You can use MySQL Reader to read data from tables in your MySQL database in real time by subscribing to binary logs. This topic describes how to configure MySQL Reader and details the required network environment and permissions.
Prerequisites
Before you configure MySQL Reader, make sure that the following prerequisites are met:
The synchronization account permissions have been configured. For more information, see Configure account permissions.
A real-time synchronization node for a MySQL data source uses the account that you configure for the MySQL data source in DataWorks to access the database. You must ensure that the account is granted the following permissions on the database:
SELECT,REPLICATION SLAVE, andREPLICATION CLIENT.Enable the binary logging feature for the MySQL instance. For more information, see Enable binary logging for MySQL.
Data Integration synchronizes incremental data from MySQL in real time by subscribing to MySQL binary logs. Therefore, you must enable the binary logging feature for MySQL before you configure a sync task in DataWorks.
Purchase an exclusive resource group for Data Integration that meets your business requirements. For more information, see Create and use an exclusive resource group for Data Integration.
Establish a network connection between the resource group for data synchronization and the database. For more information, see Network connectivity solutions.
Limits
Data Integration does not support synchronizing data from read-only instances of MySQL databases.
Real-time data synchronization from MySQL is supported only for RDS for MySQL instances that run MySQL
5.xor8.x. If you want to synchronize data from a DRDS database, do not configure it as a MySQL data source. Instead, add a DRDS data source to DataWorks. For more information, see Configure a DRDS data source.Functional indexes are not supported.
Configure MySQL Reader
Go to the DataStudio page.
Log on to the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select the desired region. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select the desired workspace from the drop-down list and click Go to Data Development.
In the Scheduled Workflow pane of the DataStudio page, move the pointer over the
 icon and choose .
icon and choose . Alternatively, find the desired workflow in the Scheduled Workflow pane, right-click the workflow name, and then choose .
In the Create Node dialog box, set the Sync Method parameter to End-to-end ETL and configure the Name and Path parameters.
Click Confirm.
On the configuration tab of the real-time synchronization node, drag to the canvas.
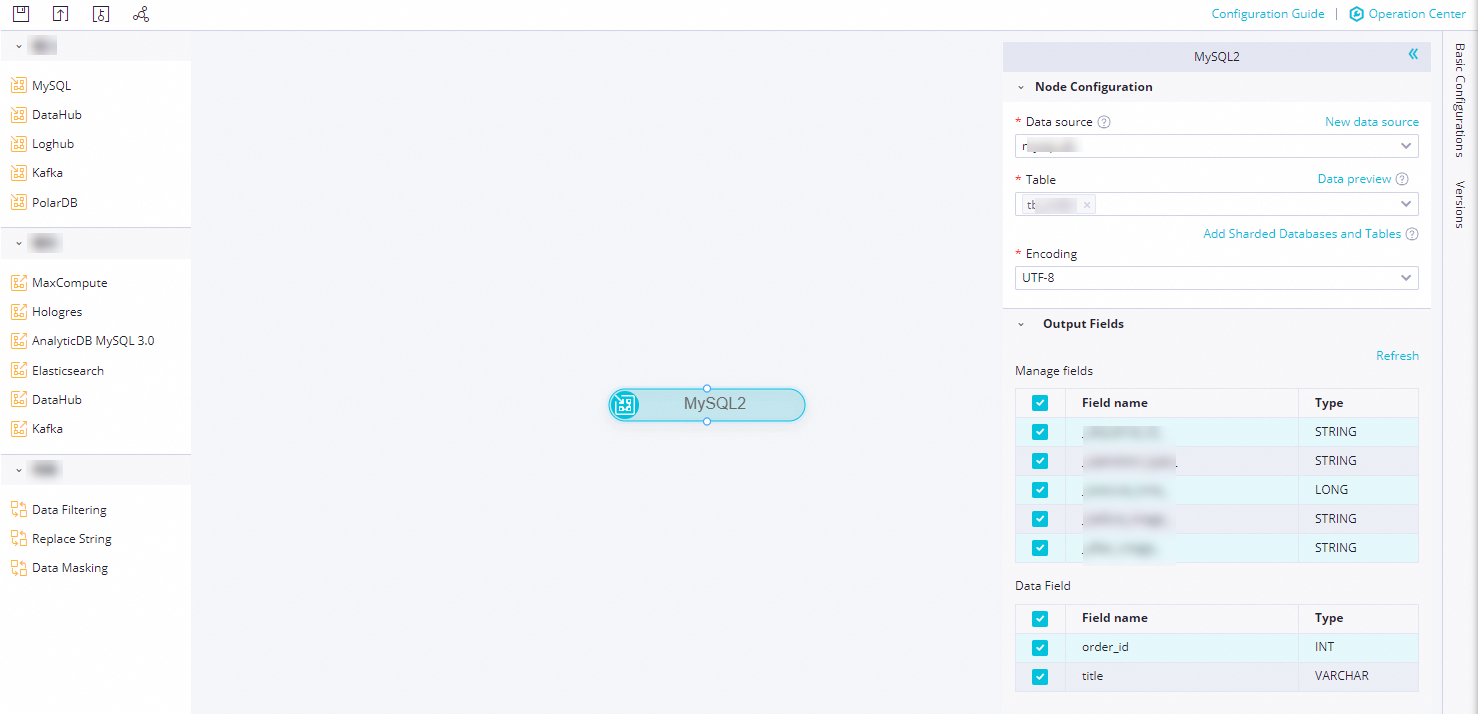
Click the MySQL node. In the Node Configuration panel that appears, configure the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Data Source
Select a configured MySQL data source. Only MySQL data sources are supported.
If no data source is available, click New Data Source on the right to go to the page to create a data source.
Table
Select the name of the table from which you want to synchronize data in the current data source. You can click Data Preview on the right to confirm your selection.
You can synchronize data from sharded databases and tables. The configured databases and tables are synchronized in real time in the task.
ImportantTo prevent execution errors, make sure that the tables in the sharded databases use the same schema. The schema includes the number of fields, field types, field names, and field order.
Output Fields
Select the fields that you want to synchronize. The fields include Management Fields and Data Fields.
Management Fields: the additional fields that are automatically added to the destination to facilitate data management, sorting, and deduplication.
Data Fields: the fields in the source table that you want to synchronize.
For more information, see Fields used for real-time synchronization.
The MySQL node supports sharding. You can click Add Sharded Databases And Tables and select the desired Data Source and Table from the drop-down lists to add multiple data sources for concurrent synchronization.
Click the
 icon in the toolbar.
icon in the toolbar.
FAQ
A real-time synchronization task for a MySQL data source reads data initially but then stops. What should I do?
Execute the following command in the database to view the binary log file to which the database instance is currently writing data.
show master statusSearch for a log entry such as
journalName=MySQL-bin.000001,position=50in the task log. Compare the binary log file in the log with the current binary log file of the database to check whether data is still being written.If data is being written to the database but the binary log position in the task log does not advance, contact a database administrator (DBA) for assistance.
What do I do if the
Cannot replicate because the master purged required binary logs.error is reported for a real-time synchronization task for MySQL?Answer: The full error message is "
Cannot replicate because the master purged required binary logs. Replicate the missing transactions from elsewhere, or provision a new slave from backup." This error occurs because the binary log record at the consumer offset cannot be found in MySQL. Check the binary log retention period for your MySQL database. When you start the synchronization task, ensure that the specified offset is within the retention period. If you cannot subscribe to the binary log, try resetting the offset to the current time.
What do I do if the
MySQLBinlogReaderExceptionerror is reported for a real-time synchronization task for MySQL?Answer: The full error message is "
MySQLBinlogReaderException: The database you are currently syncing is the standby database, but the current value of log_slave_updates is OFF, you need to enable the binlog log update of the standby database first." This error occurs because binary logging is not enabled for the secondary database. If you want to synchronize data from a secondary database, you must enable cascaded binary logging for it. Contact a DBA for assistance.For more information about how to enable binary logging, see Enable binary logging for MySQL.
What do I do if the
show master status' has an error!error is reported for a real-time synchronization task for MySQL?Answer: The full error message is "
show master status' has an error!" and the detailed error information is "Caused by: java.io.IOException: message=Access denied; you need (at least one of) the SUPER, REPLICATION CLIENT privilege(s) for this operation, with command: show master status". This error occurs because the data source account has not been granted the required permissions on the database.The account that you use to configure the data source must have the SELECT, REPLICATION SLAVE, and REPLICATION CLIENT permissions on the database. For more information about how to grant permissions to the data source account, see Step 2: Create an account and grant permissions to the account.
What do I do if the
parse.exception.PositionNotFoundException: can't find start position for xxerror is reported for a real-time synchronization task for MySQL?Answer: This error indicates that the synchronization task cannot find the specified offset. You must reset the offset.
What do I do if the following error is reported for a real-time synchronization task for MySQL:
The database offset has expired. Select another offset. The earliest available offset of the source database is xxx.Reset the offset: When you start the real-time synchronization task, reset the offset to the earliest available offset of the source database.
Adjust the binary log retention period: If the database offset frequently expires, you can increase the retention period of binary logs in the MySQL database. For example, you can set the retention period to 7 days.
Synchronize data: If data is lost, perform a full data synchronization again, or configure an offline synchronization task to manually synchronize the lost data.
Does real-time synchronization support merging different fields from multiple tables in a single database? For example, if Table A contains fields a and b, and Table B contains fields a and c, can the data be synchronized to a table that contains fields a, b, and c?
No, it does not. Real-time synchronization is supported only for multiple tables that have the exact same schema.