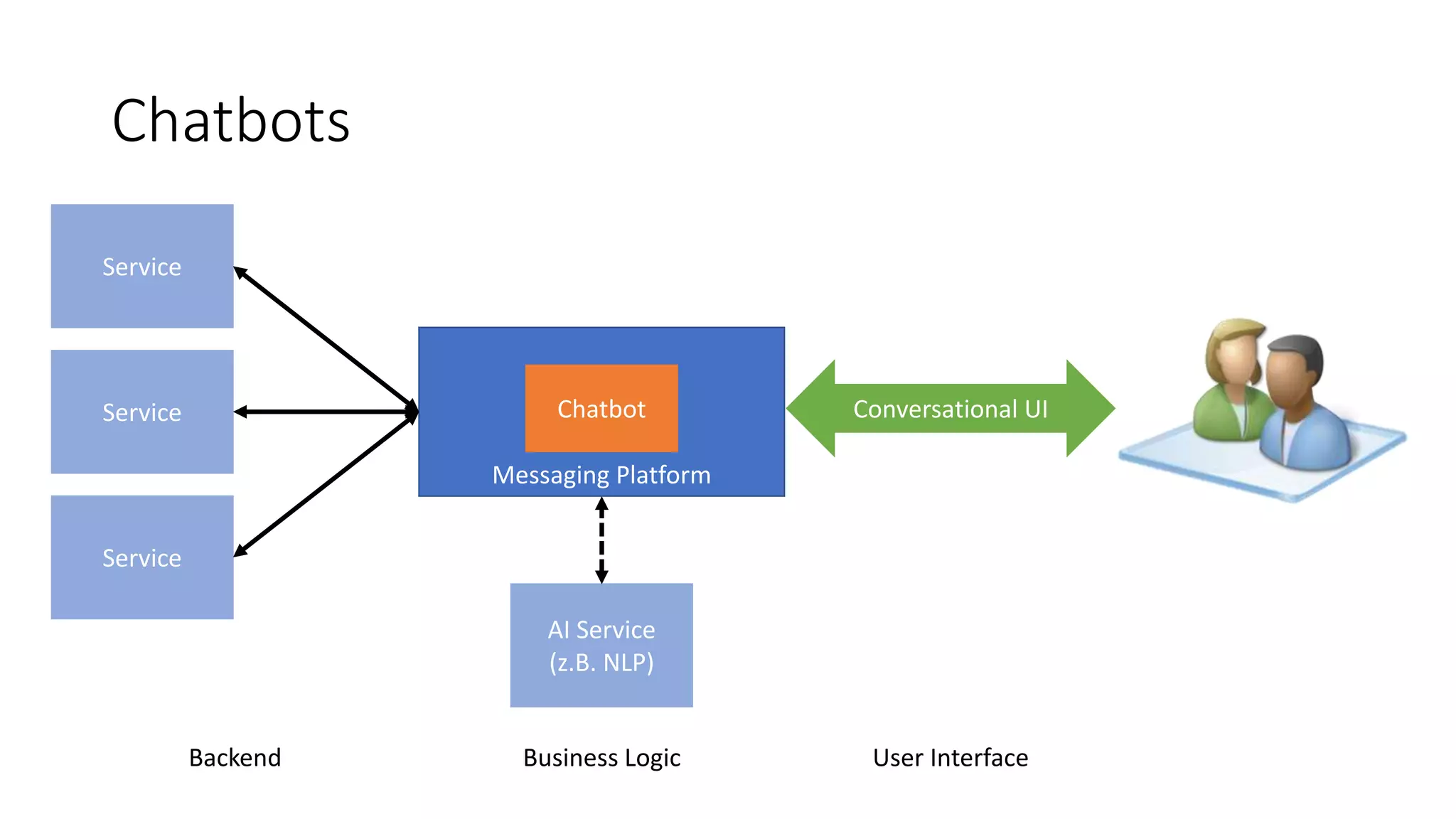
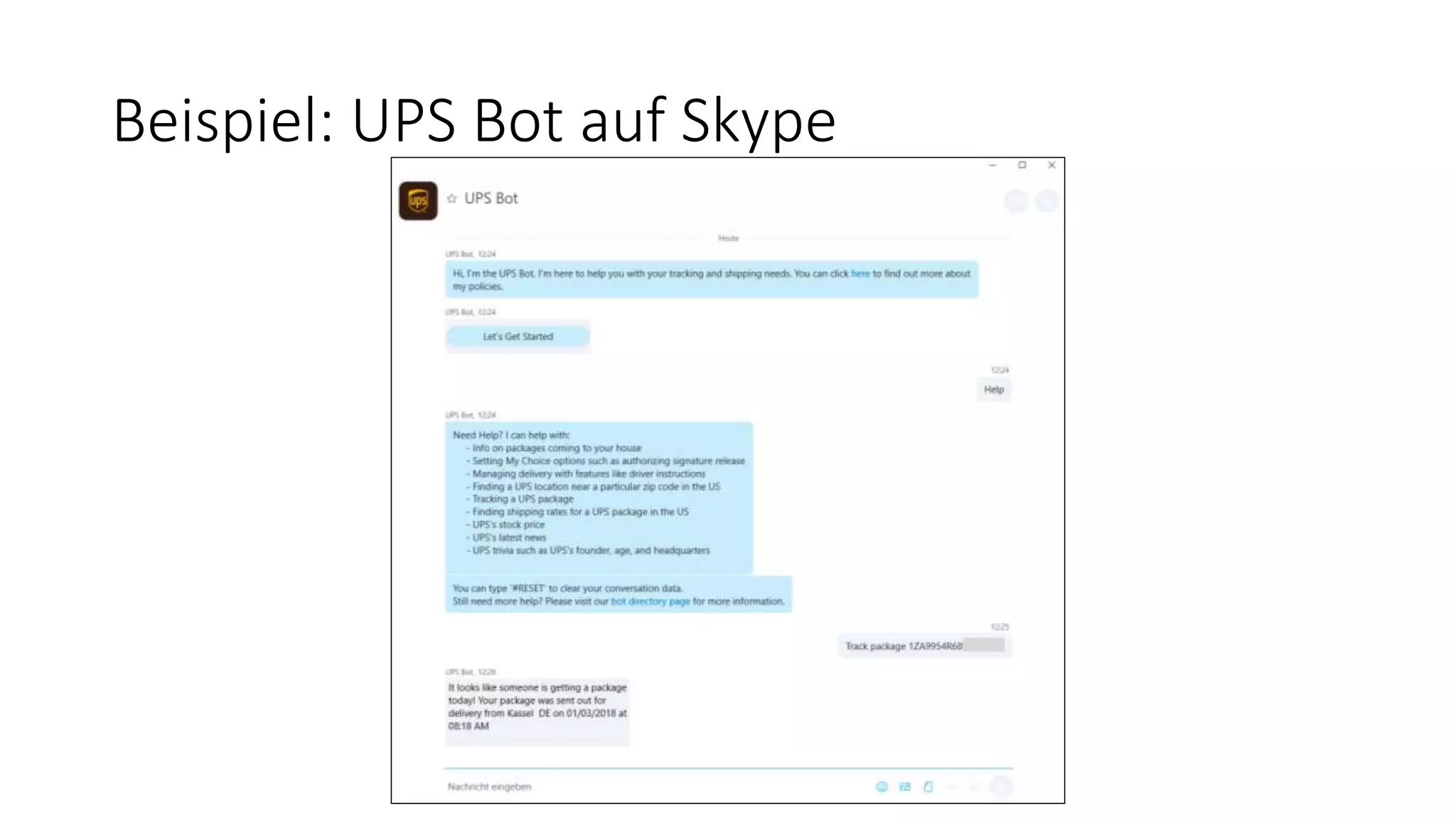
Die Präsentation beschreibt das Microsoft Bot Framework für die Entwicklung intelligenter Chatbots, die über Messaging-Plattformen kommunizieren und durch natürliche Sprachverarbeitung (NLP) anpassungsfähig werden. Es werden Anwendungsfälle und Vorteile von Chatbots in verschiedenen Bereichen wie E-Commerce und Unternehmensproduktivität erläutert, sowie technische Details zur Integration und Nutzung des Frameworks. Weiterhin werden Best Practices für die Entwicklung von Dialogen und die Implementierung von Benutzeroberflächen angesprochen.


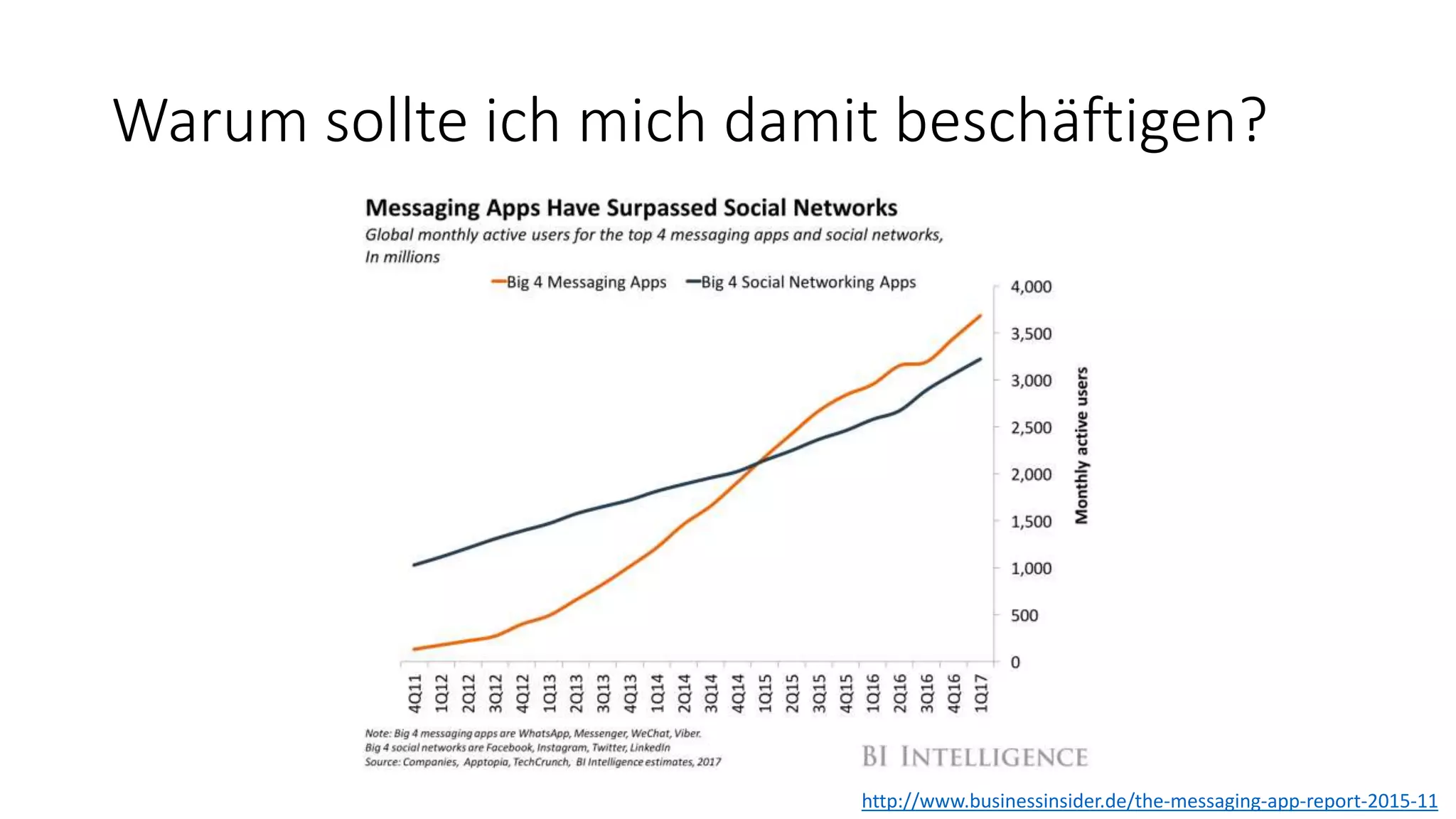
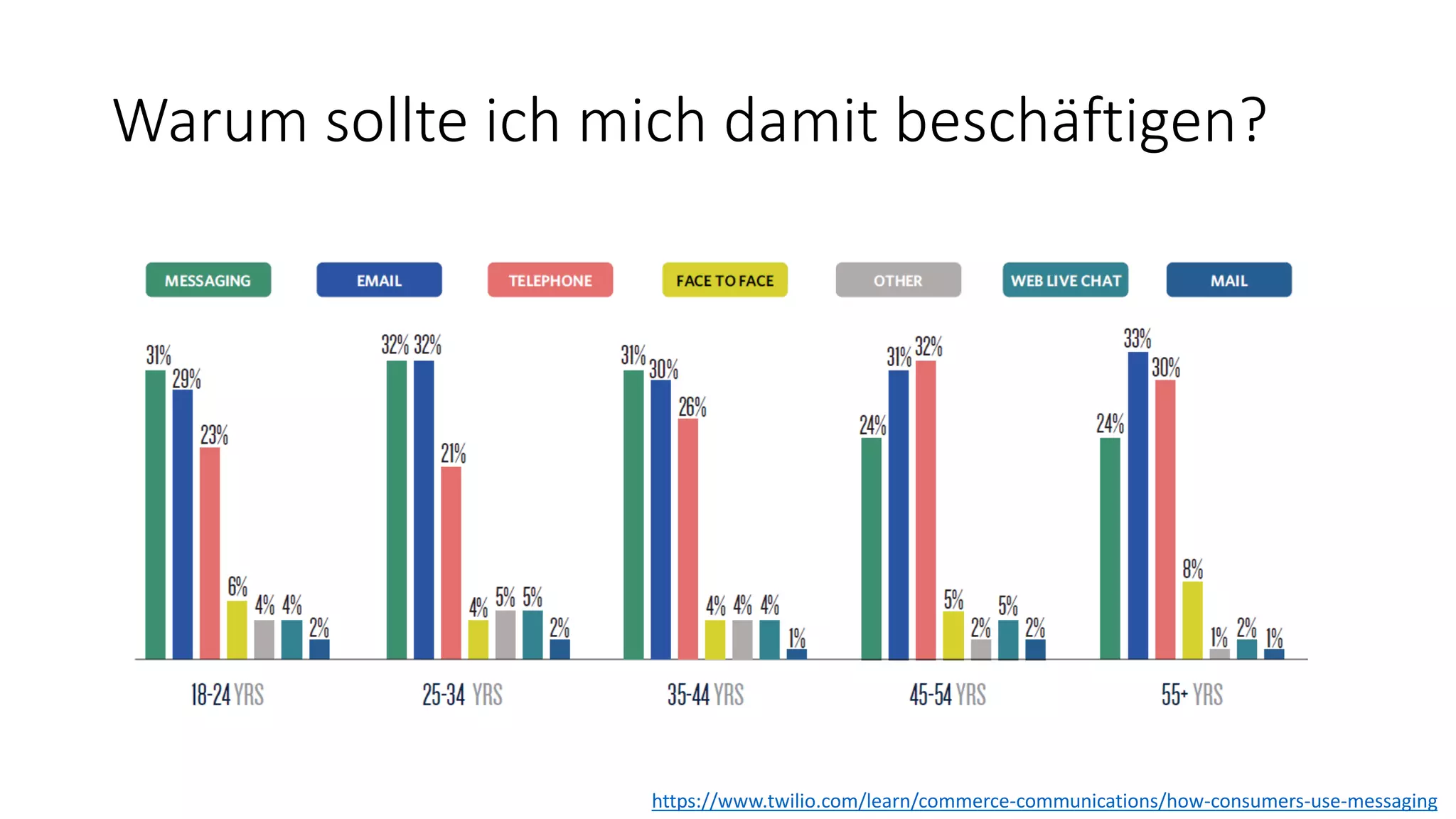
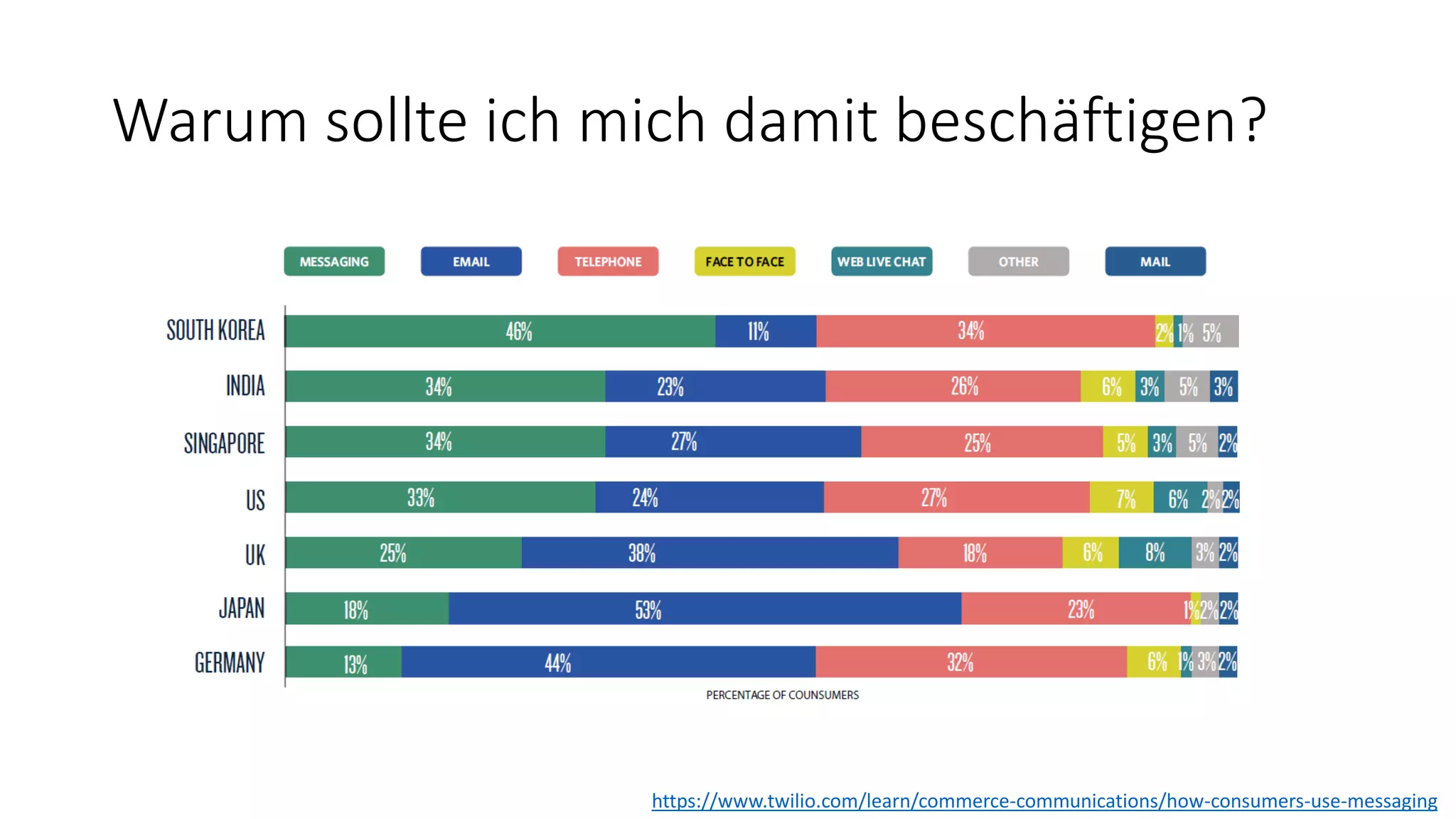
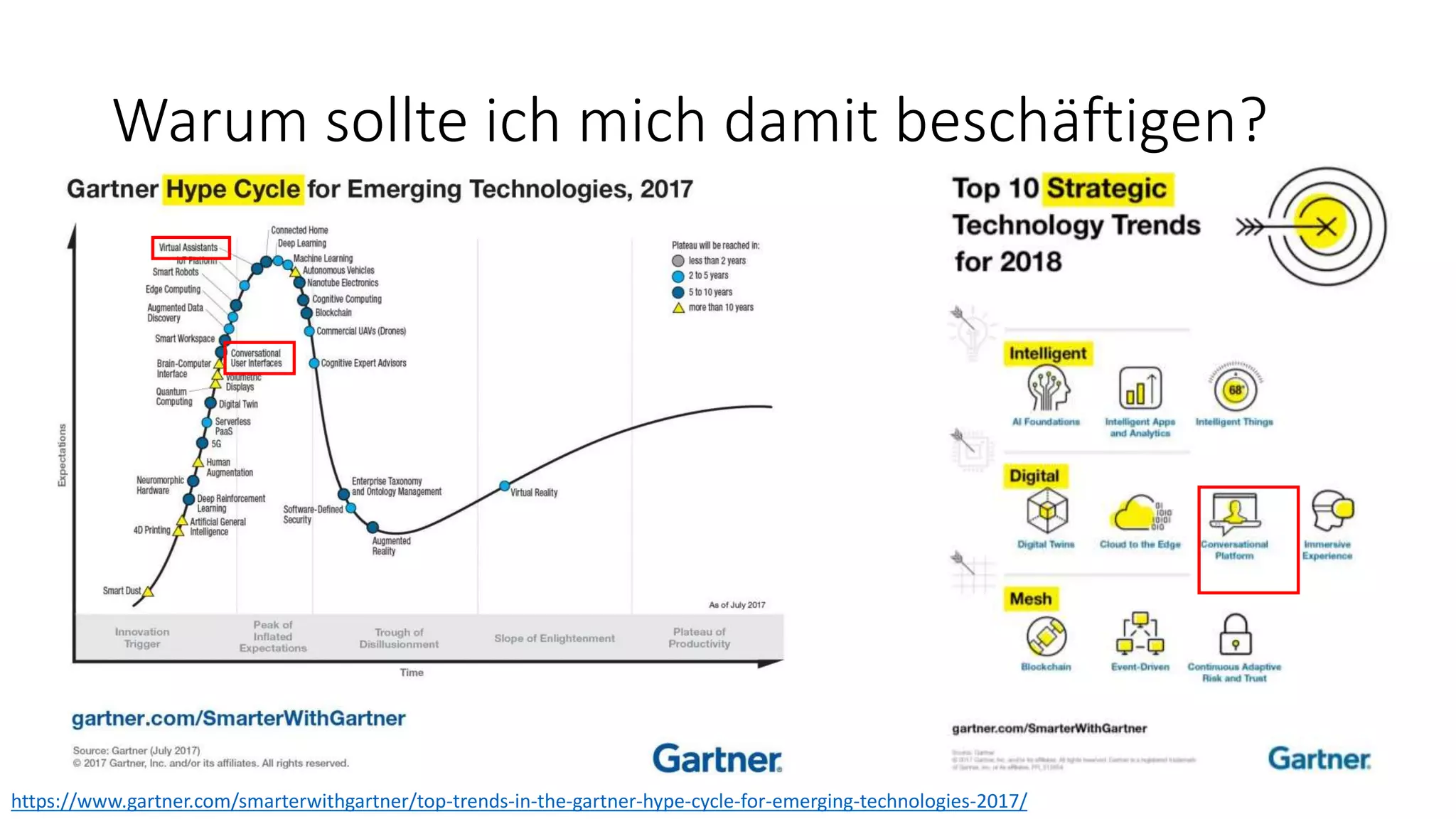
![Warum sollte ich mich damit beschäftigen? […] as messaging apps have grown to dominate both phones and workplaces, we see conversations with other humans being supplemented by intelligent chatbots. As these platforms improve, they will learn to understand the context and intent of conversations, making interactions more lifelike and therefore more compelling. The explosion of interest in the marketplace and mainstream media leads to a corresponding rise in developer interest […] (ThoughtWorks Technology Radar, Volume 16)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microsoftbotframeworkdotnet-180116130141/75/Microsoft-Bot-Framework-NET-Edition-7-2048.jpg)


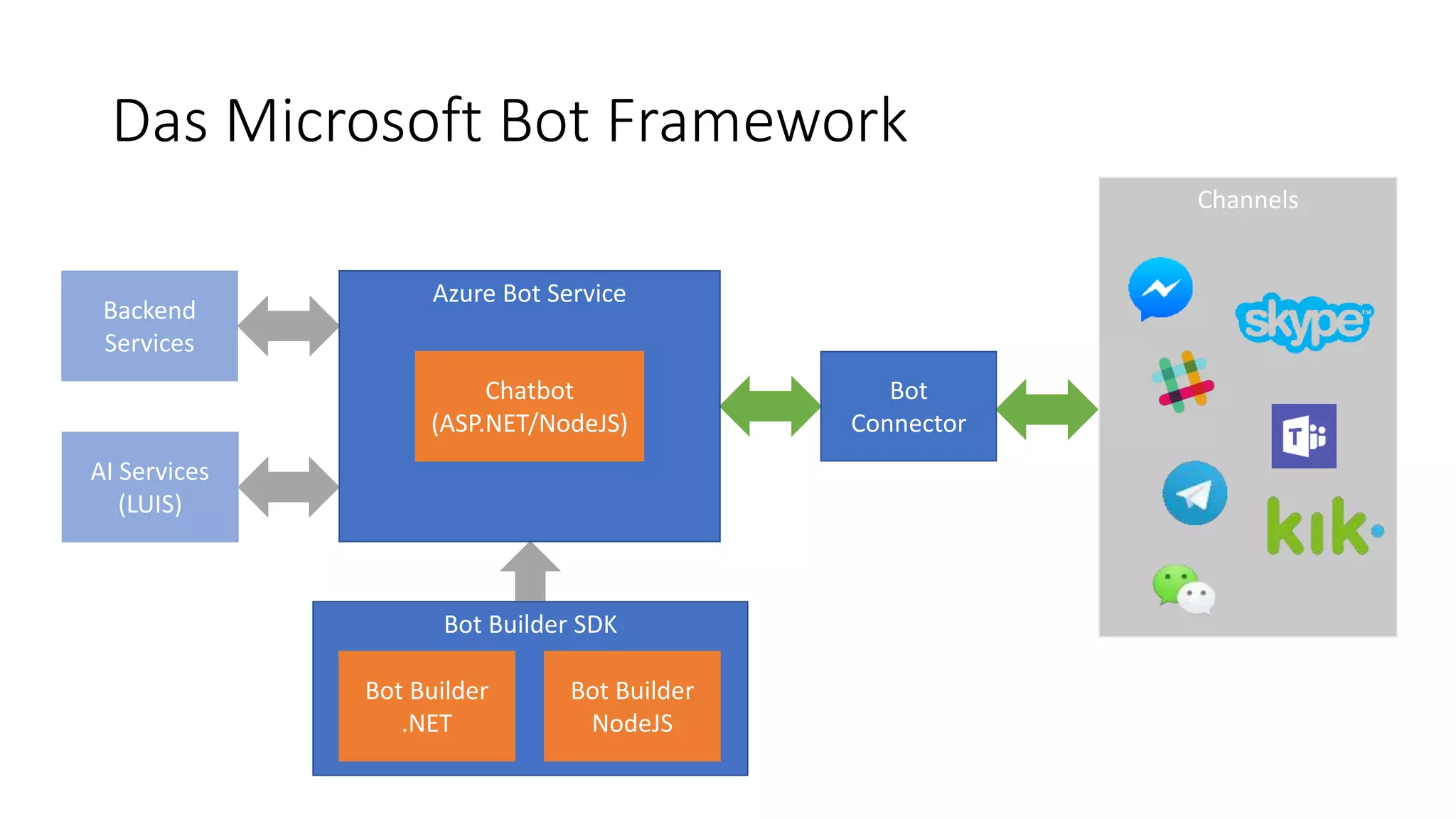
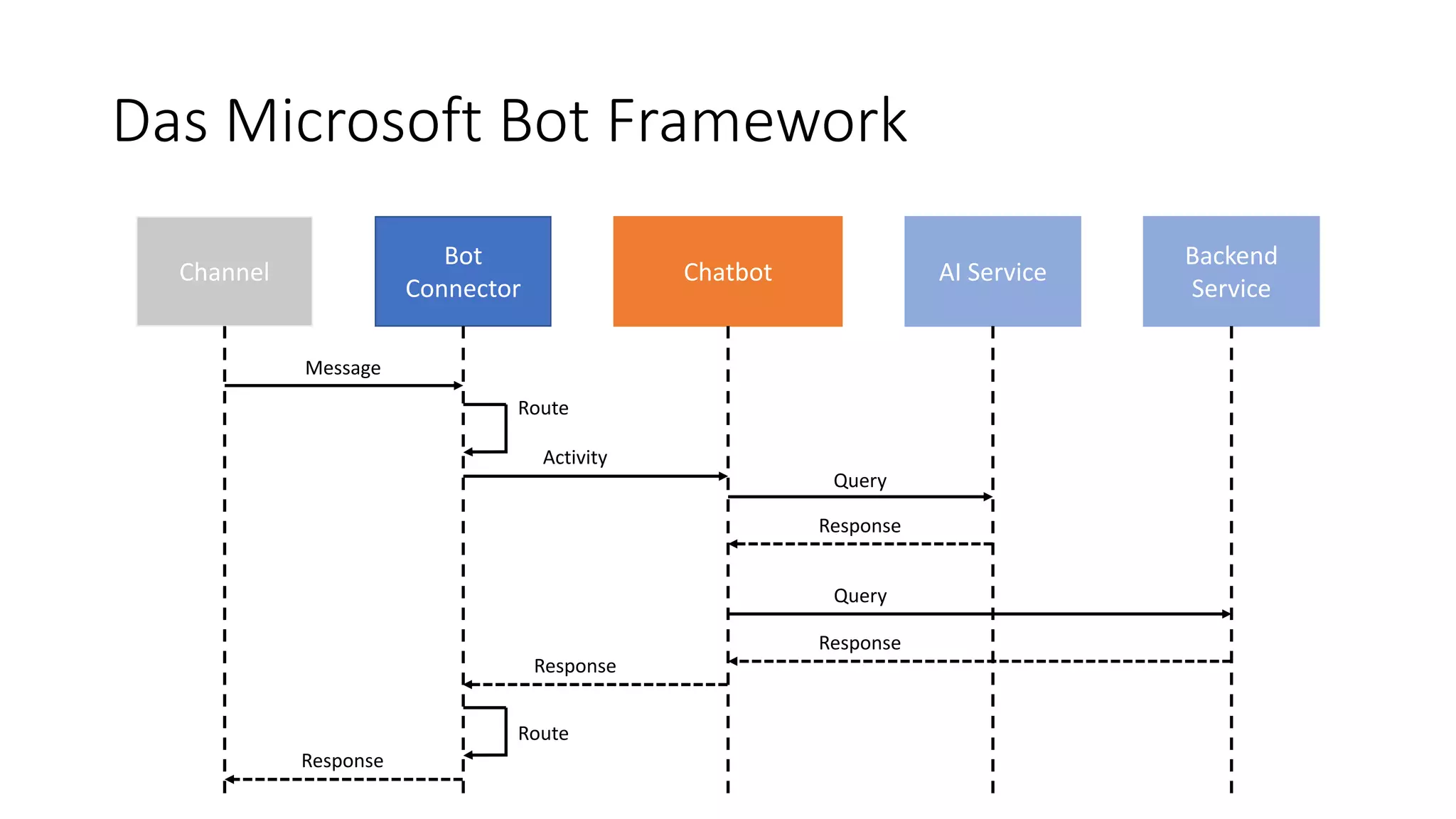
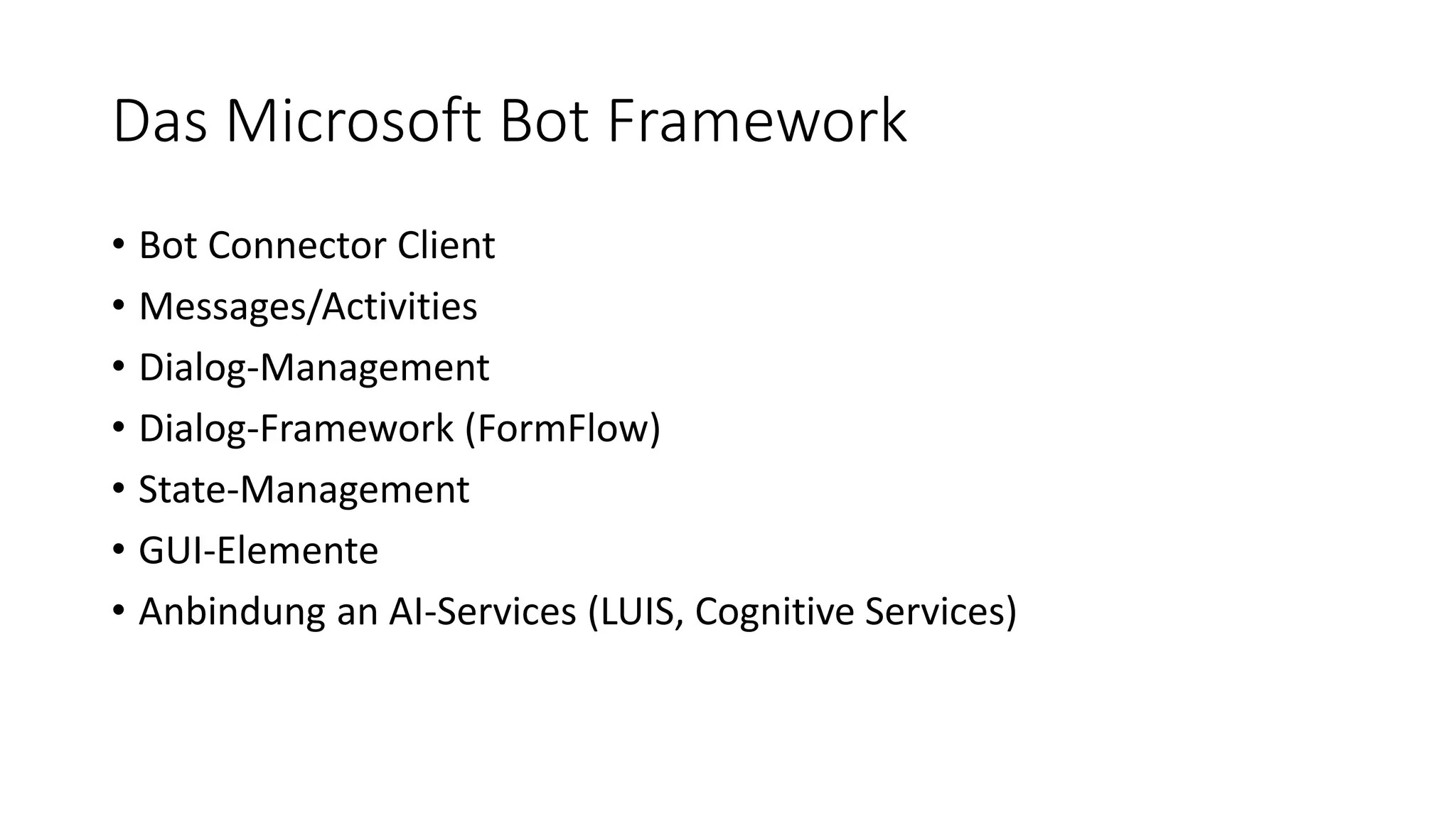
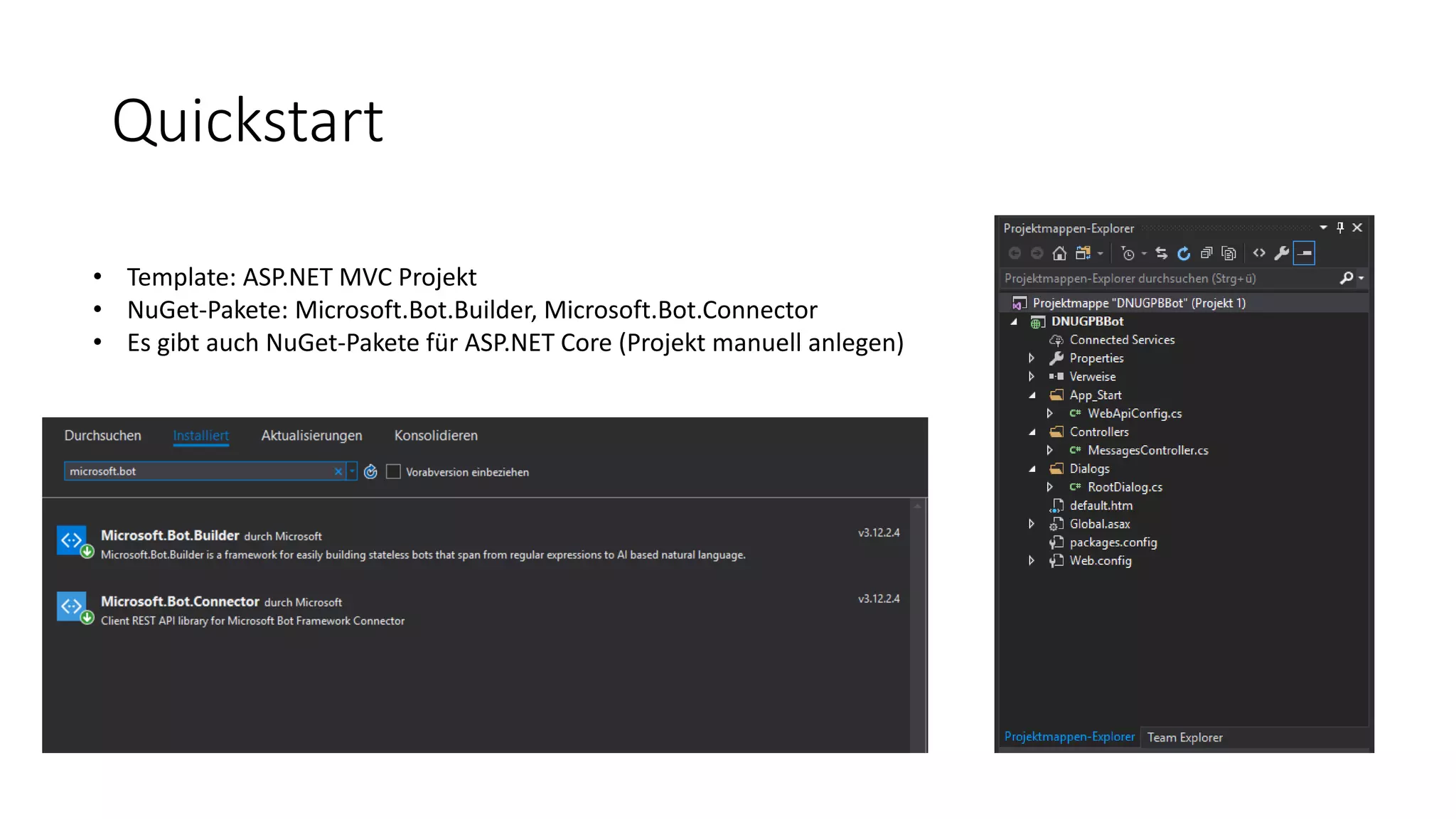
![MessagesController-Klasse public class MessagesController : ApiController { public async Task<HttpResponseMessage> Post([FromBody]Activity activity) { if (activity.Type == ActivityTypes.Message) { await Conversation.SendAsync(activity, () => new Dialogs.RootDialog()); } else { HandleSystemMessage(activity); } var response = Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK); return response; } […] } ActivityTypes.Message ActivityTypes.ConversationUpdate ActivityTypes.ContactRelationUpdate ActivityTypes.Typing ActivityTypes.Ping ActivityTypes.EndOfConversation ActivityTypes.Trigger ActivityTypes.Event ActivityTypes.Invoke ActivityTypes.DeleteUserData ActivityTypes.InstallationUpdate ActivityTypes.MessageReaction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microsoftbotframeworkdotnet-180116130141/75/Microsoft-Bot-Framework-NET-Edition-20-2048.jpg)
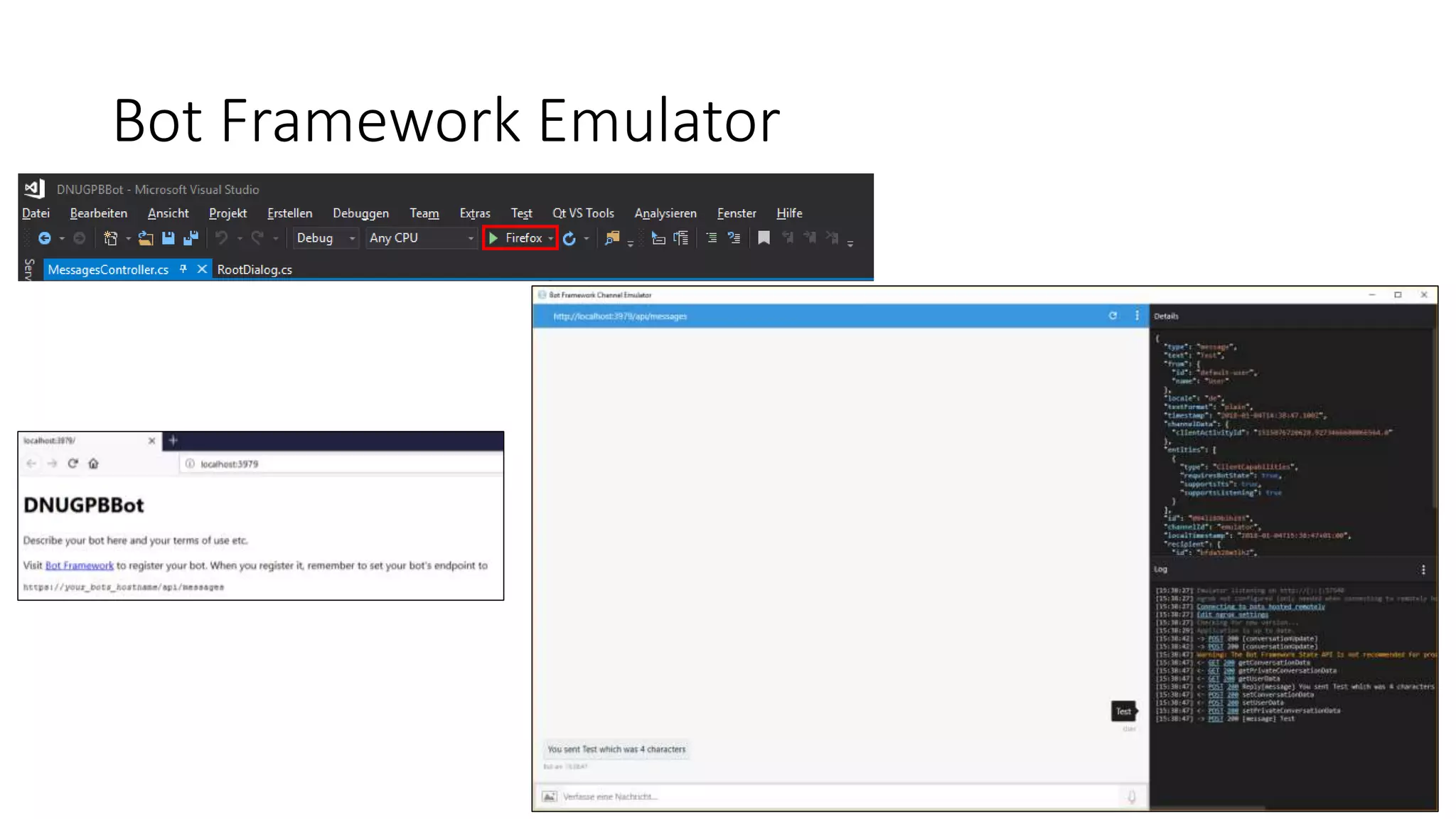
![RootDialog-Klasse [Serializable] public class RootDialog : IDialog<object> { public Task StartAsync(IDialogContext context) { context.Wait(MessageReceivedAsync); return Task.CompletedTask; } private async Task MessageReceivedAsync(IDialogContext context, IAwaitable<object> result) { var activity = await result as Activity; int length = (activity.Text ?? string.Empty).Length; await context.PostAsync($"You sent {activity.Text} which was {length} characters"); context.Wait(MessageReceivedAsync); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microsoftbotframeworkdotnet-180116130141/75/Microsoft-Bot-Framework-NET-Edition-23-2048.jpg)
![Dialog-basierte Interaktion [Serializable] public class RootDialog : IDialog<object> { public Task StartAsync(IDialogContext context) { context.Wait(MessageReceivedAsync); […] } private async Task MessageReceivedAsync(IDialogContext ctx, IAwaitable<object> result) { var activity = await result as Activity; […] IDialogContext IDialogStackIBotContext Suspended Resumed StartedStartAsync() ctx.Wait() ctx.Wait() await result as Activity ctx.Done()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microsoftbotframeworkdotnet-180116130141/75/Microsoft-Bot-Framework-NET-Edition-24-2048.jpg)
![Dialog-basierte Interaktion RootDialog SearchOptions Dialog EventSelection Dialog EventDetails Dialog EventRegistration Dialog ProfileCreation Dialog […] […] search register create](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microsoftbotframeworkdotnet-180116130141/75/Microsoft-Bot-Framework-NET-Edition-25-2048.jpg)
![Dialog-basierte Interaktion public Task StartAsync(IDialogContext context) { context.Wait(MessageReceivedAsync); […] } private Task MessageReceivedAsync(IDialogContext context, IAwaitable<object> result) { var options = new[] { "Search for Events", "Register for Event", „Create Profile" }; PromptDialog.Choice( options: options, resume: ResumeAfterChoiceAsync, […]); […] } private async Task ResumeAfterChoiceAsync(IDialogContext context, IAwaitable<string> result) { […] PromptDialog.Choice( resume: ResumeAfterSearchChoiceAsync, […]); } […] PromptDialog.Attachment PromptDialog.Choice PromptDialog.Confirm PromptDialog.Number PromptDialog.Text](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microsoftbotframeworkdotnet-180116130141/75/Microsoft-Bot-Framework-NET-Edition-26-2048.jpg)
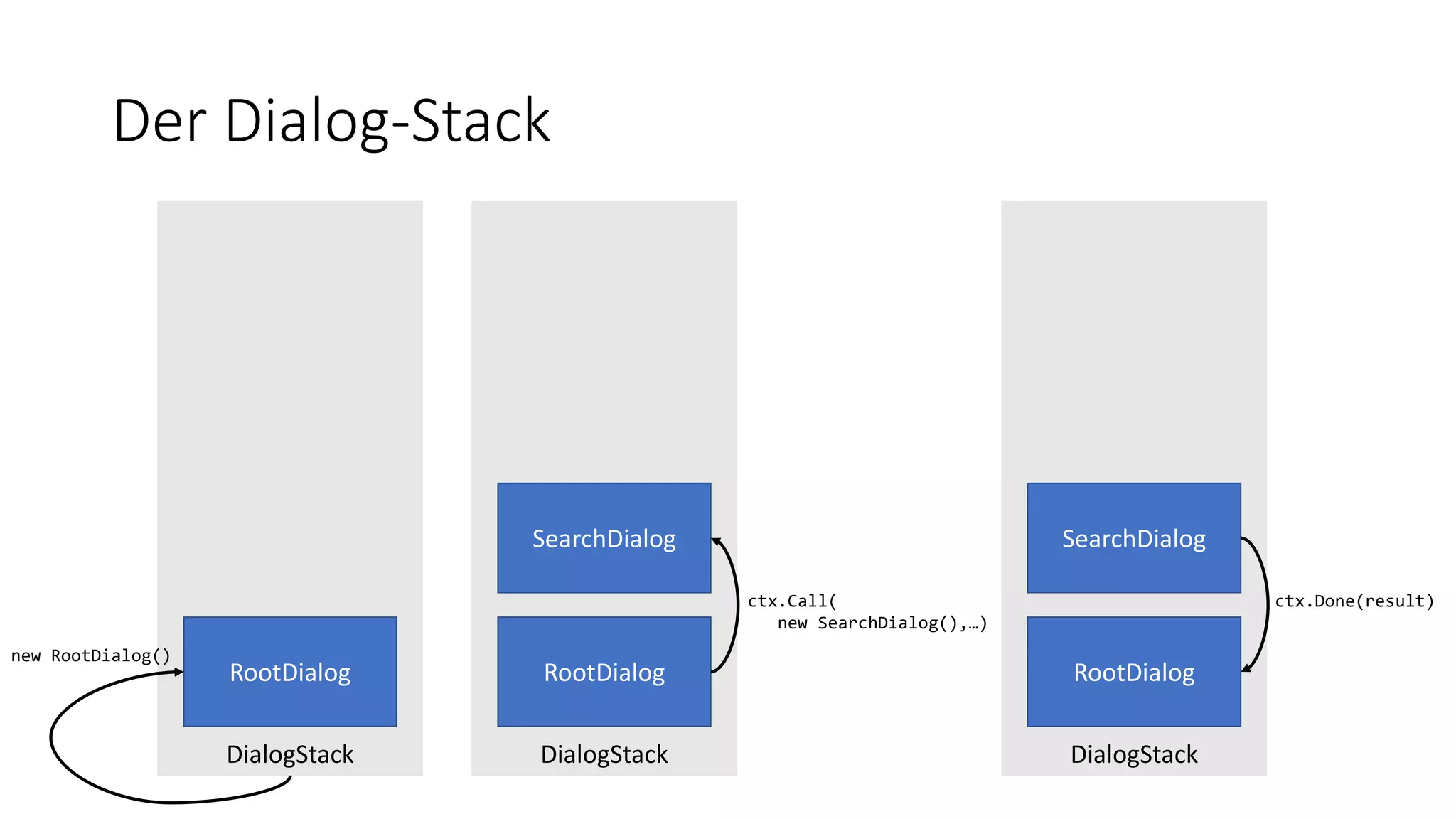
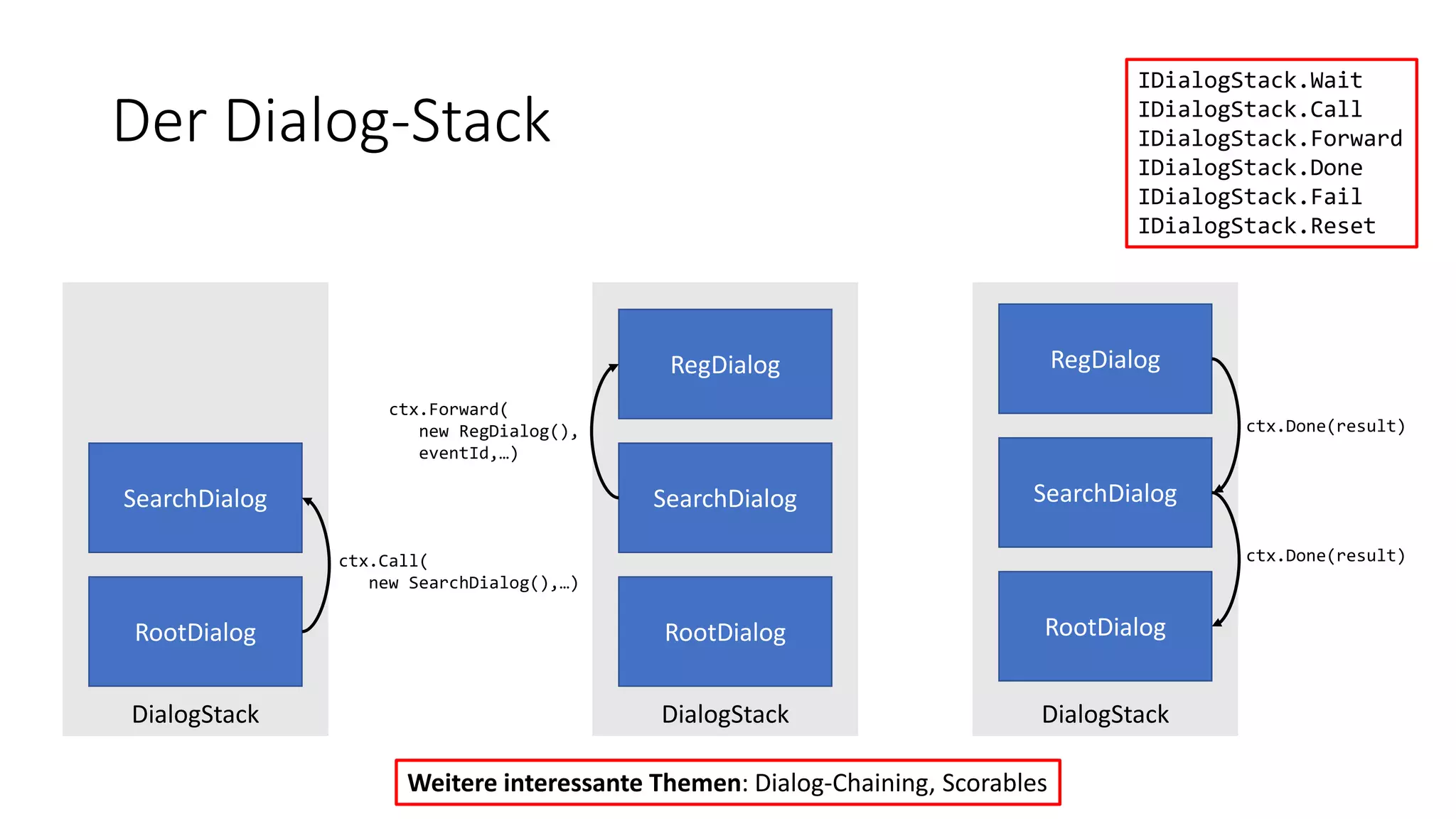
![Der Dialog-Stack public class RootDialogStack : IDialog<object> { […] private async Task ResumeAfterChoiceAsync(IDialogContext context, IAwaitable<string> result) { […] if (choice.ToLower().StartsWith("search")) { context.Call(new SearchDialog(), ResumeAfterSearchDialogAsync); } […] } private async Task ResumeAfterSearchDialogAsync(IDialogContext context, IAwaitable<int> result) { […] } […] } public class SearchDialog : IDialog<int> { […] context.Done(result); […] } IDialog<out TResult>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microsoftbotframeworkdotnet-180116130141/75/Microsoft-Bot-Framework-NET-Edition-28-2048.jpg)
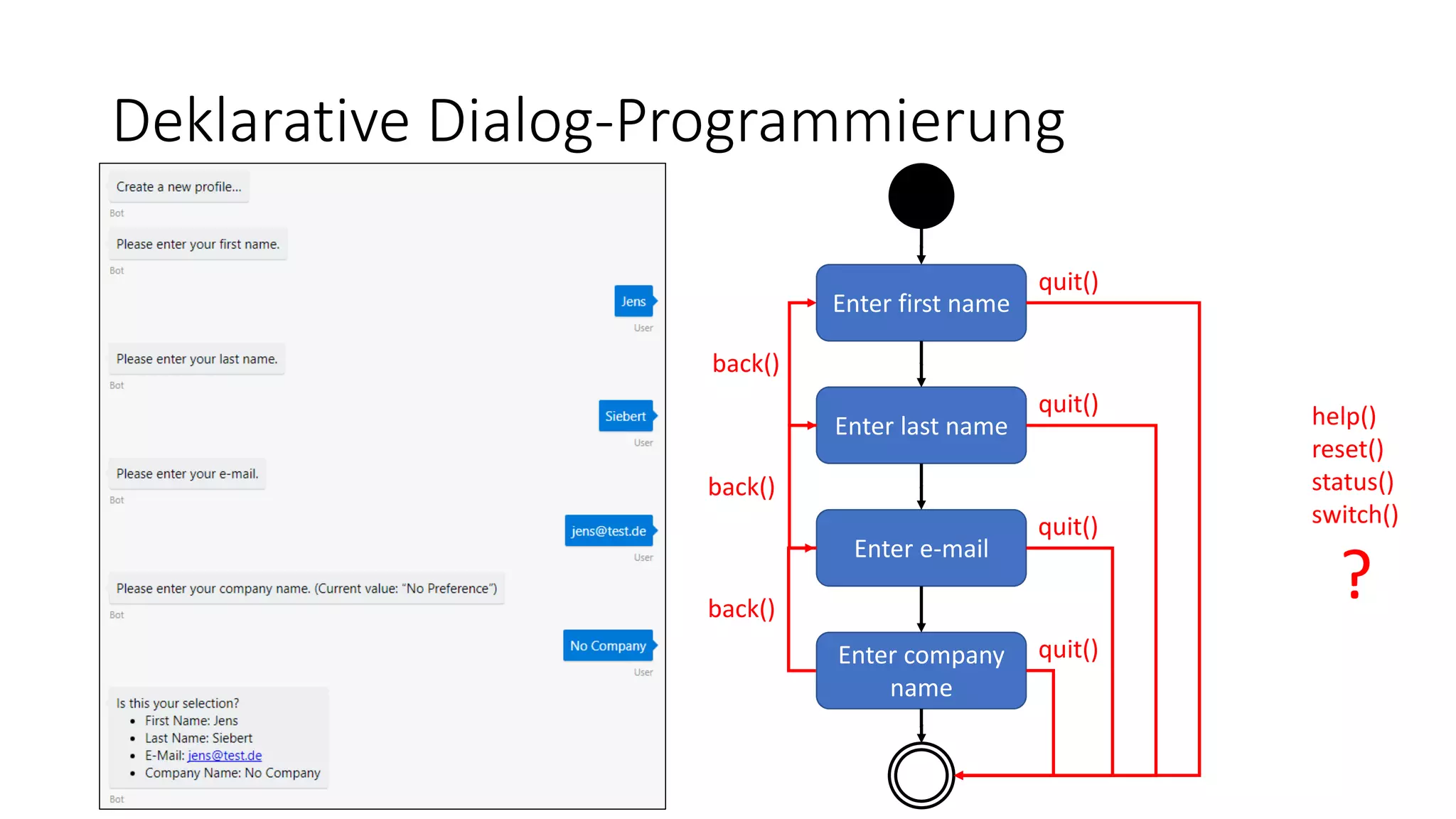
![FormFlow [Serializable] public class ProfileDialogFormFlow { [Prompt("Please enter your {&}.")] public string FirstName { get; set; } [Prompt("Please enter your {&}.")] public string LastName { get; set; } [Describe("E-Mail")] [Prompt("Please enter your {&}.")] [Pattern(@".+@.+..+")] public string EMail { get; set; } [Describe("Company Name")] [Prompt("Please enter your {&}. (Current value: "{}")")] [Optional] public string Company { get; set; } public IForm<ProfileDialogFormFlow> BuildForm() { return new FormBuilder<ProfileDialogFormFlow>() .Message("Create a new profile...") .OnCompletion(ResumeAfterProfileCreationAsync) .Build(); } […] } reflection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microsoftbotframeworkdotnet-180116130141/75/Microsoft-Bot-Framework-NET-Edition-31-2048.jpg)
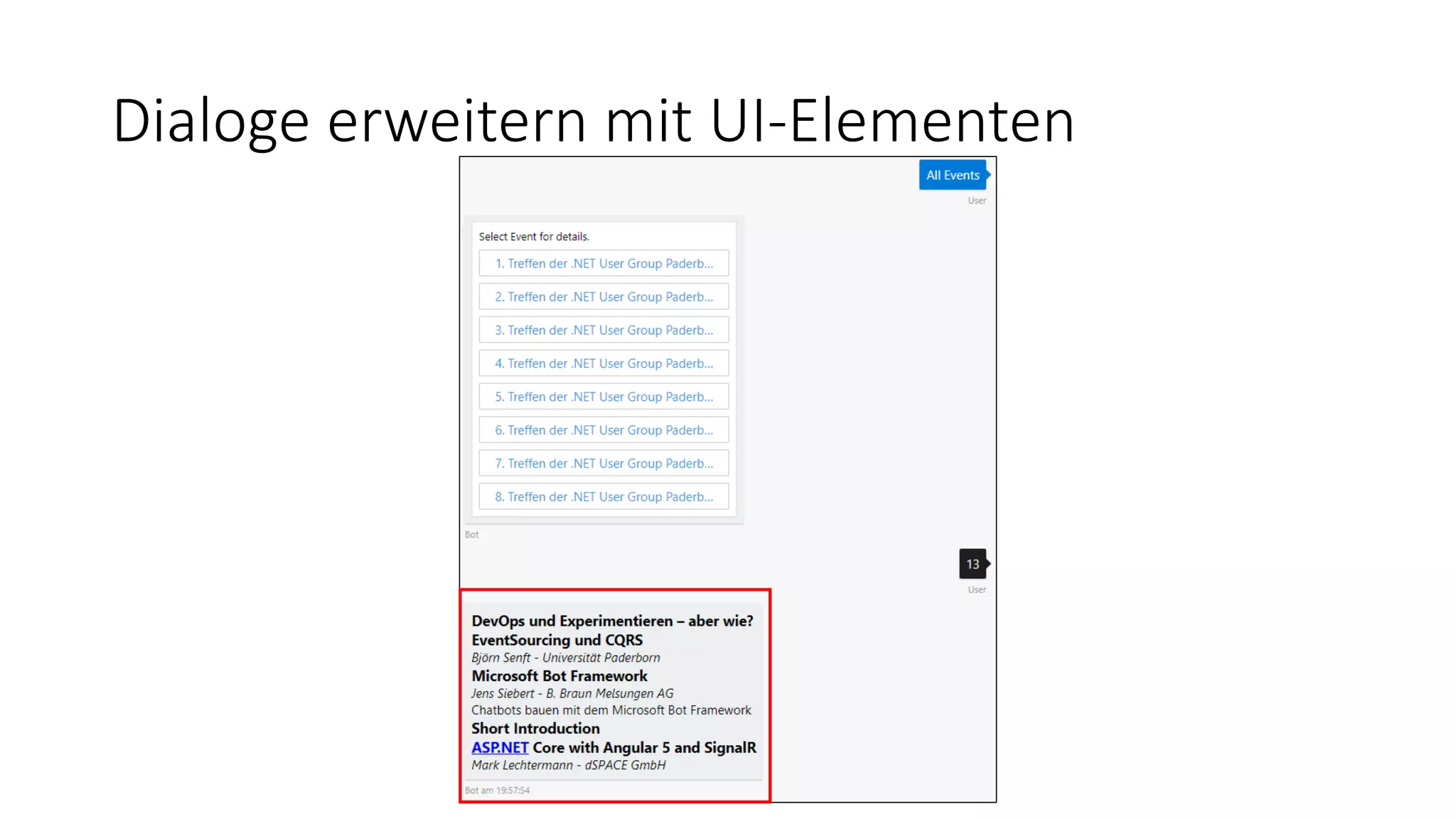
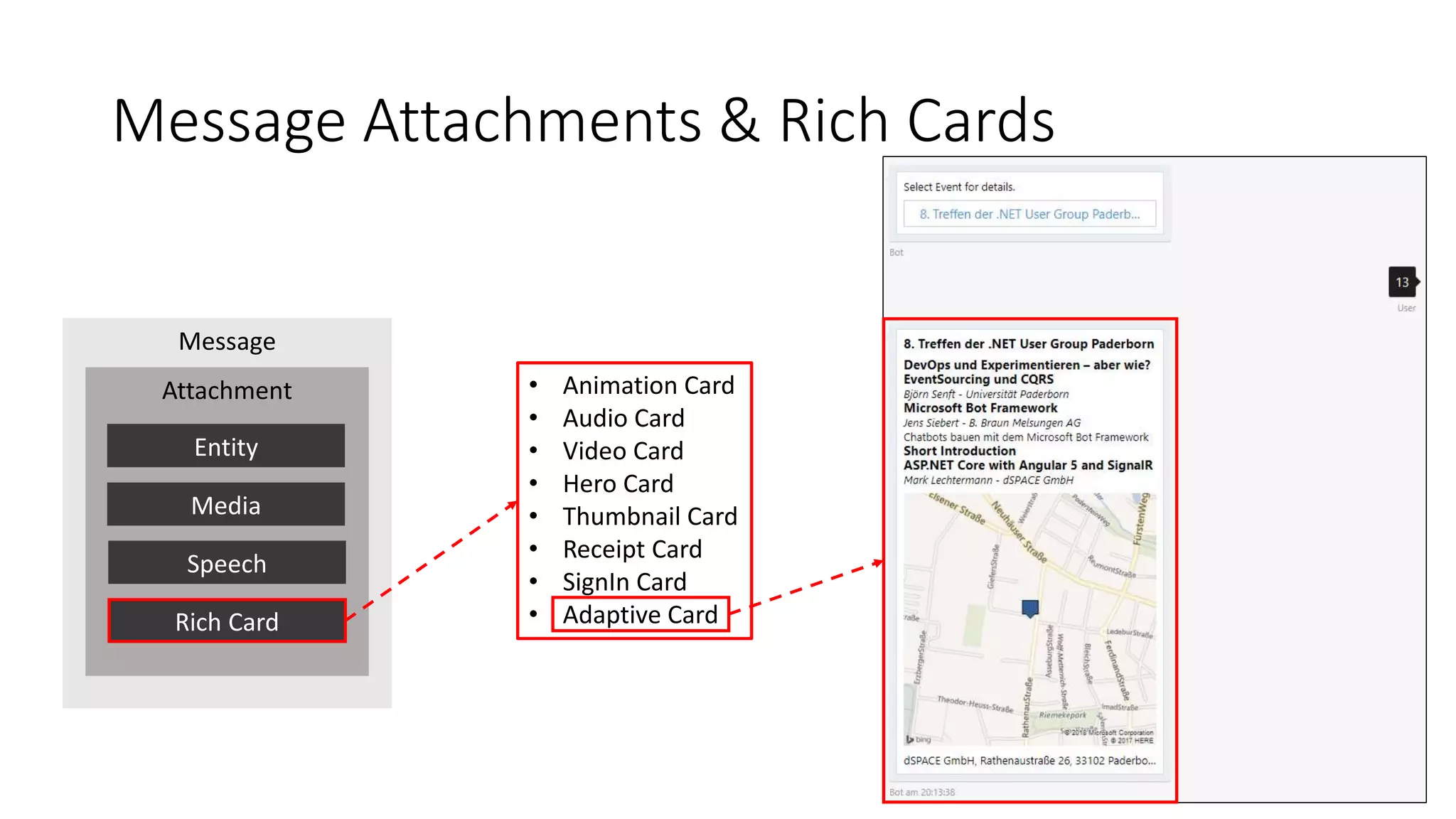
![Adaptive Cards var adaptiveCard = new AdaptiveCard(); adaptiveCard.Body.Add(new TextBlock() { Text = $"### {eventDetails.Name}", }); adaptiveCard.Body.Add(new TextBlock() { Text = converter.Convert(eventDetails.ShortDescription) }); adaptiveCard.Body.Add(new Image() { Url = $"https://dev.virtualearth.net/REST/v1/Imagery/Map/CanvasLight/{latitude},{longitude}/15? [...], Size = ImageSize.Stretch }); adaptiveCard.Body.Add(new TextBlock() { Text = $"{eventLocation.Name}, {eventLocation.Street}, {eventLocation.PLZ} {eventLocation.City}" }); var attachment = new Attachment() { ContentType = AdaptiveCard.ContentType, Content = adaptiveCard }; message.Attachments.Add(attachment);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microsoftbotframeworkdotnet-180116130141/75/Microsoft-Bot-Framework-NET-Edition-34-2048.jpg)
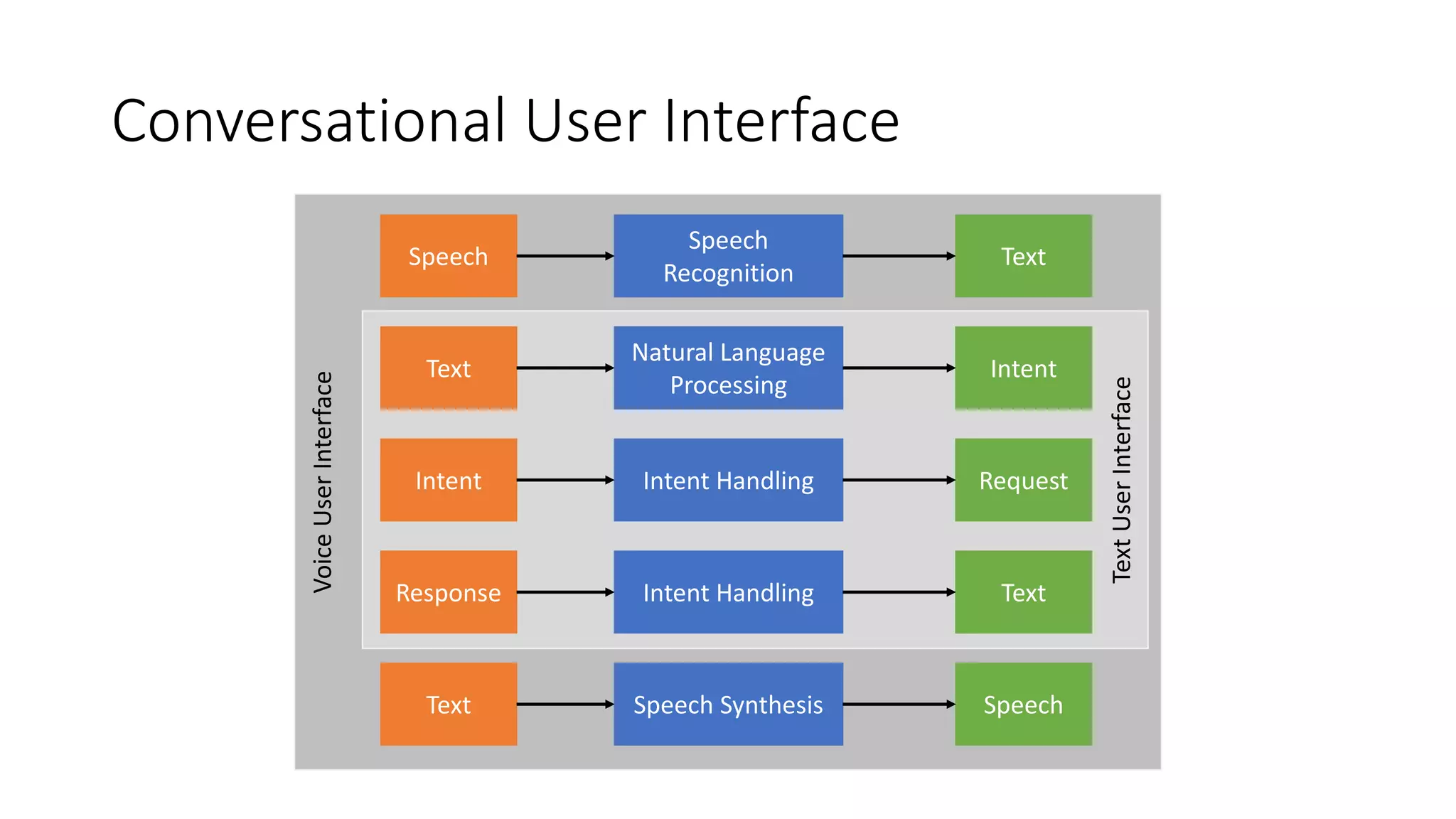
![Natural Language Processing (NLP) private Task StartAsync(IDialogContext context) { var options = new[] { „All Events", „Upcoming Events", „Past Events" }; PromptDialog.Choice( options: options, resume: ResumeAfterSearchChoiceAsync, […]); […] } private async Task ResumeAfterSearchChoiceAsync(IDialogContext context, IAwaitable<string> result) { string selection = await result; if (selection.ToLower().StartsWith(“upcoming")) { […] } else if (selection.ToLower().StartsWith(“past")) { […] } } […] - „Kommando-artig“ - Keine natürliche Sprache](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microsoftbotframeworkdotnet-180116130141/75/Microsoft-Bot-Framework-NET-Edition-35-2048.jpg)
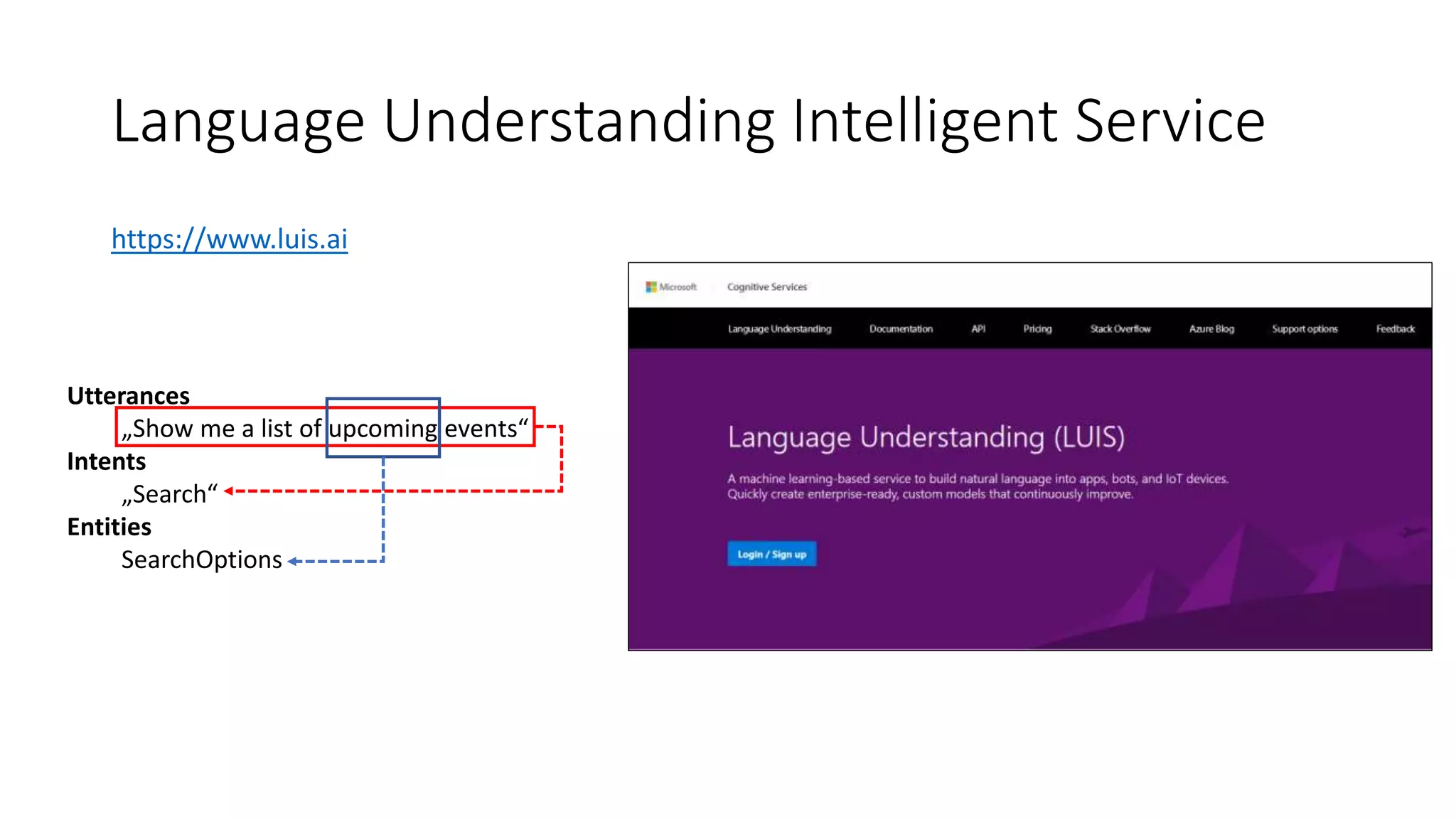
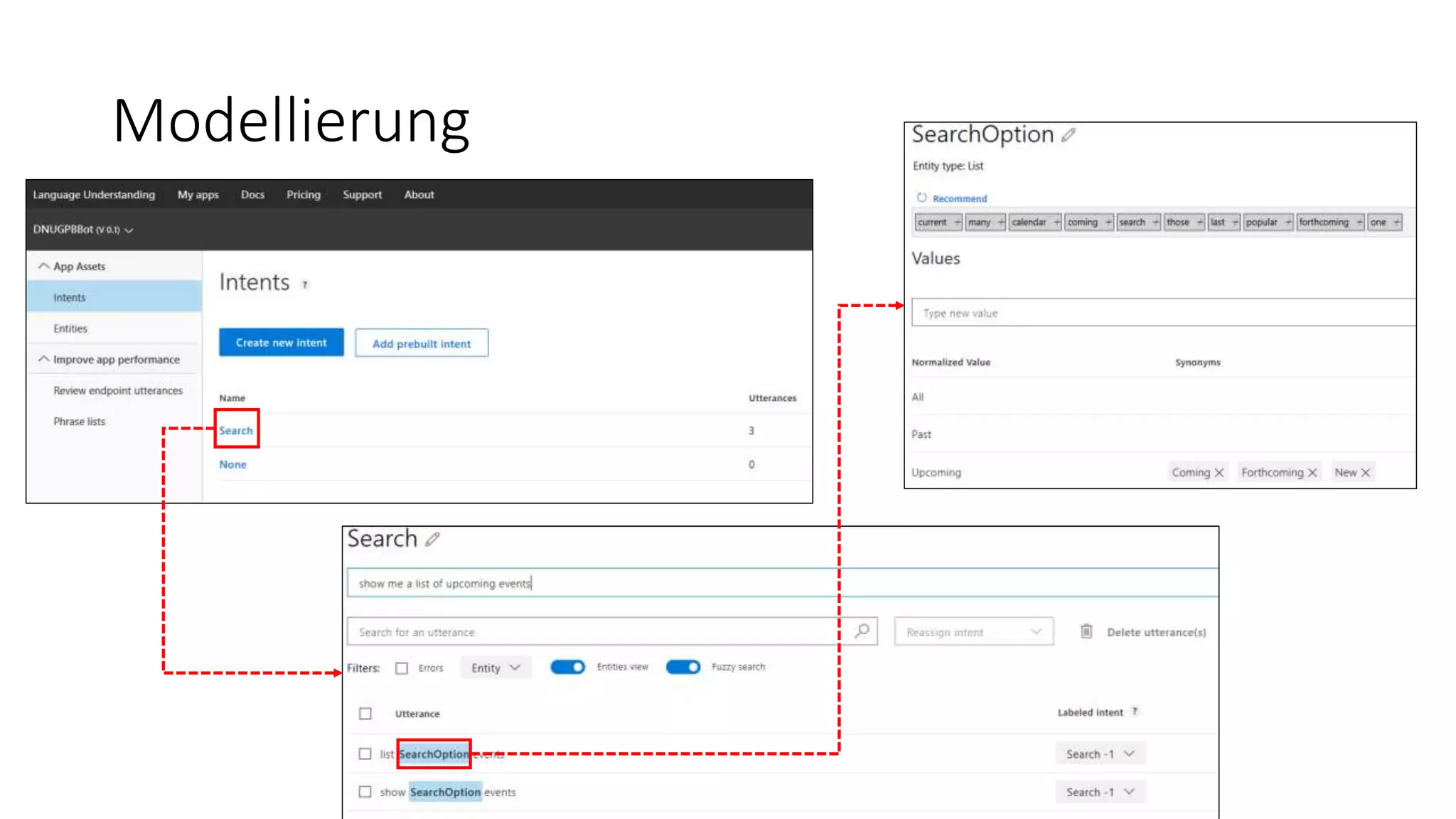
![LUIS Modell im Code einbinden [LuisModel(modelID: "a3caa935-baf8-4e5f-8c3d-…", subscriptionKey: "90f221afa6b4413995e99868a…")] [Serializable] public class SearchDialogLUIS : LuisDialog<int> { [LuisIntent("")] public async Task NoneIntent(IDialogContext context, LuisResult result) { var message = @"Sorry, I didn't get that. […]"; await context.PostAsync(message); context.Wait(MessageReceived); } [LuisIntent("Search")] public async Task SearchIntent(IDialogContext context, IAwaitable<IMessageActivity> activity, LuisResult result) { if (!result.Entities.Any()) { await NoneIntent(context, result); } var entity = result.Entities.First().Entity; […] if (entity.Equals("upcoming")) { […] } […] } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microsoftbotframeworkdotnet-180116130141/75/Microsoft-Bot-Framework-NET-Edition-39-2048.jpg)