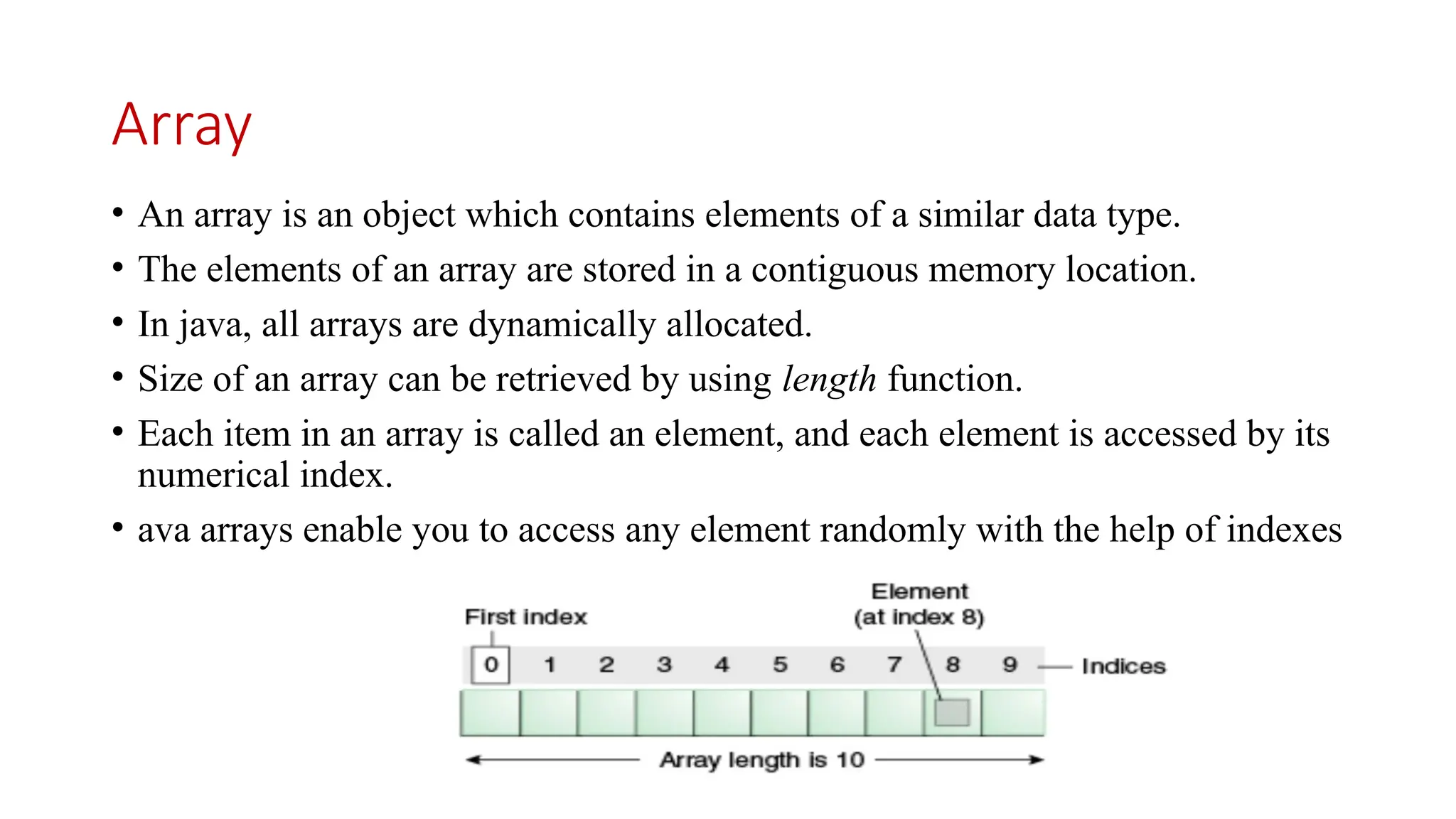
The primary distinction between an Array and a String is that an Array is a data structure that includes a collection of elements with the same data type, whereas a String is a collection of characters. Arrays and strings are supported by programming languages, including C.


![One-Dimensional Arrays A one-dimensional array is, essentially, a list of similar-typed values. Syntax type variable_name[ ]; or type[] variable_name; Example int student_roll[]; or int[] student_roll; student_roll = new int[12];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysandstrings1-250304034232-b2a492a9/75/Arrays-and-Strings-engineering-education-4-2048.jpg)
![Different ways of initializing array int student_roll[] = new int[4]; student_roll[0]=100; student_roll[1]=101; student_roll[3]=102; student_roll[4]=103; int student_roll[] = {100, 101, 102, 103}; int student_roll[] = new int[]{100, 101, 102, 103};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysandstrings1-250304034232-b2a492a9/75/Arrays-and-Strings-engineering-education-5-2048.jpg)
![// Average an array of values. class Average { public static void main(String args[]) { double nums[] = {10.1, 11.2, 12.3, 13.4, 14.5}; double result = 0; int i; for(i=0; i<nums.length; i++) result = result + nums[i]; System.out.println("Average is " + (result / 5)); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysandstrings1-250304034232-b2a492a9/75/Arrays-and-Strings-engineering-education-6-2048.jpg)
![Multidimensional Arrays In Java, multidimensional arrays are actually arrays of arrays. int twoD[][] = new int[4][5];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysandstrings1-250304034232-b2a492a9/75/Arrays-and-Strings-engineering-education-7-2048.jpg)
![// Demonstrate a two-dimensional array. class TwoDArray { public static void main(String args[]) { int twoD[][]= new int[4][5]; int i, j, k = 0; for(i=0; i<4; i++) for(j=0; j<5; j++) { twoD[i][j] = k; k++; } for(i=0; i<4; i++) { for(j=0; j<5; j++) System.out.print(twoD[i][j] + " "); System.out.println(); } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysandstrings1-250304034232-b2a492a9/75/Arrays-and-Strings-engineering-education-8-2048.jpg)
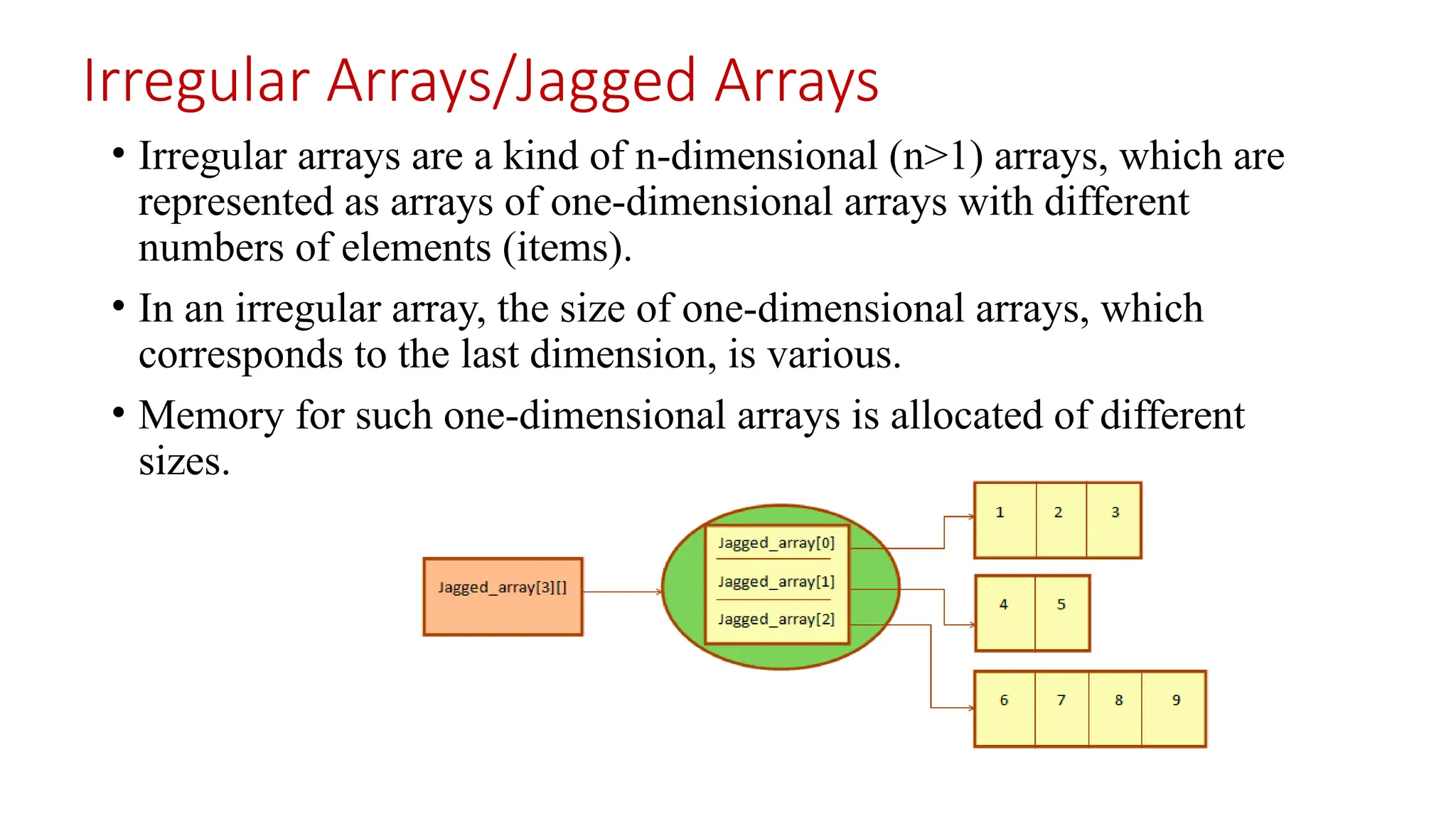
![int[][] A = new int[3][5]; // regular array int[][] B = new int[3][]; // irregular two-dimensional array int[][][] C = new int[3][4][]; // irregular three-dimensional array int[][][] D = new int[3][][]; // irregular three-dimensional array int[][][] E = new int[][][]; // error](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysandstrings1-250304034232-b2a492a9/75/Arrays-and-Strings-engineering-education-10-2048.jpg)
![public class JaggedDemo { public static void main(String args[]){ int[][] arr = new int[2][]; //first row has 3 columns arr[0] = new int[3]; //second row has 4 columns arr[1] = new int[4]; int counter = 0; //initializing array for(int i=0; i < arr.length; i++){ for(int j=0; j < arr[i].length; j++){ arr[i][j] = counter++; } } //printing array for(int i=0; i < arr.length; i++){ System.out.println(); for(int j=0; j < arr[i].length; j++){ System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " "); } } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysandstrings1-250304034232-b2a492a9/75/Arrays-and-Strings-engineering-education-11-2048.jpg)
![Array References class ArrayDemo{ public static void main(String args[]) { int arr1[] = new int[10]; int arr2[] = new int[10]; int i; System.out.println("Entering arr1 elements:"); for(i=0; i<10;i++){ arr1[i]=i; } System.out.println("Entering arr2 elements:"); for(i=0; i<10;i++){ arr2[i]=-i; } System.out.println("Array 1 elements are:"); for(i=1; i<10;i++){ System.out.println(arr1[i]); } System.out.println("Array 2 elements are:"); for(i=0; i<10;i++){ System.out.println(arr2[i]); } arr2=arr1; System.out.println("Array 2 elements are:"); for(i=0; i<10;i++){ System.out.println(arr2[i]); } arr2[3]=50; System.out.println("Array 1 elements are:"); for(i=0; i<10;i++){ System.out.println(arr1[i]); } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysandstrings1-250304034232-b2a492a9/75/Arrays-and-Strings-engineering-education-12-2048.jpg)
![Using the Length Member length is an instance variable of an array object that contains size of the array/ number of elements that the array can hold. class ArrayDemo{ public static void main(String args[]) { int arr1[] = new int[10]; int arr2[] = new int[10]; int i; System.out.println("Entering arr1 elements:"); for(i=0; i<arr1.length;i++){ arr1[i]=i; } System.out.println("Array 1 elements are:"); for(i=1; i<arr1.length;i++){ System.out.println(arr1[i]); } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysandstrings1-250304034232-b2a492a9/75/Arrays-and-Strings-engineering-education-13-2048.jpg)
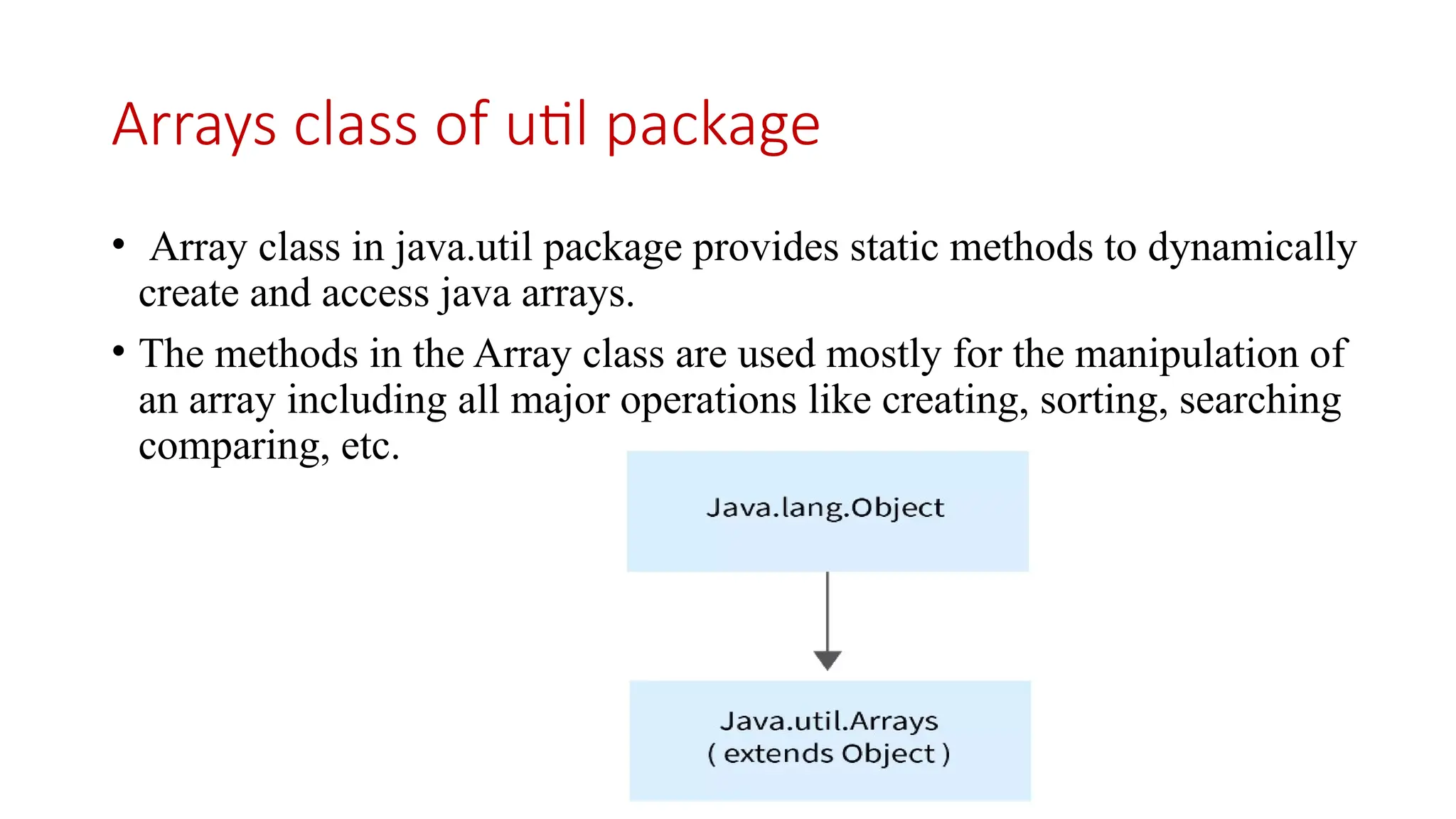
![• java.util.Arrays class provides lot's of methods here, the frequently used and important Arrays class methods are as follows, static int binarySearch(int[] a, int key) - Searches the specified array of ints for the specified value using the binary search algorithm. static boolean deepEquals(Object[] a1, Object[] a2) - Returns true if the two specified arrays are deeply equal to one another. static void fill(int[] a, int val) - Assigns the specified int value to each element of the specified array of ints. static void sort(int[] a) - Sorts the specified array into ascending numerical order. static int[] copyOf(int[] original, int newLength) - Copies the specified array, truncating or padding with zeros (if necessary) so the copy has the specified length. static String toString(int[] a) - Returns a string representation of the contents of the specified array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysandstrings1-250304034232-b2a492a9/75/Arrays-and-Strings-engineering-education-15-2048.jpg)
![Example program import java.util.Arrays; public class Scaler { public static void main(String[] args) { int Arr[] = { 10, 20, 11, 21, 31 }; Arrays.sort(Arr); int Key = 31; System.out.println( Key + " found at index = " + Arrays.binarySearch(Arr, Key)); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysandstrings1-250304034232-b2a492a9/75/Arrays-and-Strings-engineering-education-16-2048.jpg)

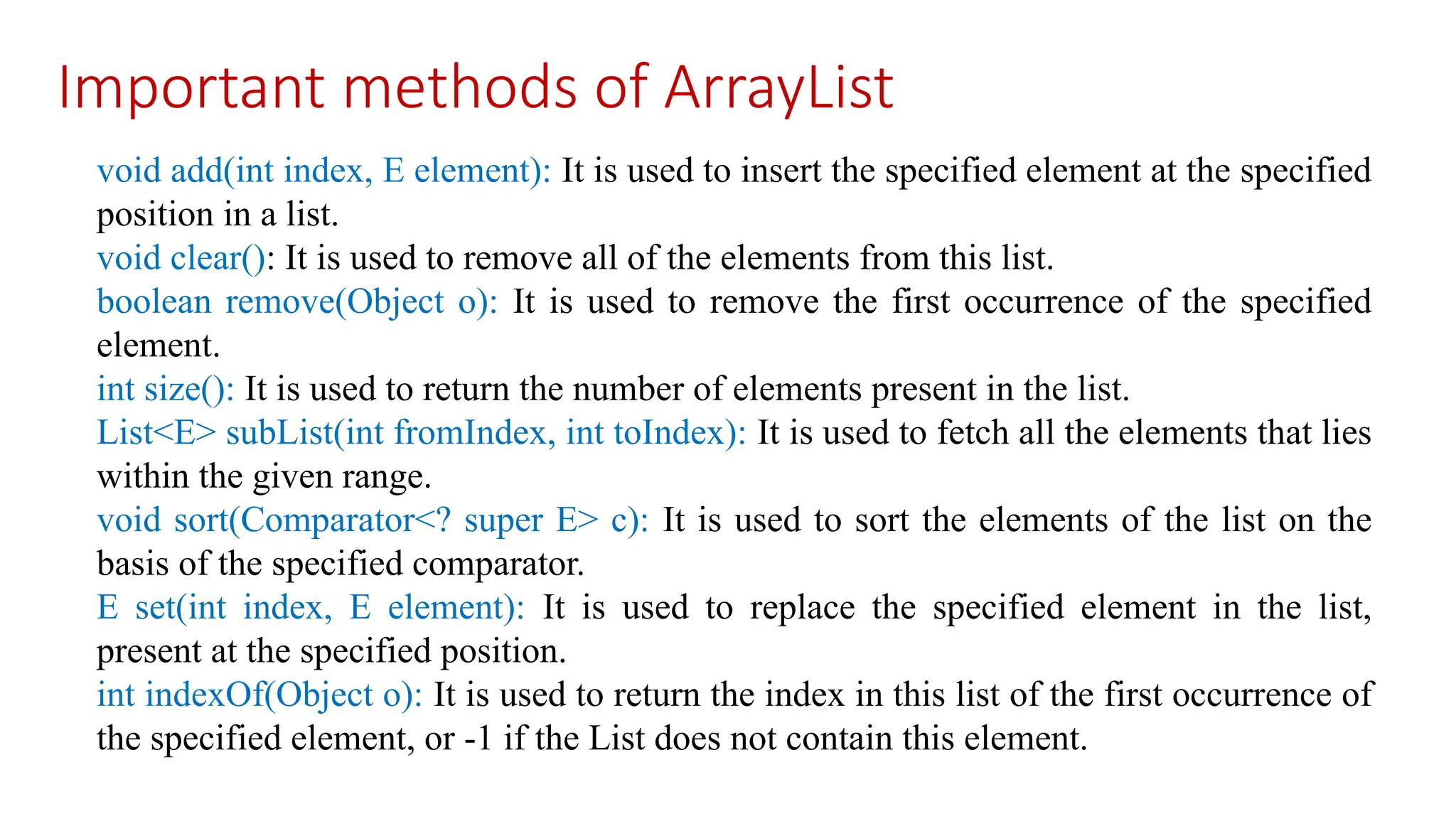
![Example Programs import java.util.*; public class ArrayListExample1{ public static void main(String args[]){ ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<String>(); //Creating arraylist list.add("Mango");//Adding object in arraylist list.add("Apple"); list.add("Banana"); list.add("Grapes"); //Printing the arraylist object System.out.println(list); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysandstrings1-250304034232-b2a492a9/75/Arrays-and-Strings-engineering-education-19-2048.jpg)
![import java.util.*; public class ArrayListExample4{ public static void main(String args[]){ ArrayList<String> al=new ArrayList<String>(); al.add("Mango"); al.add("Apple"); al.add("Banana"); al.add("Grapes"); //accessing the element System.out.println("Returning element: "+al.get(1)); //changing the element al.set(1,"Dates"); //Traversing list for(String fruit:al) System.out.println(fruit); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysandstrings1-250304034232-b2a492a9/75/Arrays-and-Strings-engineering-education-20-2048.jpg)
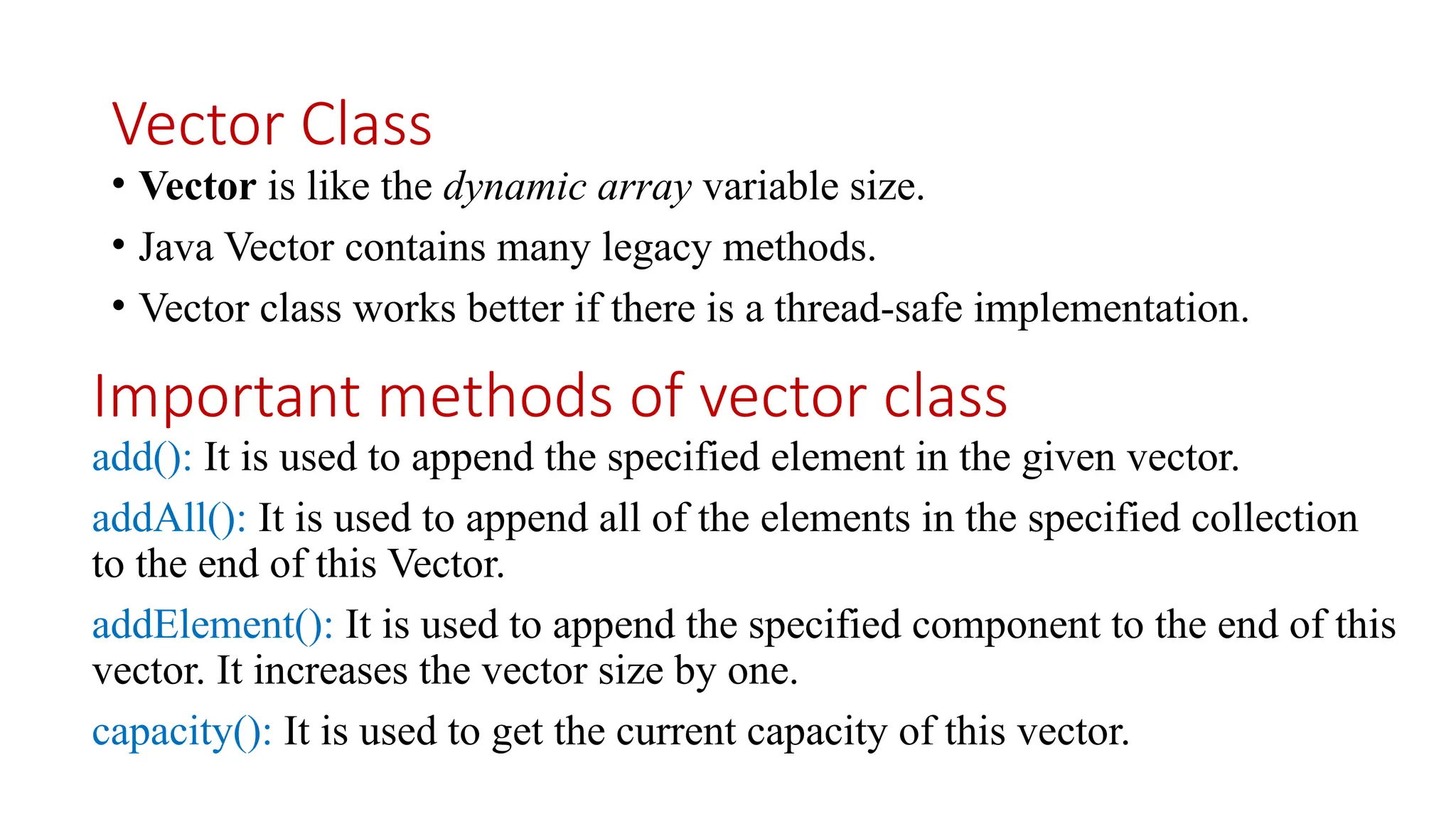

![import java.util.*; public class VectorExample2 { public static void main(String args[]) { //Create an empty Vector Vector<Integer> in = new Vector<>(); //Add elements in the vector in.add(100); in.add(200); in.add(300); in.add(200); in.add(400); in.add(500); in.add(600); in.add(700); //Display the vector elements System.out.println("Values in vector: " +in); //Remove the element at index 4 System.out.println("Remove element at index 4: " +in.remove(4)); System.out.println("New Value list in vector: " +in); //Get the element at specified index System.out.println("Element at index 1 is = "+in.get(1)); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysandstrings1-250304034232-b2a492a9/75/Arrays-and-Strings-engineering-education-23-2048.jpg)