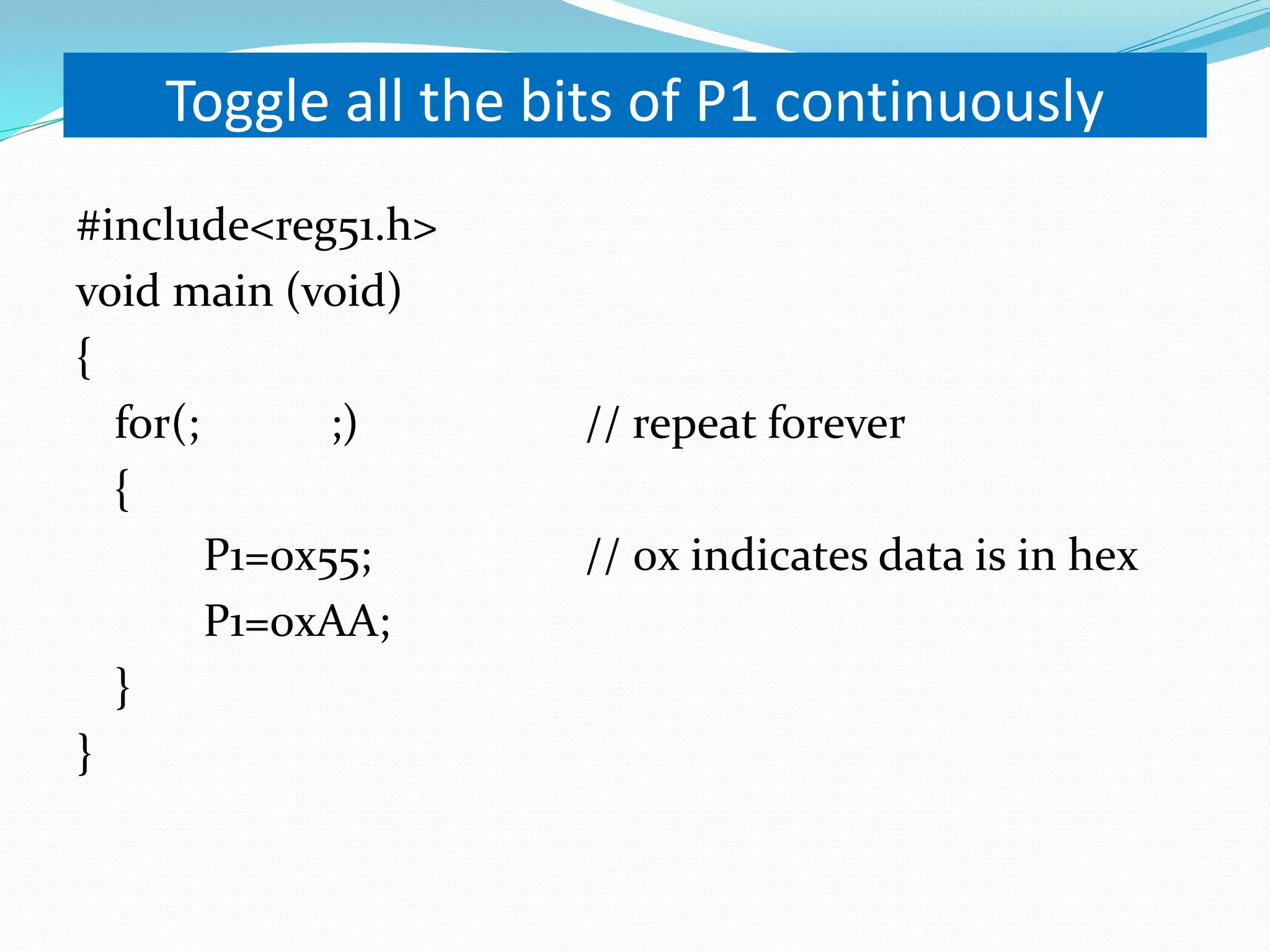
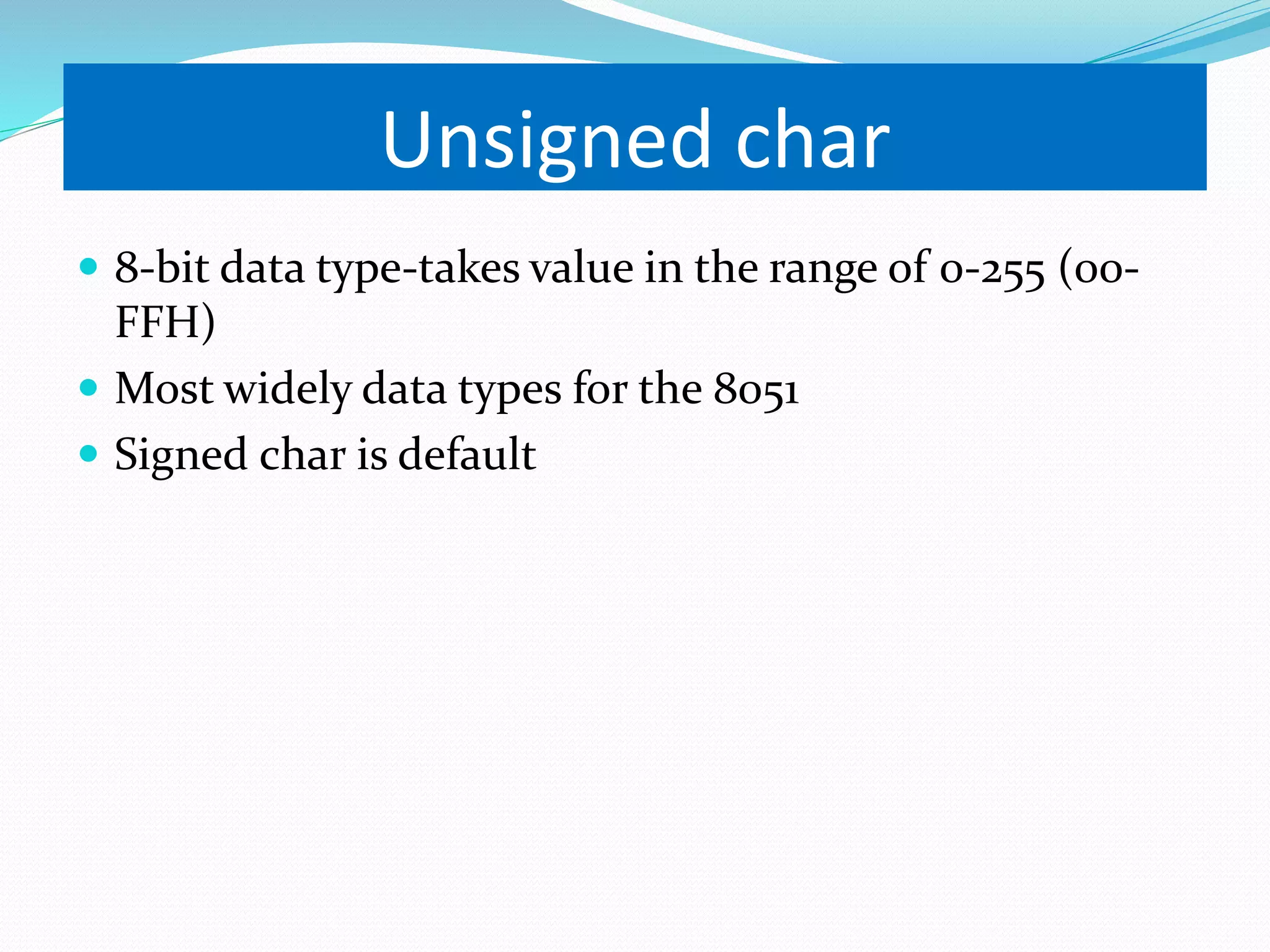
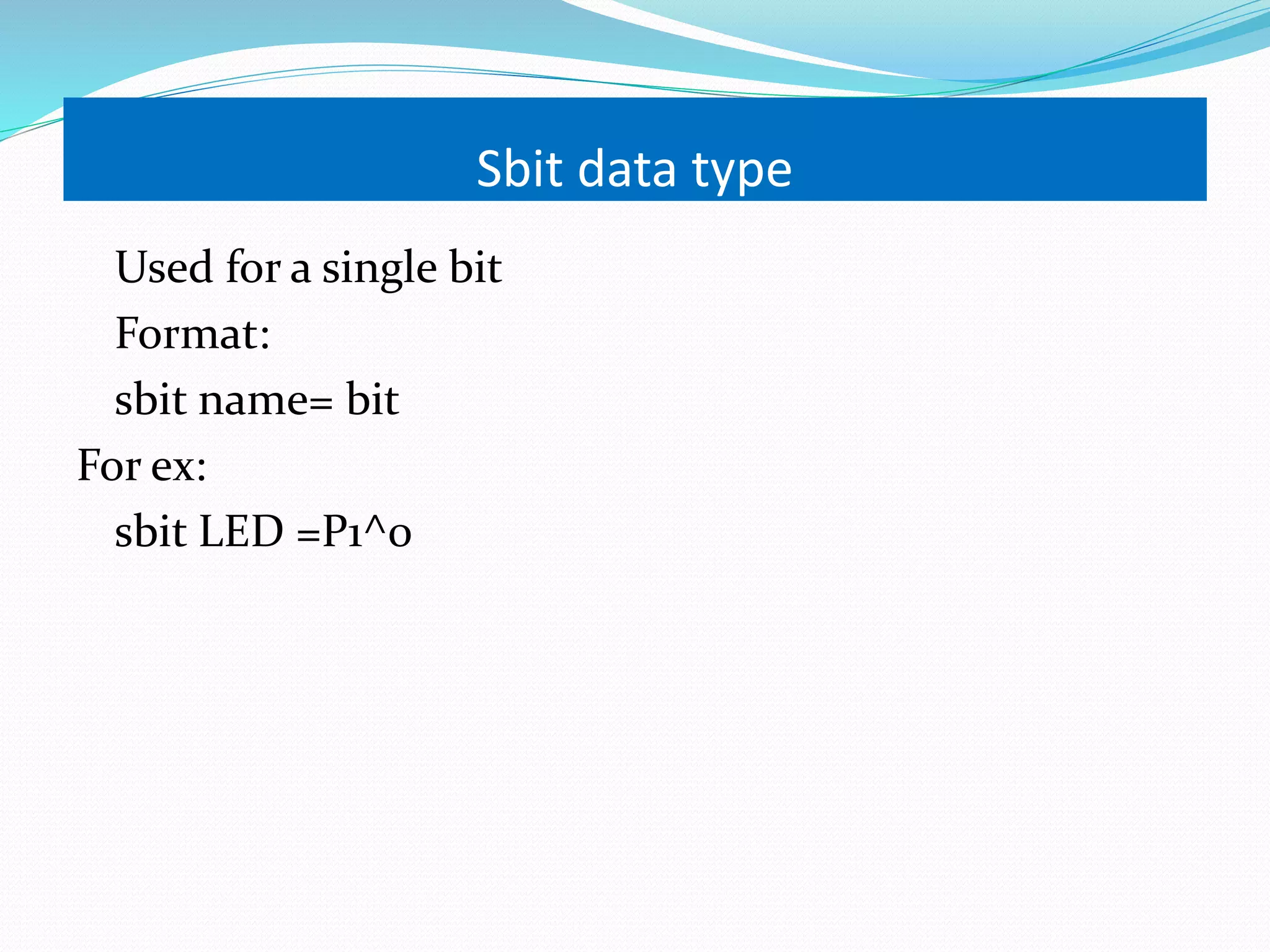
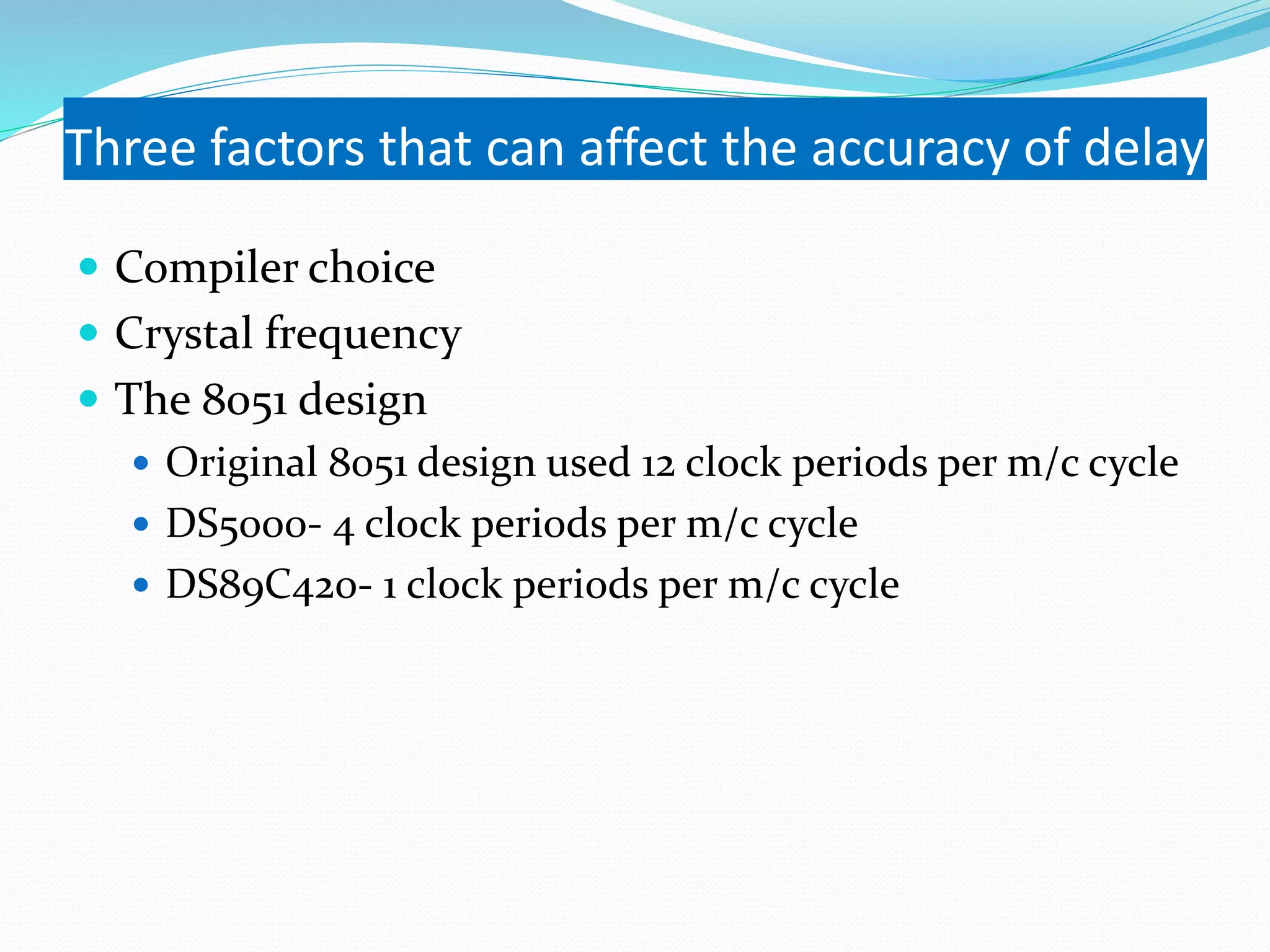
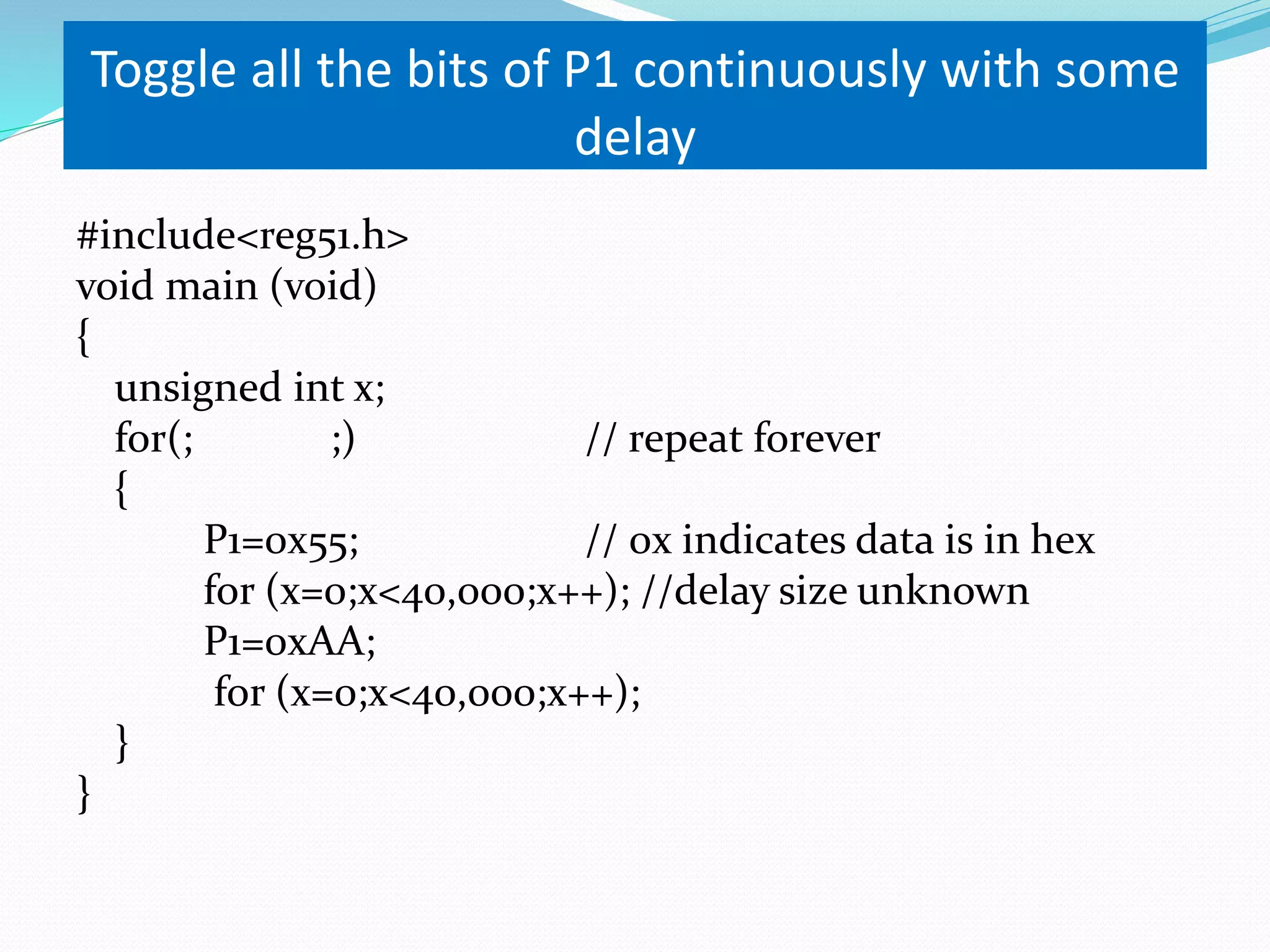
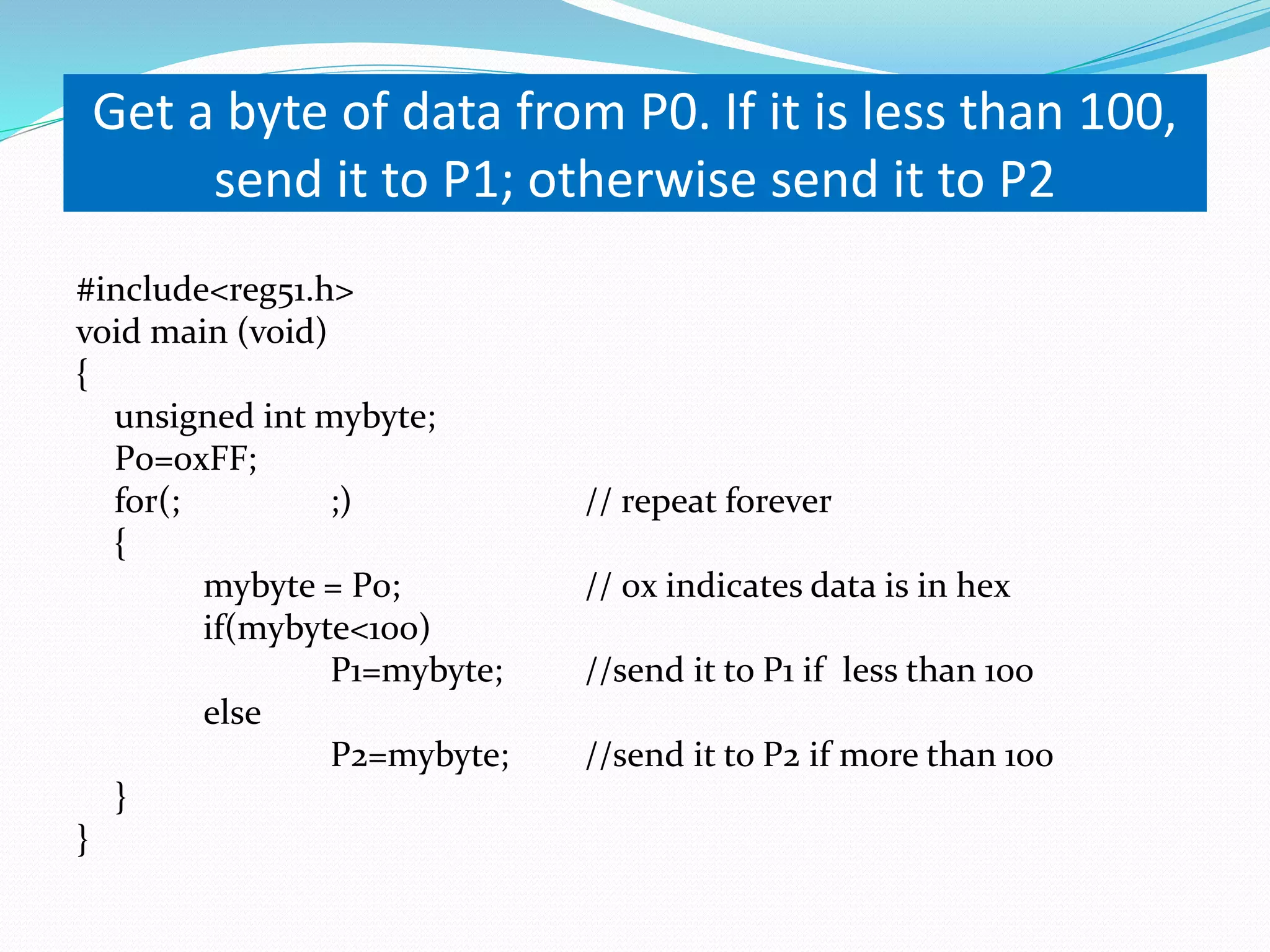
This document provides an overview of programming the 8051 microcontroller in C. It discusses machine language, assembly language, and high-level languages. It then demonstrates how to create a hex file using a compiler, burn it to a microcontroller, and use ISP and a universal programmer. Several examples of 8051 C code are provided, including toggling port bits, using data types like unsigned char, delay loops, and reading/writing port values.