Introduction to MQL5 (Part 27): Mastering API and WebRequest Function in MQL5
Introduction
Welcome back to Part 27 of the Introduction to MQL5 series! Have you ever wondered how MetaTrader 5 can interact with other platforms? If so, you should read this article.
This article will concentrate on understanding the operation of APIs and how MetaTrade 5 may communicate with external servers through the WebRequest() function. To make the learning process more applicable, we will work on a small project in which MetaTrader 5 integrates with Telegram. You will discover how to use the Telegram API to send, edit, and remove messages from MetaTrader 5 with this project.
The purpose of this article is to introduce you to the basic ideas underlying MQL5 WebRequest communication and APIs. In the next articles, we'll go deeper by examining more intricate API use cases and real-world applications for the WebRequest() function.
Application Programming Interface (API)
An API is a collection that allows communication between two software programs. It can be compared to a bridge that spans a system. In the trading industry, APIs enable your trading platform (such as MetaTrader 5) to communicate and receive data from websites, email servers, and other external services like Telegram.
The Telegram API is used by MetaTrader 5 to connect to Telegram's servers. After processing your request from MetaTrader 5, the next thing is for the API to forward it to the appropriate group. This allows two systems to understand one another, causing this process to occur promptly and effortlessly.
HTTP, the same protocol that web browsers utilize, is one of the main communication protocols used by APIs. WebRequest() is an MQL5 function that acts as a mediator between your trading platform and the external server, handling this connection. We will understand API more by exploring the term in its three components: application, programming, and interface.
Application
Any software program that carries out particular functions is called an application. It may be a website, a mobile app like Telegram, or even MetaTrader 5. Every program handles its own internal data and functions.
Programming
Code is written during programming to allow systems to communicate, and APIs allow developers to utilize an application's capabilities without being fully aware of how it operates internally.
Interface
An interface is where two systems communicate with one another. It outlines the information that can be shared and the manner in which they can communicate. For instance, you can still search and play movies using your computer even if they are not saved. When you click "Play," YouTube contacts its server and begins playing the video. Upon selecting "Play," YouTube sends your request to its server and starts playing the video. Likewise, MetaTrader 5 can send and receive messages when it connects to an external platform via an API.
A system that enables communication between applications using well-defined programming instructions is referred to as an application programming interface. It serves as the link between your trading platform and other platforms, like email or Telegram, enabling automation.
Analogy:
Imagine Nikolai, a boy. He has a lot of skill, but despite all his talents, he can't do everything all by himself. He might need help, for example, with singing. Rather than acquiring all of these abilities, Nikolai has an invisible companion named API. "API, please ask my friend Ivan to sing this song for me," or "API, tell Anastasia to help me cook dinner," are the phrases Nikolai uses to communicate with his unseen friend whenever he needs assistance with something he is unable to perform. Ivan or Anastasia is swiftly connected via the API, which then sends the request and returns the outcome.
It is not a must for Nikolai to know how Ivan sings. All he has to know is what to ask and how to use the API; this is precisely how APIs work in the digital world.
Nikolai serves as a metaphor for your primary application in this story, such as MetaTrader 5. The bridge that connects MetaTrader 5 to other platforms, such as email or Telegram, is called the Invisible Friend (API). MetaTrader 5 does not need to understand how Telegram's internal system operates to send a message to the messaging app. It just makes a request with the WebRequest function, and Telegram receives it.
WebRequest() Function
Let's examine the WebRequest() function, one of the most crucial MQL5 tools that enables contact with external platforms, now that we know what an API is and how it aids MetaTrader 5 in doing so. To put it simply, WebRequest() serves as a conduit between an external web server and your MetaTrader 5 terminal. It enables data transmission and reception between your EA and the internet. This function is useful whether you want to communicate with a custom API, and retrieve data from a web service.
Imagine a scenario: the server is an office across the street, and your MetaTrader 5 is a trader seated at an office. Messages are moved between the two offices by the WebRequest() function. Using GET, or POST, for instance, you can instruct the courier on what message to send, where to deliver it, and how to deliver it.
The WebRequest() function is used to retrieve information from the web by communicating with an external server, and can be used in different ways. There are two ways to use the WebRequest() function.
The first version looks like this:
int WebRequest( const string method, // HTTP method const string url, // URL const string cookie, // cookie const string referer, // referer int timeout, // timeout const char &data[], // the array of the HTTP message body int data_size, // data[] array size in bytes char &result[], // an array containing server response data string &result_headers // headers of server response );
The second version looks like this:
int WebRequest( const string method, // HTTP method const string url, // URL const string headers, // headers int timeout, // timeout const char &data[], // the array of the HTTP message body char &result[], // an array containing server response data string &result_headers // headers of server response );
The most common version offers greater versatility, particularly when utilizing contemporary APIs like Telegram's. It is perfect for managing requests that need more than just "key=value" communication since it lets you define custom headers to meet the needs of the API. Because it provides the flexibility required to send, edit, and even delete messages using the Telegram API, this second version of the WebRequest() function will be the primary subject of this article. You'll be able to manage every aspect of your communication with other servers by comprehending how this version operates, from sending your first message to Telegram to monitoring updates in real time.
The WebRequest() function is particularly user-friendly because MQL5 has simplified things for developers. You don't have to be concerned about what is going on in the background operations that take place when communicating online. The most crucial thing is to first understand how the function's parameters work, as each one is crucial to how your request is delivered and how the response is received.
Method
The HTTP method is WebRequest()'s first parameter, and it helps communicate your desired action to a remote server. Using "GET" or "POST" in MQL5 helps in making the right choice since it affects where your data is stored, and how it handles your request.
GET:
This is used to request read-only data.
POST:
In MQL5, depending on how the server is configured, POST can be used to create, remove, or modify data in addition to sending data to it.
URL
The URL is the web address that instructs MQL5 on where to send your request.
Examples:const string url = telegram_api_url + "/bot" + bot_token + "/sendMessage"; const string url = telegram_api_url + "/bot" + bot_token + "/editMessageText"; const string url = telegram_api_url + "/bot" + bot_token + "/deleteMessage";
Every one of these URLs performs a specific task on the Telegram server. The WebRequest() function sends your data to the given URL, and the Telegram API handles it according to the endpoint that was chosen. For example, you may instruct Telegram to generate a new message in a chat by using the sendMessage endpoint. You instruct it to change an existing message when you use editMessageText. Additionally, you are telling it to erase a message when you use deleteMessage.
telegram_api_url:
This is the identifier used for the variable that stores the API:
const string telegram_api_url = "https://api.telegram.org";
All Telegram bot requests are forwarded to this base URL. It can be viewed as the "main building" in which all Telegram bots function. This main address is where all of your actions begin, including sending, editing, and deleting messages.
/bot:
Telegram knows that you are attempting to contact a bot rather than a legitimate user account thanks to this section. The following activities will be handled by the Telegram bot system, as indicated by this keyword. To put it simply, /bot functions as a notice indicating that "this request is meant for the bot department" inside the main Telegram building.
bot_token:
The bot token is a long string of characters and numbers that are used as the bot's access key; it is one of the most important parts of any API connection. This key enables direct contact between your MQL5 program and the server. Every time your EA sends a WebRequest, the token notifies Telegram that "This request is from my bot, and I have permission to perform this action." It also acts as a password to access the bot.
Your bot token must always be kept private and secure due to its importance because anyone with access to your bot can take control of it and send messages on your behalf. Keeping it in a secure area, such as a different configuration file or as an external input variable in your EA, is therefore a smart habit. To link your MetaTrader 5 program to Telegram, I will show you how to retrieve your bot token directly from Telegram using BotFather later in this article.
string url = telegram_api_url + "/bot" + bot_tokin + "/sendMessage";
"Hey, I want to send a message using the sendMessage endpoint," is essentially what you're telling Telegram. This is my token to demonstrate it.
Headers
The next parameter we are exploring is the header. This is more like an instruction or authorization you add to the request.
Example:
const string headers = "";
Timeout
This parameter is used to specify how long the EA should wait for a response from the server after sending a request.
Example:
int timeout = 5000; // 5000 milliseconds = 5 seconds
MetaTrader 5 will wait five seconds for a response in this case. After that period of time, MetaTrader 5 stops attempting to connect, and the request fails. Timeout might be compared to waiting for a friend to pick up the phone. You may elect to hang up if they don't answer within ten seconds. "If the server does not reply within the time I set, I will stop waiting" is another statement made by your MetaTrader 5 software.
Data
The actual message you wish to send from MetaTrader 5 to the external platform is stored in a char array variable, which is crucial.
string body = "chat_id=" + chatID + "&text=Hello from MT5!"; StringToCharArray(body, data, 0);
Since data is transferred as bytes rather than just text, the message is converted from a regular string into a character array. To determine which particular message has to be modified, the message ID is also utilized.
Example:
string body = "chat_id=" + chatID + "&message_id=" + MessageID + "&text=Hello from MT5!"; StringToCharArray(body, data, 0);
And if you want to delete a message that has already been sent, you can do this:
string body = "chat_id=" + chatID + "&message_id=" + MessageID; StringToCharArray(body, data, 0);
The chat_id is a distinct identifier for your Telegram group or bot, more like your unique username. It provides the server with the precise location of where to send your message, and it can be compared to a home address. An incorrect chat_id will prevent the message from ever reaching the group of chats the message is expected to reach. Every Telegram group has its own distinct ID, so by adding this to the body of your message, you are essentially saying the message is to be sent to a precise address.
Each message you send has a message_id, which is a unique identification number attached to it. This unique number is useful when you want to delete or edit the message in your code.
Conversely, the bot_token serves as your bot's password or access key. It is a special authentication key that links your particular Telegram bot to your MetaTrader 5 application. It can be compared to your bot's ID card. Your message will never be sent since Telegram won't be able to identify which bot is requesting it without this token.
Now, to make things clearer:
- The Chat ID tells the server where to send the message.
- Next, the message ID lets it know which specific message to modify or delete.
- The bot_token tells Telegram who is making the request.
Later in this article, I'll explain how to get your chat ID, message ID, and bot token back and how to utilize them correctly on Telegram.
Let's now examine the data[] array in more detail. The delivery box that transports your message from MetaTrader 5 to the Telegram server is called Data[]. The first thing to do is to insert the text you wish to send into a string variable named "body." For example, "Hello from MT5!" To ensure that this message travels across the network safely, you must correctly bundle it before sending it out. It accomplishes this by utilizing StringToCharArray() to transform your message (string) into a character array that the WebRequest() courier can comprehend.
Result
The WebRequest() function's result variable holds the server's answer, including extra information like the message ID or confirmation that the message was sent successfully.
Example:char res[]; WebRequest("POST", url, "", 5000, data, res, resHeaders); Print(CharArrayToString(res));
Result:
{ "ok": true, "result": { "message_id": 24, "from": { "id": 9467412345, "is_bot": true, "first_name": "MQL5 API BOT", "username": "MQL5APItest_bot" }, "chat": { "id": -400395312345, "title": "Bot Testing Group", "type": "supergroup" }, "date": 1761412345, "text": "Hello from MT5!" } } The message_id is crucial in this case. You can later update or remove the precise message using this ID. Therefore, you will utilize that message_id when making another WebRequest call if you choose to change the message text or remove it completely.
Consider it this way: Telegram provides you with a delivery receipt (stored inside res[]) upon sending a message over MetaTrader 5, verifying the delivery and allocating a tracking number (the message ID). You may always locate, modify, or delete the message at a later time using that number.
Result Headers
The headers that the server returns after processing your request are stored in this final parameter of the WebRequest() function. It is declared as:
string resHeaders = ""; WebRequest("POST", url, "", 5000, data, res, resHeaders); Print(resHeaders);
Output:
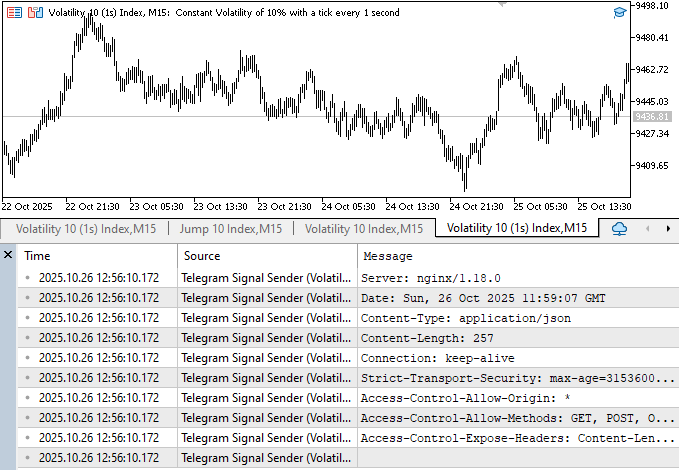
The headers and the body (or content) are the two primary components that the web server typically provides in response to a request sent by your MQL5 software. This header data from the server's response is captured by the result_headers parameter.
These headers frequently include crucial technical information like
- The content type, which tells you the format of the response.
- Server name and version.
- The date and time of the response.
- Connection type, which indicates whether the connection stays open or not.
This data gives you security and connection information, verifies that your request was properly received by the Telegram server, and indicates the kind of content that was returned. It's critical to realize that the WebRequest() function uses headers and result_headers for various purposes. The data you transmit to the server with your request is represented by the third argument, headers. These headers specify the kind of data you are delivering and, if necessary, contain authentication information.
In contrast, the data that the server returns to you is stored in the final parameter (result_headers). Along with other helpful technical information, it explains how the request was handled and what kind of material was returned. This process can be simplified by comparing it to the exchange of mail between two offices. Similar to a label you affix to a letter before sending it, the headers parameter describes what is within and how it should be treated. The result_headers option indicates the envelope's origin, date of dispatch, and method of delivery, much like the stamps and marks on an envelope you receive back. Although they have different functions in the communication between MetaTrader 5 and an external server, both are crucial.
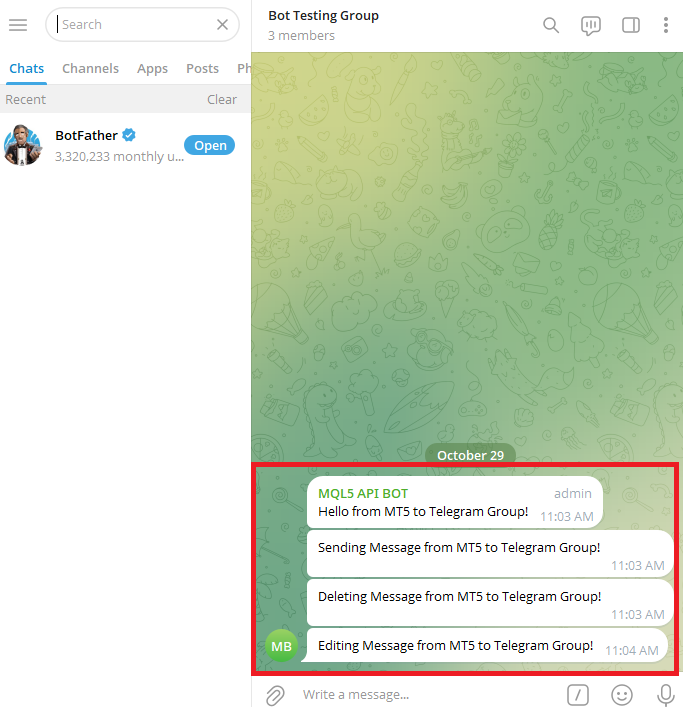
Sending Message from MetaTrader 5 to Telegram Bot
Now that you have a thorough understanding of how MQL5 APIs and the WebRequest() function operate, it is time to apply what you have learned. This part will teach us how to send a message from MetaTrader 5 to a Telegram bot, putting theory into practice. This is the point at which everything we have discussed starts to make sense. To allow your MetaTrader 5 software to send, updates, or delete messages on a Telegram bot or group.
To access the Options window on your MetaTrader 5 software, press Ctrl + O. Next, select the tab for Expert Advisors. The "Allow WebRequest for listed URL" checkbox is located beneath this section. To activate the box, click on it.
Then, in the field below, type in the following URL:
https://api.telegram.org 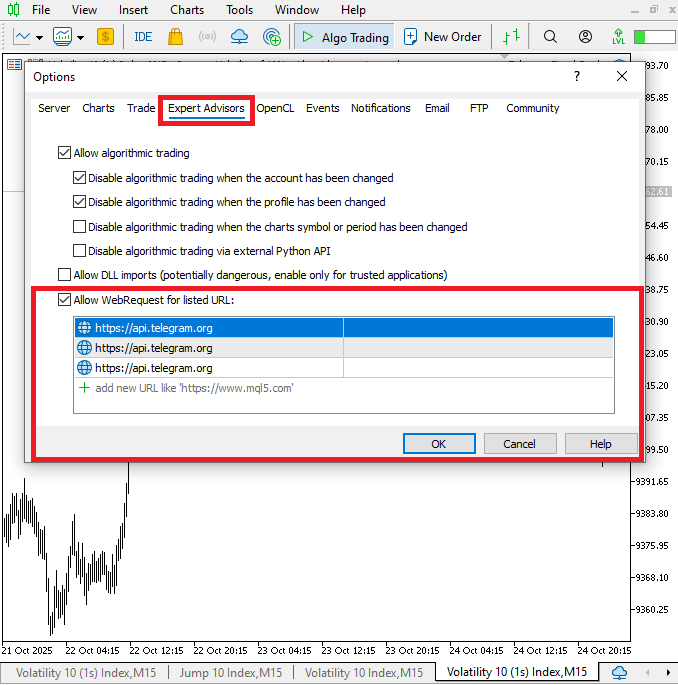
Search for BotFather.
Select /newbot to create a new bot.
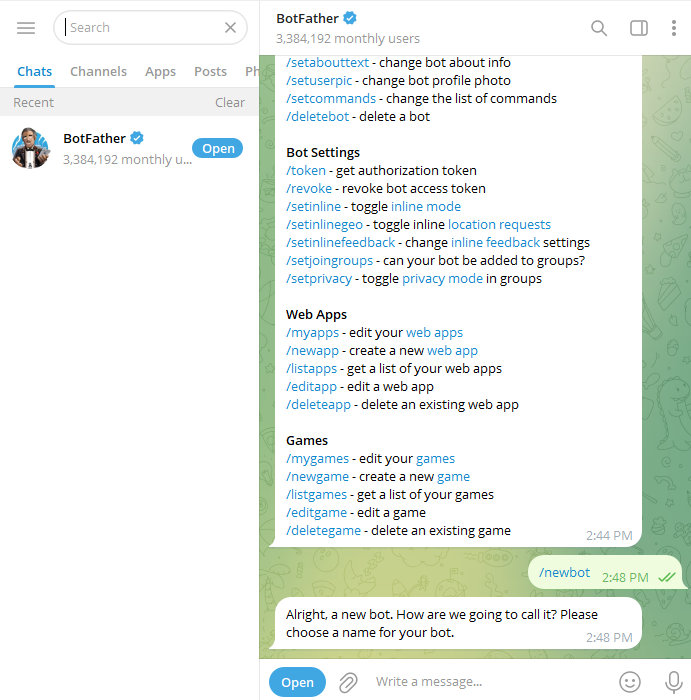
Choose a display name for your bot.
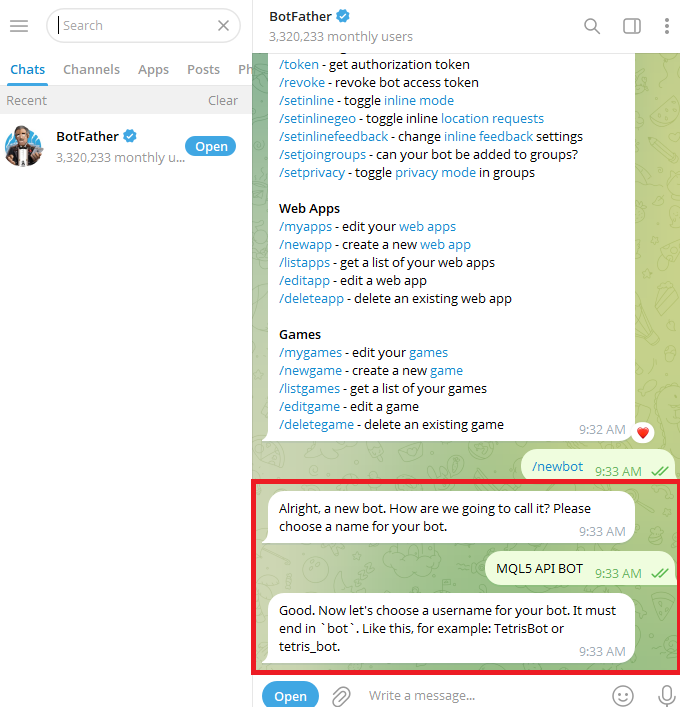
Choose a username, and it must finish in "bot" or "_bot."
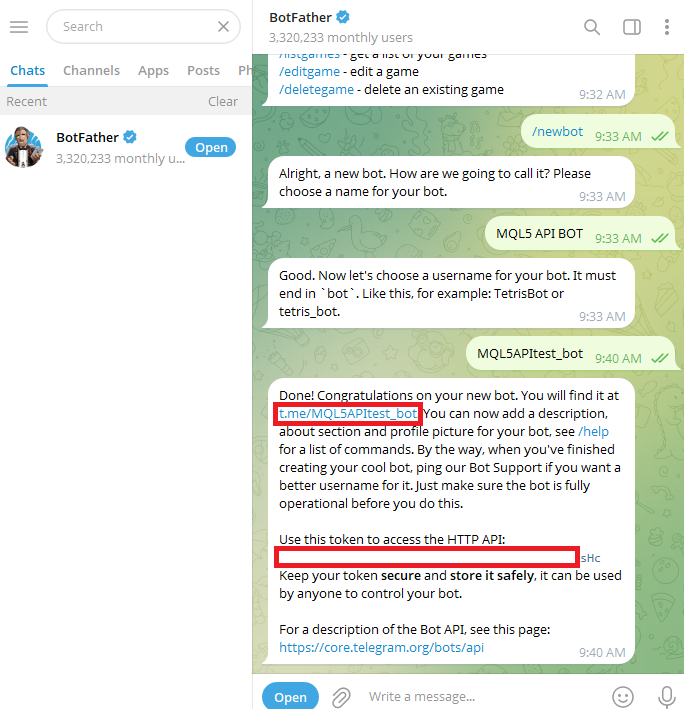
A message will immediately be sent to you, and this message will include two important details:
- Your Bot Token—This is a unique key that allows you to connect your bot with external platforms like MetaTrader 5. You’ll use it inside your MQL5 code when sending messages through the Telegram API.
- Your Bot Link—This is the link to your bot; click on it to open your bot directly and start a chat.
Enter this URL in the address bar of your browser.
https://api.telegram.org/bot<YourBotToken>/getUpdates Put the real token you got from BotFather in token of <YourBotToken>.
For instance, your URL should resemble this if your token is 123456789:ABCdefGhIJklMNopQRstuVWxyz:
https://api.telegram.org/bot123456789:ABCdefGhIJklMNopQRstuVWxyz/getUpdates 
A page displaying some text will open. A box will appear in front of "Pretty-print" on that page. Click on the link.
Go back to your Telegram bot and click on the Start button.
Go back to your browser and refresh the page.
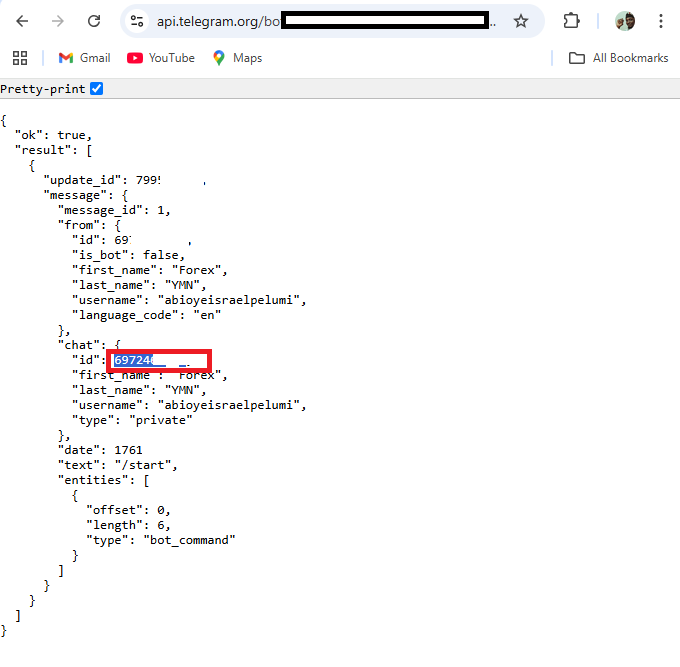
The page will display a fresh update. Your bot has been successfully activated, according to this update. Additionally, it will offer helpful data like your chat ID, which you will need to send messages to your Telegram bot from MetaTrader 5. The next step is to create a new EA file in MetaEditor 5 after completing all the previously mentioned stages.
Using your chat ID and bot token, you will access Telegram's API in this EA. From there, you will send personalized messages straight from MetaTrader 5. This is the first step in the practical section, where you apply all you've learned about WebRequest() and API communication.
Example:const string method = "POST"; const string telegram_api_url = "https://api.telegram.org"; const string bot_chatID = "6972412345"; const string headers = ""; const int time_out = 5000; const string bot_token = "8345012345:AAHdAPtMQR6VHEQeHk1y_H9IuL3zc5abcde"; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- char data[]; char res[]; string resHeaders = ""; string body = "chat_id=" + bot_chatID + "&text=Hello from MT5!"; StringToCharArray(body, data, 0); string url = telegram_api_url + "/bot" + bot_token + "/sendMessage"; WebRequest(method,url,headers,time_out,data,res,resHeaders); //--- return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
Output:
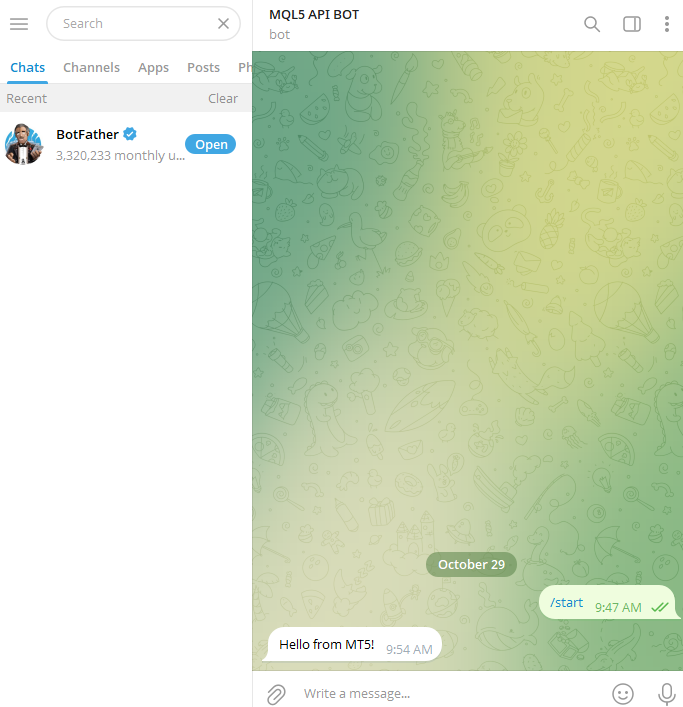
Explanation:
The chat ID, headers, timeout, HTTP method, Telegram API URL, and bot token were all specified as constants. MetaTrader 5 is informed that data will be delivered to the server by using the POST method. No other headers are required; the chat ID identifies the particular Telegram group or chat, and MetaTrader 5 will wait five seconds for a response before timing out.
Three variables are declared inside the OnInit() function: data, res, and resHeaders. The data array contains the character format of the message to be transmitted, as WebRequest() needs binary data. The response from the server is saved in res, and resHeaders contain further data from the server, such as the date and the kind of content.
The OnInit() function declares three variables: data, res, and resHeaders. Because WebRequest() requires binary data, the data array provides the message's character format. The server's answer is stored in res, and resHeaders holds additional information from the server, like the date and the kind of content. The next step is to build the complete Telegram API URL that will handle the message request. This is done with the line:
string url = telegram_api_url + "/bot" + bot_token + "/sendMessage";
Here, all the parts are combined to create a full link like this:
https://api.telegram.org/bot8345012345:AAHdAPtMQR6VHEQeHk1y_H9IuL3zc5abcde/sendMessage. This URL tells the server that we want to send a message using the bot whose token is provided.
WebRequest(method, url, headers, time_out, data, res, resHeaders); The POST method and the given URL are used to send the data from the char array to the Telegram API. Although they are empty here, headers can contain additional information. How long MetaTrader 5 waits for a response is determined by the time_out. While resHeaders gathers extra response information, including server type, content length, date, and connection data, the server's answer is stored in the res array.
In summary, this program links MetaTrader 5 to your Telegram bot and adds a little greeting to your Telegram chat that reads, "Hello from MetaTrade 5!"
Sending Message from MetaTrader 5 to Telegram Group
The next step is to learn how to send messages to a Telegram group instead of a Telegram bot, and the process is a similar but a little different for groups than for bots.
Click on the group's profile icon after creating a Telegram group.
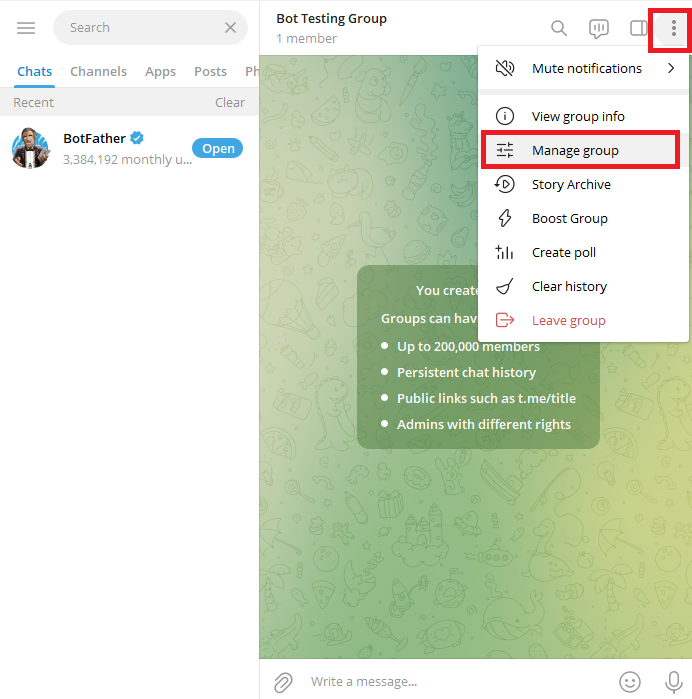
Navigate to “Manage Group” from the options that appear, then click on “Administrators.”
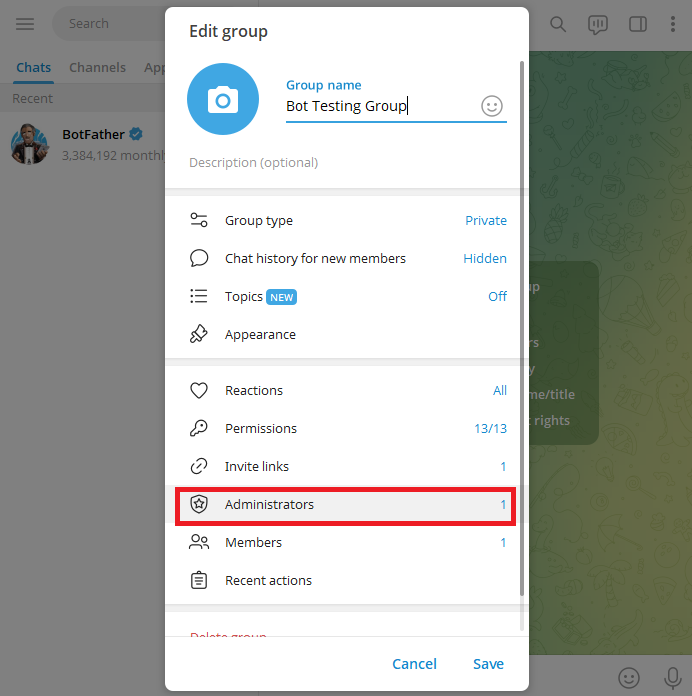
Click on “Add Administrator” and use the search bar to look for the Telegram bot you created earlier using its username (for example, @MQL5APTtest_bot).
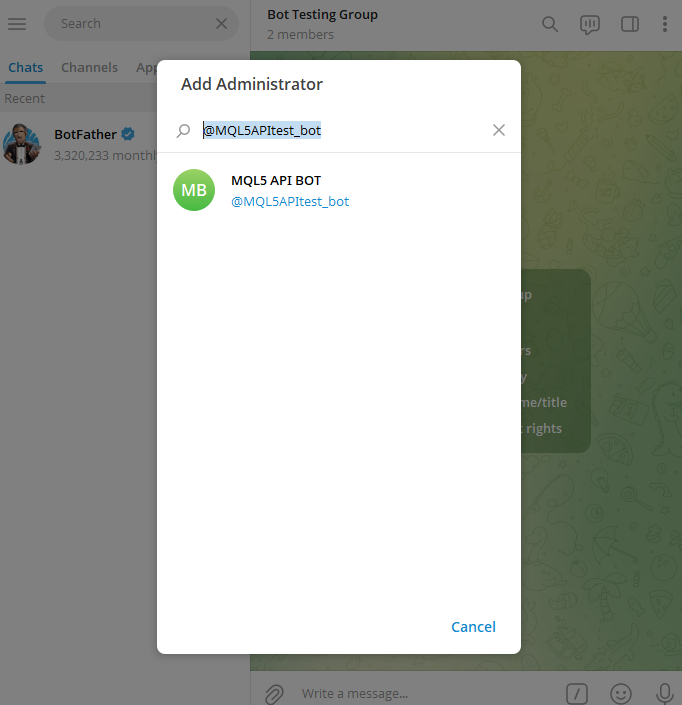
After selecting your bot, give it the necessary permissions to operate in the group.
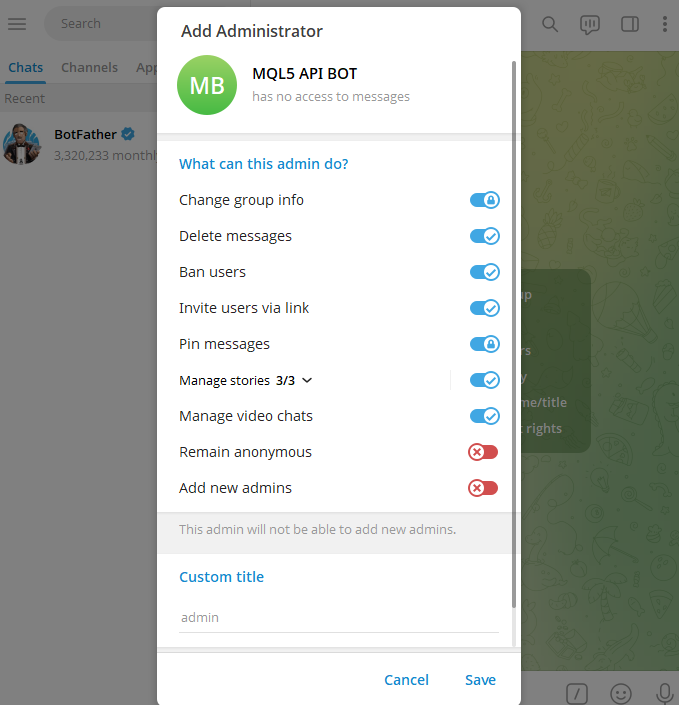
Go back to your Telegram group and send a message.
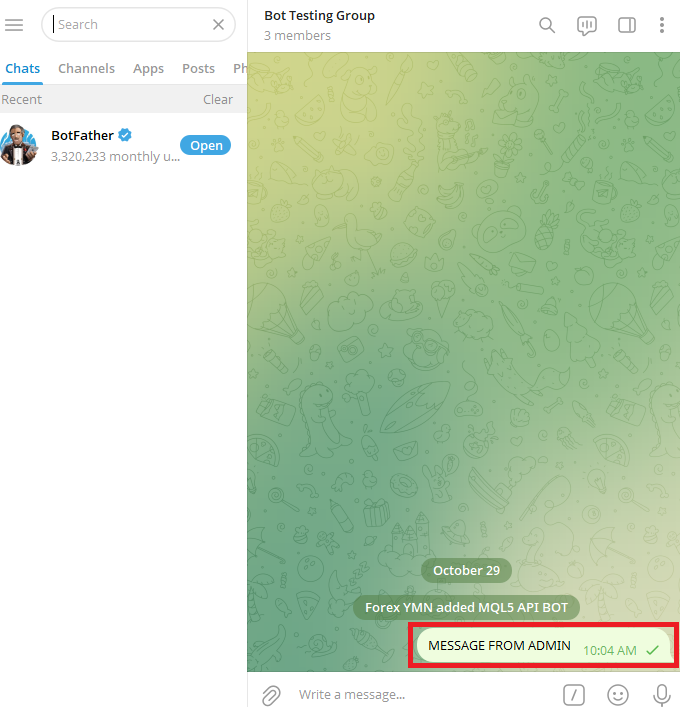
Go back to your browser and open the Telegram API link again:
https://api.telegram.org/bot<YourBotToken>/getUpdates A JSON response with information about the message you just sent to the group will appear after you reload the website. The chat_id of your Telegram group can be found in the chat area of this response. To send messages directly to that group, you will use this chat_id in your MetaTrader 5 code.
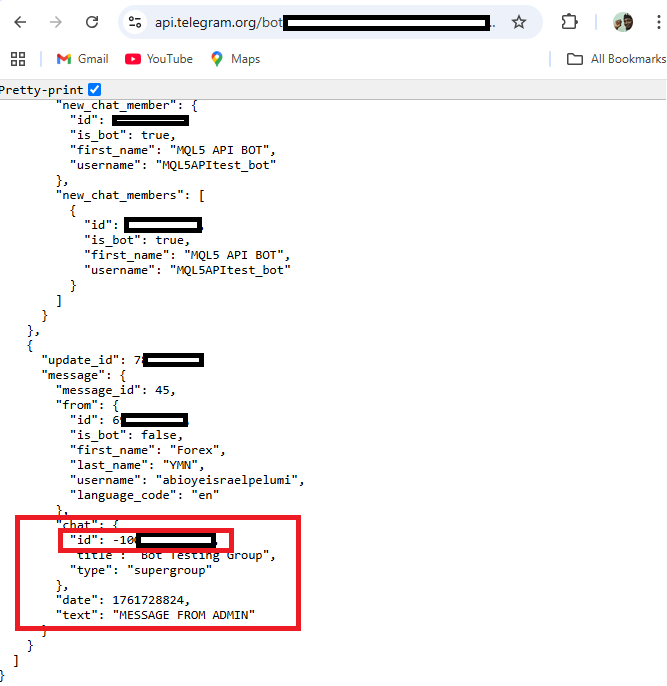
You can now utilize your Telegram group's chat ID in your MQL5 code since you were able to retrieve it. Any message or notification you send from MetaTrader 5 will now travel straight to that particular Telegram group as your program can pinpoint the exact location of messages thanks to this conversation ID.
Example:const string method = "POST"; const string telegram_api_url = "https://api.telegram.org"; const string bot_chatID = "6972412345"; const string headers = ""; const int time_out = 5000; const string group_chatID = "-1003271234567"; const string bot_token = "8345012345:AAHdAPtMQR6VHEQeHk1y_H9IuL3zc5abcde"; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- char data[]; char res[]; string resHeaders = ""; string body = "chat_id=" + group_chatID + "&text=Hello from MT5!"; StringToCharArray(body, data, 0); string url = telegram_api_url + "/bot" + bot_token + "/sendMessage"; WebRequest(method,url,headers,time_out,data,res,resHeaders); //--- return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
Output:
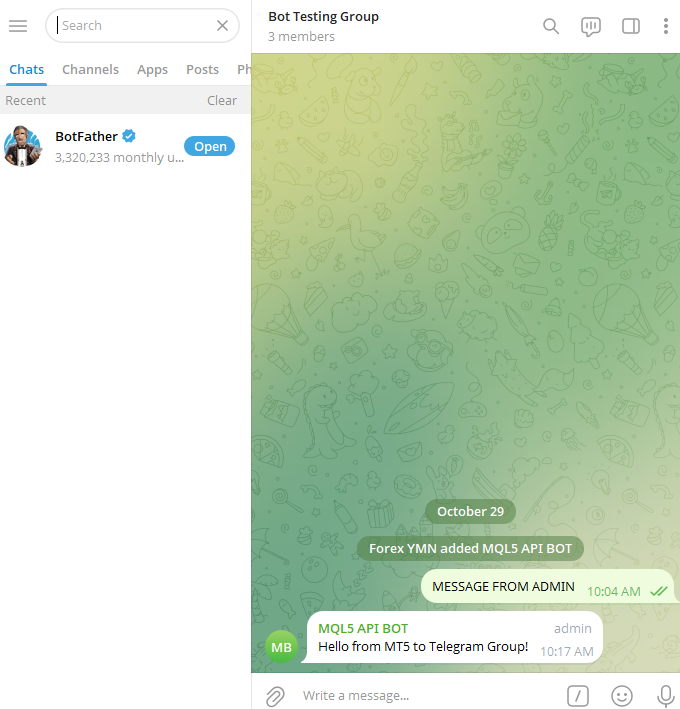
Explanation:
We declared a string variable to store the group chat ID. However, use group_chatID if you want the message to be delivered to your Telegram group.
Additionally, we used the line Print(CharArrayToString(res)); to obtain the server's answer. Important information is included in this answer, particularly the message_id of the transmitted message. In the following section, we'll learn how to change or remove the message straight from MetaTrader 5; thus, this message ID will be quite helpful.
Deleting Message with WebRequest() Function
A delete request can be sent straight to the Telegram server using the WebRequest() function. Bots can remove messages from groups as long as you know the message ID of the message you wish to remove. The bot can remove messages in the group as well as the messages it sends because it is an administrator (depending on the rights you provided it before).
For this reason, it was crucial that we printed the results earlier. Recall that the server's response to us looked like this:
{ "ok": true, "result": { "message_id": 34, "from": { "id": 1234500523, "is_bot": true, "first_name": "MQL5 API Bot", "username": "MQL5APItest_bot" }, "chat": { "id": -1234577012345, "title": "Bot Testing Group", "type": "supergroup" }, "date": 1761498168, "text": "Hello from MT5 to Telegram Group!" } } You can see from this answer that Telegram returns helpful data, such as the message_id. You can use the WebRequest function to change or remove that particular message later thanks to this ID.
The only time you'll get the message ID is when it was sent by the EA. If the message was manually sent by you to the group, you'll then need to go to "https://api.telegram.org/bot<YourBotToken>/getUpdates" by searching for the message, and copy its ID.
https://api.telegram.org/bot<YourBotToken>/getUpdates Example:
const string method = "POST"; const string telegram_api_url = "https://api.telegram.org"; const string bot_chatID = "6972412345"; const string group_chatID = "-1003277012345"; const string headers = ""; const int time_out = 5000; const string bot_token = "8345012345:AAHdAPtMWR6VHEQeHk1y_H9IuL3zc5abcde"; const string MessageID = "34"; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- char data[]; char res[]; string resHeaders = ""; const string url = telegram_api_url + "/bot" + bot_token + "/deleteMessage"; string body = "chat_id=" + group_chatID +"&message_id=" + MessageID; StringToCharArray(body, data, 0); WebRequest(method,url,headers,time_out,data,res,resHeaders); // Print(CharArrayToString(res)); //--- return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
Explanation:
The POST option is selected. Telegram's API requires POST to delete messages, although it could look like DELETE should be used. You instruct MQL5 to transmit data to the server in the request body by using POST. Consider POST as sending the Telegram server a letter containing instructions. You still need to write the message in a letter and send it, even if the command is to delete it.
The message you wish to remove is identified by its MessageID. Telegram assigns a distinct message ID to each message sent by a human or by the bot in a chat. You can instruct the Telegram server on which message to remove by using this ID. This message ID is often obtained from the server's response following a message send.
To create the complete endpoint for removing messages, the URL comprises multiple components. Telegram's API address is the base URL. The request is coming from a bot, as indicated by the bot component. The special authentication key for your bot is called the bot token. Lastly, if you include deleteMessage, the server will know that you wish to delete something. When combined, these URLs indicate the precise location to send your deletion request.
The chat and message IDs are included in the request's body. Telegram is informed by the message ID which particular message to remove and the chat ID which chat or group the message belongs to. The command you are giving to the server is basically included in this body.
Editing Message with WebRequest() Function
Using the WebRequest() function to alter a message will be our final topic of discussion. You should be aware that you can only alter messages that were sent by your bot when it comes to editing. The bot cannot alter messages sent by other users directly to the group.
Sending or removing a message functions similarly to editing. We are also using both the bot token and message ID.
The POST method, the relevant URL endpoint for message editing, and a body including the chat ID, message ID, and the updated text you wish to send are all required when using the WebRequest() function. This keeps the message ID constant while enabling your MetaTrader 5 software to update the message dynamically.
Example:
const string method = "POST"; const string telegram_api_url = "https://api.telegram.org"; const string bot_chatID = "6972412345"; const string group_chatID = "-10032771234567"; const string headers = ""; const int time_out = 5000; const string bot_token = "345012345:AAHdAPtMWR6VHEQeHk1y_H9IuL3zc5abcde"; const string MessageID = "35"; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- char data[]; char res[]; string resHeaders = ""; string new_message = "Updated message text from MT5!"; string url = telegram_api_url + "/bot" + bot_token + "/editMessageText"; string body = "chat_id=" + group_chatID +"&message_id=" + MessageID + "&text=" + new_message; StringToCharArray(body, data, 0); WebRequest(method,url,headers,time_out,data,res,resHeaders); Print(CharArrayToString(res)); //--- return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
Explanation:
The new message text that you wish to send is first defined. The original message in the Telegram group or chat will be replaced by this material. The URL is then created by fusing the endpoint /editMessageText, your bot token, and the base Telegram API URL. Telegram is particularly informed by this endpoint that the request intends to alter an existing message. Next comes the creation of the request's body. The message ID indicates which particular message to modify, the chat ID indicates which conversation or group the message belongs to, and the additional text you want in the message is all contained in it. Ultimately, a character array is created from the body string. This is required because to deliver the message body over the web, the WebRequest method needs it in a character array format.
Conclusion
This article taught you the basics of using MQL5's WebRequest() function and APIs. We explored how MetaTrader 5 can interact with an external platform such as Telegram through a hands-on project. You learned how to send, edit, or remove messages straight from MetaTrader 5, get chat and group IDs, and build a Telegram bot. To give you a better grasp of practical API integration, we will go one step further in the upcoming articles by learning how to accept and process data from external APIs.