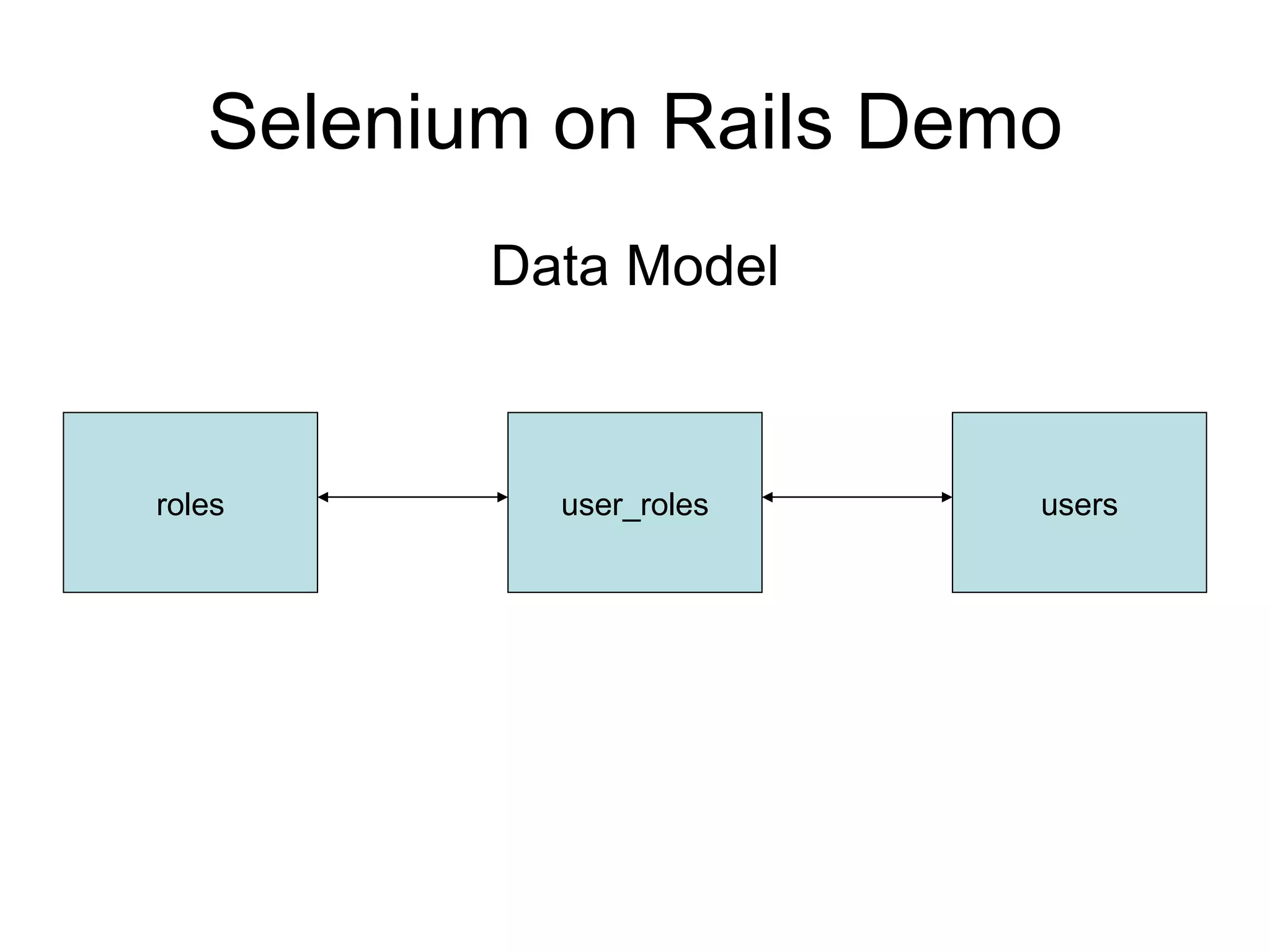
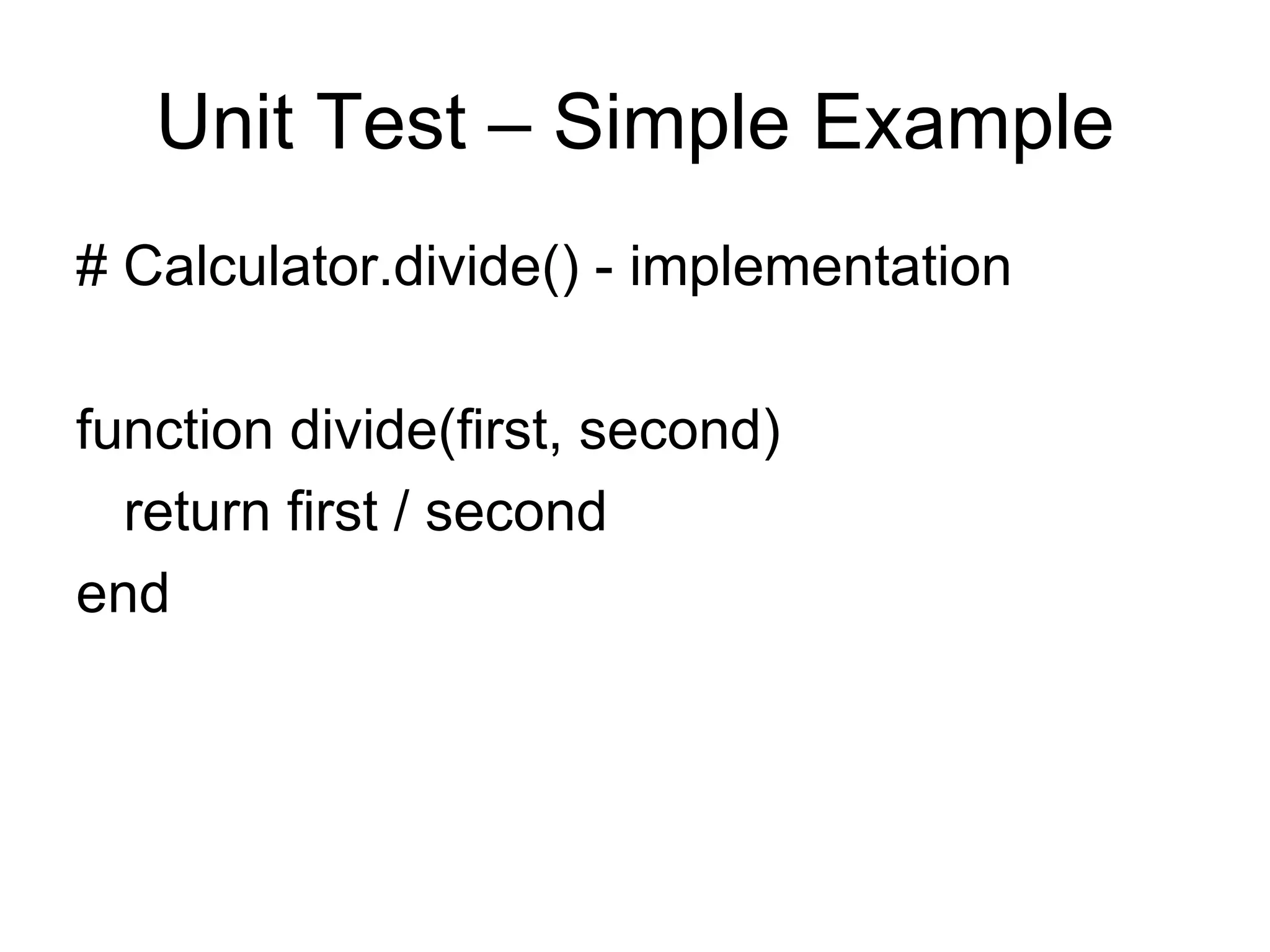
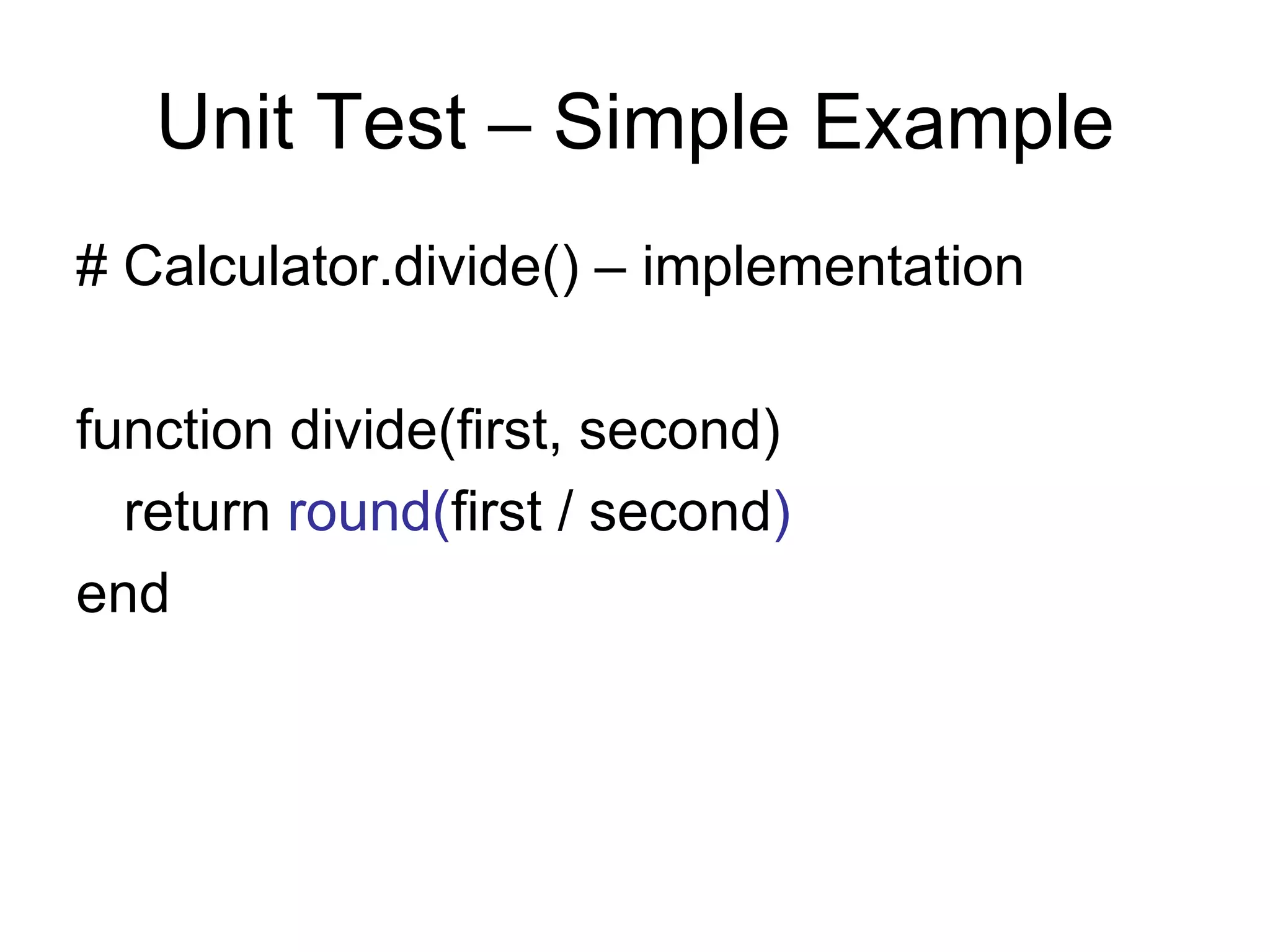
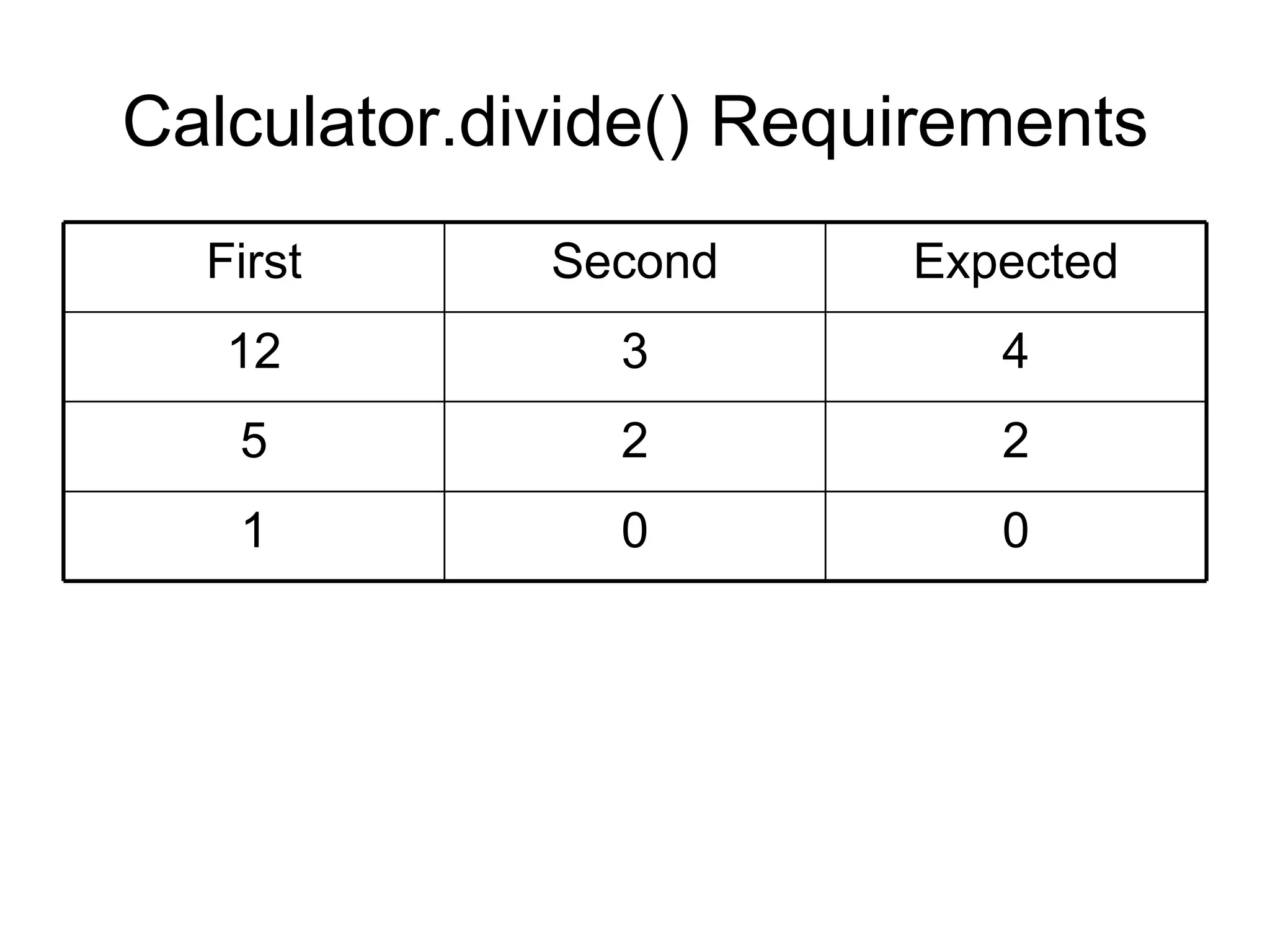
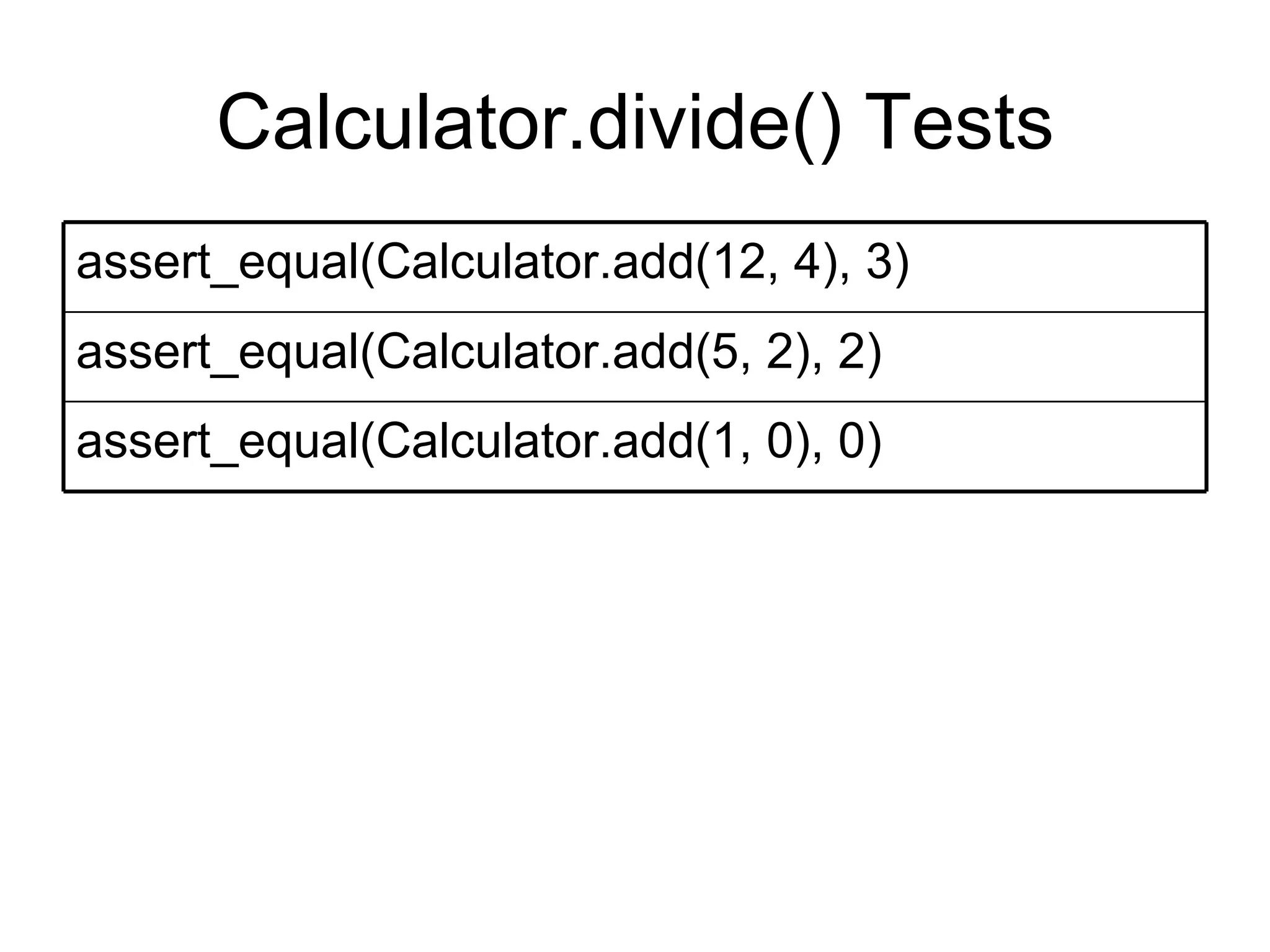
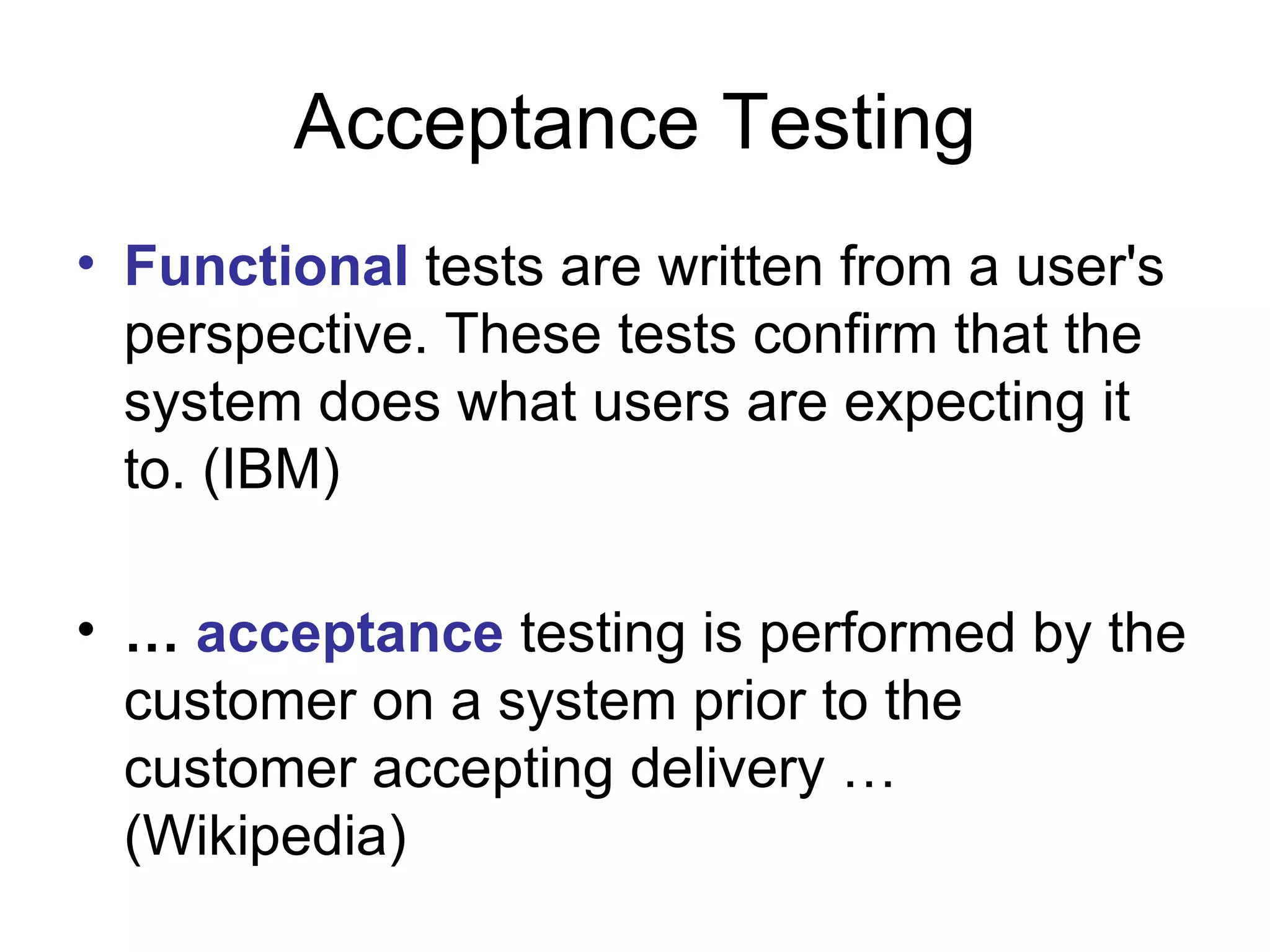
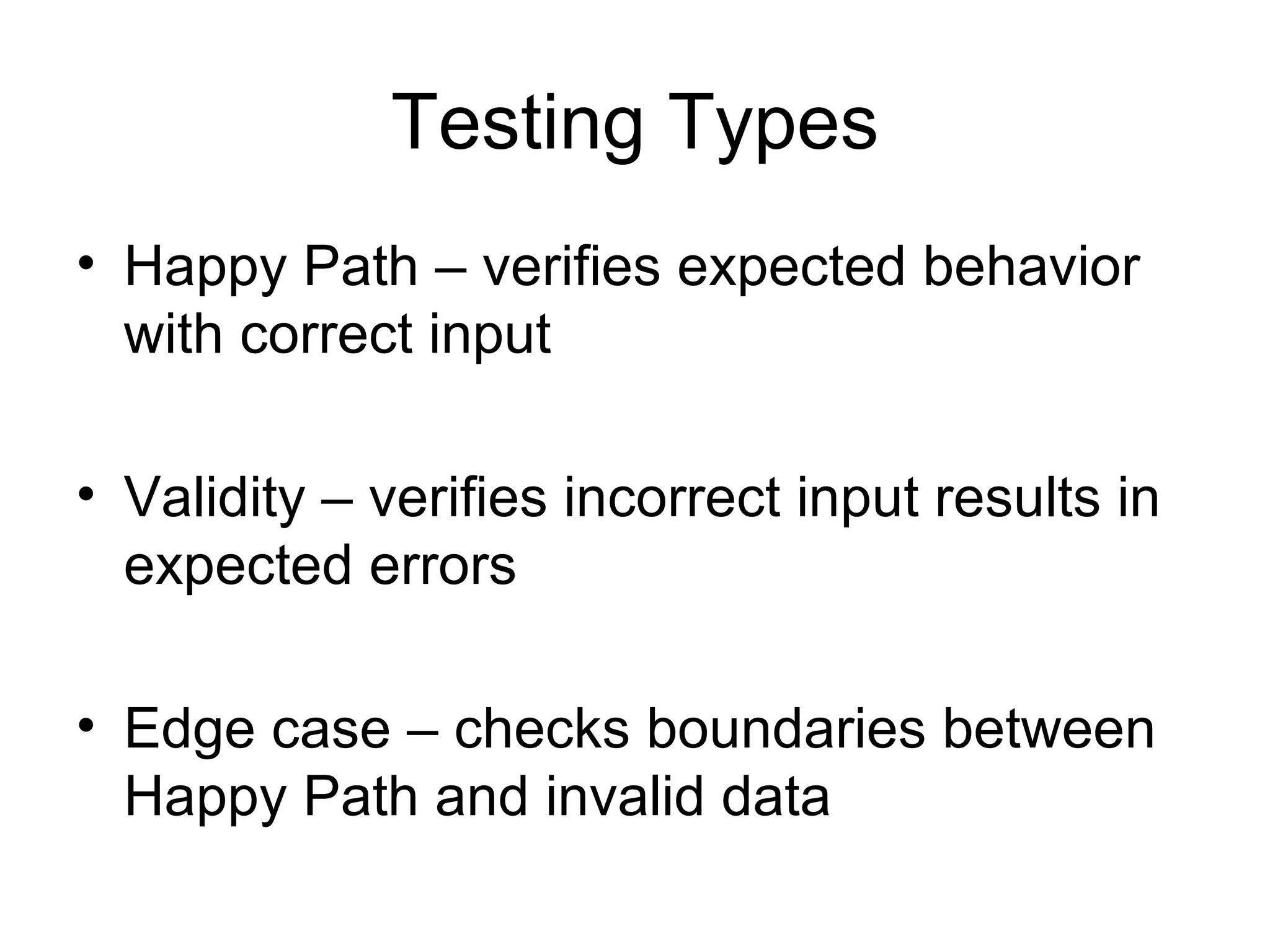
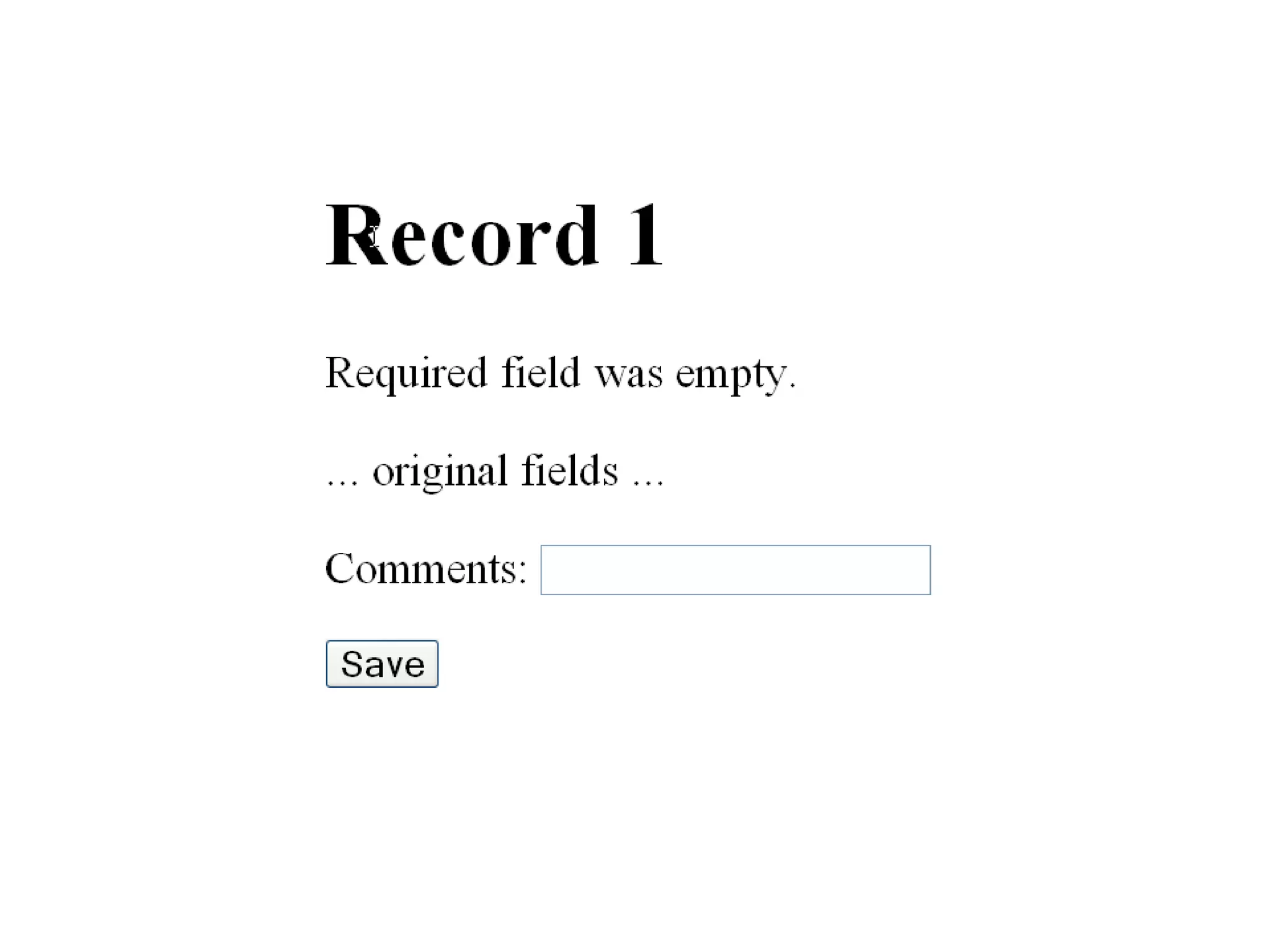
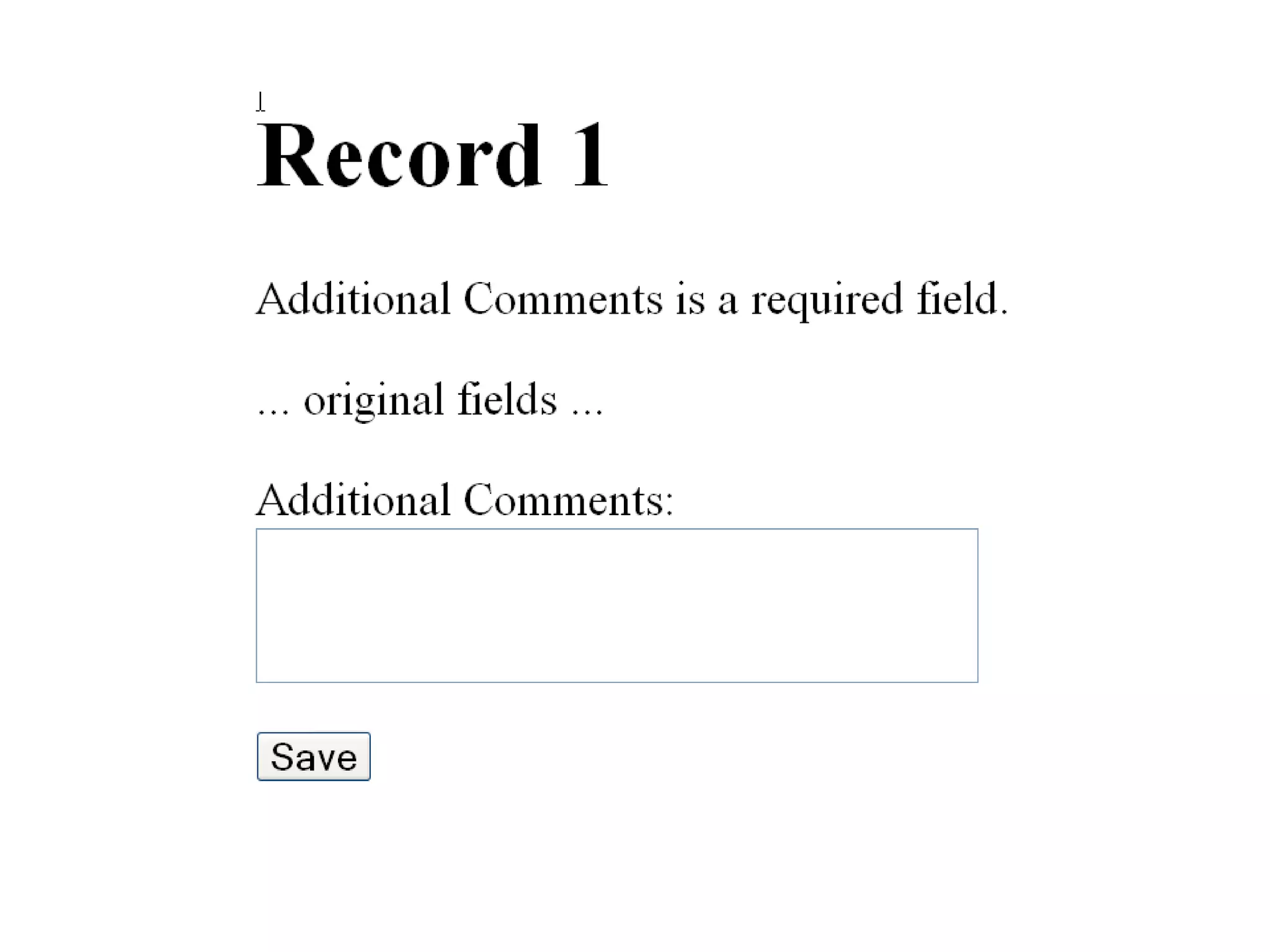
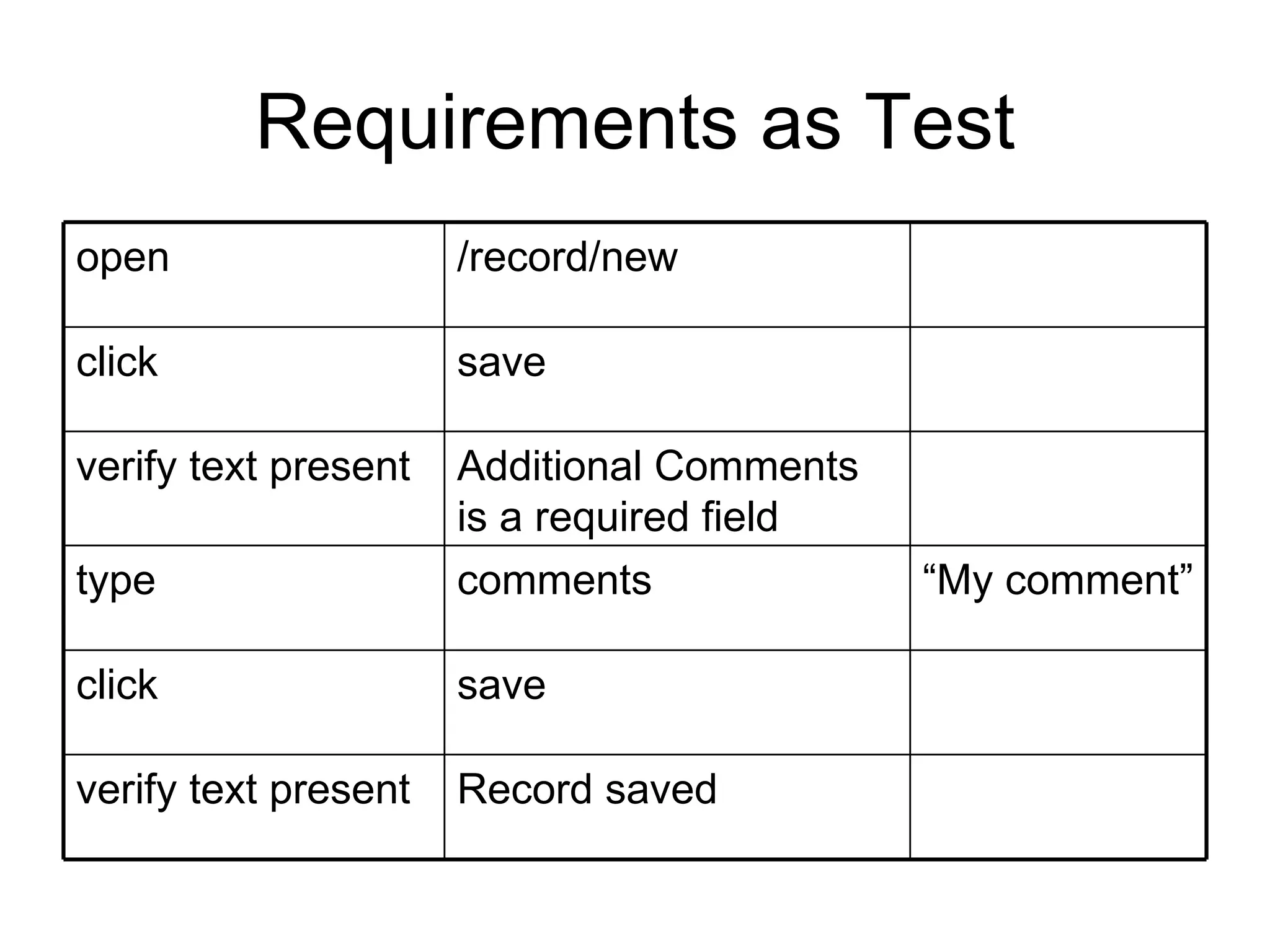
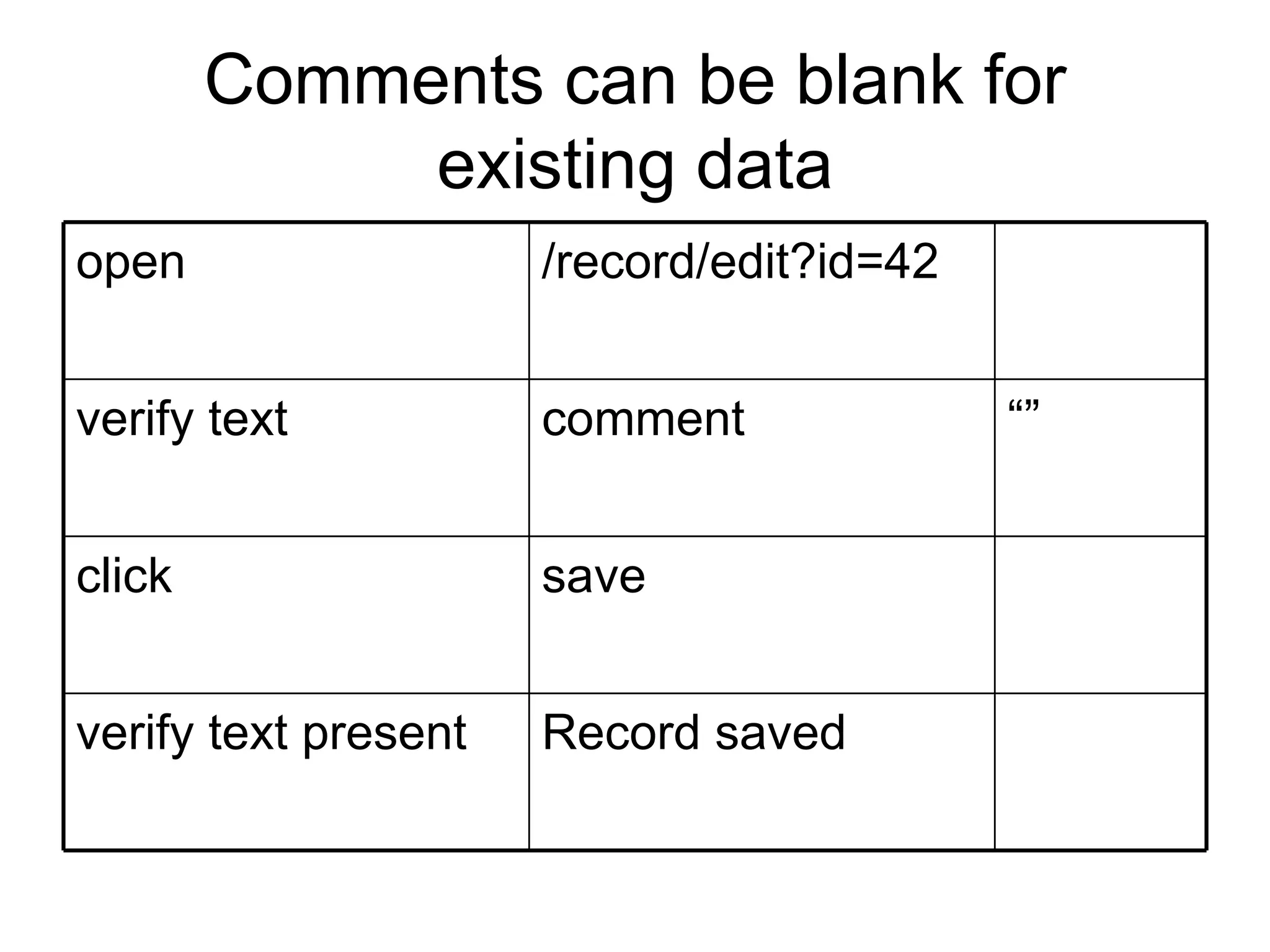
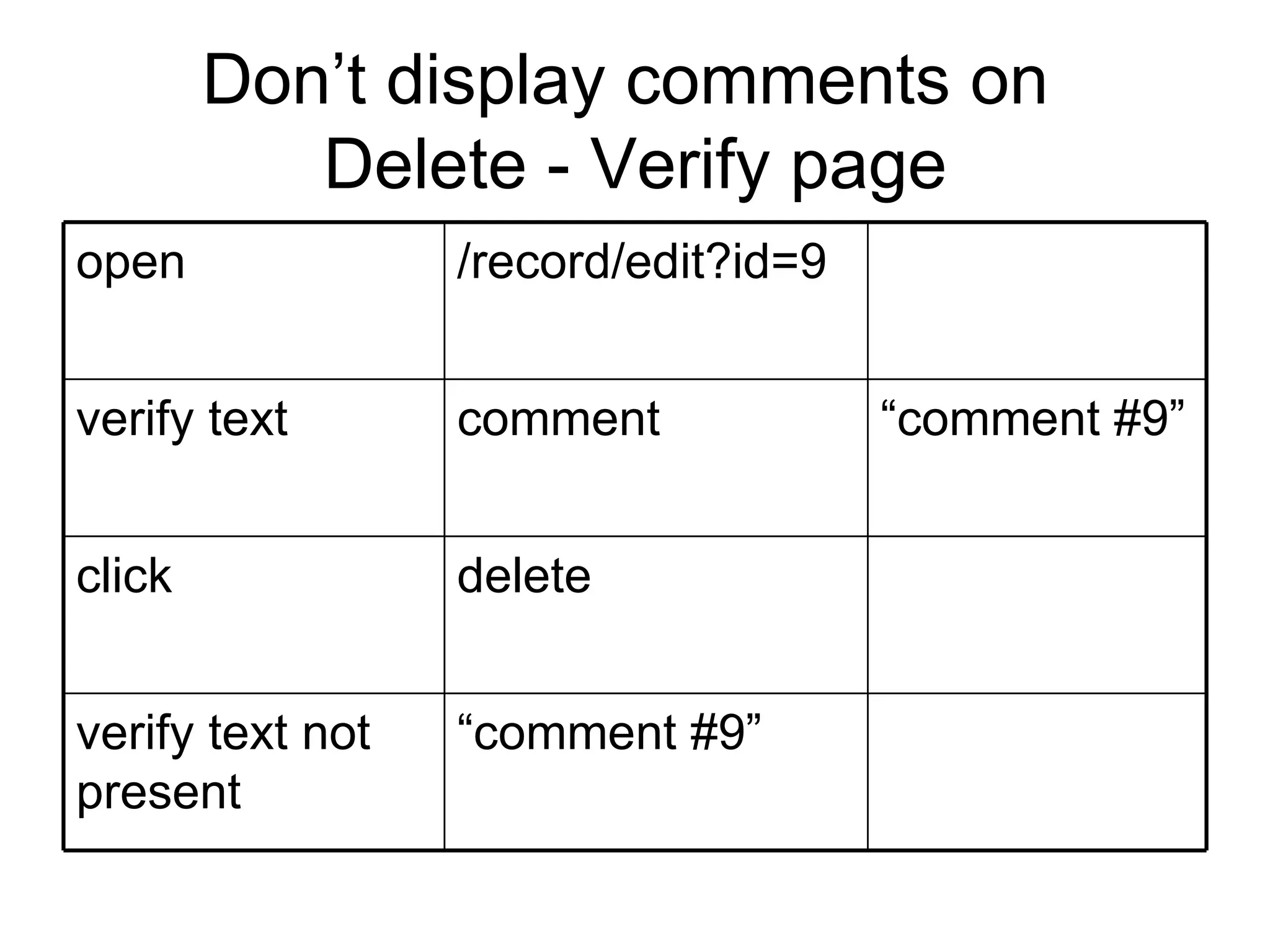
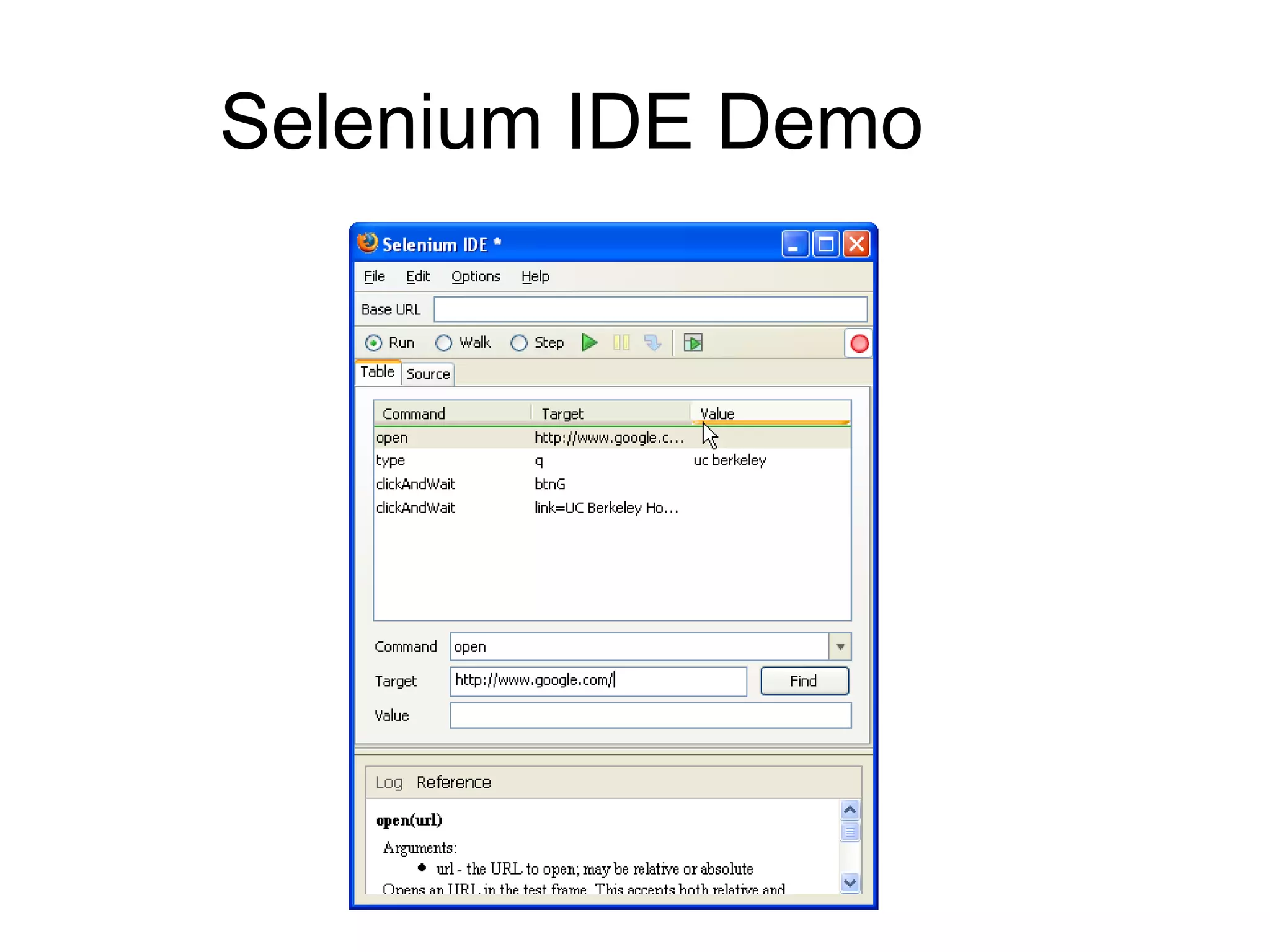
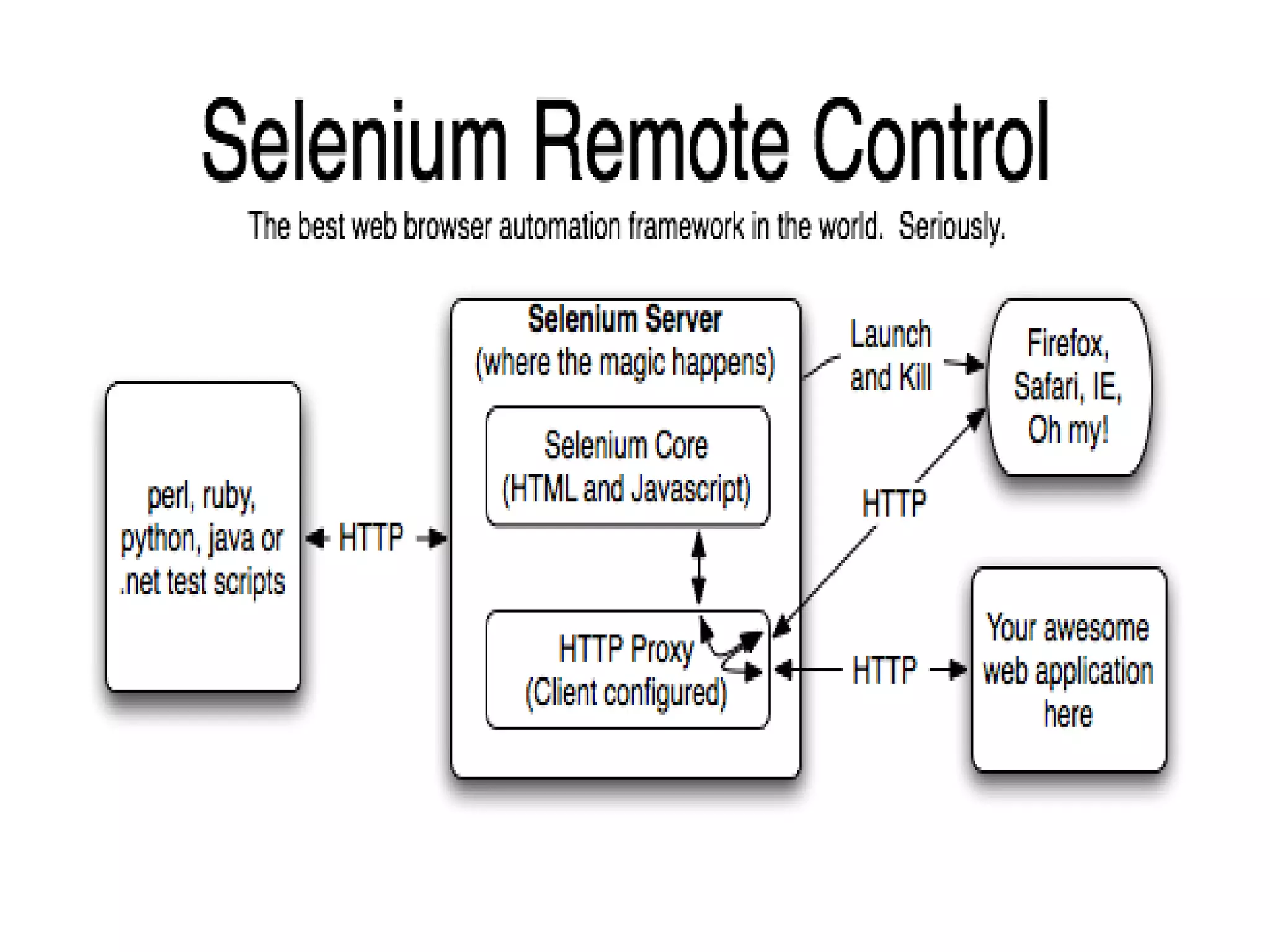
The document discusses acceptance testing with Selenium. It provides examples of unit testing code with assertions to validate functionality. It explains that acceptance tests are written from the user perspective to validate requirements and are performed near the end of a project by the customer before accepting delivery. Selenium allows automating acceptance tests by controlling browsers to simulate user actions and verify outcomes.






































![Selenium Element Selectors id=some_id or name=some_name dom=document.forms[1].myDropdown xpath=//img[@alt=‘Some alt text’] link=some link text css=cssSelectorSyntax](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acceptancetestingwithselenium-1227967942427904-9/75/Acceptance-Testing-With-Selenium-51-2048.jpg)



![C# (NUnit) Example using Selenium; using NUnit.Framework; namespace MyTests { [TestFixture] public class GoogleTest { private ISelenium sel; [SetUp] public void SetUp() { sel = new DefaultSelenium("localhost", 4444, "*firefox", "http://www.google.com"); sel.Start(); } [Test] public void testGoogle() { sel.Open("http://www.google.com/webhp"); sel.Type("q", "hello world"); sel.Click("btnG"); sel.WaitForPageToLoad("5000"); Assert.AreEqual("hello world - Google Search", sel.GetTitle()); } [TearDown] public void TearDown() { sel.Stop(); } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acceptancetestingwithselenium-1227967942427904-9/75/Acceptance-Testing-With-Selenium-56-2048.jpg)
![C# (NUnit) Example [Test] public void testGoogle() { sel.Open("http://www.google.com/webhp"); sel.Type("q", "hello world"); sel.Click("btnG"); sel.WaitForPageToLoad("5000"); Assert.AreEqual("hello world - Google Search", sel.GetTitle()); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acceptancetestingwithselenium-1227967942427904-9/75/Acceptance-Testing-With-Selenium-57-2048.jpg)