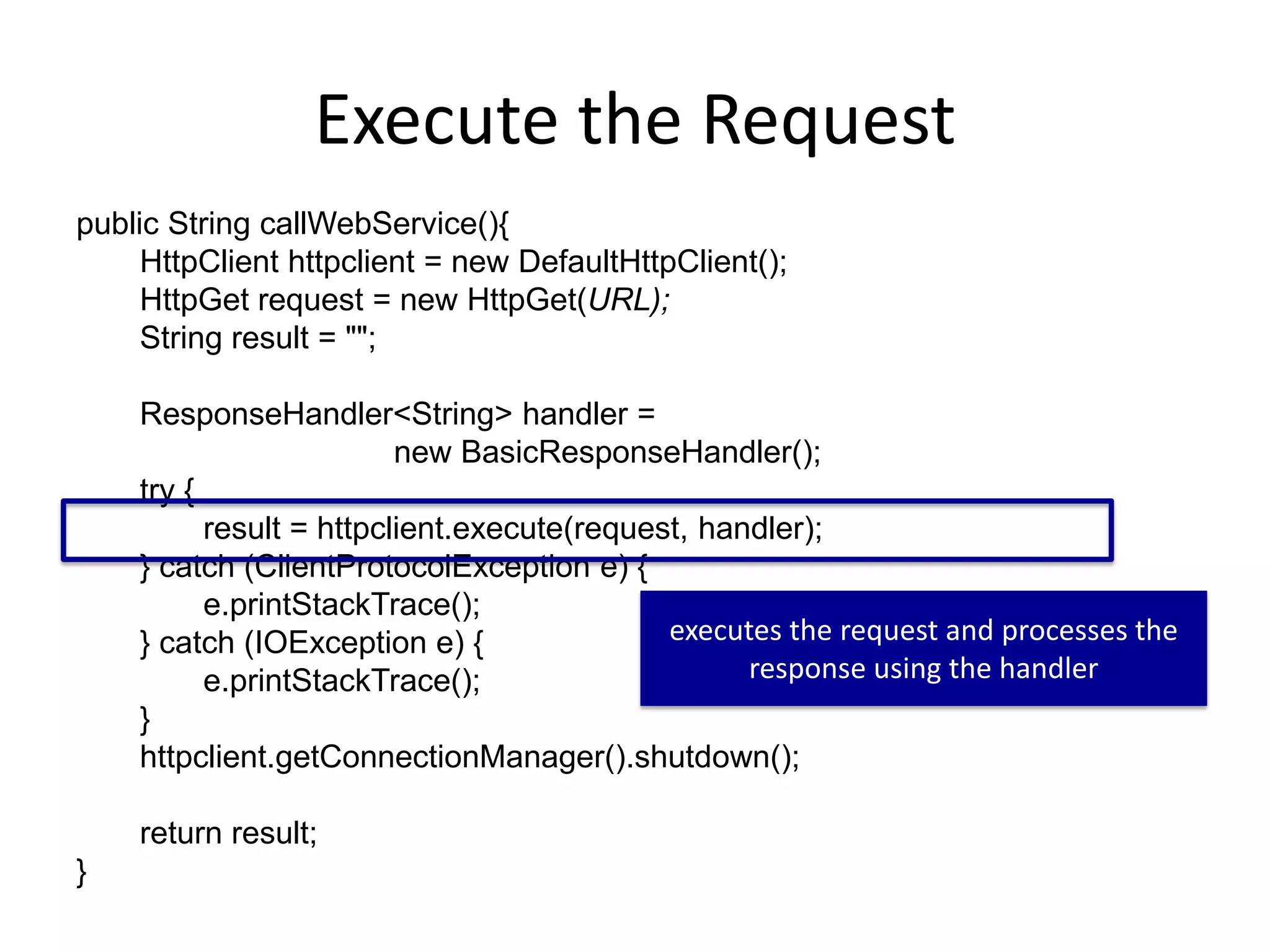
This document discusses using web services in Android development. It covers making HTTP requests to web services, parsing the response, and creating your own basic web service using PHP. Key points include constructing the URL, executing asynchronous HTTP requests, checking response codes, and parsing XML or JSON responses. The document provides code samples for making a request and handling the response. It also discusses possible issues like blocking the UI thread during the request and suggests using threads to avoid this. Finally, it proposes an exercise to build an accessible application using a web service and GPS.












![JSON { "employees": [ { "firstname":"John" , "lastname":"Doe" }, { "firstname":"Anna" , "lastname":"Smith" }, { "firstname":"Peter" , “lastname":"Jones" } ] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androiddev3-150925070518-lva1-app6891/75/Android-dev-3-16-2048.jpg)
![JSON • Name/Value Pairs: “name” : “value” – "firstname":"John" • JSON Objects: , … - – { "firstname":"John" , "lastname":"Doe" } • JSON Arrays: * …, …, … + [ { "firstname":"John" , "lastname":"Doe" }, { "firstname":"Anna" , "lastname":"Smith" }, … ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androiddev3-150925070518-lva1-app6891/75/Android-dev-3-17-2048.jpg)