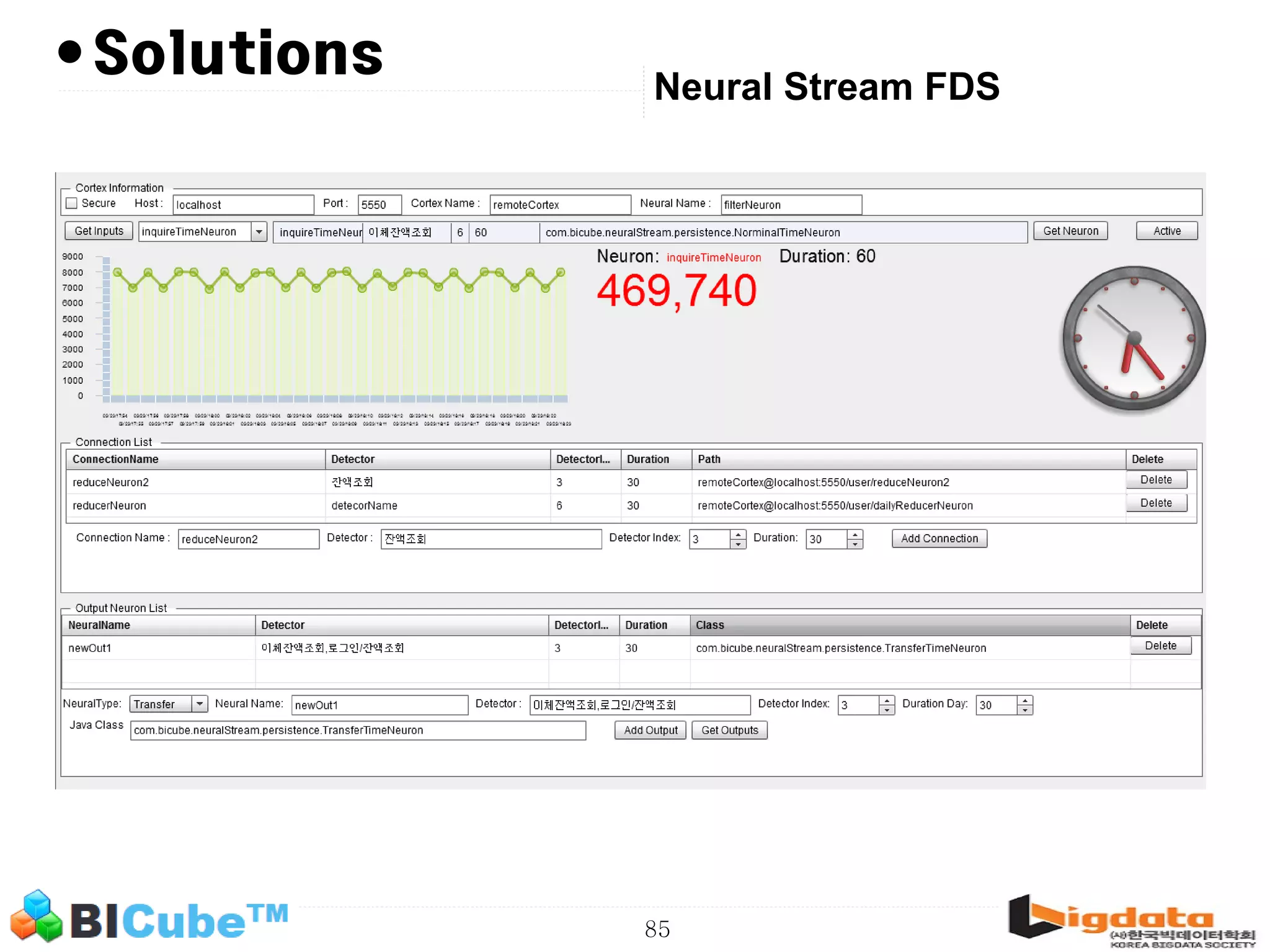
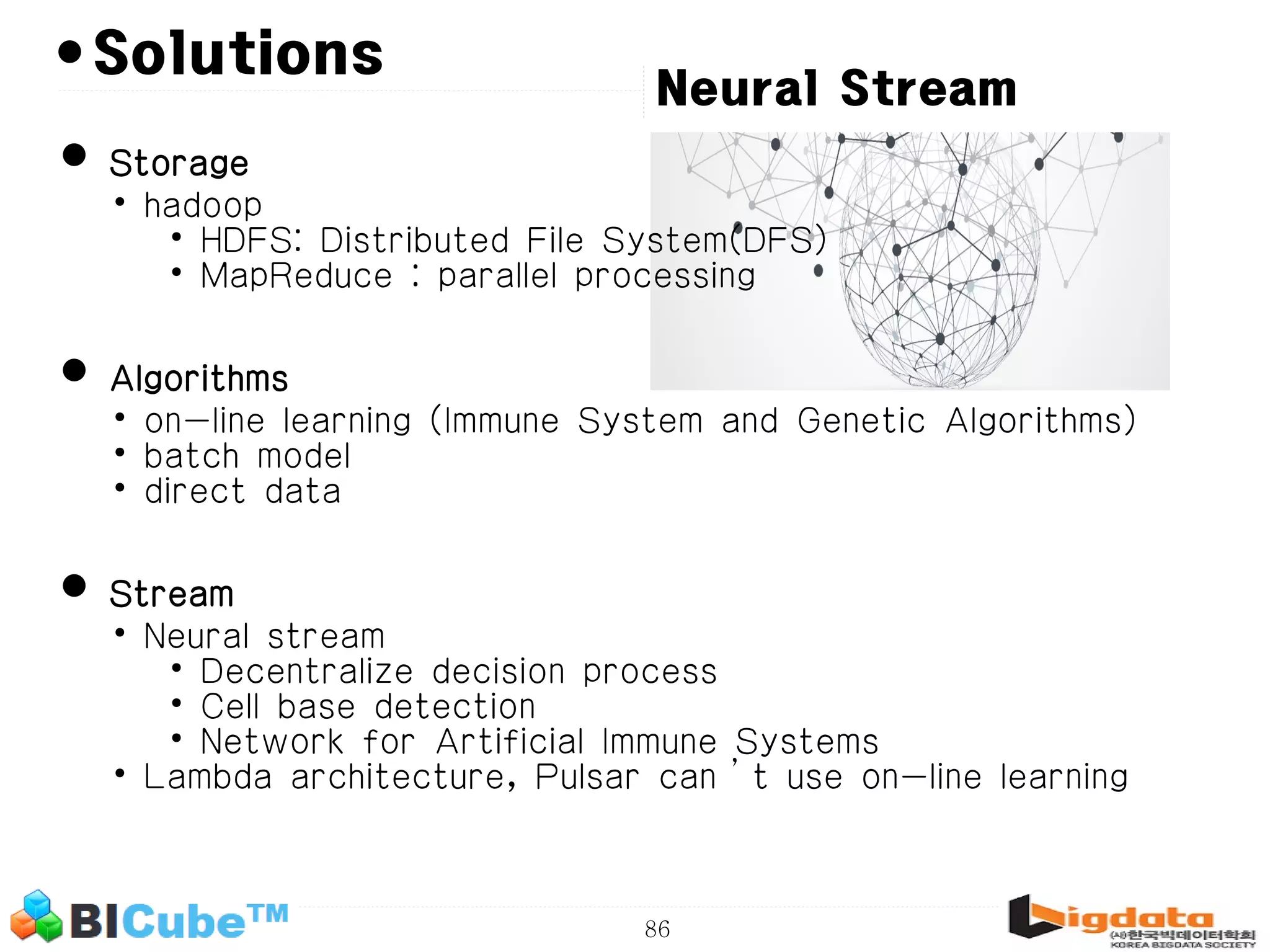
The document discusses big data and machine learning techniques for fraud detection. It covers topics like big data ecosystems, Lambda architecture, real-time processing, machine learning algorithms like decision trees and neural networks, and challenges of fraud detection like processing billions of transactions in real-time. Fraud detection requires monitoring all transactions in real-time to detect unusual patterns and block compromised cards as quickly as possible to prevent fraud.