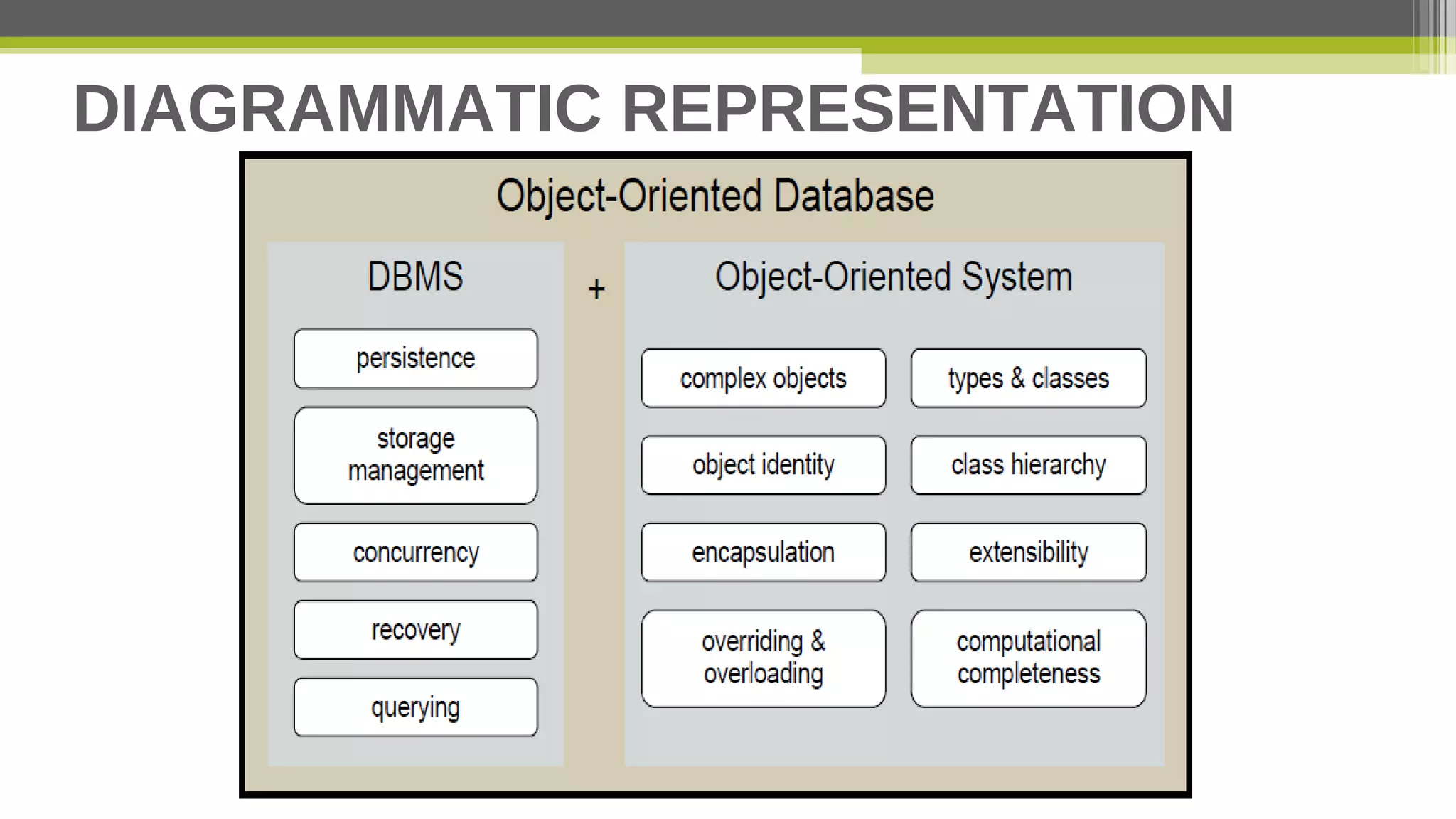
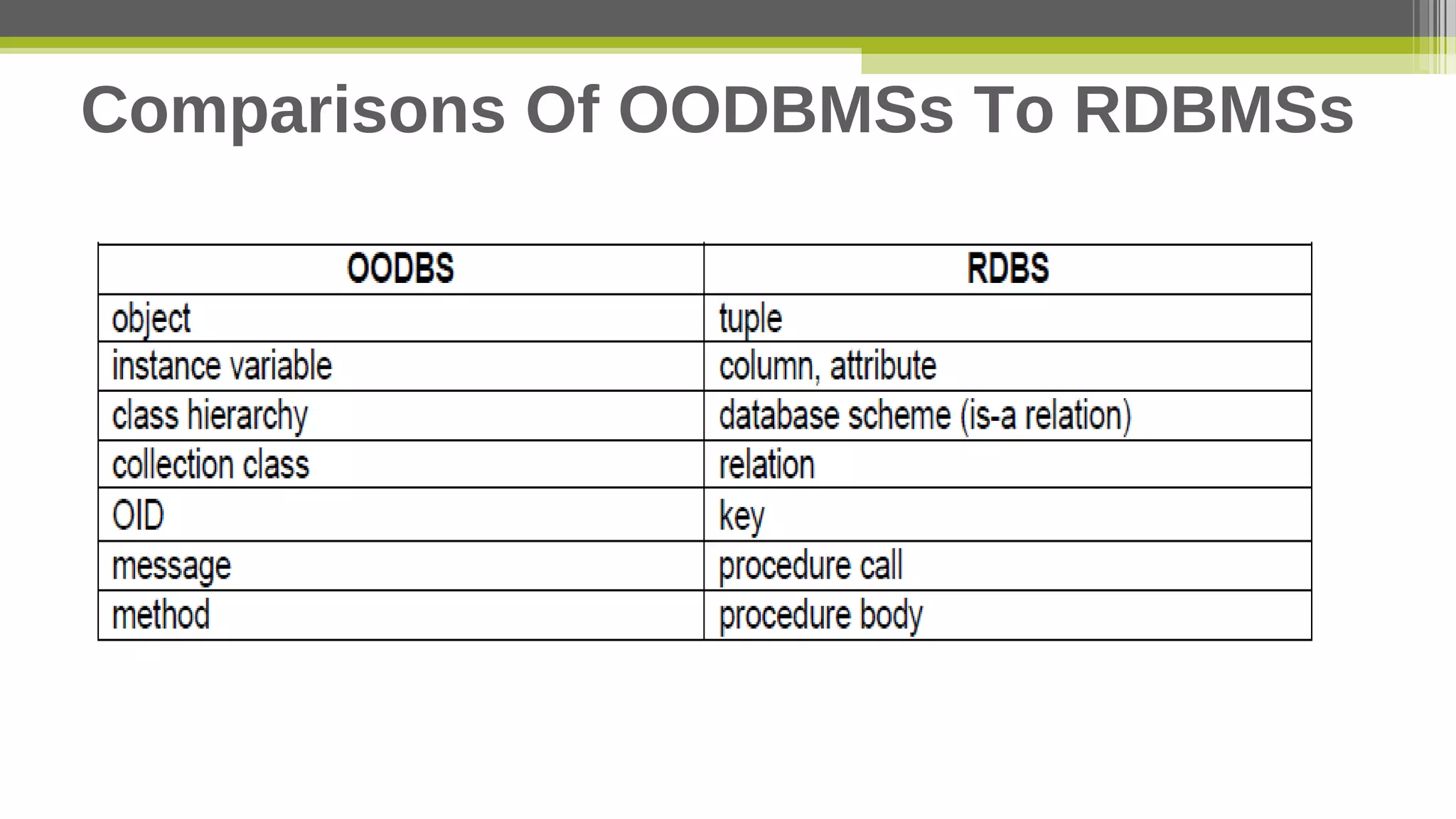
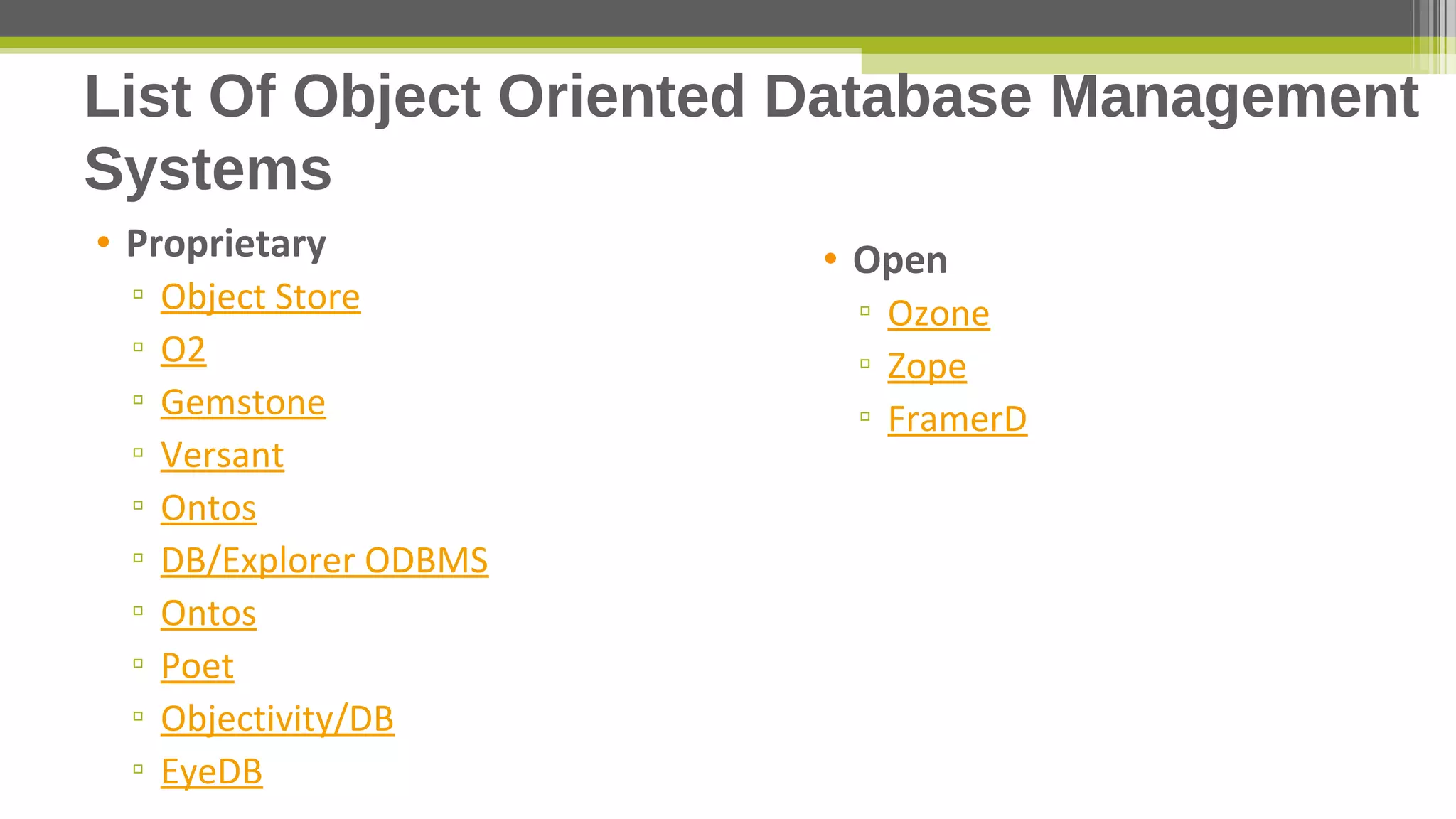
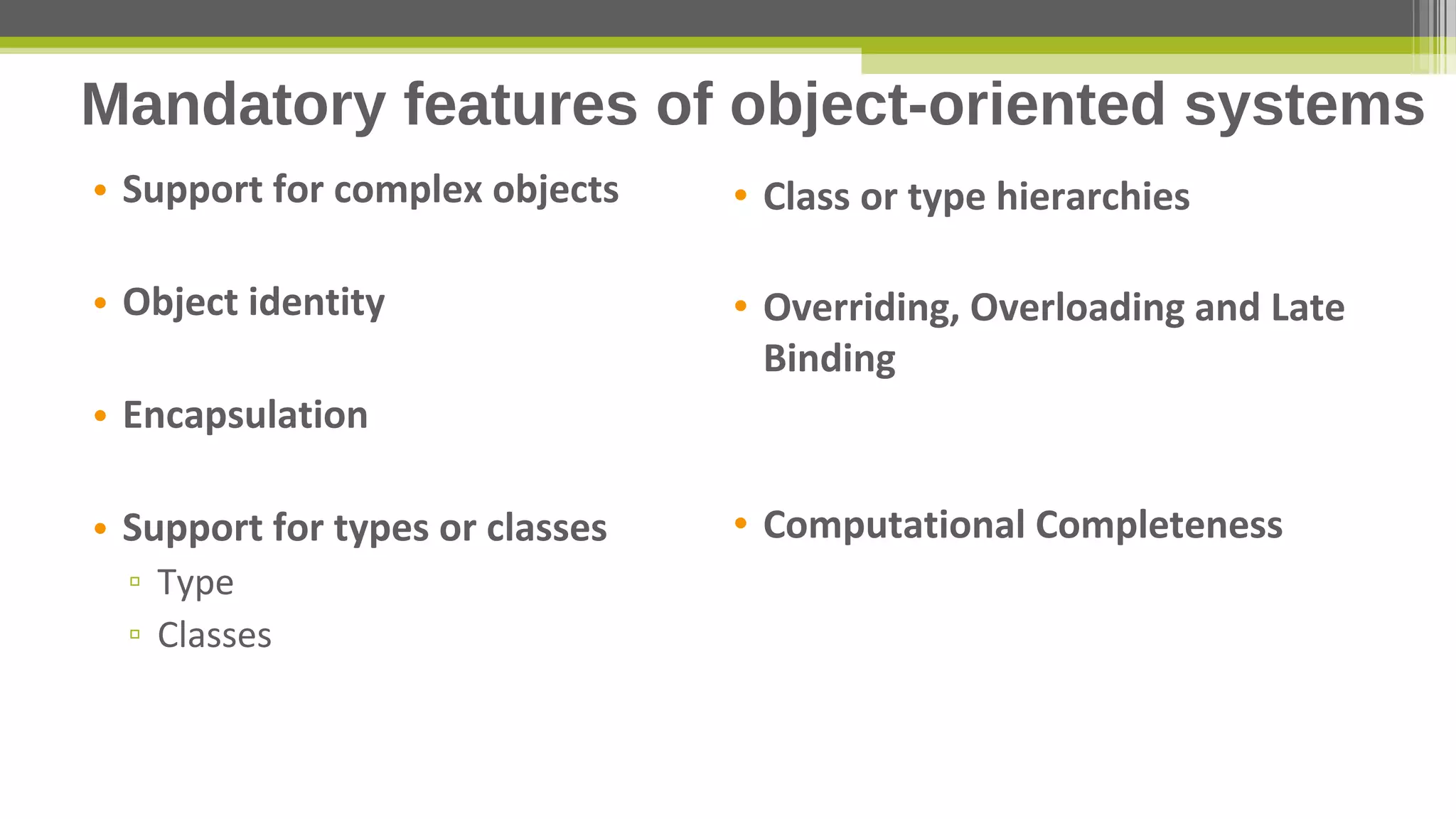
This document provides an overview of object-oriented database management systems (OODBMS), which combine object-oriented programming principles with database management. It discusses how OODBMSs support encapsulation, polymorphism, inheritance and ACID properties while allowing for complex objects, relationships, and queries of large amounts of data. The document also lists advantages and disadvantages of OODBMSs compared to relational database systems and examples of both proprietary and open-source OODBMSs.