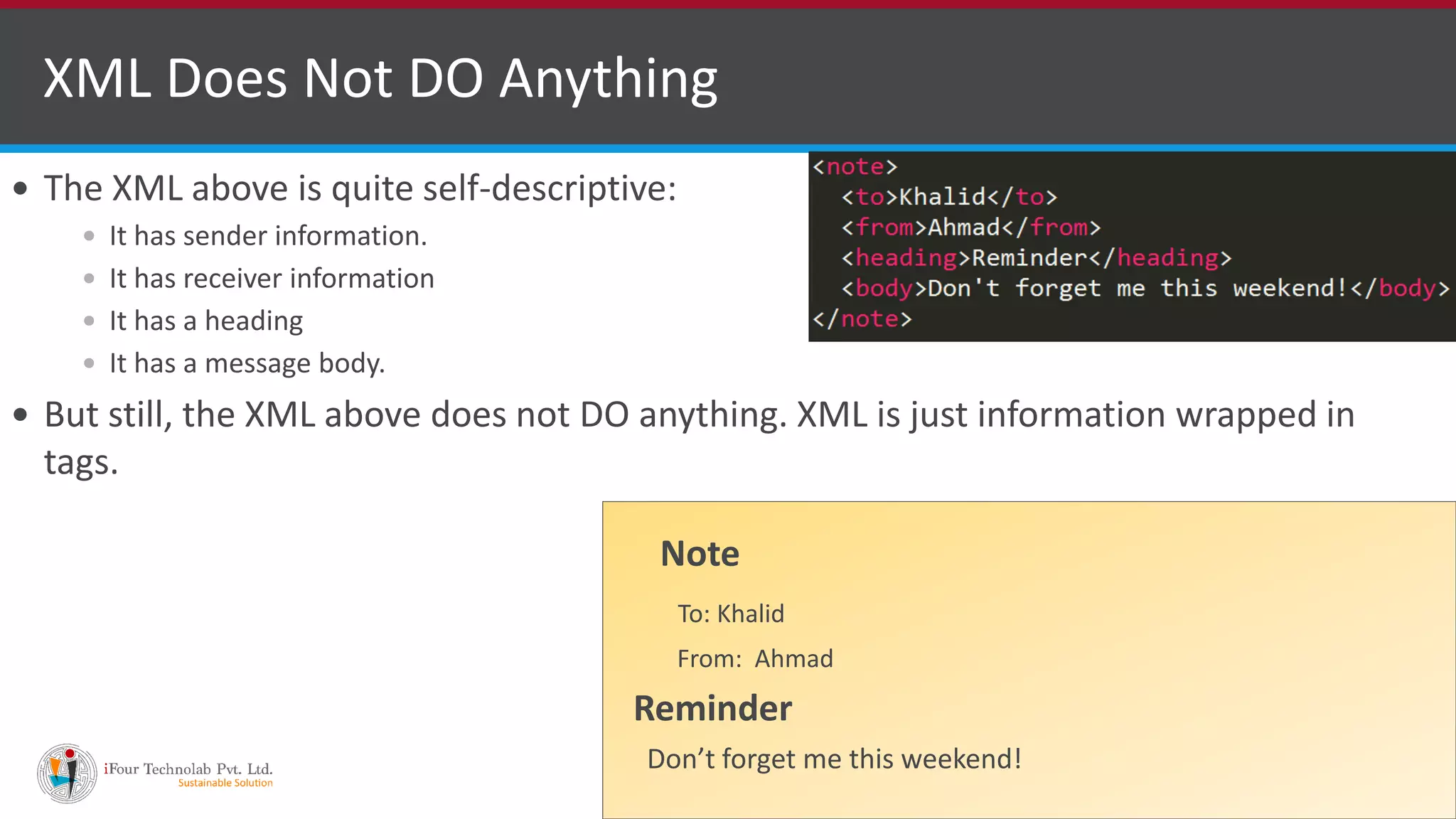
The document provides an introduction to XML, outlining what it is, its main differences from HTML, and its key features and benefits. XML stands for Extensible Markup Language and was designed to describe data, allowing users to define their own tags. It simplifies data sharing and transport between systems by providing a software- and hardware-independent format for storing and exchanging information. XML has elements with opening and closing tags that follow a strict hierarchical structure and its tags are case sensitive.