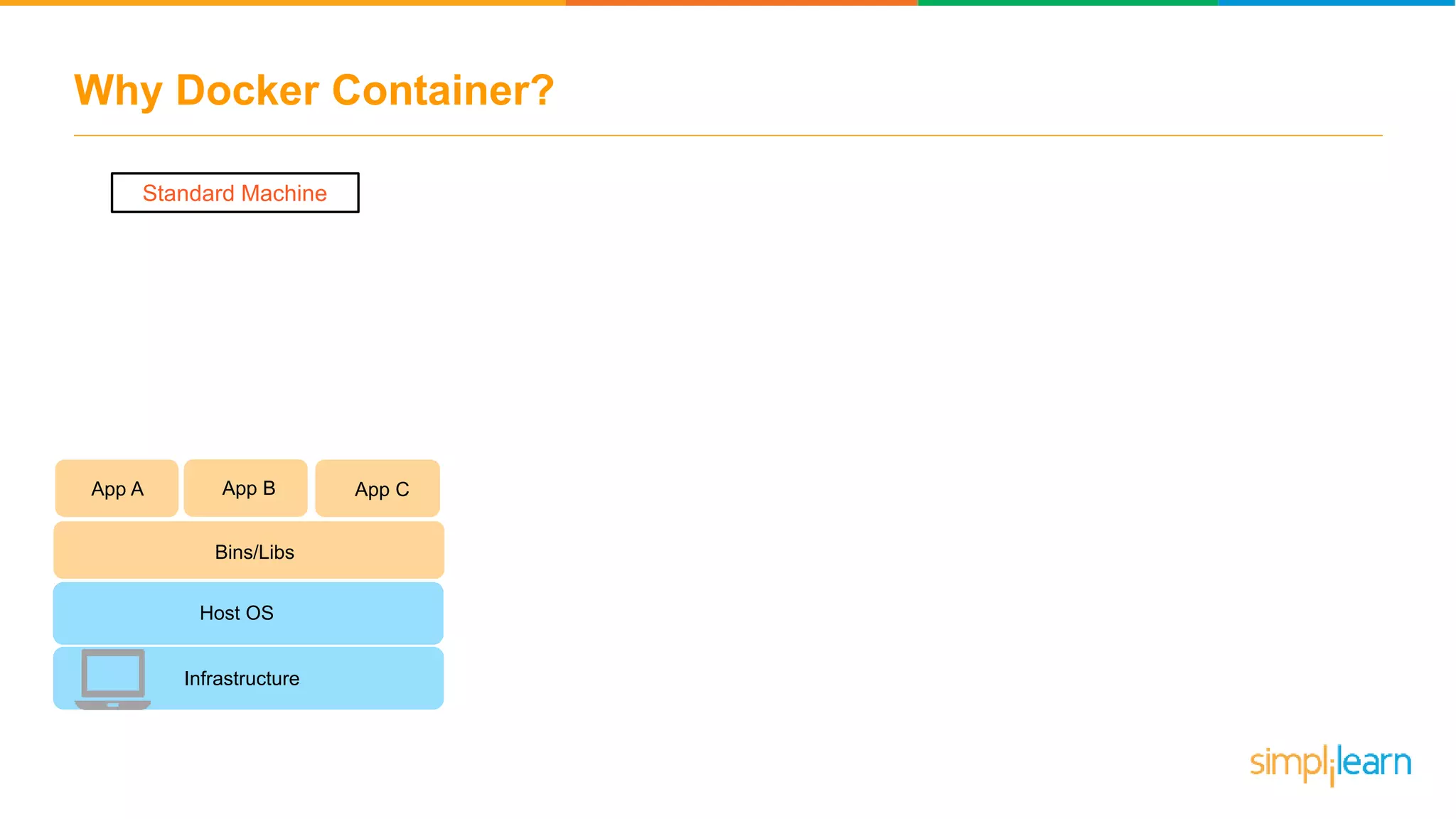
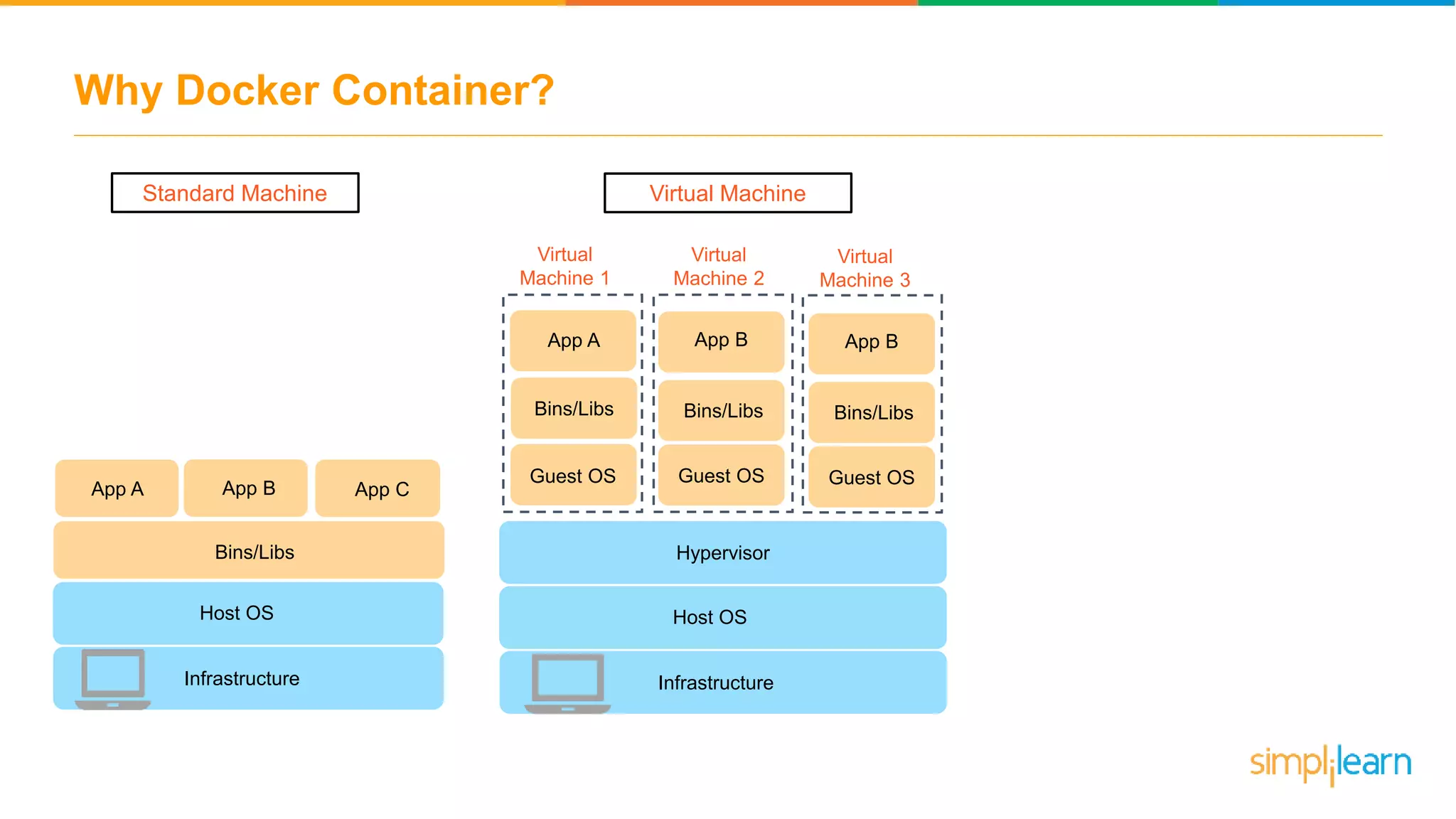
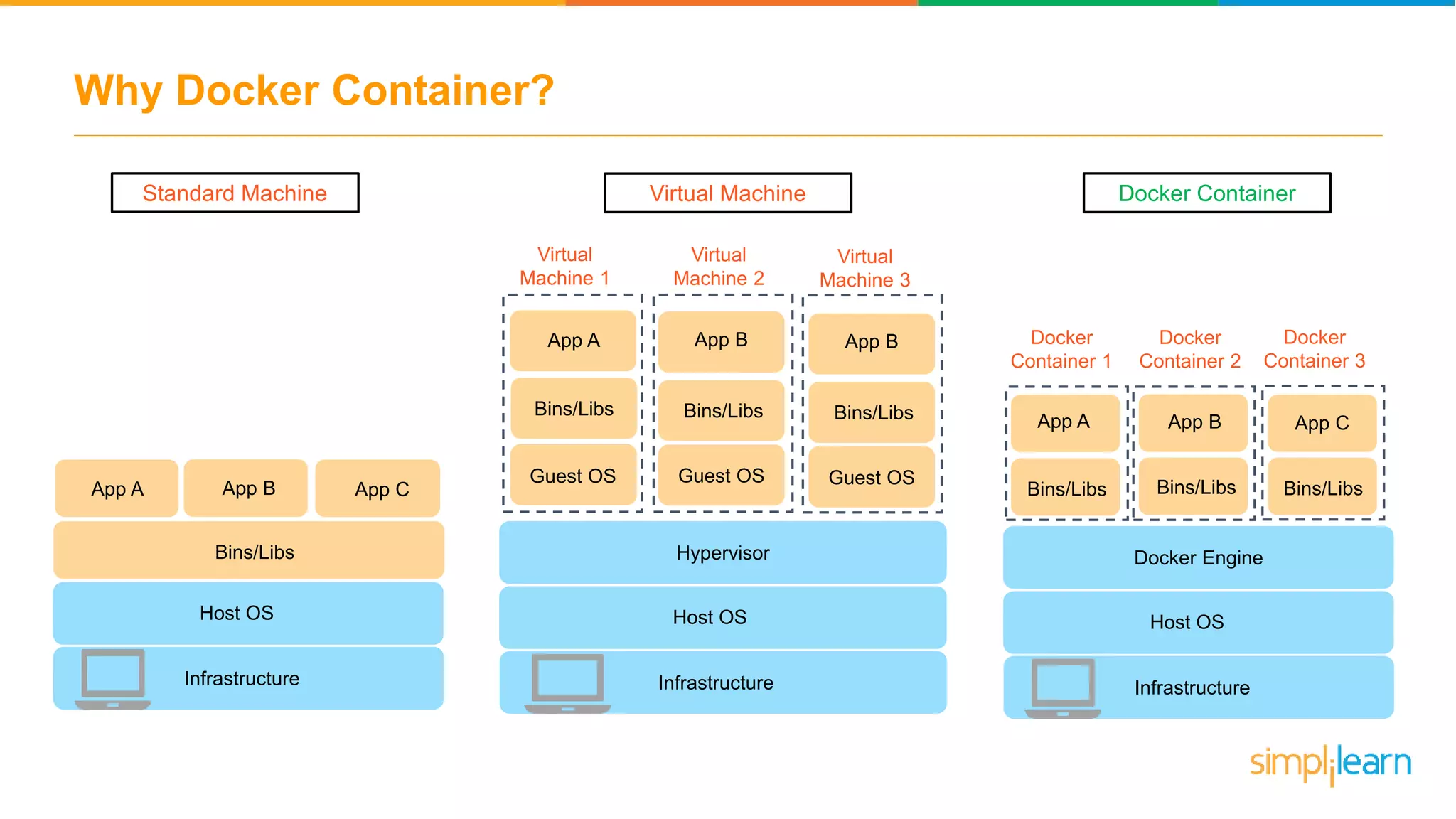
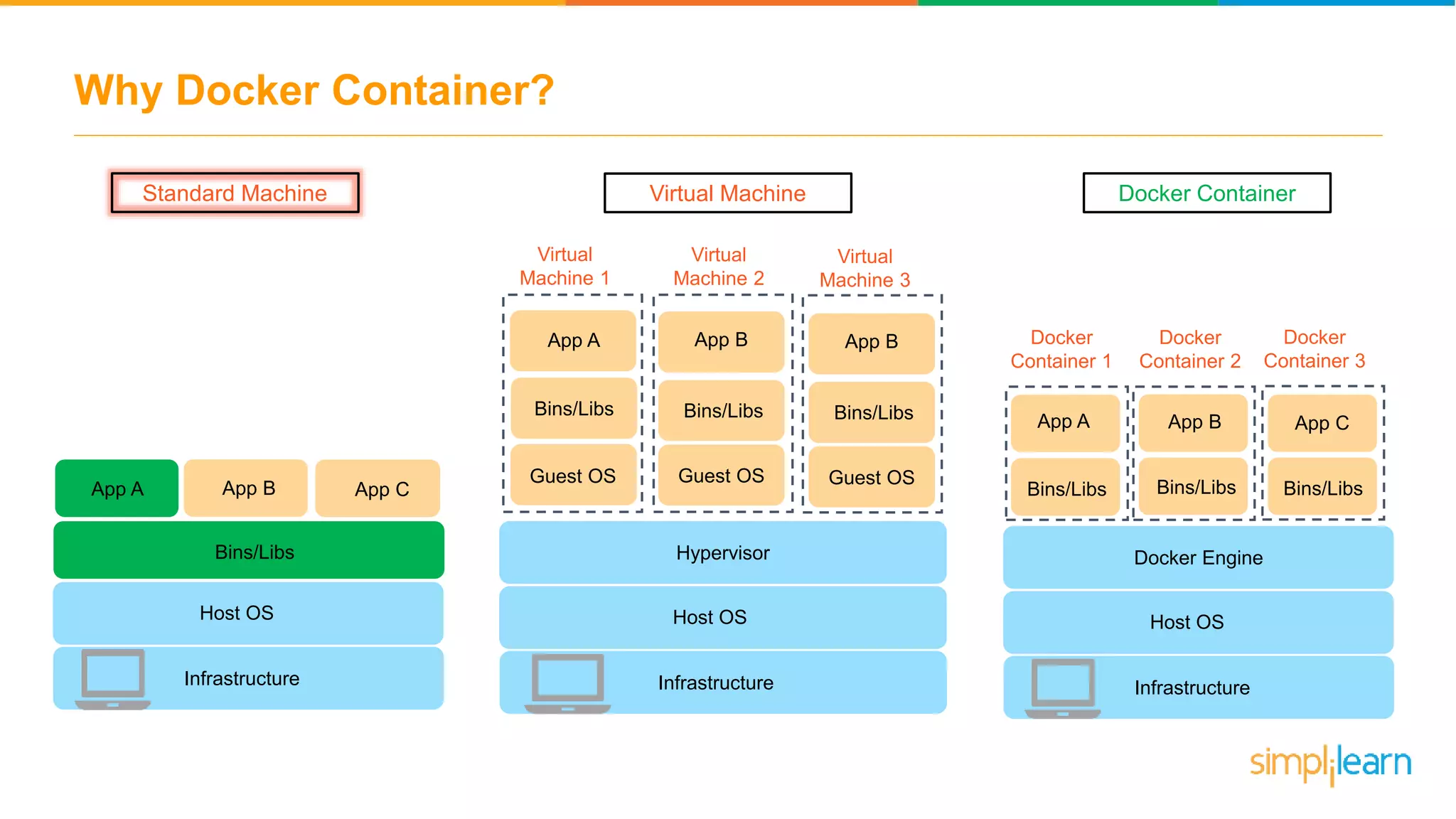
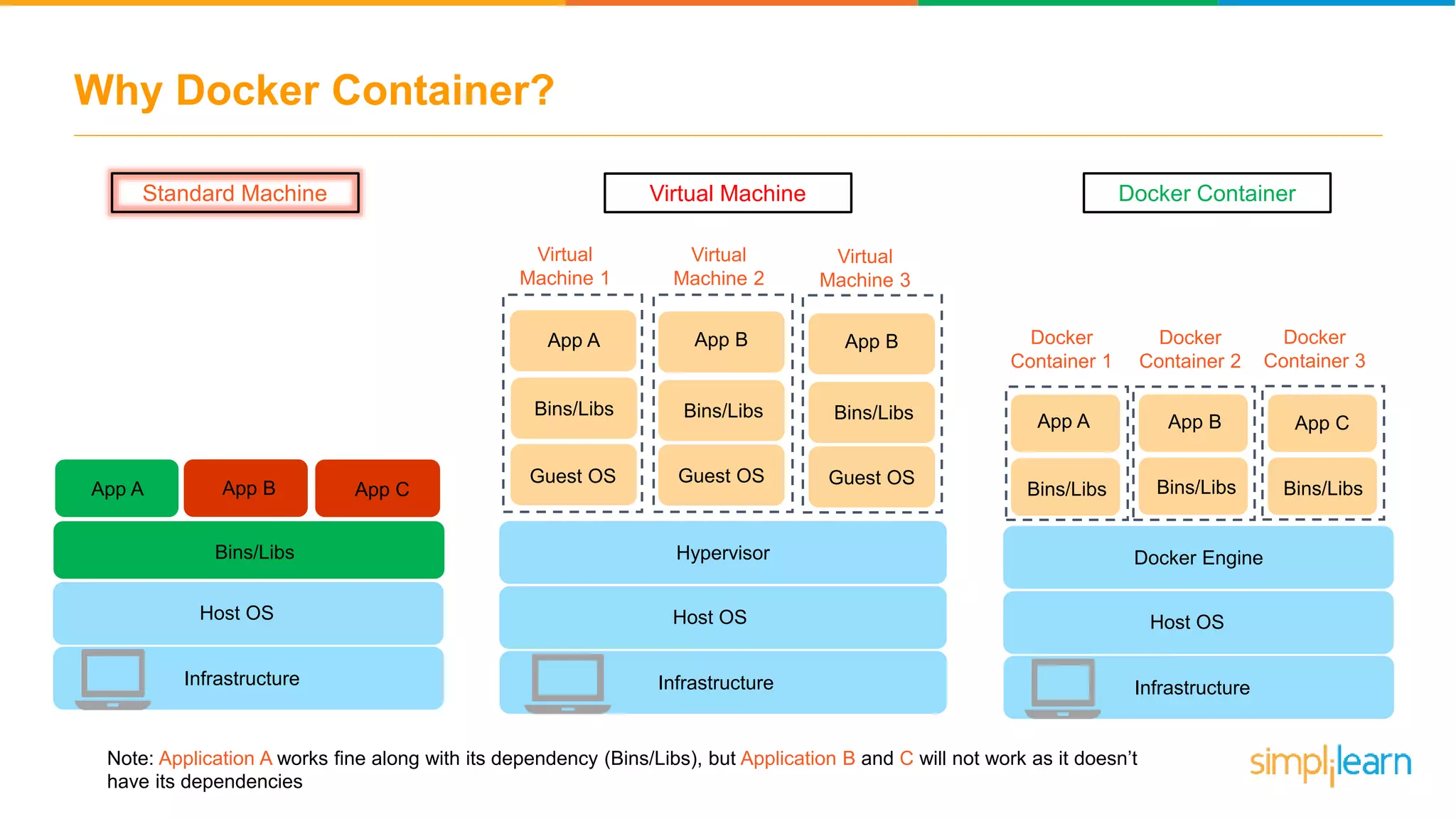
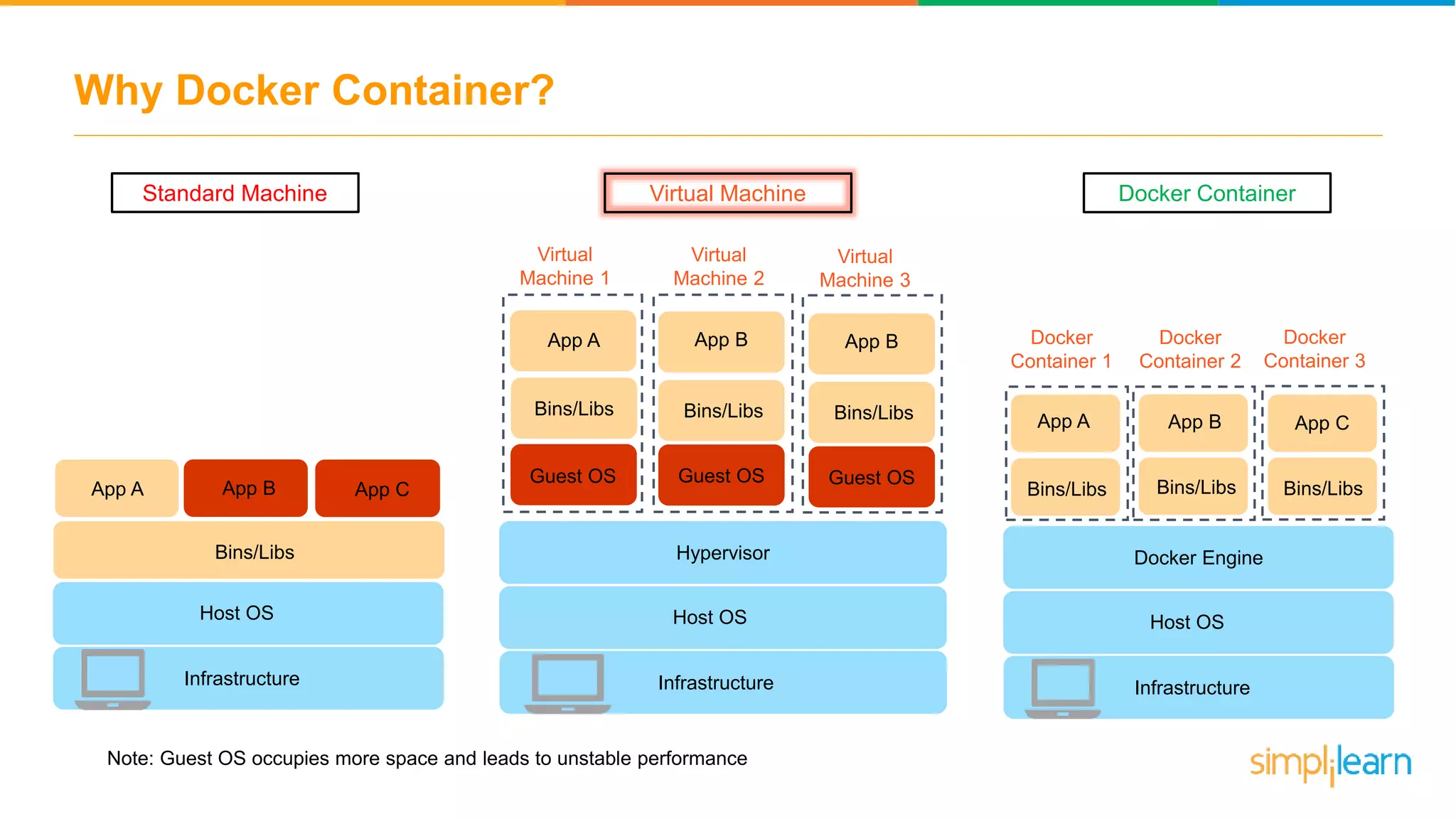
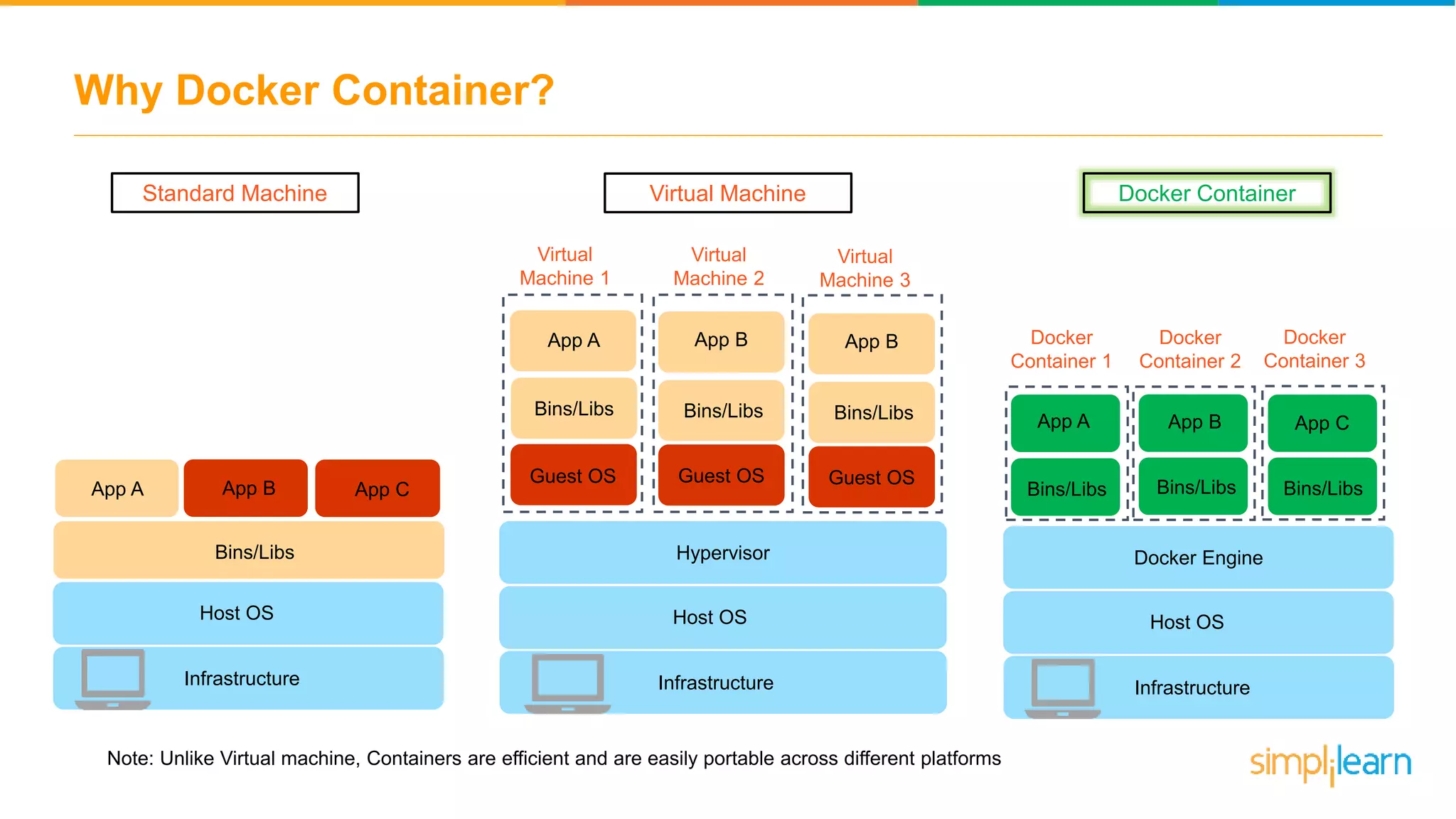
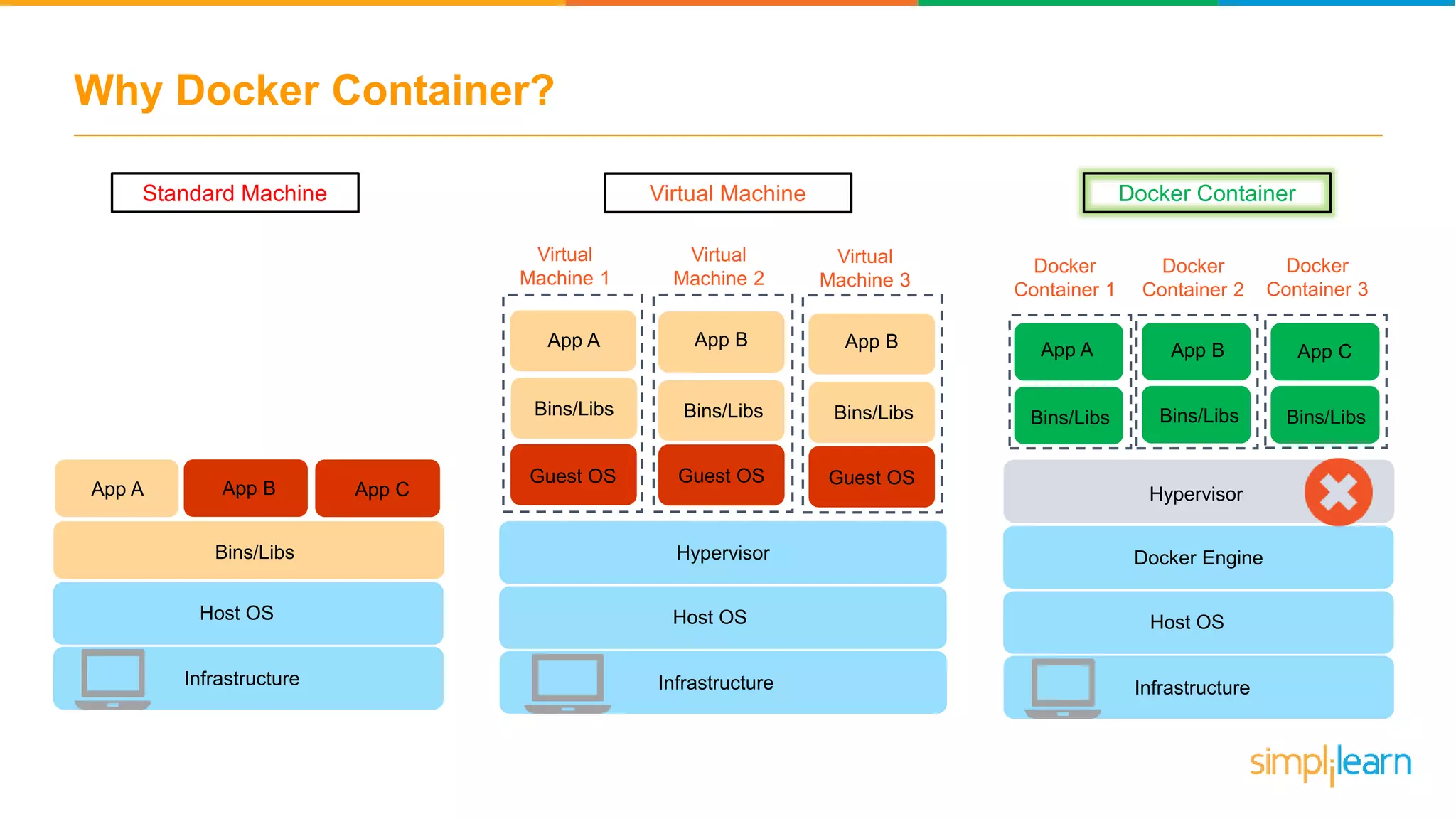
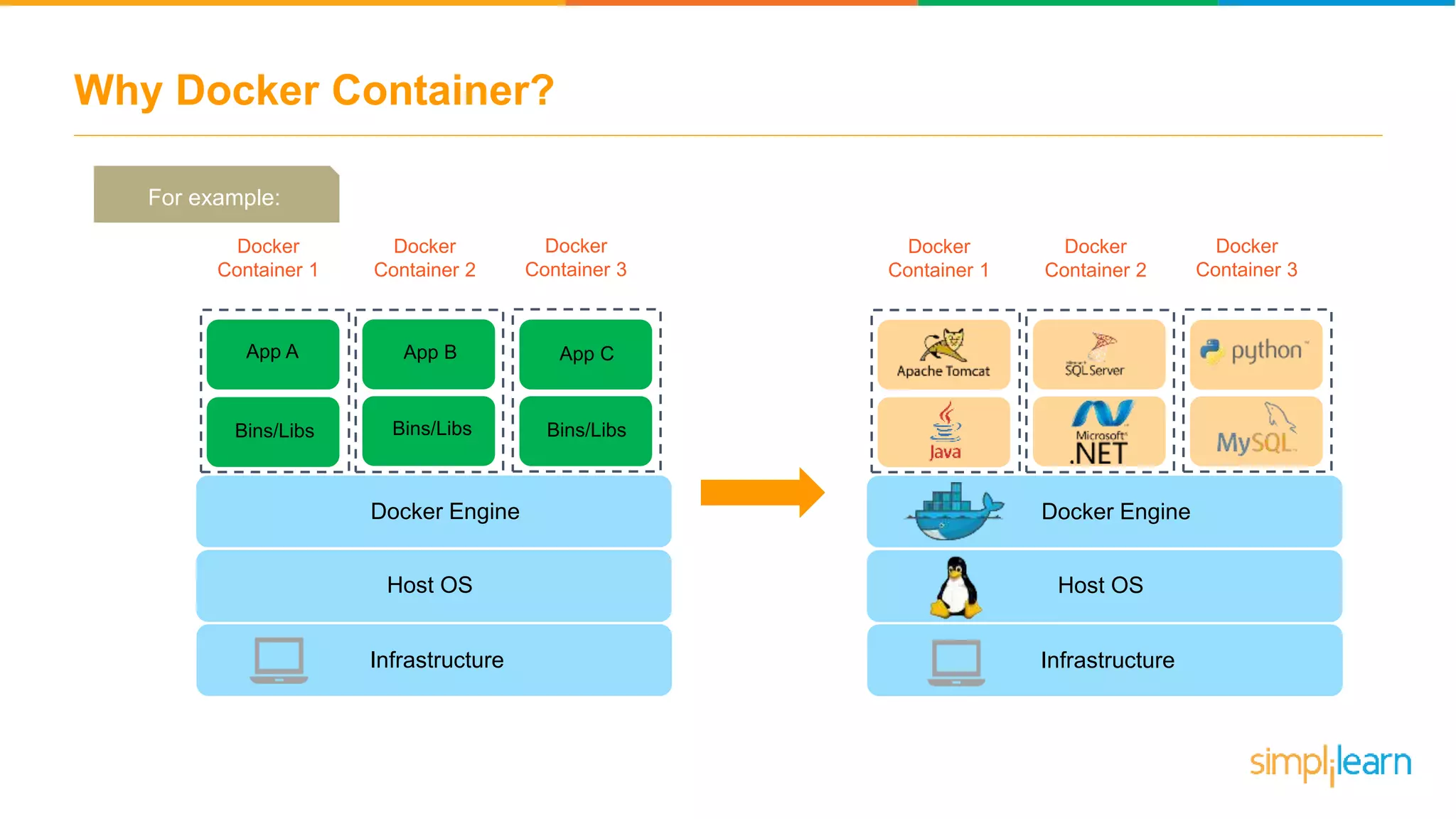
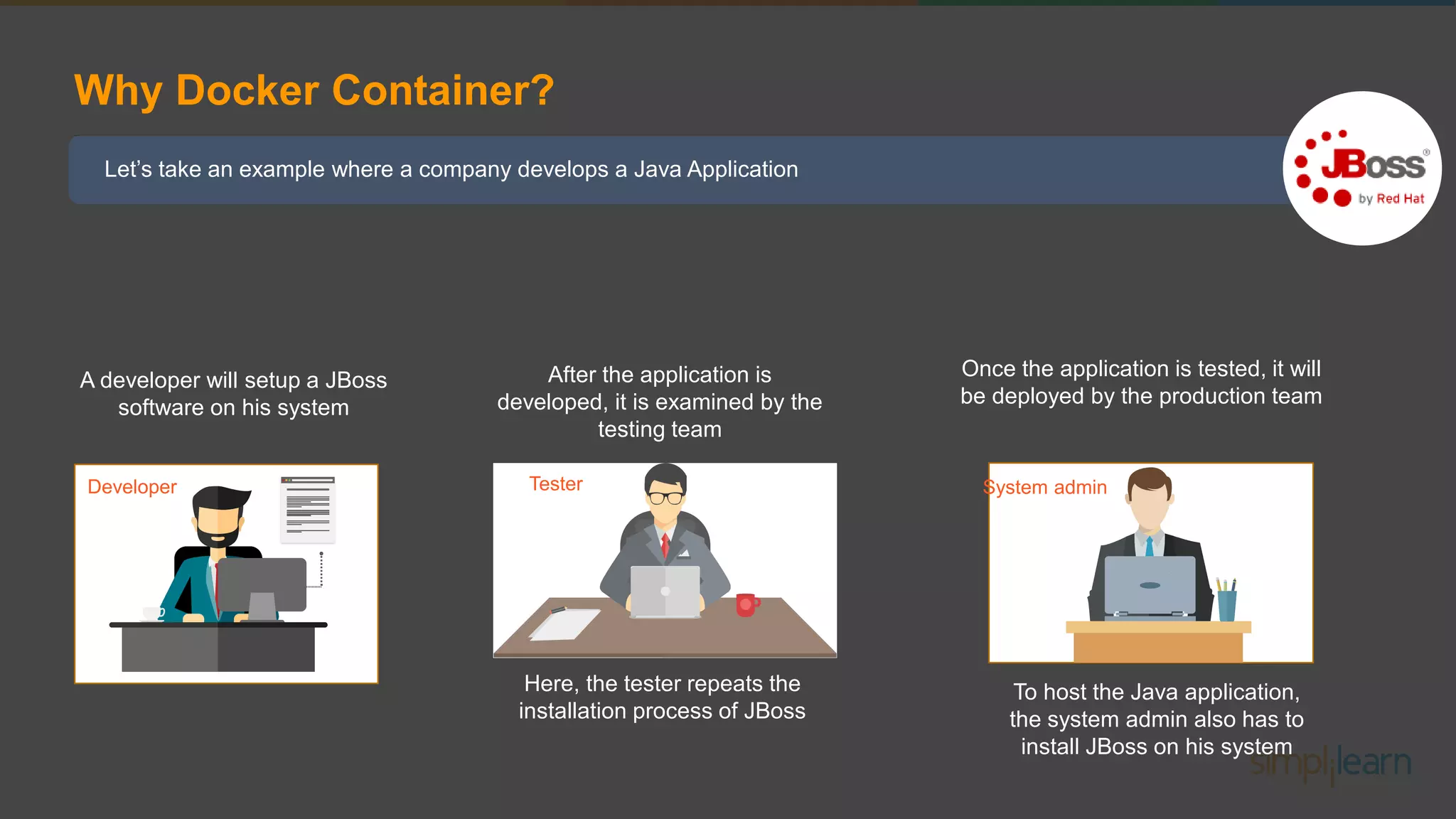
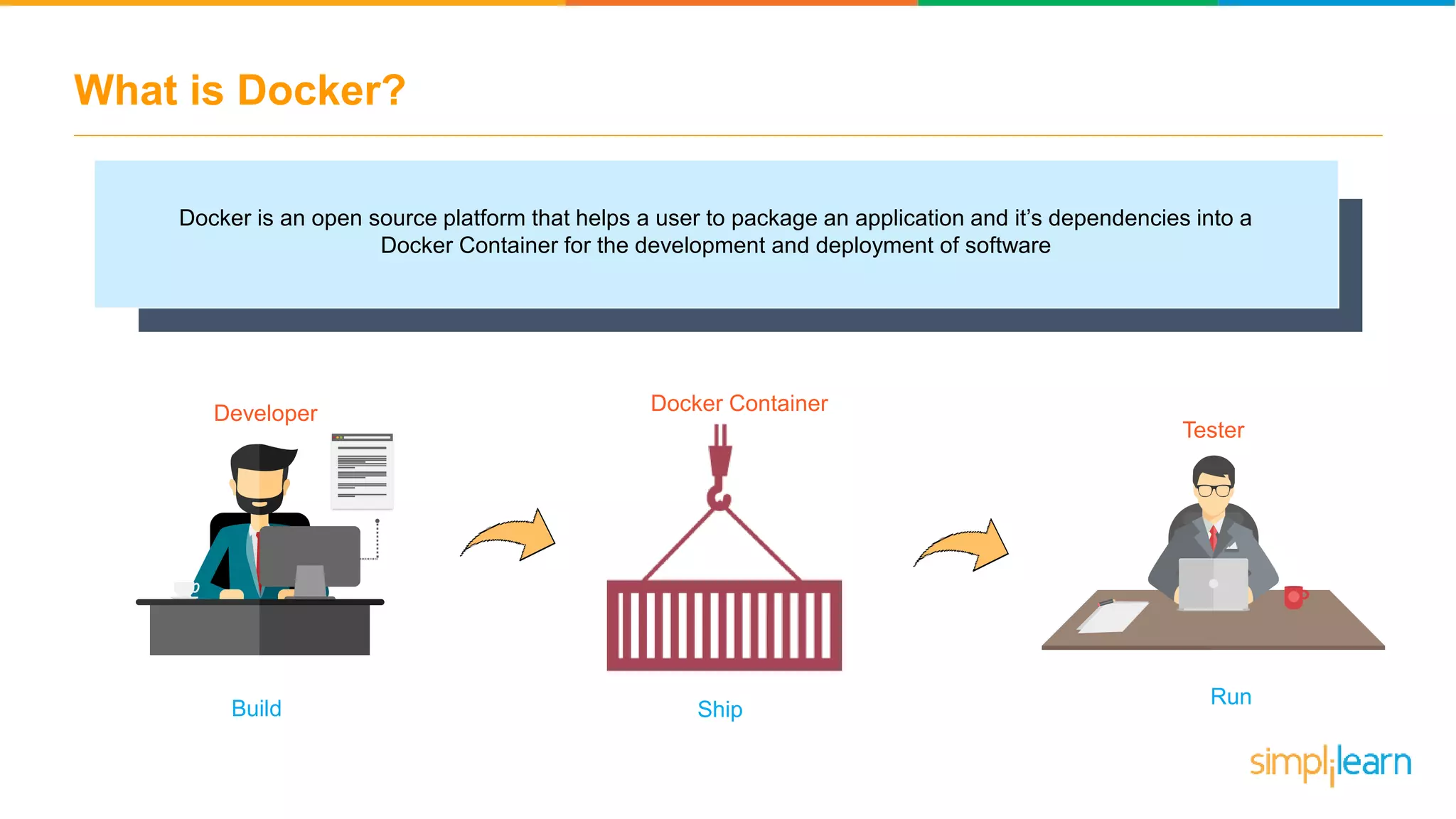
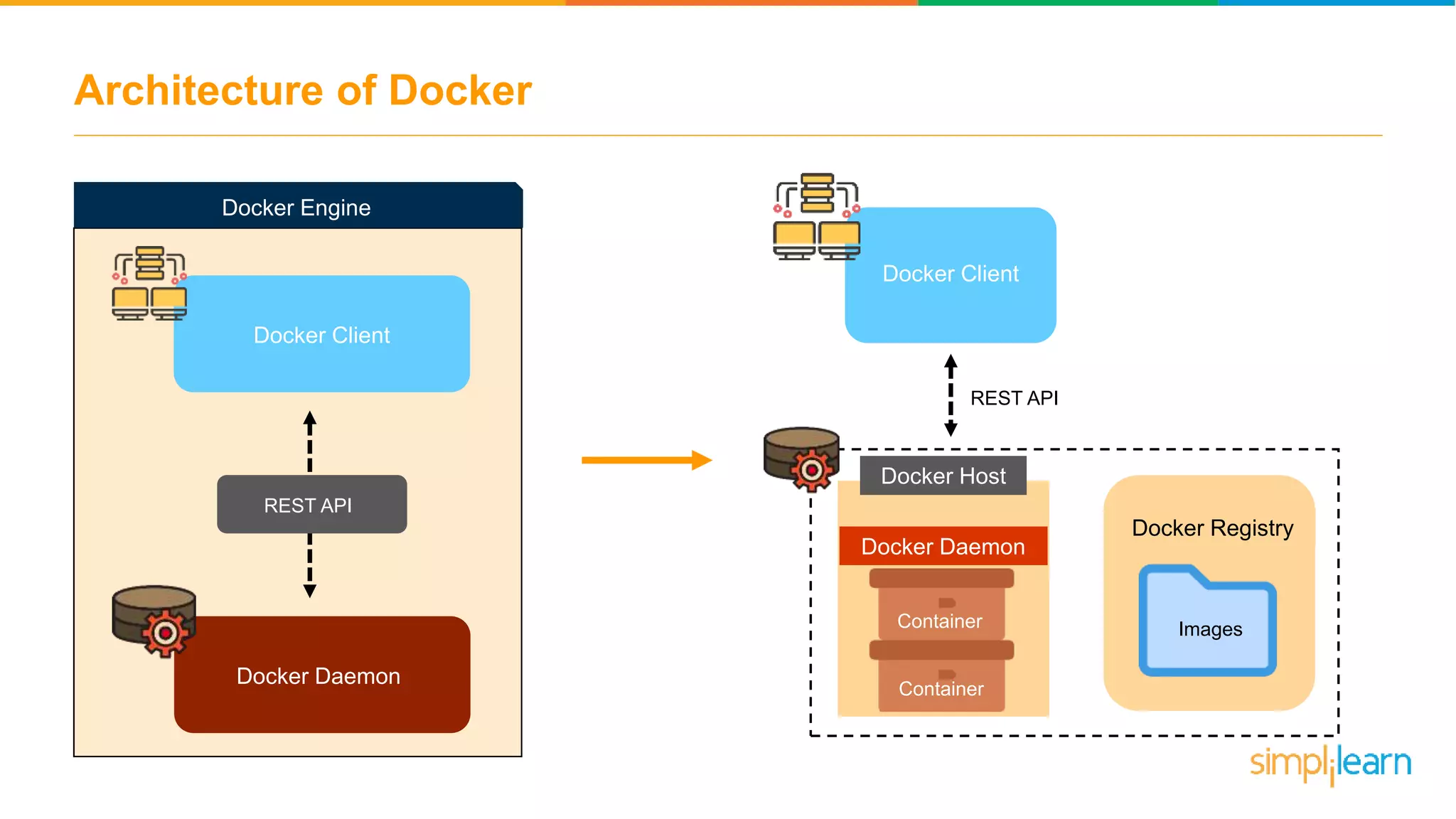
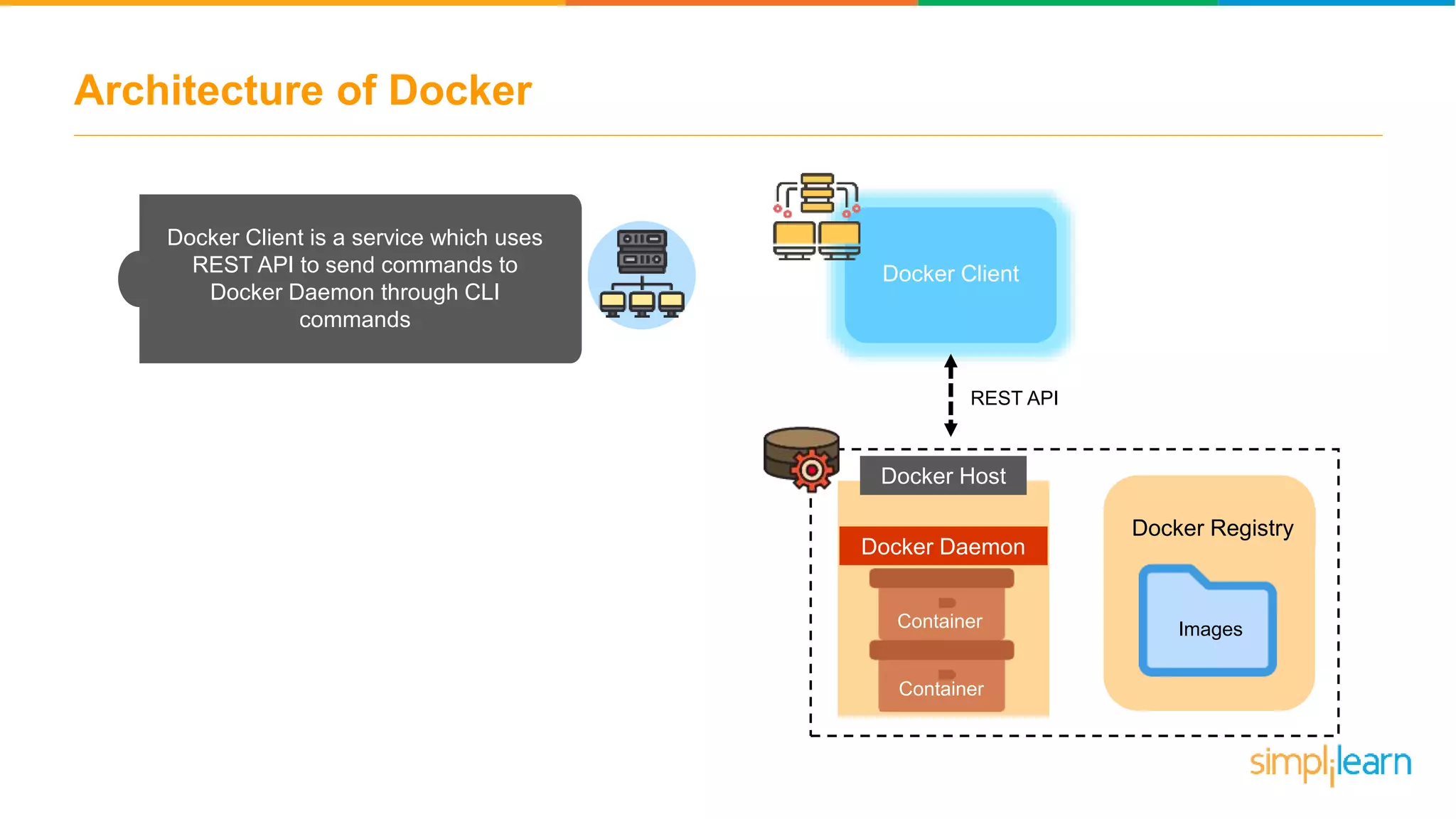
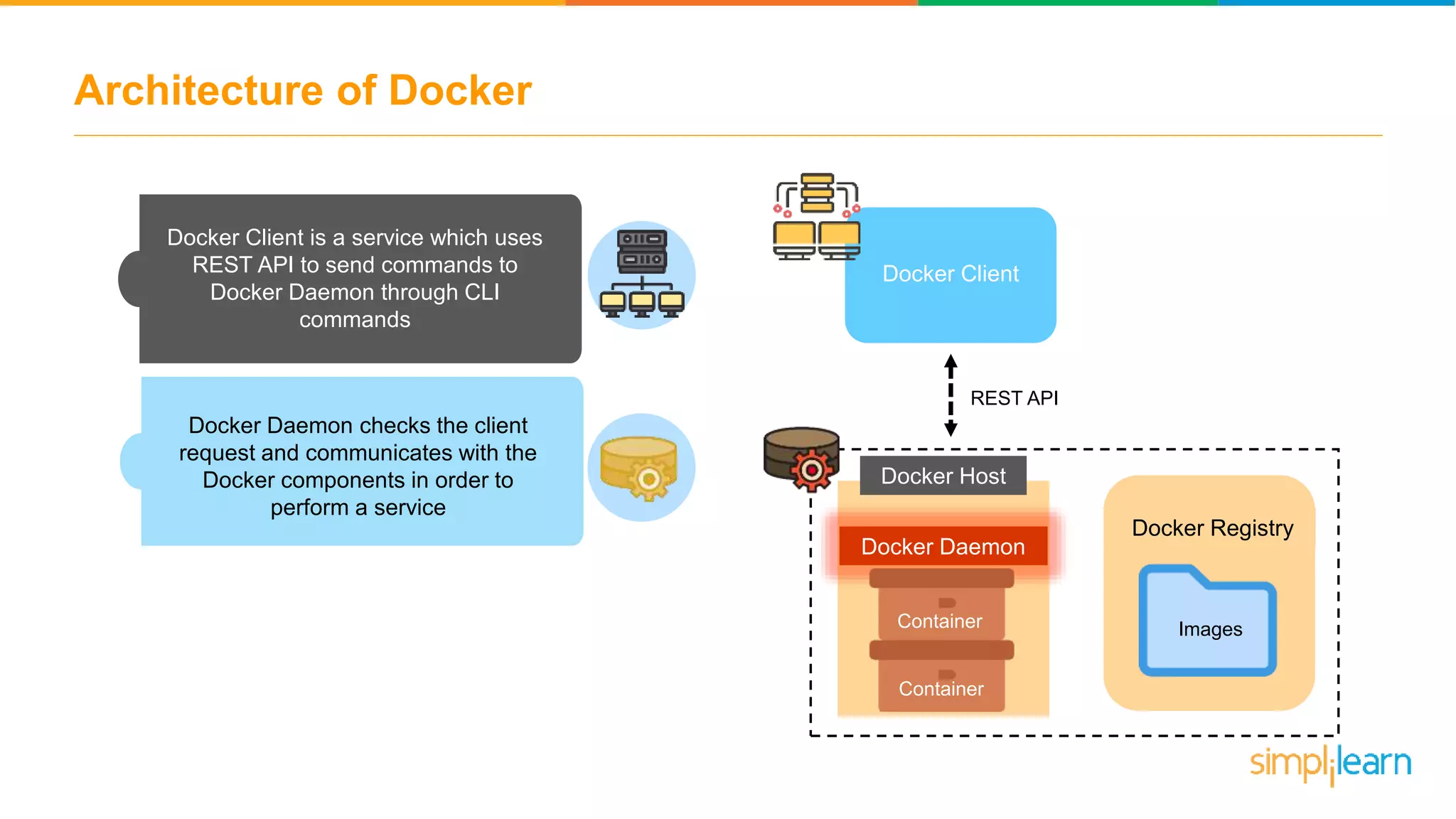
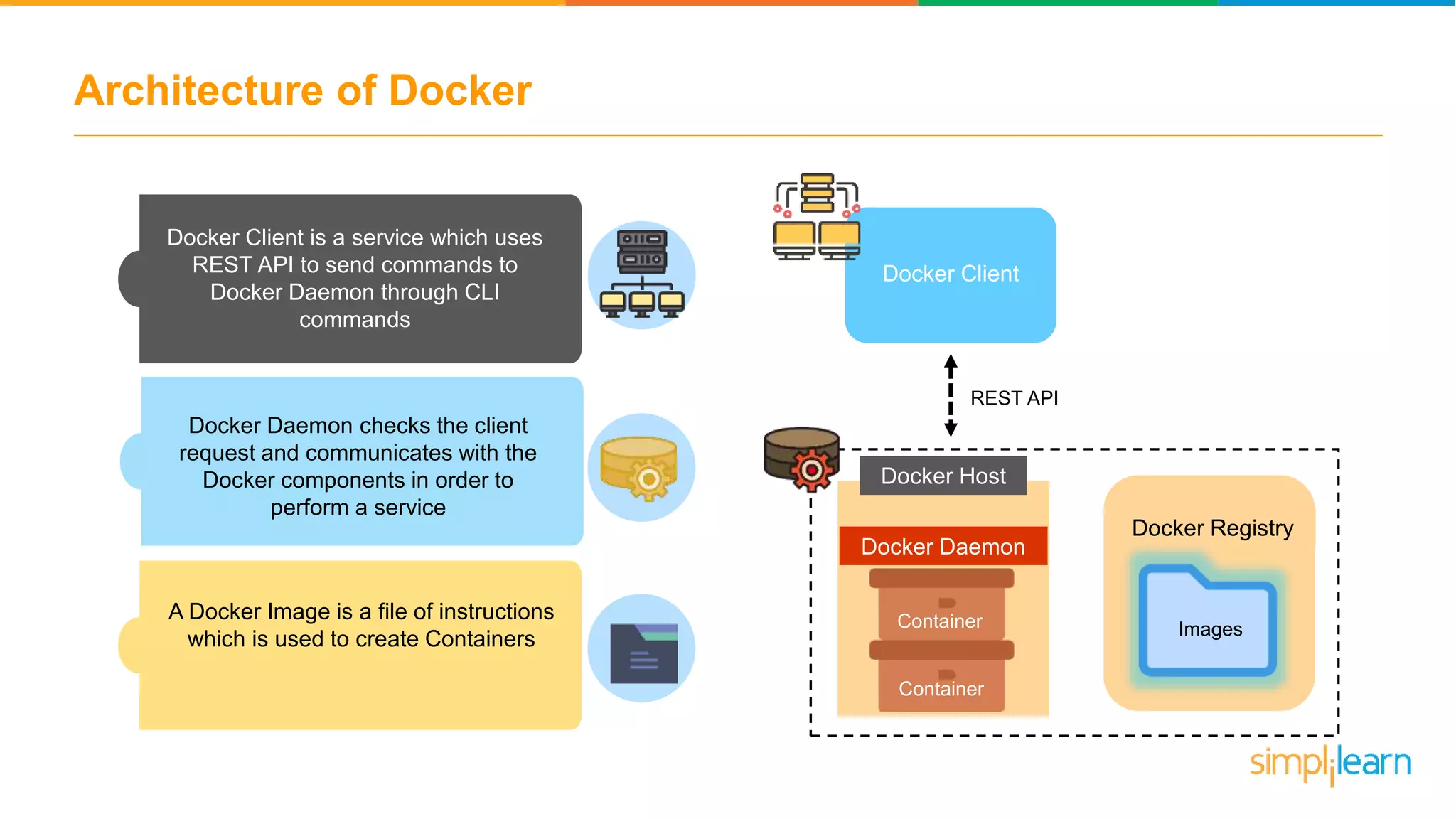
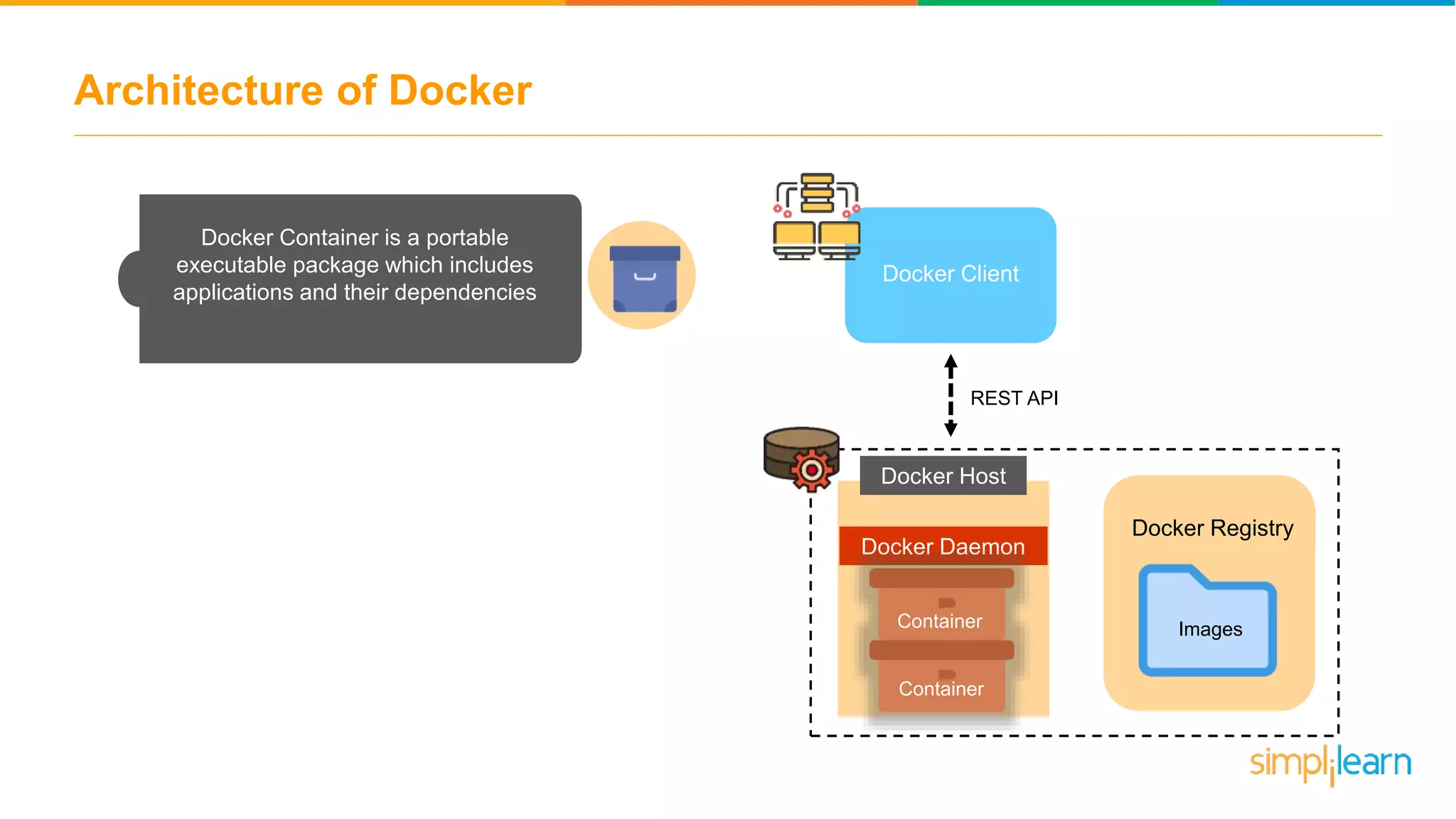
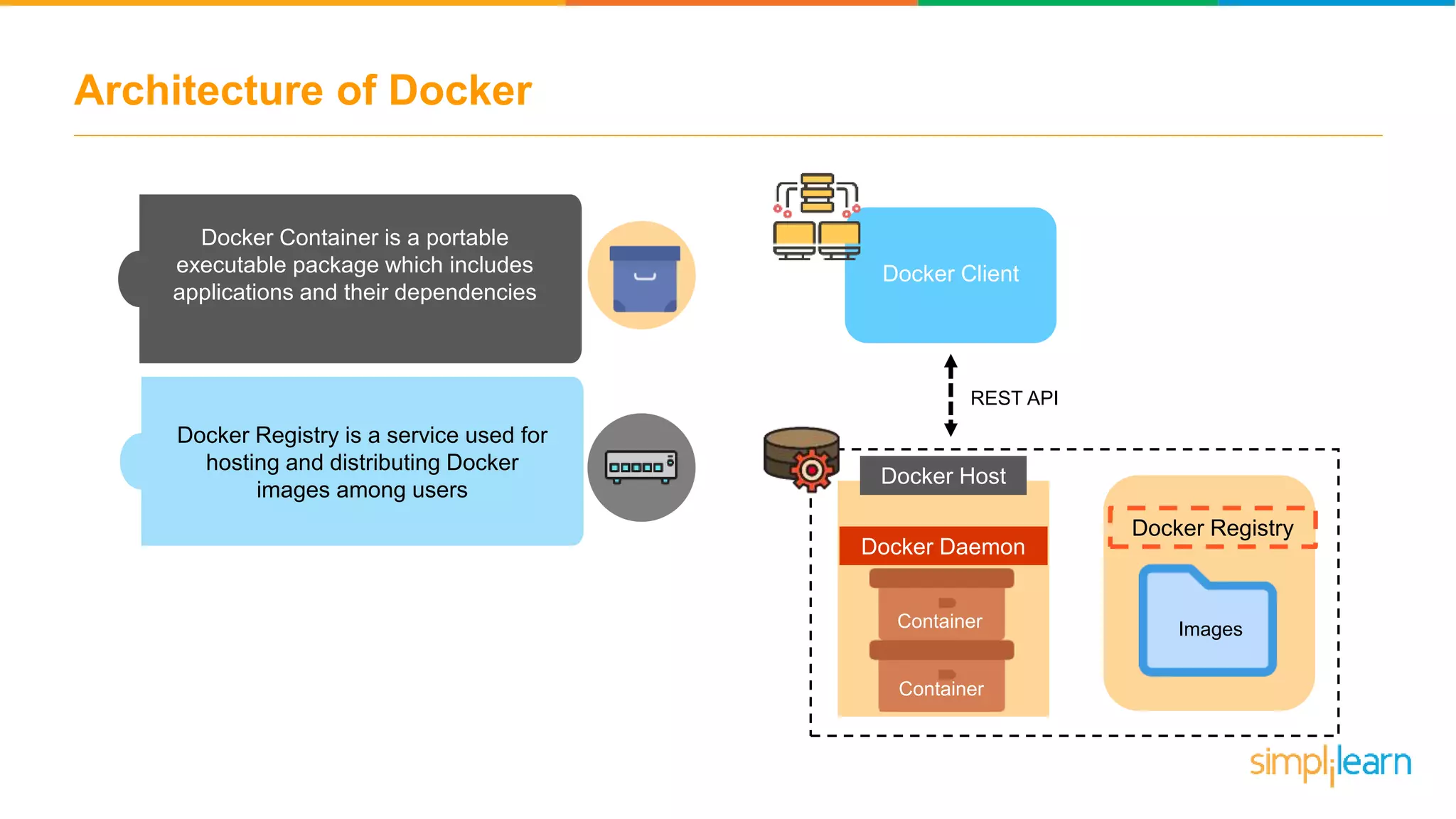
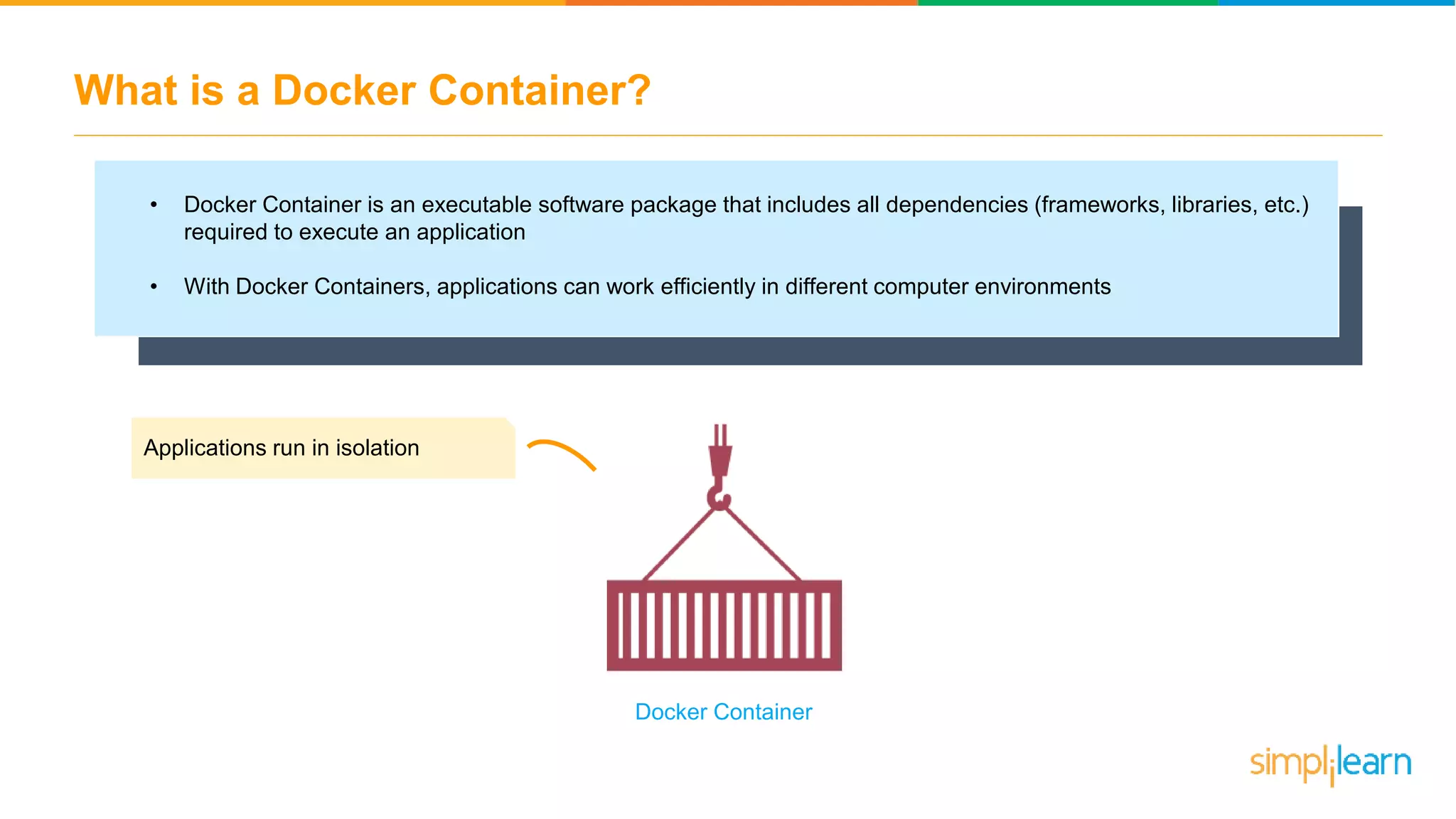
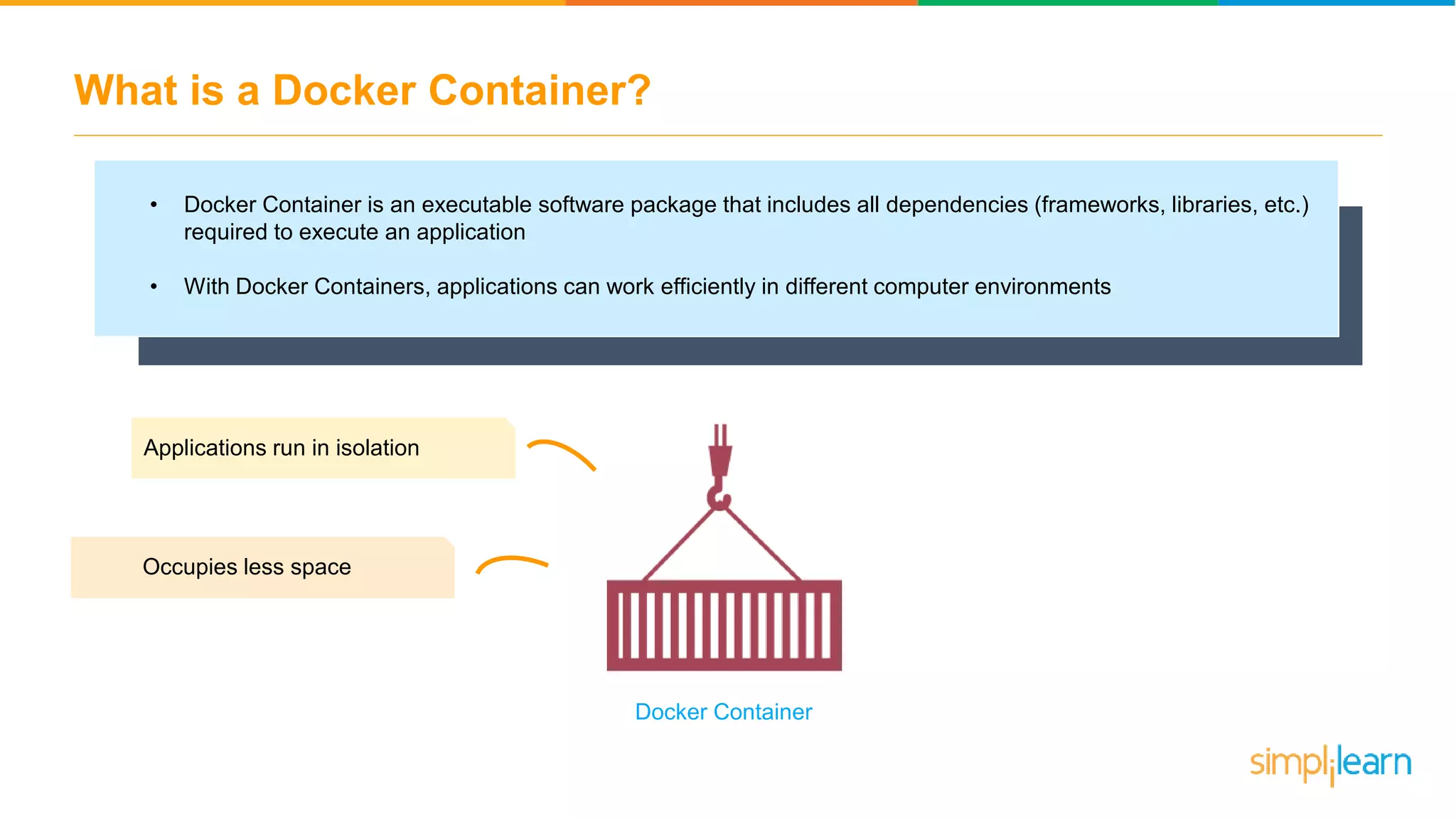
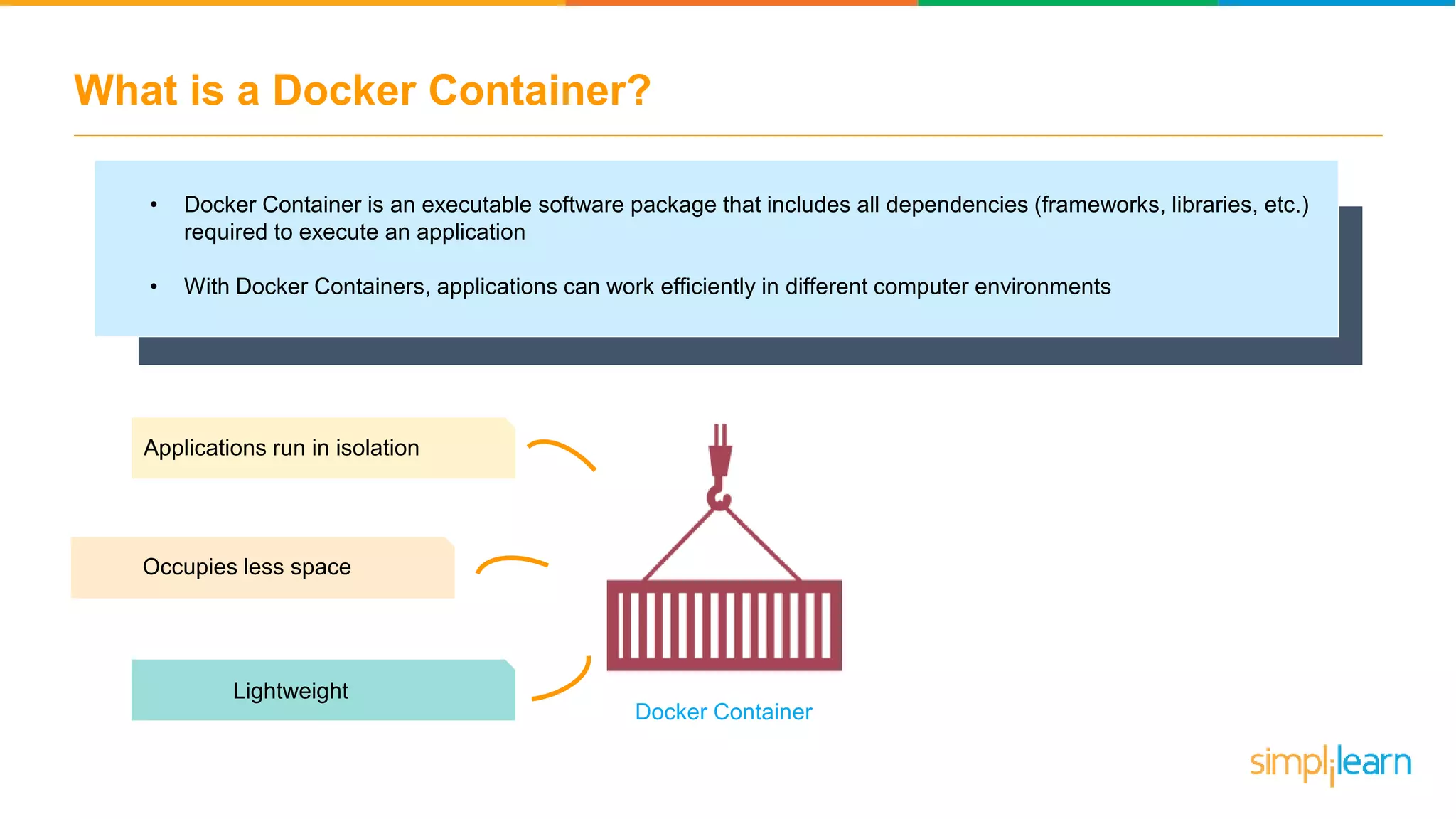
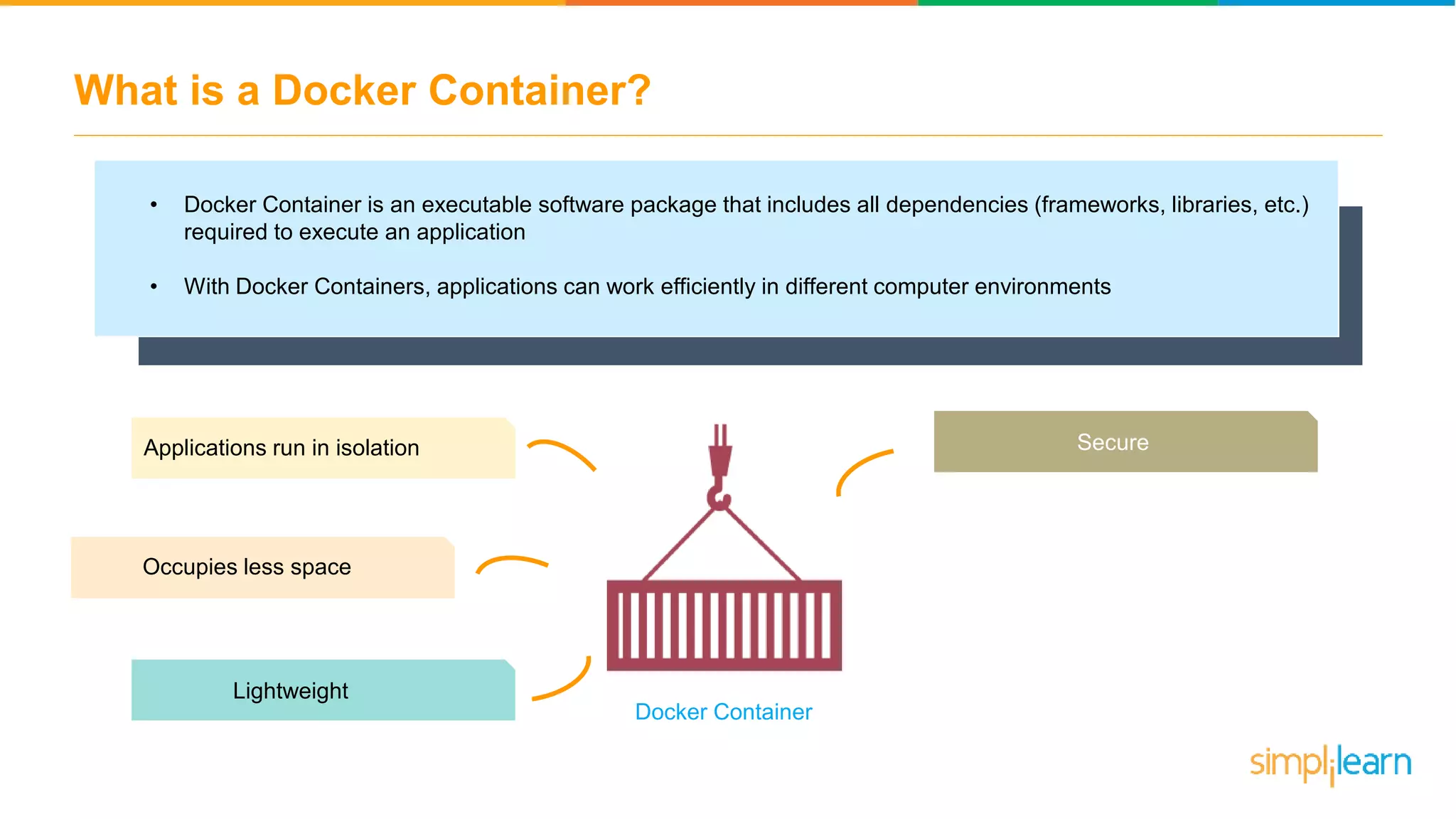
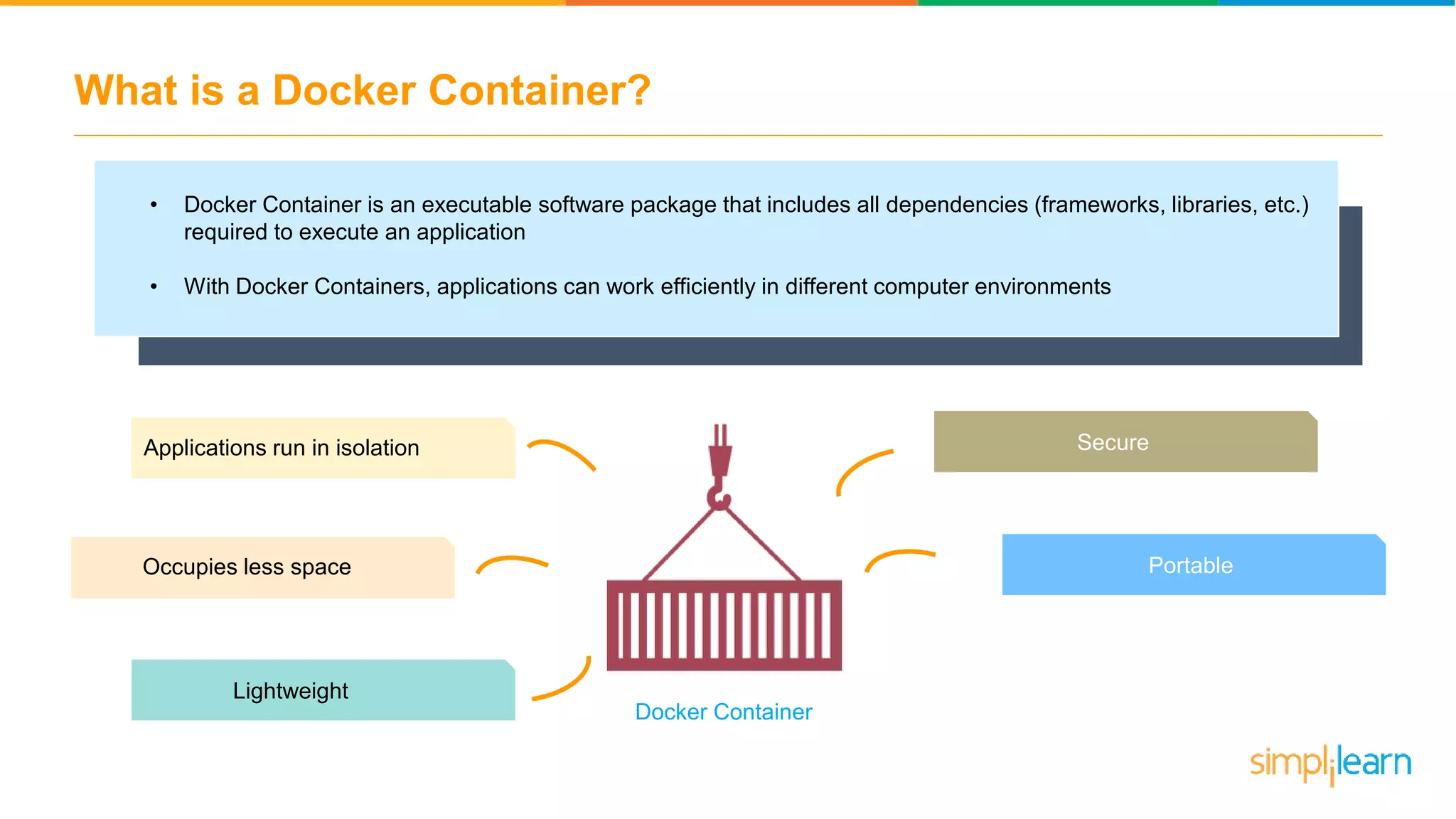
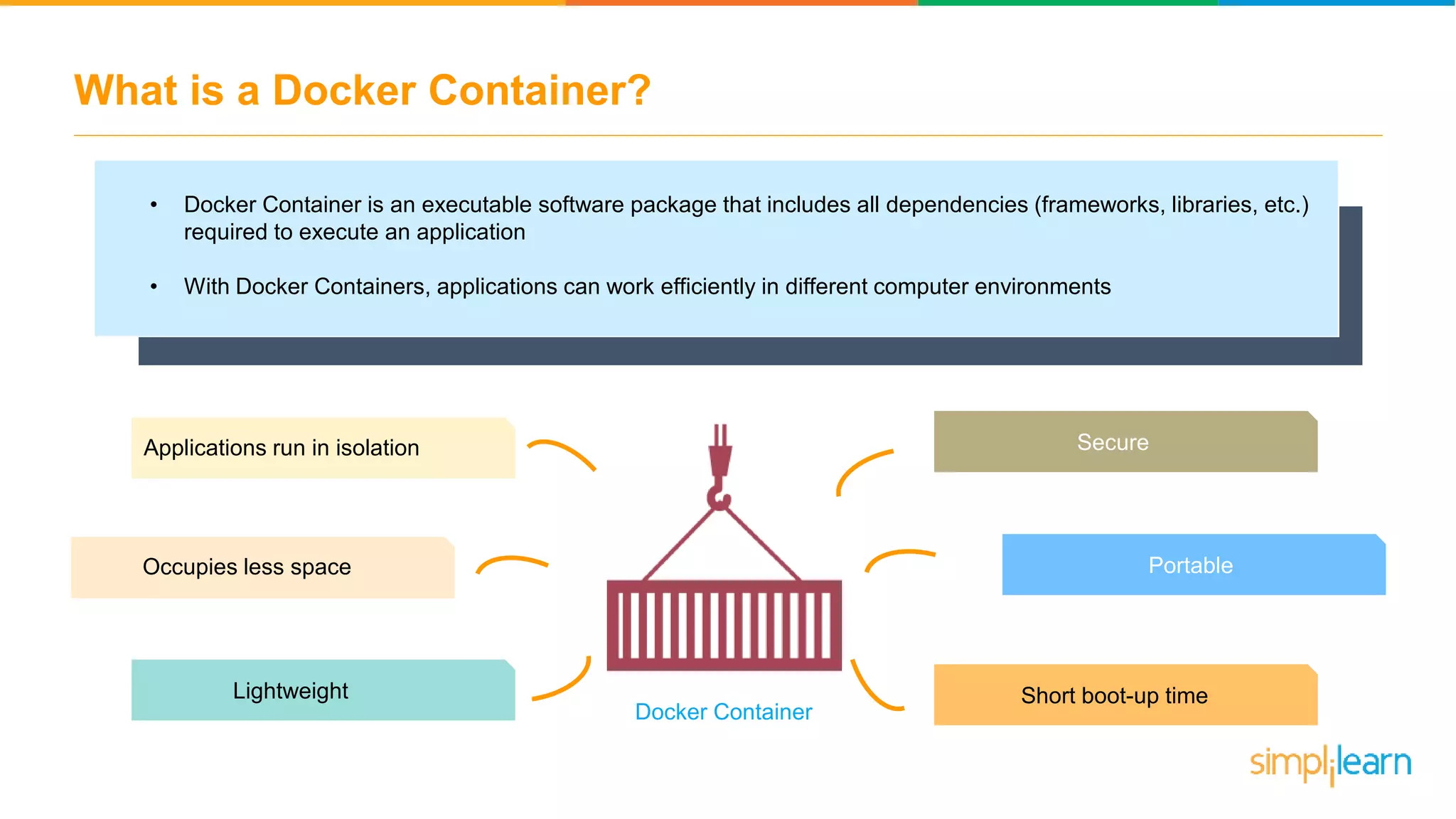
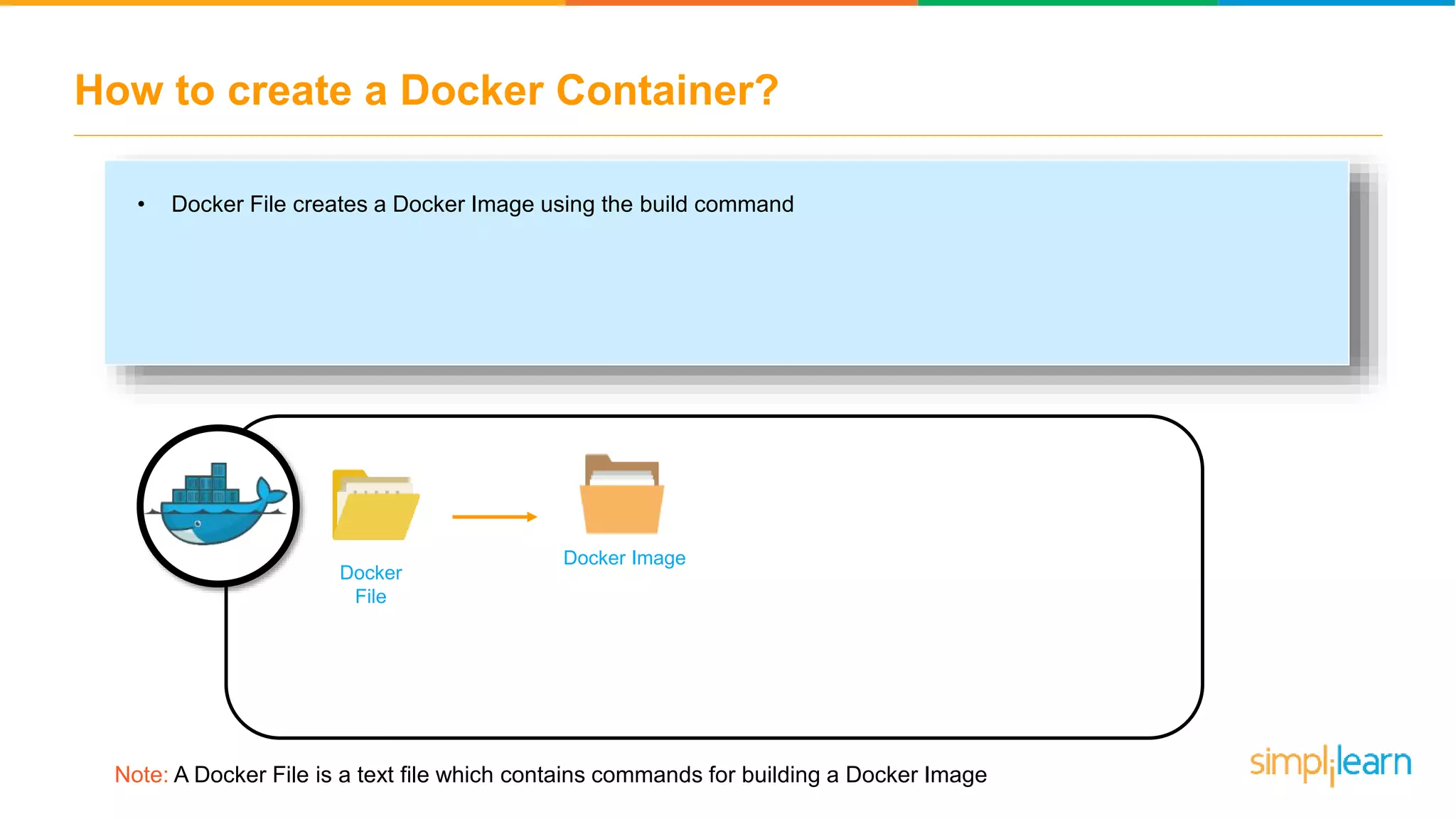
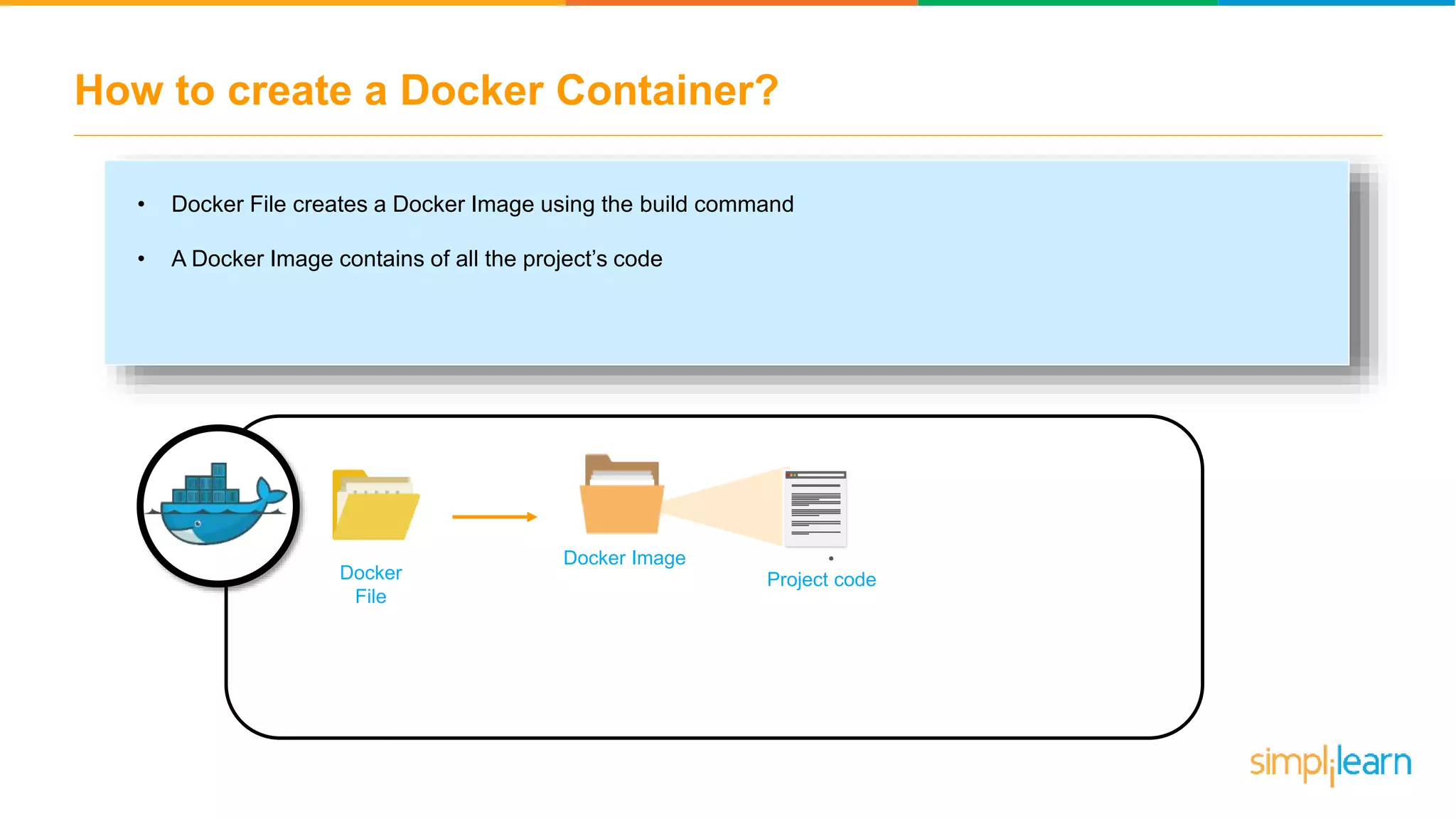
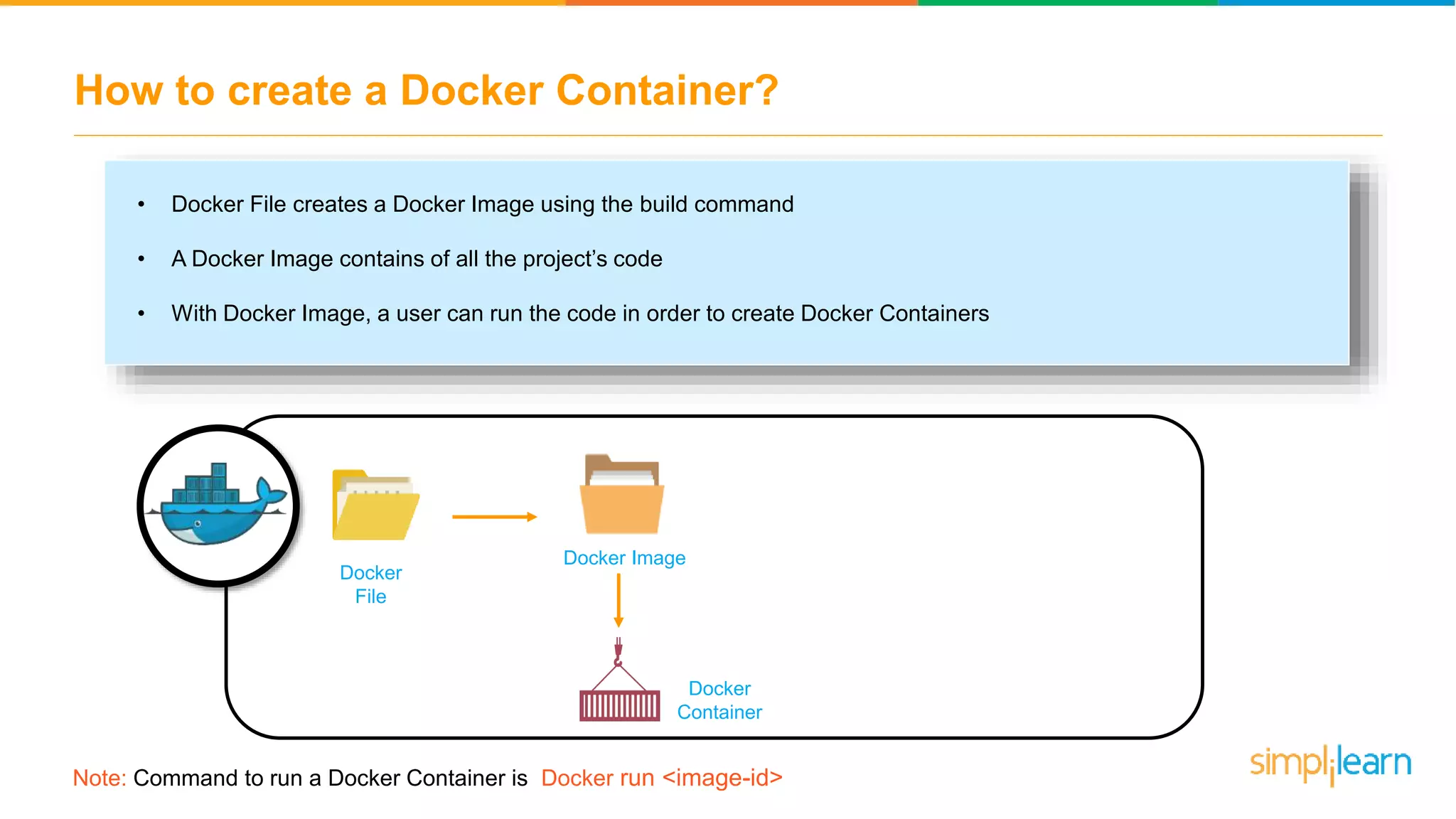
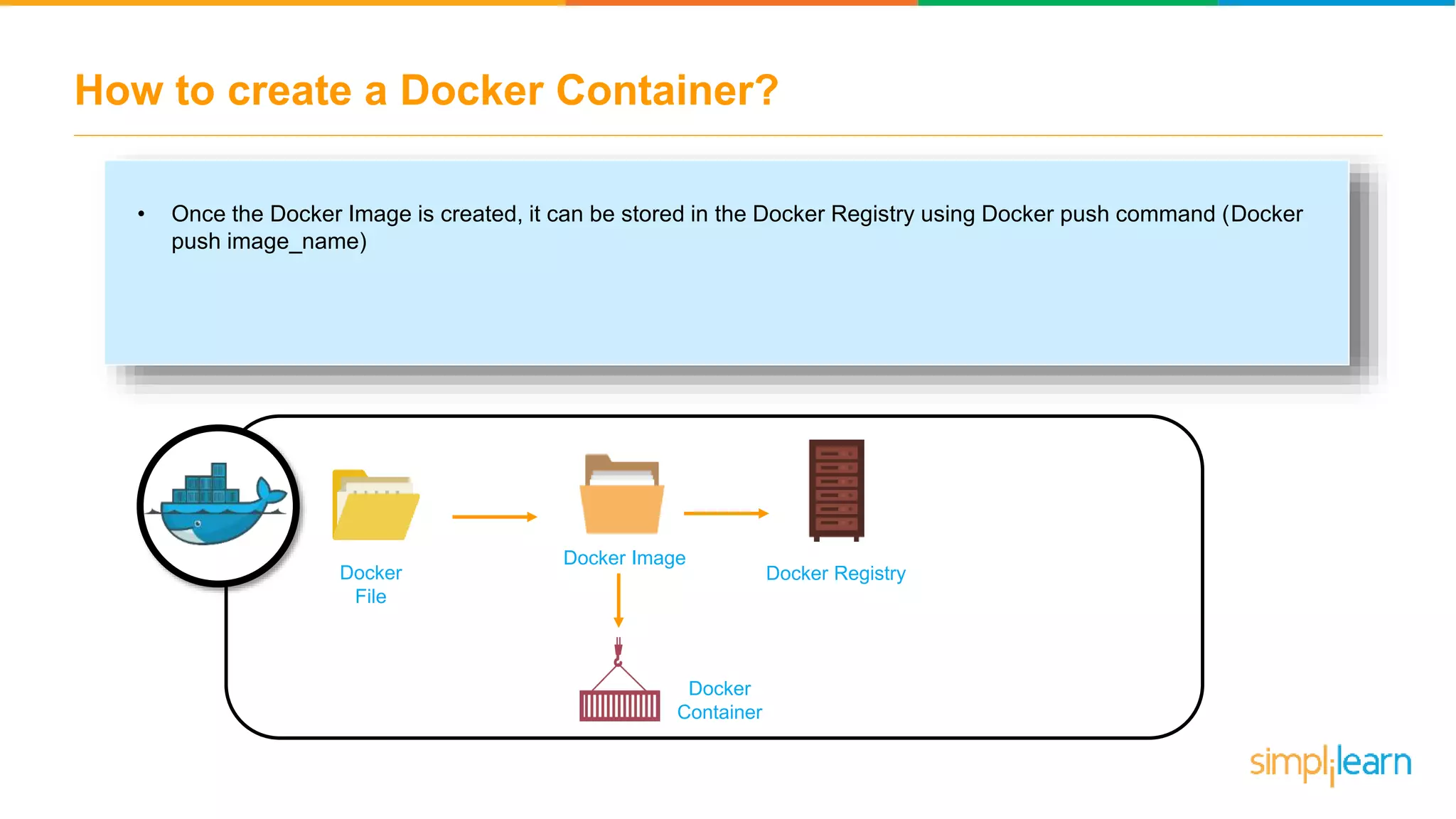
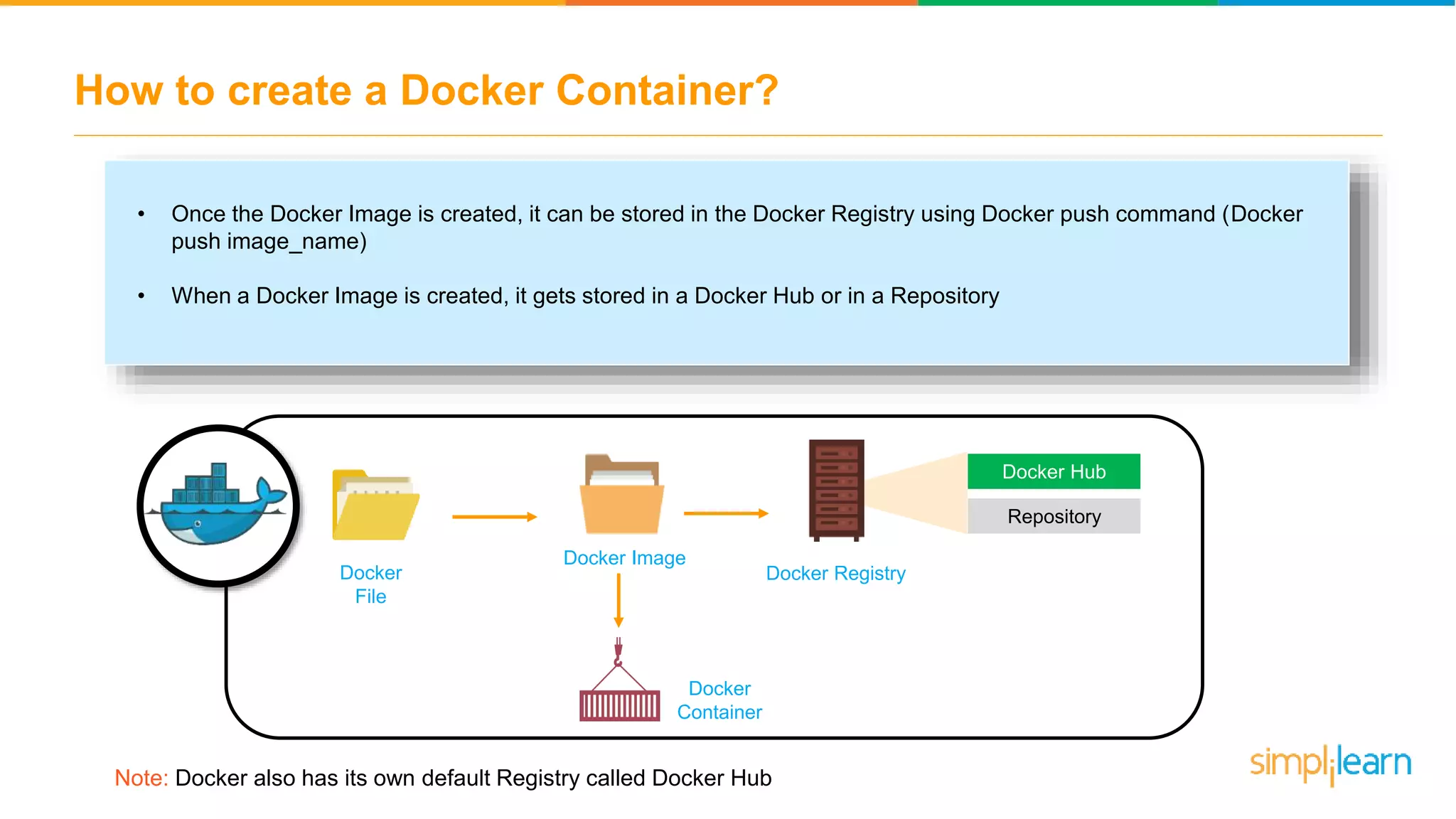
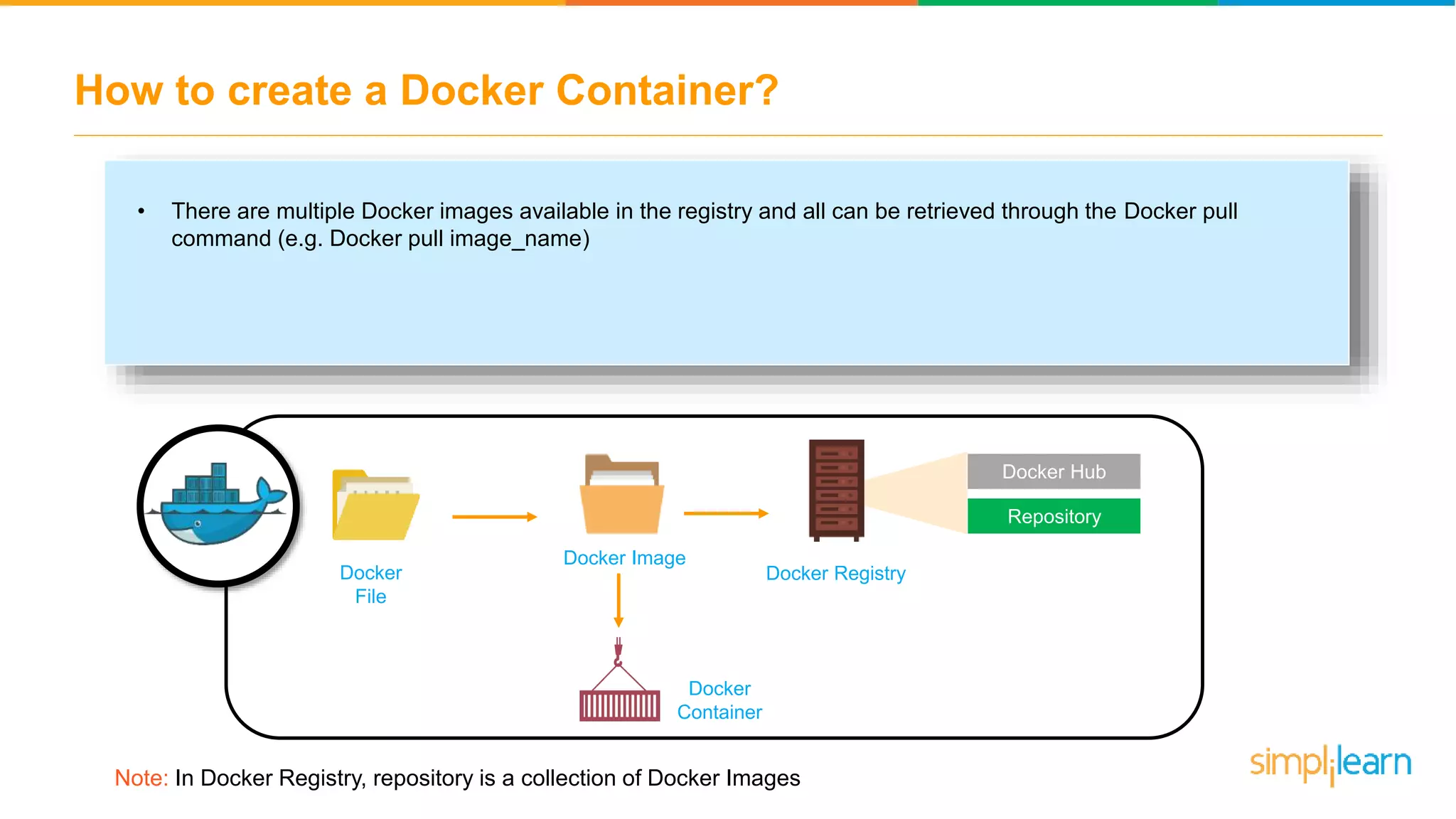
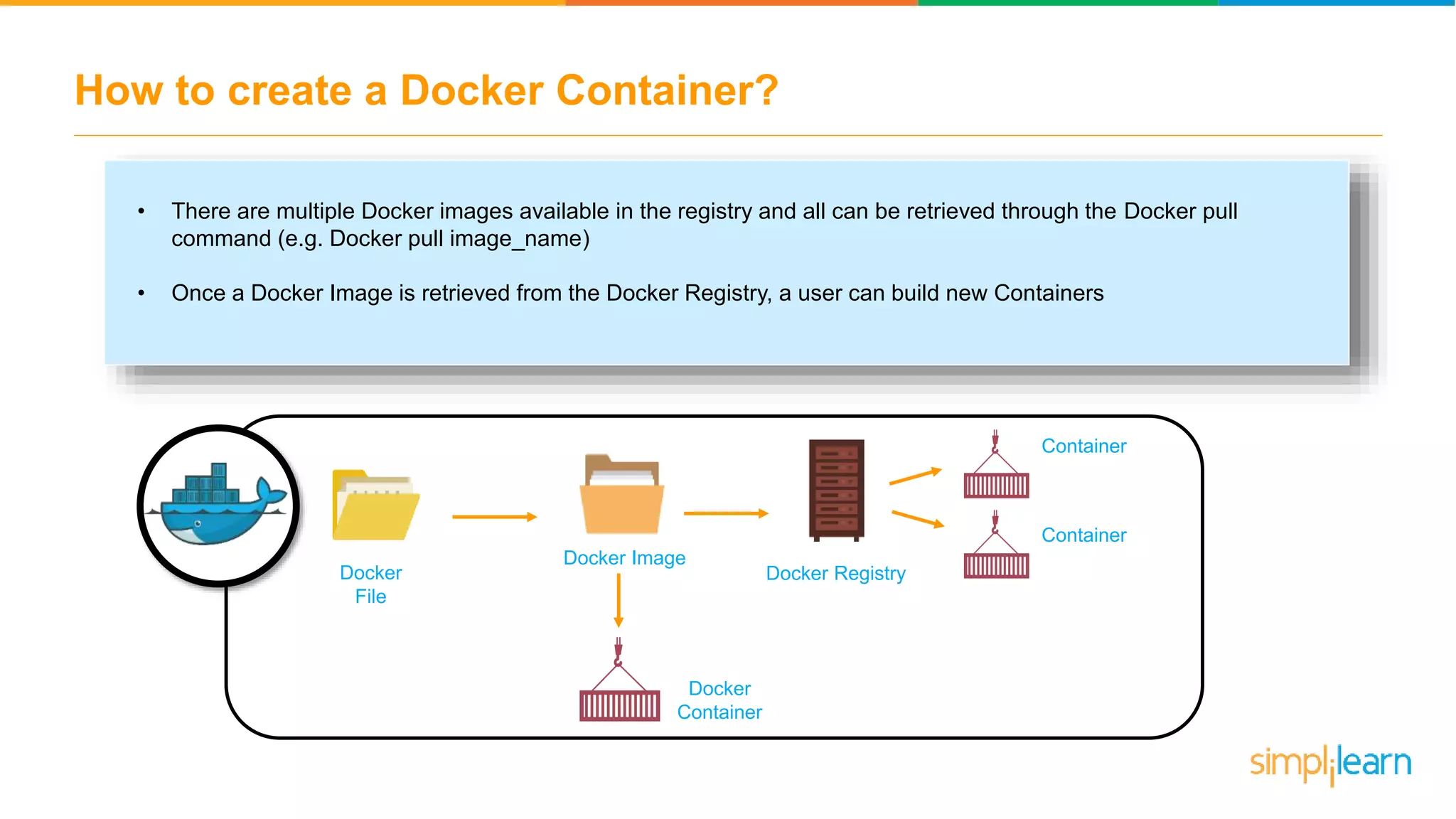
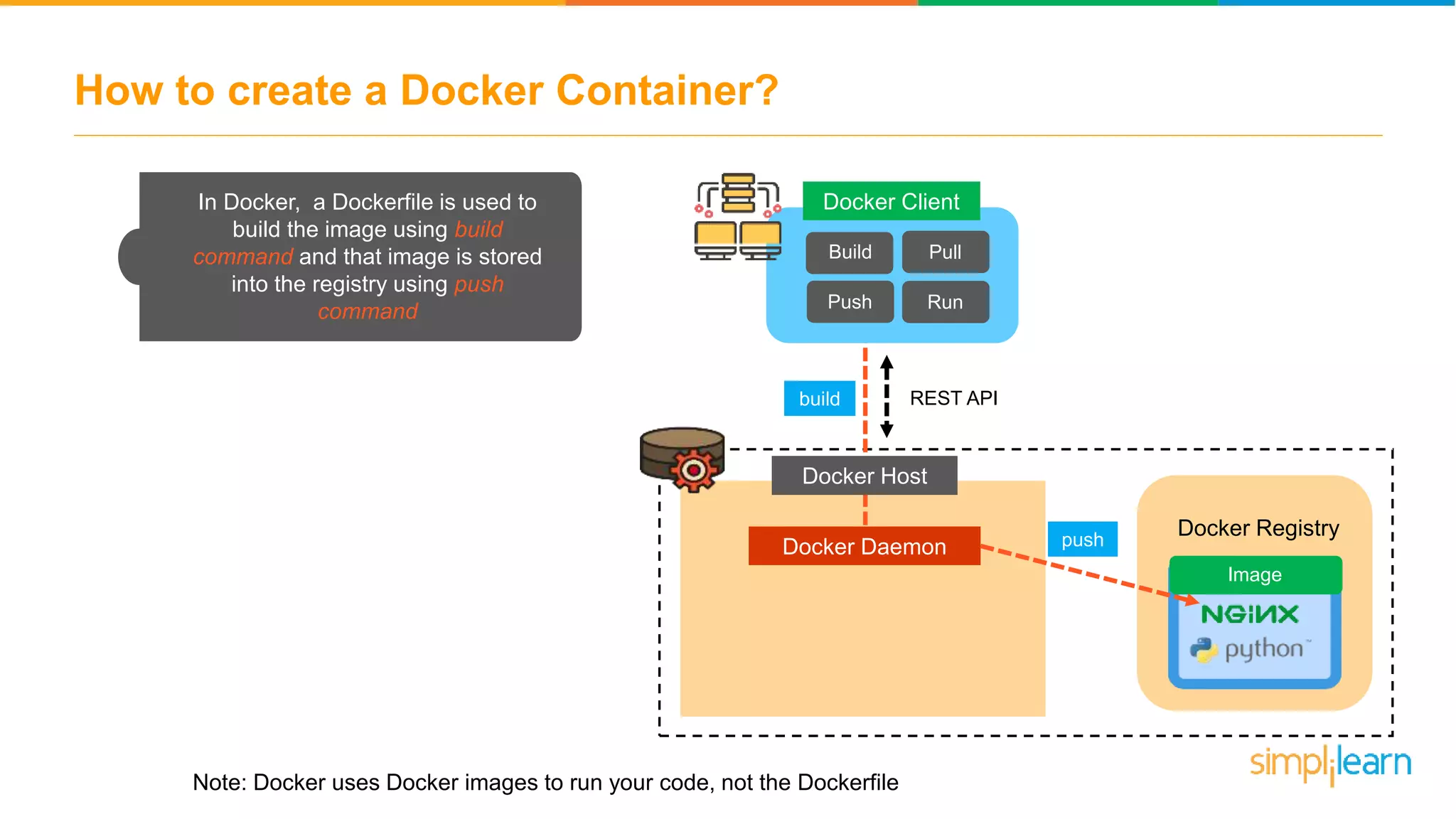
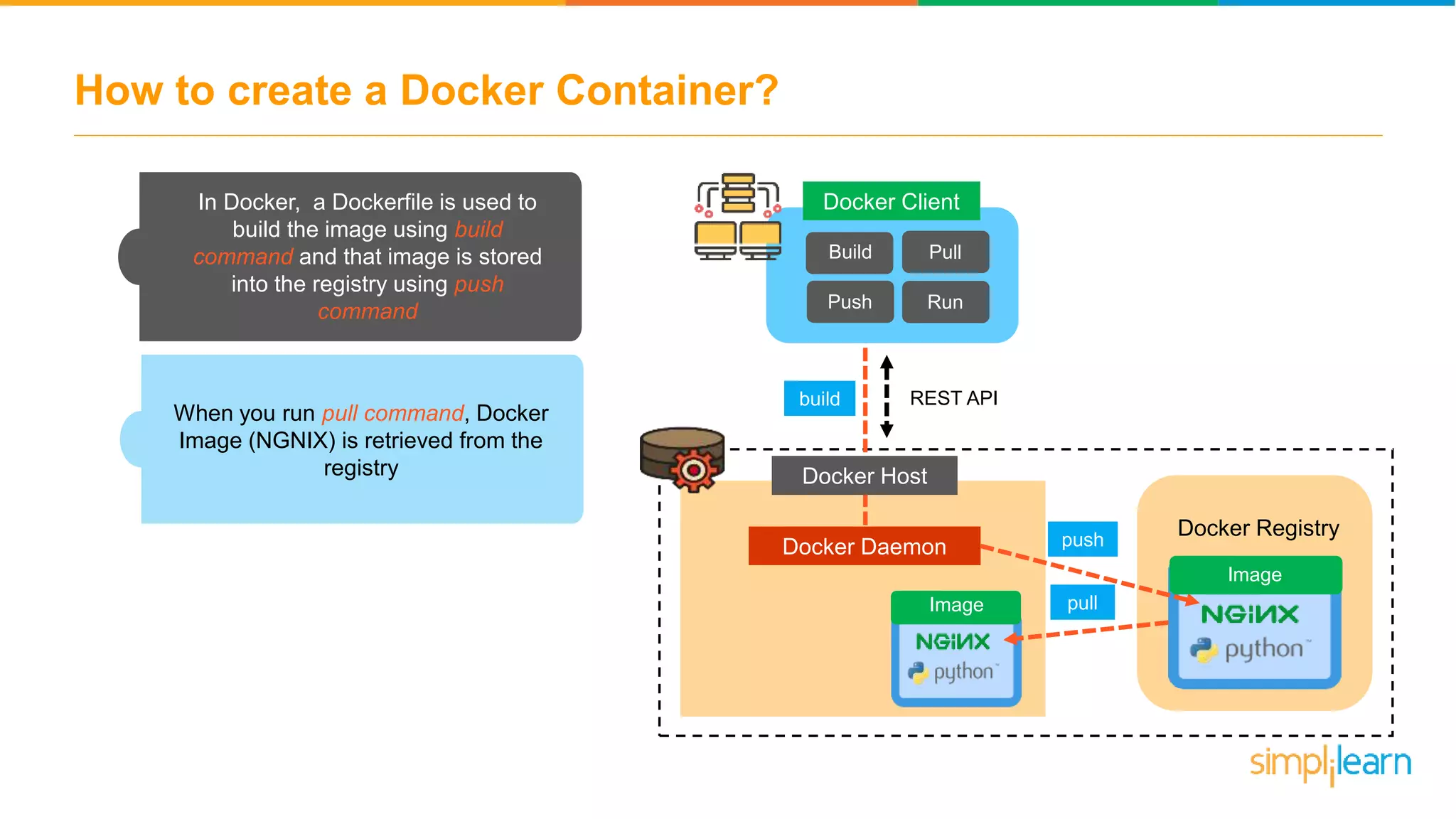
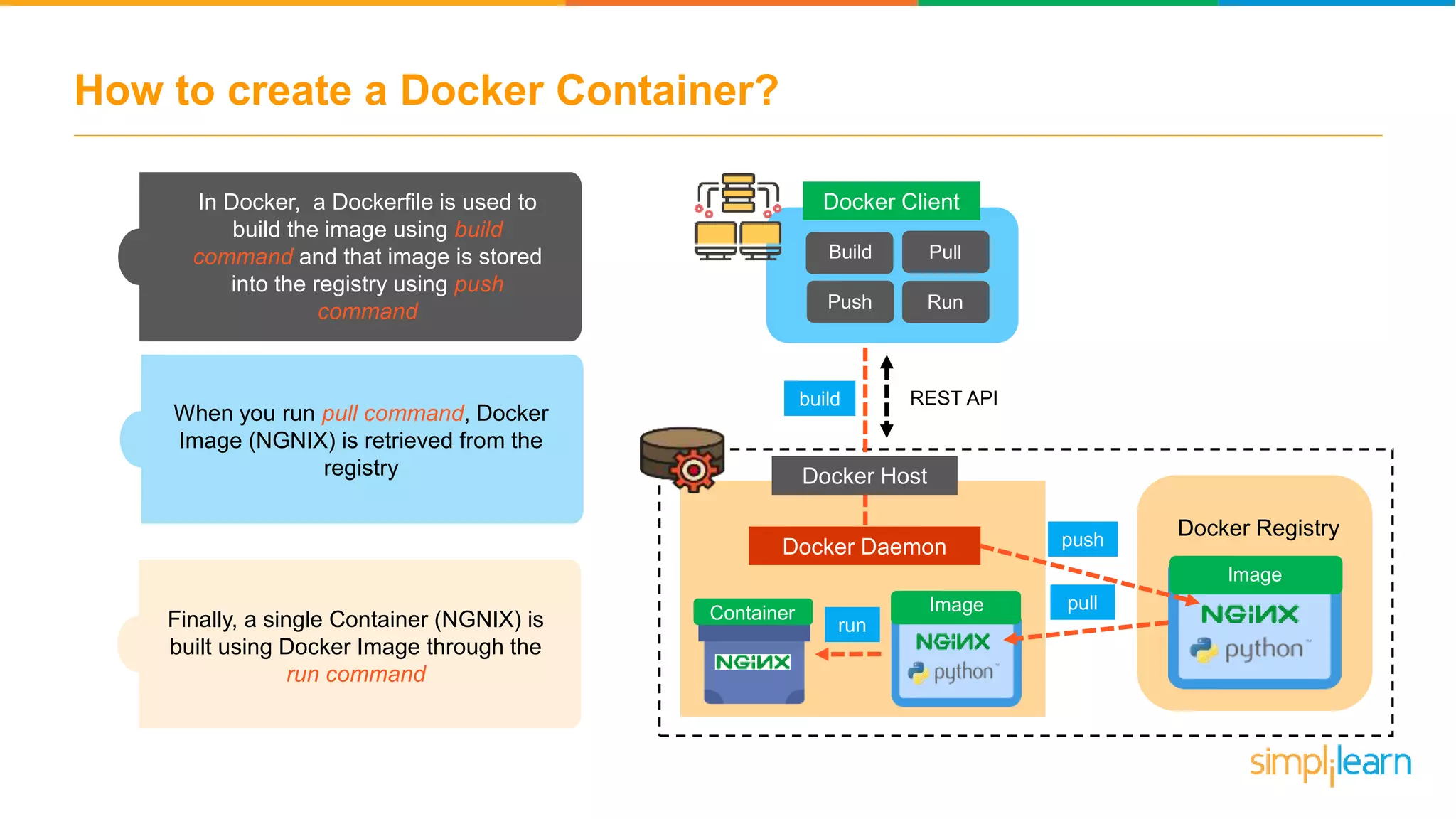
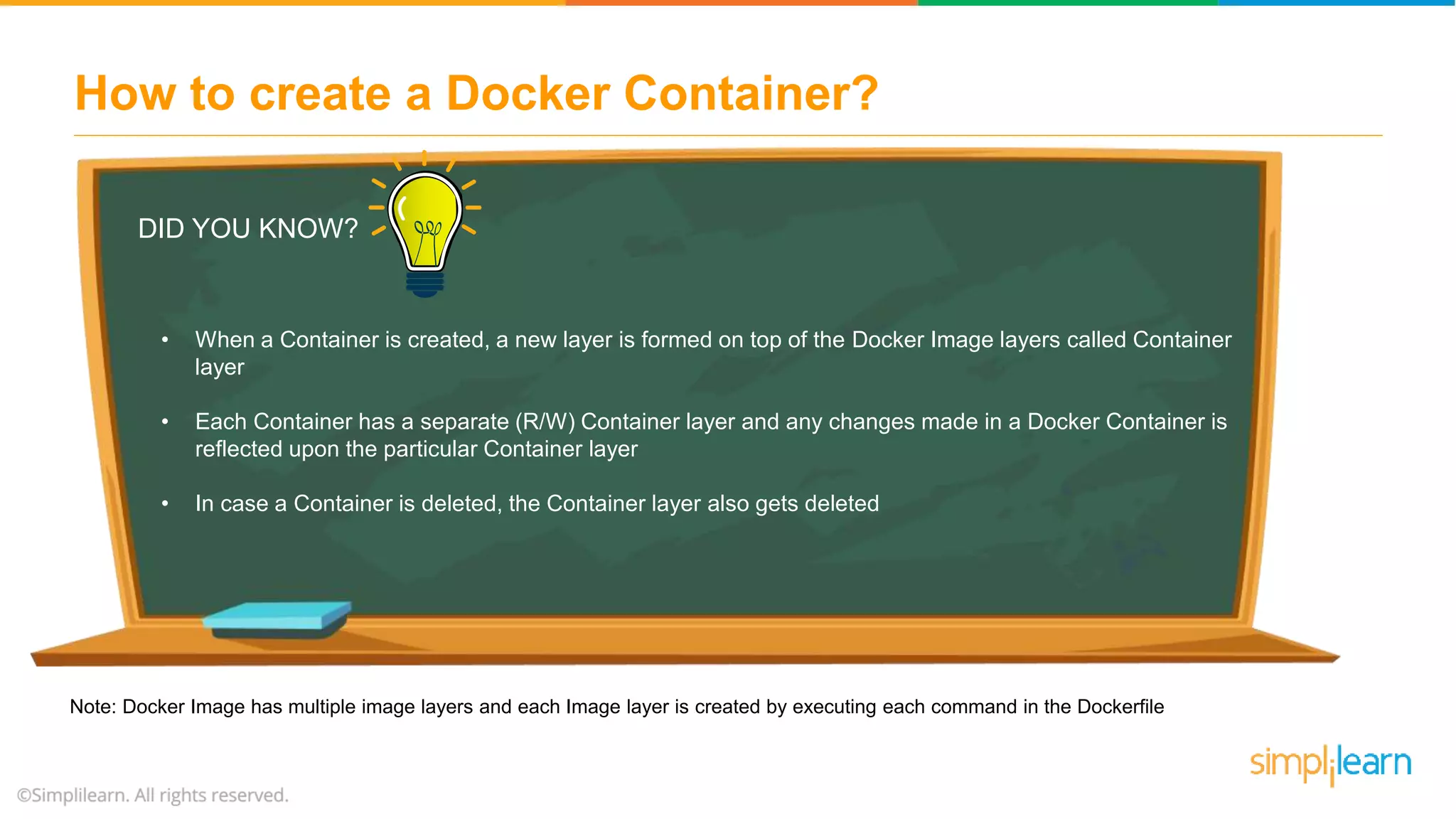
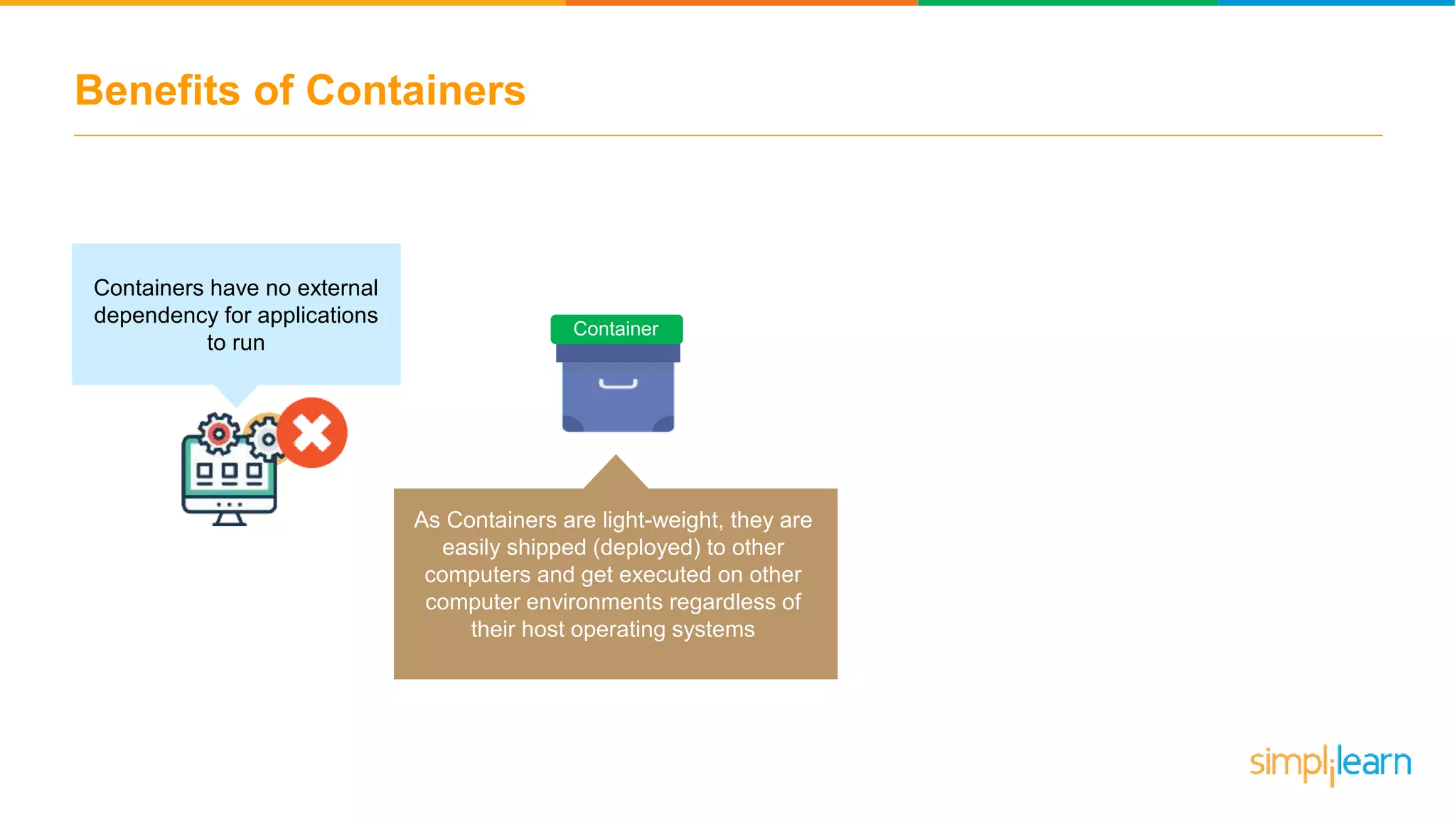
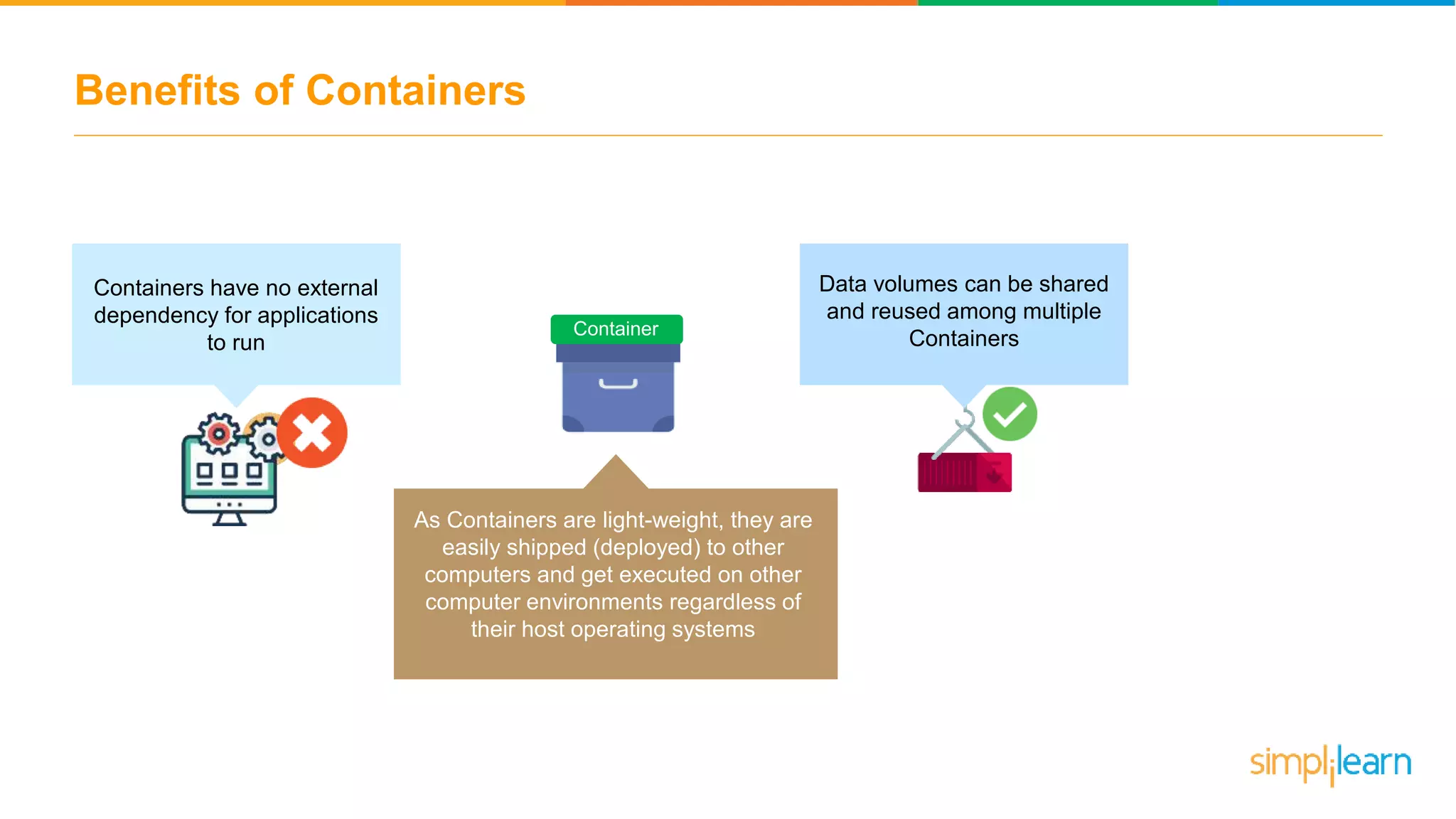
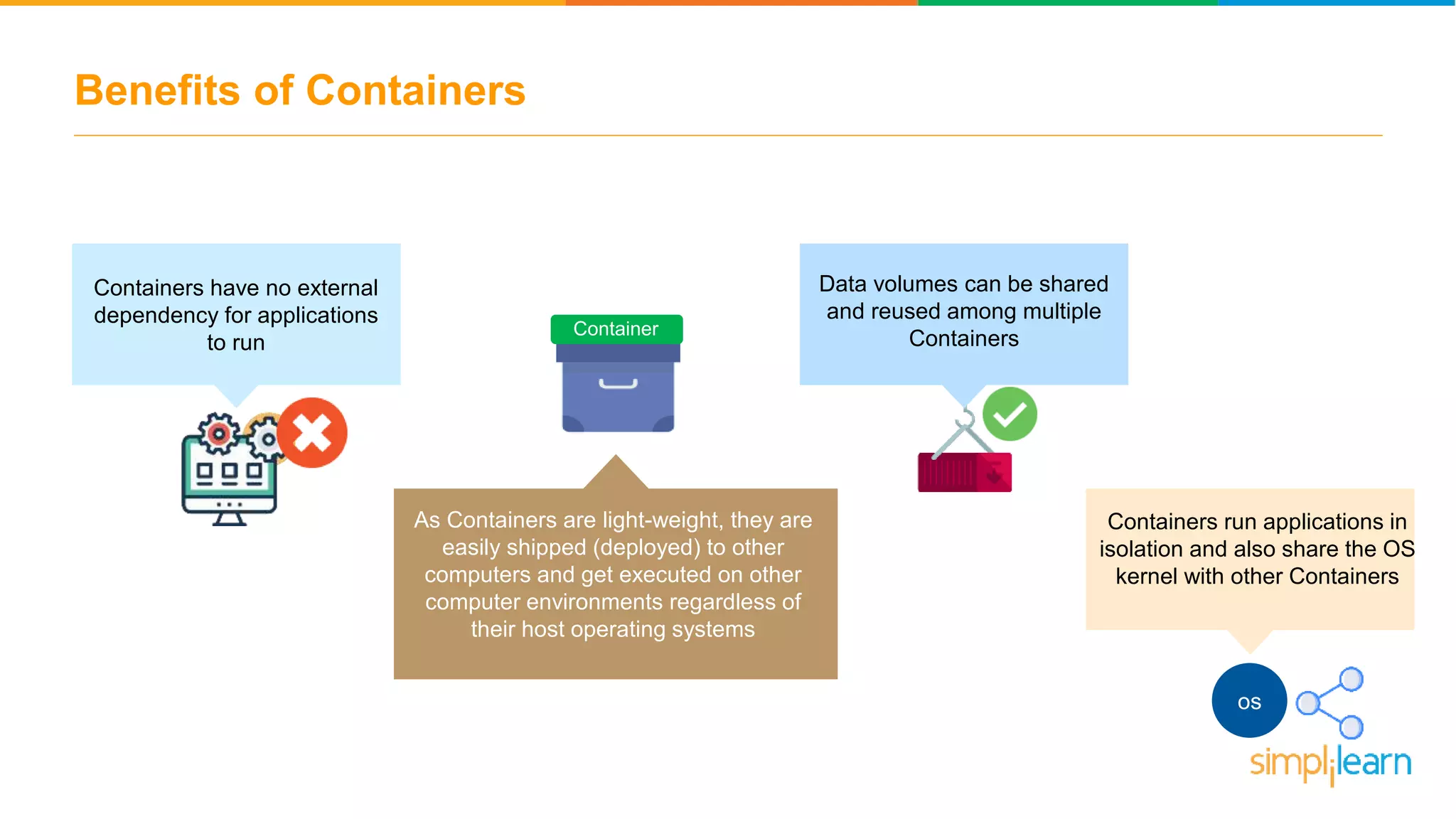
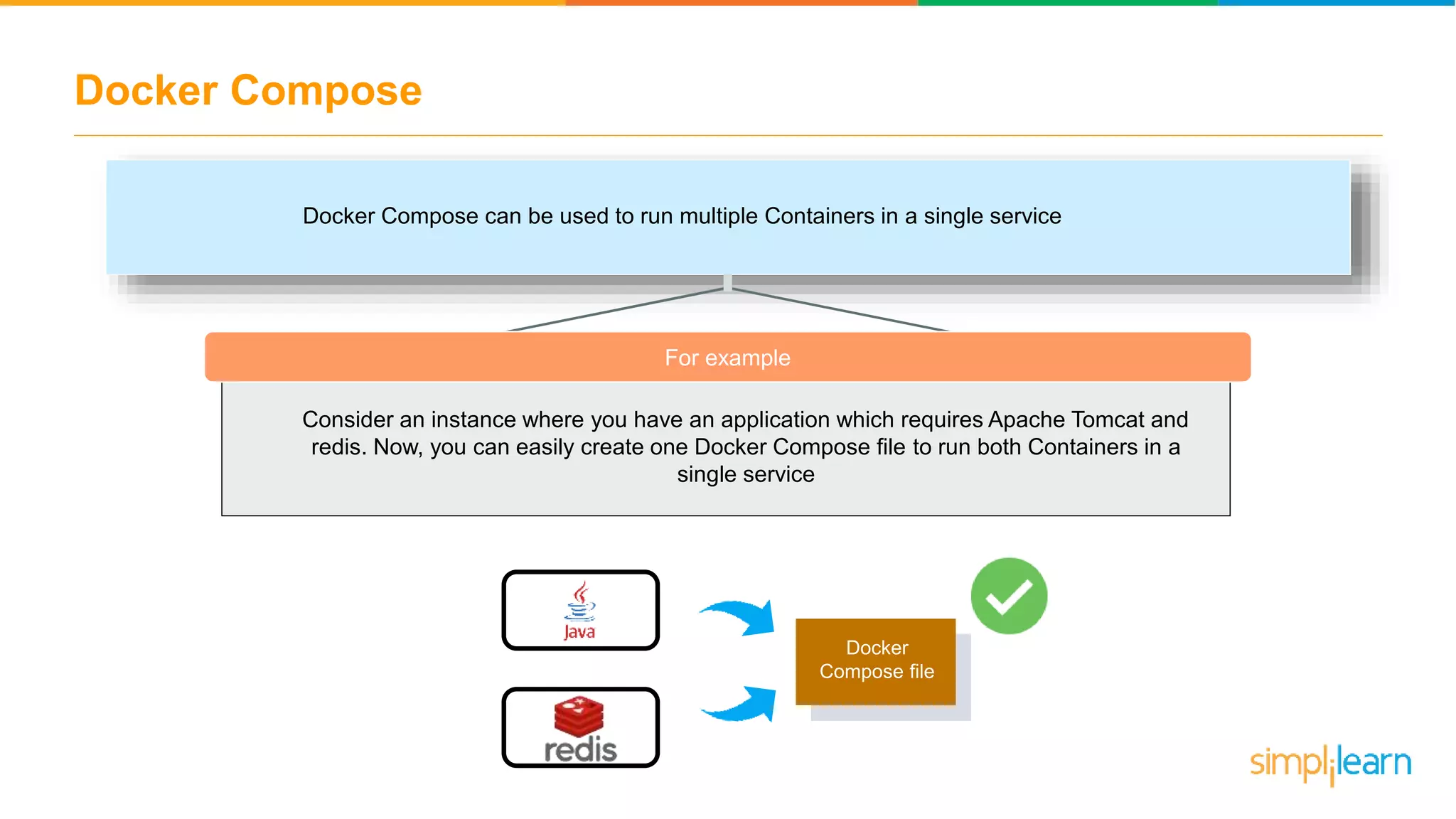
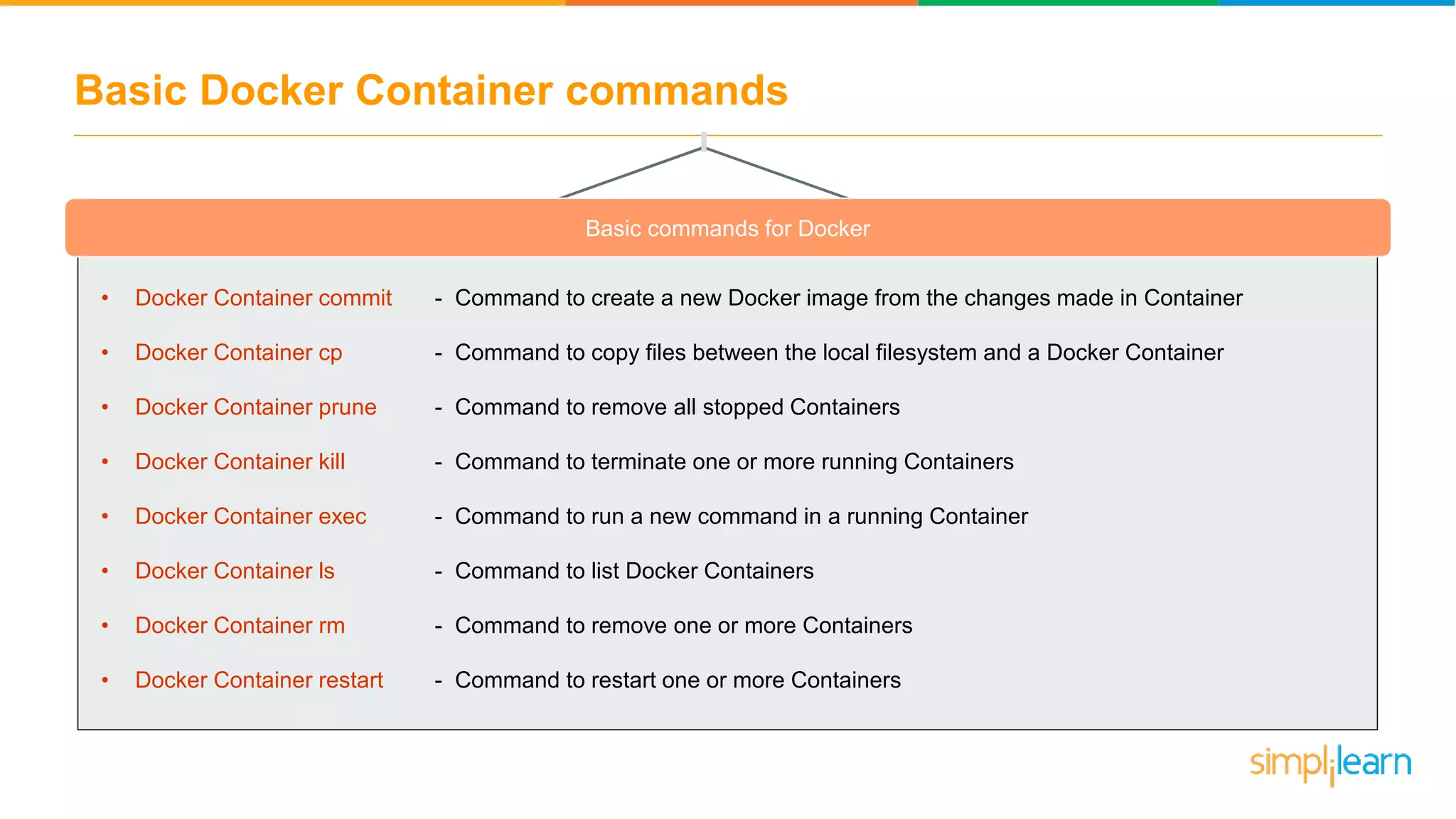
The document discusses the concept and benefits of Docker containers as a solution for application development and deployment. It highlights how Docker simplifies the packaging of applications with their dependencies, allowing them to run consistently across different environments, as well as improving efficiency compared to traditional virtual machine setups. The document also covers the architecture of Docker, the process of creating containers, and key commands for managing them.