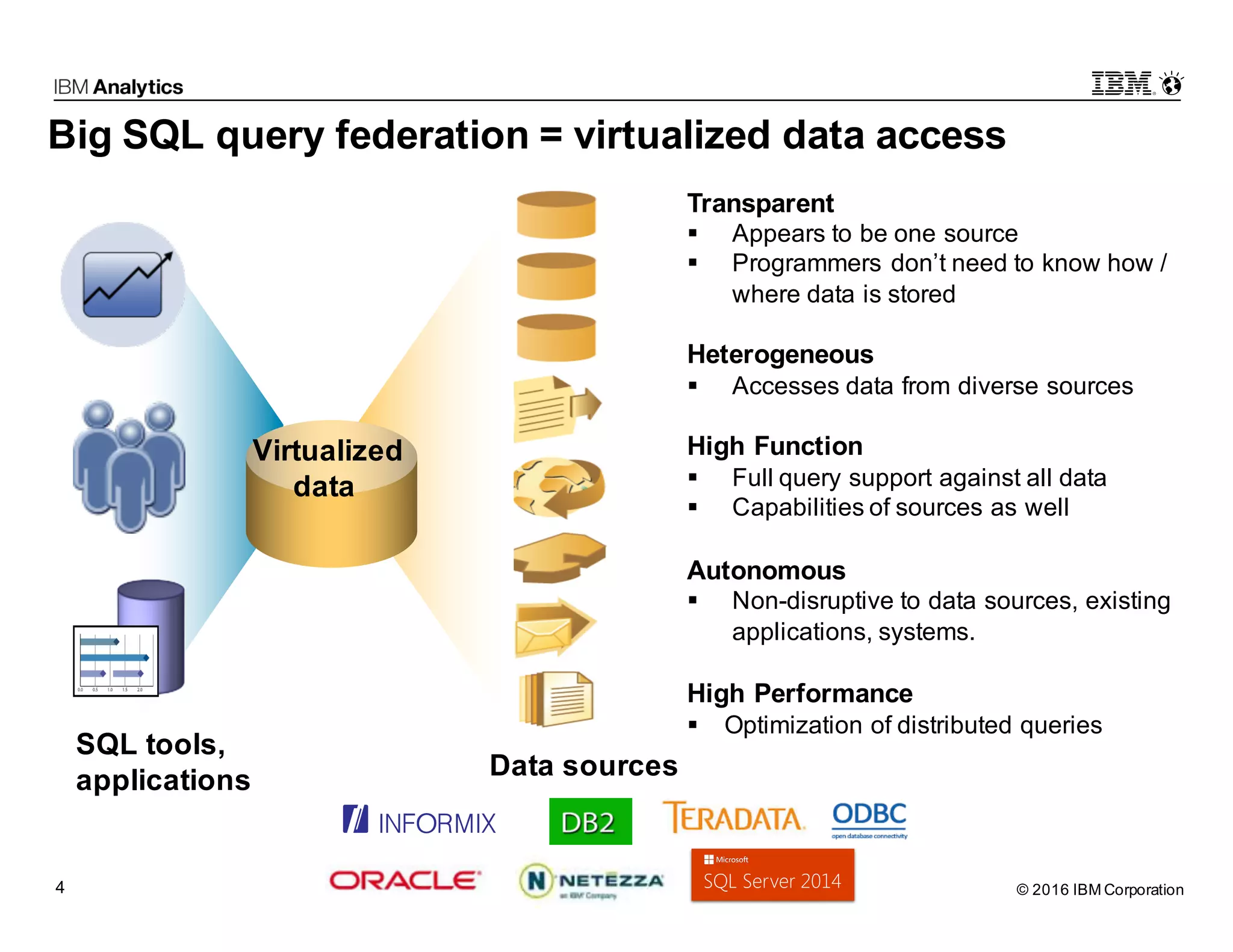
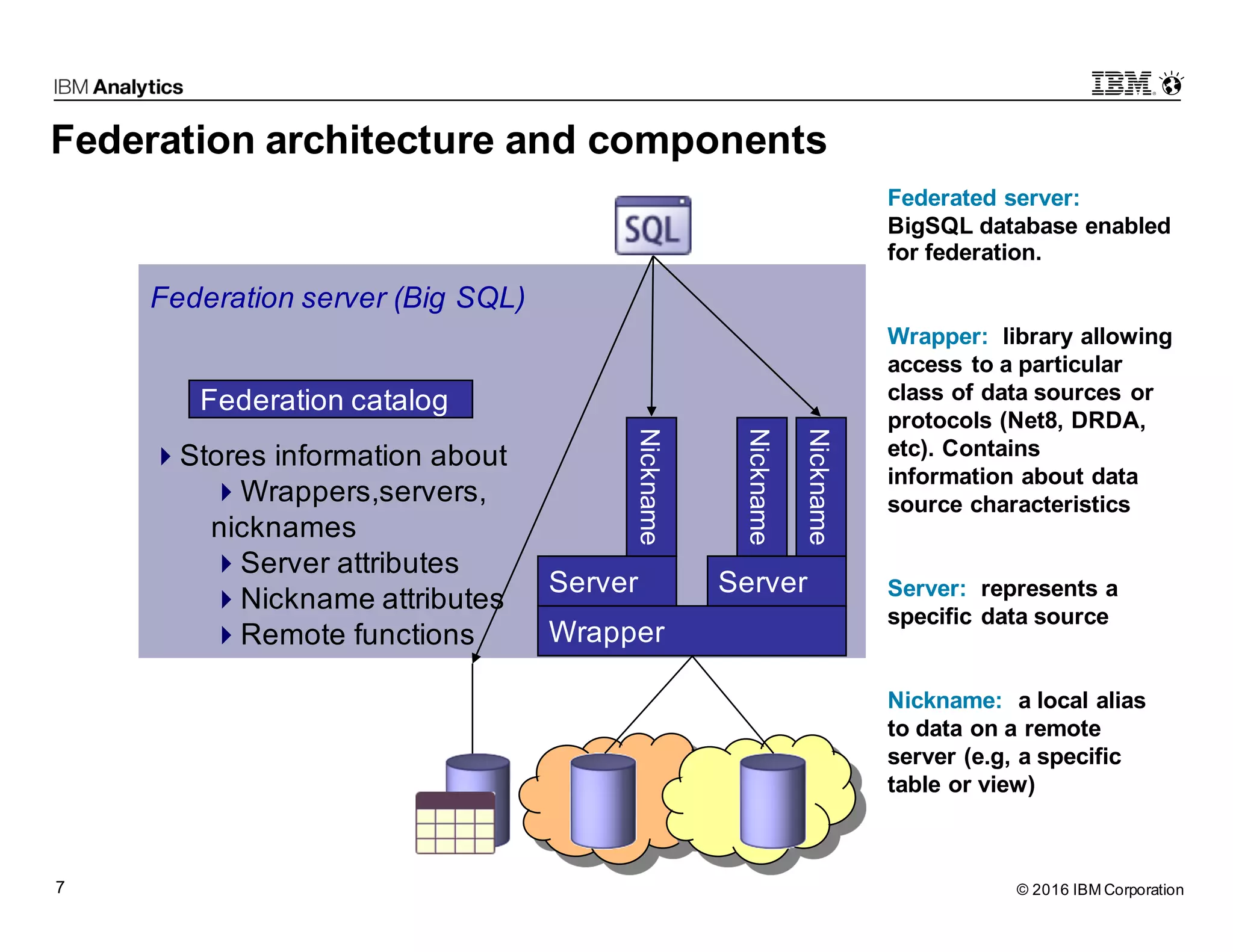
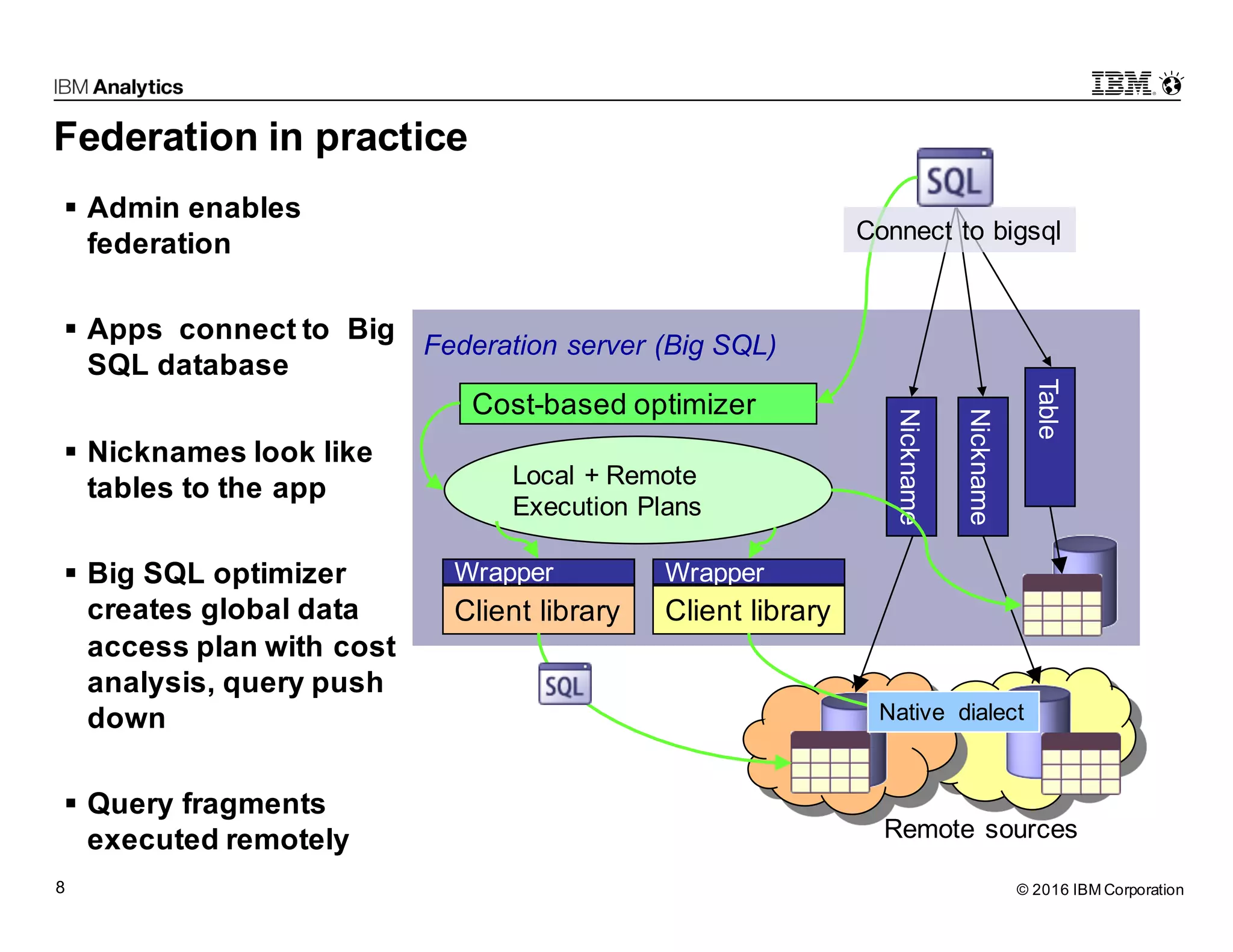
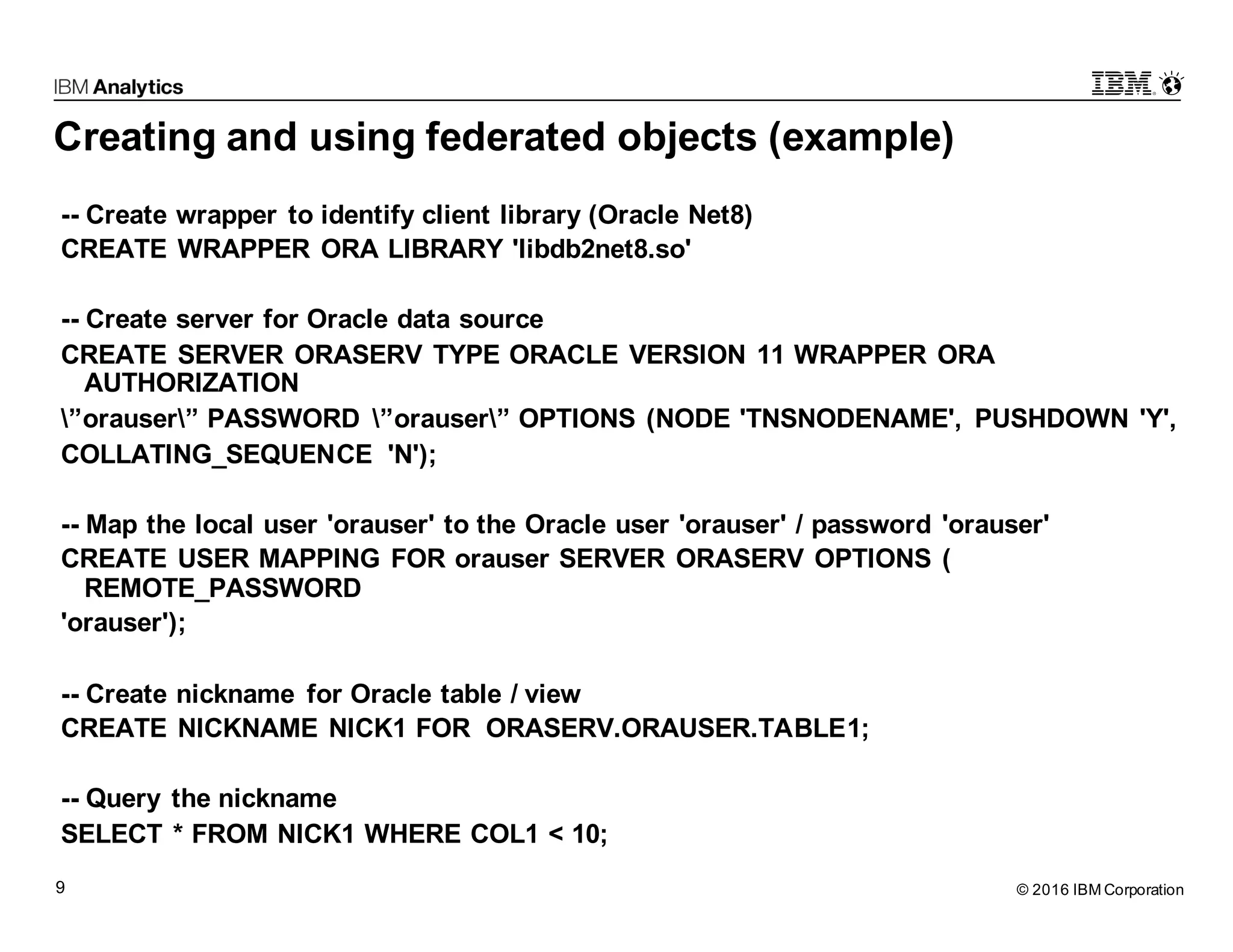
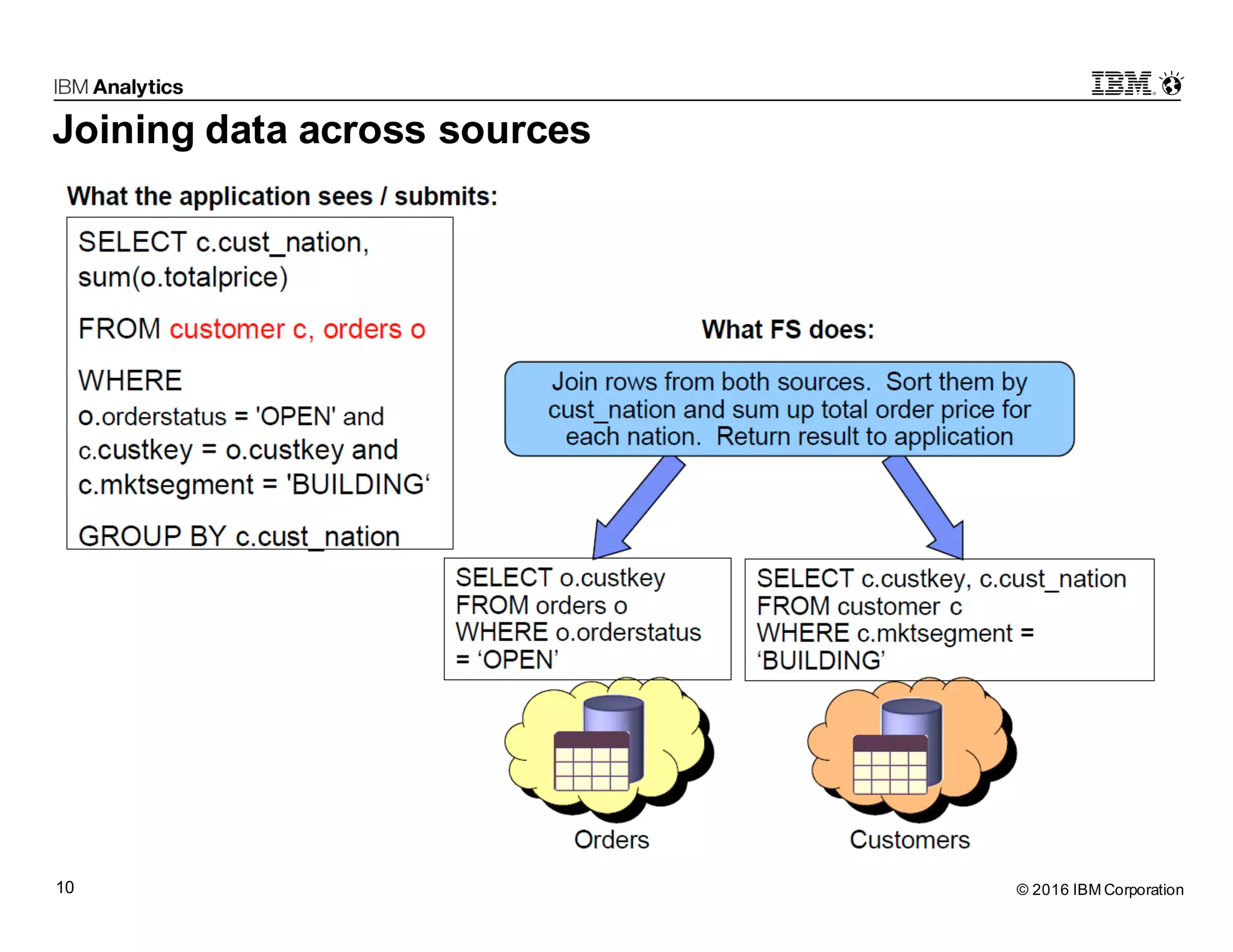
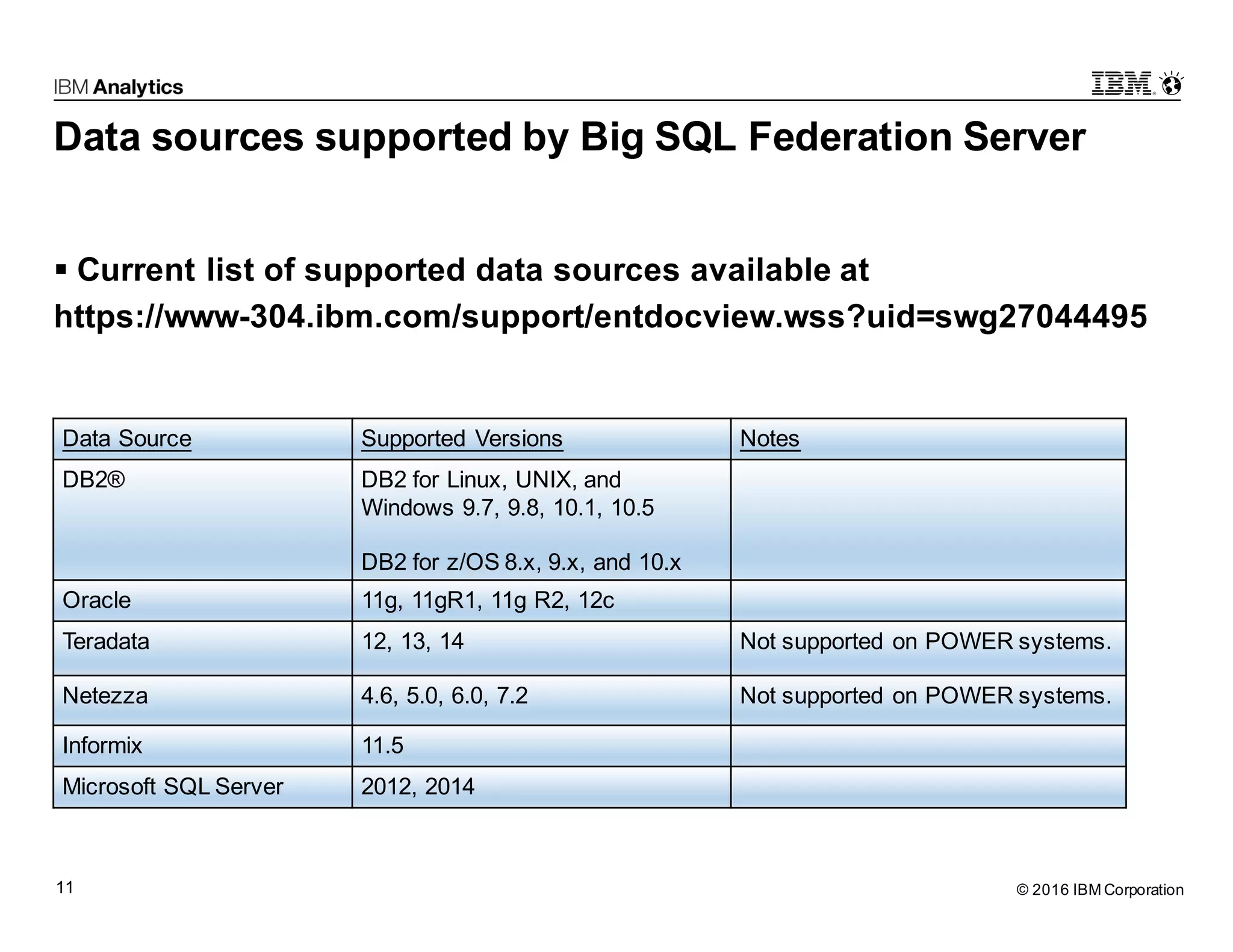
Big SQL Federation is an integration technology that allows users to transparently query data from Hadoop and various remote relational database sources using standard SQL. It offers key features such as full query support, optimization for distributed queries, and access to a wide range of data sources, making it valuable for analytics and data integration. The document outlines the architecture, setup, and use cases for federating queries across disparate data sources without the need for physical integration.