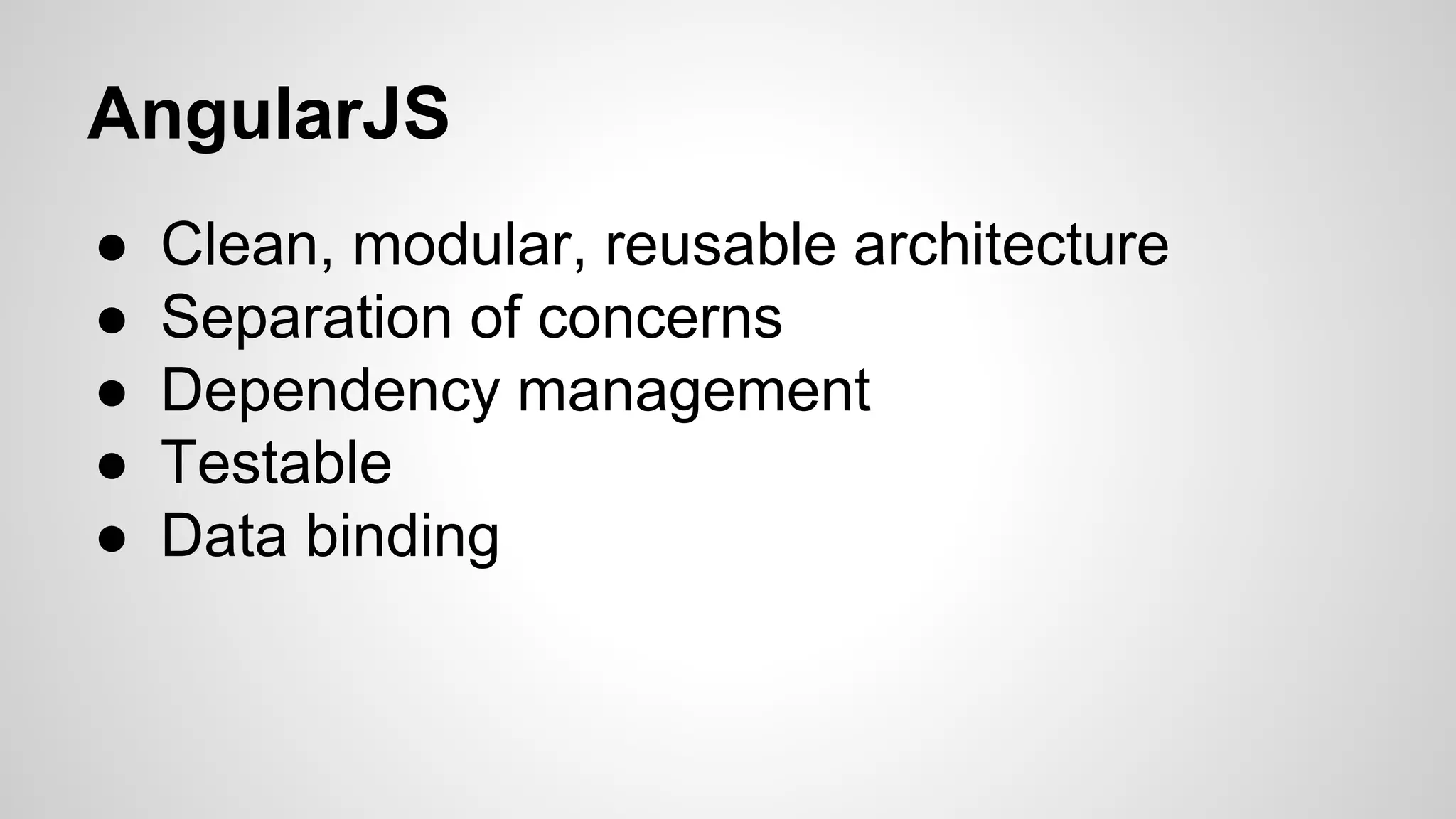
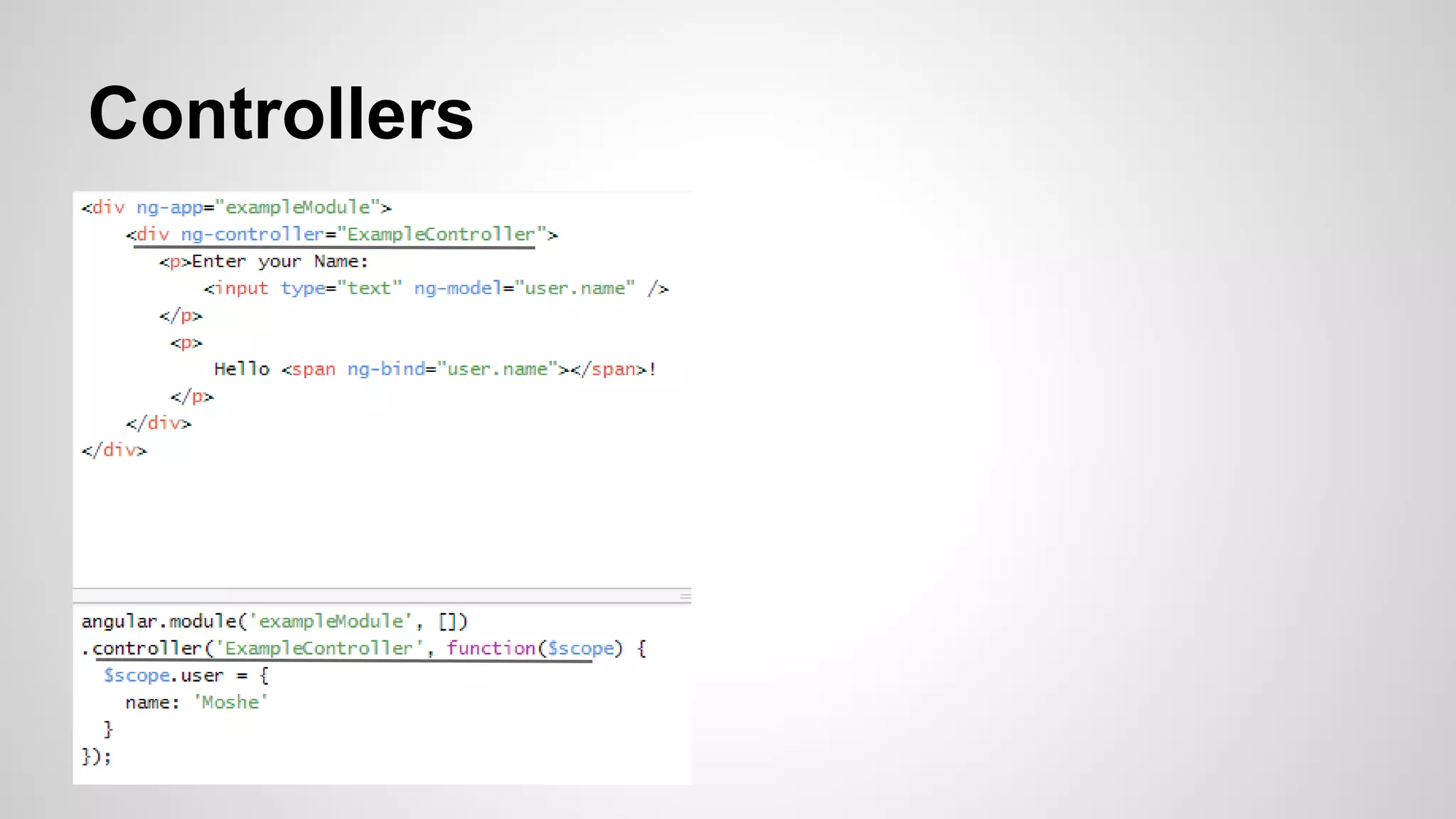
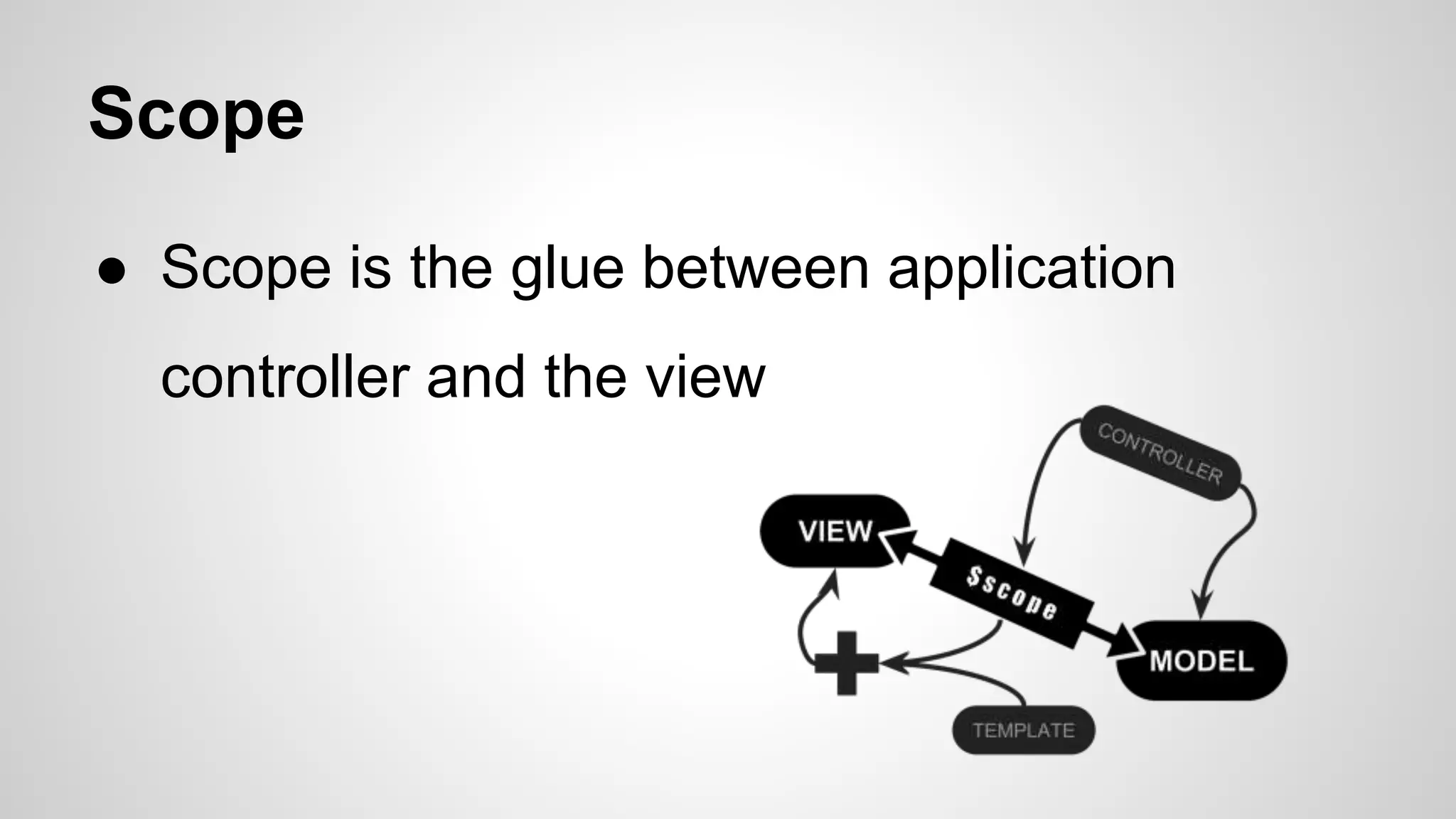
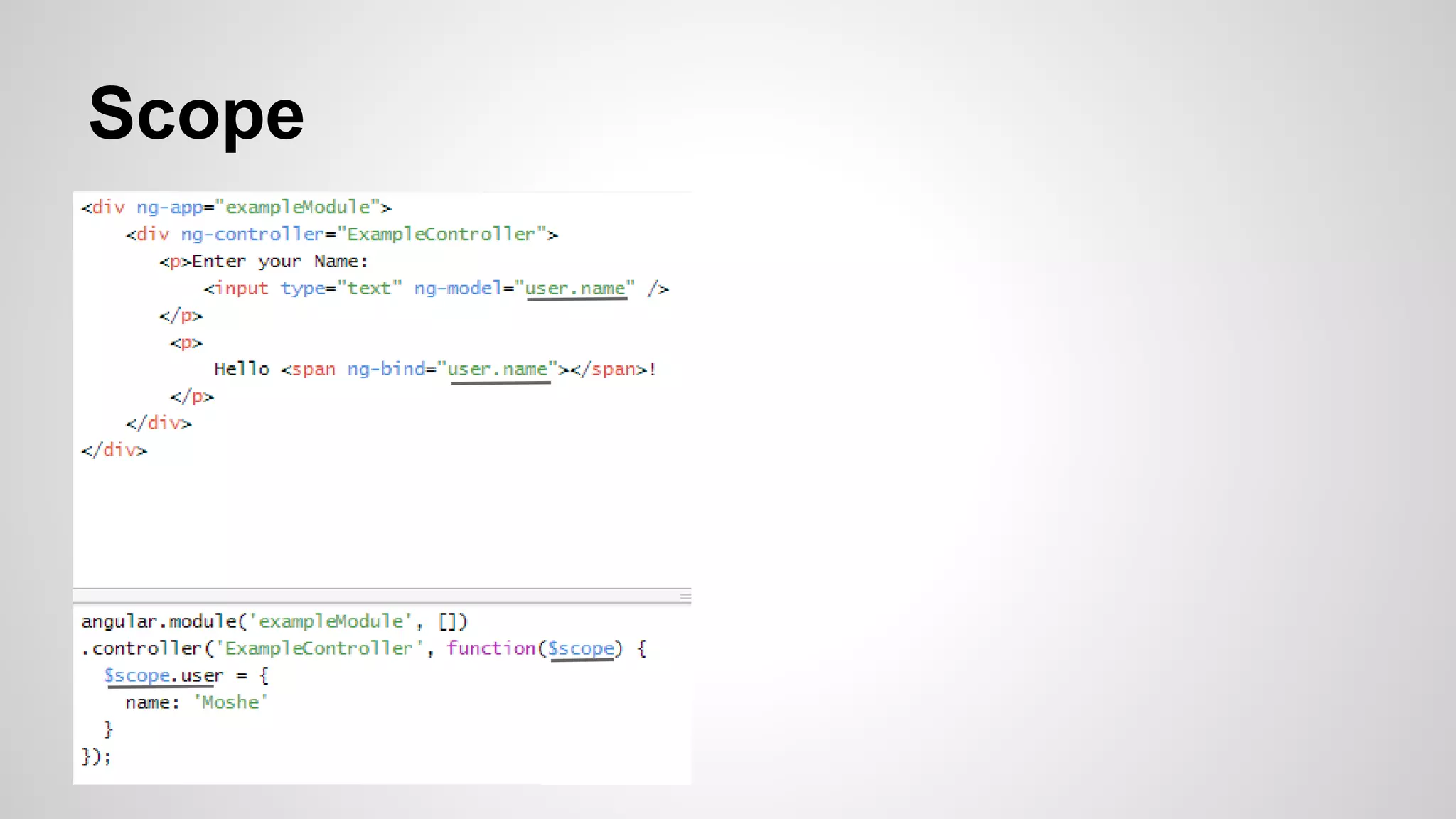
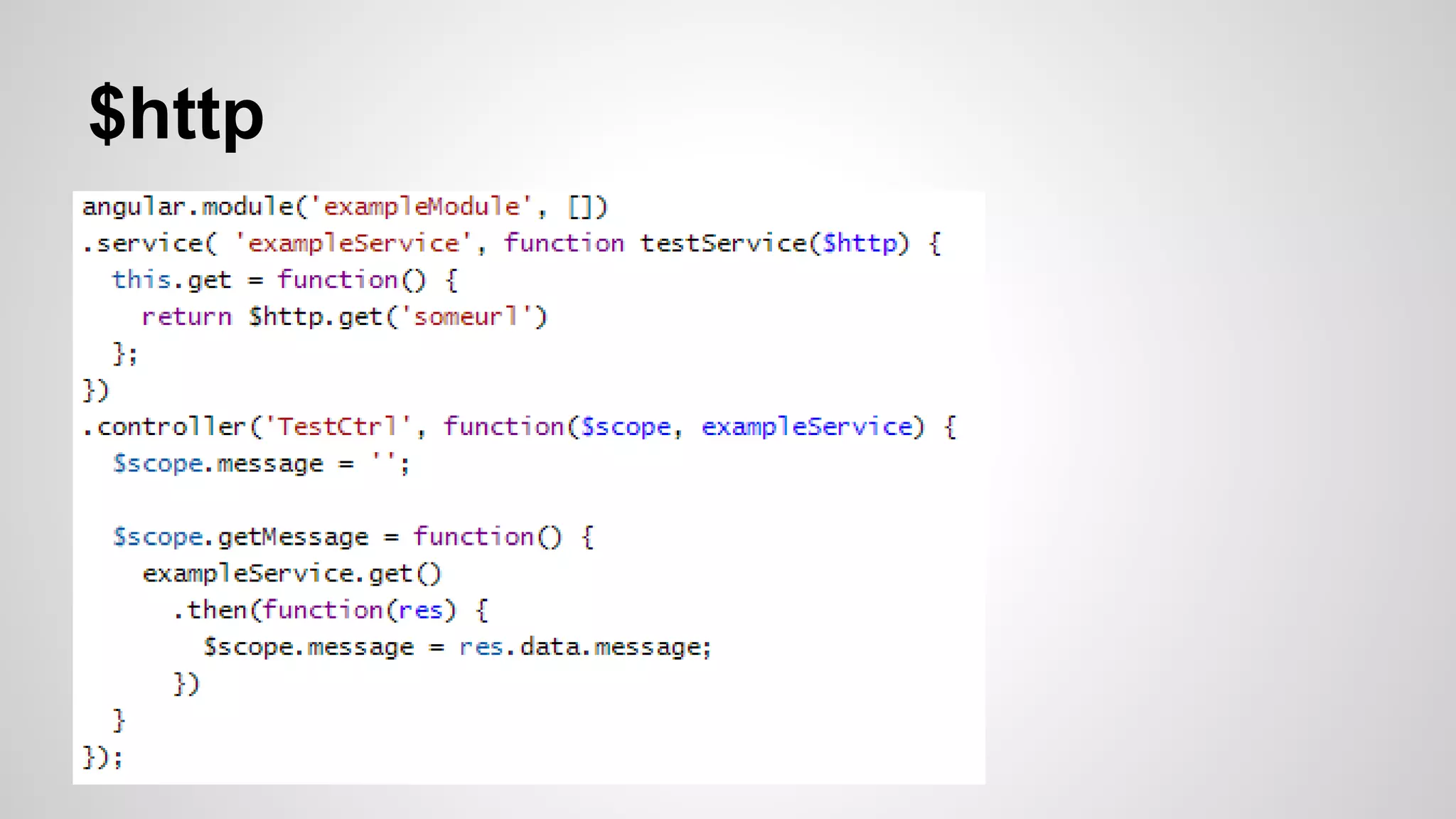
The document provides an overview of the AngularJS framework. It introduces AngularJS and its key concepts including controllers, scopes, directives, core directives like ng-model and ng-repeat, services, and filters. It also provides details about the author such as their background in food engineering, web development at IBM, and 2 years of experience developing with AngularJS. Code examples are included to illustrate several AngularJS concepts.