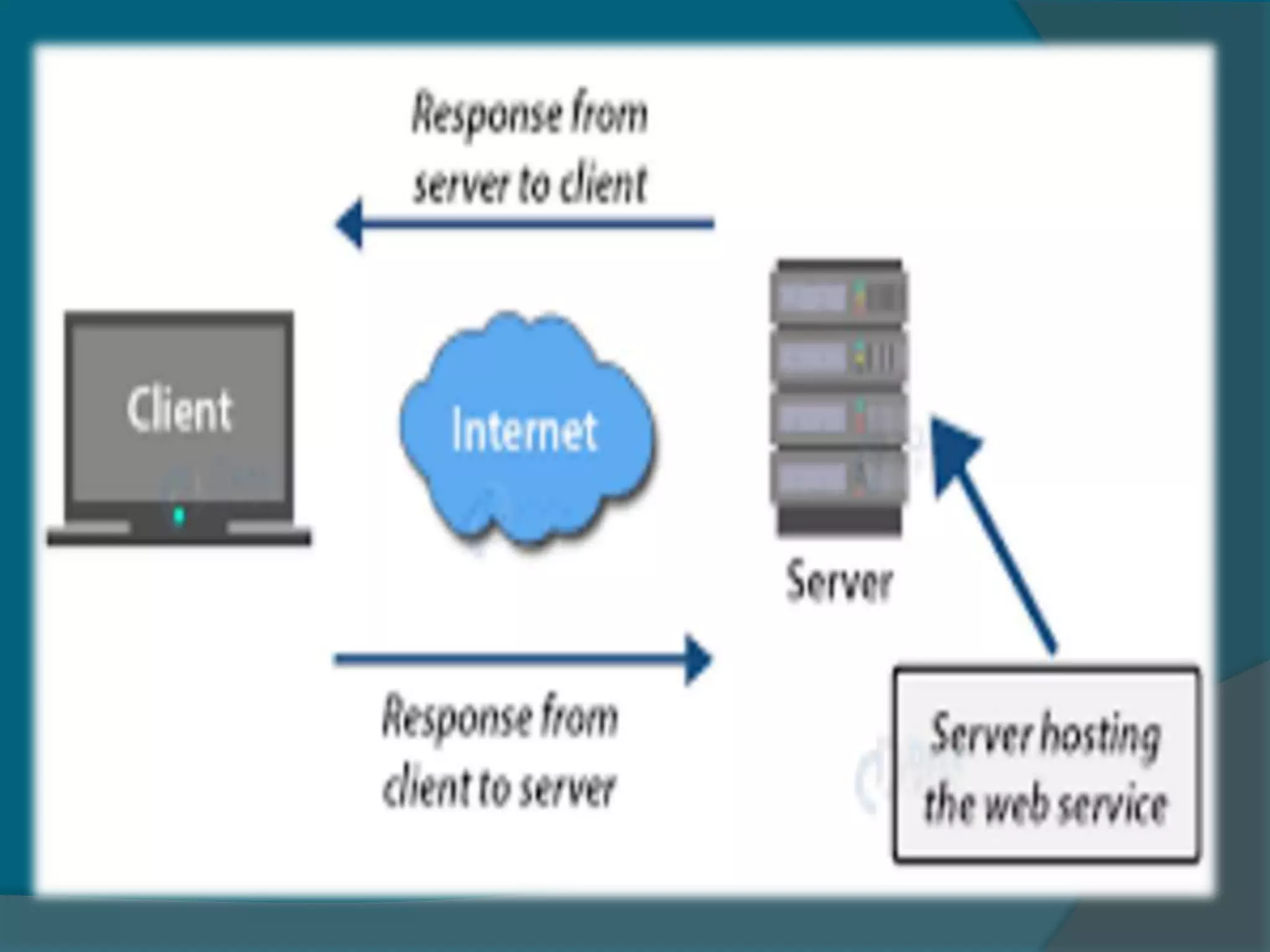
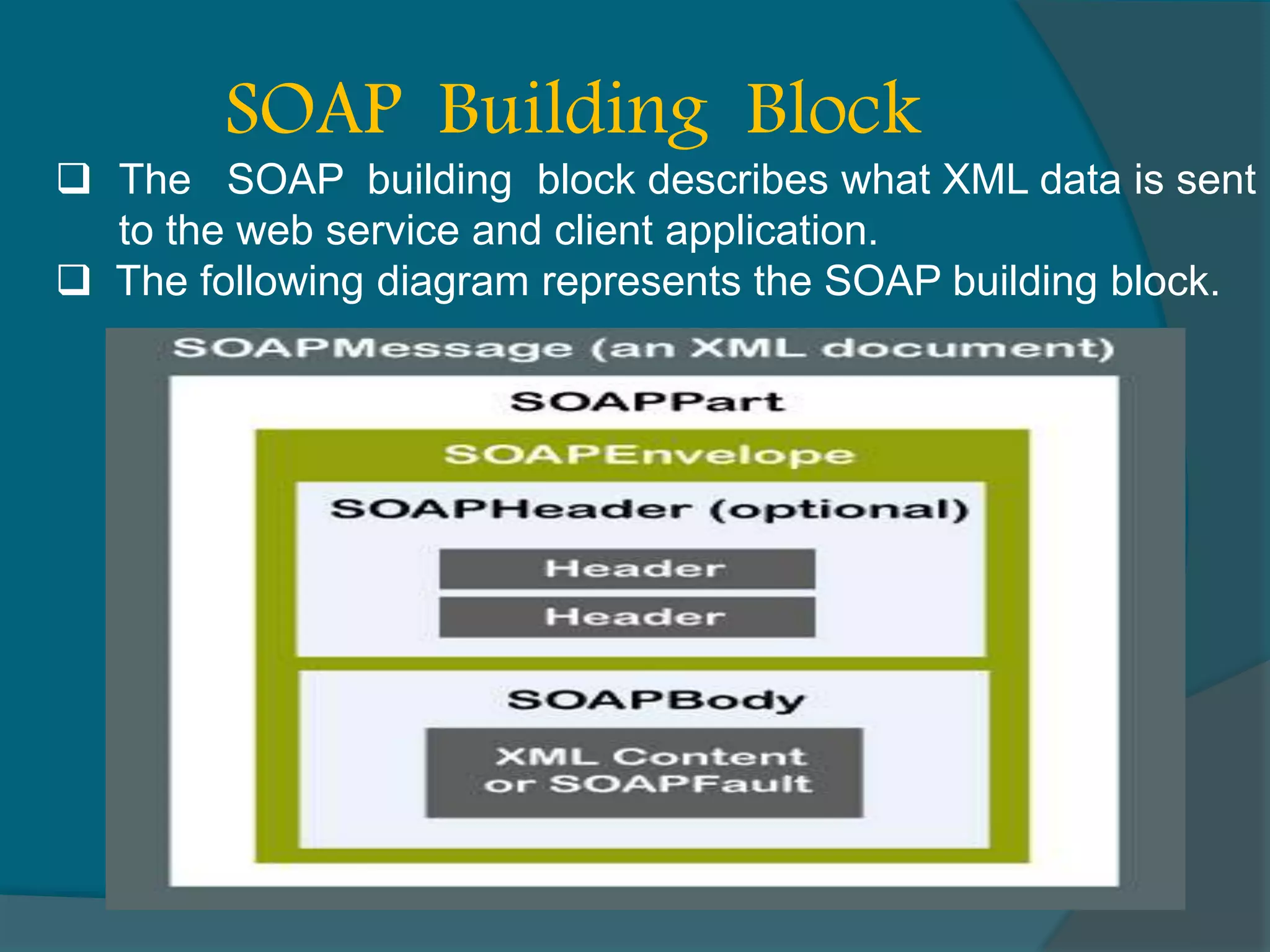
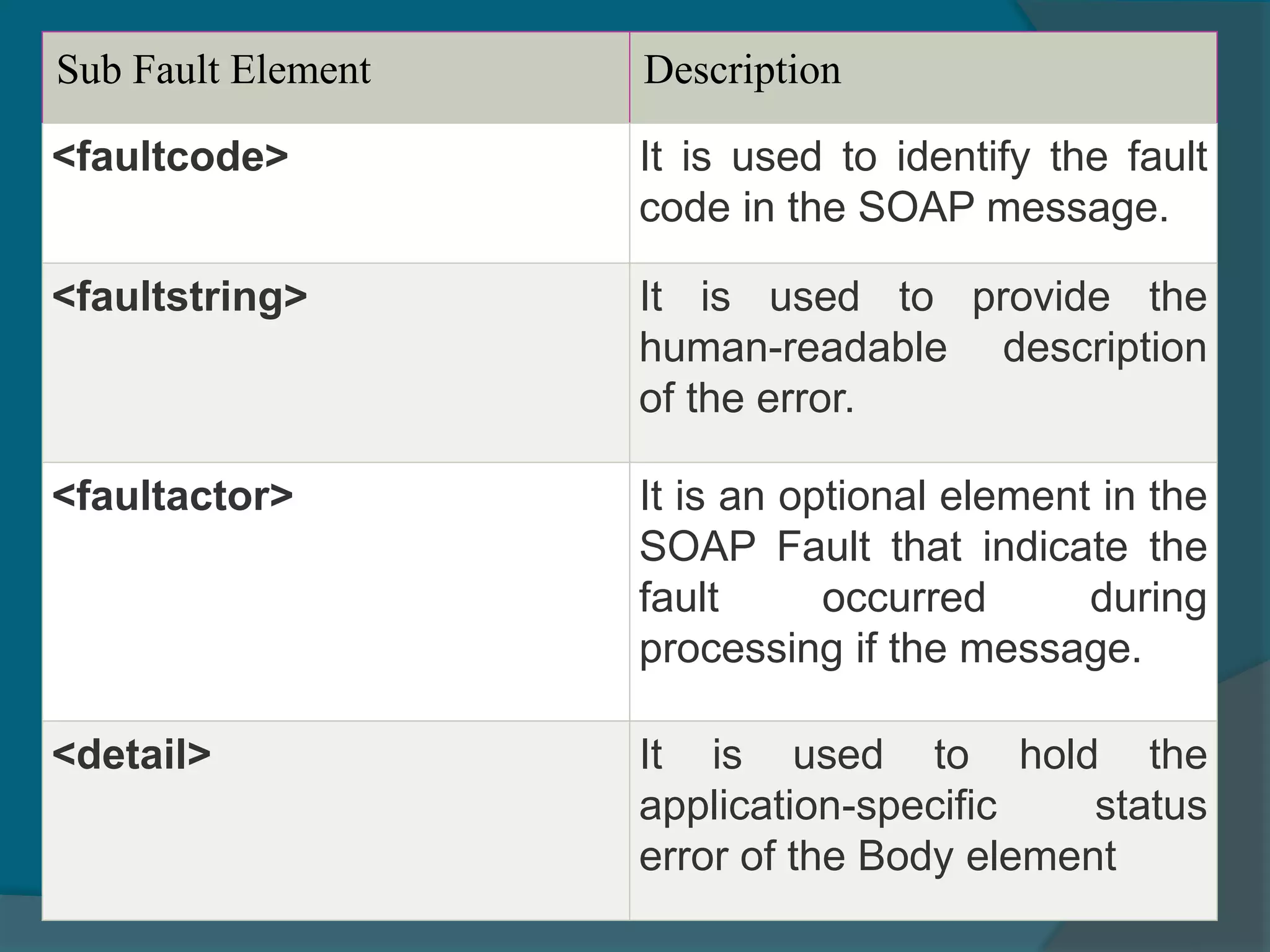
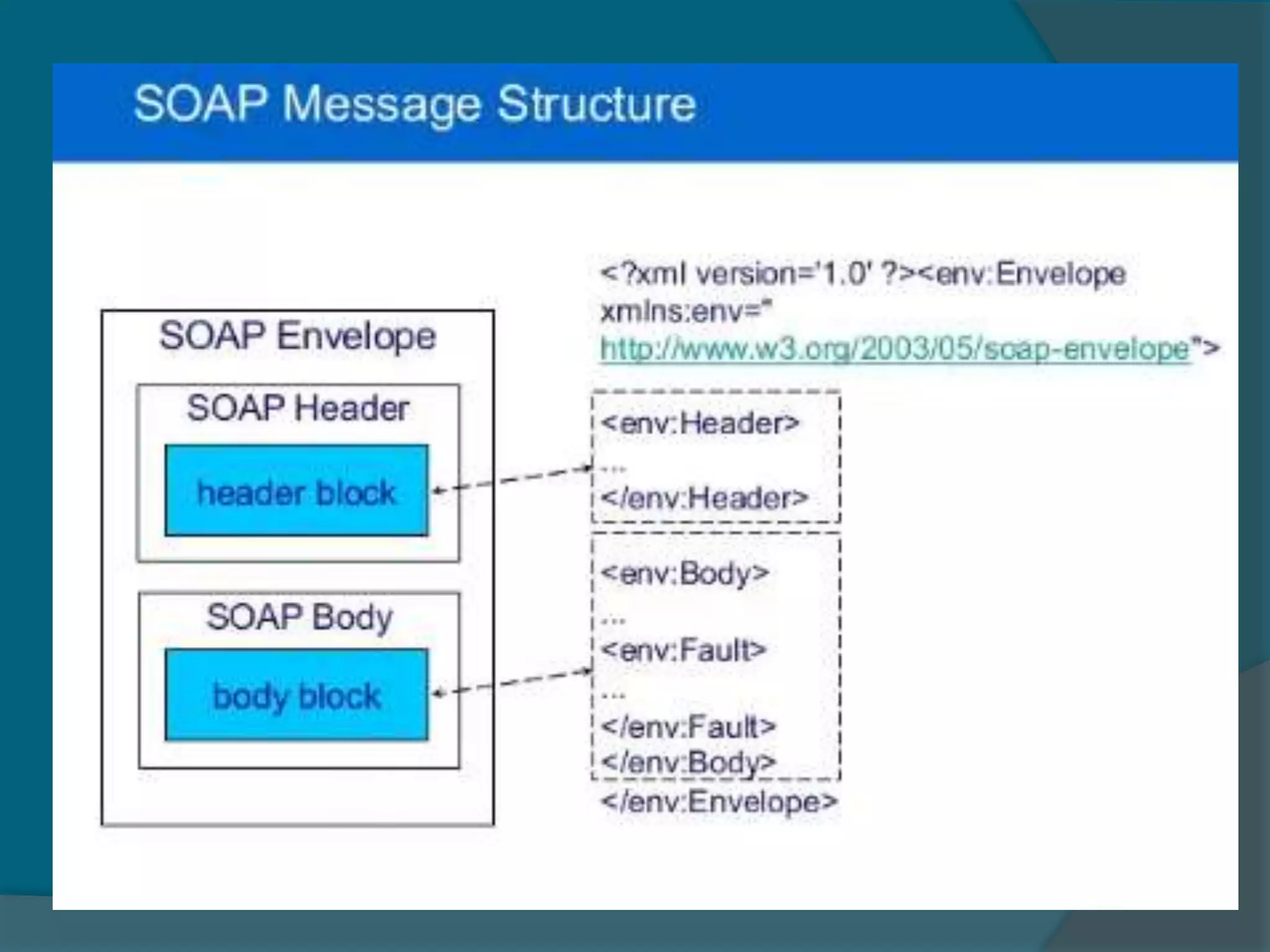
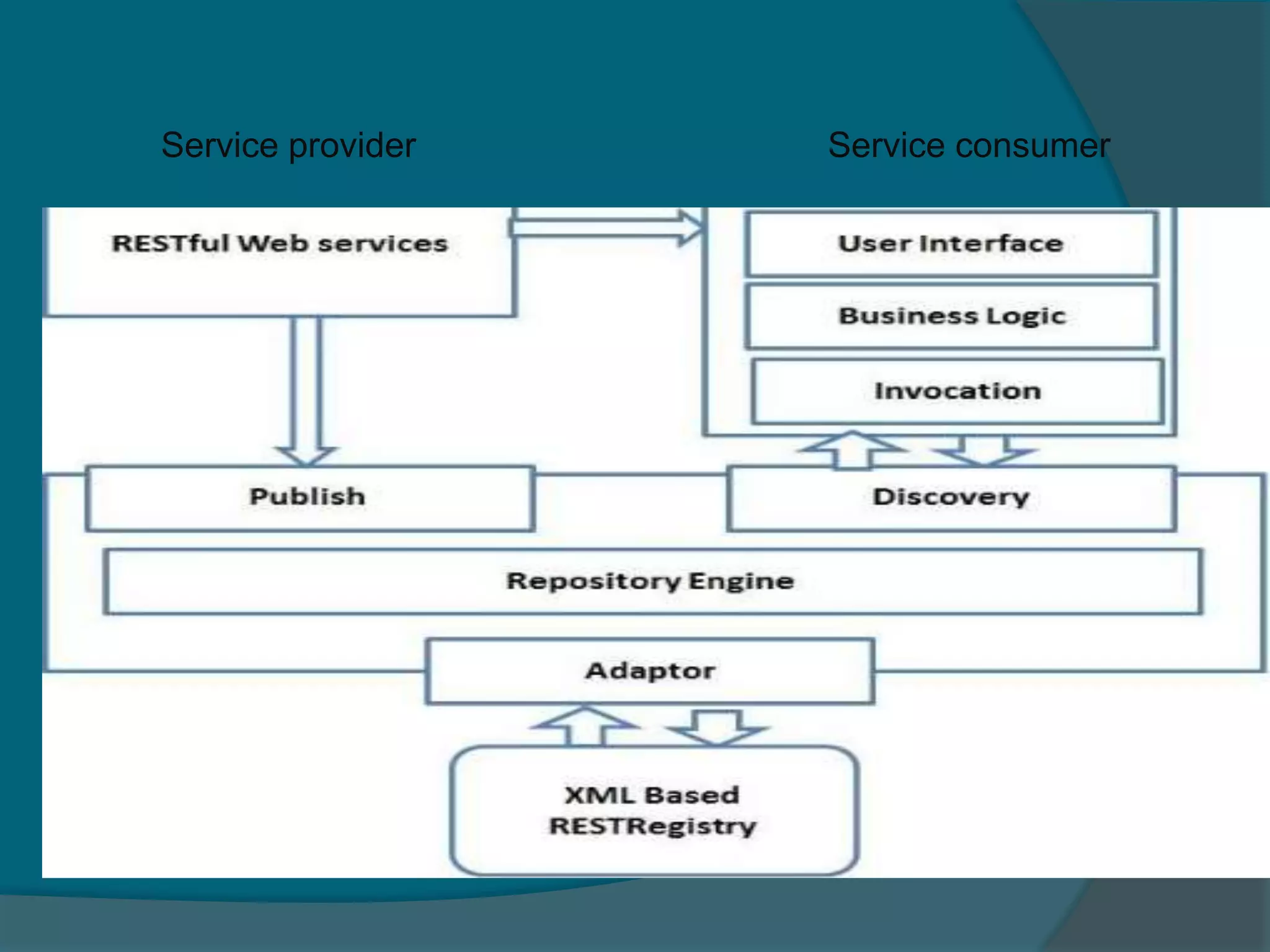
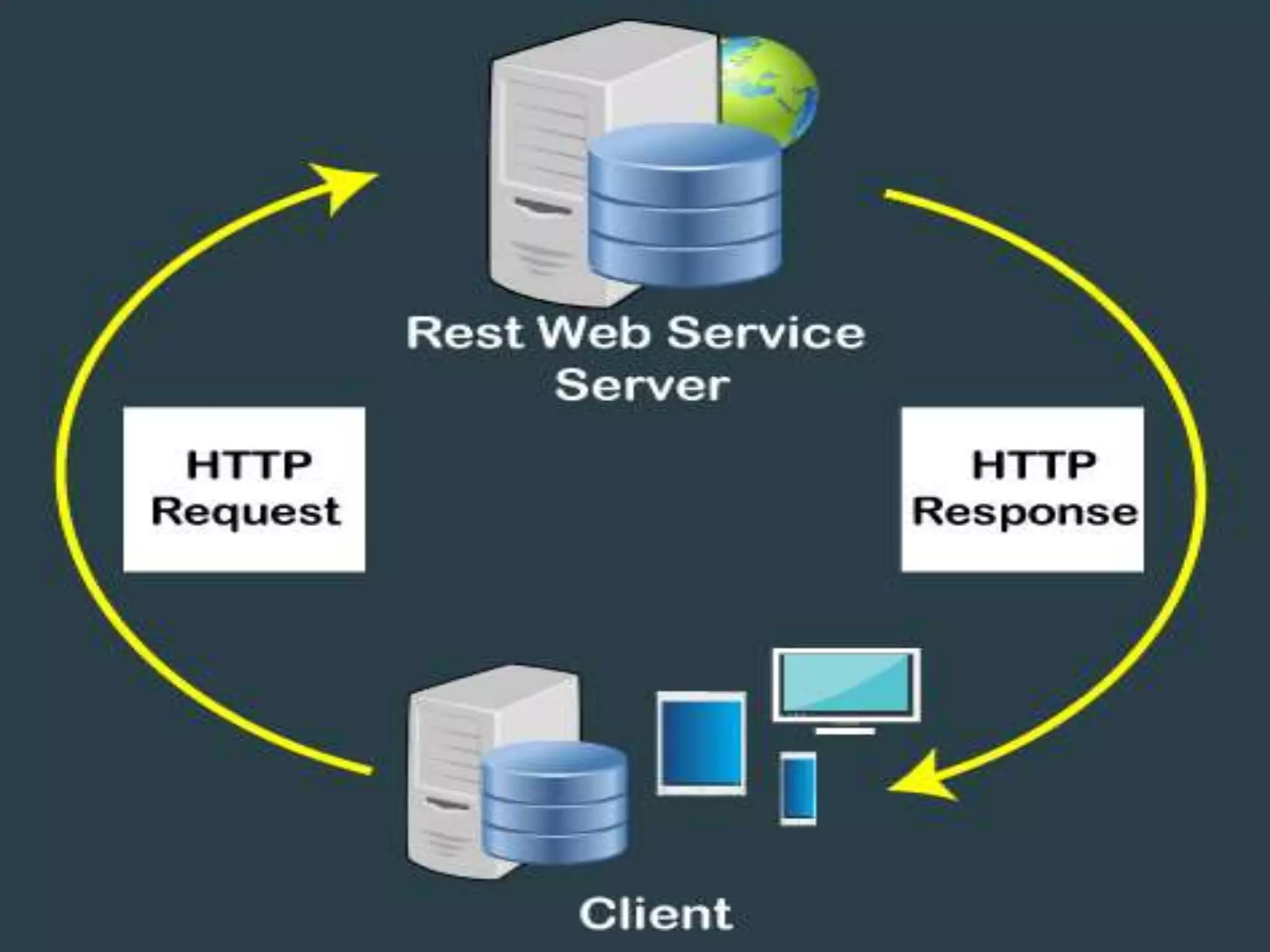
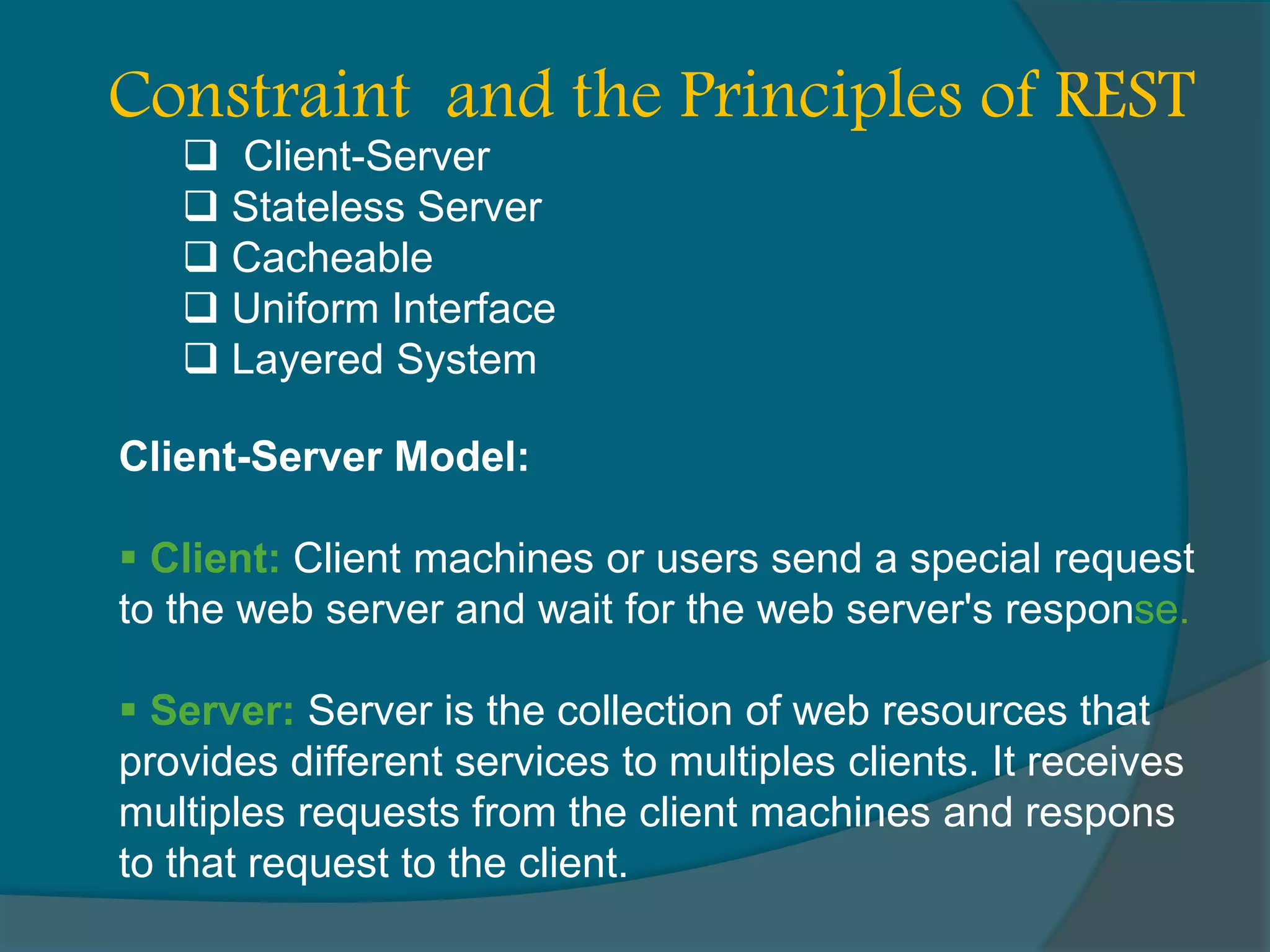
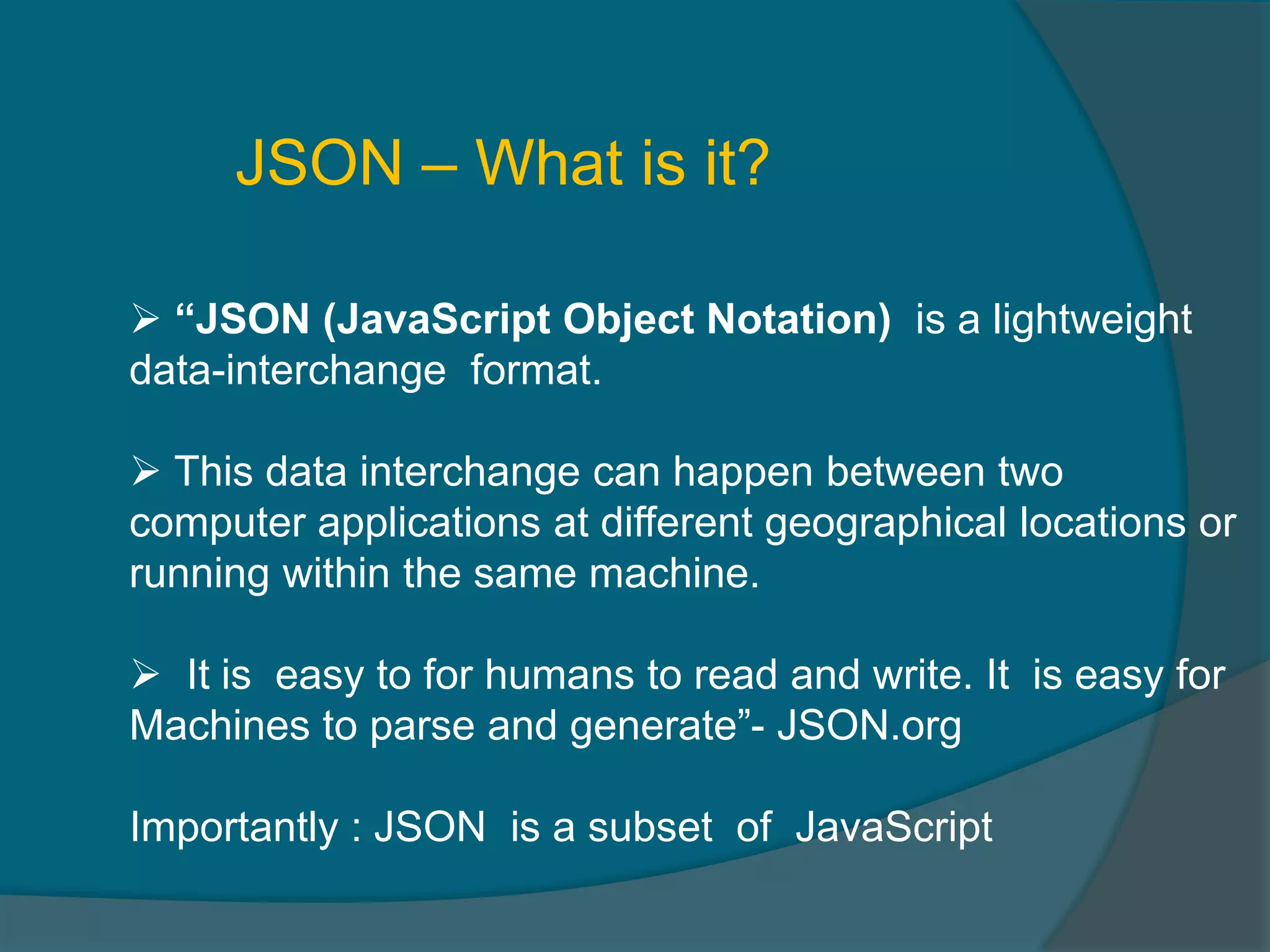
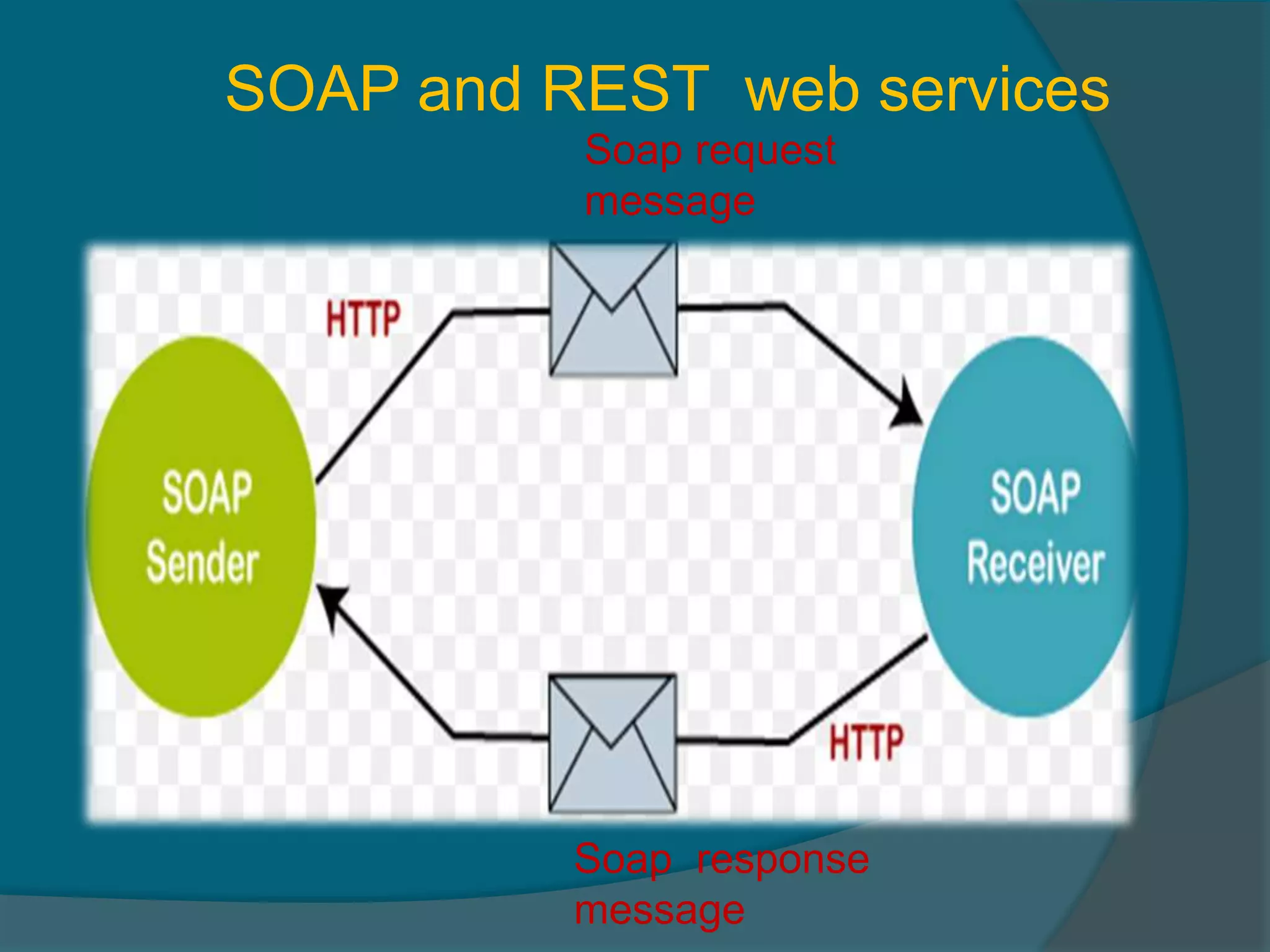
This document provides an overview of publishing and consuming web services. It defines web services and discusses SOAP and REST-based web services. SOAP web services use XML and HTTP, have advantages like language independence but disadvantages like being slow. REST services operate on resources using HTTP methods and have constraints like being stateless and cacheable. The document also discusses JSON web services and schemas for describing REST interfaces.