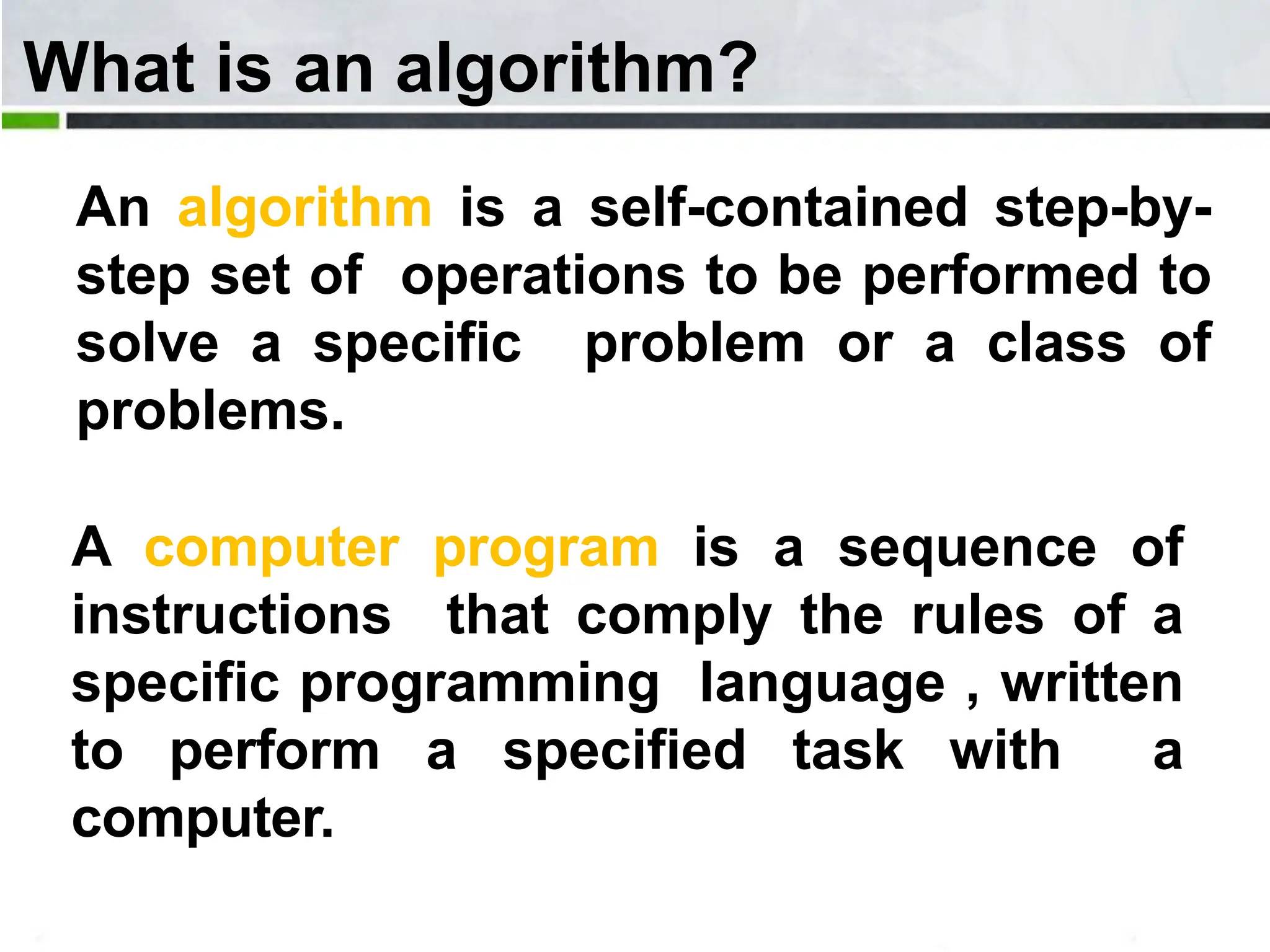
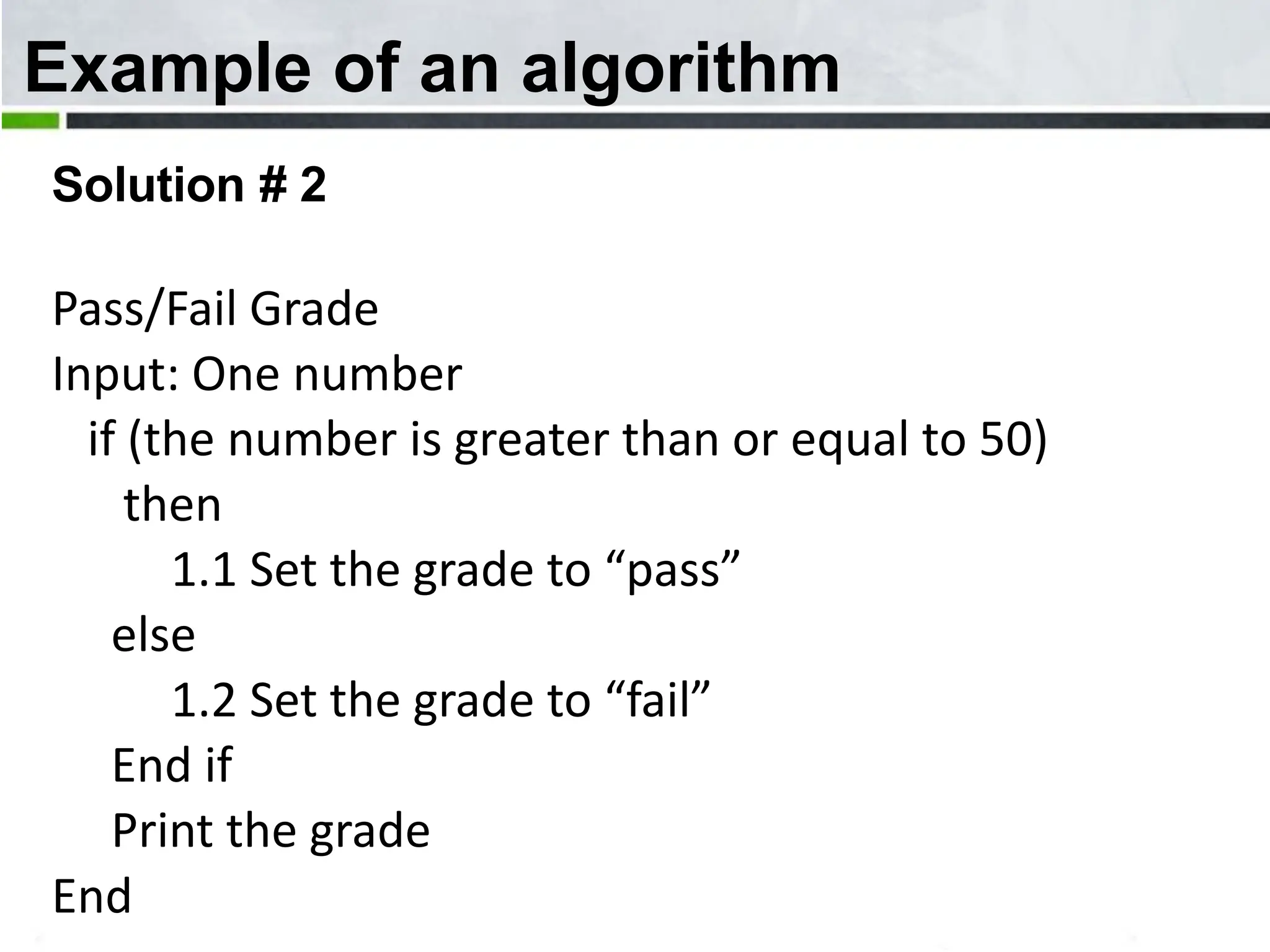
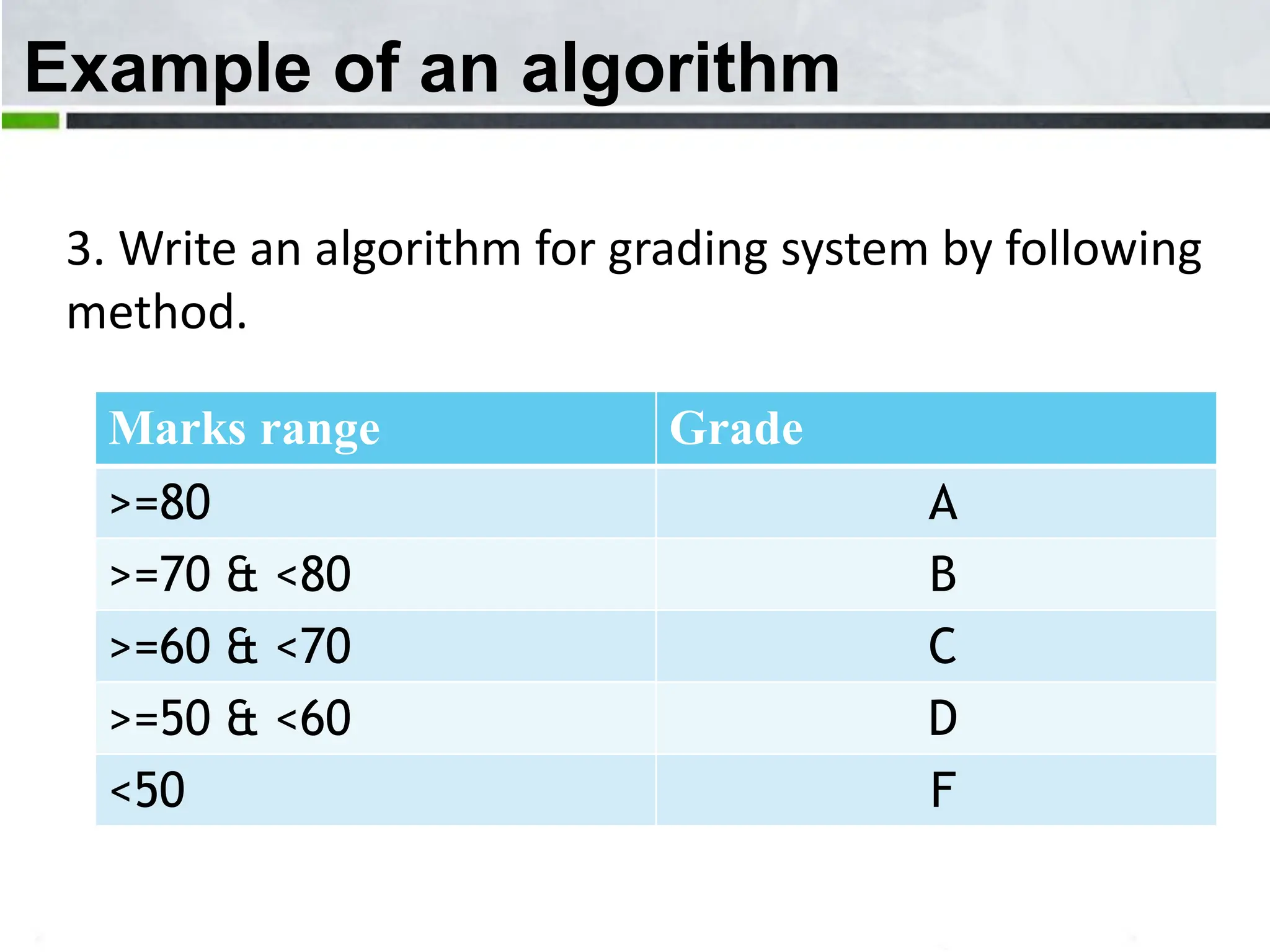
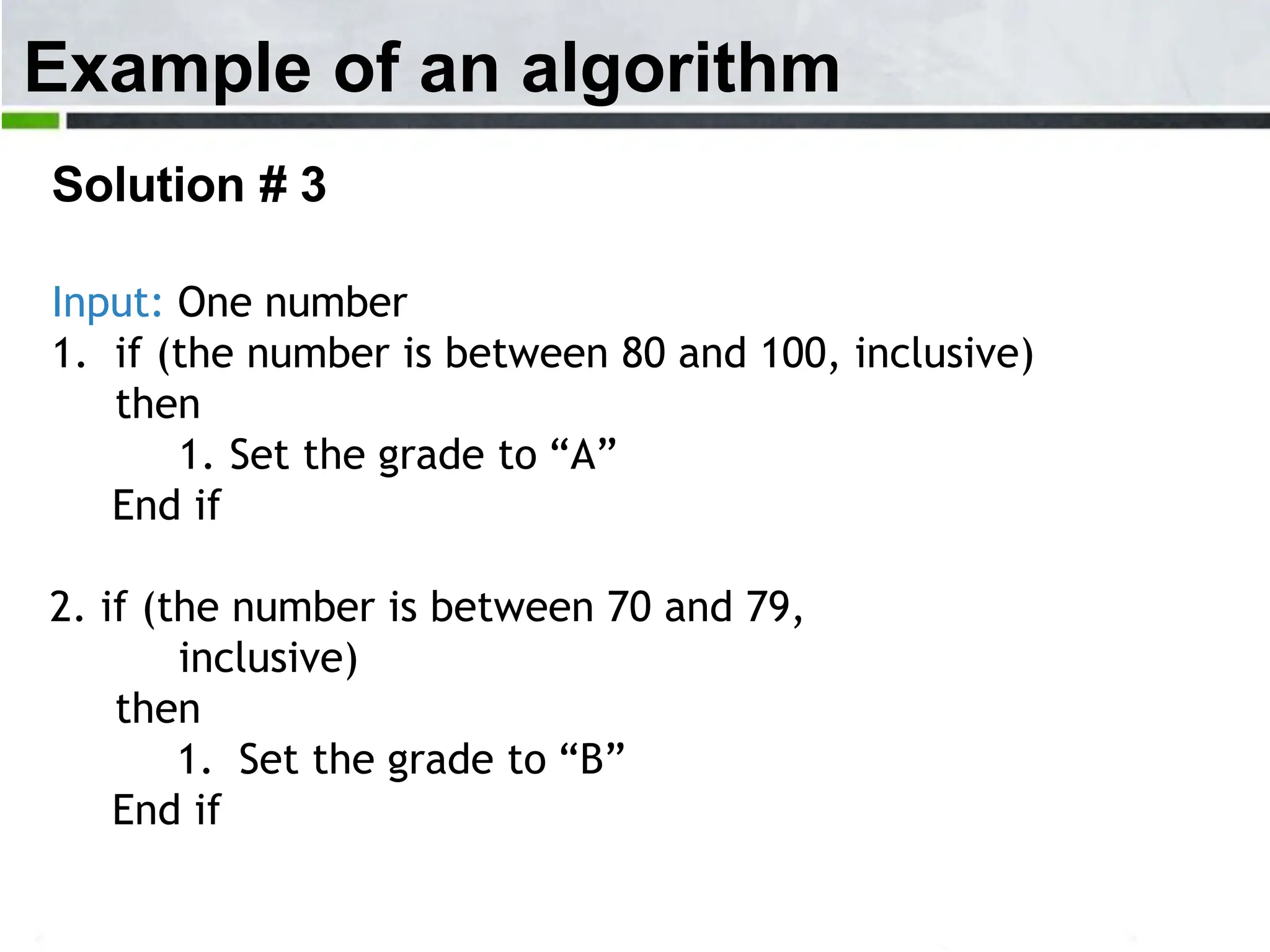
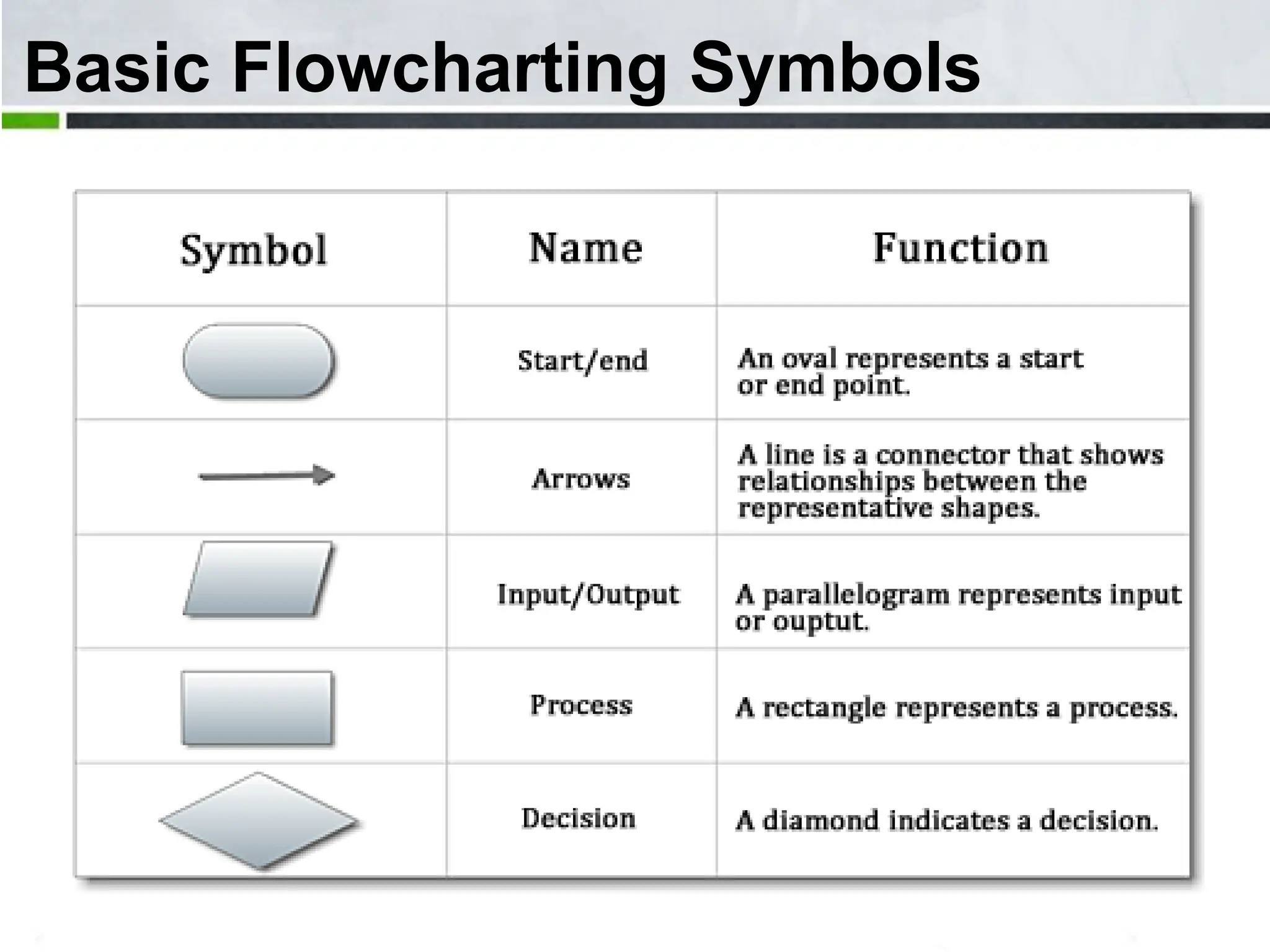
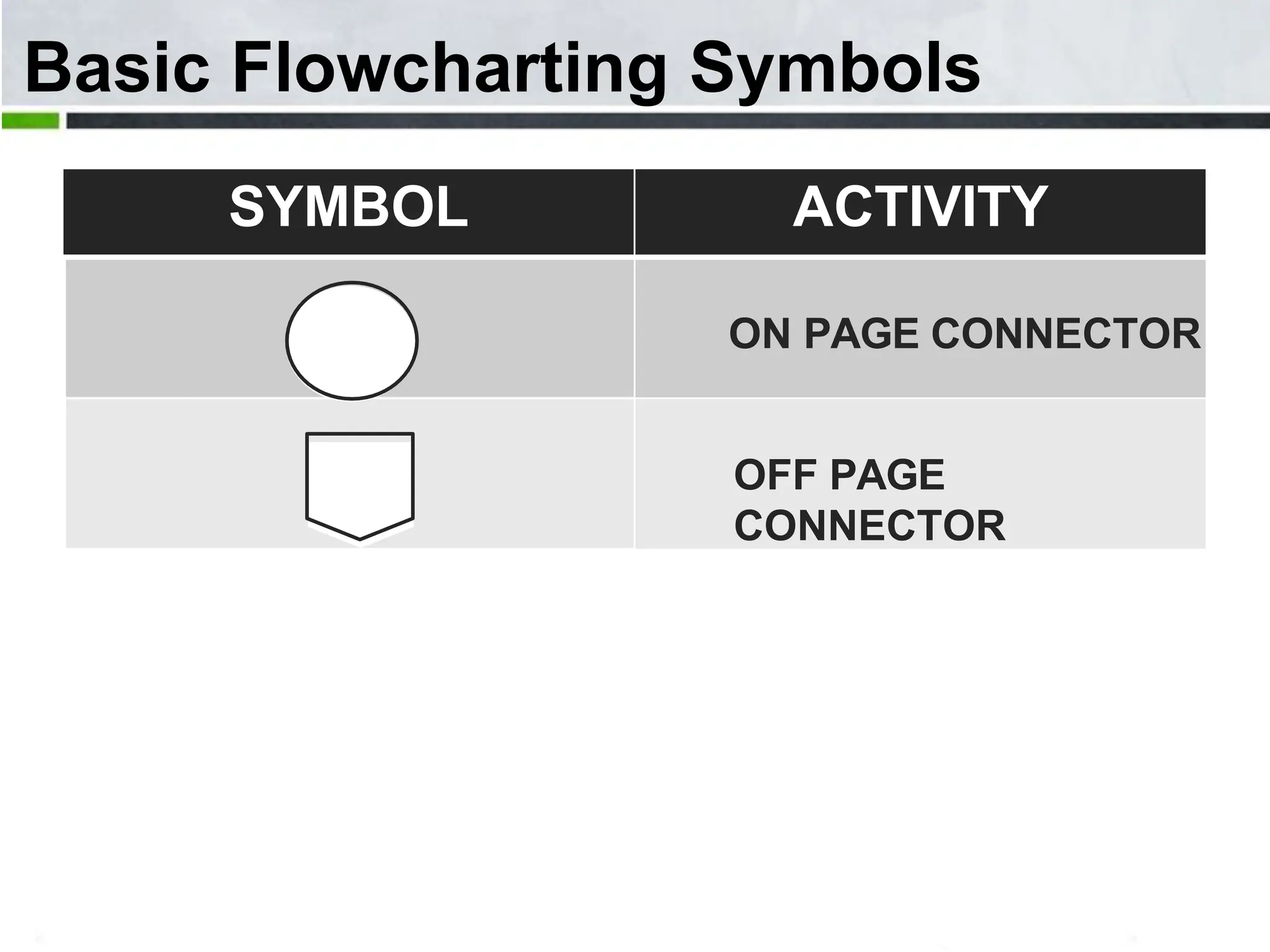
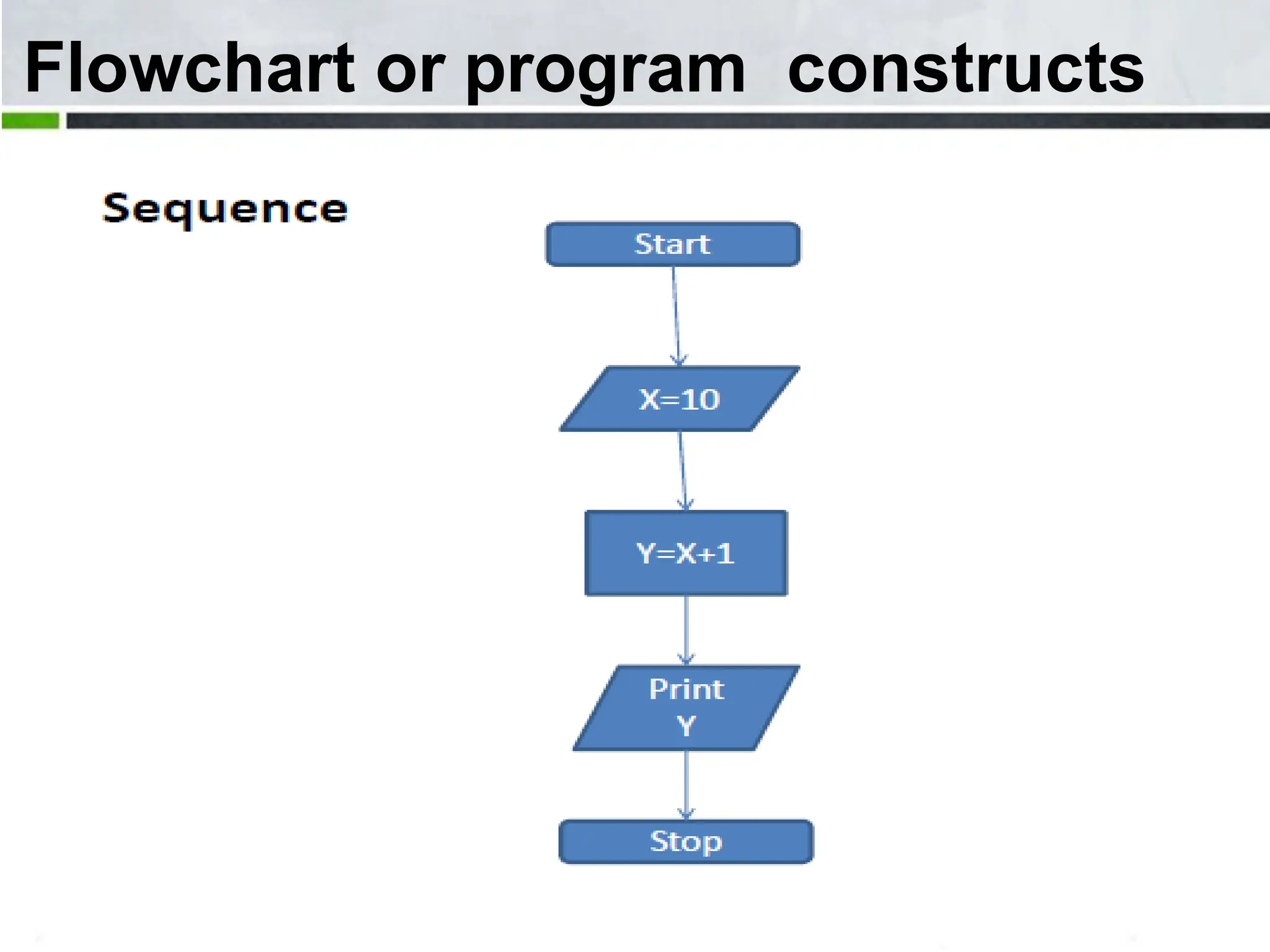
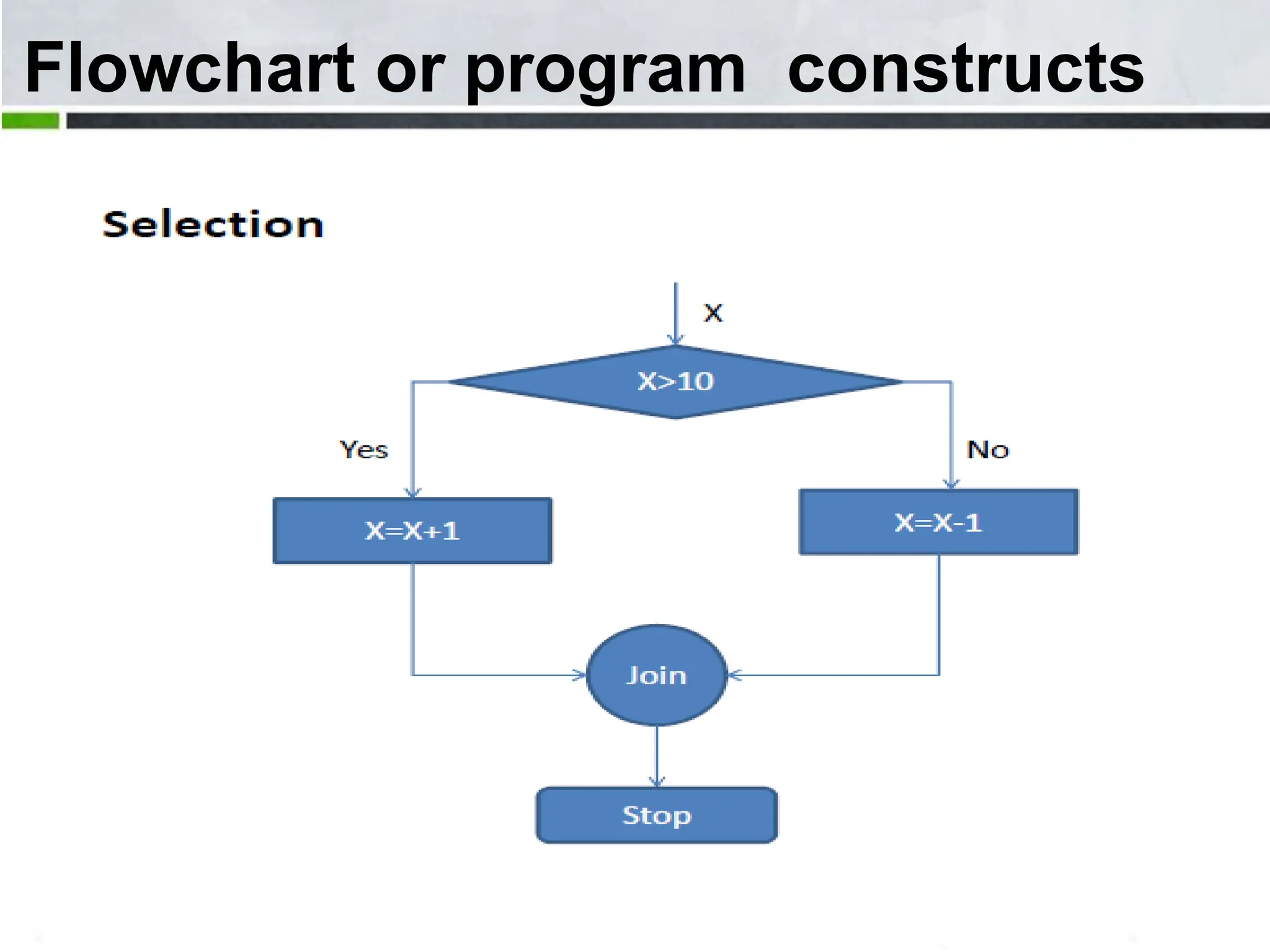
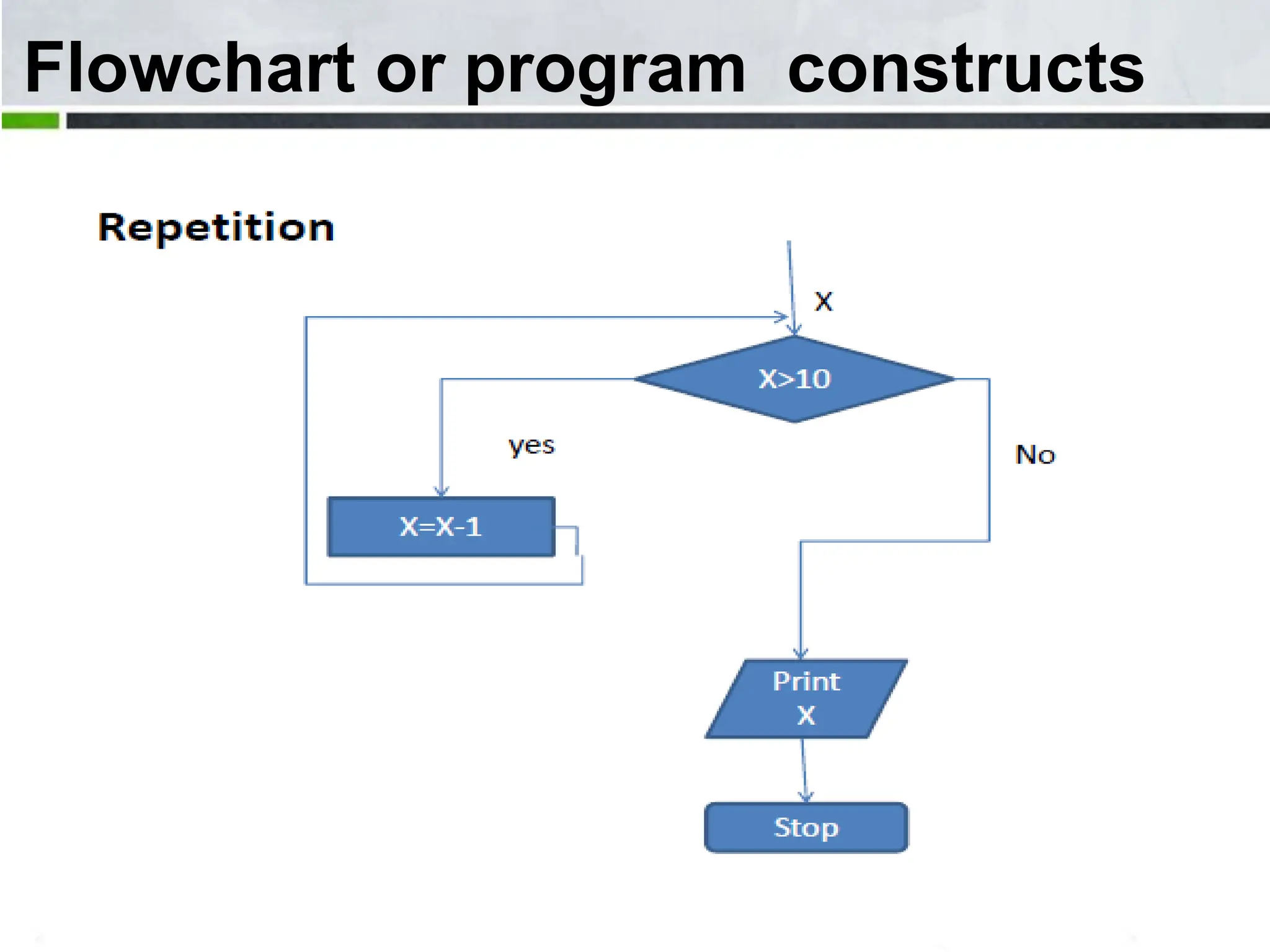
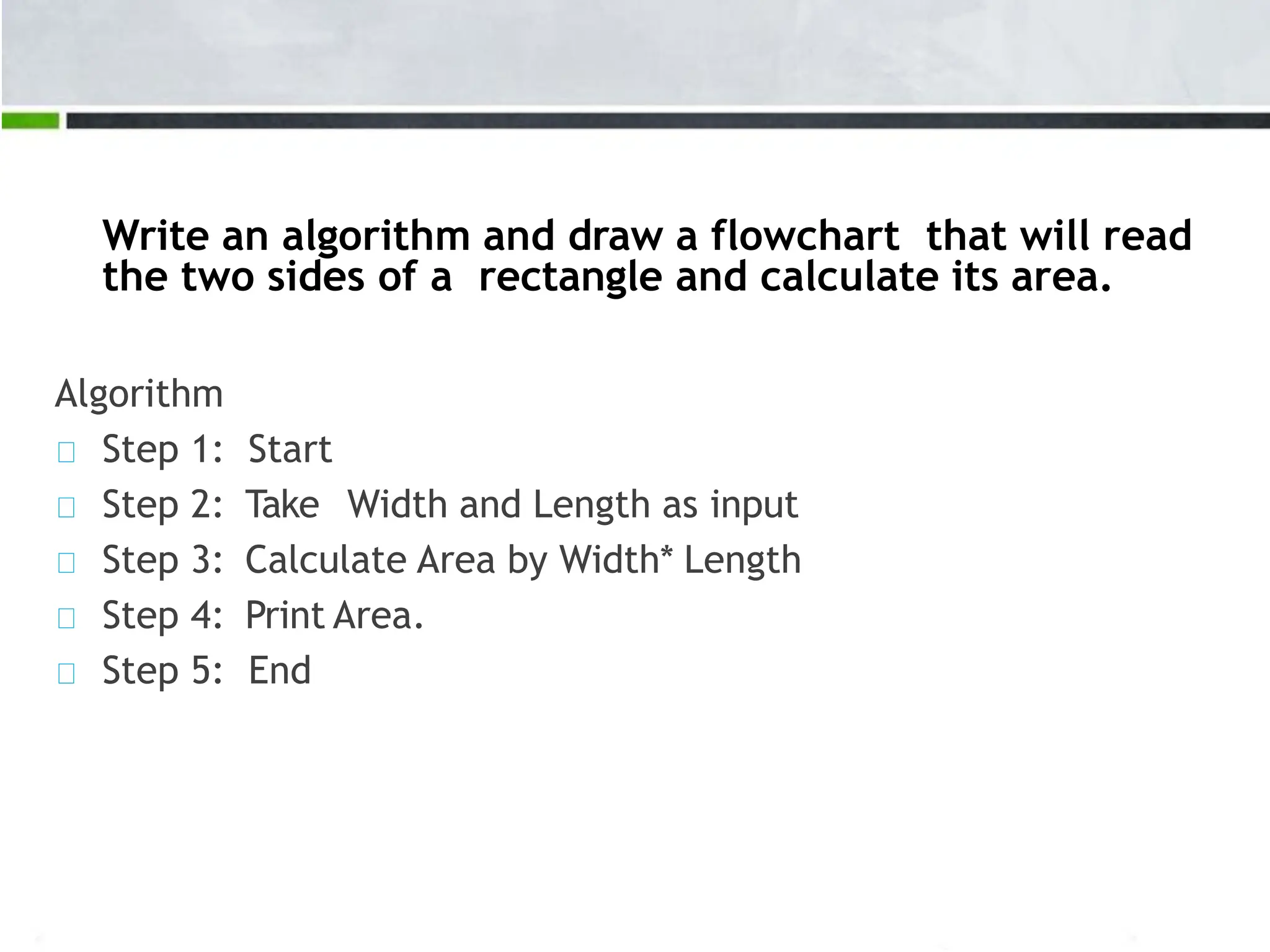
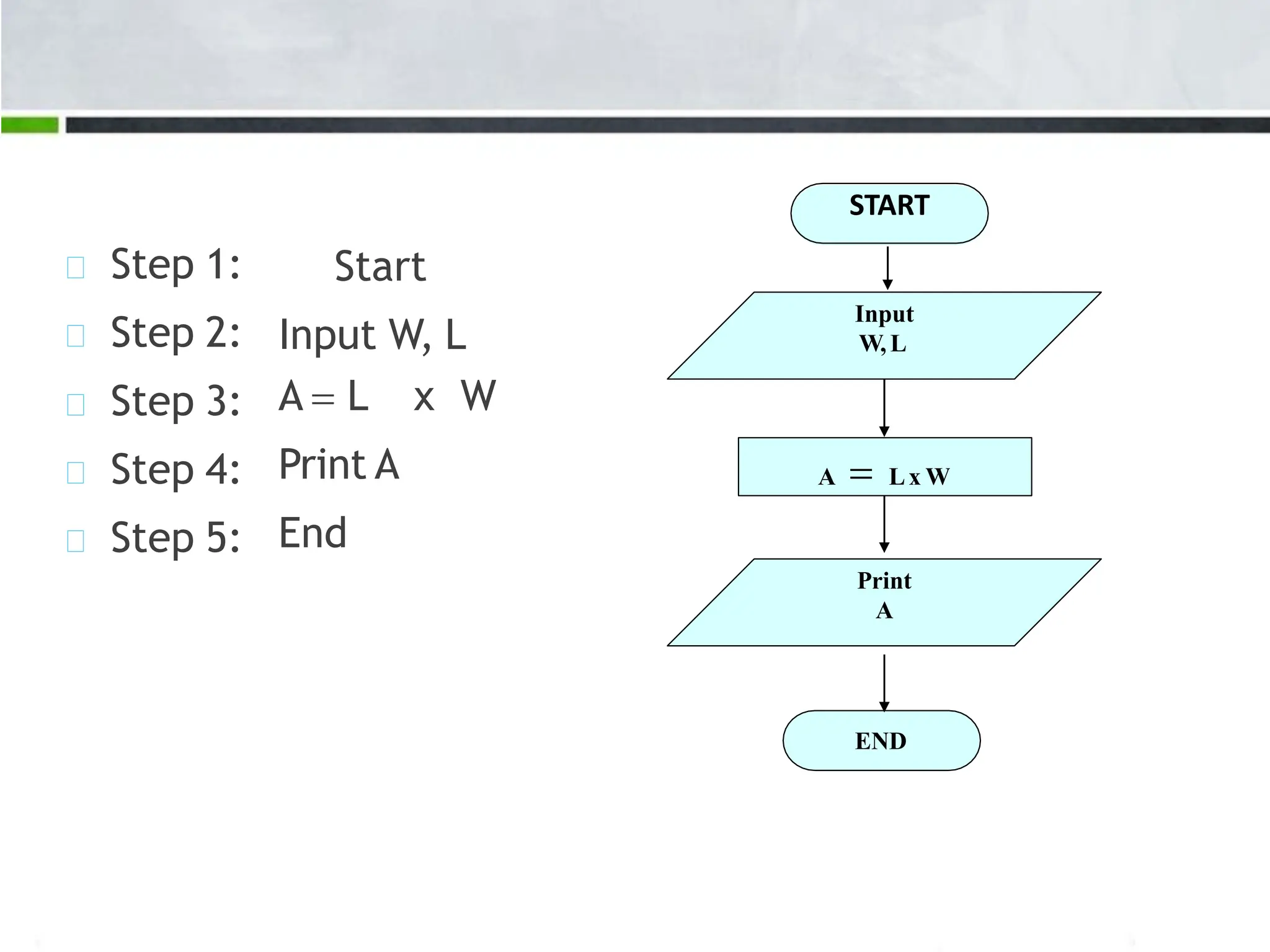
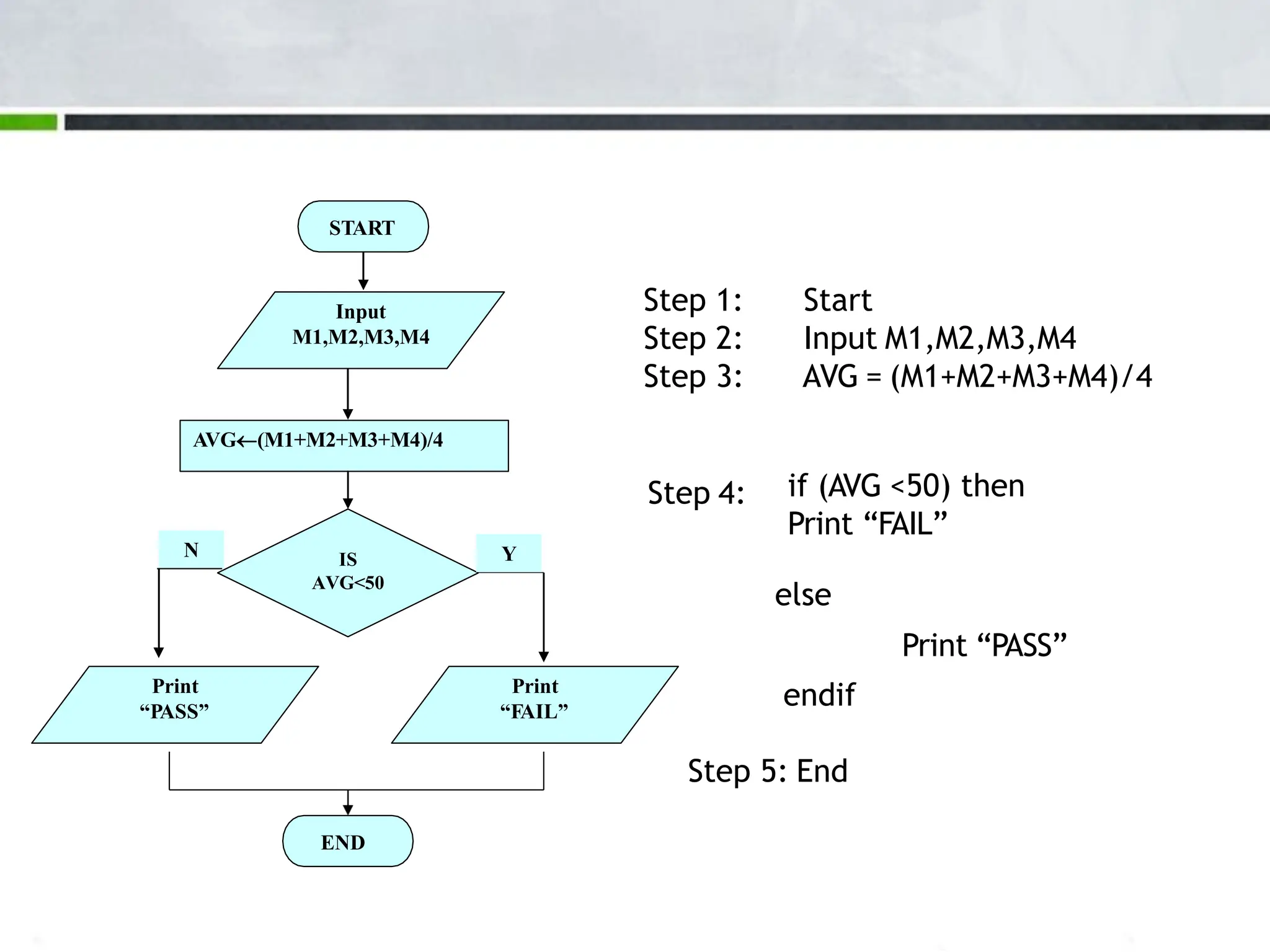
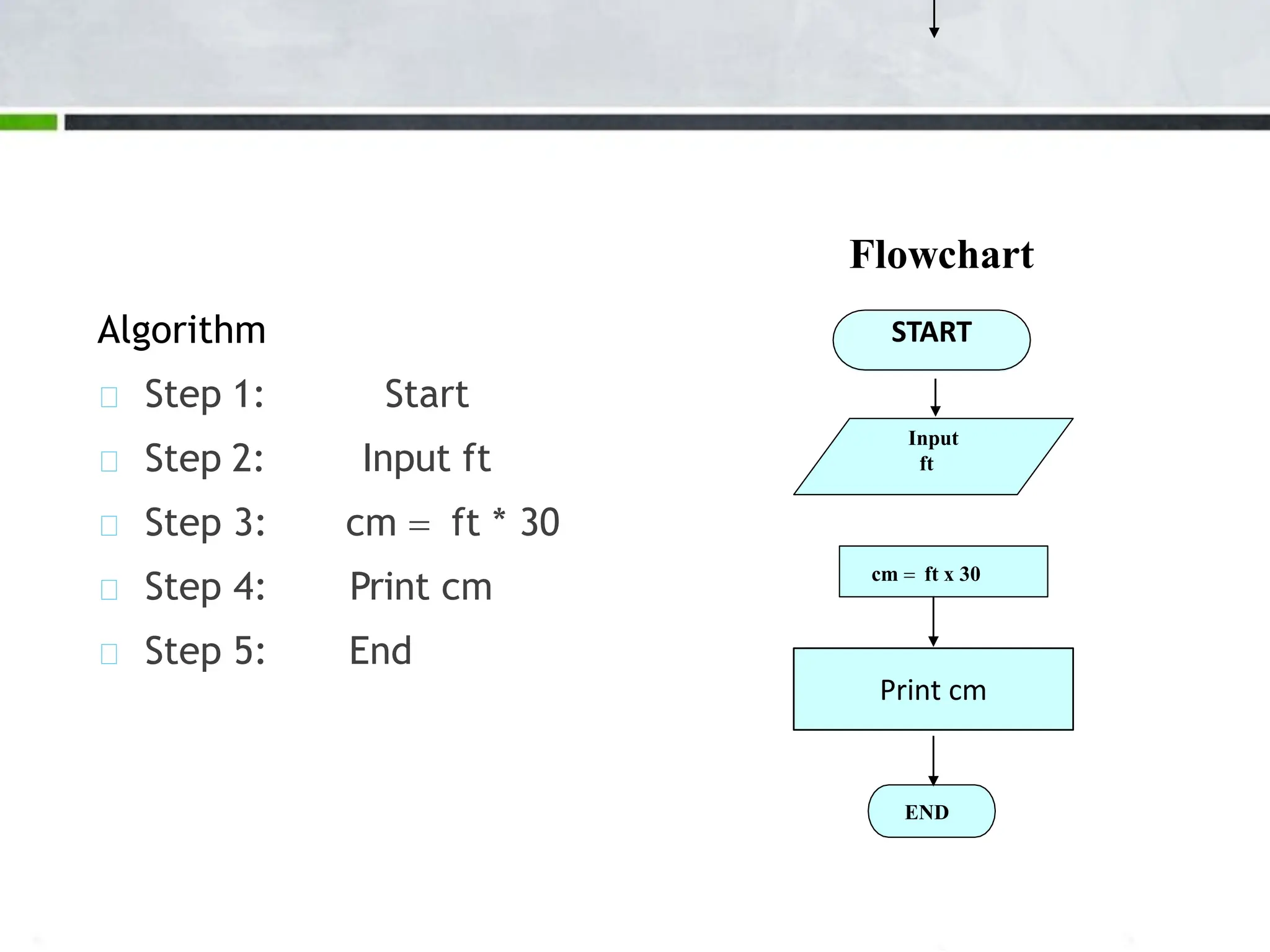
An algorithm is a step-by-step process to solve a problem. It must be understandable by humans. The document provides examples of algorithms such as driving to a friend's house and grading systems. It also discusses flowcharts which use symbols to visually represent information flow in an algorithm. Examples are given to draw flowcharts for calculating rectangle area based on width and length, finding average marks of four subjects, and converting feet to centimeters.