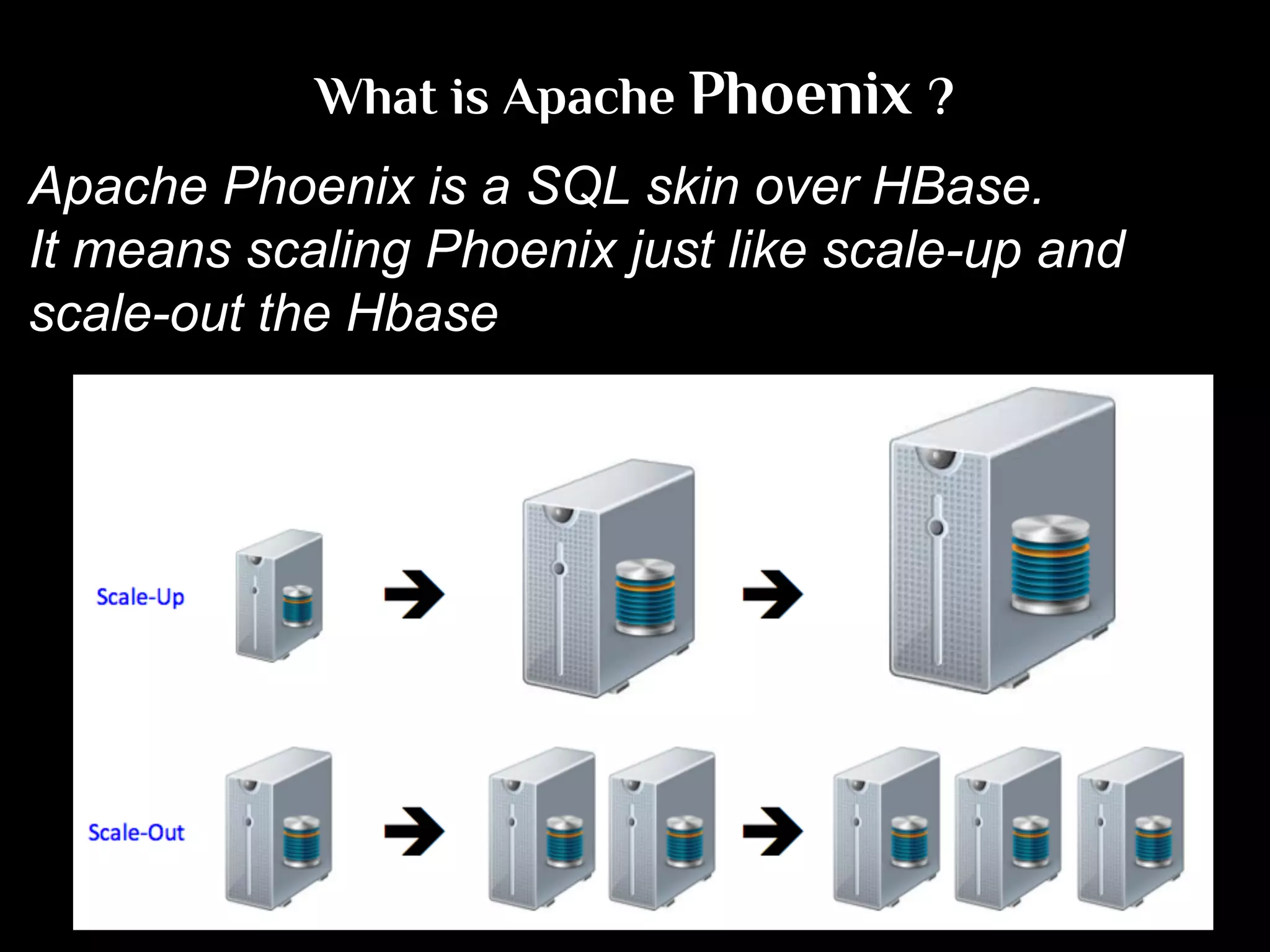
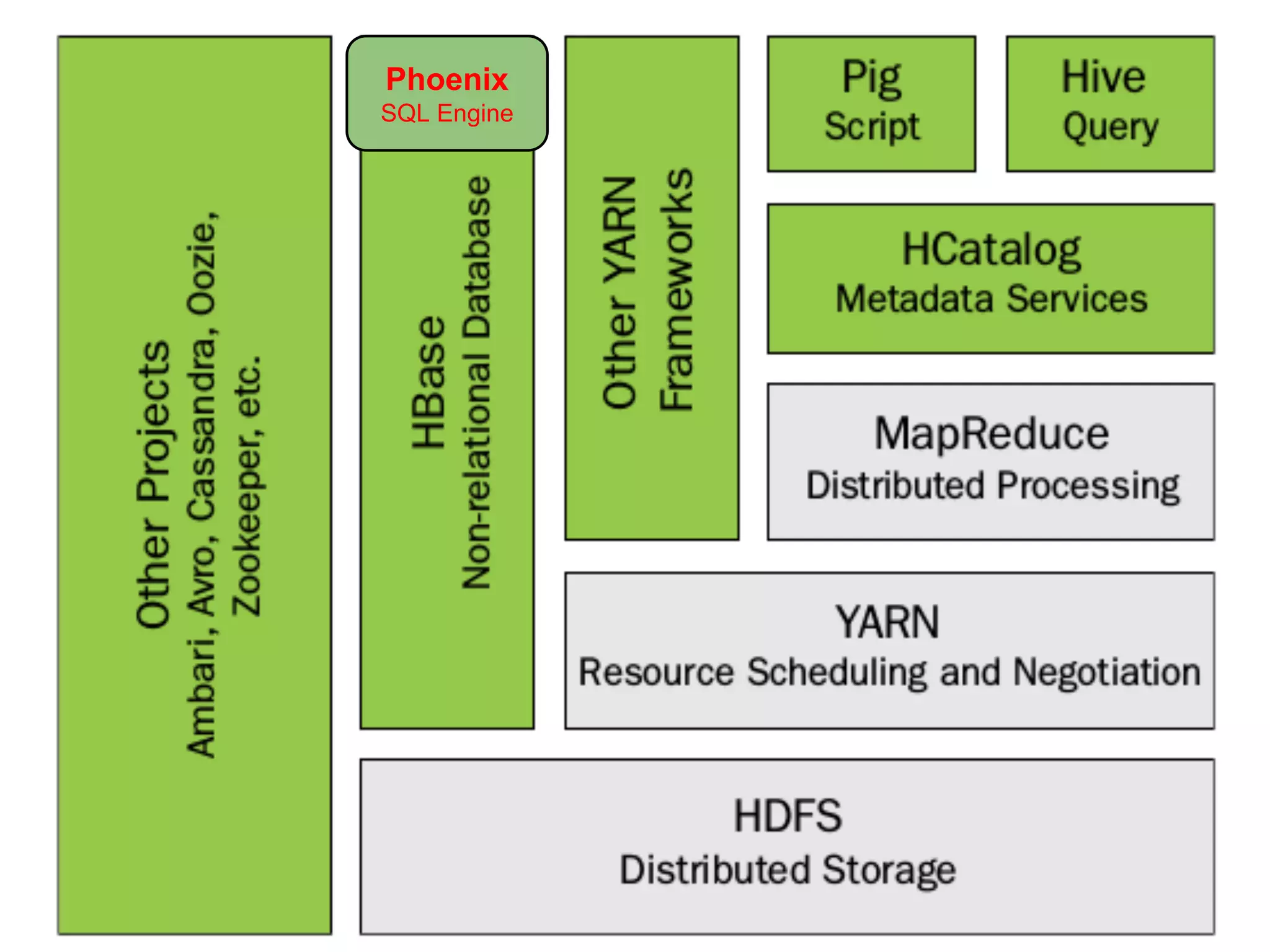
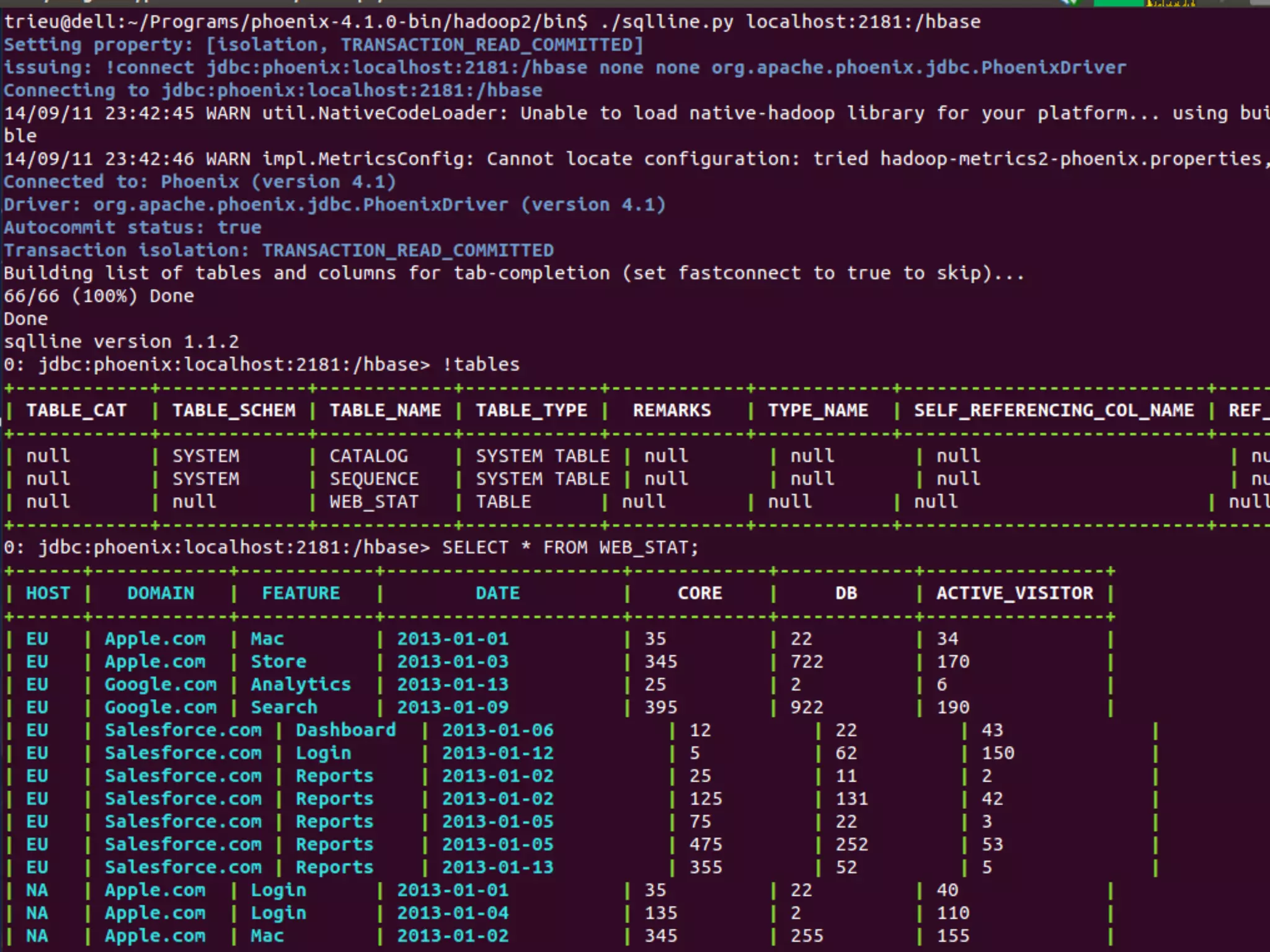
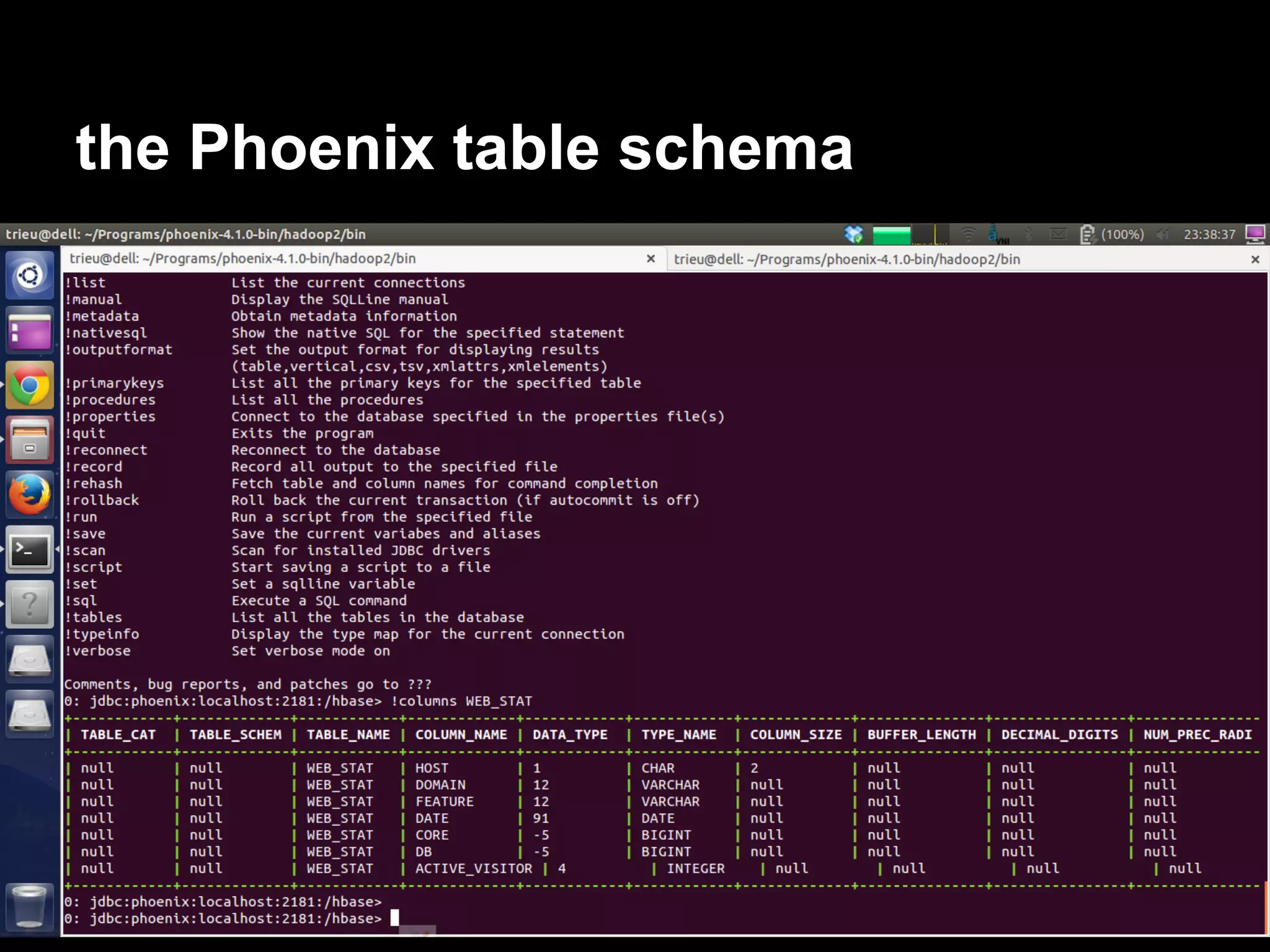
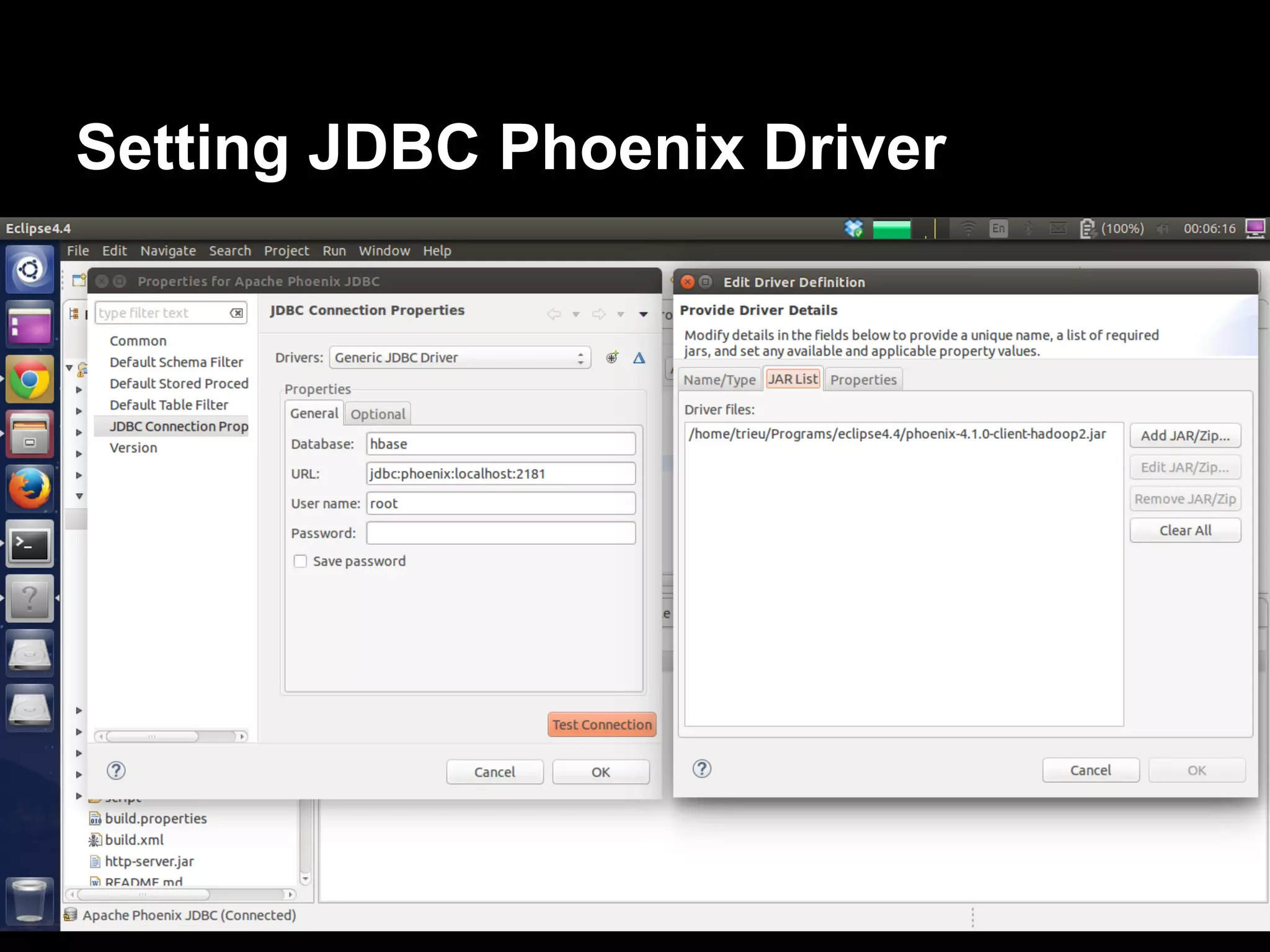
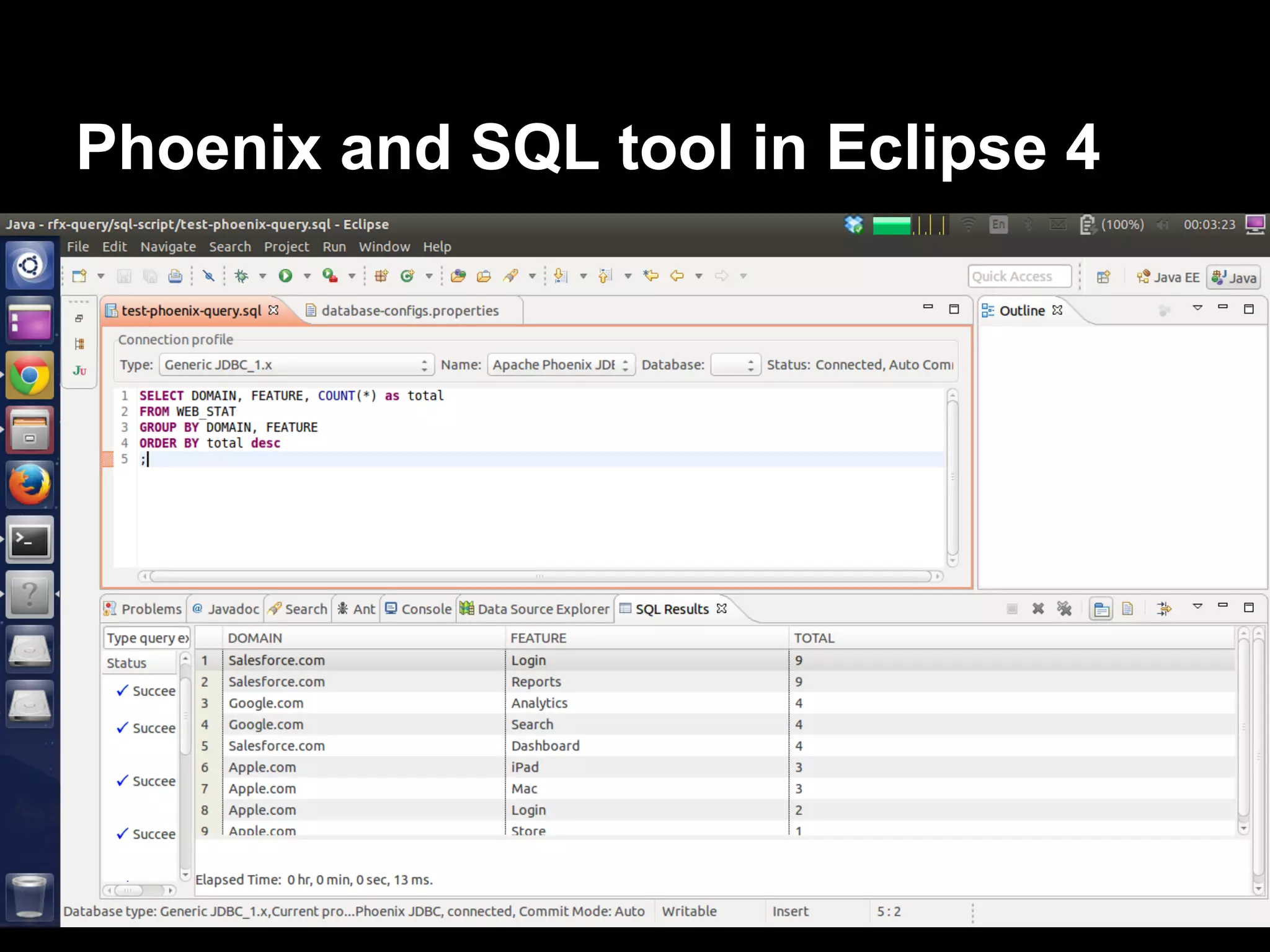
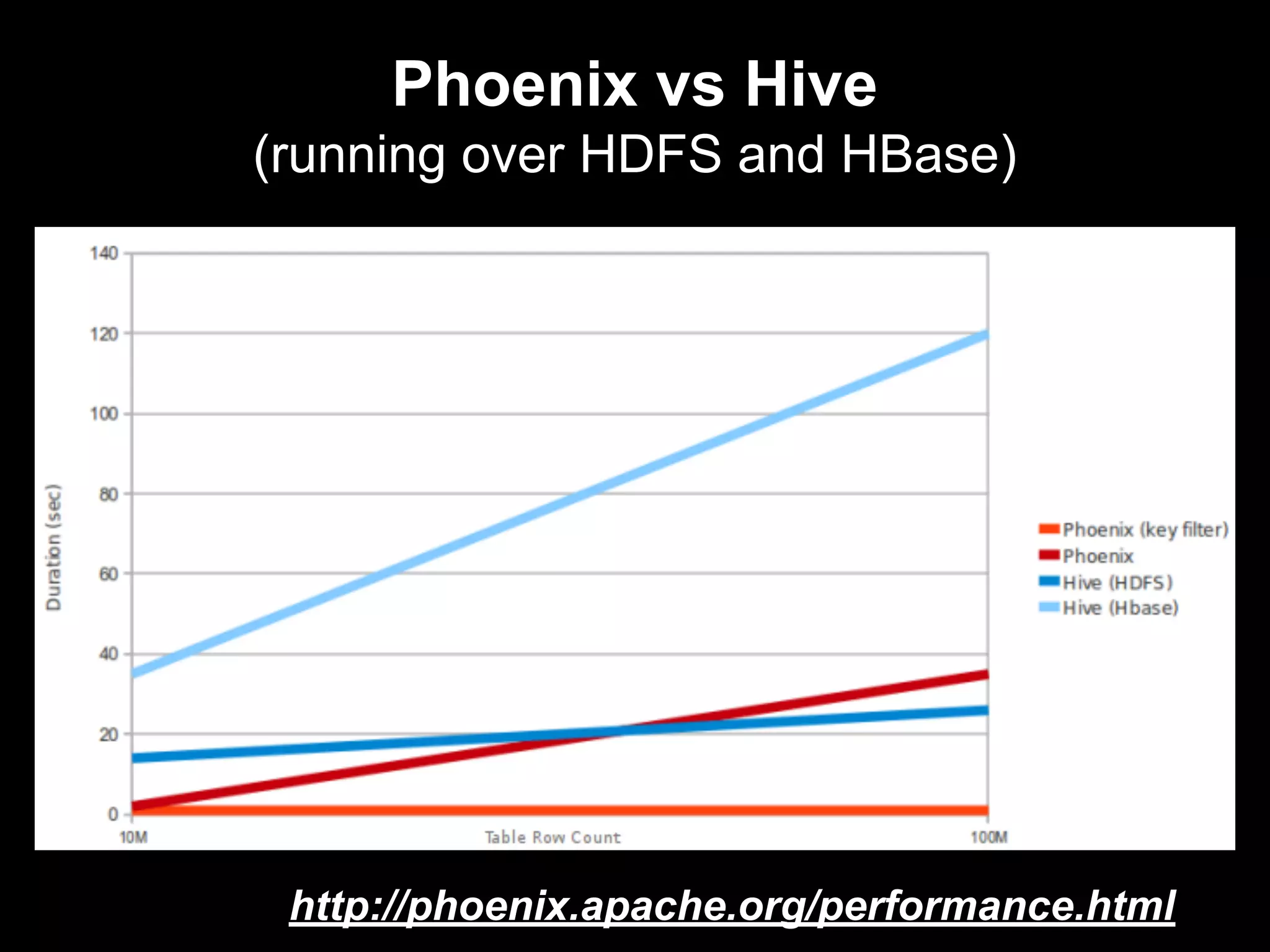
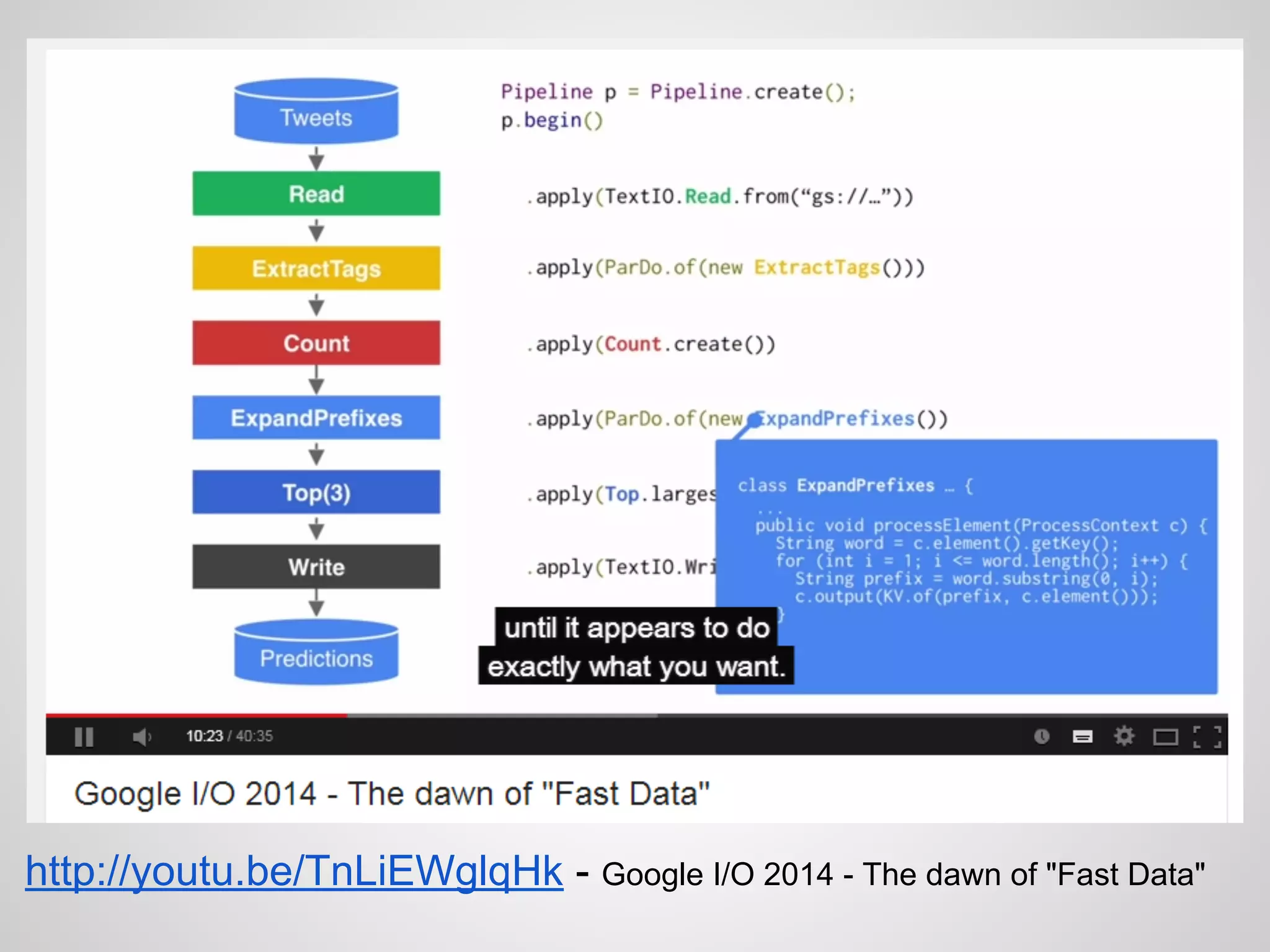
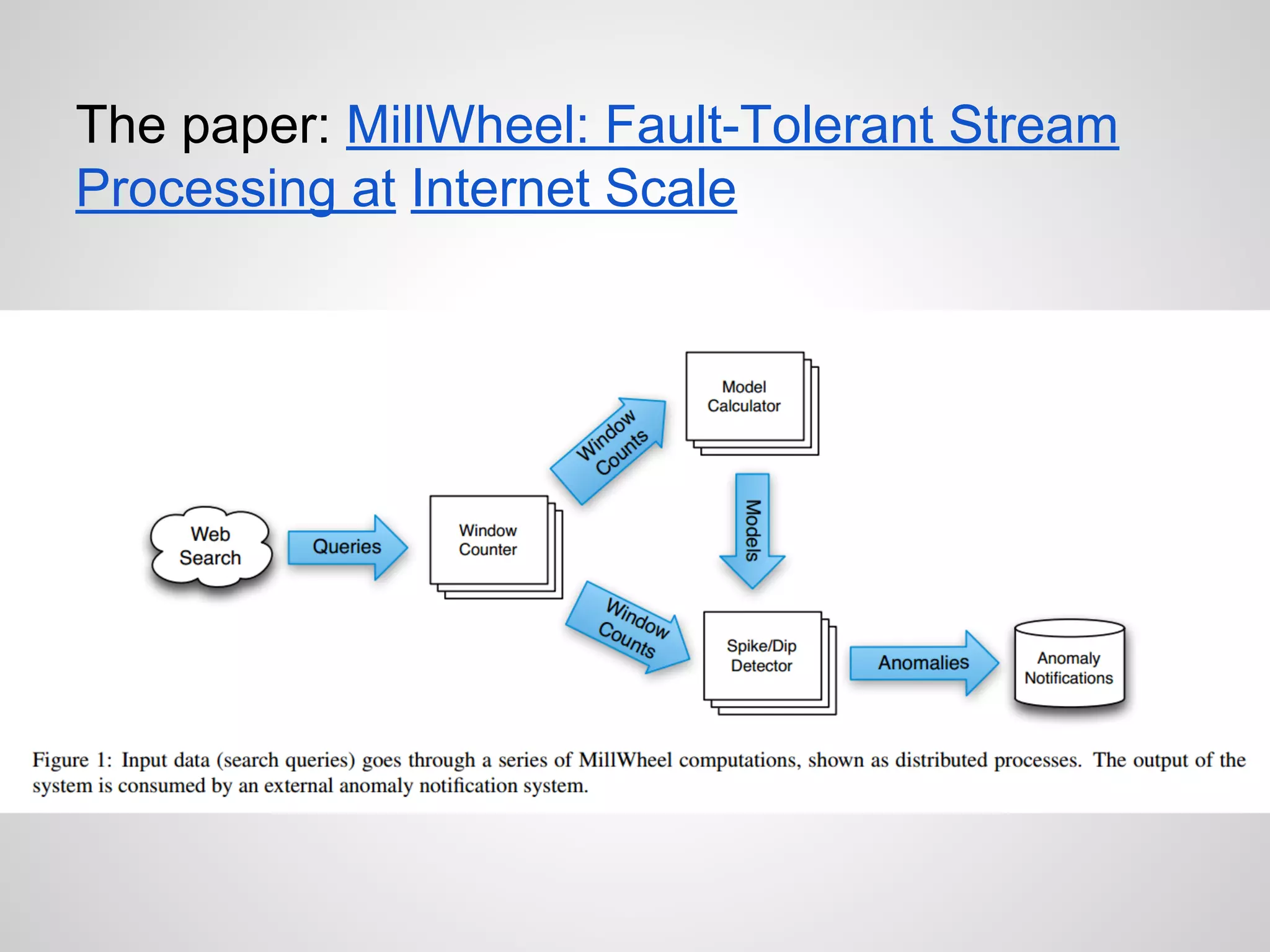
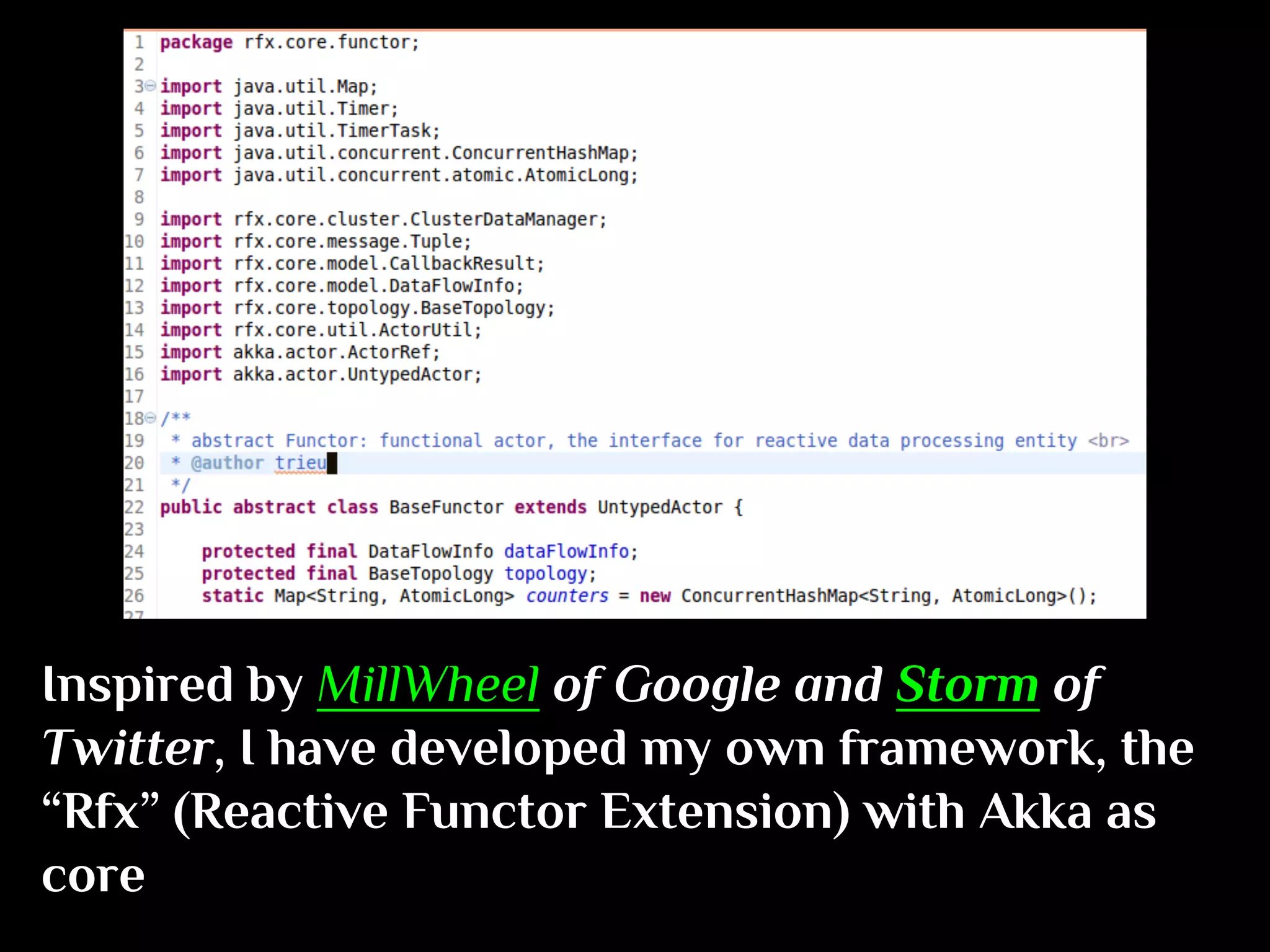
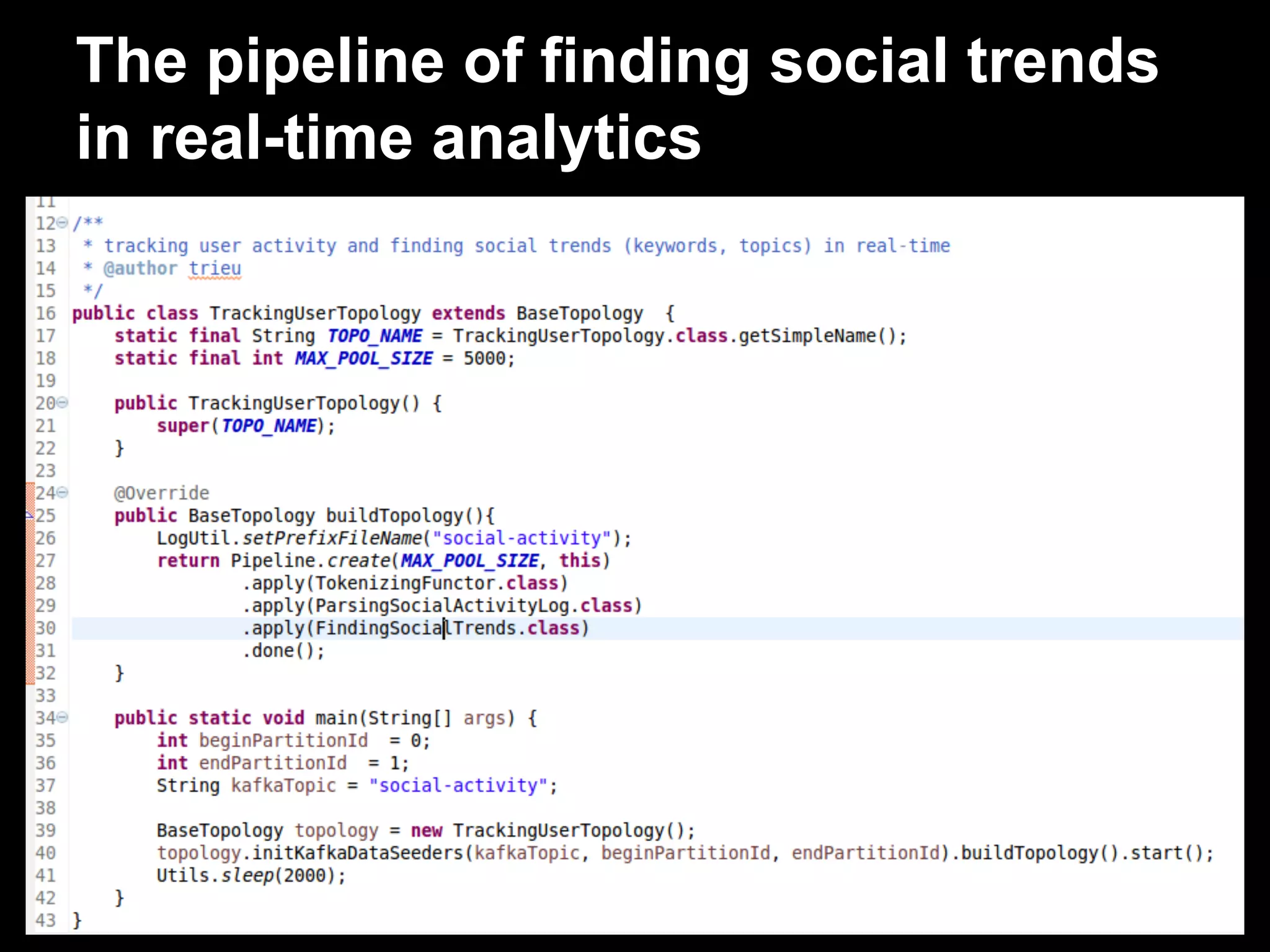
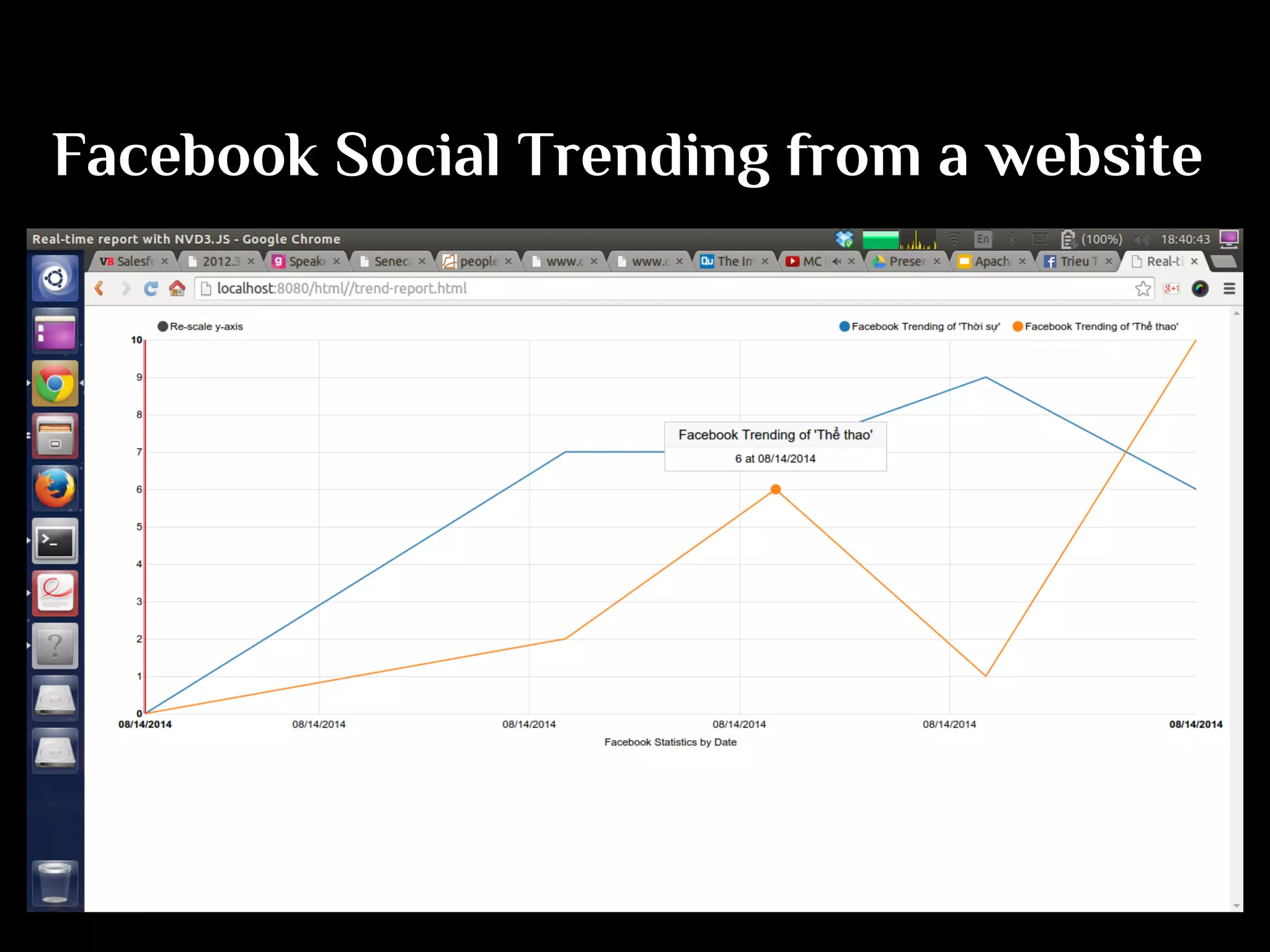
The document discusses the challenges and solutions in real-time big data processing, focusing on the limitations of traditional relational databases and the need for systems like Apache Phoenix and actor models such as Akka. It introduces common issues in big data systems, such as size, complexity, and technology, while highlighting the benefits of using open-source tools for enhanced data analytics. Furthermore, it explains the actor model's significance in concurrent computing and presents various resources for further exploration of the subject.