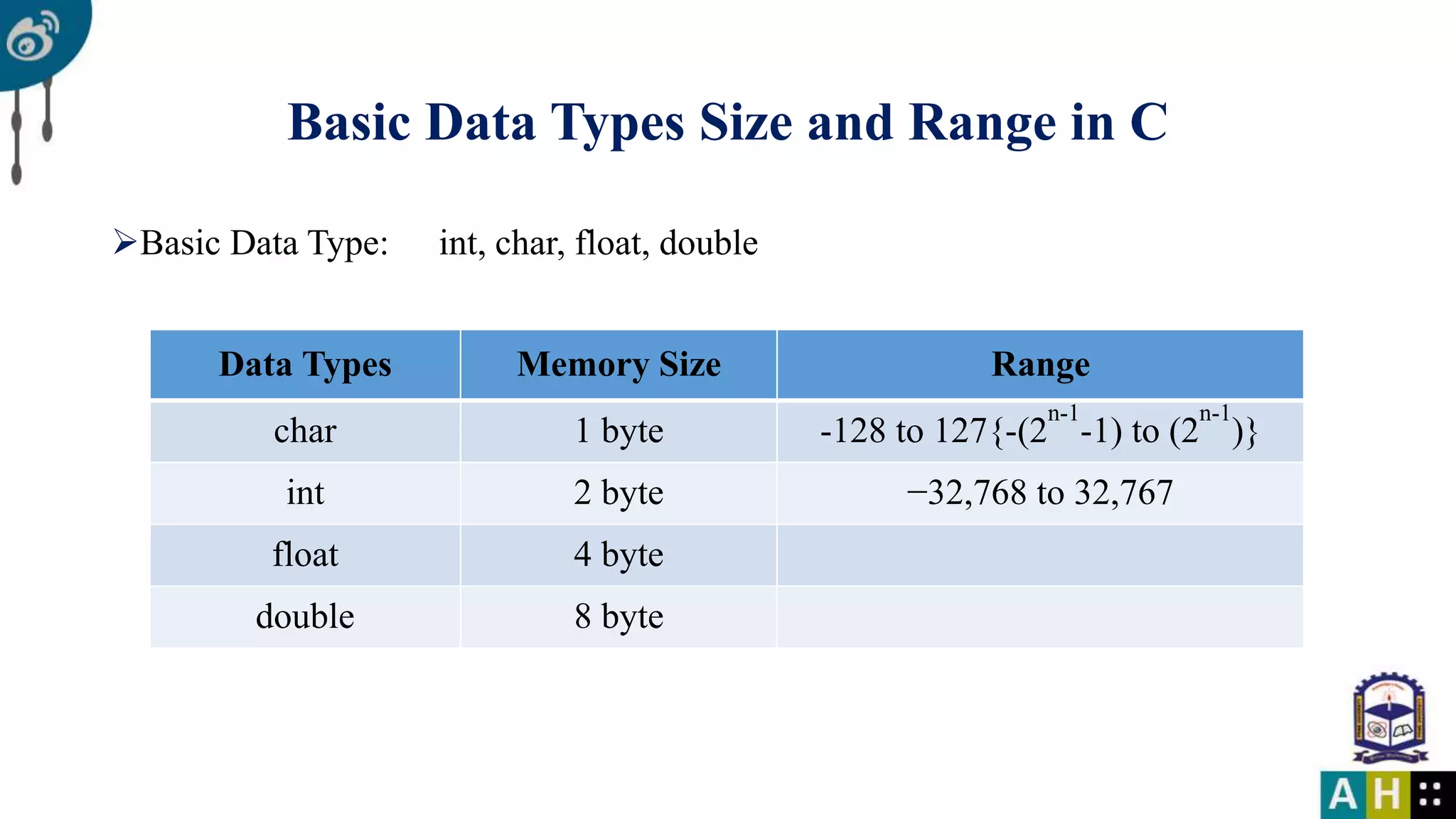
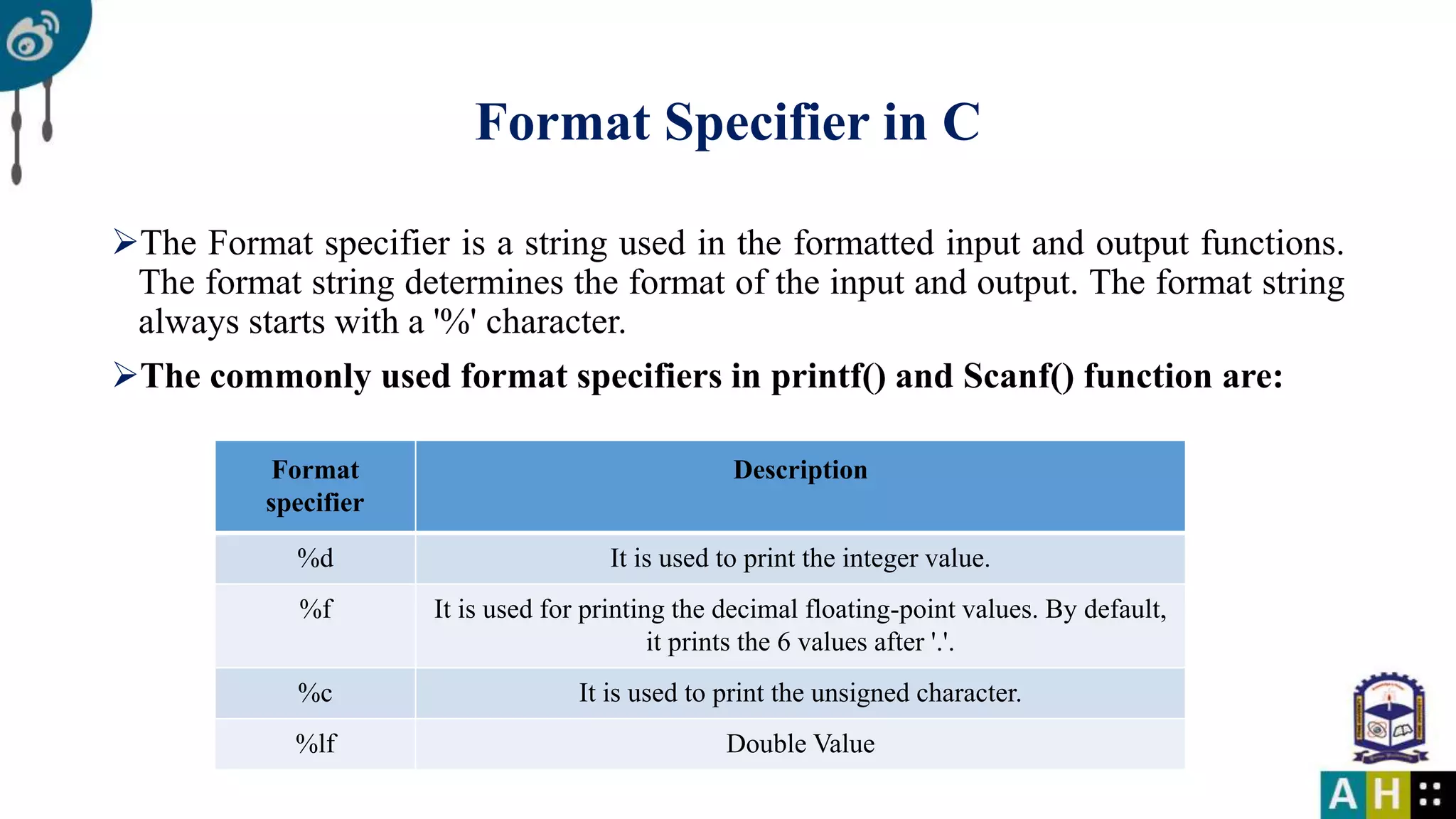
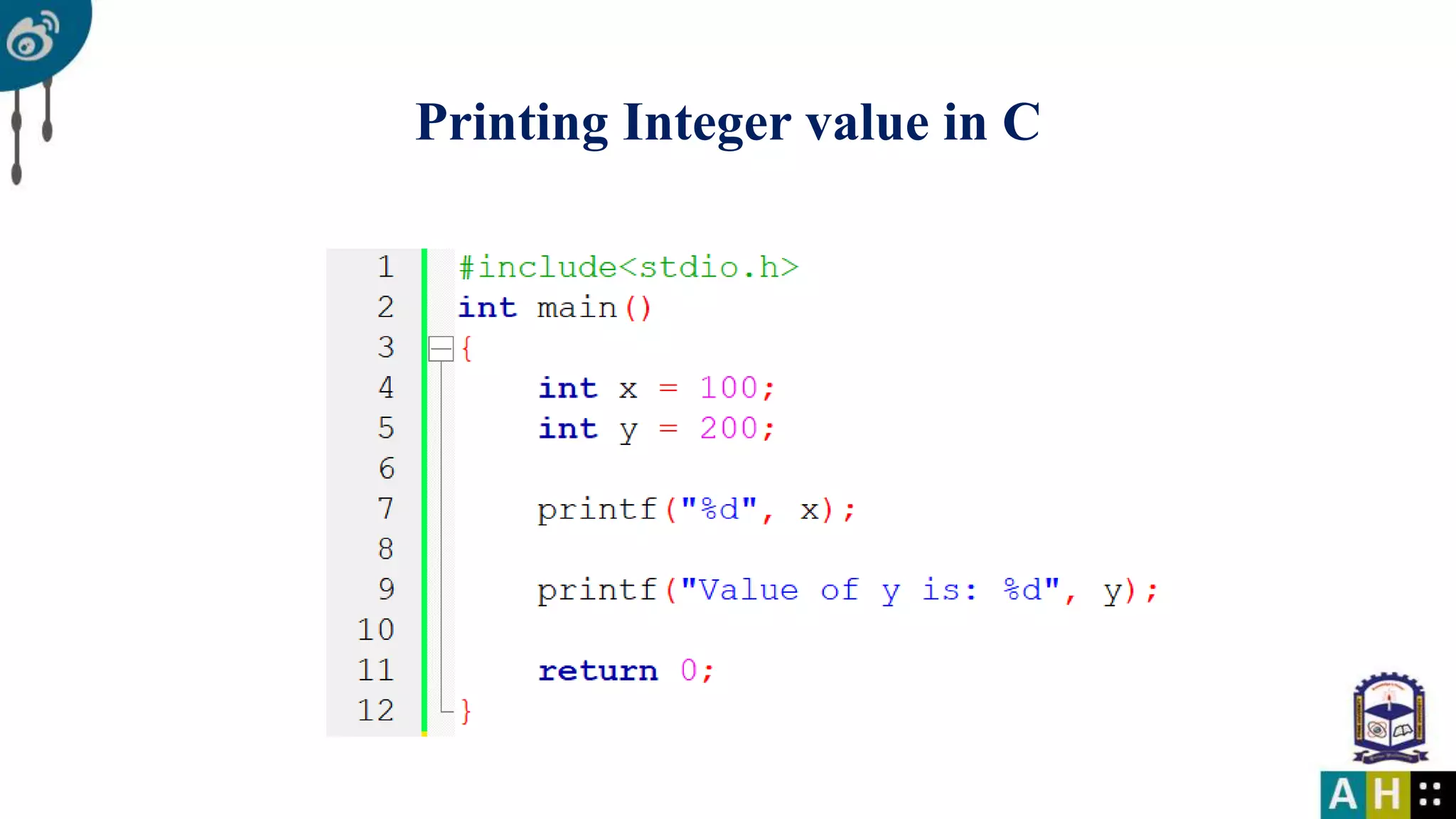
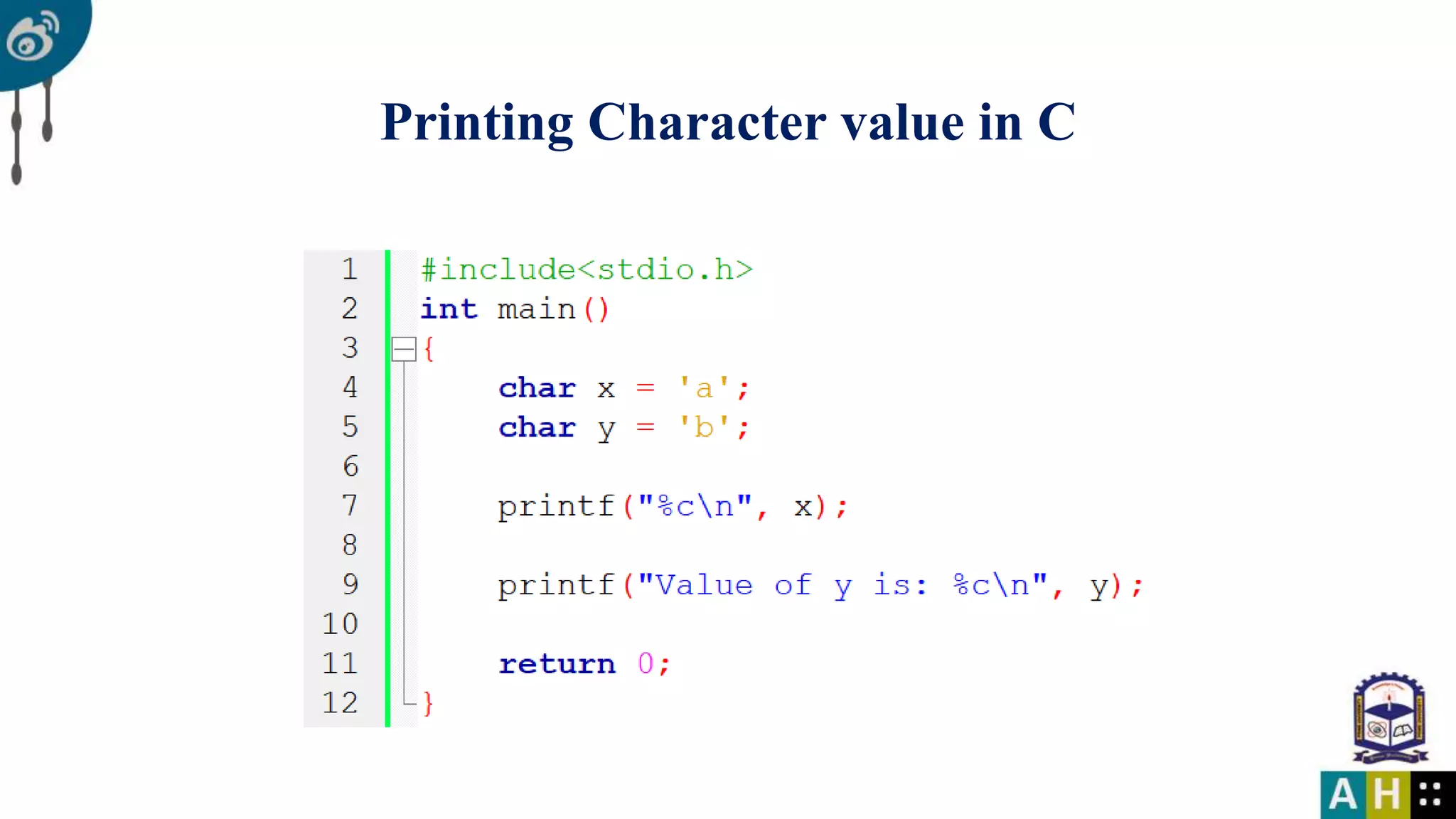
This document introduces C programming, covering essential components such as including libraries, the main function, and printing to the console. It explains variables, data types, their declaration, and the rules for naming them. The document also details format specifiers used in input and output functions.