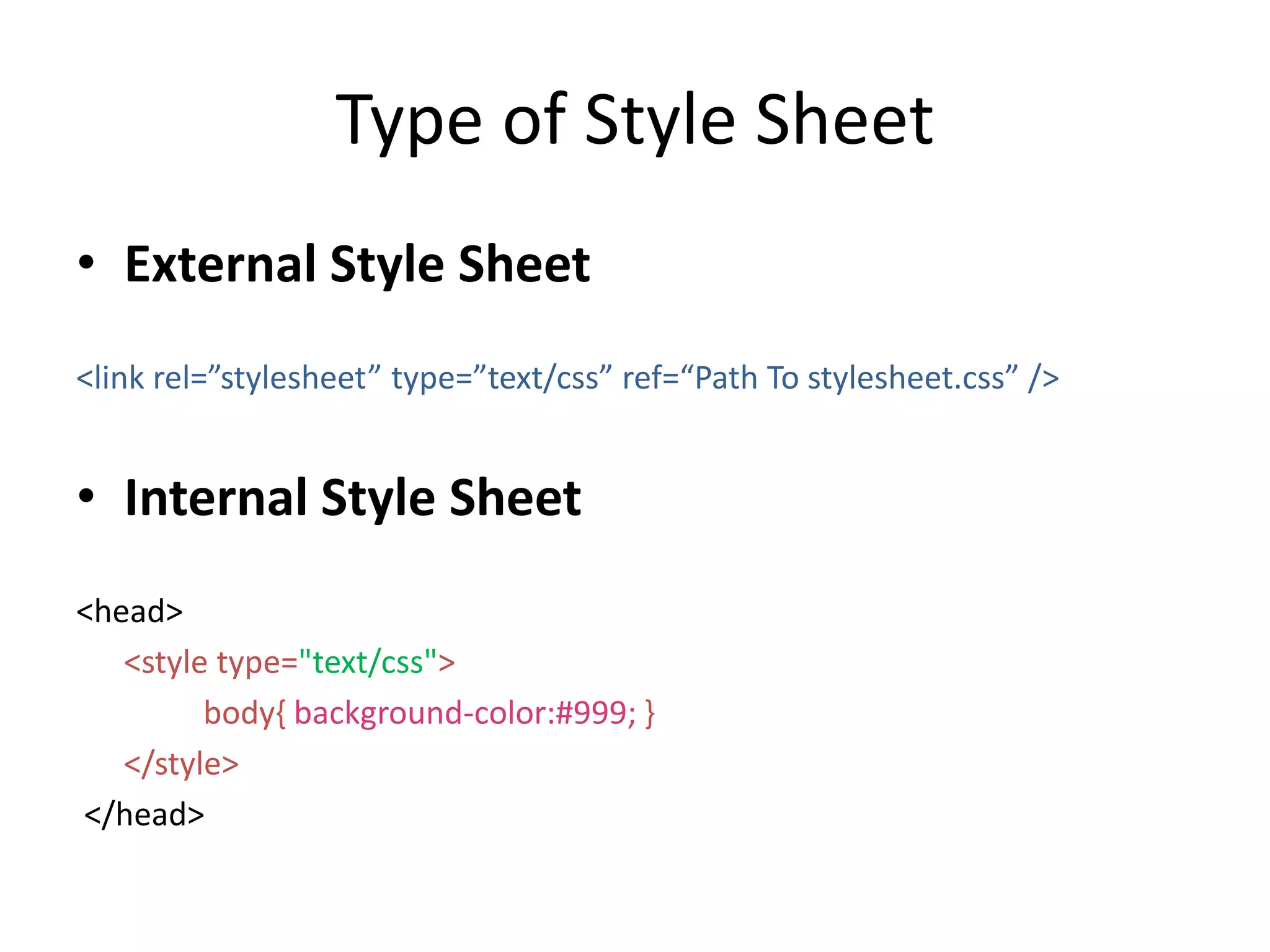
The document provides a detailed overview of web applications, discussing static and dynamic websites, web browsers, web servers, URLs, and HTTP/HTTPS protocols. It explains web hosting, the importance of local servers for testing, and highlights advantages of websites for businesses. It also introduces HTML and CSS, including their functions, basic tags, and benefits, emphasizing the roles of these technologies in web development.