SDK Configuration
This guide covers configuration for both Python and TypeScript SDKs, including basic setup, advanced options, and debugging capabilities.
Getting Started
Python SDK
The recommended approach to configuring the Python SDK is to use the opik configure command. This will prompt you to set up your API key and Opik instance URL (if applicable) to ensure proper routing and authentication. All details will be saved to a configuration file.
Opik Cloud
Self-hosting
If you are using the Cloud version of the platform, you can configure the SDK by running:
You can also configure the SDK by calling configure from the Command line:
The configure methods will prompt you for the necessary information and save it to a configuration file (~/.opik.config). When using the command line version, you can use the -y or --yes flag to automatically approve any confirmation prompts:
TypeScript SDK
For the TypeScript SDK, configuration is done through environment variables, constructor options, or configuration files.
Installation:
Basic Configuration:
You can configure the Opik client using environment variables in a .env file:
Or pass configuration directly to the constructor:
Configuration Methods
Both SDKs support multiple configuration approaches with different precedence orders.
Configuration Precedence
Python SDK: Constructor options → Environment variables → Configuration file → Defaults
TypeScript SDK: Constructor options → Environment variables → Configuration file (~/.opik.config) → Defaults
Environment Variables
Both SDKs support environment variables for configuration. Here’s a comparison of available options:
Using .env Files
Both SDKs support .env files for managing environment variables. This is a good practice to avoid hardcoding secrets and to make your configuration more portable.
For Python projects, install python-dotenv:
For TypeScript projects, dotenv is automatically loaded by the SDK.
Create a .env file in your project’s root directory:
Python usage with .env file:
TypeScript usage with .env file:
The TypeScript SDK automatically loads .env files, so no additional setup is required:
Using Configuration Files
Both SDKs support configuration files for persistent settings.
Python SDK Configuration File
The Python SDK uses the TOML format. The configure method creates this file automatically, but you can also create it manually:
Opik Cloud
Self-hosting
TypeScript SDK Configuration File
The TypeScript SDK also supports the same ~/.opik.config file format as the Python SDK. The configuration file uses INI format internally but shares the same structure:
Opik Cloud
Self-hosting
By default, both SDKs look for the configuration file in your home directory (~/.opik.config). You can specify a different location by setting the OPIK_CONFIG_PATH environment variable.
Debug Mode and Logging
Both SDKs provide debug capabilities for troubleshooting integration issues.
Python SDK Debug Mode
To enable debug mode for the Python SDK, set these environment variables before importing opik:
Using with .env file:
Then in your Python script:
TypeScript SDK Debug Mode
The TypeScript SDK uses structured logging with configurable levels:
Available log levels: SILLY, TRACE, DEBUG, INFO (default), WARN, ERROR, FATAL
Enable debug logging:
Or in .env file:
Programmatic control:
Advanced Configuration
Python SDK Advanced Options
HTTP Client Configuration
The Opik Python SDK uses the httpx library to make HTTP requests. The default configuration applied to the HTTP client is suitable for most use cases, but you can customize it by registering a custom httpx client hook as in following example:
Make sure to add the hook before using the Opik SDK.
TypeScript SDK Advanced Options
Batching Configuration
The TypeScript SDK uses batching for optimal performance. You can configure batching behavior:
Global Flush Control
Configuration Reference
Python SDK Configuration Values
TypeScript SDK Configuration Values
Troubleshooting
Python SDK Troubleshooting
SSL Certificate Error
If you encounter the following error:
You can resolve it by either:
- Disable the TLS certificate check by setting the
OPIK_CHECK_TLS_CERTIFICATEenvironment variable tofalse - Add the Opik server’s certificate to your trusted certificates by setting the
REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLEenvironment variable
Health Check Command
If you are experiencing problems with the Python SDK, such as receiving 400 or 500 errors from the backend, or being unable to connect at all, run the health check command:
This command will analyze your configuration and backend connectivity, providing useful insights into potential issues.
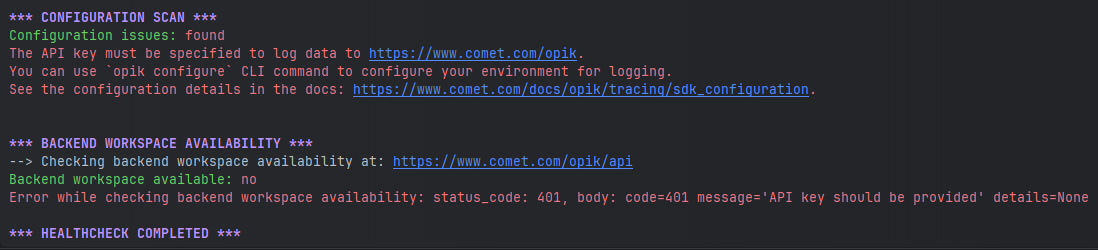
Reviewing the health check output can help pinpoint the source of the problem and suggest possible resolutions.
TypeScript SDK Troubleshooting
Configuration Validation Errors
The TypeScript SDK validates configuration at startup. Common errors:
- “OPIK_URL_OVERRIDE is not set”: Set the
OPIK_URL_OVERRIDEenvironment variable - “OPIK_API_KEY is not set”: Required for Opik Cloud deployments
- “OPIK_WORKSPACE is not set”: Required for Opik Cloud deployments
Debug Logging
Enable debug logging to troubleshoot issues:
Or programmatically:
Batch Queue Issues
If data isn’t appearing in Opik:
- Check if data is batched: Call
await client.flush()to force sending - Verify configuration: Ensure correct API URL and credentials
- Check network connectivity: Verify firewall and proxy settings
General Troubleshooting
Environment Variables Not Loading
- Python: Ensure
load_dotenv()is called before importingopik - TypeScript: The SDK automatically loads
.envfiles - Verify file location:
.envfile should be in project root - Check file format: No spaces around
=in.envfiles
Configuration File Issues
- File location: Default is
~/.opik.config - Custom location: Use
OPIK_CONFIG_PATHenvironment variable - File format: Python uses TOML, TypeScript uses INI format
- Permissions: Ensure file is readable by your application

