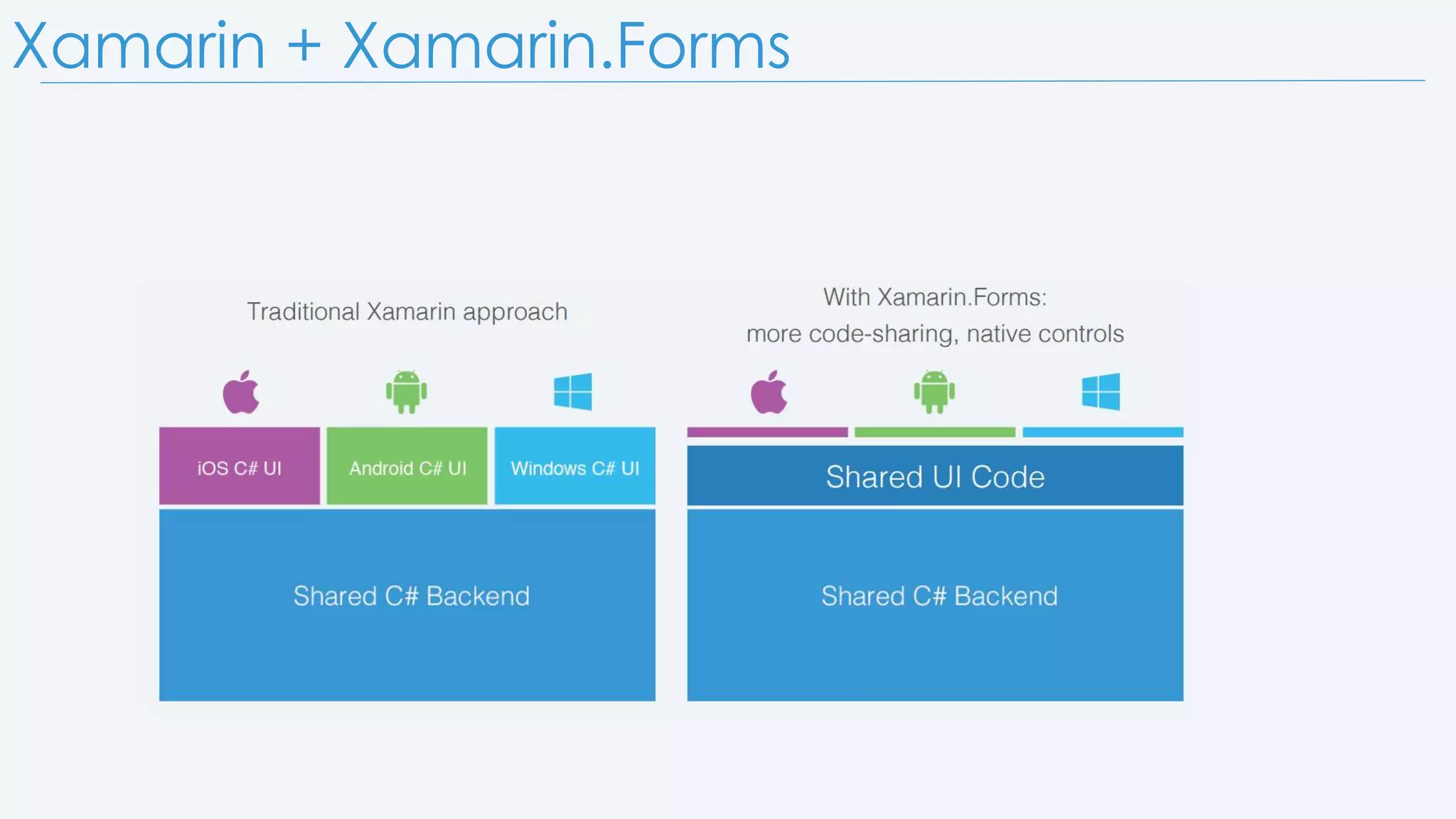
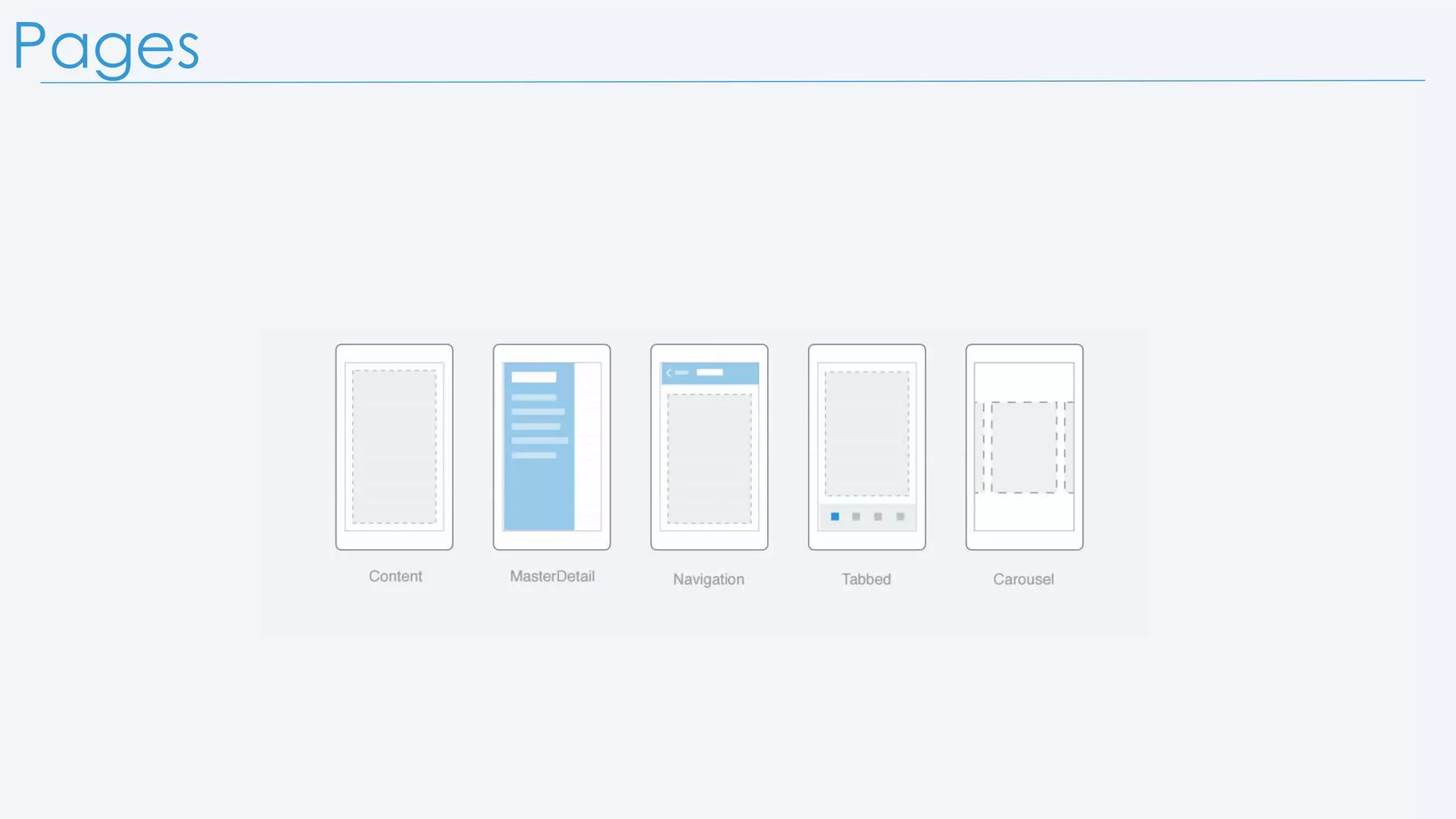
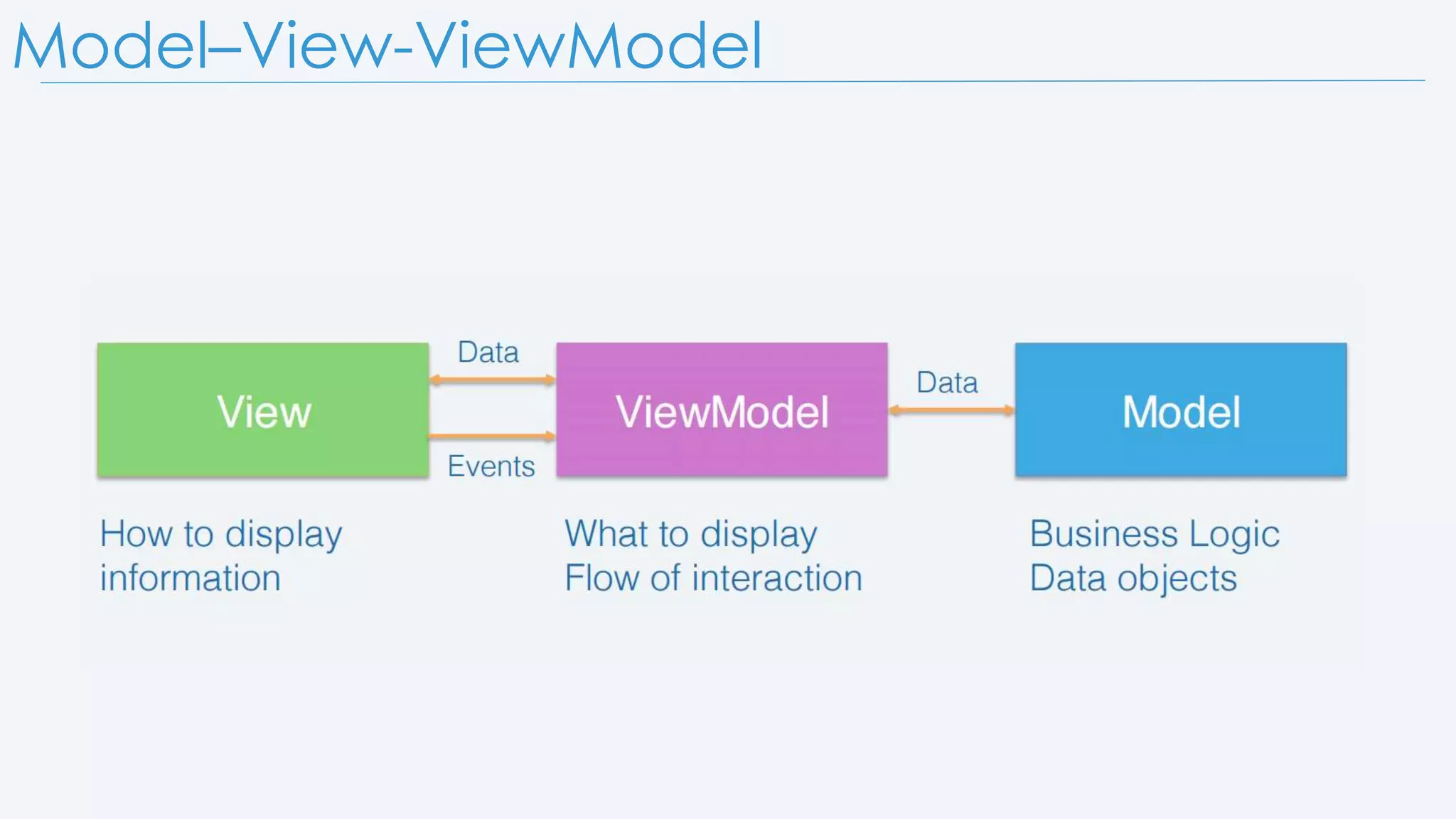
The presentation provides an overview of Xamarin and Xamarin.Forms, including its history and a simple demo application. It covers the Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) pattern and explains the implementation of the DependencyService with its components: interface, registration, and location. The speaker, Dimitar Ivanov, also shares personal links to connect and learn more.



![How the DependencyService Works ? There are three parts to a DependencyService implementation: Interface - An Interface in the shared code that defines the functionality that requires platform-specific code. Registration - An implementation of the Interface in each platform- specific application project, along with an assembly attribute that 'registers' the class so that the DependencyService can create instances of it. [assembly:Dependency(typeof(‘className’))] Location - calling DependencyService.Get<>() in shared code to get a platform-specific instance of the Interface at run time, thereby allowing the shared code to access the underlying platform.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xamarinforms-150323075621-conversion-gate01/75/Your-first-application-with-Xamarin-Forms-8-2048.jpg)