After you configure data sources, networks, and resources, you can create a real-time sync task. This task establishes a sync channel for real-time incremental synchronization of data from a single table or an entire database. This topic describes how to create a real-time sync task and view its status.
Prerequisites
You have configured the required data sources. Before you configure a sync task, you must configure the source and destination databases. This lets you select the data sources by name during the sync task configuration to control data reads and writes. For more information about the data sources that support real-time synchronization and how to configure them, see Supported data sources for real-time synchronization.
NoteFor more information about data source features, see Data source overview.
A resource group with the required specifications is purchased and attached to the workspace. For more information, see Use a serverless resource group and Add and use an exclusive resource group for Data Integration.
A network connection is established between the resource group and the data source. For more information, see Network connectivity.
Go to Data Development
For some channels, you can configure single-table real-time sync tasks in the Data Development module. For more information about supported channels, see Supported data sources.
Go to the Data Development page.
Log on to the DataWorks console. After you switch to the destination region, click in the navigation pane on the left. From the drop-down list, select the target workspace and click Go To Data Development.
Step 1: Create a real-time sync task
Create a business flow. For more information, see Create a business flow.
Create a real-time sync task.
Create a real-time sync task in one of the following two ways.
Method 1: Expand the business flow, right-click .
Method 2: Double-click the business flow name, click Create Node, and then drag the Real-time Synchronization node from the Data Integration folder to the business flow editing panel on the right.
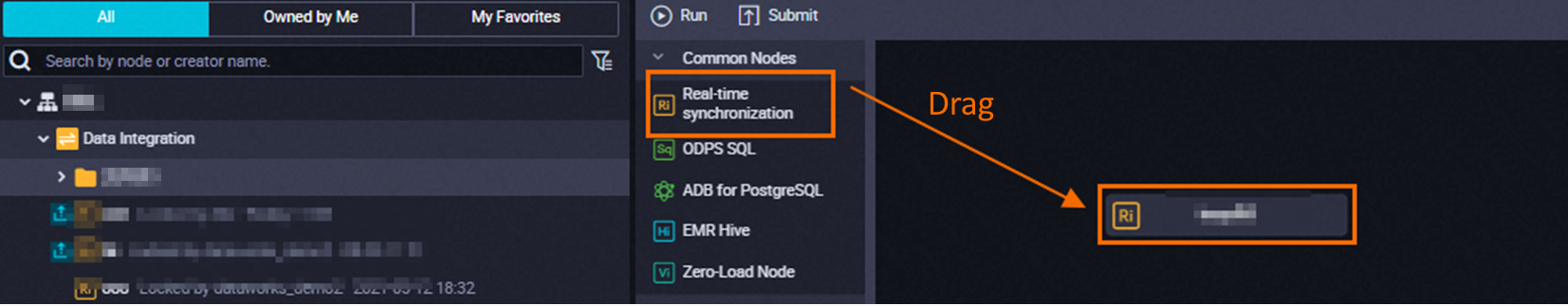
In the Create Node dialog box, configure the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Node Type
The default value is Real-time Synchronization.
Sync Method
To synchronize incremental data from a single table in real time, set Sync Method to Single-table (Topic) To Single-table (Topic) ETL. This method is used to synchronize data from one or more tables to a single destination table in real time.
NoteA single-table real-time sync task supports writing data to only one destination table. To synchronize data to multiple tables, use one of the following solutions:
To filter data, replace strings, or mask data during synchronization, create multiple single-table real-time sync tasks.
To synchronize data from multiple tables to multiple tables, you can create multiple single-table real-time sync tasks. For some data sources, you can also configure a real-time sync task for an entire database.
To first synchronize full data and then synchronize incremental data to the destination in real time, use a synchronization solution. For more information, see Configure a real-time sync task for an entire database.
To synchronize incremental data from an entire database in real time, select a sync method for database change data, such as Database change data synchronization to MaxCompute.
Path
The folder where the real-time sync task is stored.
Name
The node name must be 1 to 128 characters in length and can contain letters, Chinese characters, digits, underscores (_), and periods (.).
Step 2: Configure a resource group
Real-time sync tasks can run only on serverless resource groups or exclusive resource groups for Data Integration. On the configuration page of the real-time sync task, click Basic Configuration in the right-side navigation pane. From the Resource Group drop-down list, select a resource group that is connected to the database network.
If you have created a resource group but the resource group is not displayed, you must check whether the resource group is associated with your workspace. For more information, see Use serverless resource groups or Create and use an exclusive resource group for Data Integration.
Run real-time sync tasks and offline sync tasks on different resource groups. This prevents resource preemption and interference between tasks. For example, contention for CPU, memory, and network resources can slow down offline sync tasks, increase the latency of real-time sync tasks, or even cause tasks to be terminated by the out-of-memory (OOM) killer in cases of extreme resource shortage.
Serverless resource groups allow you to specify an upper limit for the compute units (CUs) that a sync task can use. If your sync task fails with an OOM error because of insufficient resources, you can increase the CU limit for the resource group.
Step 3: Configure the real-time sync task
Configure a single-table real-time sync task
Configure the source data source.
In the Input section on the left side of the real-time sync task configuration page, drag the target source data source component to the right-side panel.
Click the source component and configure the parameters in the Node Configuration pane on the right.
The following source data source types are supported for single-table data synchronization. Configuration details are provided for each type.
Optional: Configure a data transform.
During real-time data synchronization, you can configure a data transform to convert the input data into the desired output format.
In the Transform section on the left side of the real-time sync task configuration page, drag the required data transform component to the right-side panel.
The following data transforms are supported for single-table data synchronization:
Data filtering: You can filter data based on rules, such as field size. Only data that meets the rules is retained.
String replacement: You can replace fields of the string type.
Data masking: You can mask data in a single table during real-time synchronization and then store the data in a specified database.
Click the transform component and configure the parameters in the Node Configuration pane on the right.
Configure the destination data source.
In the Output section on the left side of the real-time sync task configuration page, drag the target destination data source component to the right-side panel.
Click the destination component and configure the parameters in the Node Configuration pane on the right.
The following destination data source types are supported for single-table data synchronization. Configuration details are provided for each type.
Configure the upstream and downstream dependencies for the source and destination components.
After you add the source and destination components, connect them with lines. Data is synchronized from the upstream component to the downstream component based on the connection.
Configure a real-time sync task for an entire database
Set the synchronization source and rules.
In the Data Source section, select the Type and Data Source name of the data source to be synchronized.
Select the tables to be synchronized.
In the Select Source Tables For Synchronization section, all tables in the selected data source are displayed. In the Source Database And Table section, select one or more tables that you want to synchronize, and click the
 icon to move them to the Selected Database And Table list.Important
icon to move them to the Selected Database And Table list.ImportantIf a selected table does not have a primary key, it cannot be synchronized in real time.
Set the mapping rules for table names.
In this step, you can select the source database and tables to be synchronized. By default, the synchronization solution writes data from the source database and tables to a schema and tables with the same names in the destination. If the schema or tables do not exist in the destination, they are automatically created. You can also use Set Mapping Rules For Table (Database) Names to define the final schema or table names in the destination. This lets you write data from multiple tables to a single table or update a fixed prefix for source database or table names to another prefix in the destination.
Source Table Name And Destination Table Name Conversion Rule: You can use a regular expression to convert the source table name to the final destination table name.
Example 1: Write data from source tables with the `doc_` prefix to destination tables with the `pre_` prefix.

Example 2: Write data from multiple tables to a single destination table.
To synchronize data from tables named "table_01", "table_02", and "table_03" to a single table named "my_table", configure the regular expression conversion rule as follows: Set Source to `table.*` and Destination to `my_table`.

Destination Table Name Rule: You can use a combination of built-in variables to generate the destination table name. You can also add a prefix and a suffix to the converted destination table name. The following built-in variables are available:
${db_table_name_src_transed}: The table name that is generated by the Source Table Name And Destination Table Name Conversion Rule.
${db_name_src_transed}: The destination schema name that is generated by the Source Database Name And Destination Schema Name Conversion Rule.
${ds_name_src}: The source data source name.
Example: To further process the table name generated by the Source Table Name And Destination Table Name Conversion Rule, use `${db_table_name_src_transed}` to represent the result from the previous step, which is `my_table`. You can then add a prefix and a suffix to this built-in variable, such as `pre_${db_table_name_src_transed}_post`. The final mapped destination table name is `pre_my_table_post`.
Source Database Name And Destination Schema Name Conversion Rule: You can use a regular expression to convert the source schema name to the final destination schema name.
Example: Replace the `doc_` prefix of the source database name with the `pre_` prefix.

Select the destination data source and configure the destination table or topic.
On the Set Destination Table Or Topic page, configure the basic information for the Destination Data Source, such as the write mode and partition settings. The specific configuration varies depending on the data source.
Click Refresh Source And Destination Table Mapping to create the mapping between the source and destination tables.
You can customize the destination schema and table names, and add constants or variables to the destination table using Edit Additional Fields. The specific configuration varies depending on the data source.
NoteIf many tables are synchronized, the process may be slow. Please wait for the process to complete.
Optional: Set table-level synchronization rules.
Some synchronization solutions support custom table-level DML processing policies. When an insert, update, or delete operation occurs in the source table, you can define the corresponding processing policy here.
NoteThe supported DML operations may vary for different data sources. Whether a synchronization solution supports DML processing policies is indicated on the product UI. For the DML support status of each data source, see Supported DML and DDL operations.
Set DDL message processing rules.
The source data source may involve many DDL operations. During real-time synchronization, you can set processing policies for different DDL messages that are synchronized to the destination. The supported DDL operations may vary for different data sources. For more information, see Supported DML and DDL operations. On the page, you can set DDL processing policies for each destination database type. The following table describes the different DDL message processing policies.
DDL message type
Processing policy
Create Table
When DataWorks receives a DDL message of the corresponding type, the processing policy is as follows:
Normal Processing: Forwards the message to the destination data source for processing. Because different destination data sources may have different policies for handling DDL messages, DataWorks only forwards the message.
Ignore: Discards the message without sending it to the destination data source.
Alert: Discards the message and records an alert in the real-time synchronization log. The alert indicates that the message was discarded due to an execution error.
Error: The real-time sync task immediately fails and stops running.
Drop Table
Add Column
Drop Column
Rename Table
Rename Column
Alter Column Type
Truncate Table
Configure runtime resources.
The concurrency control feature limits the maximum concurrency for reading from and writing to the database.
You can control whether the sync task tolerates dirty data.
If dirty data is not allowed, the sync task fails and exits if dirty data is generated during execution.
If dirty data is allowed, the sync task ignores the dirty data and continues to run normally. The dirty data is not written to the destination.
Click Complete Configuration.
Step 4: Commit and publish the real-time sync task
In the toolbar, click the
 icon to save the node.
icon to save the node.In the toolbar, click the
 icon to commit the node.
icon to commit the node.In the Submit New Version dialog box, enter a Change Description.
Click OK.
If you are using a workspace in standard mode, you must publish the task to the production environment after you commit it. In the top menu bar, click Task Publication. For more information, see Publish a task.
Step 5: Run the real-time sync task
You cannot directly run a real-time sync task in Data Development. You must publish the task to the Operation Center, and then start it and view its status in the Operation Center.
After the task is configured, you can start and manage it on the page. For more information, see O&M for real-time sync tasks.
Appendixes
Task migration
You can migrate a single-table real-time integration task that is configured on the DataStudio page to the Data Integration page by clicking Migrate To Primary Site.
The following real-time integration tasks are currently supported:
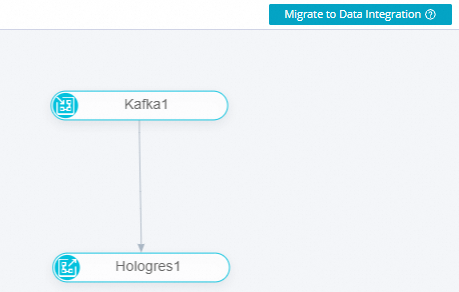
A single-table real-time integration task from Kafka to MaxCompute.
A single-table real-time integration task from Kafka to Hologres.
Double-click the single-table real-time integration task that you want to migrate. On the task editing page, click Migrate To Primary Site to migrate the task.
In the upper-left corner, click the
 icon and choose . On the Sync Task page, the successfully migrated single-table real-time integration task appears in the task list.
icon and choose . On the Sync Task page, the successfully migrated single-table real-time integration task appears in the task list.
After a task is migrated to the primary site, you can perform O&M operations directly in Data Integration instead of in the Operation Center. The task will no longer be visible in the Operation Center. The migration does not affect saved task configurations or running tasks.
After migration, the original task is moved to the recycle bin in Data Development. You can perform subsequent editing and O&M actions only on the task list page in the Data Integration primary site.
Data Development operations
To create a real-time sync task in Data Development, see the following information.
To create a real-time sync task in a workspace that is participating in the public preview of the new DataStudio, see Real-time synchronization node.
To create a real-time sync task in a workspace that is not participating in the public preview of the new DataStudio, see Real-time synchronization task.