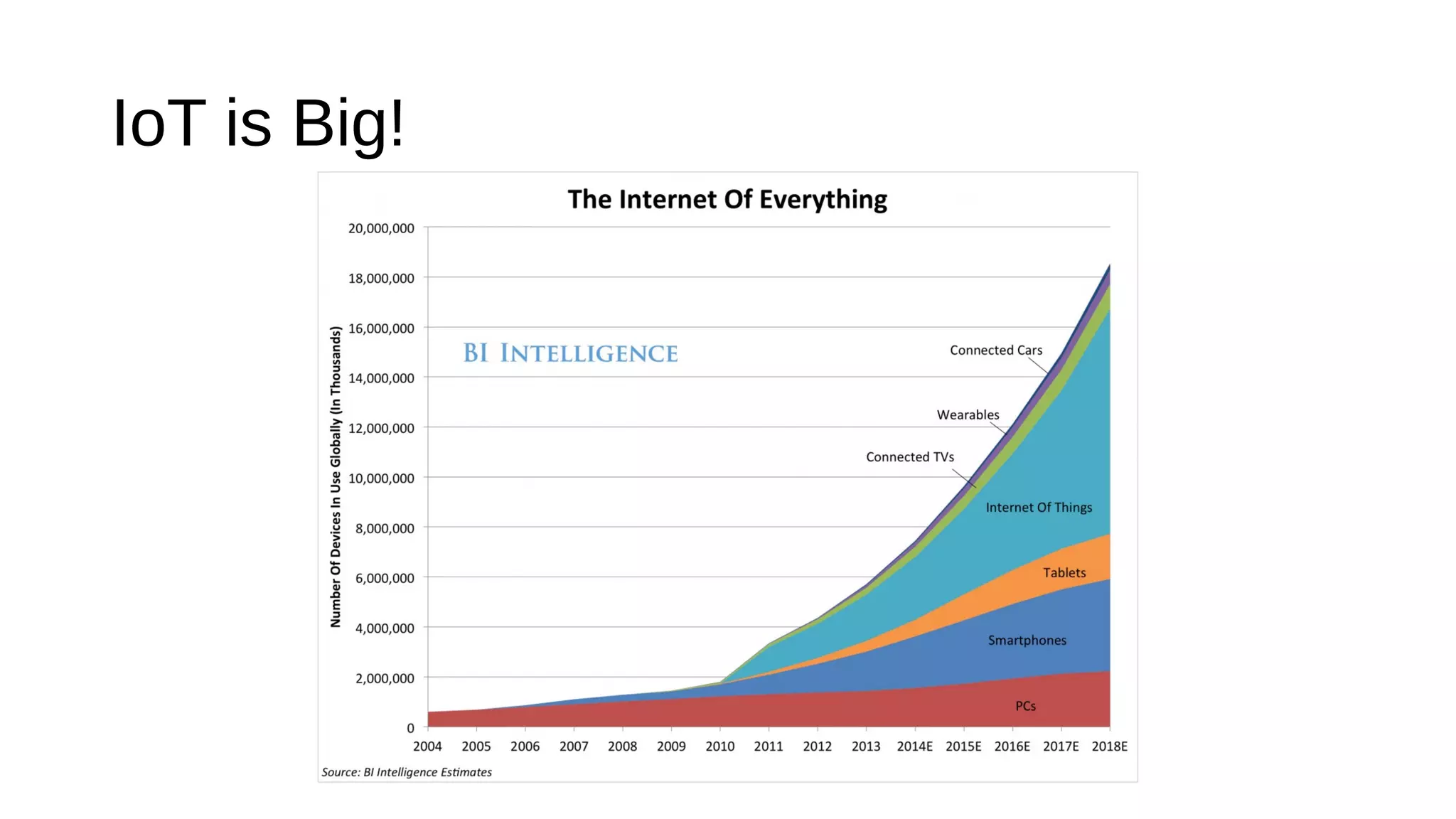
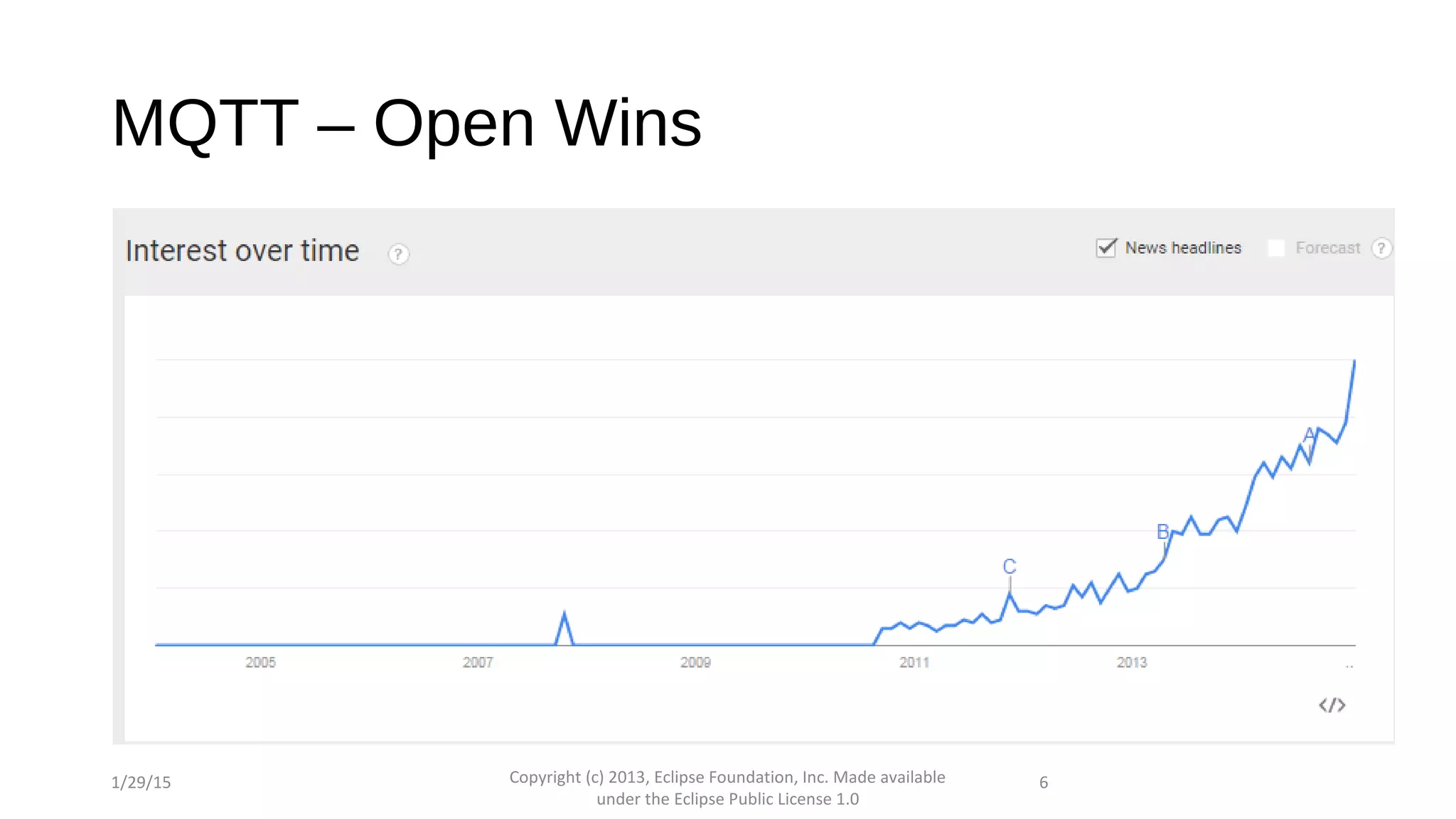
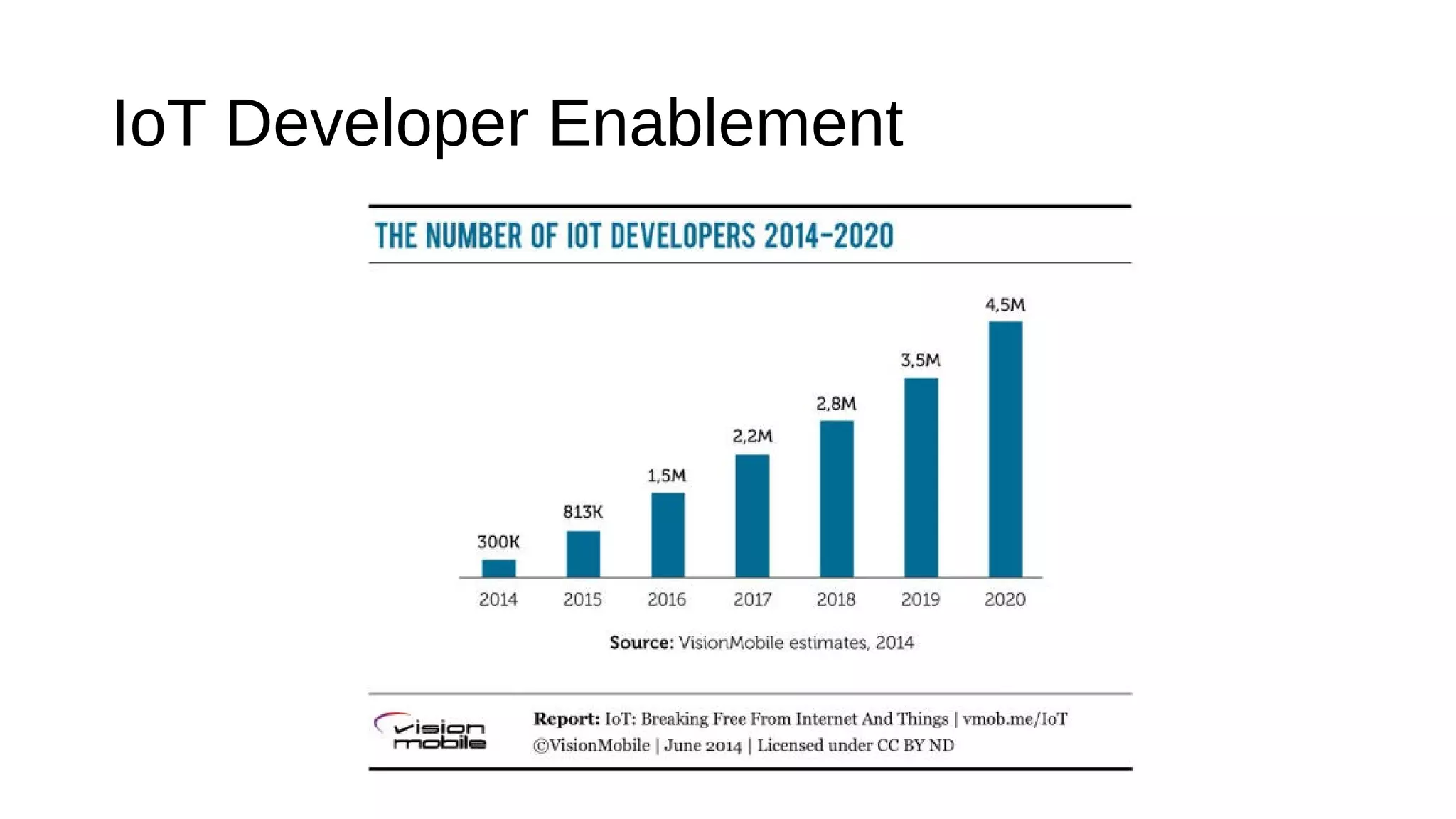
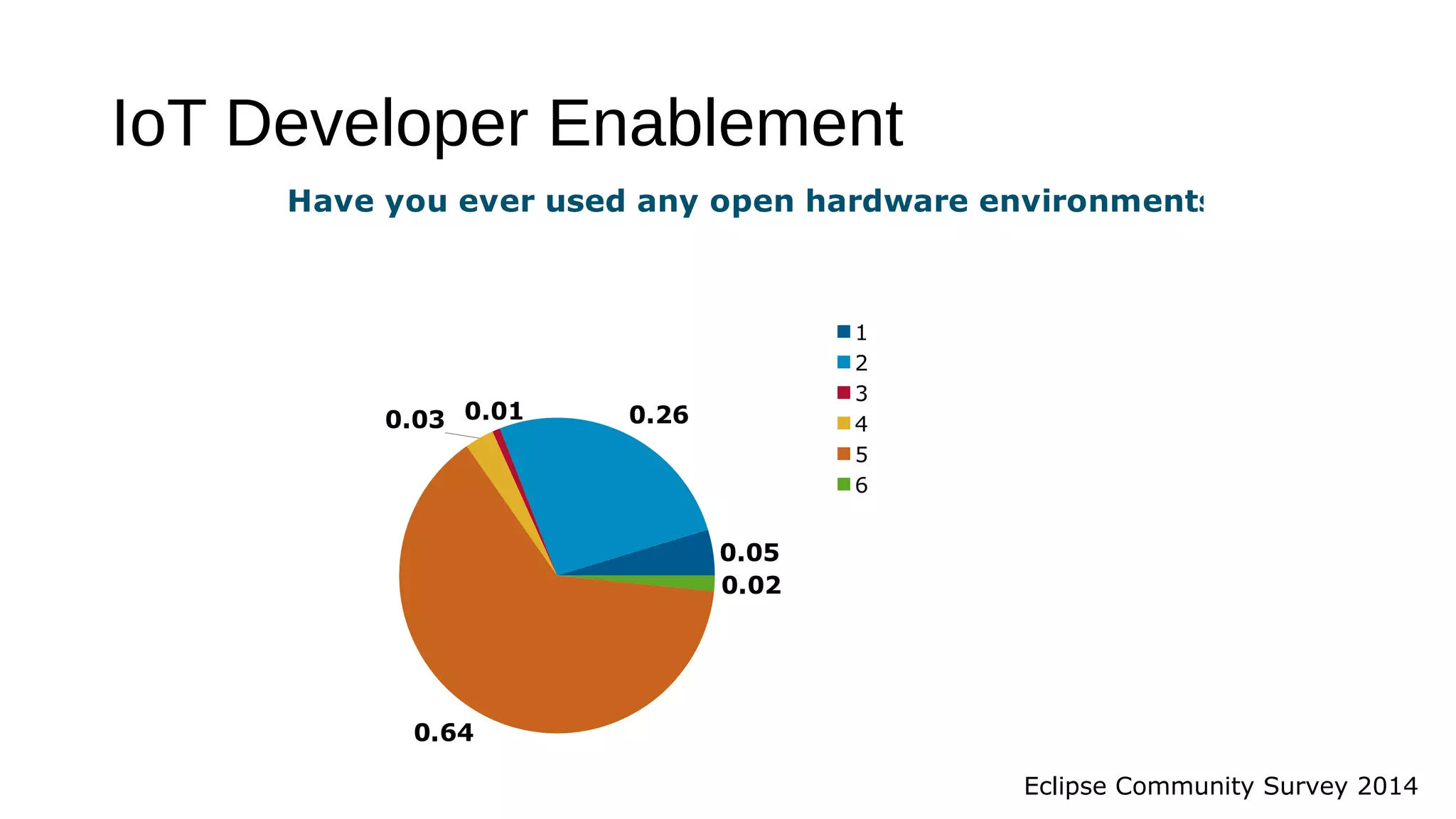
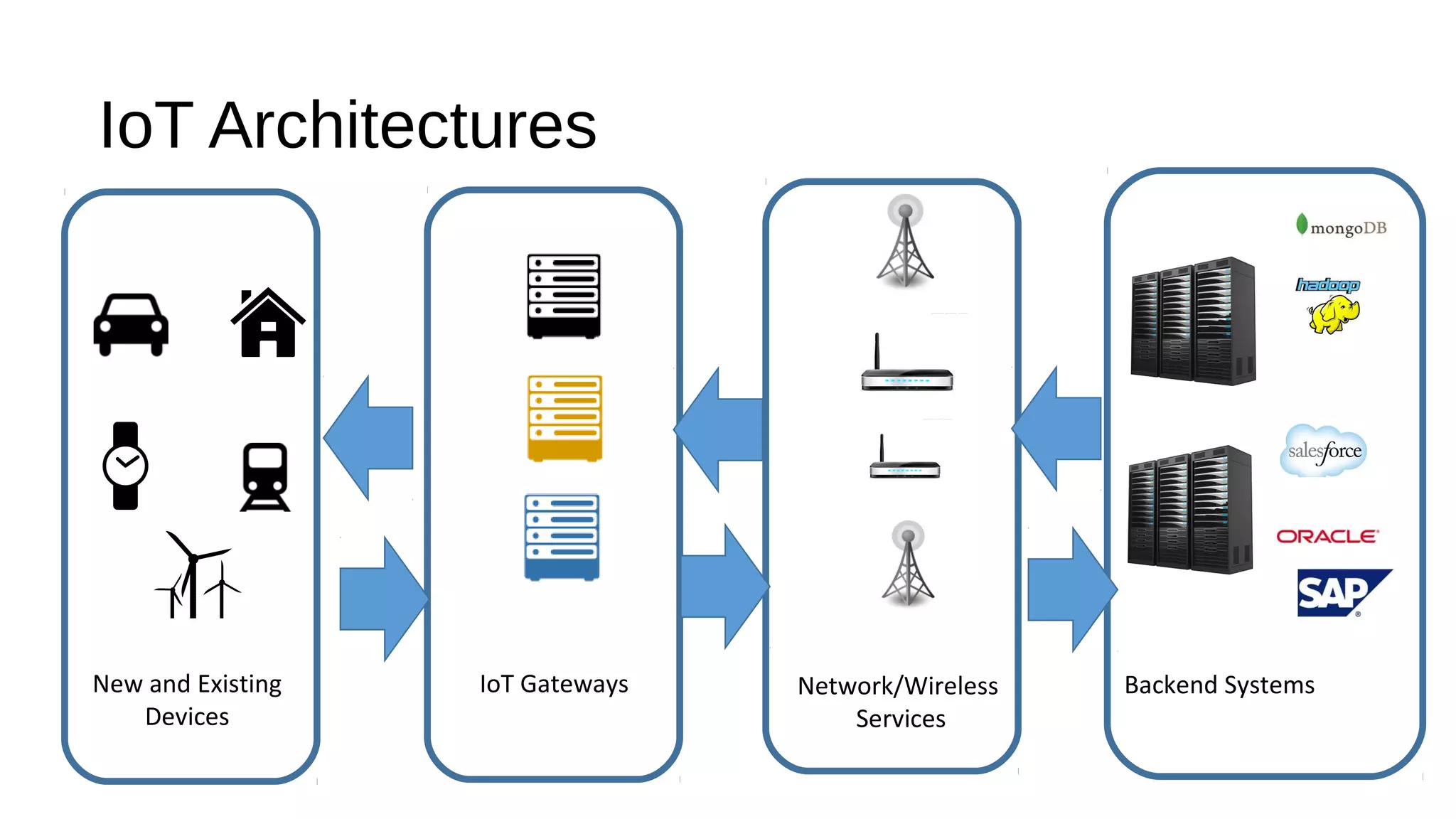
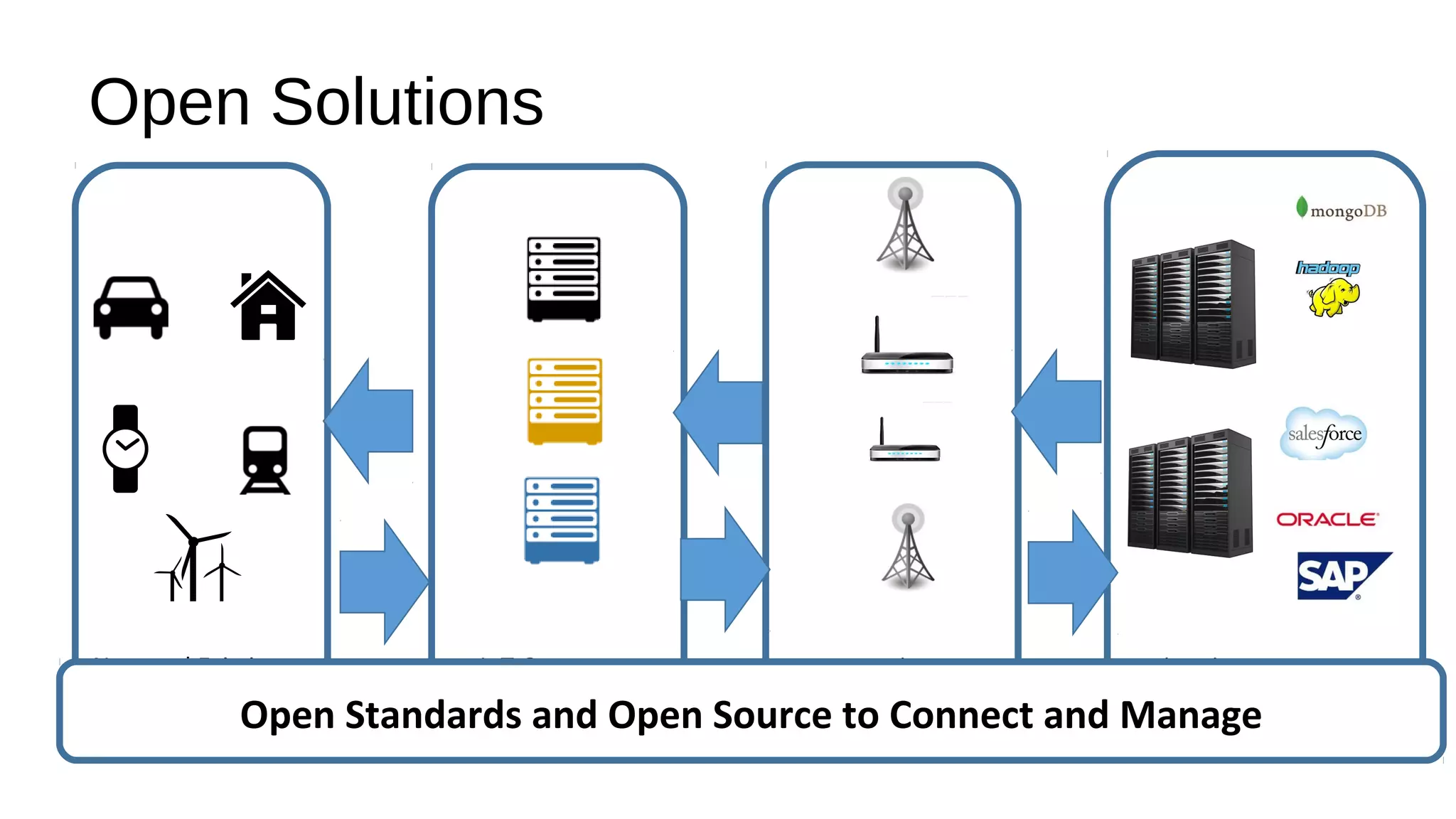
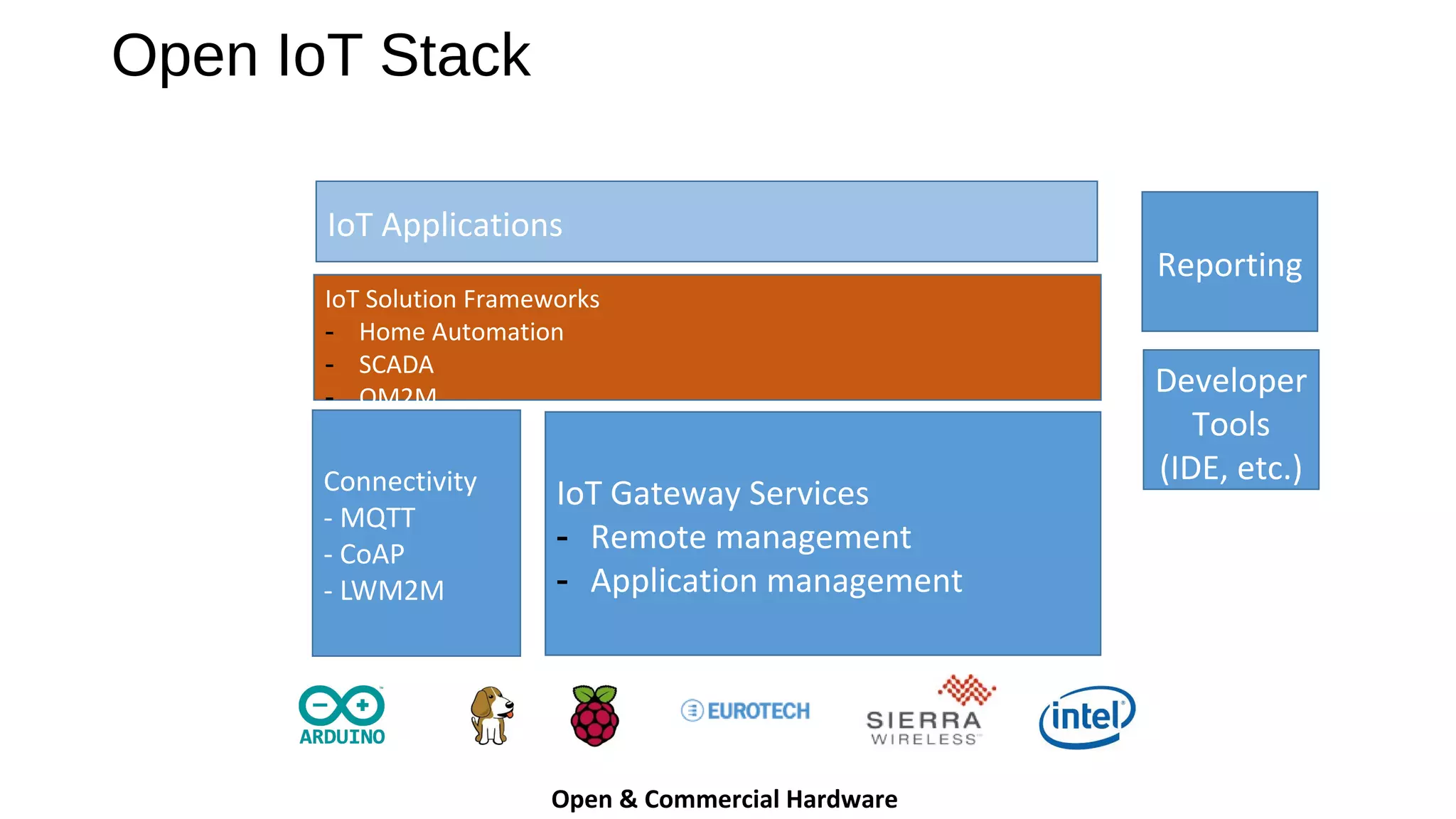
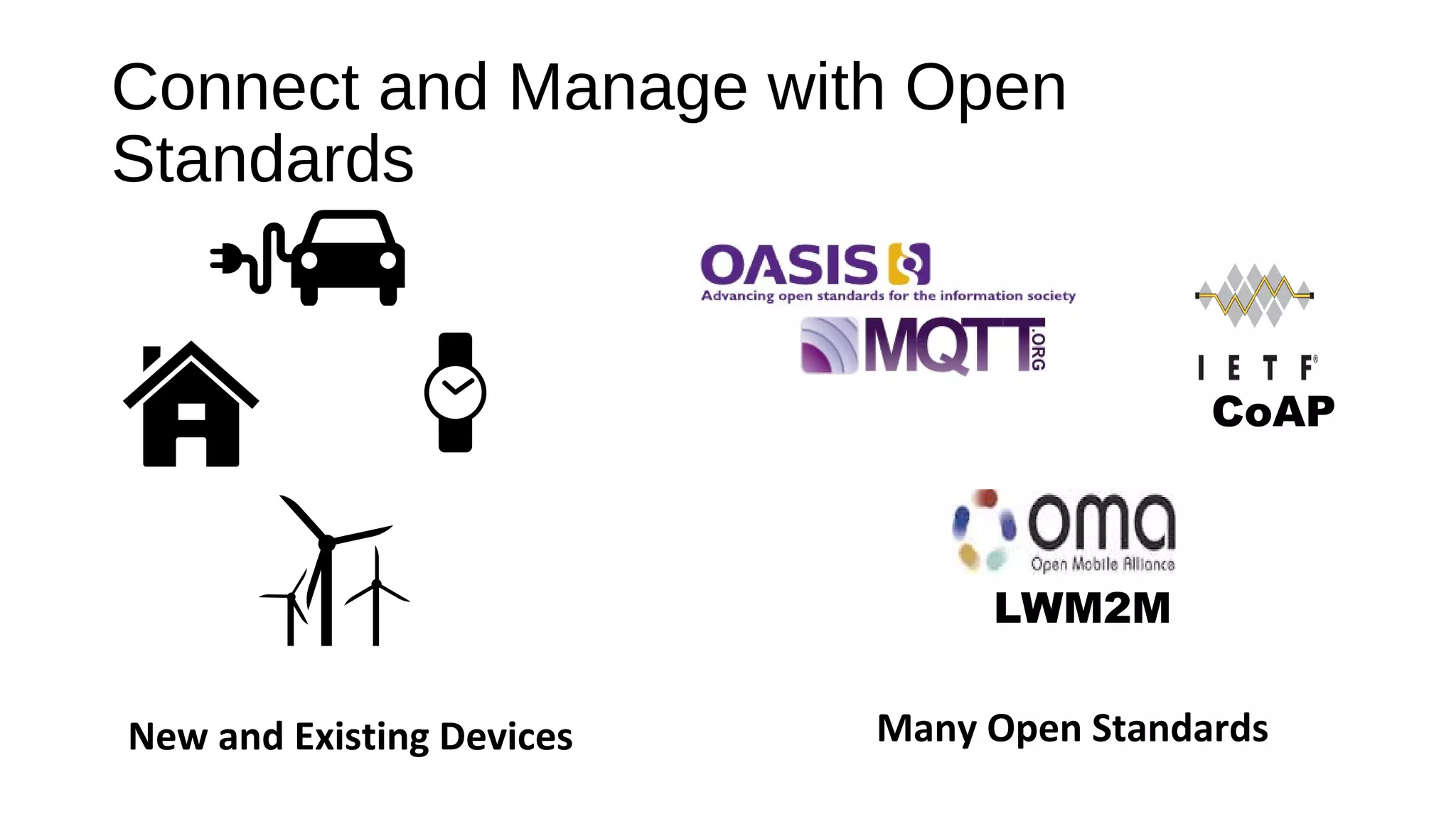
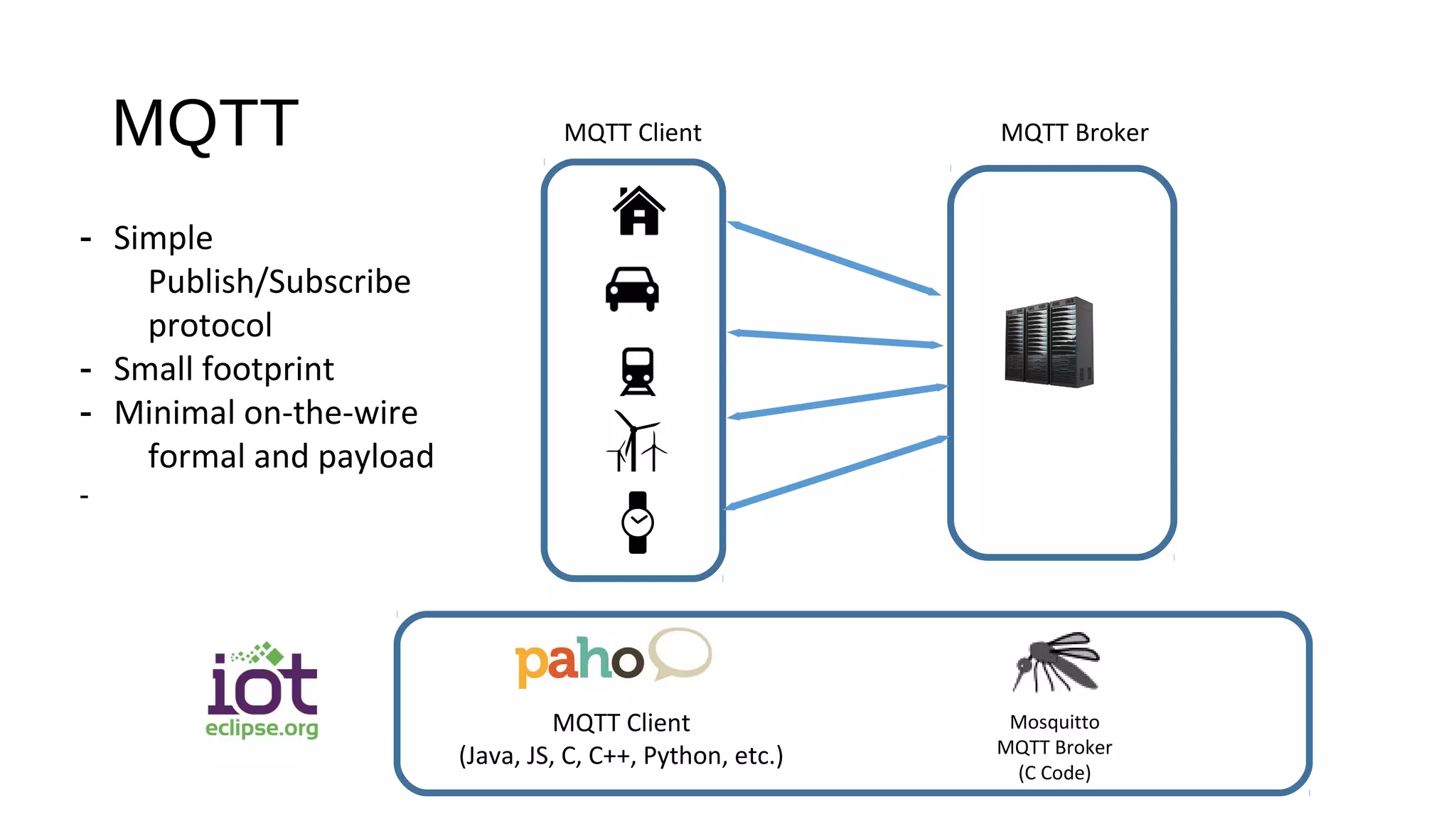
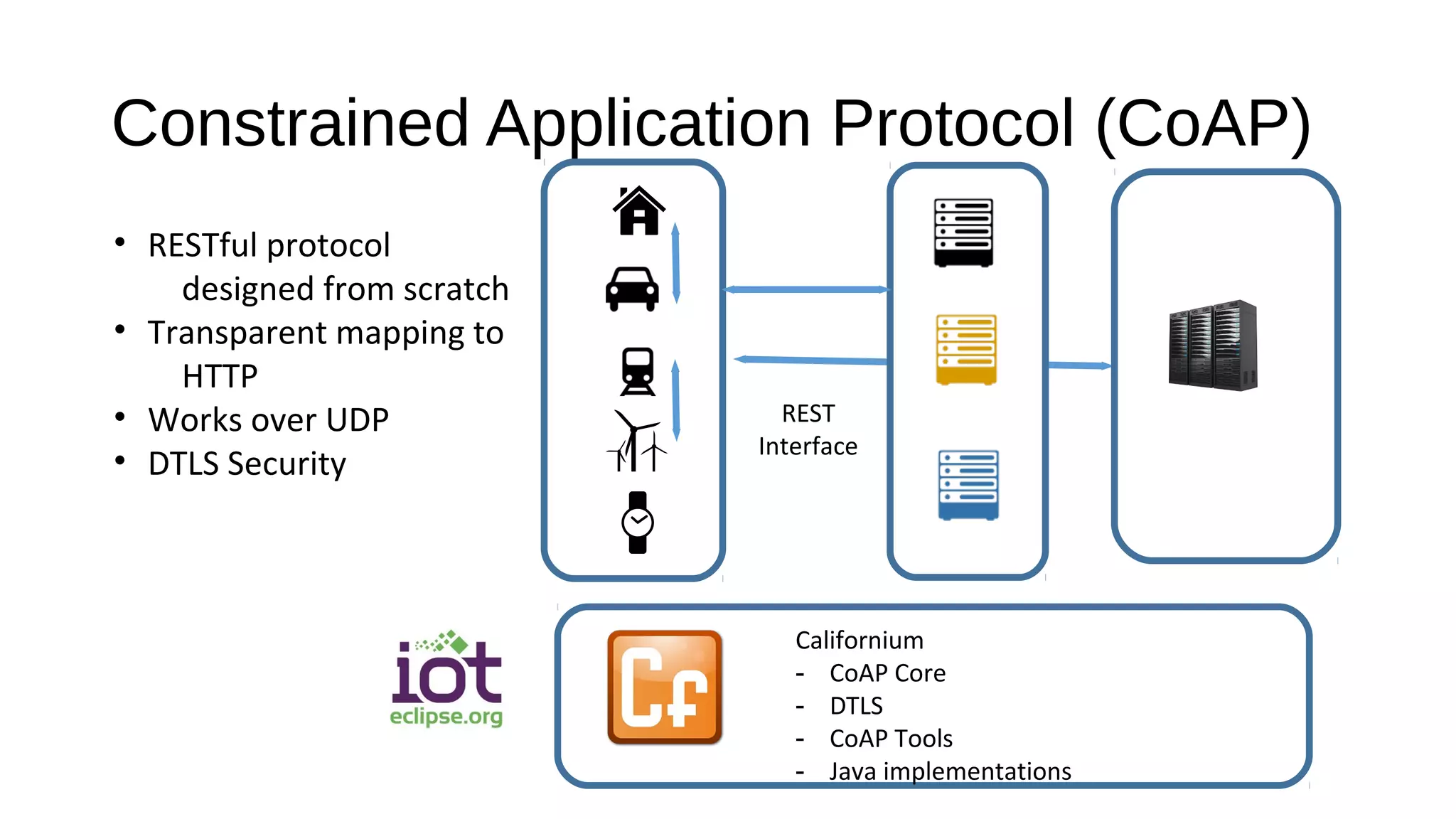
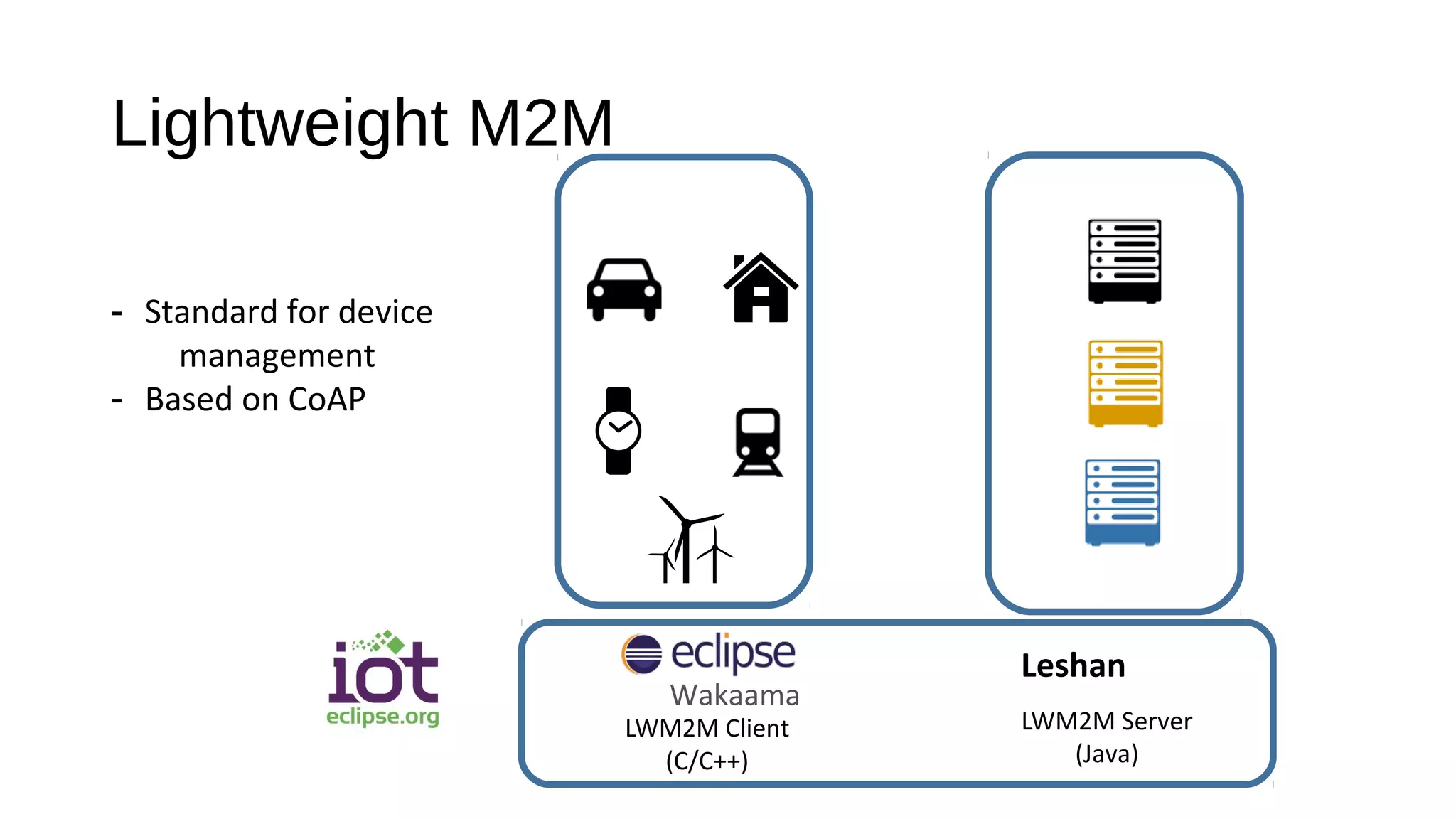
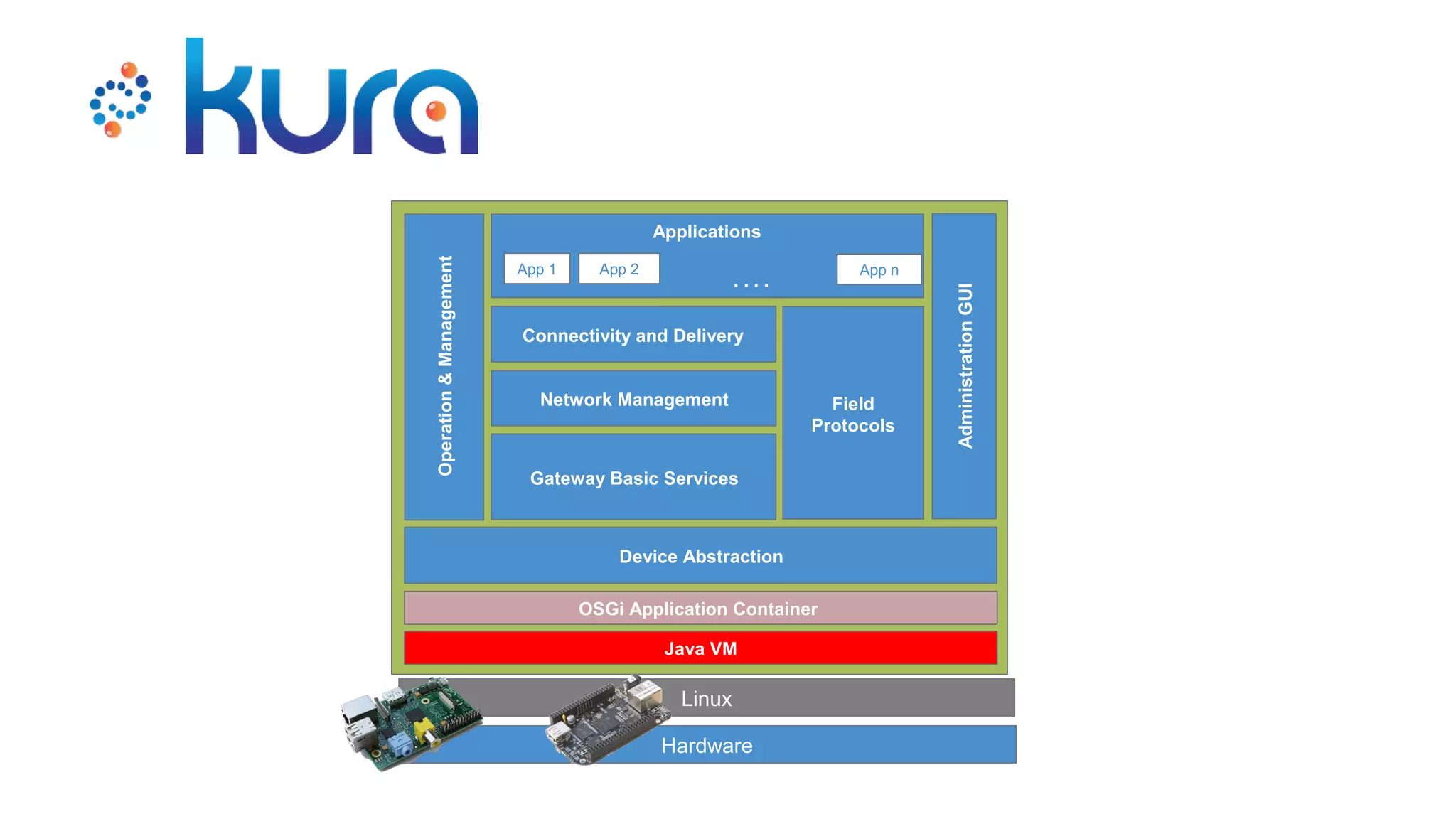
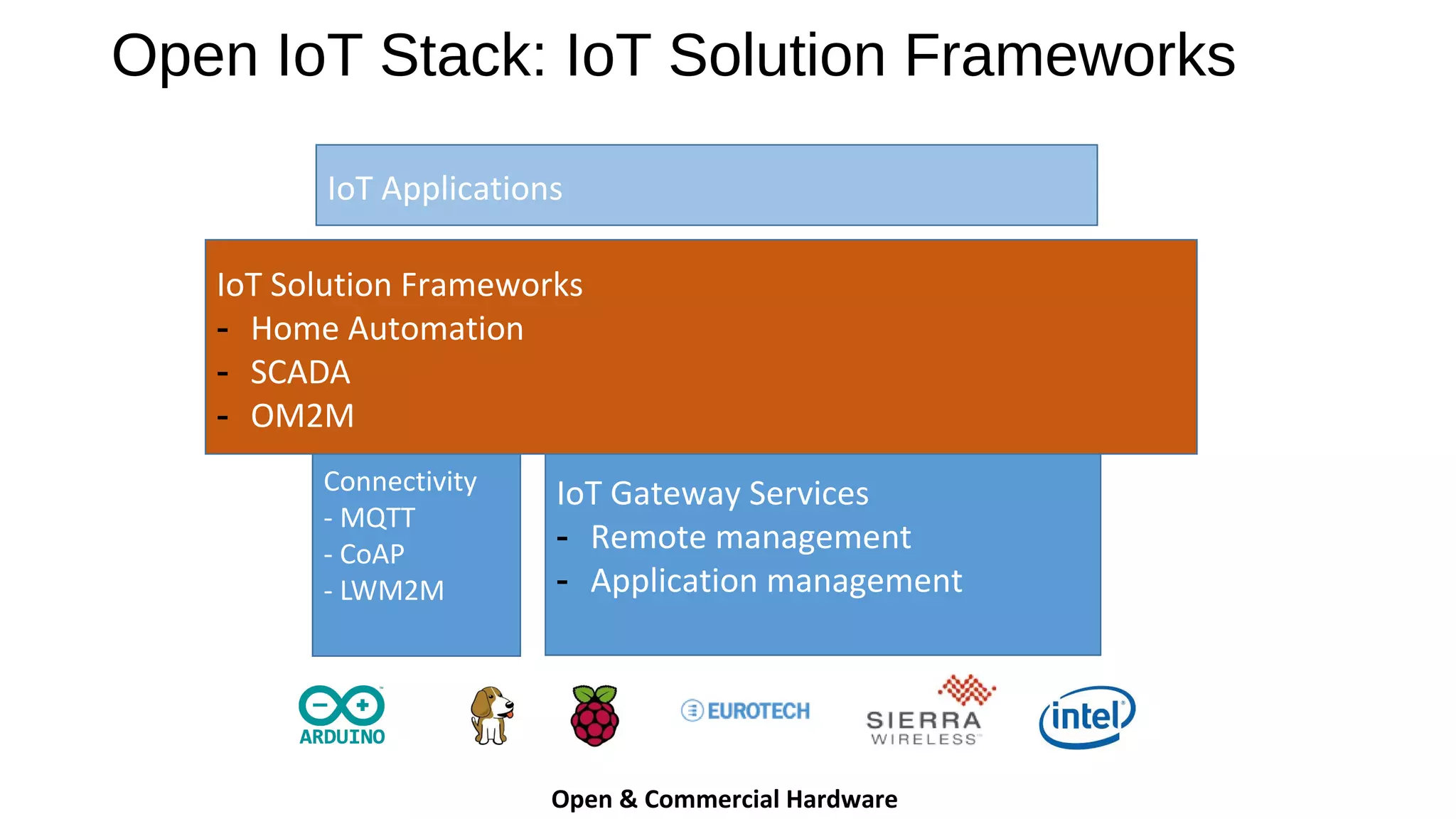
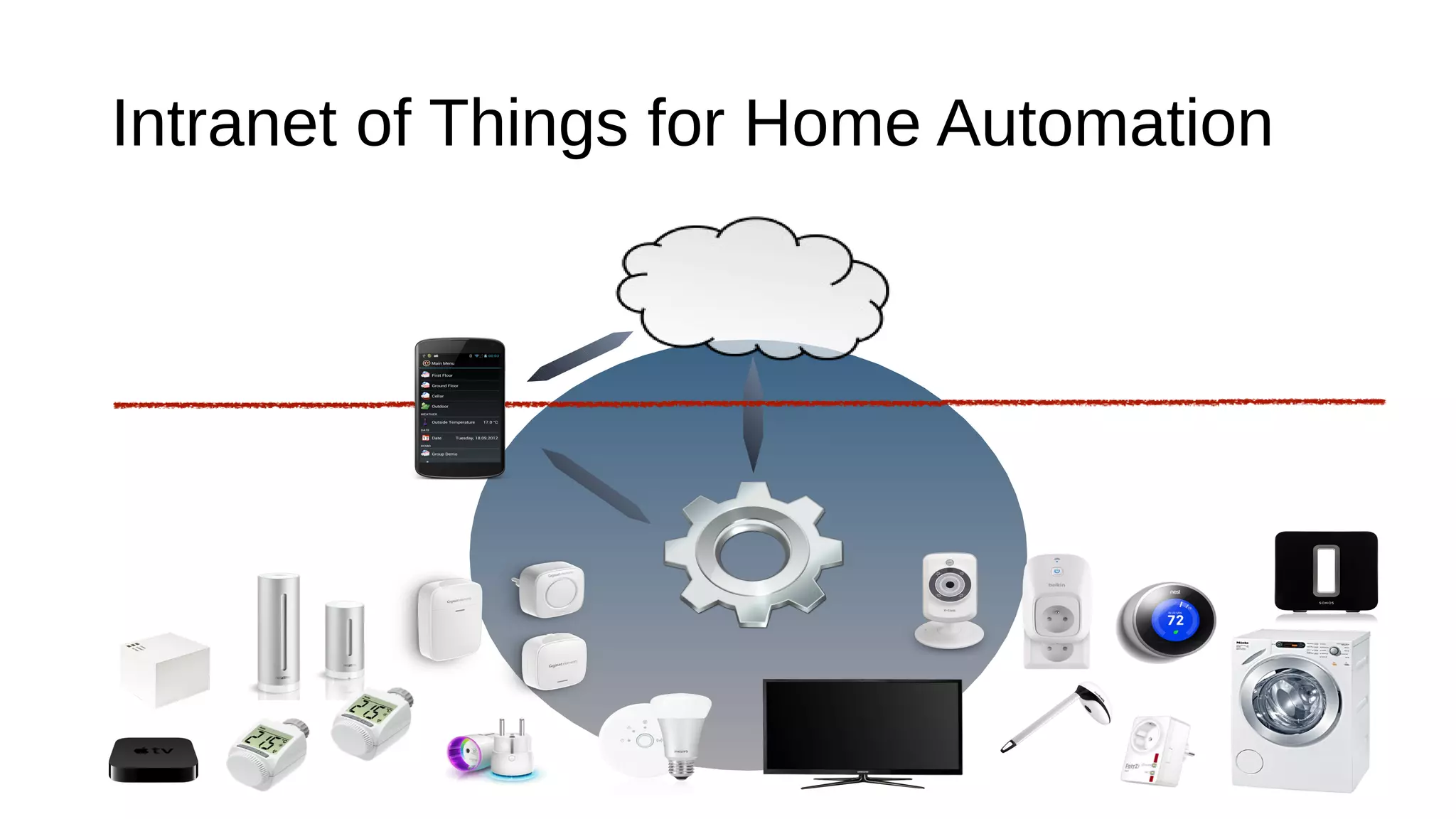
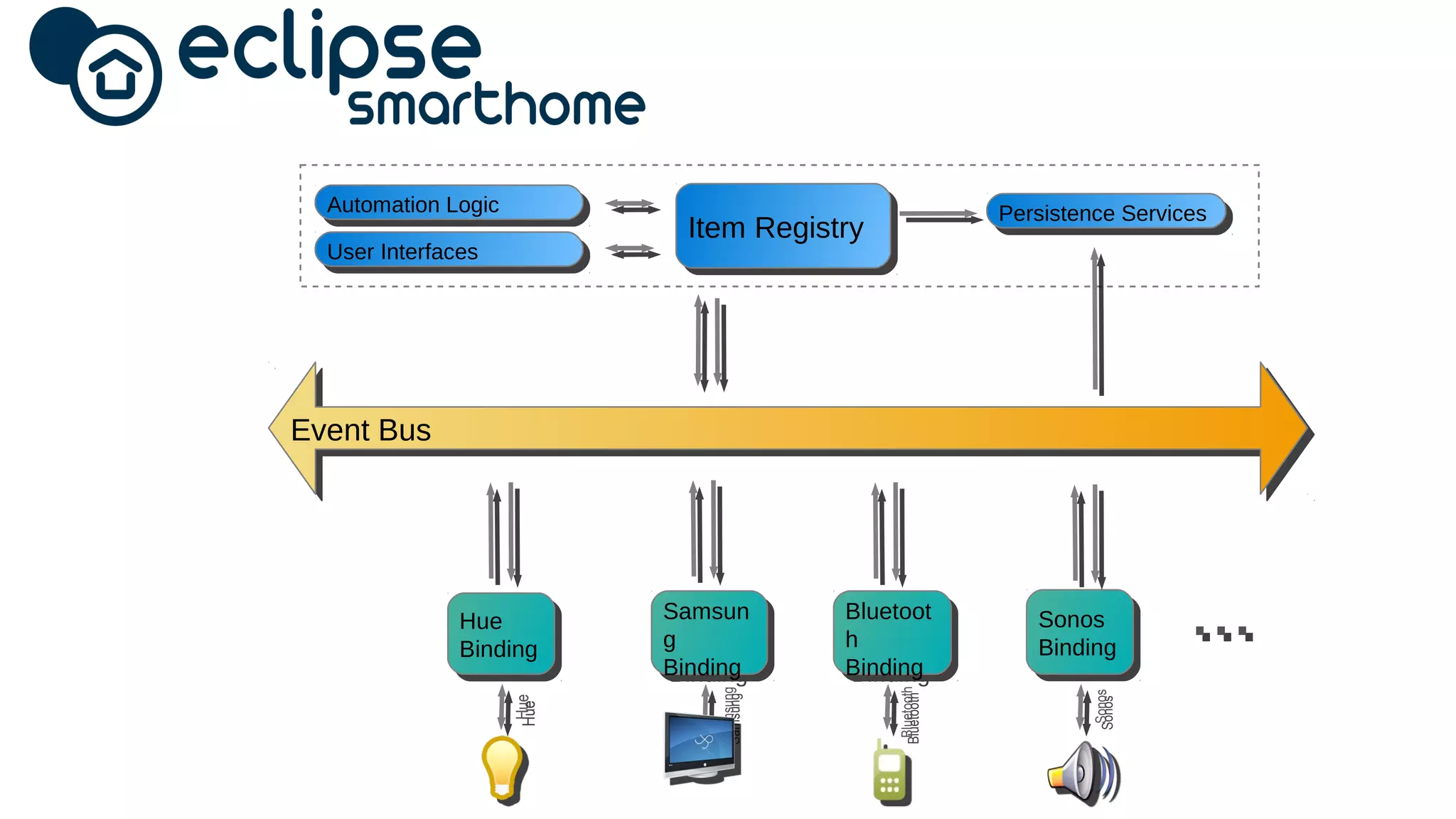
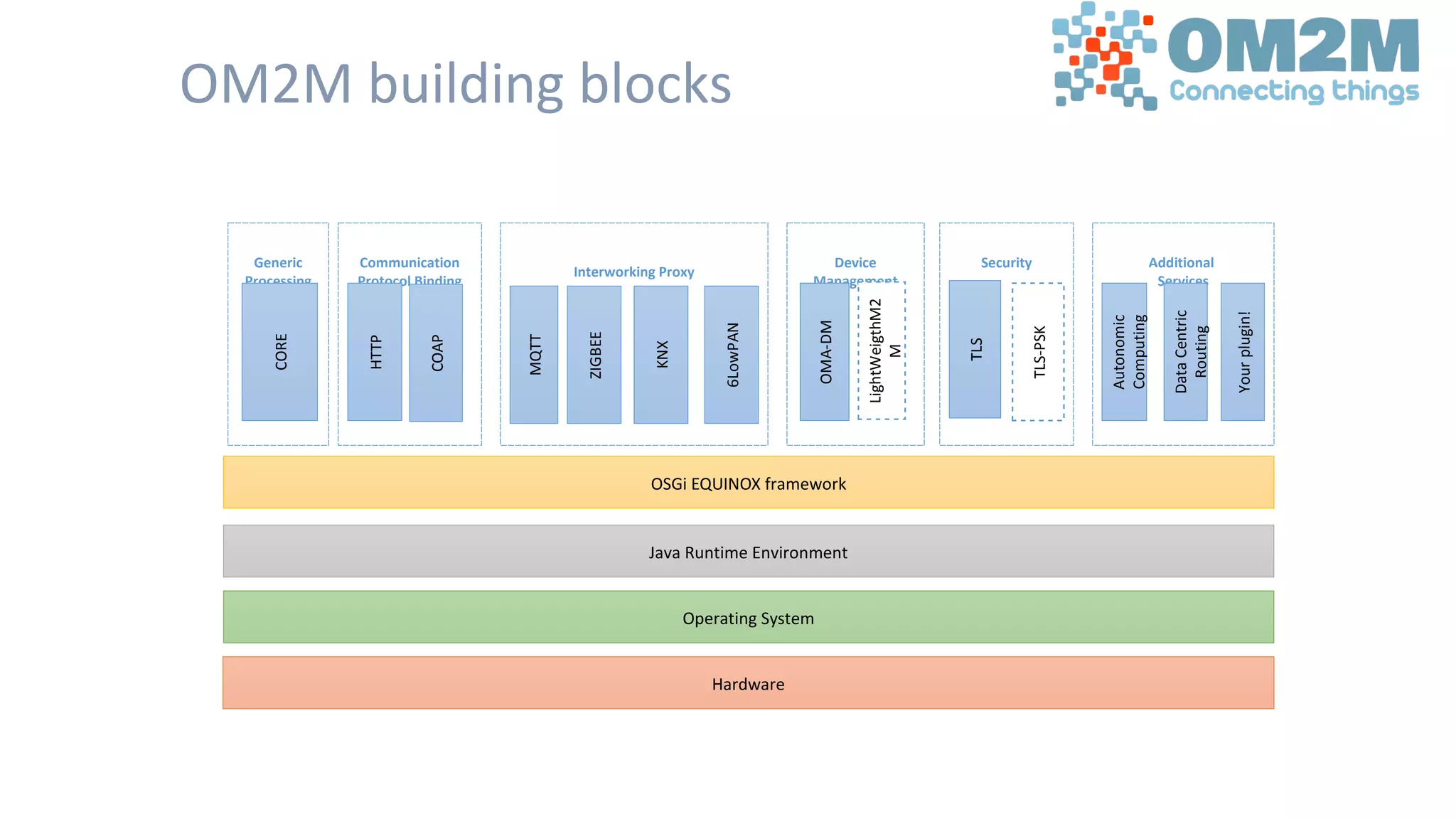
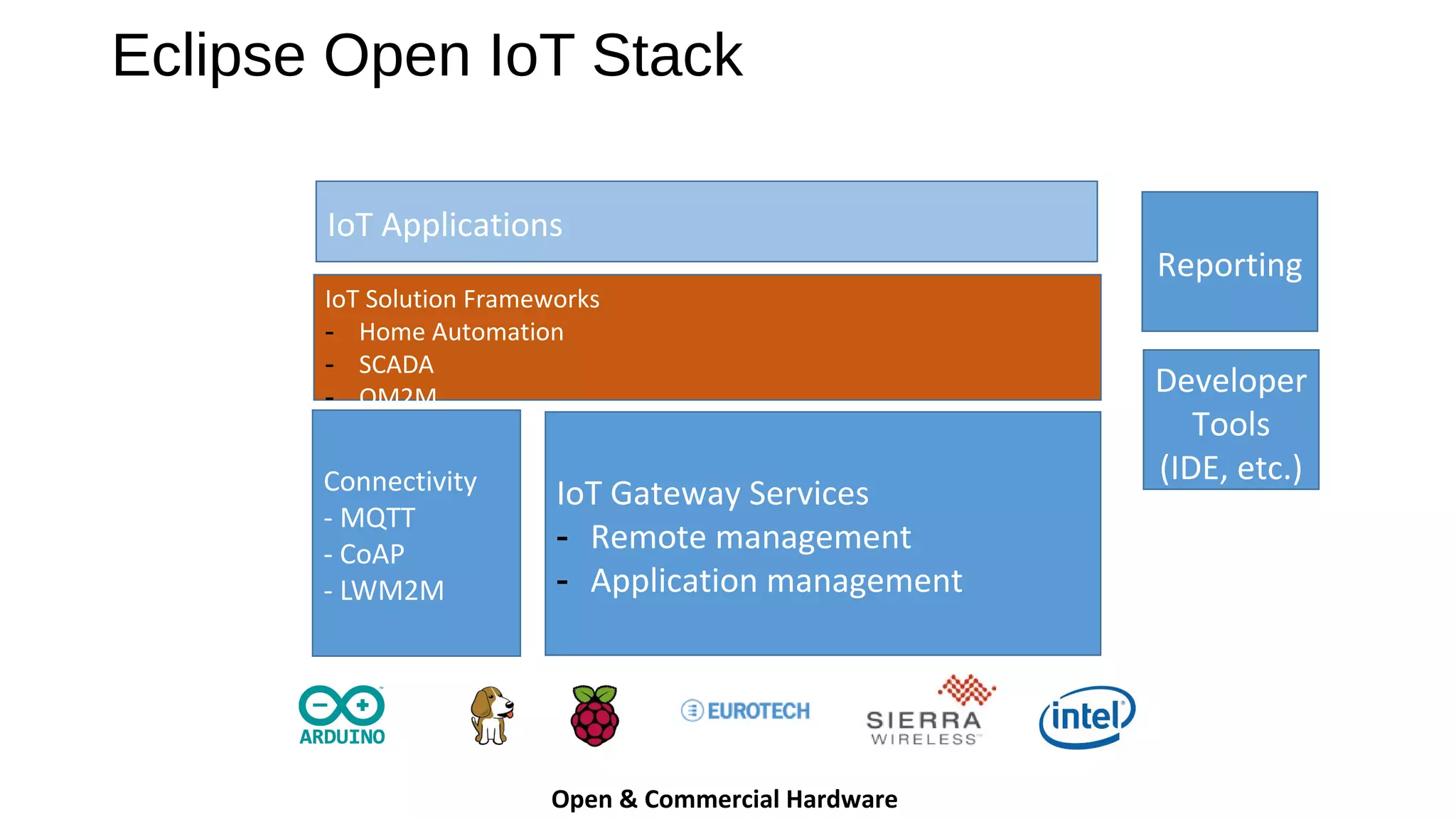
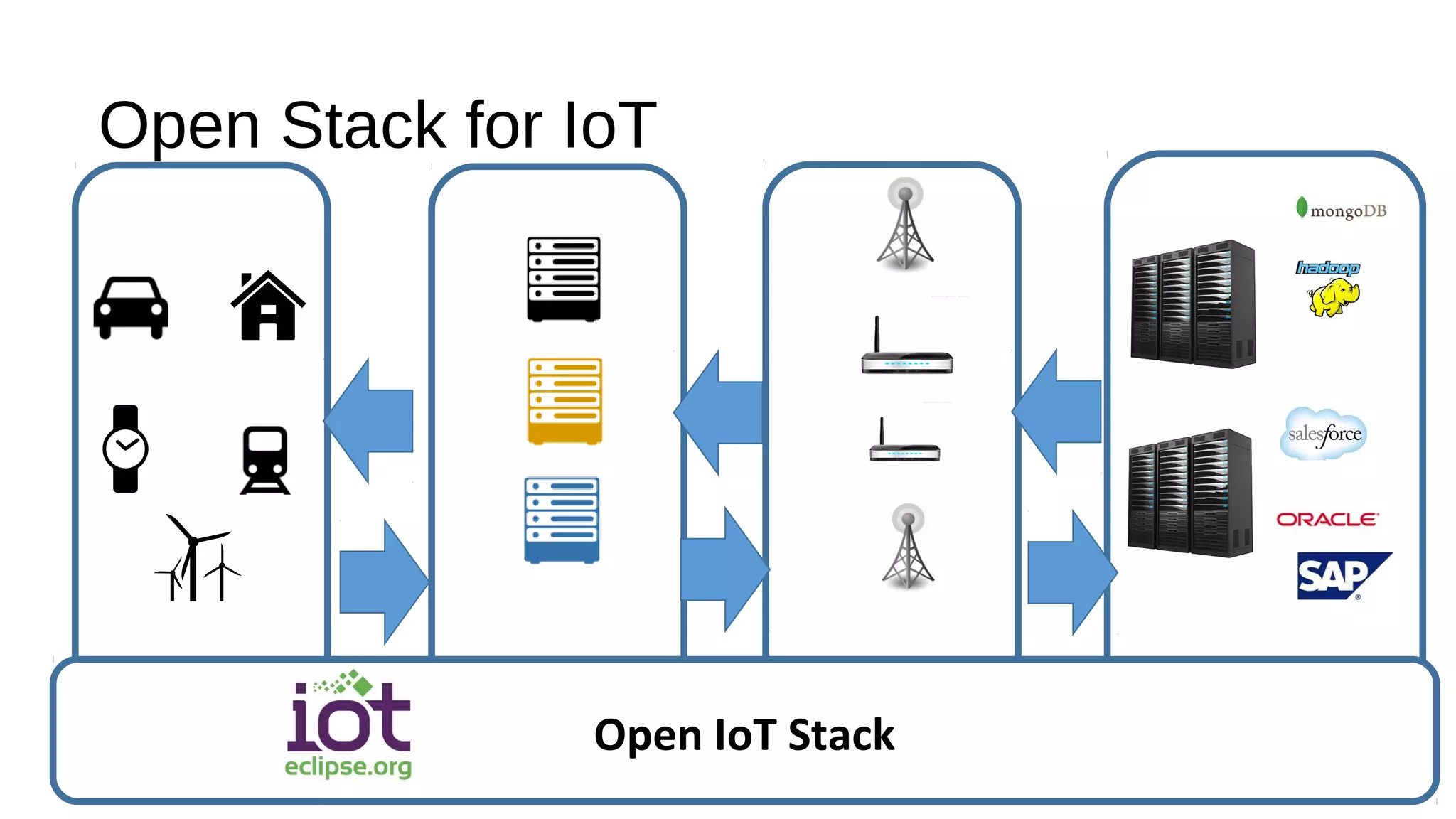
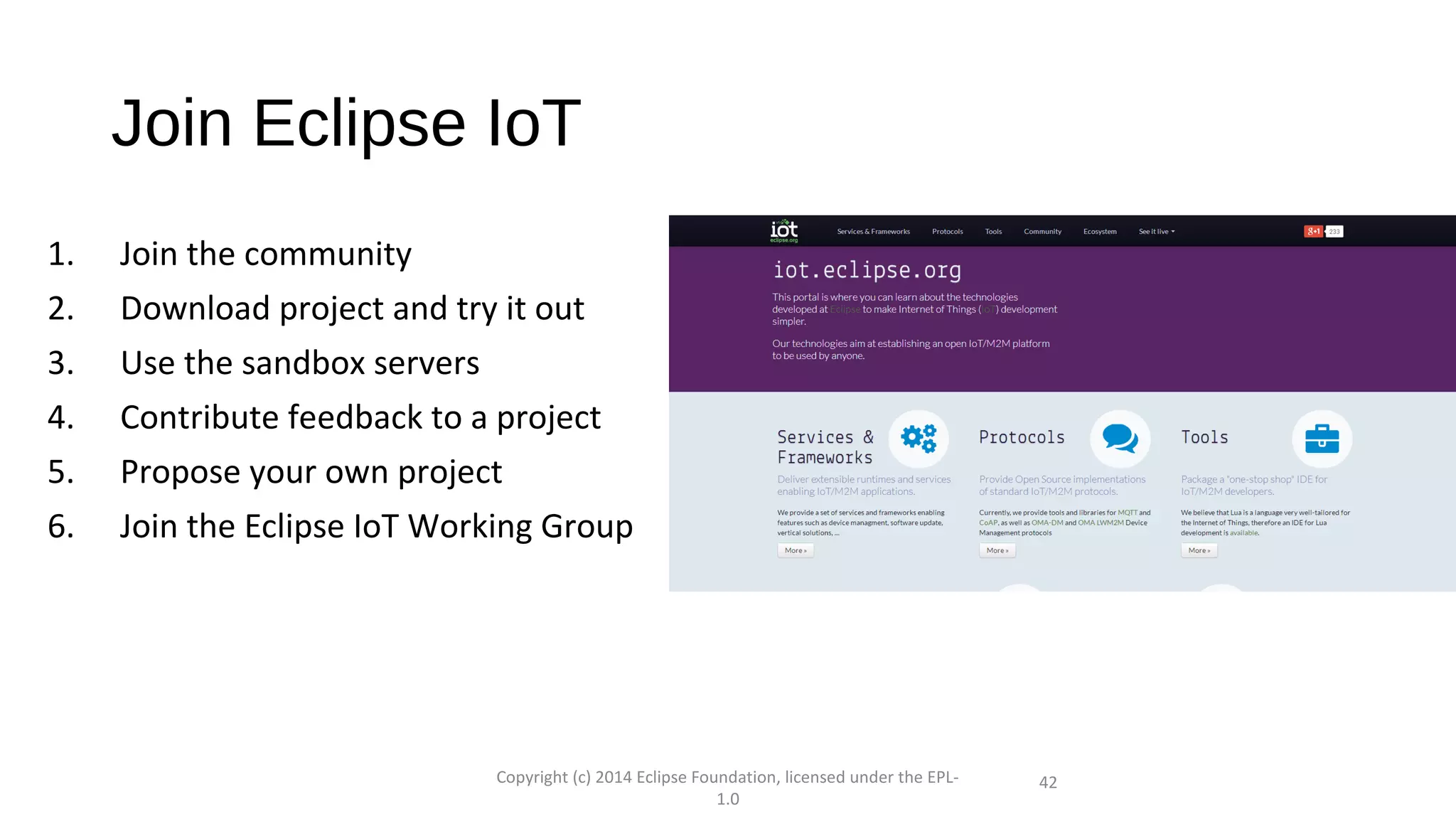
The document discusses the open source Internet of Things (IoT) stack developed by the Eclipse Foundation. It describes how the open IoT stack provides open connectivity standards like MQTT, CoAP, and LWM2M to connect devices. It also includes IoT gateway services for remote management and application management. The stack supports various IoT solution frameworks for home automation, SCADA systems, and the OM2M standard. The Eclipse Foundation aims for an open ecosystem for IoT development and provides tools and projects through its open IoT stack.