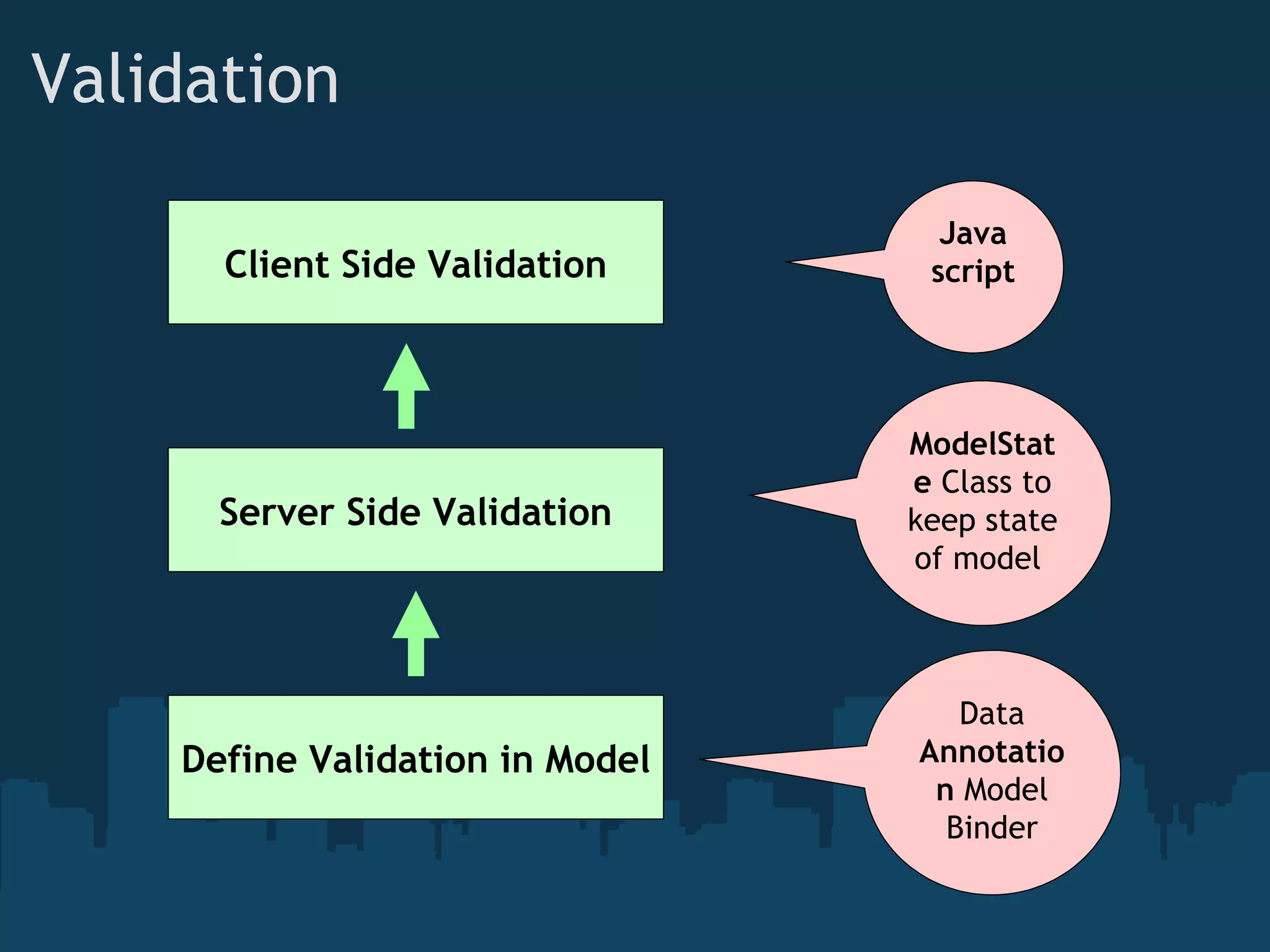
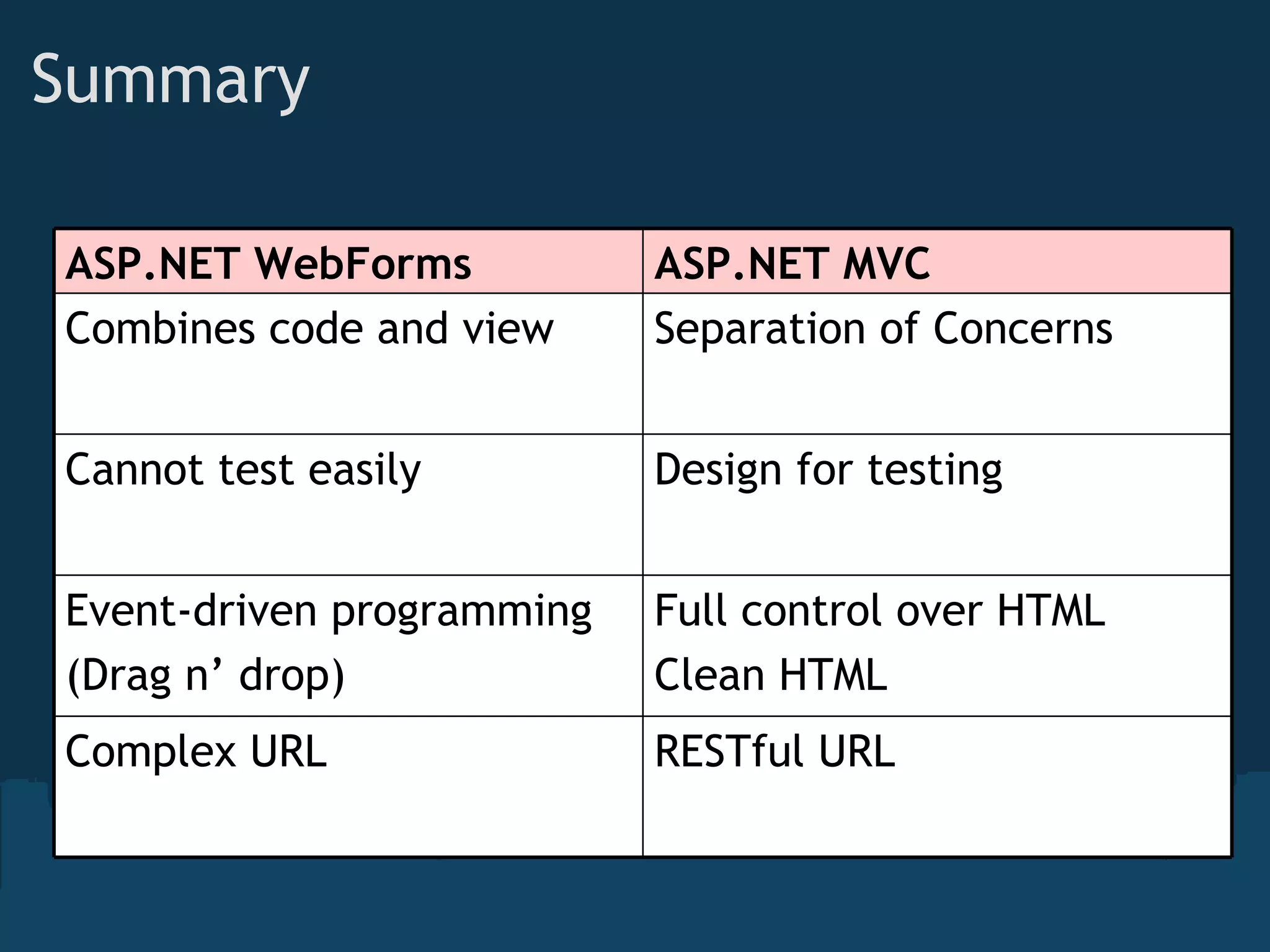
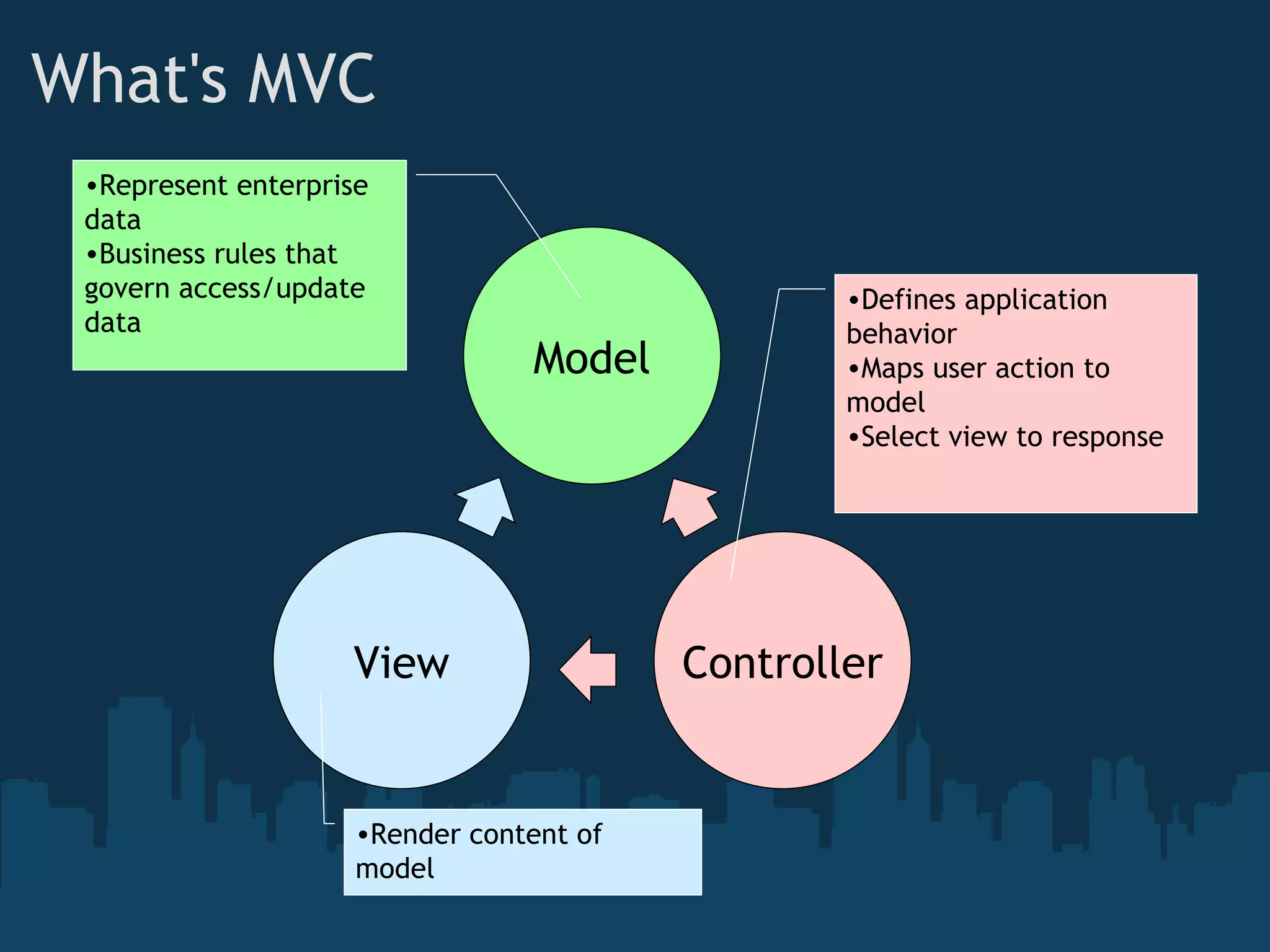
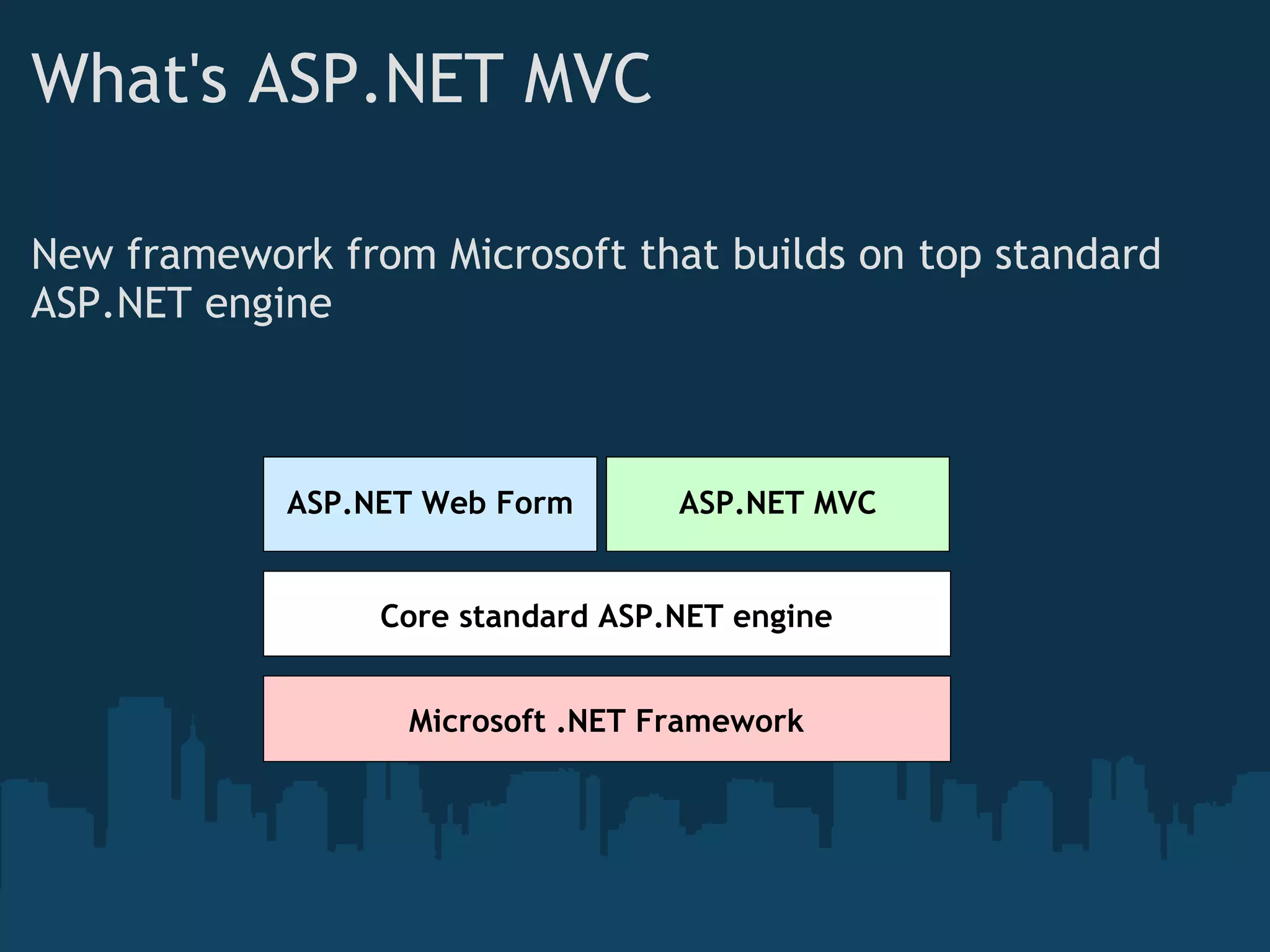
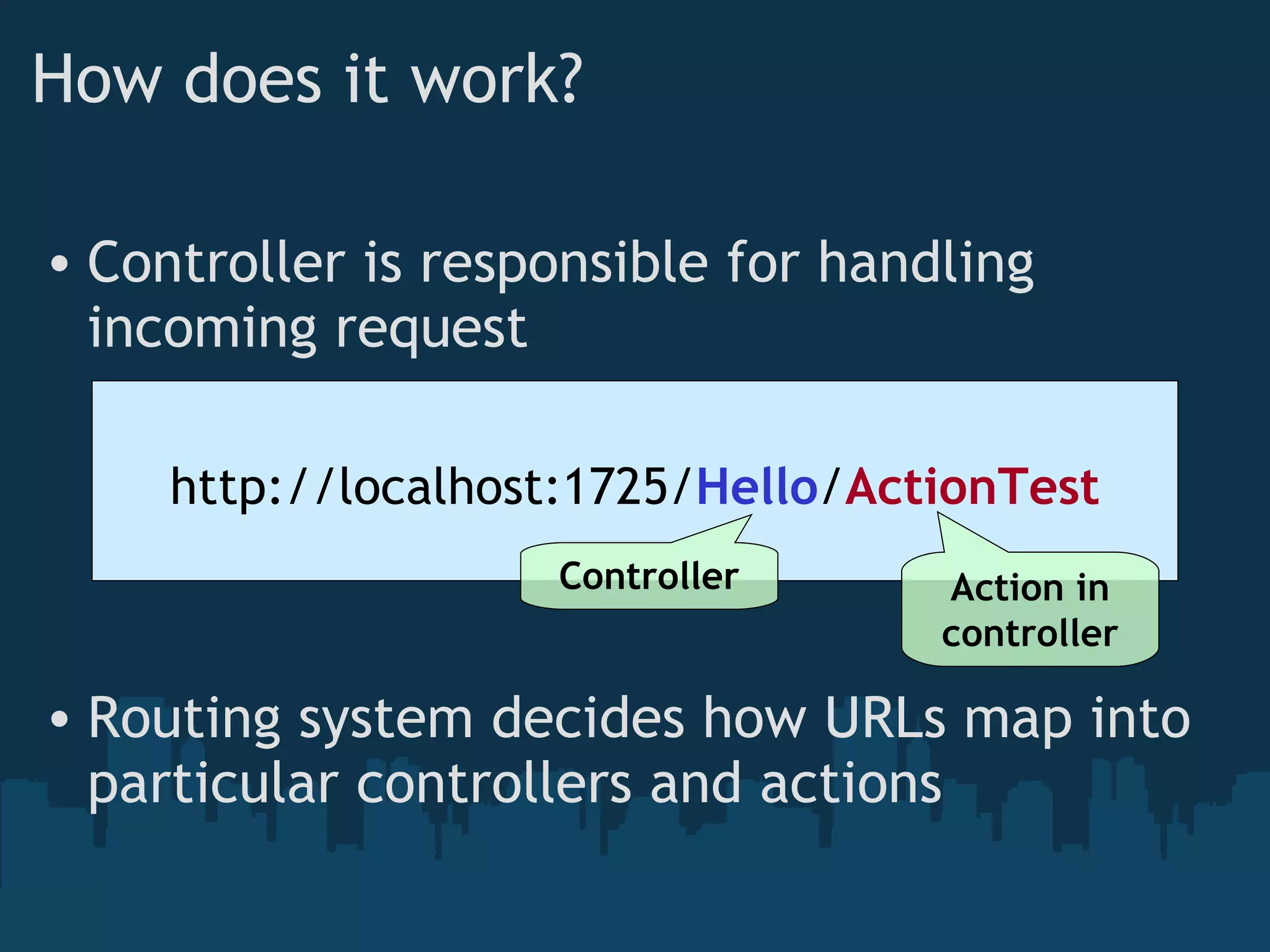
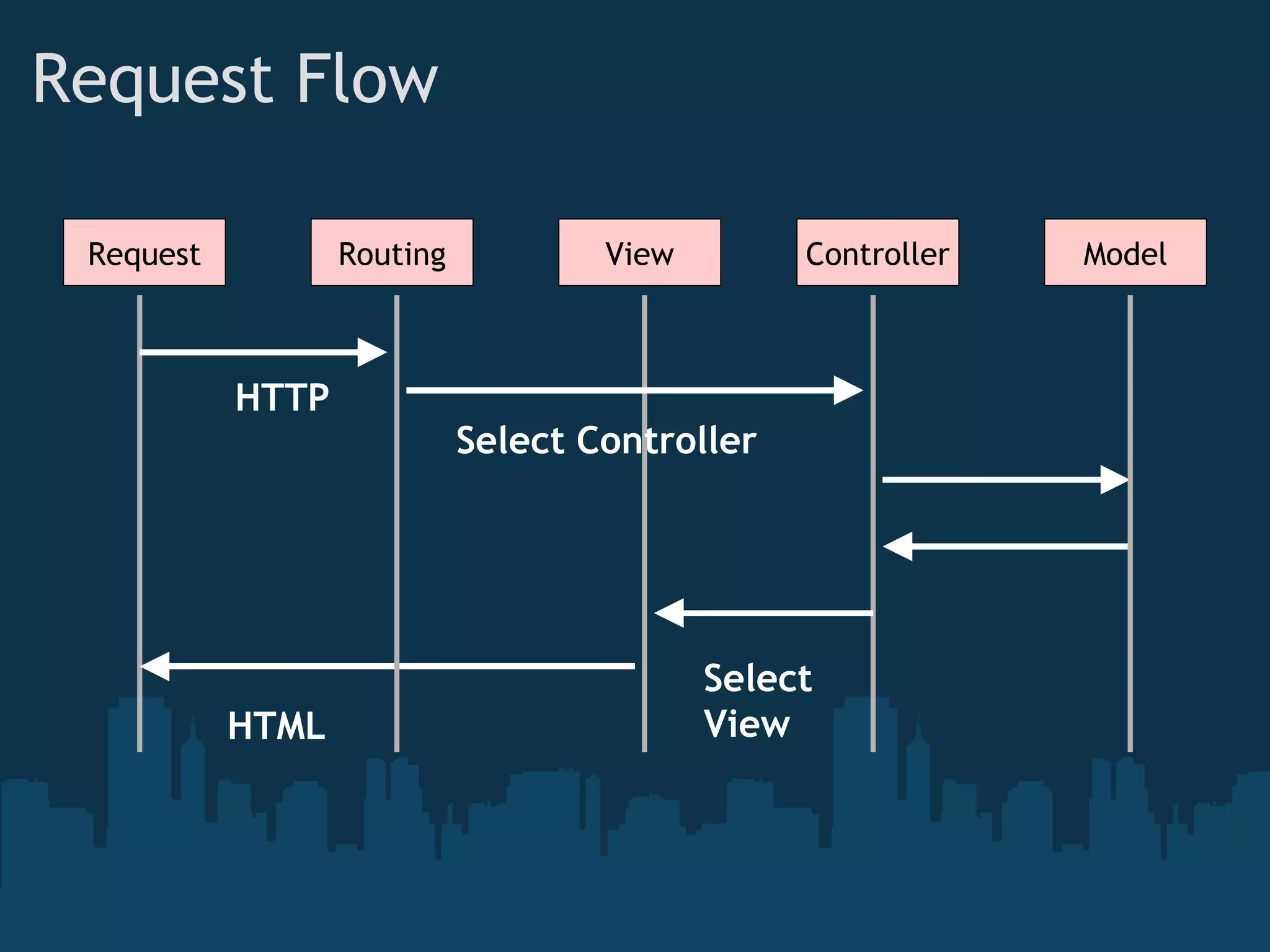
The document introduces ASP.NET MVC, which is a framework from Microsoft that builds on the standard ASP.NET engine. It follows the model-view-controller (MVC) pattern to separate application behavior, user interface, and data access. The goals of ASP.NET MVC include testability, friendly URLs, leveraging existing ASP.NET features, and full control of HTML. It also discusses how ASP.NET MVC works, including routing, controllers, actions, and views. Demos are provided for basic routing and controllers as well as models, HTML helpers, forms, and validation.










![Request variable Action method parameter ModelBinder Handling post request Public ActionResult Create() { string subject = Request.Form[“Subject”]; } Public ActionResult Create( string Subject ) { // do something } Public ActionResult Create( Commentary commentary ) { // do something }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aspnetmvc-091216083112-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-ASP-NET-MVC-15-2048.jpg)