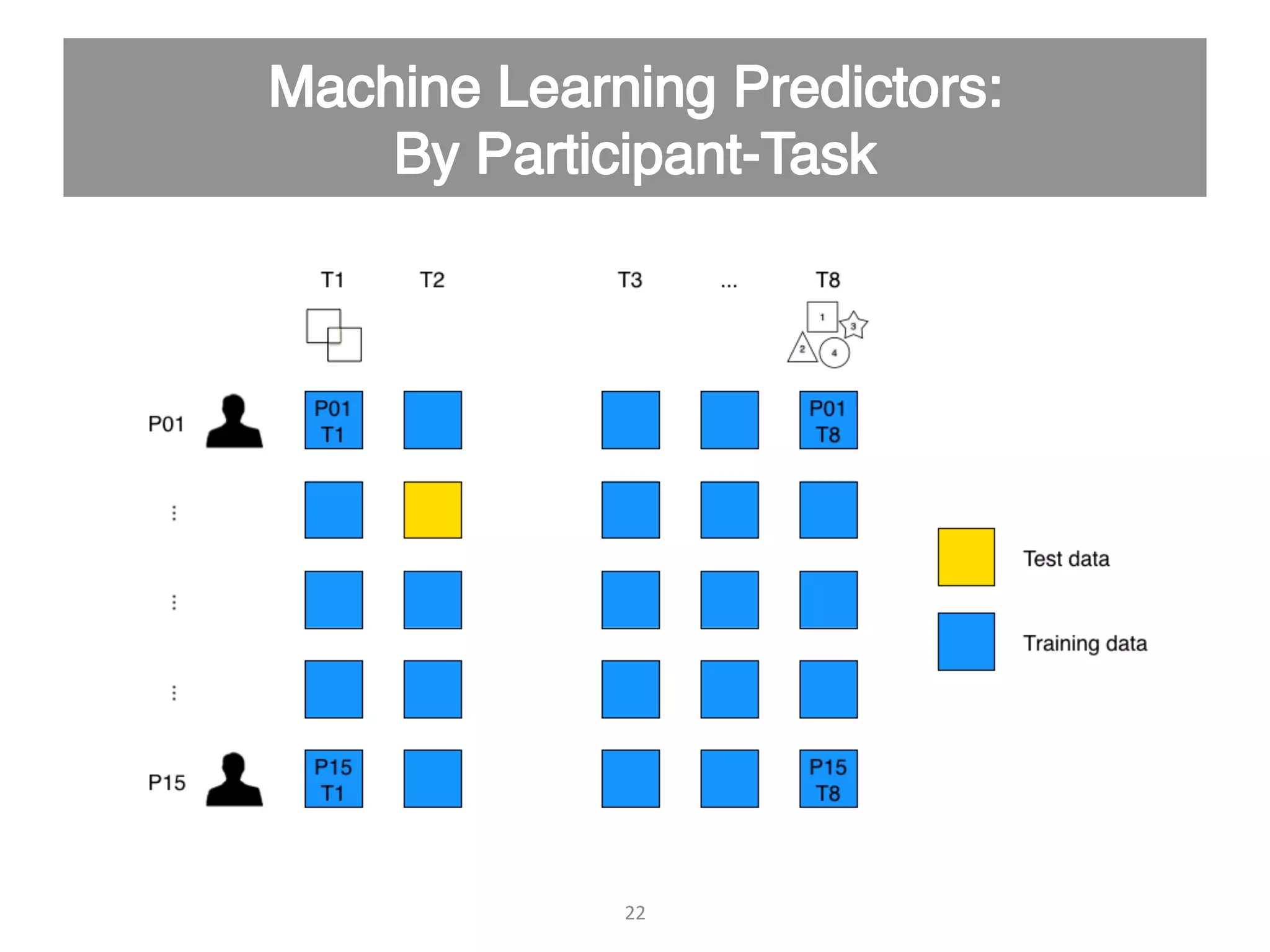
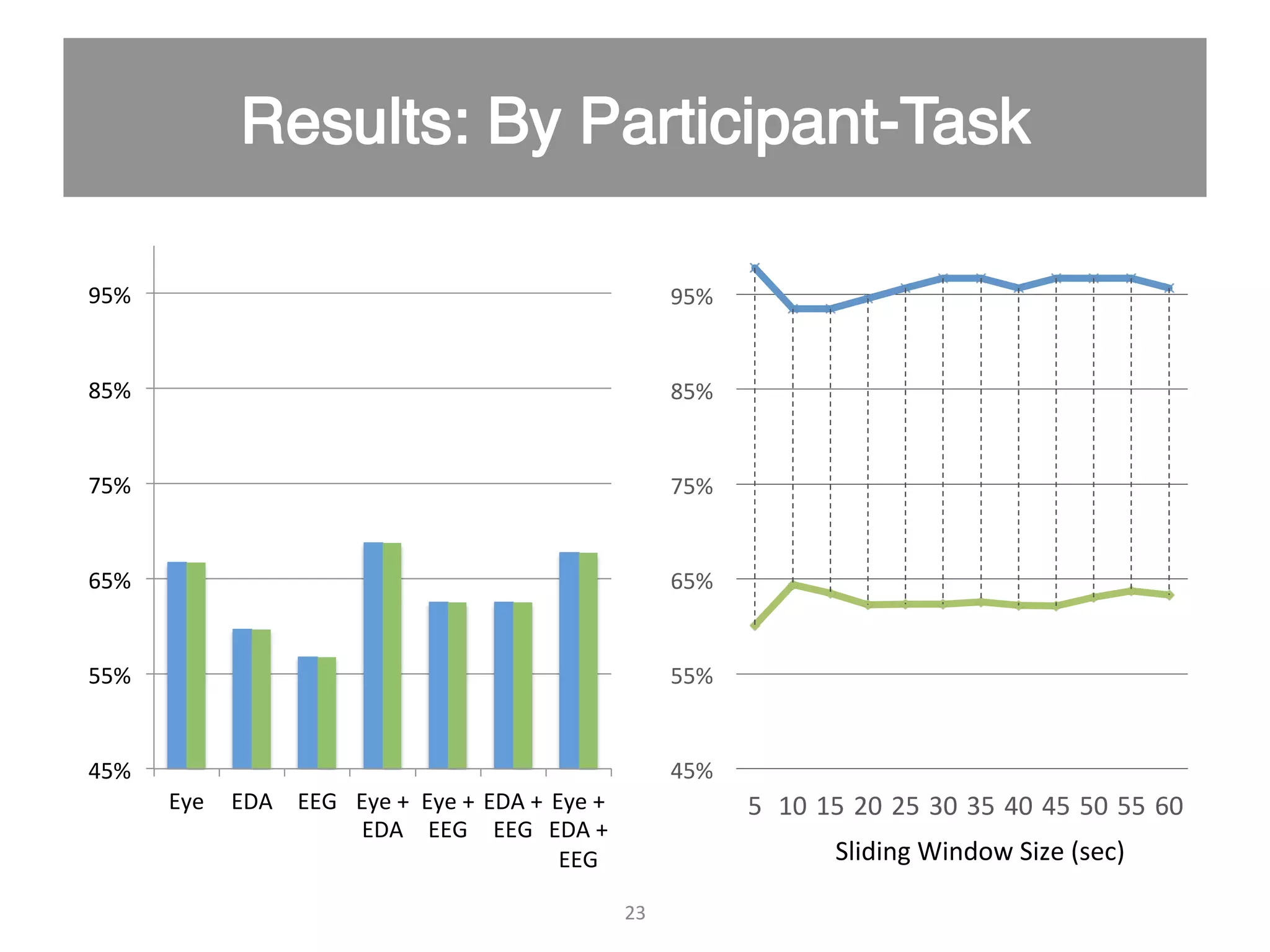
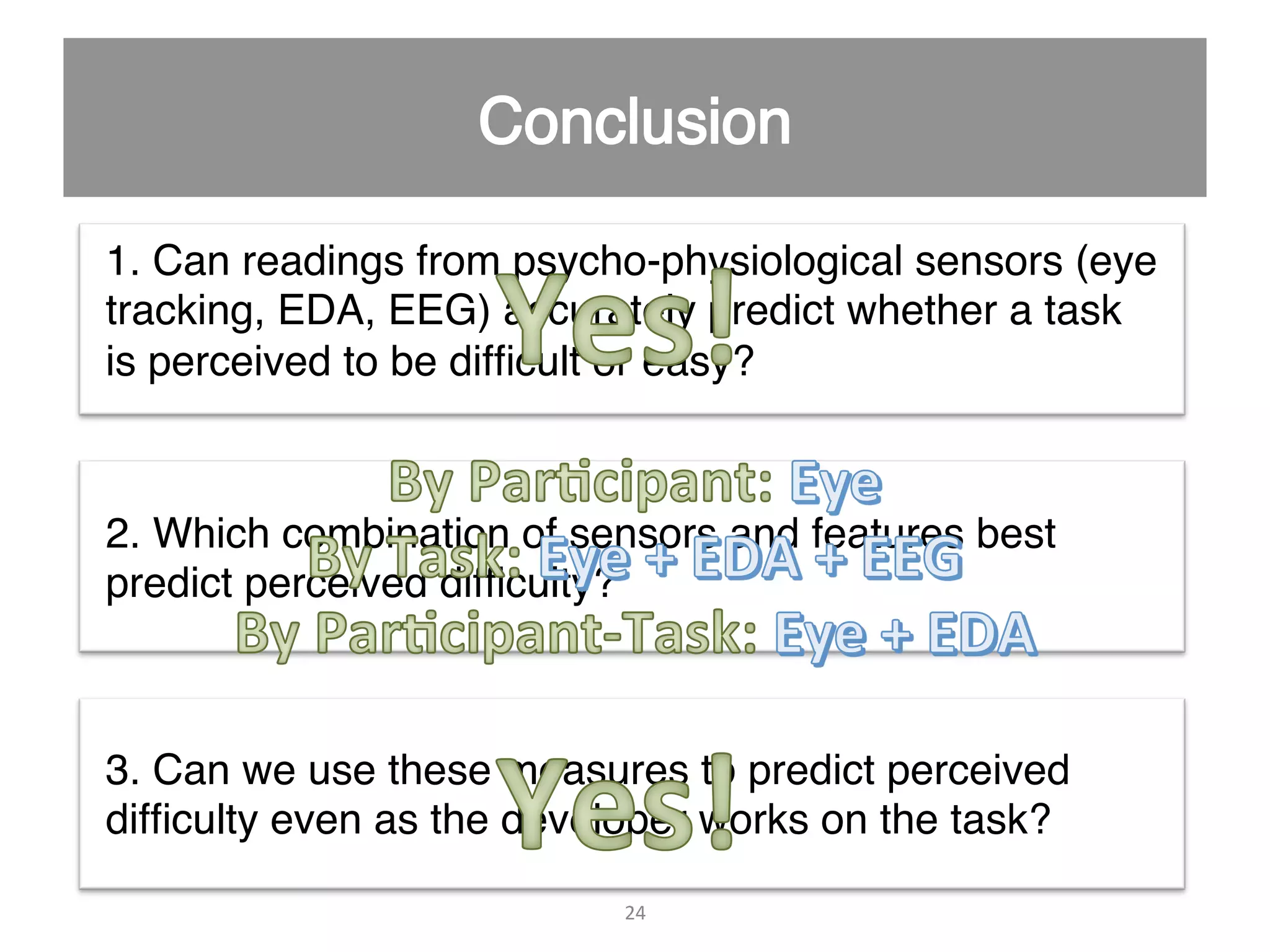
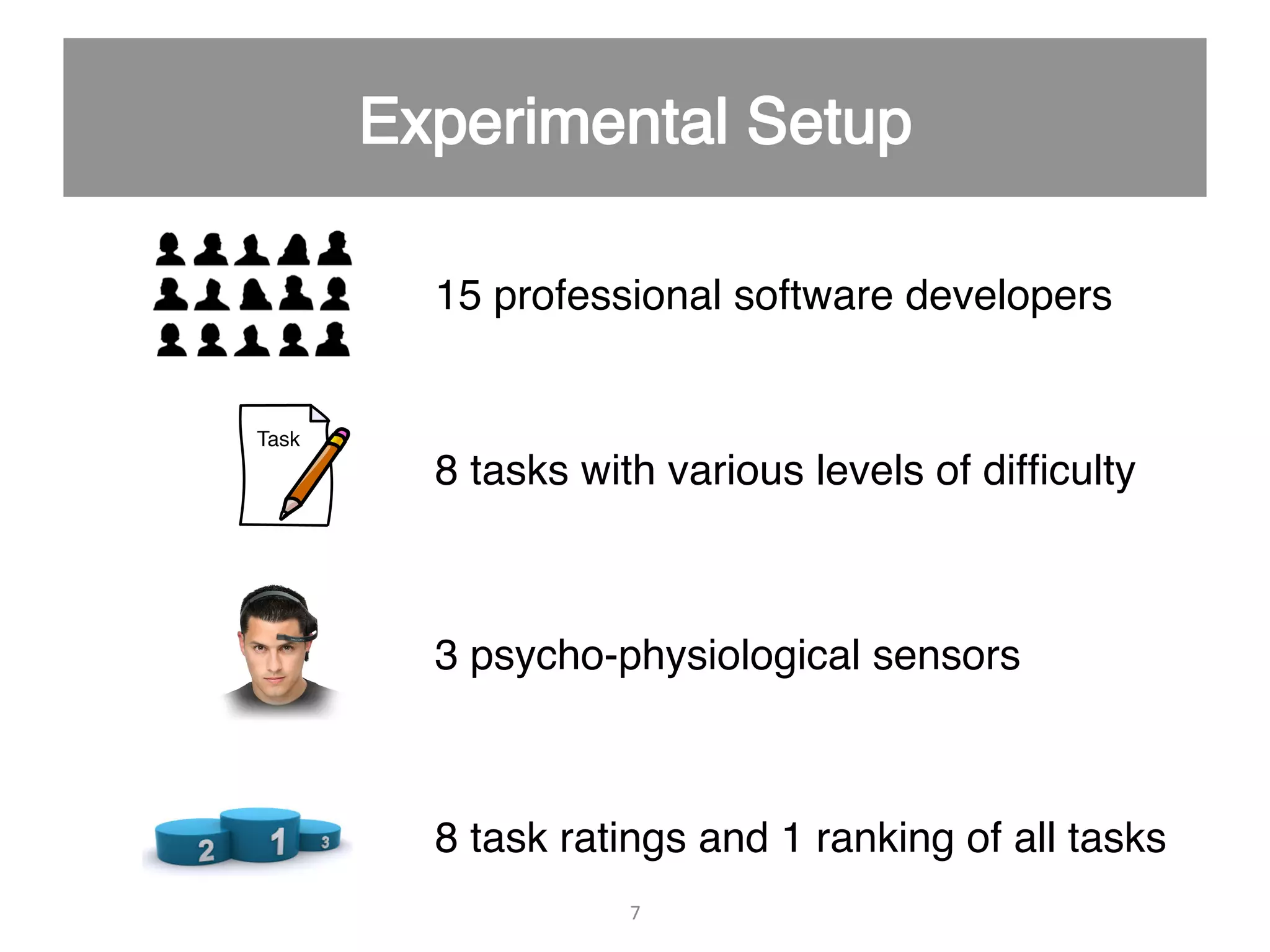
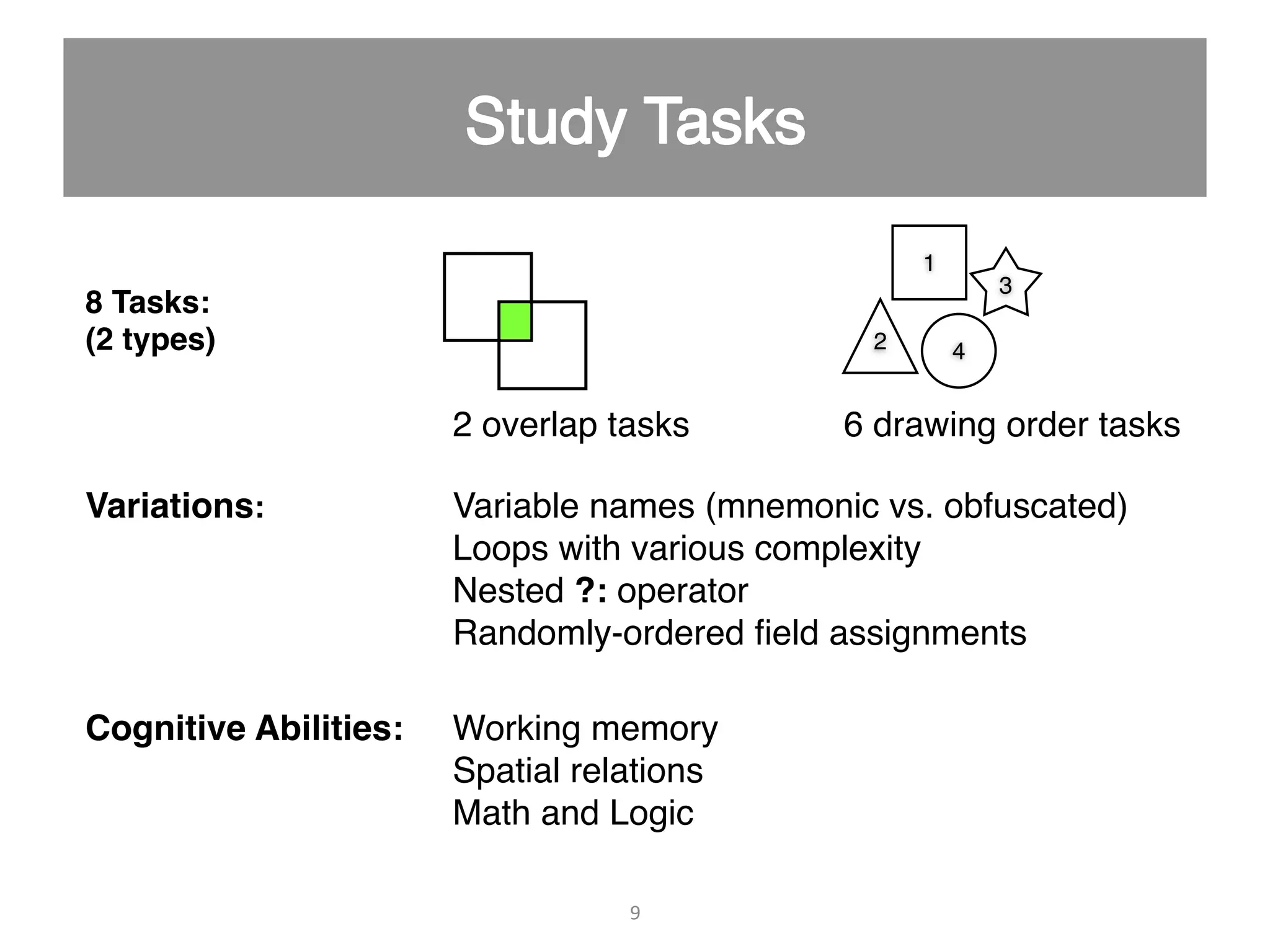
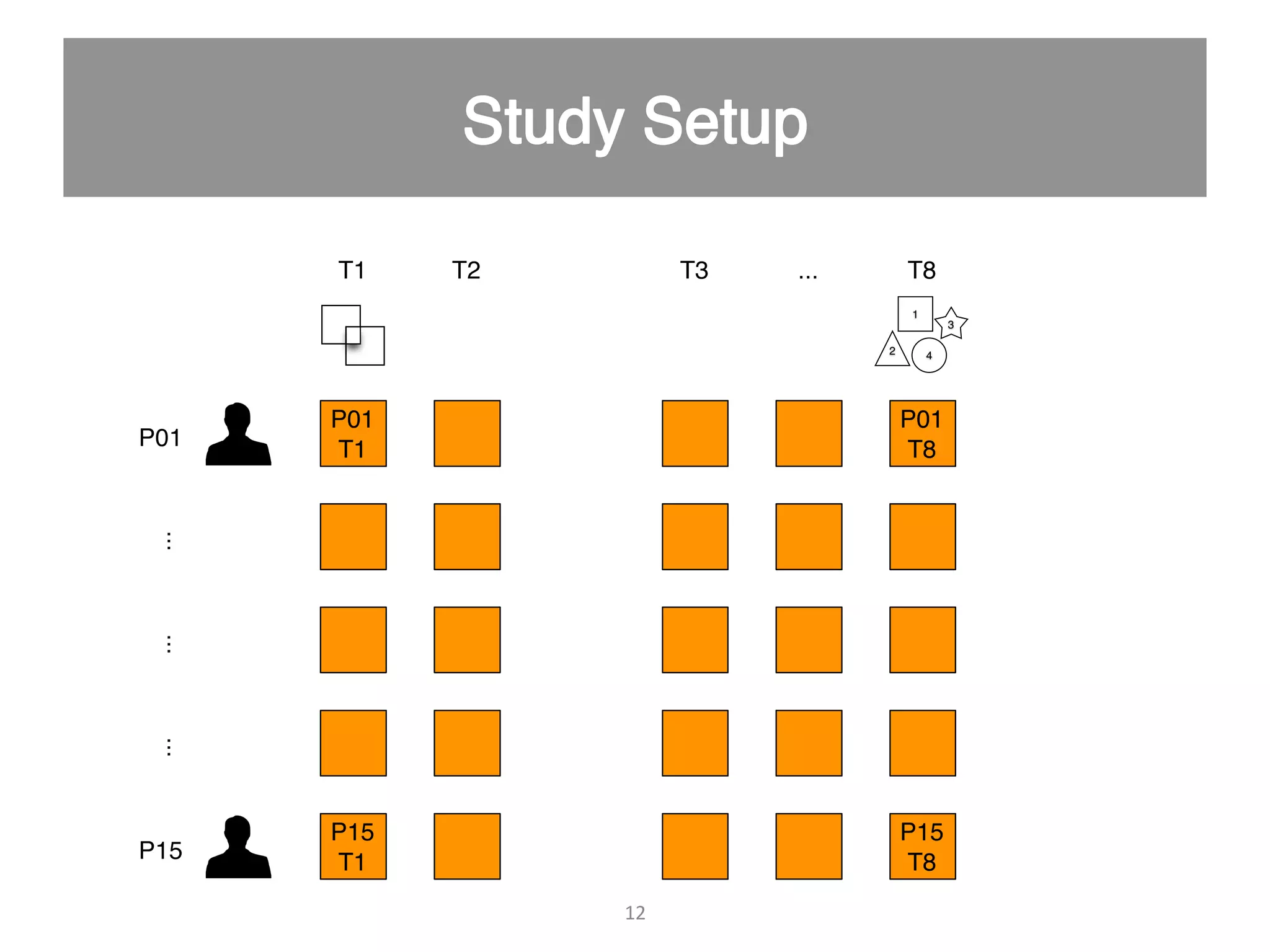
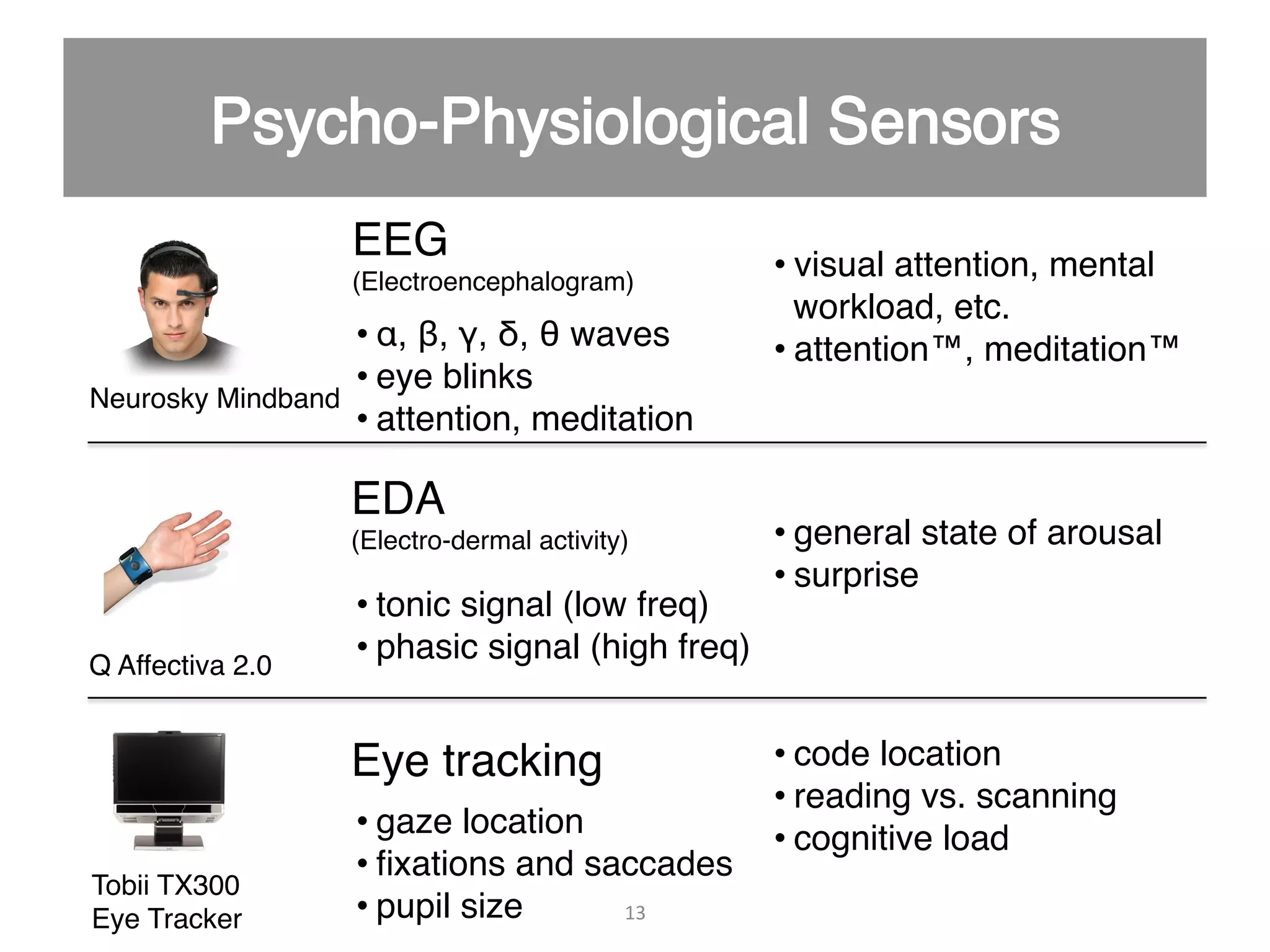
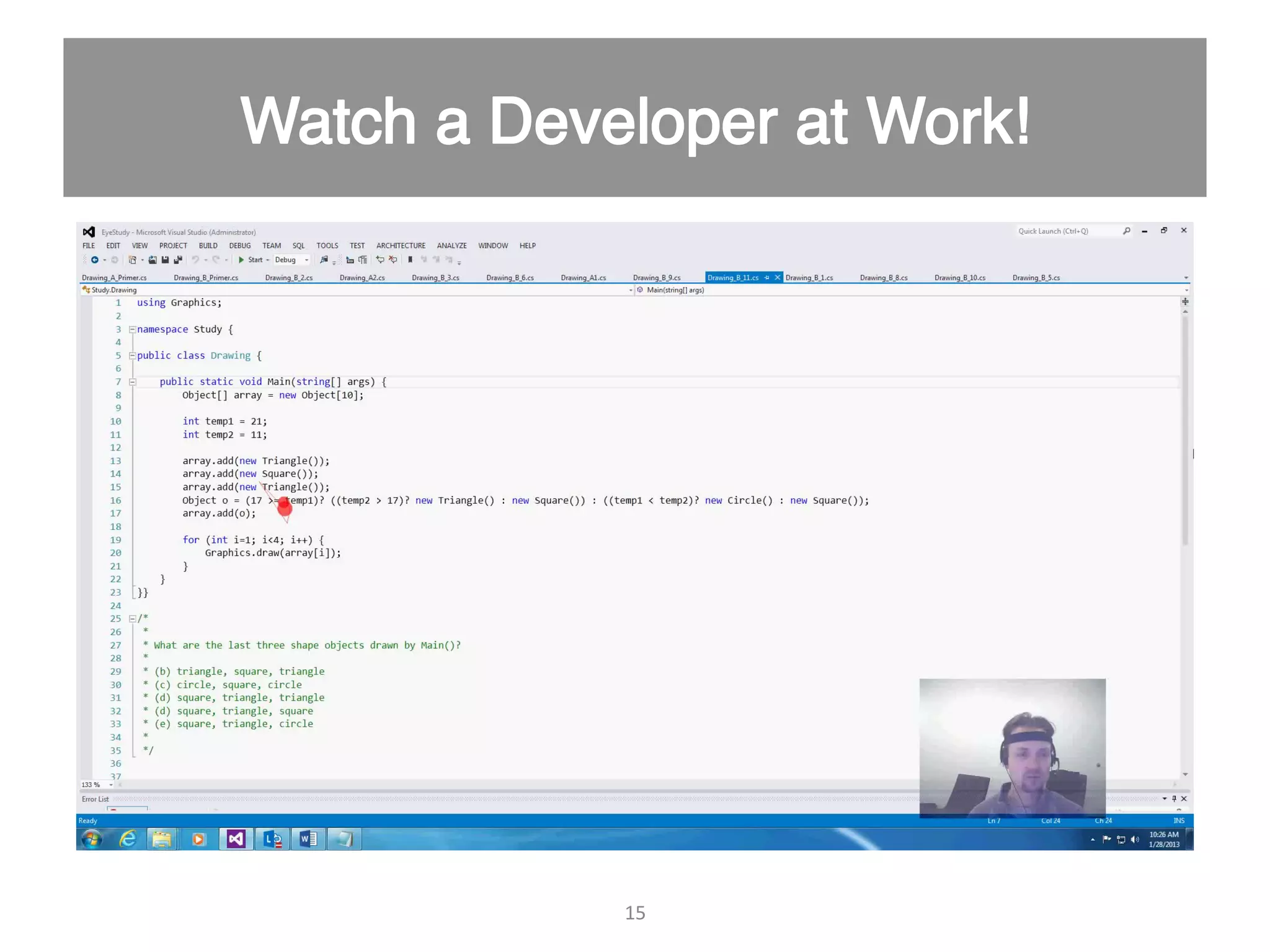
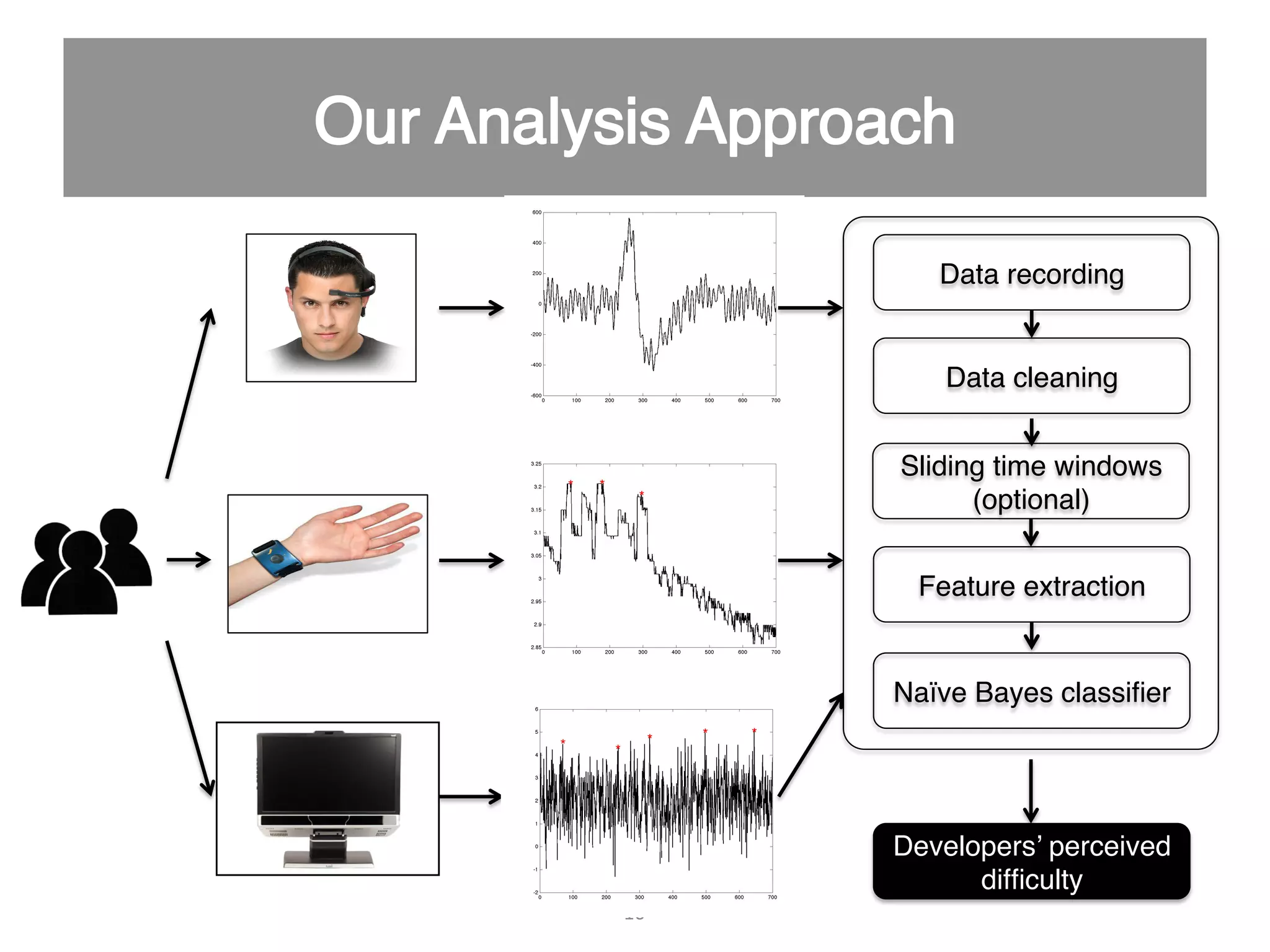
This document discusses using psycho-physiological sensors to analyze the cognitive and emotional states of software developers in relation to task difficulty and productivity. The study seeks to correlate these states with perceived task difficulty and long-term outcomes such as bug rates and productivity, testing various combinations of sensors. The findings suggest that integrating multiple metrics could enhance understanding of developers' experiences and improve software engineering practices.

![using Graphics; namespace Study { public class Drawing { public static void Main(string[] args) { Circle c = new Circle(); Triangle t1 = new Triangle(); Square s = new Square(); Triangle t2 = new Triangle(); Graphics.draw(t2); Graphics.draw(t1); Graphics.draw(c); Graphics.draw(s); } } } using Graphics; namespace Study { public class Drawing { public static void Main(string[] args) { Object objectA = new Circle(); Object objectK = new Circle(); Object objectX = new Square(); Object objectB = new Triangle(); Graphics.draw(objectX); Graphics.draw(objectA); Graphics.draw(objectB); Graphics.draw(objectK); } } } 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usingpsycho-physiologicalsensorstoassesstaskdifficultyinsoftwaredevelopment-140604115034-phpapp01/75/Using-psycho-physiological-sensors-to-assess-task-difficulty-in-software-development-2-2048.jpg)





![10 using Graphics; namespace Study { class Drawing { public static void Main(string[] args) { Rectangle t = new Rectangle(); t.leftBottom = new Point(2,2); t.leftTop = new Point(2,6); t.rightTop = new Point(6,6); t.rightBottom = new Point(6,2); Graphics.draw(t); Rectangle s = new Rectangle(); s.leftTop = new Point(11,5); s.leftBottom = new Point(5,5); s.rightBottom = new Point(5,9); s.rightTop = new Point(11,9); Graphics.draw(s); } }} Do these rectangles overlap?"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usingpsycho-physiologicalsensorstoassesstaskdifficultyinsoftwaredevelopment-140604115034-phpapp01/75/Using-psycho-physiological-sensors-to-assess-task-difficulty-in-software-development-10-2048.jpg)
![11 using Graphics; namespace Study { class Drawing { public static void Main(string[] args) { Rectangle t = new Rectangle(); t.leftBottom = new Point(2,2); t.leftTop = new Point(2,6); t.rightTop = new Point(6,6); t.rightBottom = new Point(6,2); Graphics.draw(t); Rectangle s = new Rectangle(); s.leftTop = new Point(11,5); s.leftBottom = new Point(5,5); s.rightBottom = new Point(5,9); s.rightTop = new Point(11,9); Graphics.draw(s); } }} using Graphics; namespace Study { class Drawing { public static void Main(string[] args) { Rectangle v = new Rectangle(); v.leftTop = new Point(1,8); Rectangle x = new Rectangle(); x.rightBottom = new Point(13,3); x.rightTop = new Point(13,10); x.leftBottom = new Point(7,3); v.rightTop = new Point(3,8); x.leftTop = new Point(7,10); v.rightBottom = new Point(3,5); Graphics.draw(x); v.leftBottom = new Point(1,5); Graphics.draw(v); } }} Do these rectangles overlap?"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usingpsycho-physiologicalsensorstoassesstaskdifficultyinsoftwaredevelopment-140604115034-phpapp01/75/Using-psycho-physiological-sensors-to-assess-task-difficulty-in-software-development-11-2048.jpg)
![• Task difficulty metrics were highly correlated. " • NASA TLX vs. task difficulty ranking
Spearman: r[116] = 0.587, p < 0.01" • Task difficulty ranking vs. task completion time
Spearman: r[116] = 0.724, p < 0.01" • We created simplified metrics by nominalizing NASA TLX and task difficulty ranking into Boolean easy/difficult." • Correlation: Boolean NASA TLX score vs. Boolean task difficulty
Chi2(1, 116) = 57.954, p < 0.01 (accuracy 85%)" • Triangulation between metrics helps validates our results." 17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usingpsycho-physiologicalsensorstoassesstaskdifficultyinsoftwaredevelopment-140604115034-phpapp01/75/Using-psycho-physiological-sensors-to-assess-task-difficulty-in-software-development-17-2048.jpg)