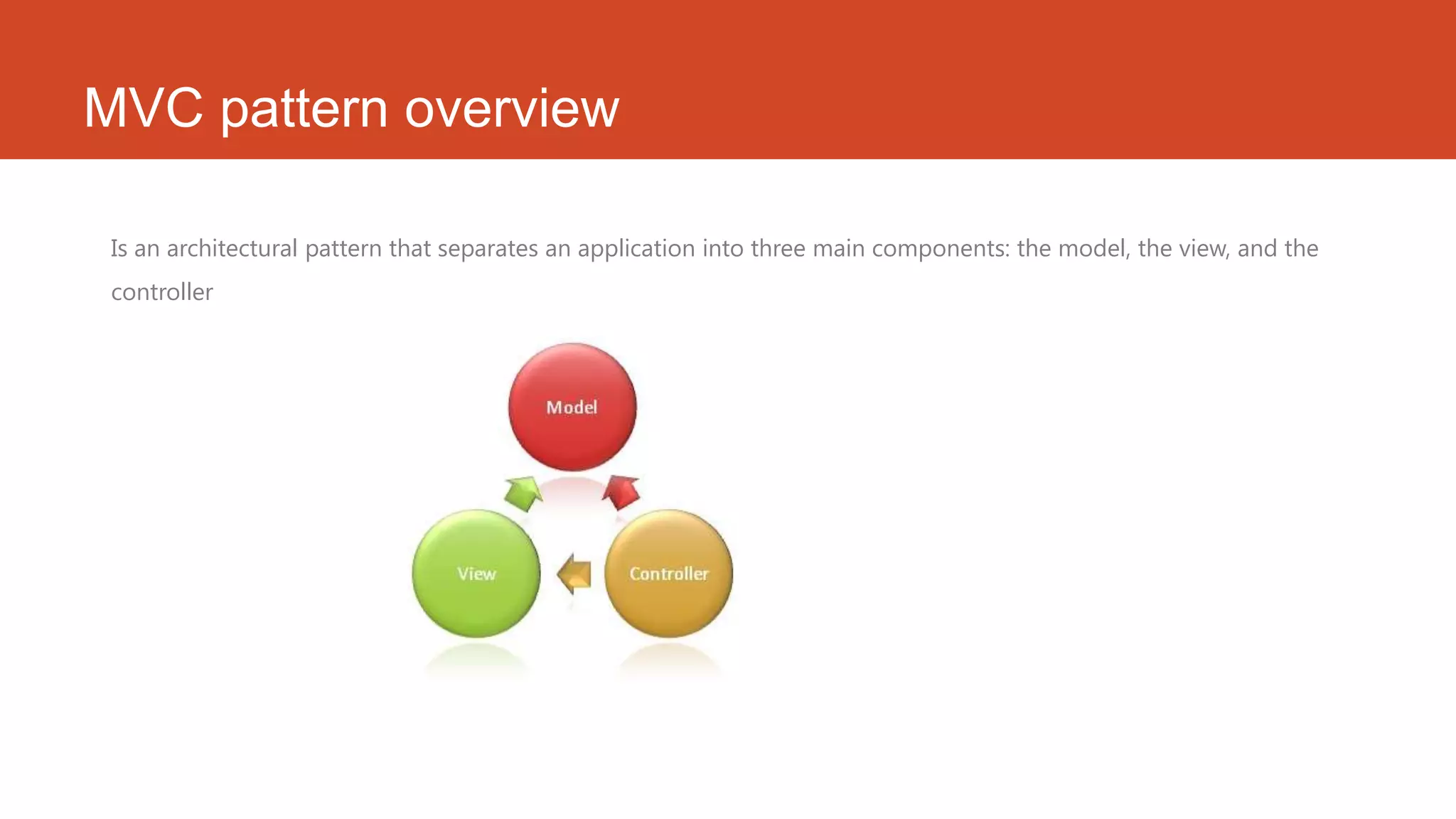
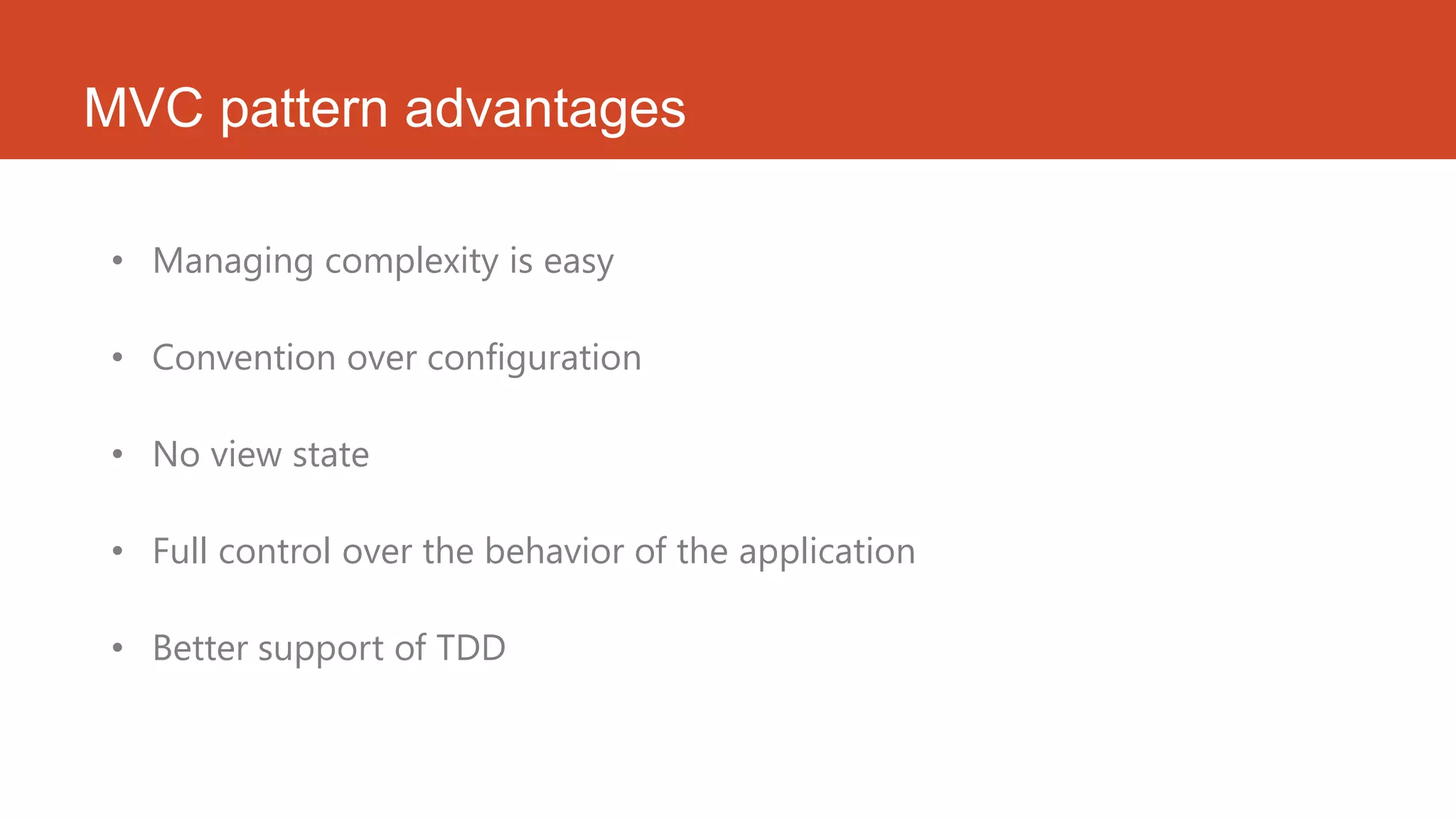
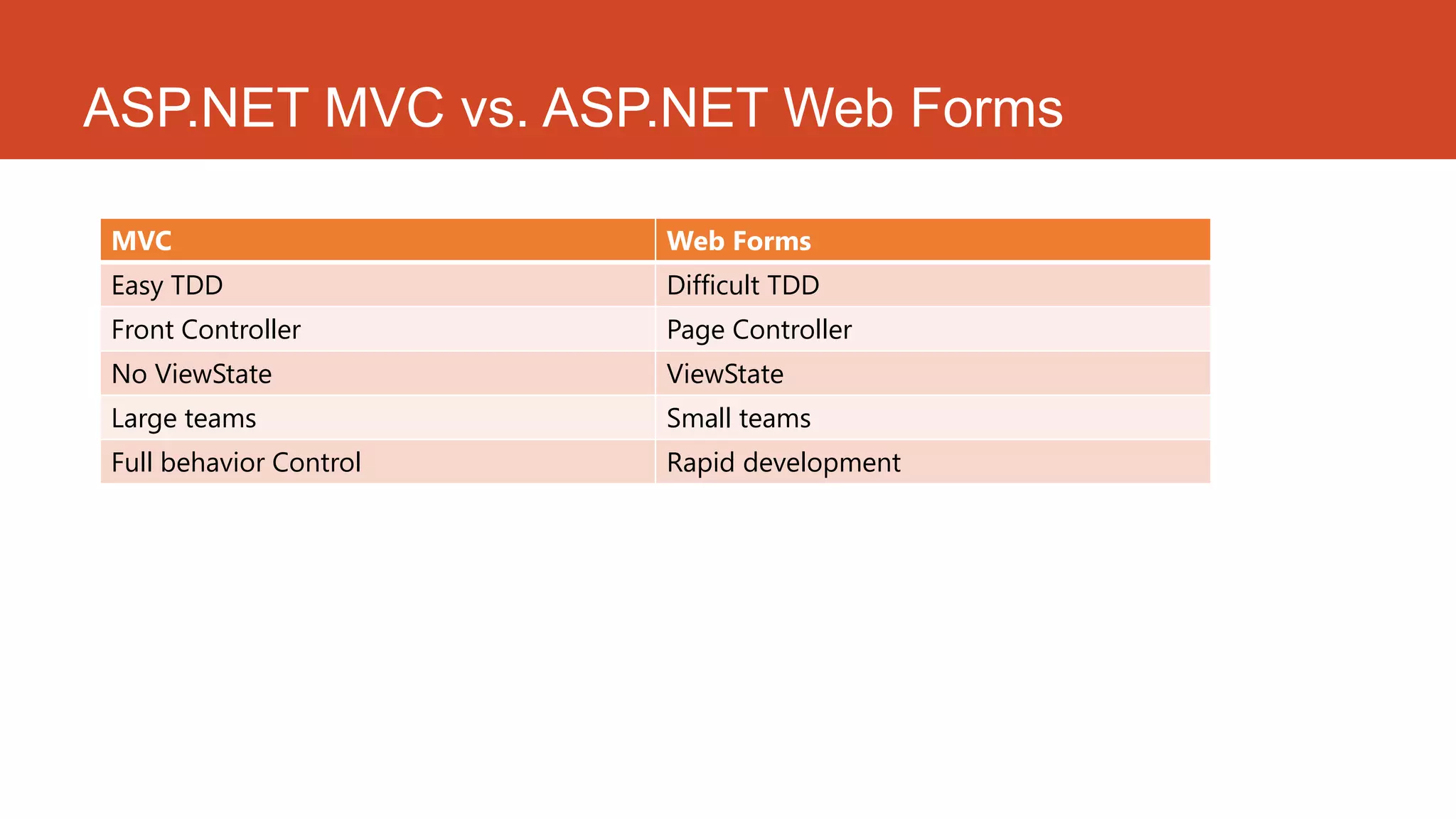
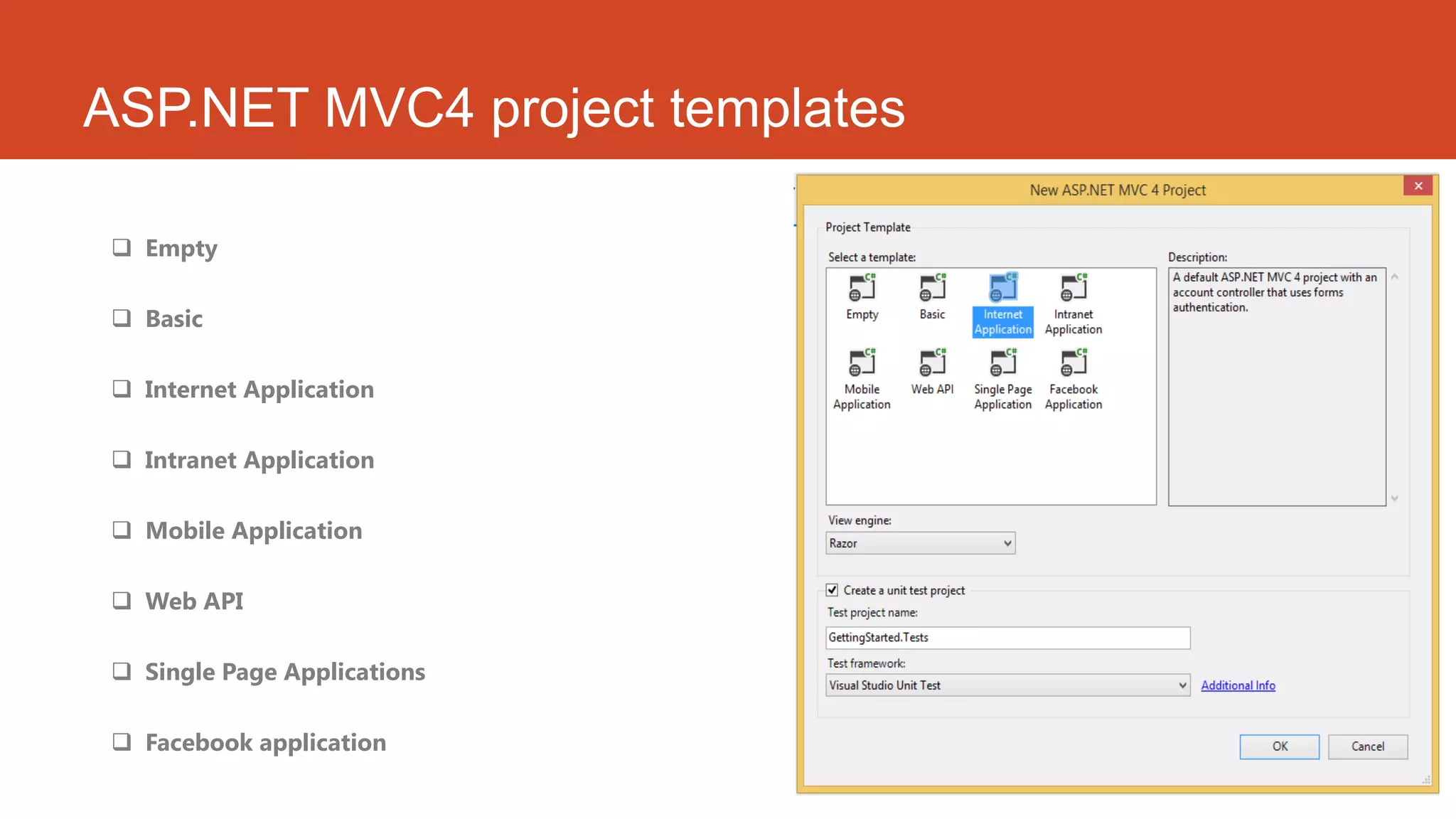
ASP.NET MVC is a web application framework that follows the model-view-controller pattern. It separates an application into three main components: the model, the view, and the controller. ASP.NET MVC provides advantages like managing complexity easily, following convention over configuration, giving full control over application behavior, and supporting test-driven development well. ASP.NET MVC 4 introduced new features like ASP.NET web API, project template enhancements, mobile project templates, display modes, and bundling/minification.