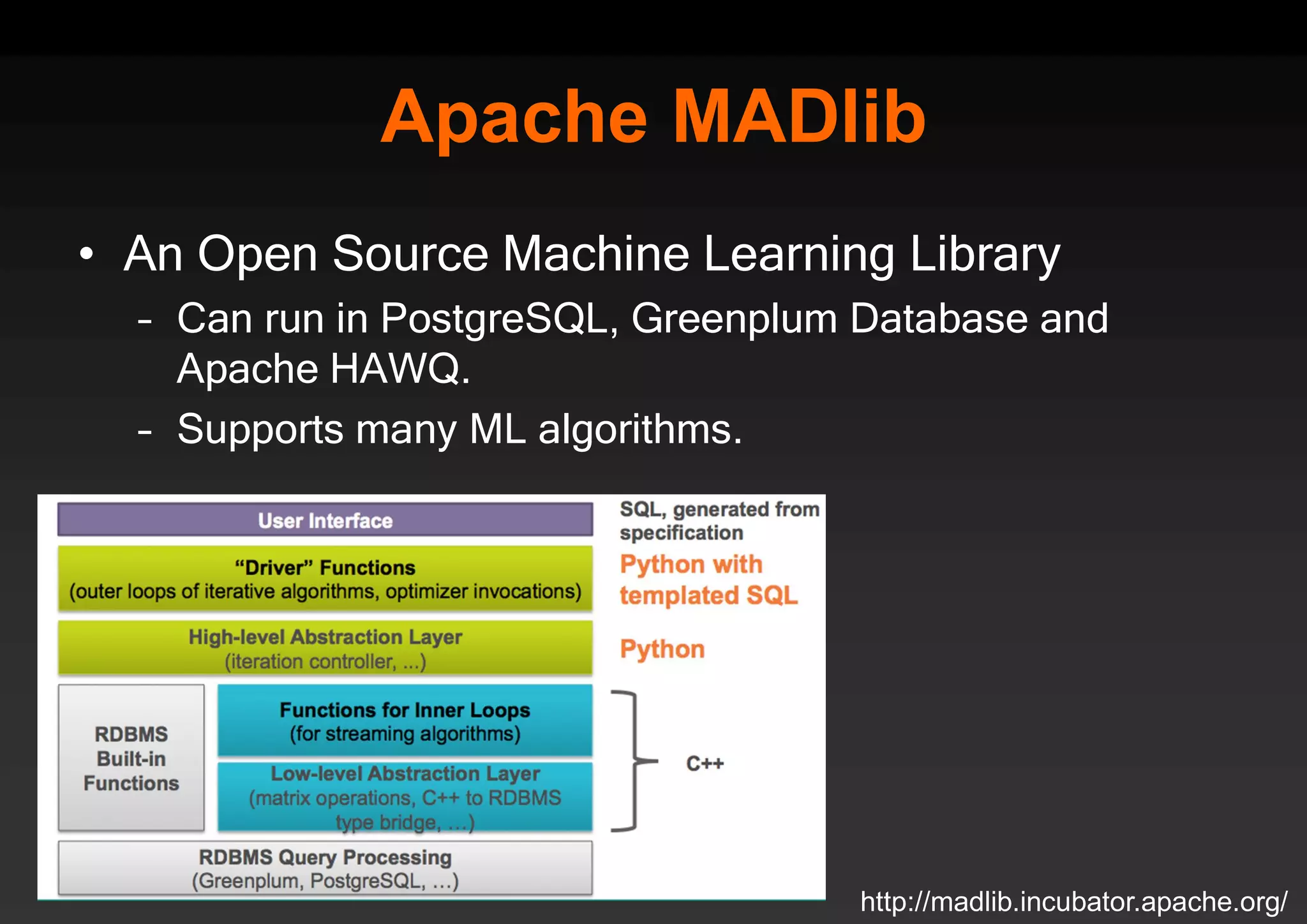
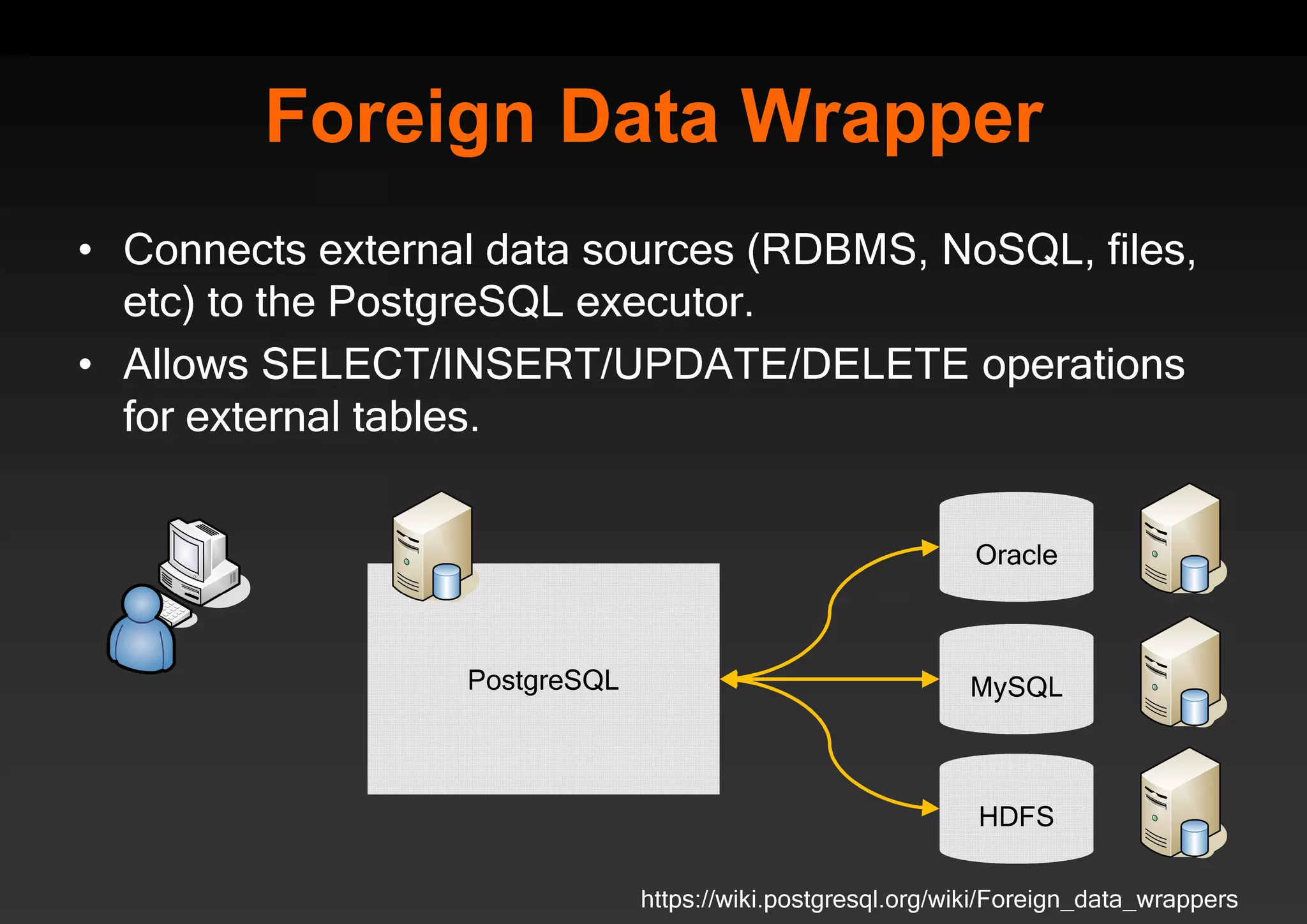
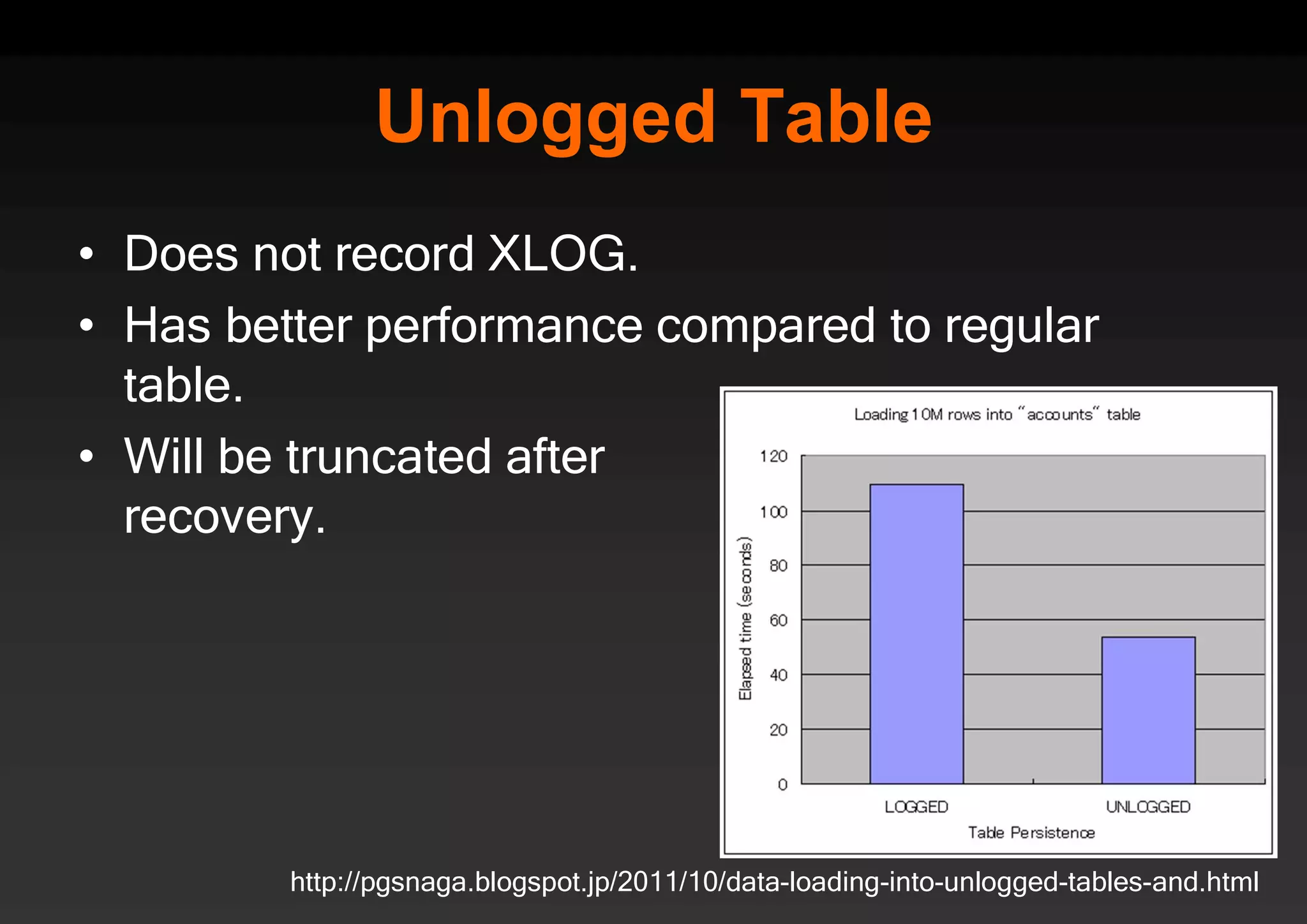
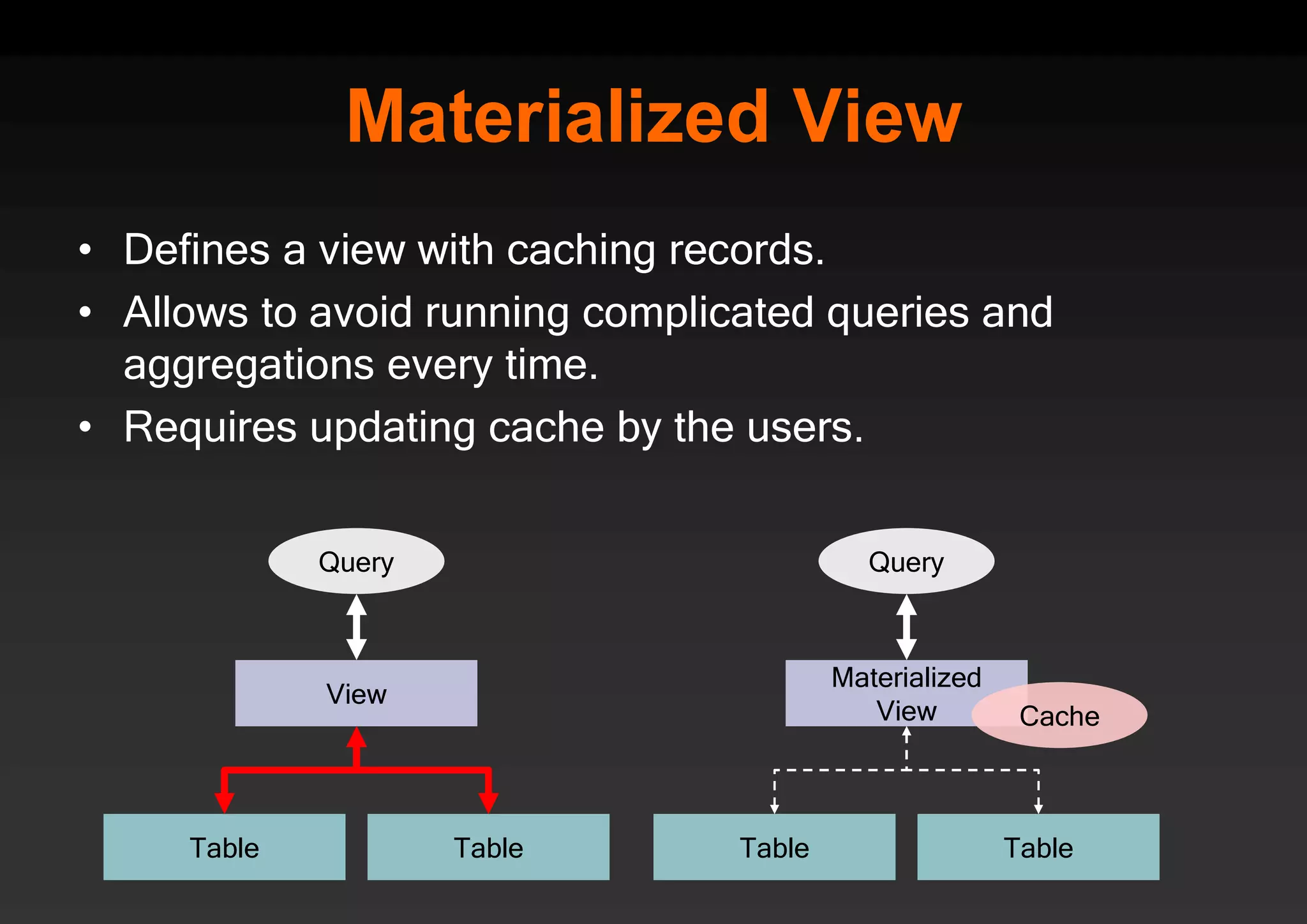
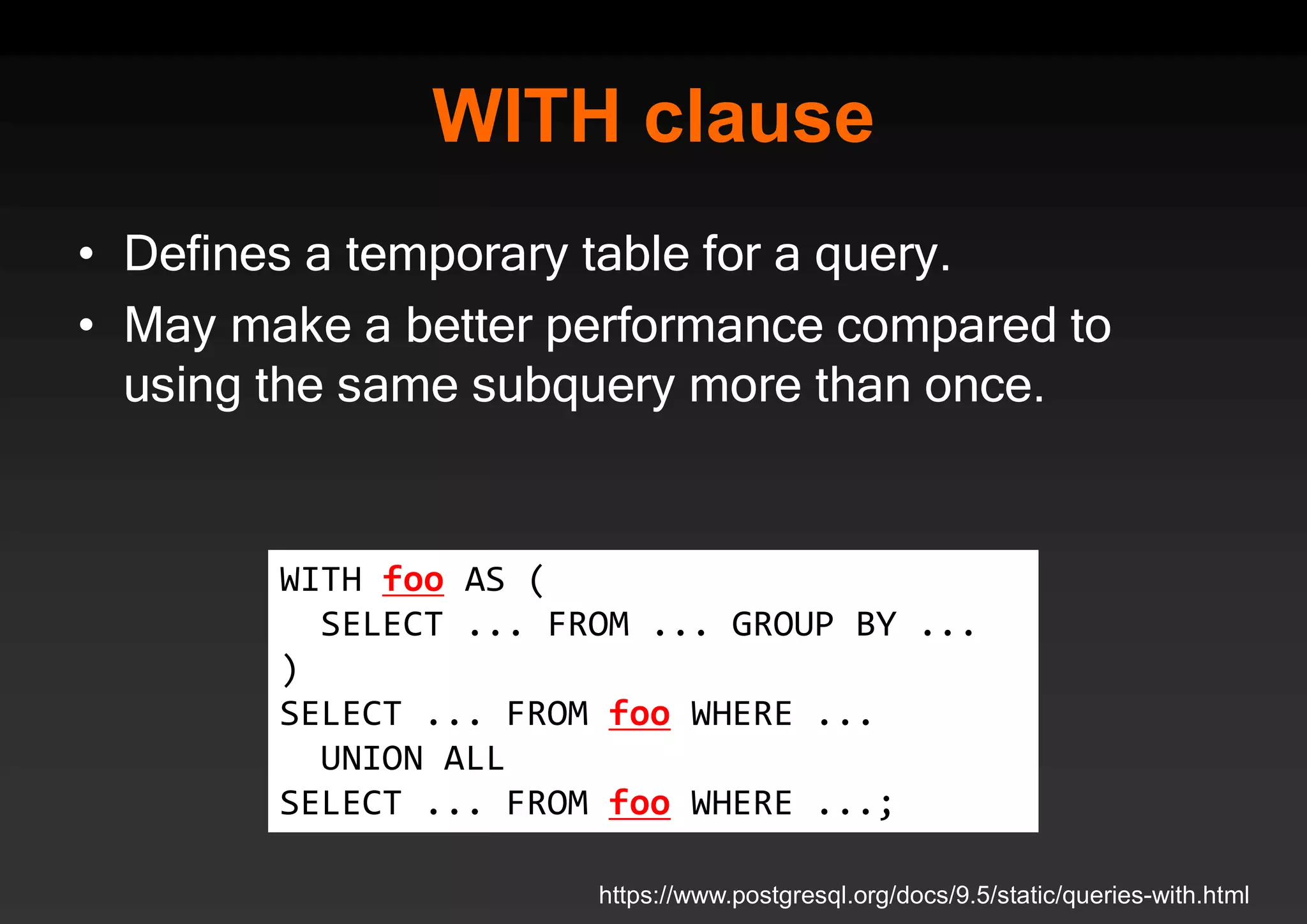
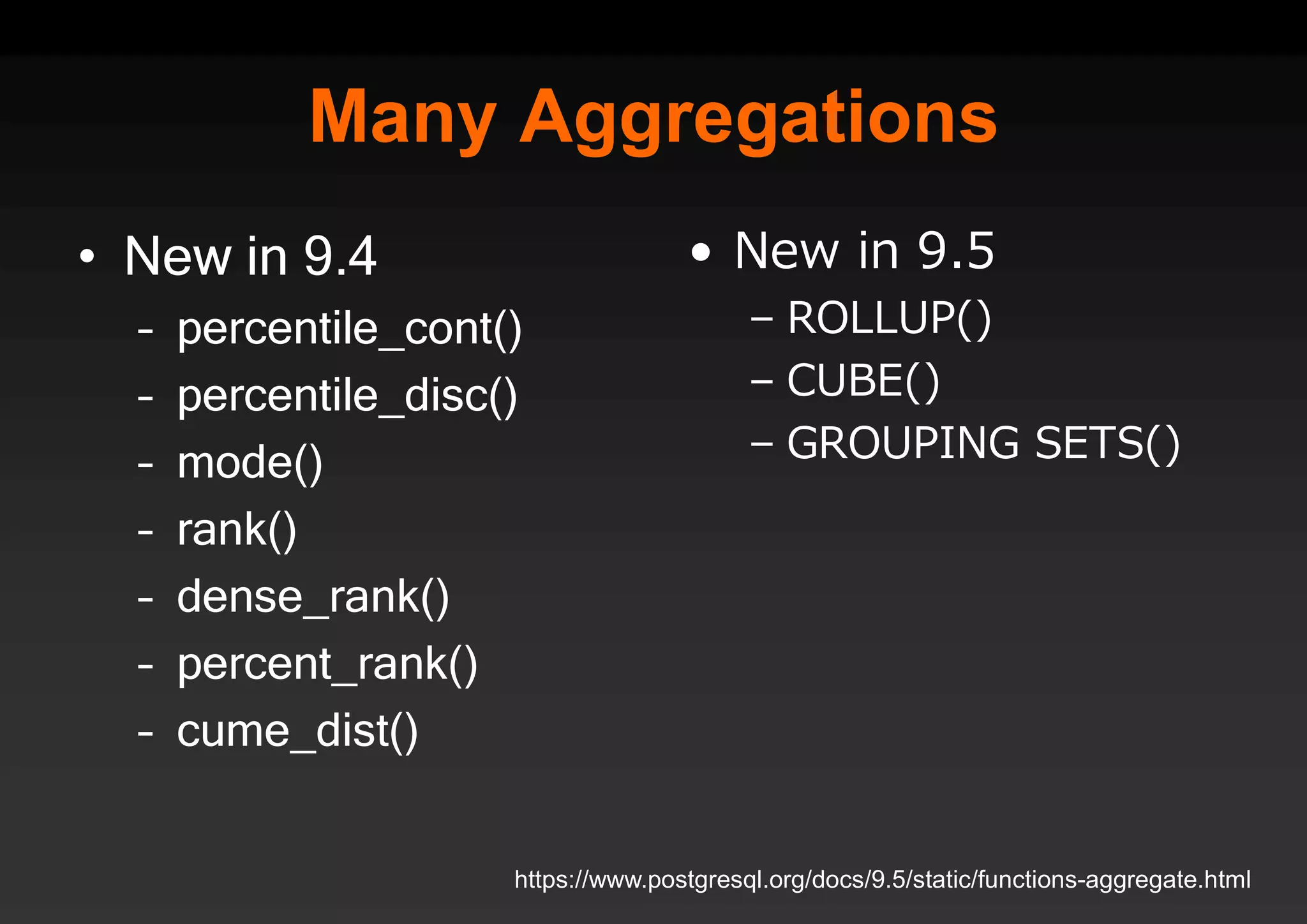
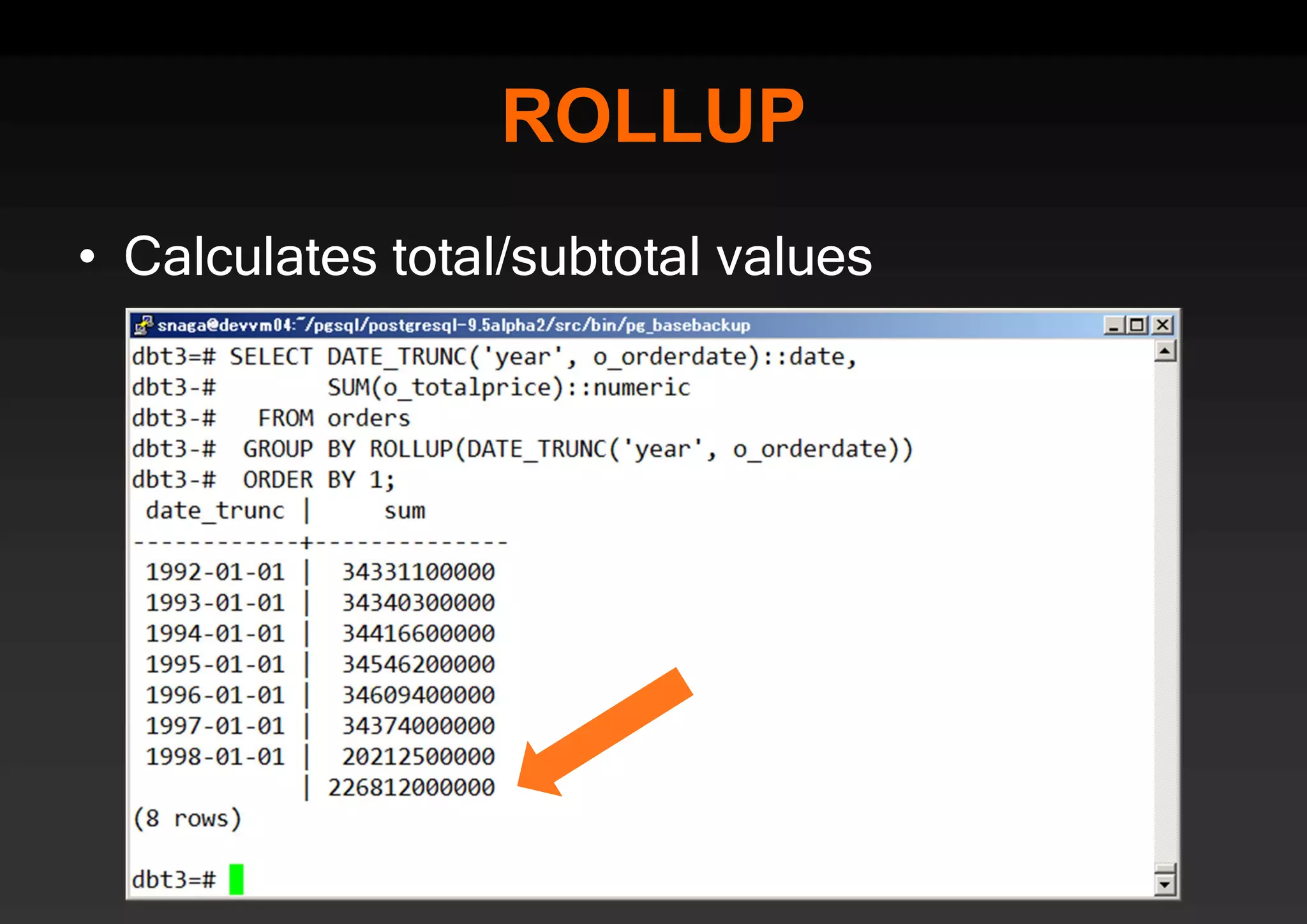
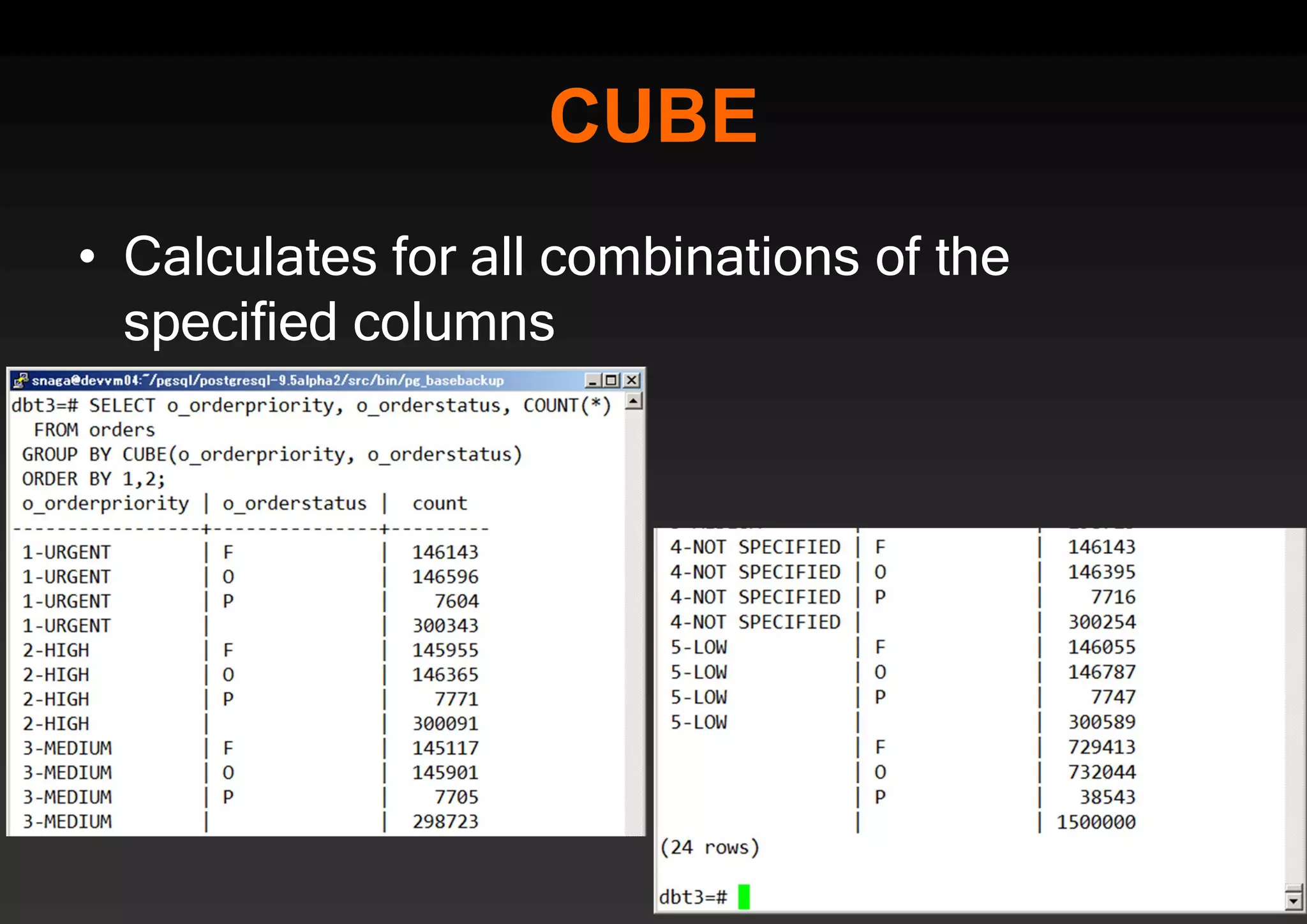
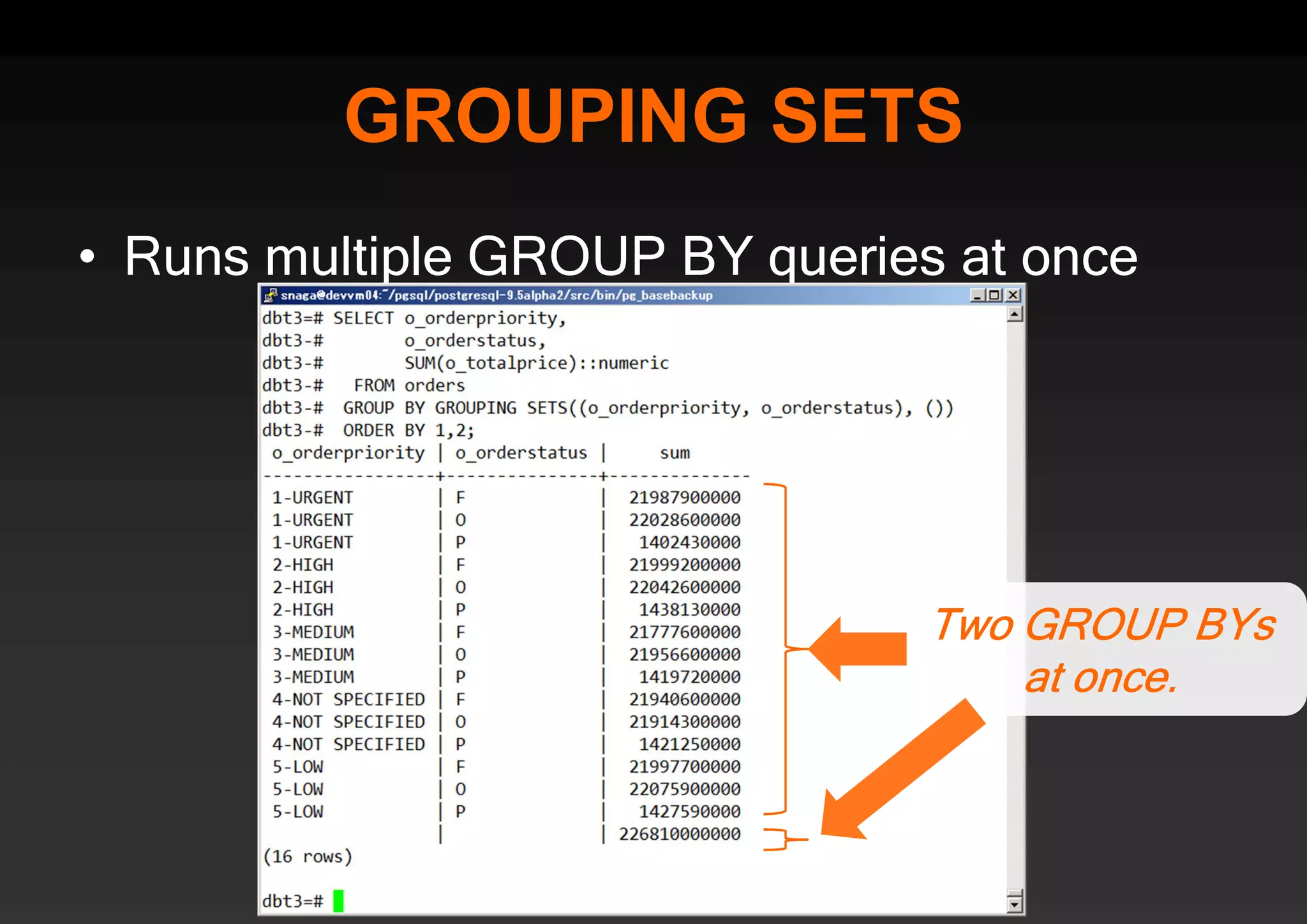
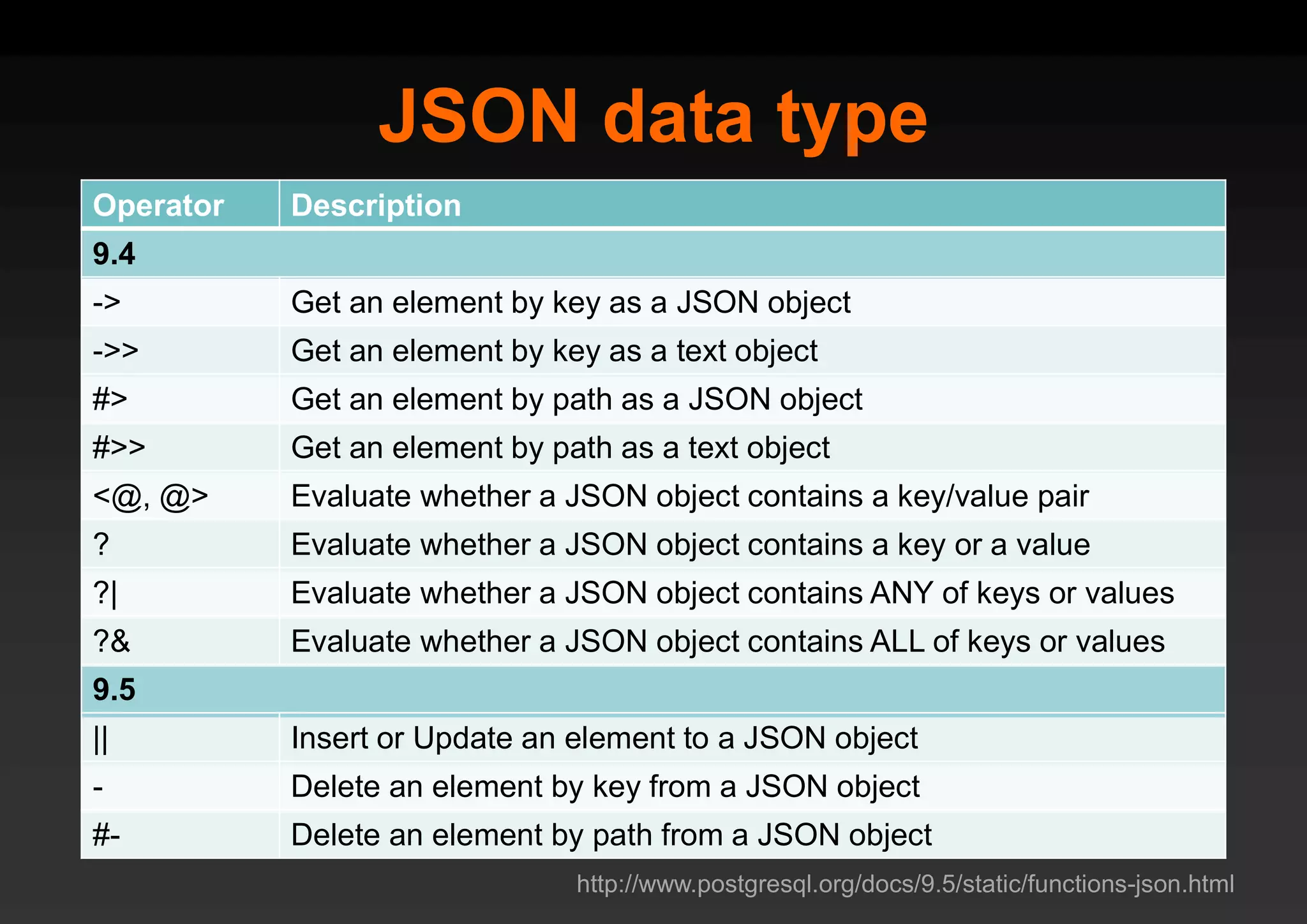
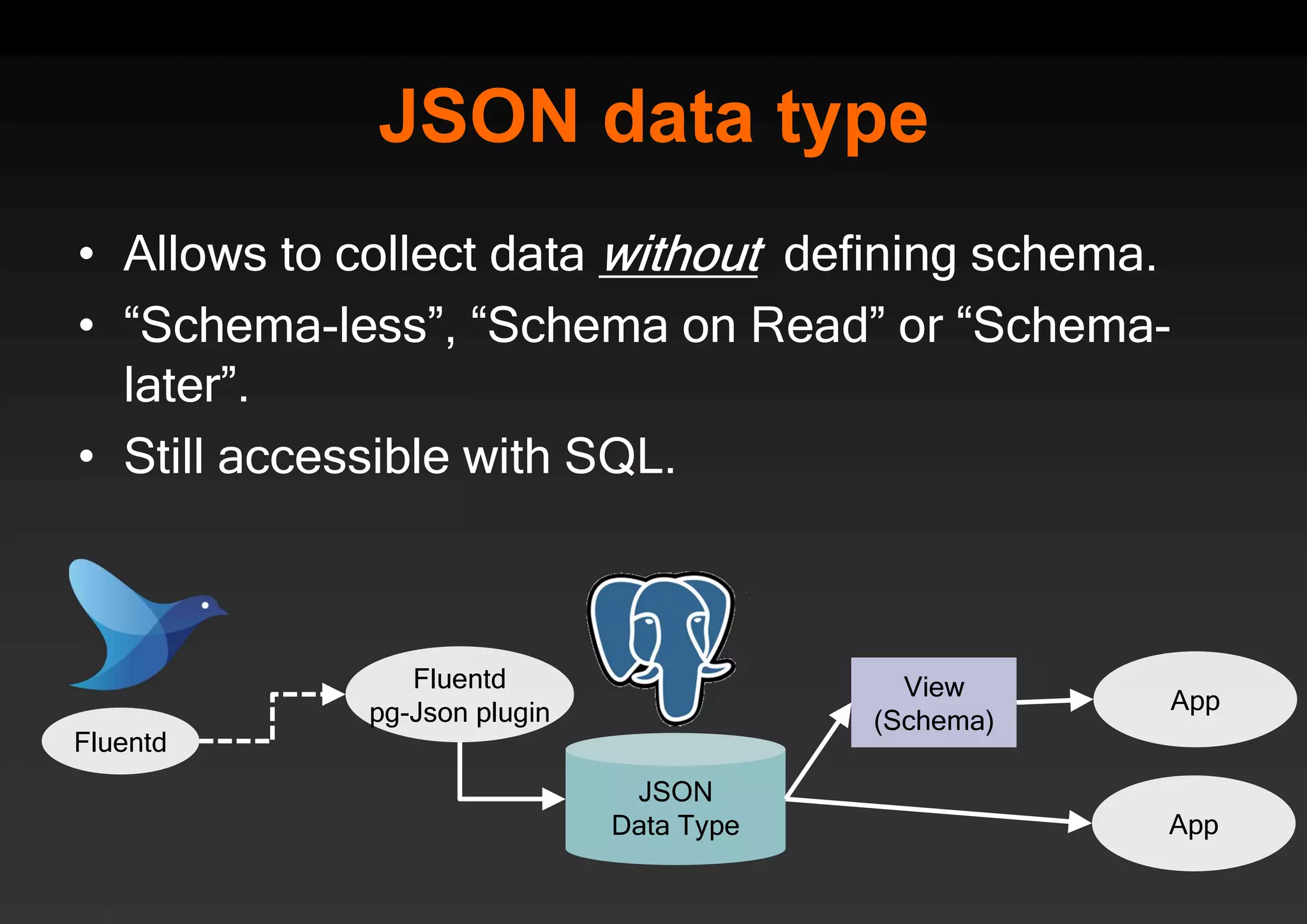
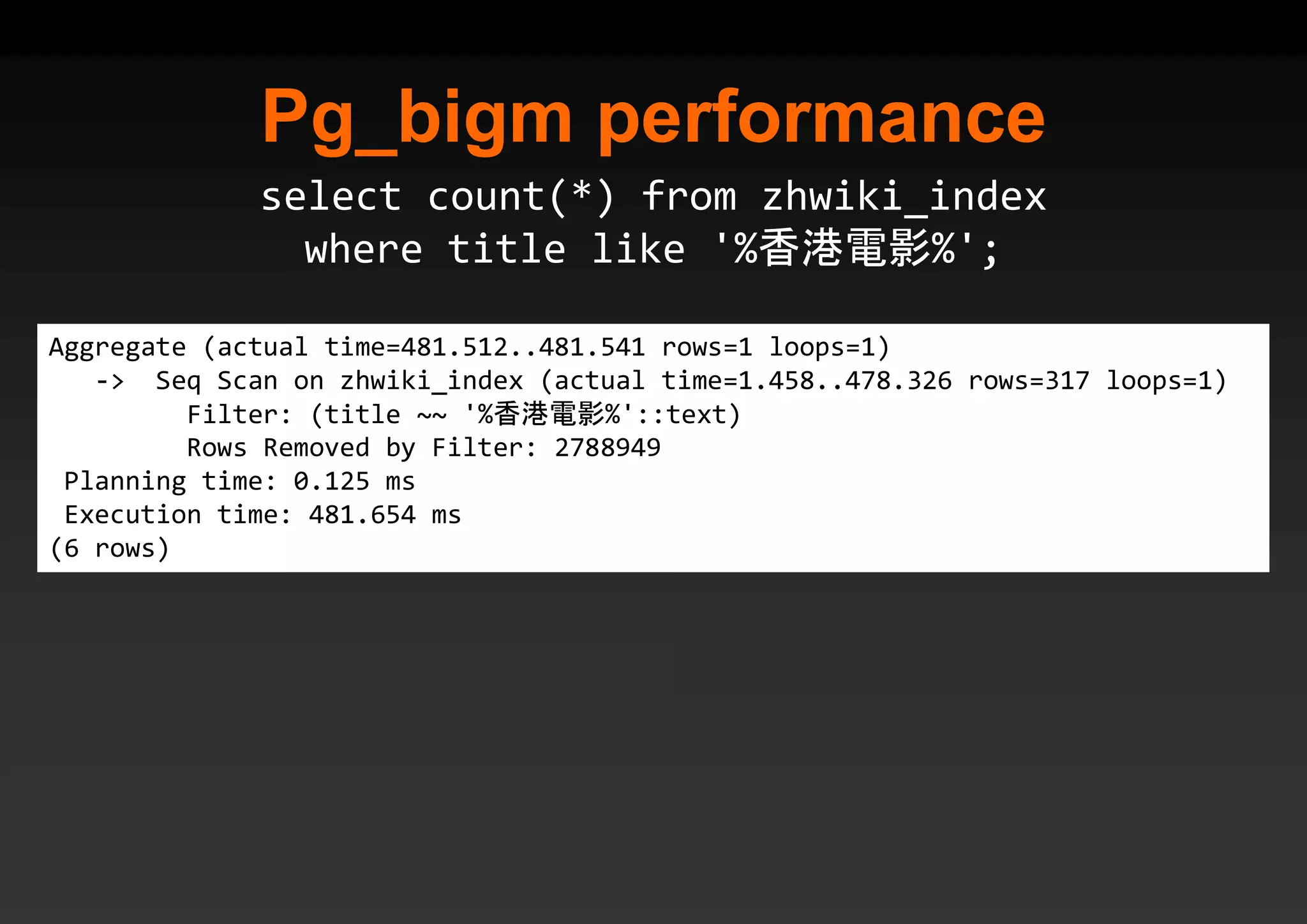
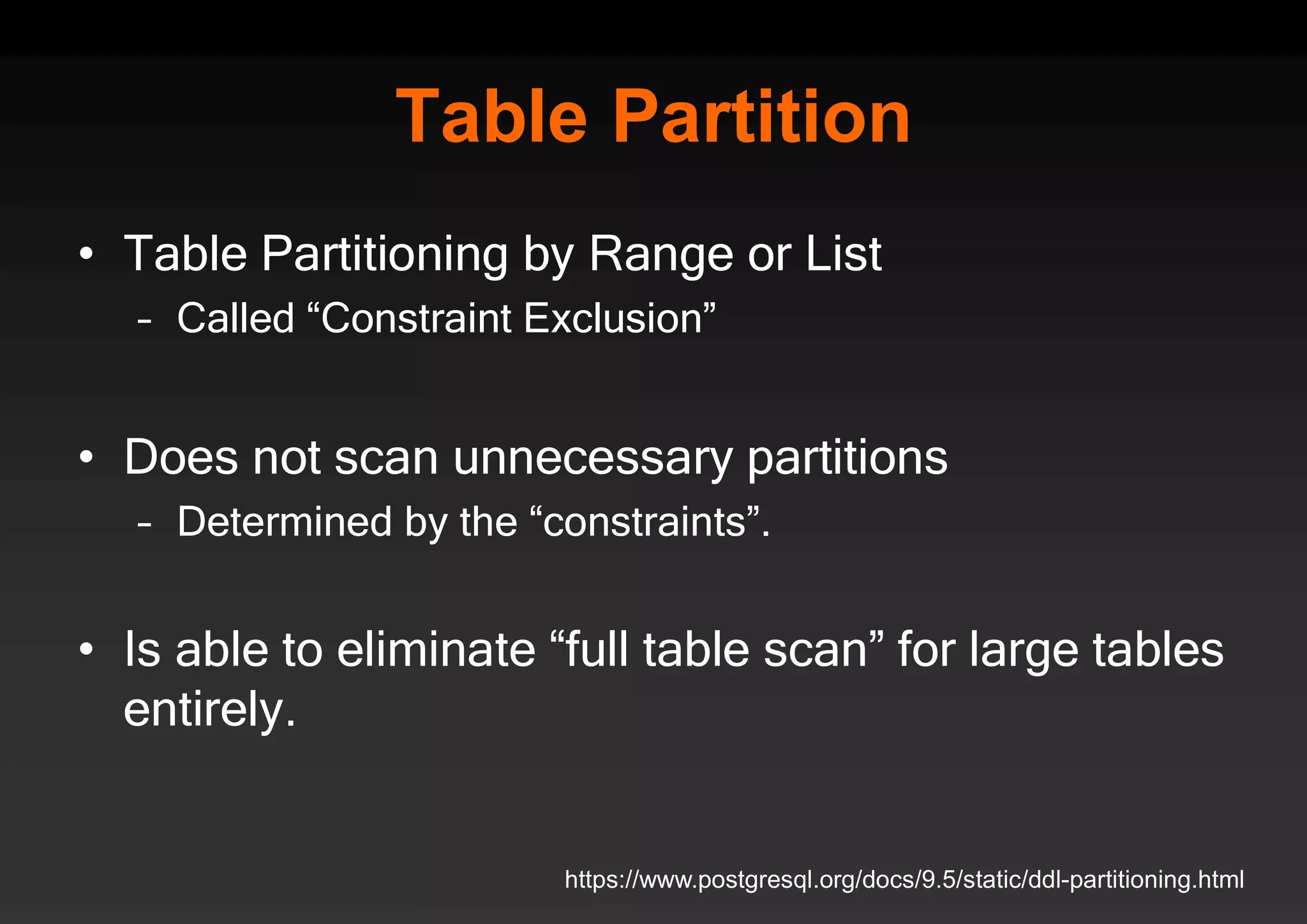
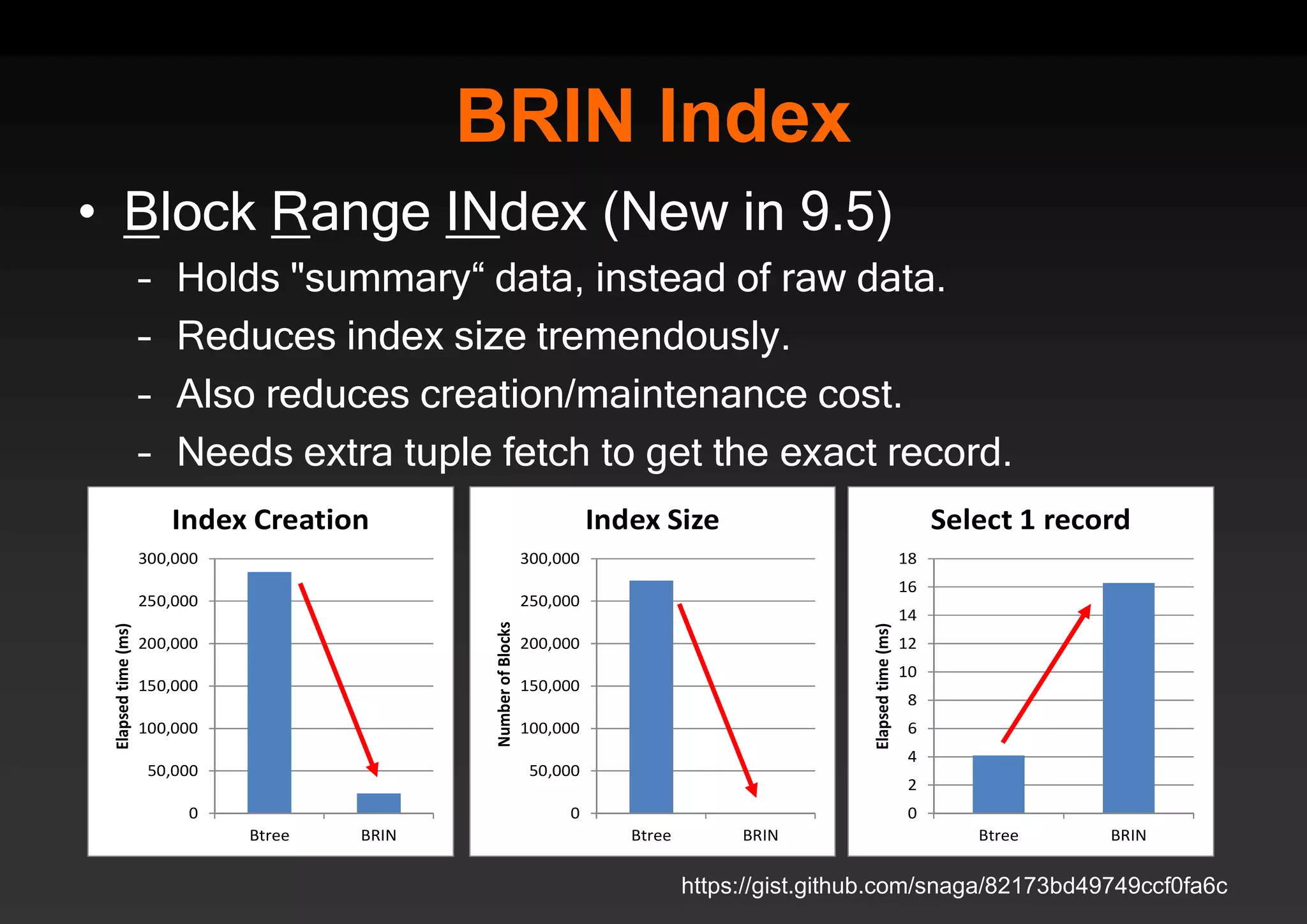
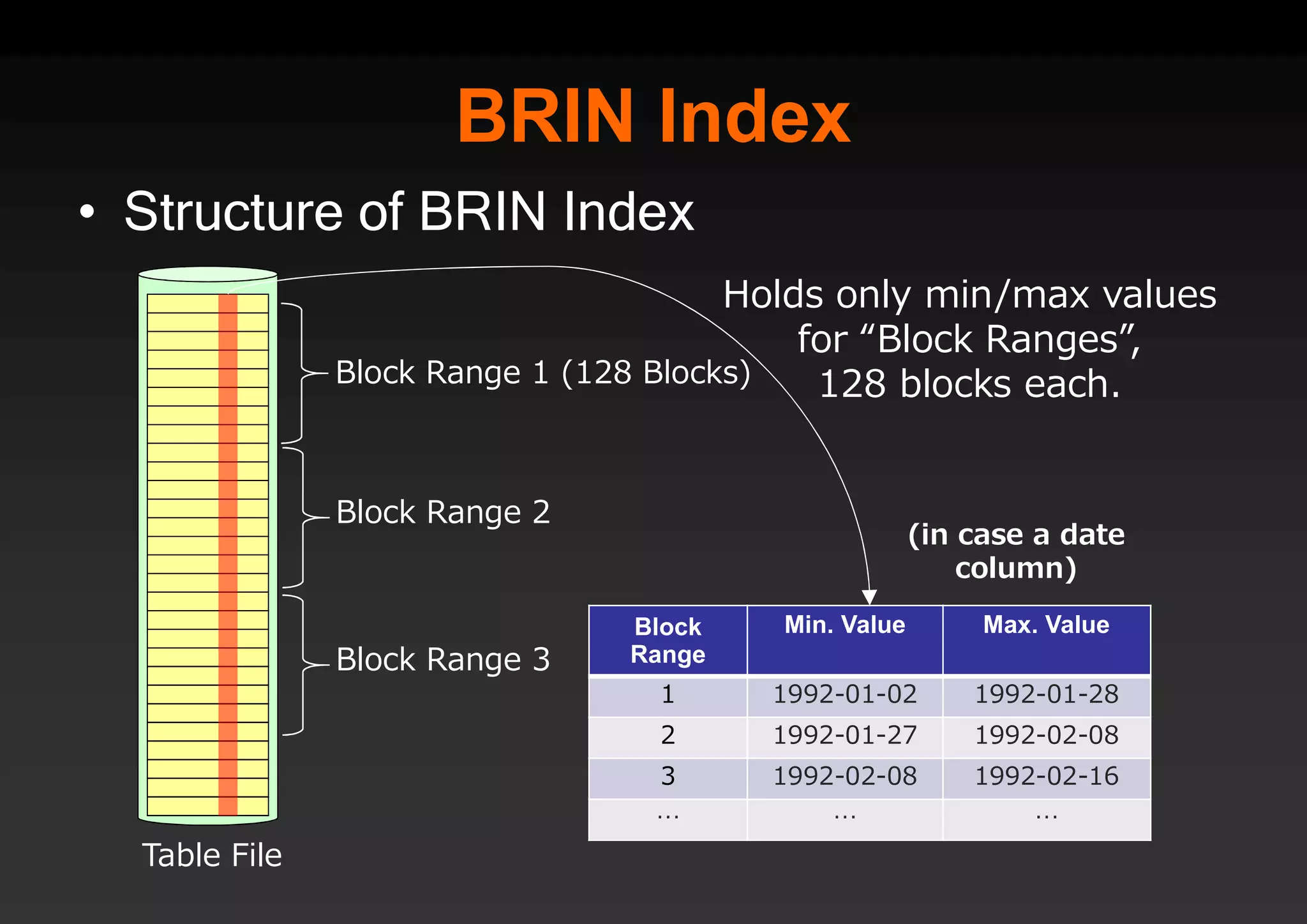
PostgreSQL provides several advantages for analytics projects: 1) It allows connecting to external data sources and performing analytics queries across different data stores using features like foreign data wrappers. 2) Features like materialized views, transactional DDLs, and rich SQL capabilities help build effective data warehouses and data marts for analytics. 3) Performance optimizations like table partitioning, BRIN indexes, and parallel queries enable PostgreSQL to handle large datasets and complex queries efficiently.















![UDF by Python CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION dumpenv(OUT text, OUT text) RETURNS SETOF record AS $$ import os for e in os.environ: plpy.notice(str(e) + ": " + os.environ[e]) yield(e, os.environ[e]) $$ LANGUAGE plpythonu;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10reasonswhyyoushouldstartanalyticsprojectfinal-160625063736/75/10-Reasons-to-Start-Your-Analytics-Project-with-PostgreSQL-37-2048.jpg)
![UDF by Python CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION dumpenv(OUT text, OUT text) RETURNS SETOF record AS $$ import os for e in os.environ: plpy.notice(str(e) + ": " + os.environ[e]) yield(e, os.environ[e]) $$ LANGUAGE plpythonu; testdb=# select * from dumpenv() order by 1 limit 10; column1 | column2 --------------------+----------------------- G_BROKEN_FILENAMES | 1 HISTCONTROL | ignoredups HISTSIZE | 1000 HOME | /home/snaga HOSTNAME | localhost.localdomain LANG | ja_JP.UTF-8 LC_COLLATE | C LC_CTYPE | C LC_MESSAGES | C LC_MONETARY | C (10 rows)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10reasonswhyyoushouldstartanalyticsprojectfinal-160625063736/75/10-Reasons-to-Start-Your-Analytics-Project-with-PostgreSQL-38-2048.jpg)