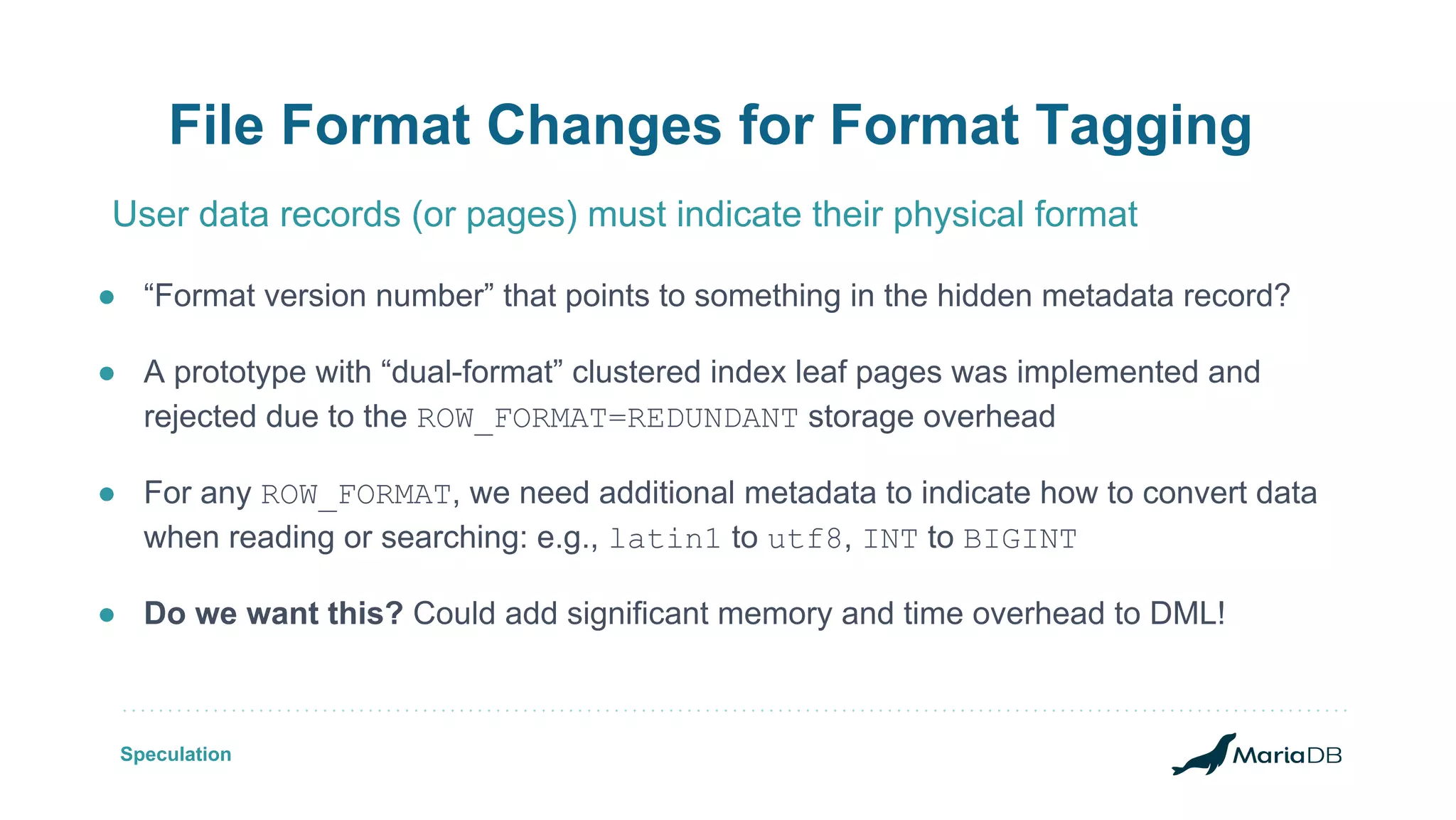
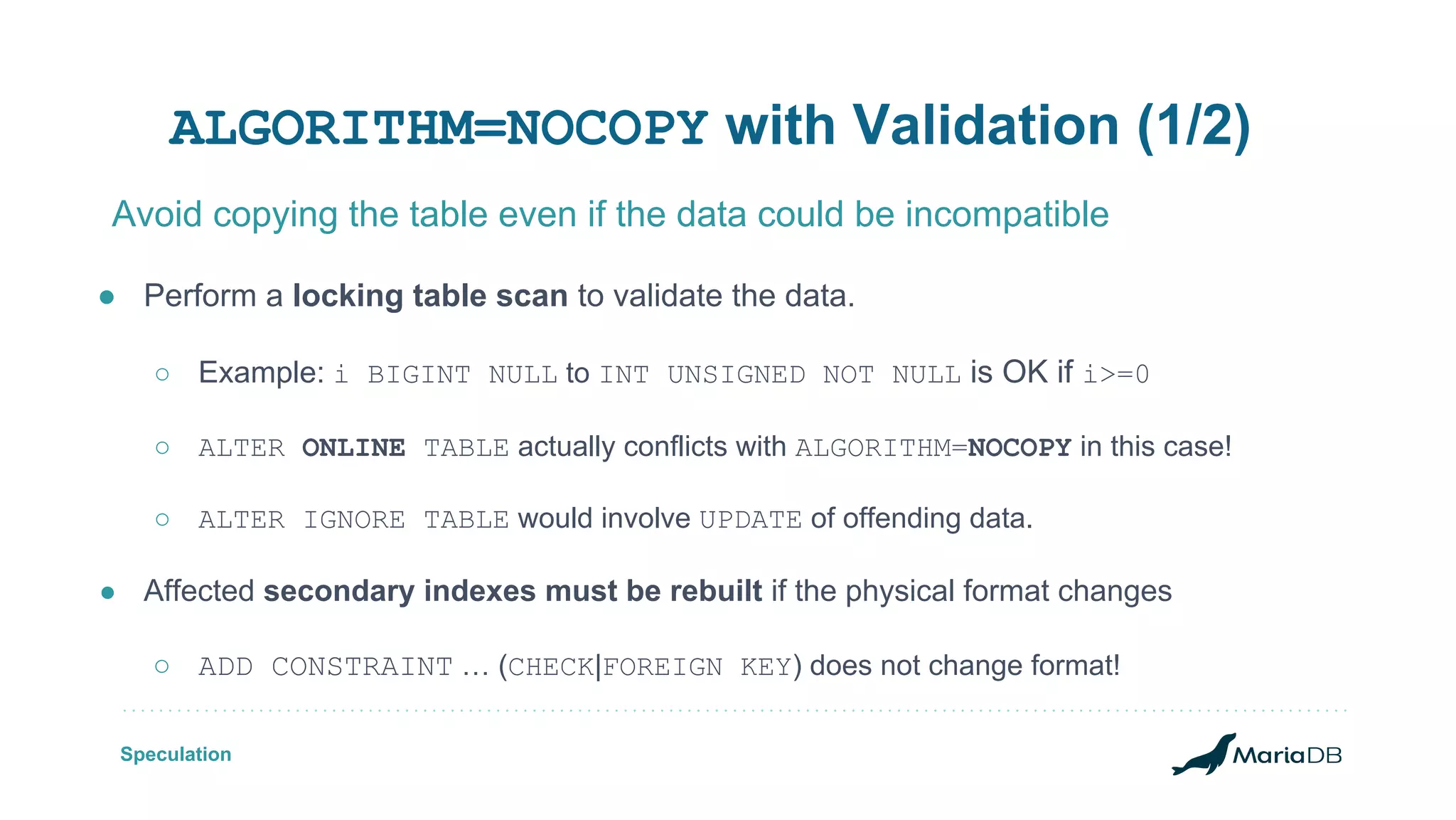
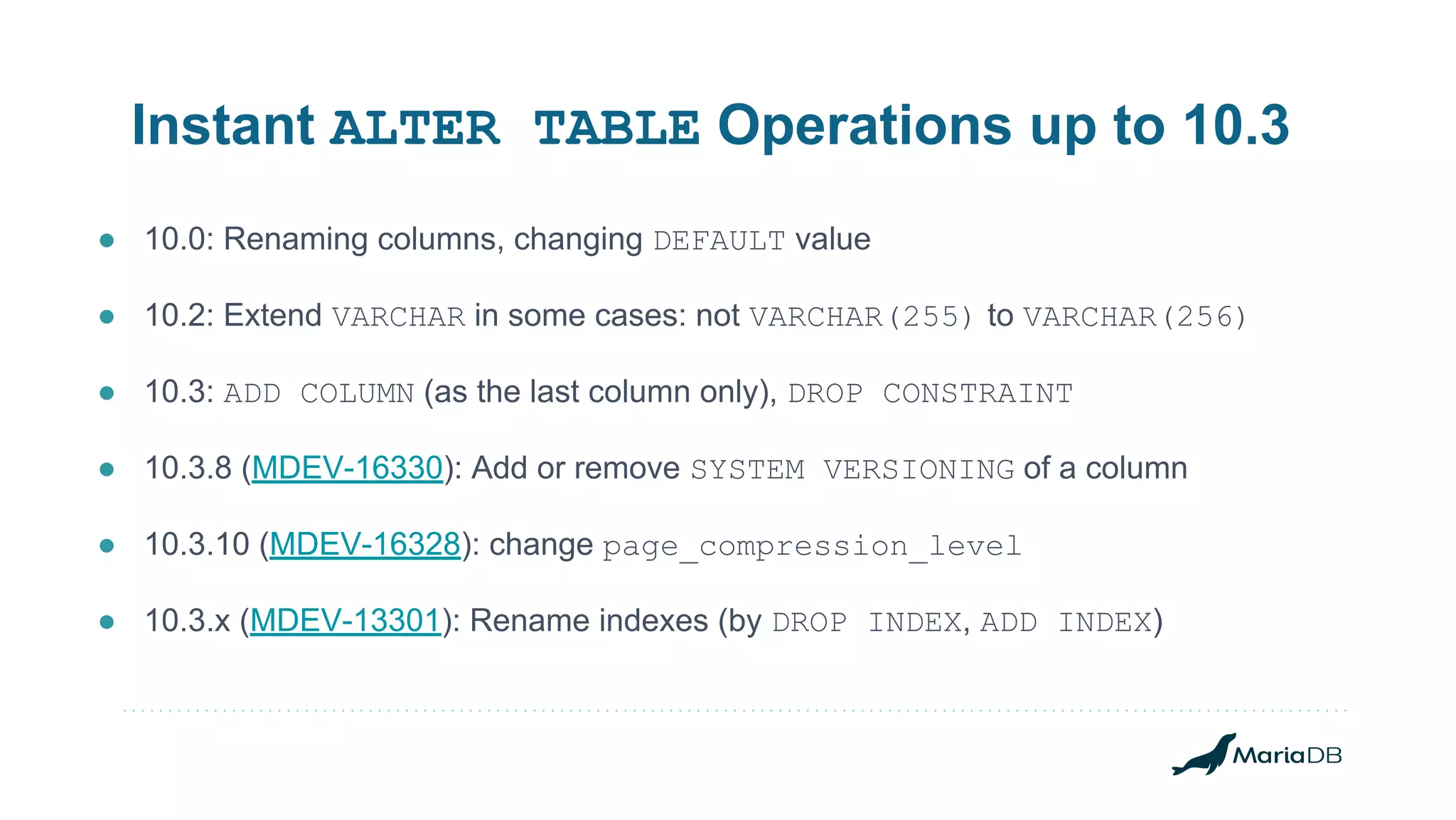
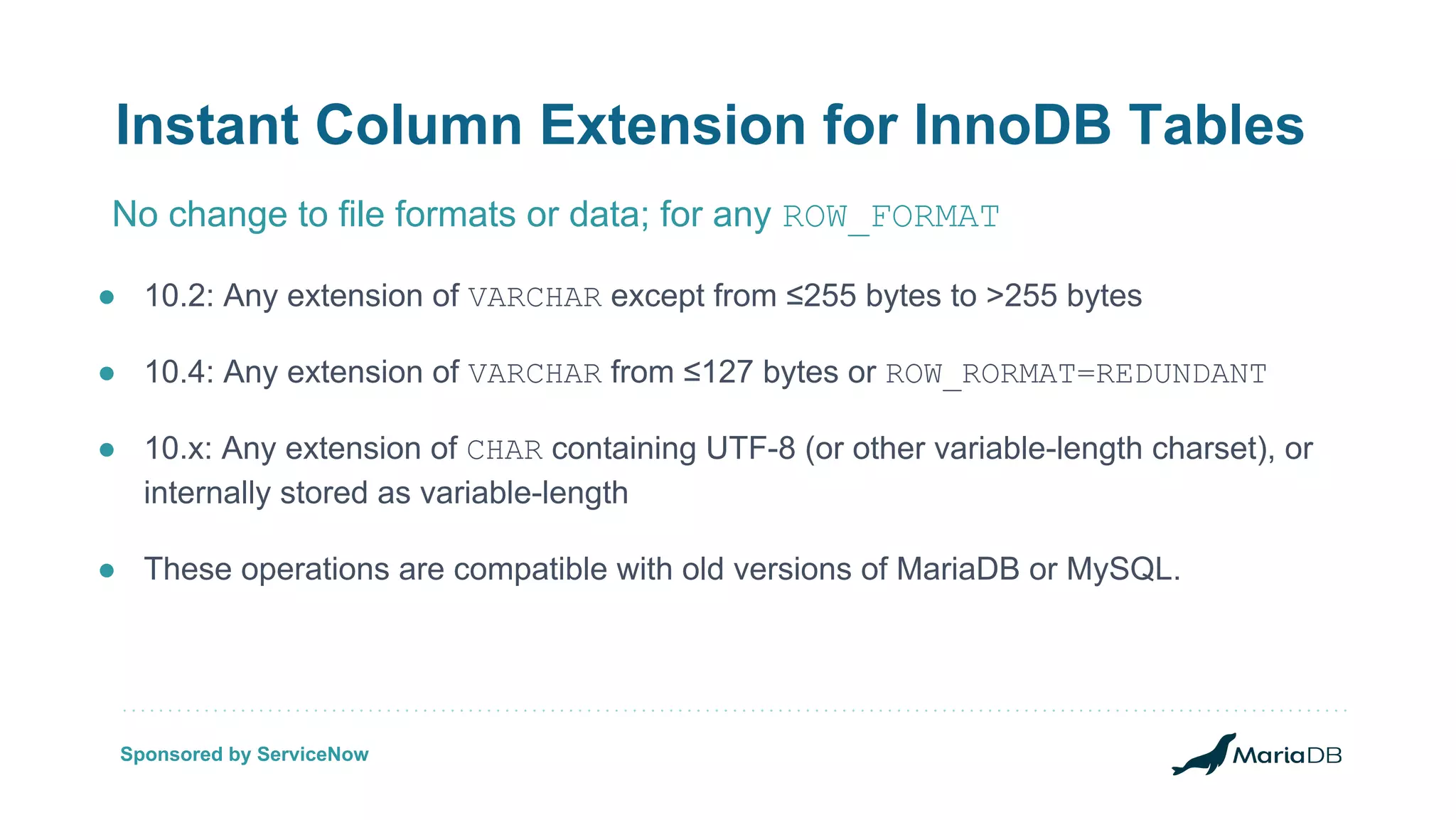
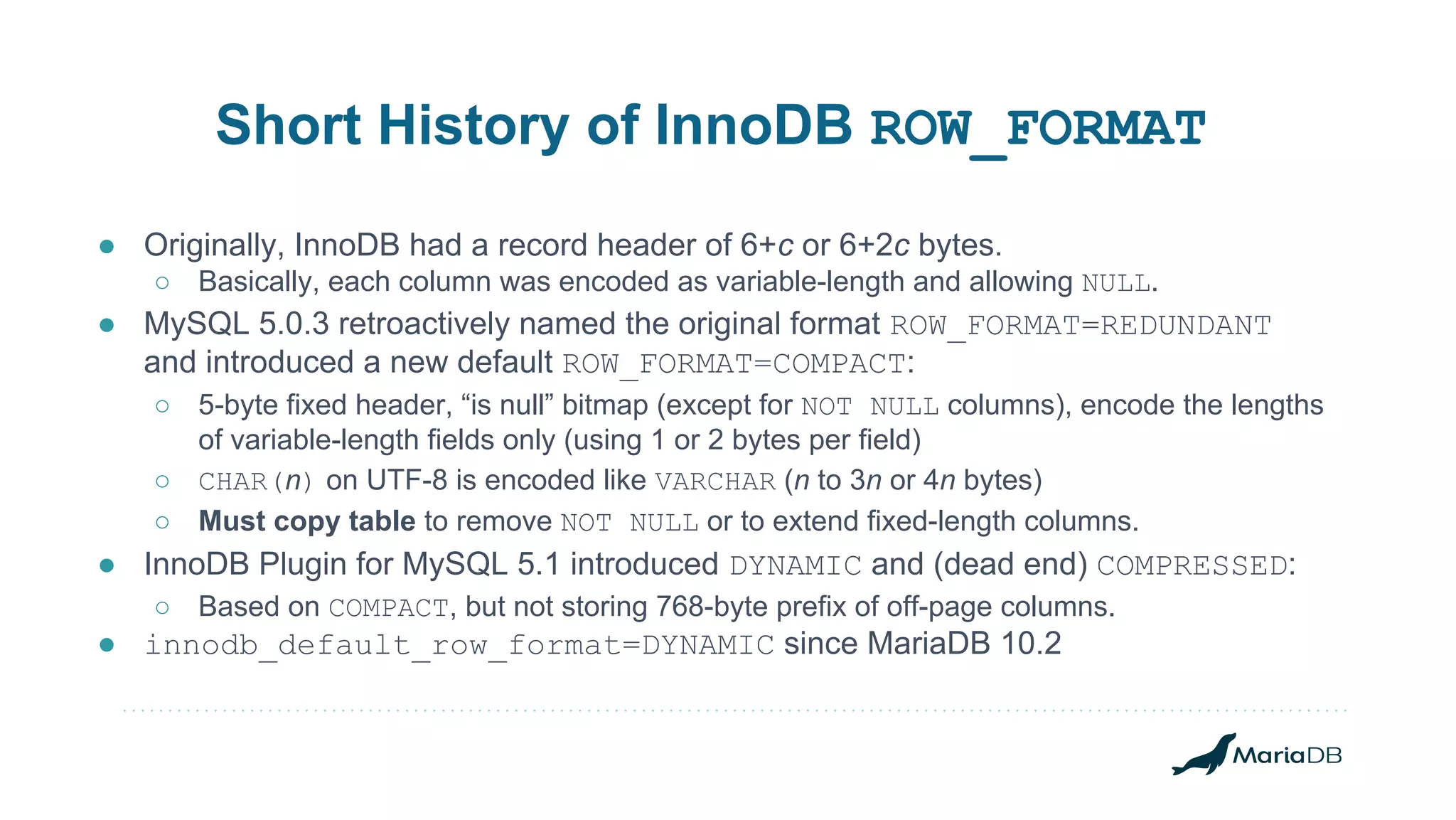
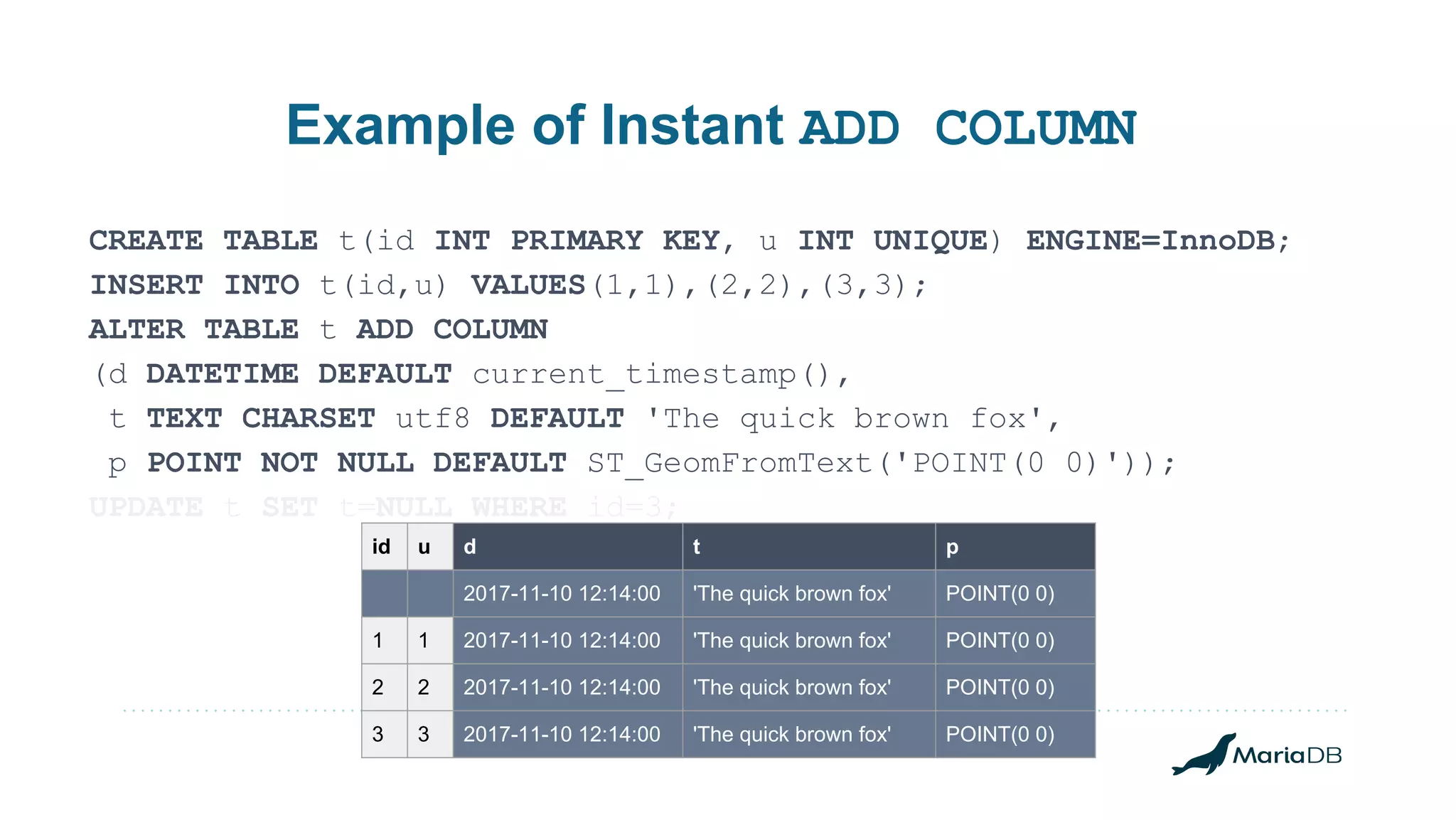
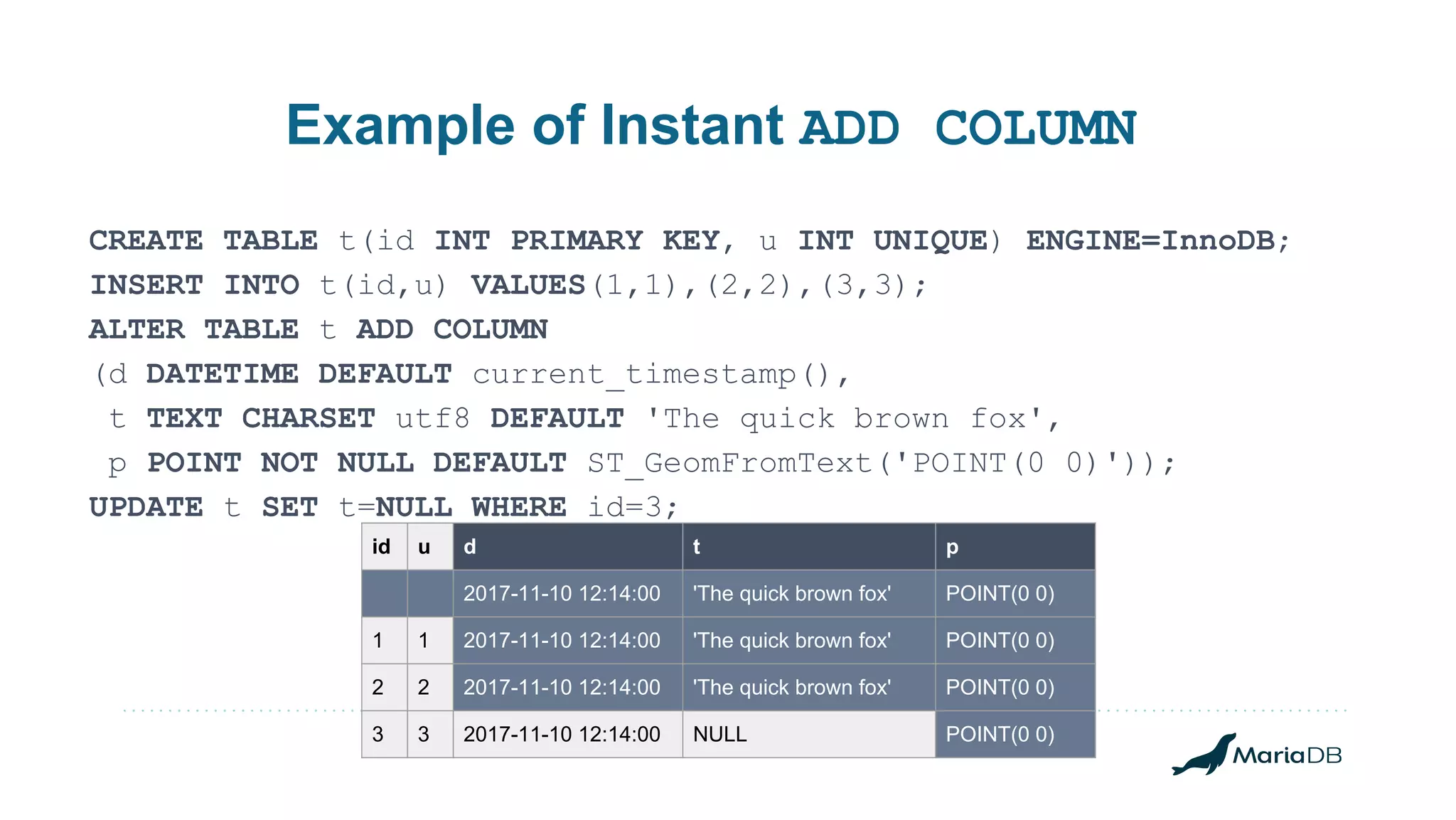
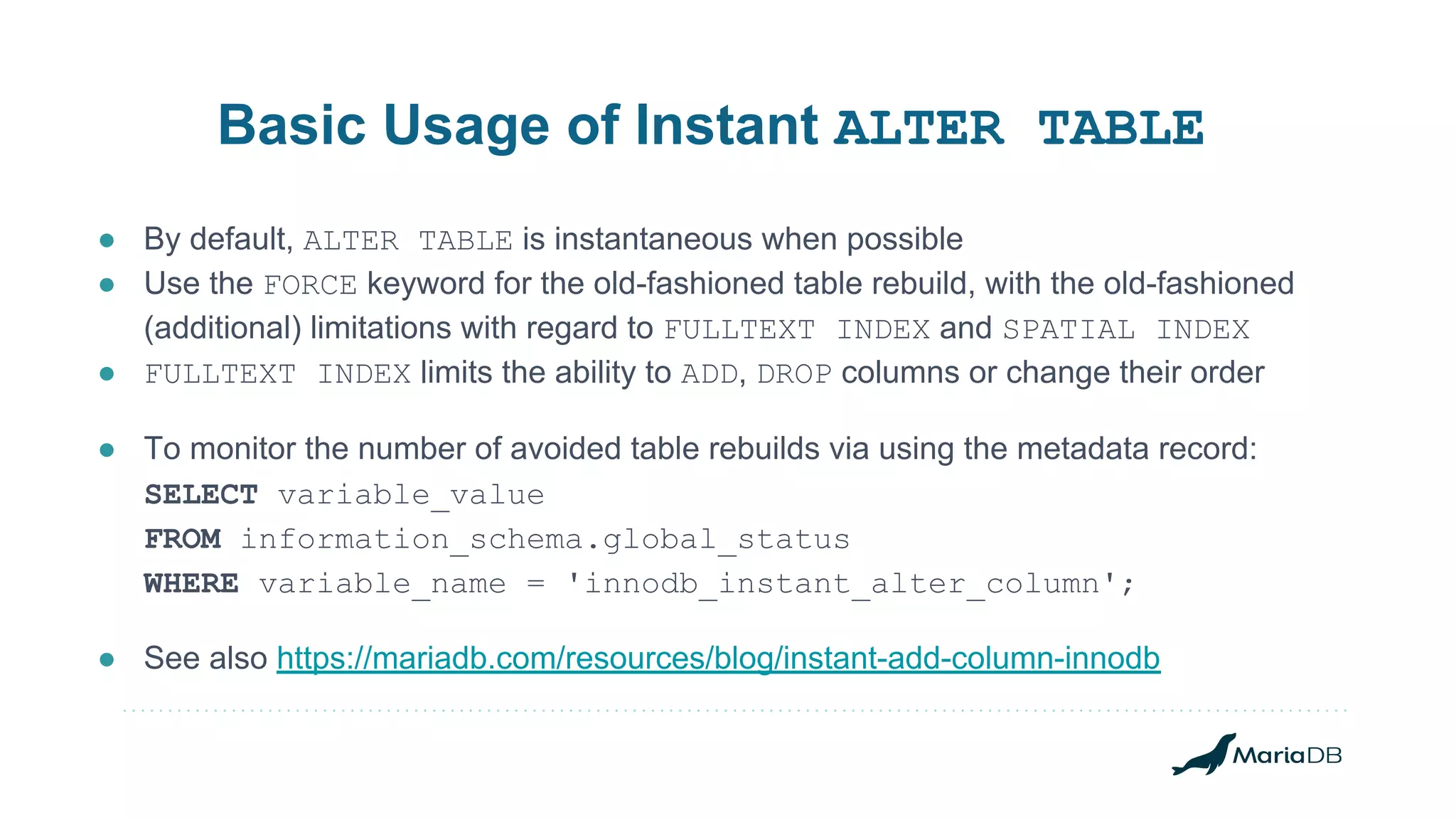
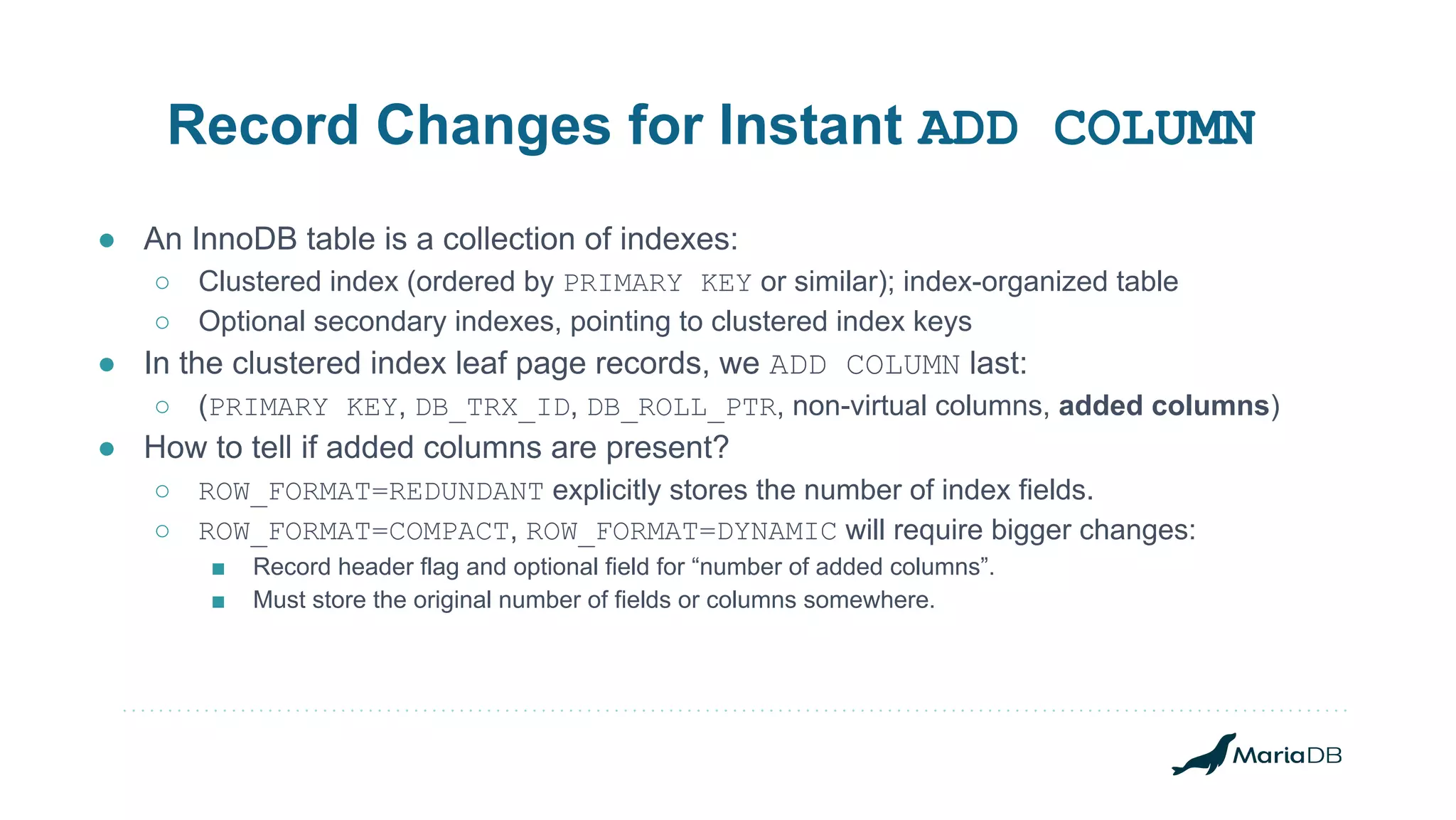
The document discusses improvements to the alter table operation in MariaDB, particularly focusing on the InnoDB storage engine across different versions. Key enhancements include the introduction of instant operations for adding and modifying columns, as well as changes to the data format to reduce the need for table copying during these operations. It also highlights the limitations associated with certain index types and details how various mechanisms can affect performance during table alterations.
![• “Fast index creation”: ADD [UNIQUE] INDEX, ADD PRIMARY KEY • ALGORITHM=INPLACE starting with MySQL 5.6 and MariaDB 10.0 ○ Misleading name “inplace”; some operations may rebuild the table! ■ (ADD|DROP) COLUMN, ADD PRIMARY KEY, CHANGE…[NOT] NULL ○ Some operations are instantaneous: rename column, change DEFAULT, … ○ Sometimes sloppily called “online” even when no concurrent DML is allowed History of Native ALTER TABLE in InnoDB Starting with InnoDB Plugin for MySQL 5.1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/altertableimprovementsinmariadb-190305235346/75/ALTER-TABLE-Improvements-in-MariaDB-Server-3-2048.jpg)
![• InnoDB supports two classes of operations in online ALTER TABLE: ○ ADD [UNIQUE] INDEX: create indexes without copying the table ○ online table rebuild: ADD PRIMARY KEY or ADD, DROP, MODIFY columns • InnoDB refuses ALTER ONLINE TABLE or ALTER TABLE…LOCK=NONE if: ○ A FULLTEXT or SPATIAL index is being created ○ The table needs to be rebuilt while FULLTEXT or SPATIAL index are present ALTER ONLINE TABLE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/altertableimprovementsinmariadb-190305235346/75/ALTER-TABLE-Improvements-in-MariaDB-Server-4-2048.jpg)







![• Replication slave will only start after commit→huge lag (to be fixed in MDEV-11675) • The online_log needs to be buffered (in memory or temporary files) ○ The size depends on the concurrent DML workload; hard to predict! ○ Written before commit; DML duplicate key errors make also ALTER TABLE fail Watch out for MDEV-16329 Cross-Engine ALTER ONLINE TABLE ○ Keep engine-native for ADD [UNIQUE] INDEX or ALGORITHM=INSTANT Problems with Online Table Rebuild Why are tools like GH-OST still used instead of ALTER ONLINE TABLE? MariaDB Server 10.5?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/altertableimprovementsinmariadb-190305235346/75/ALTER-TABLE-Improvements-in-MariaDB-Server-21-2048.jpg)