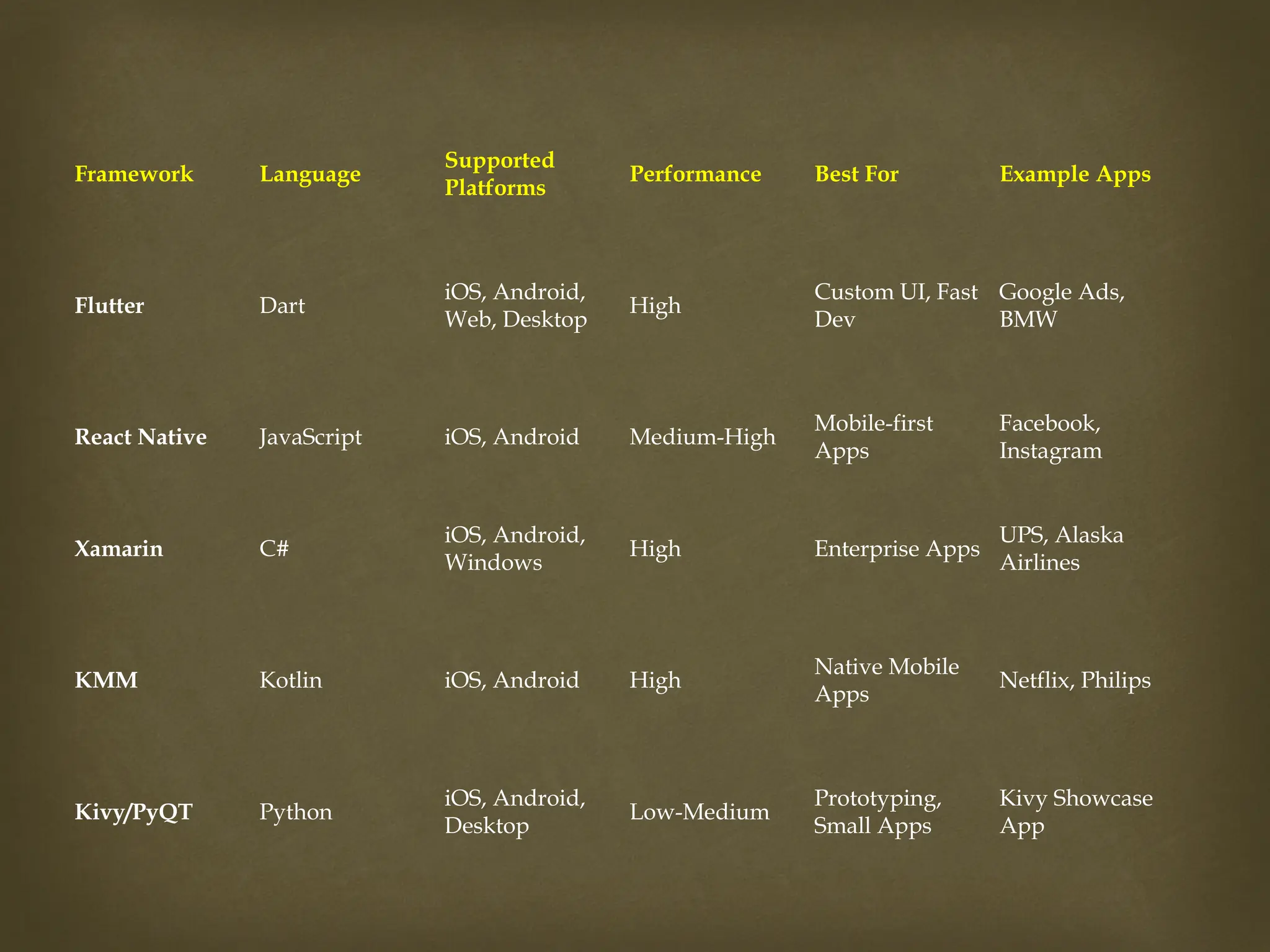
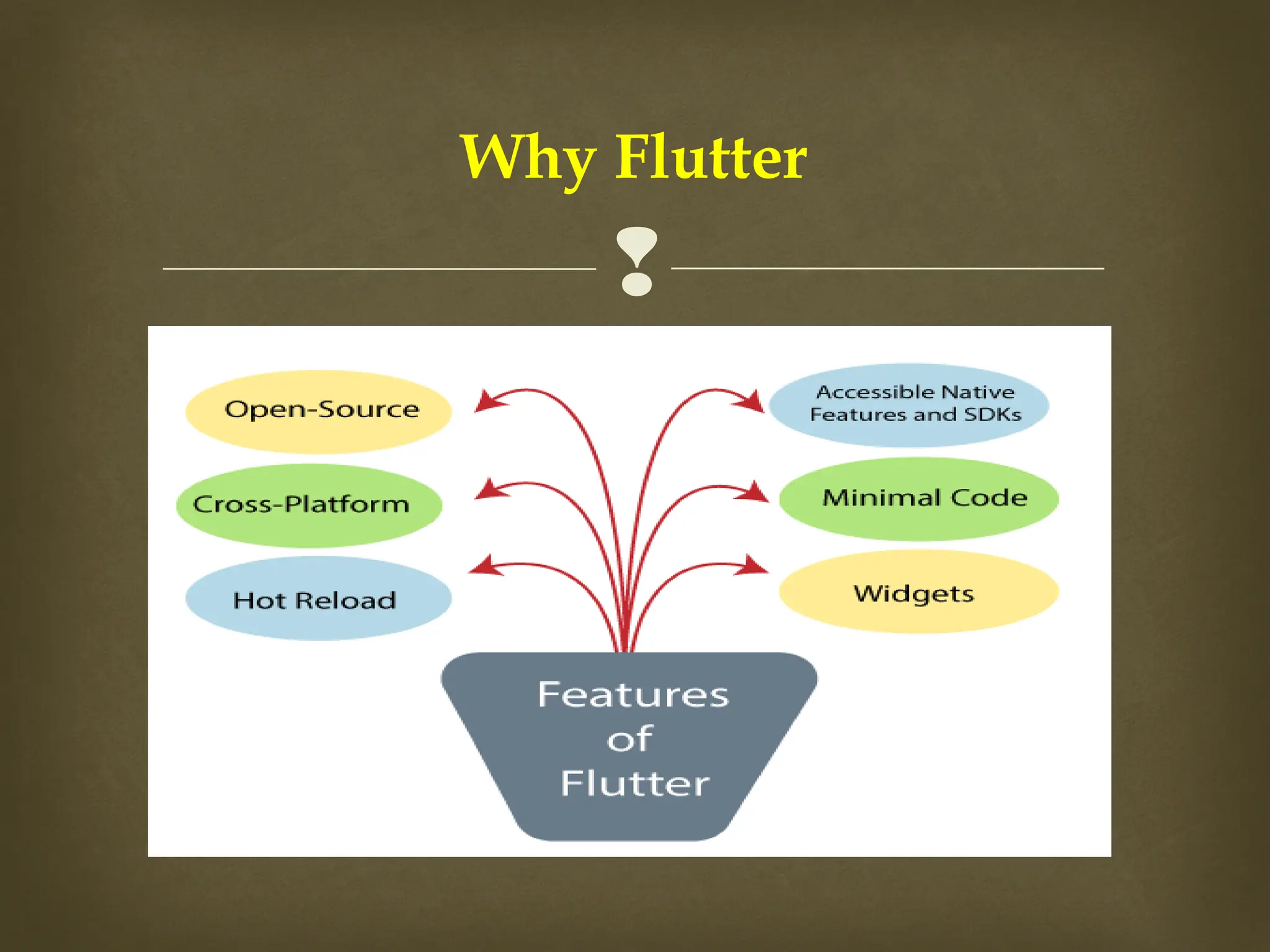
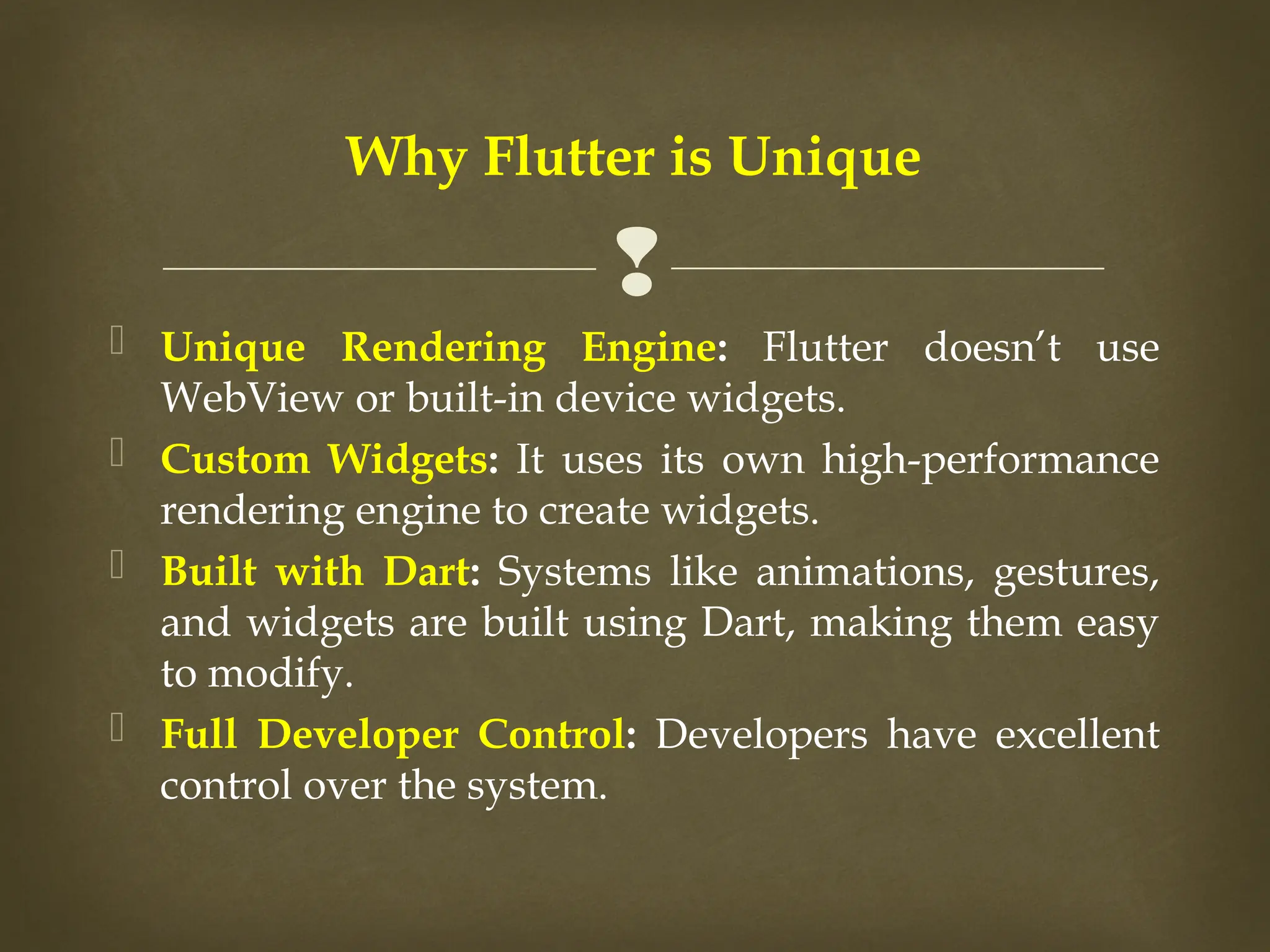
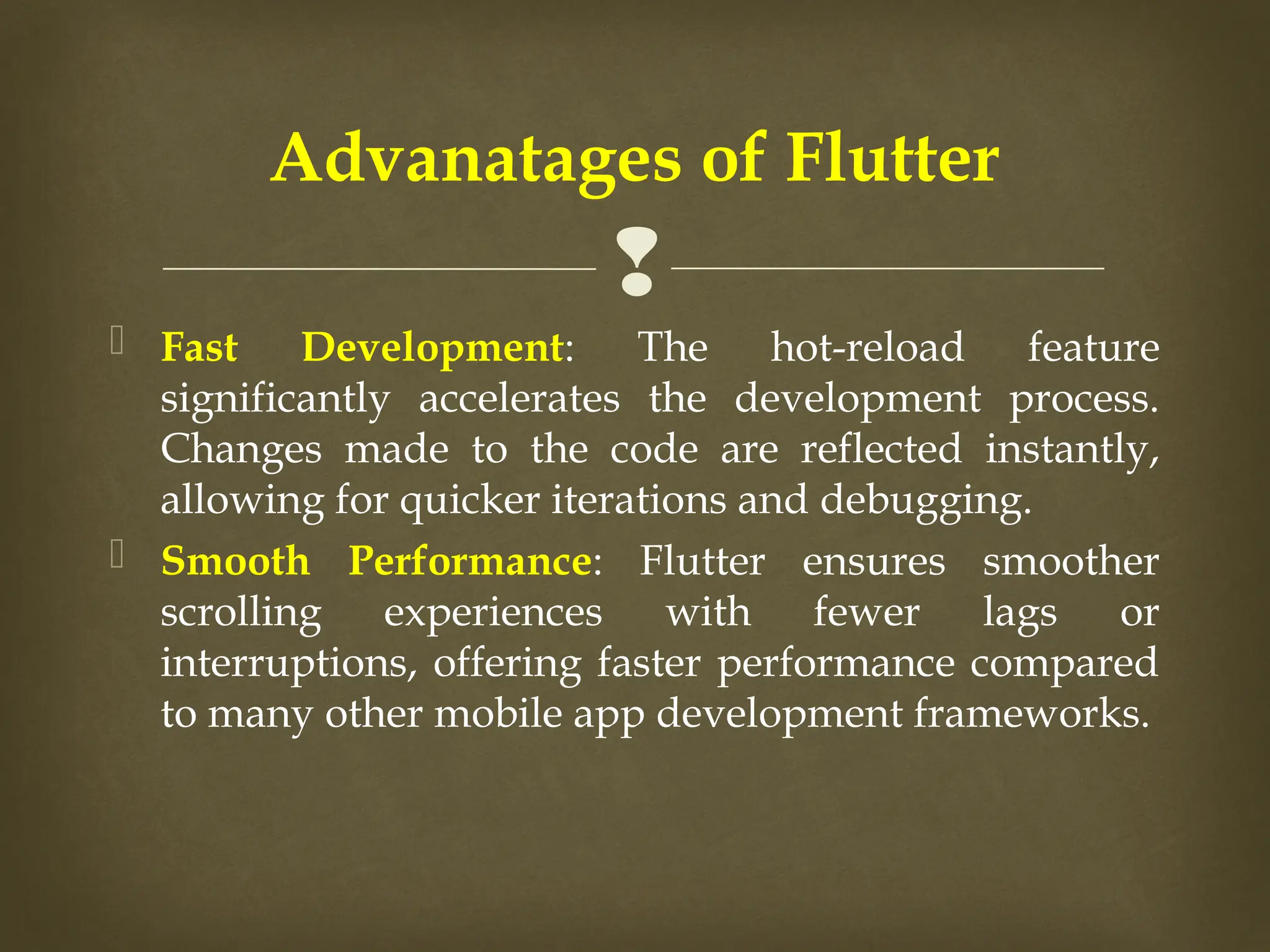
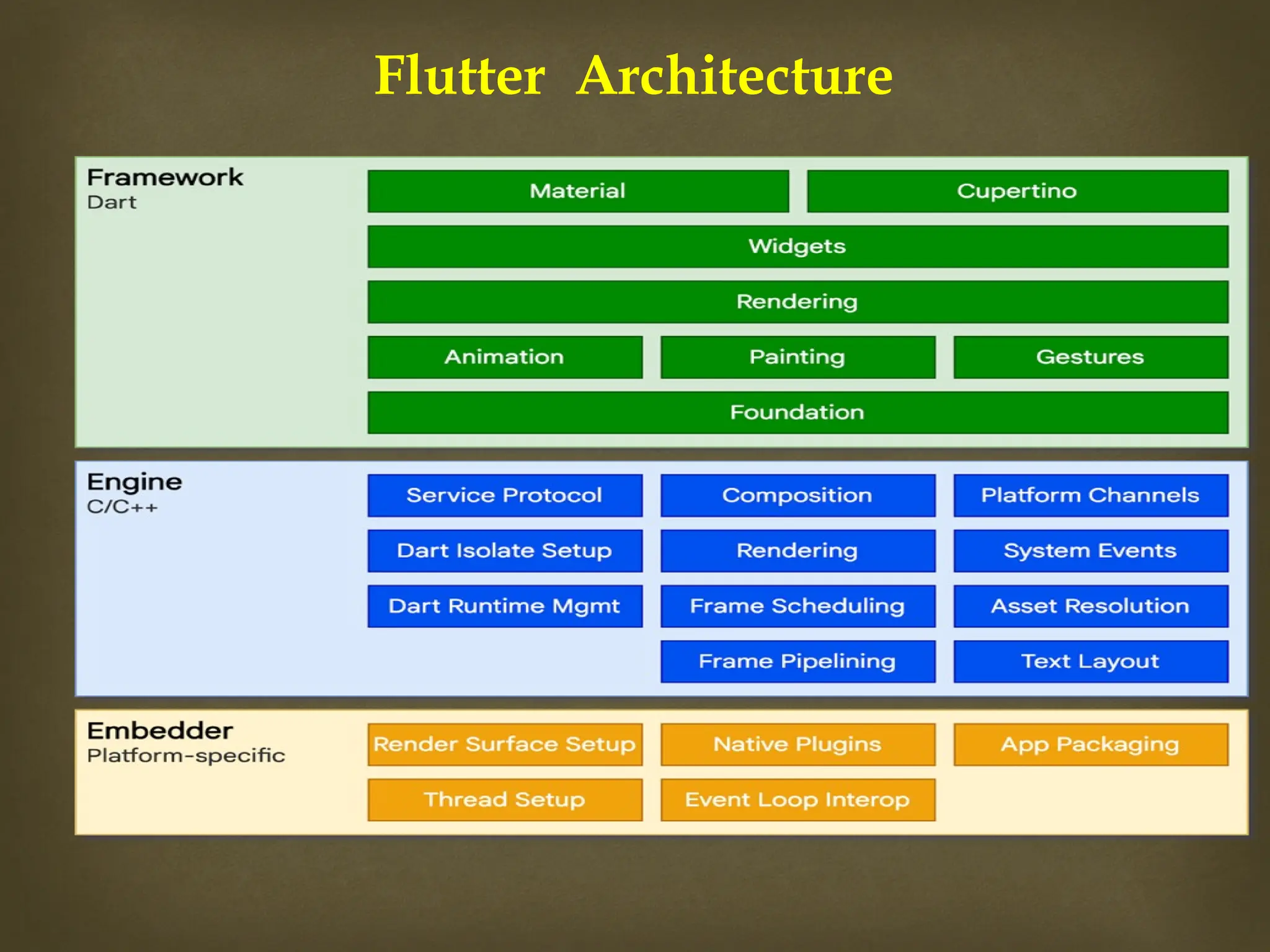
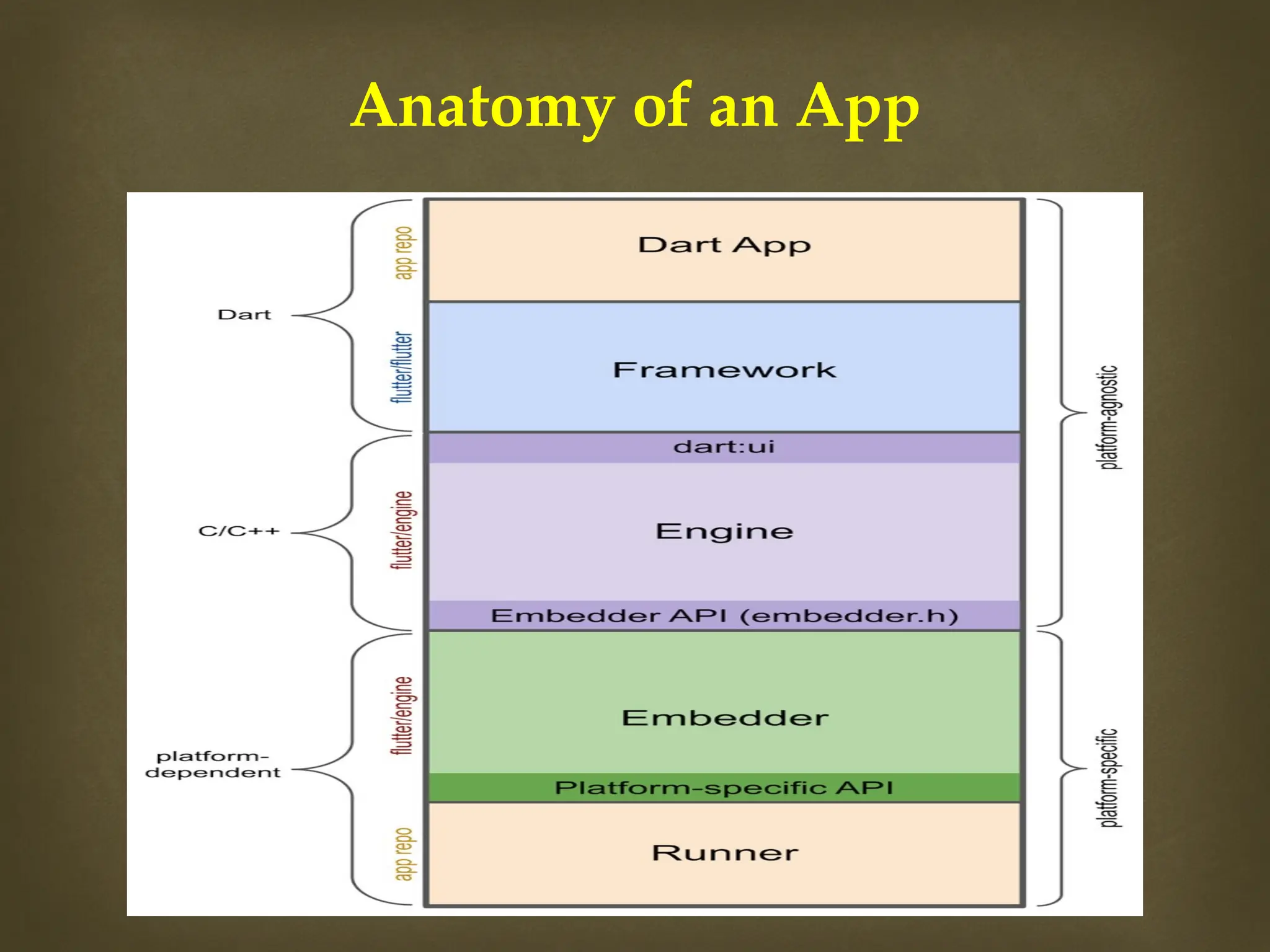
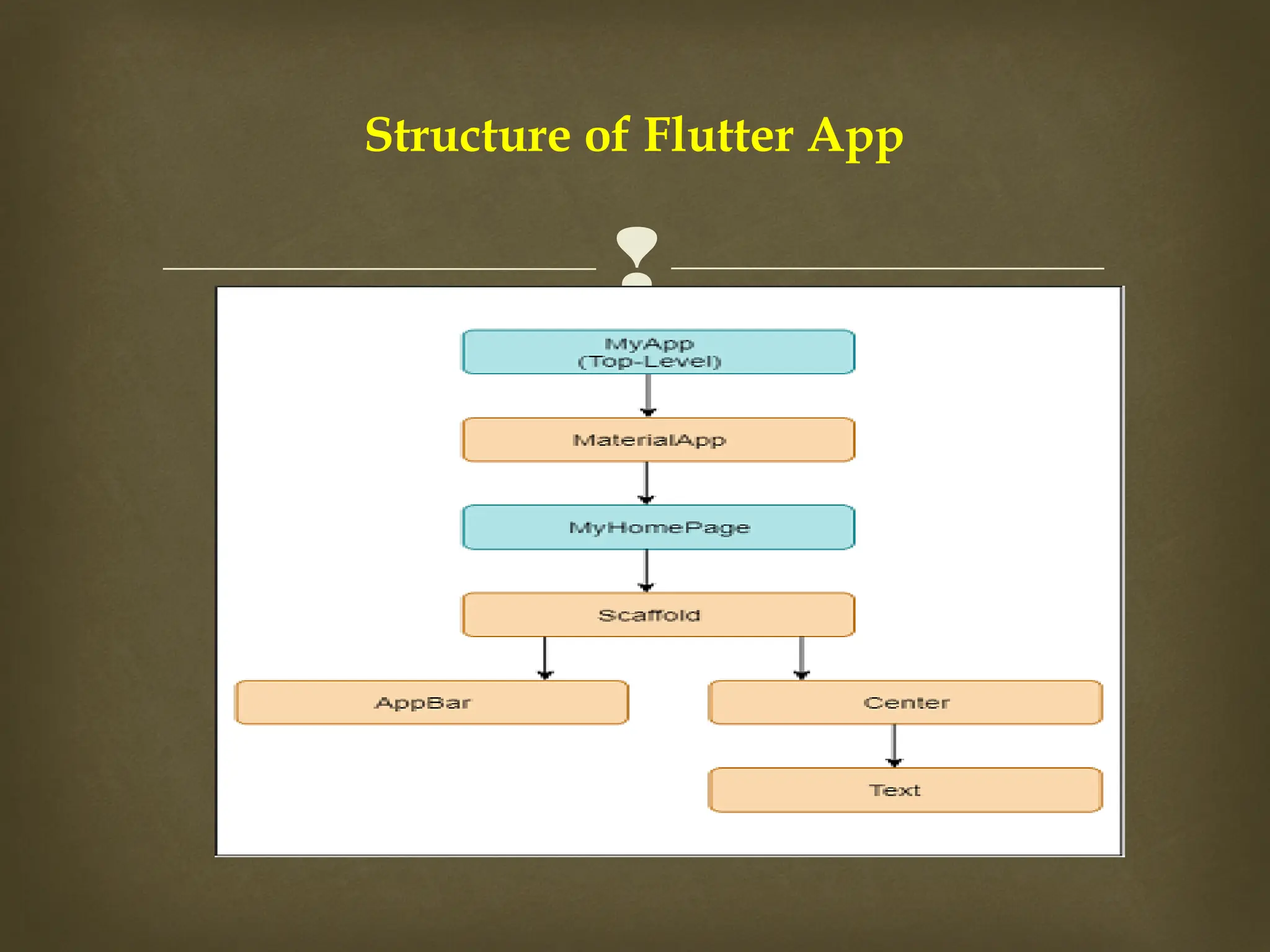
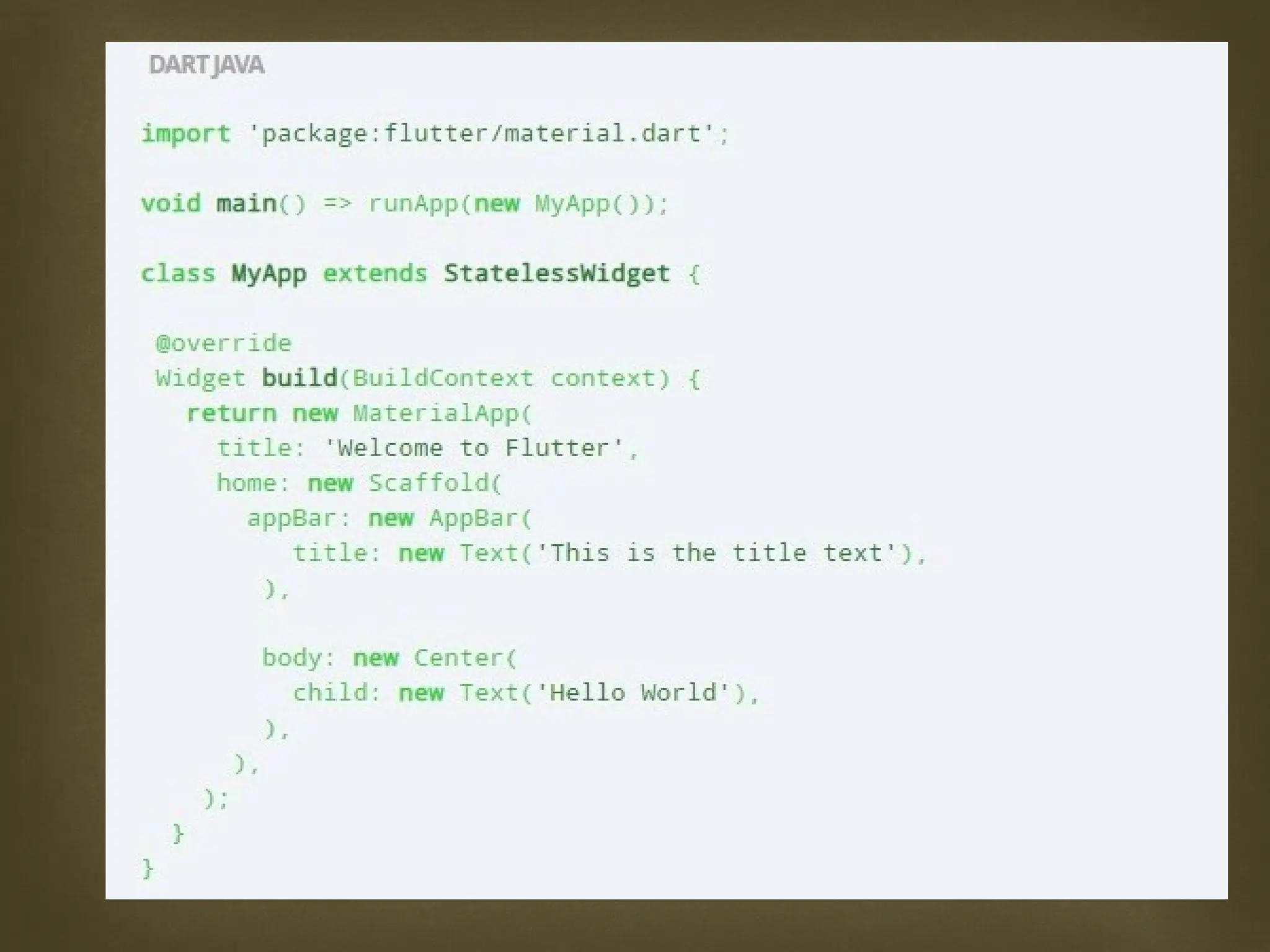
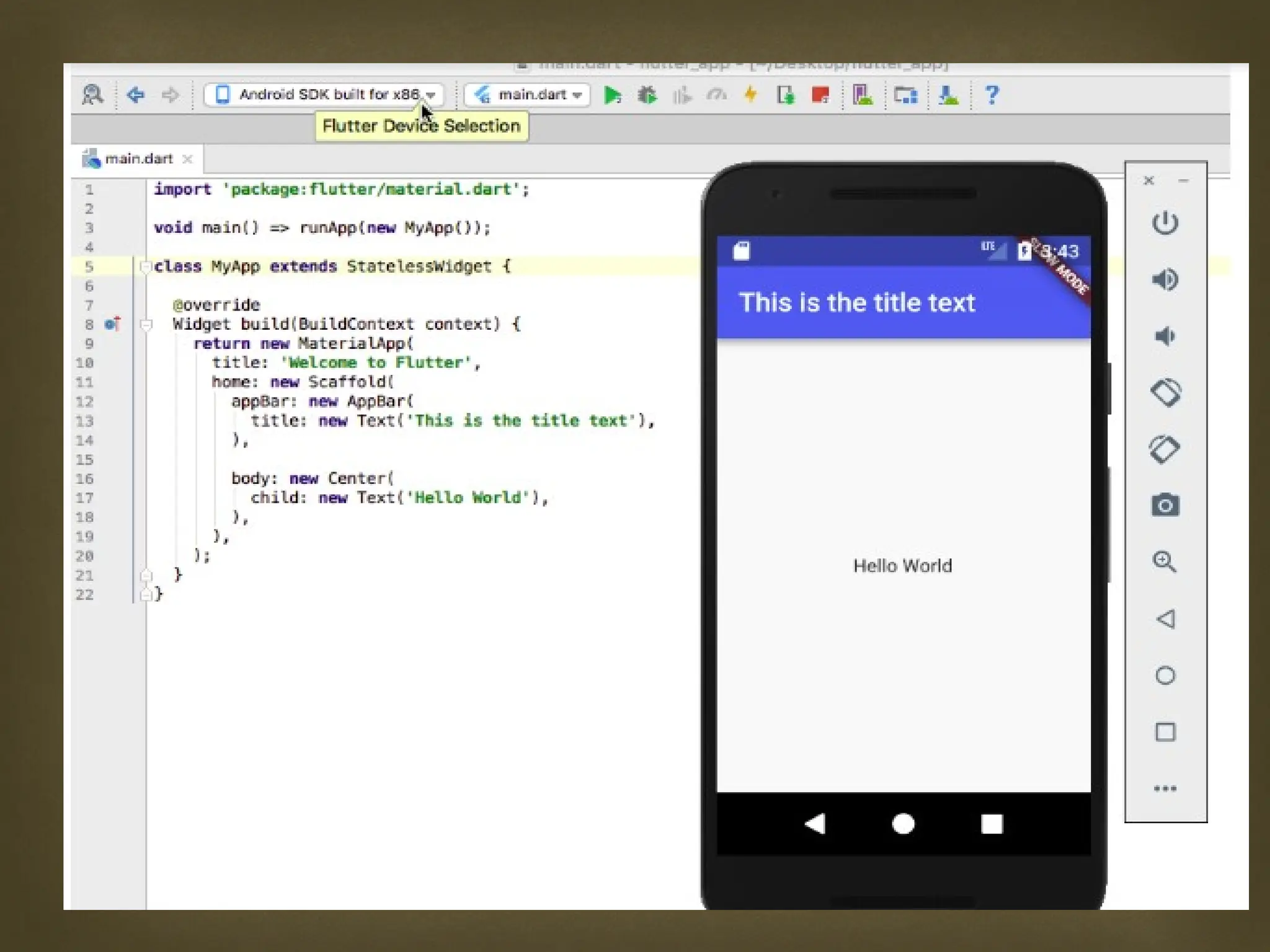
The document provides an overview of Flutter, a cross-platform UI toolkit developed by Google for building natively compiled applications across mobile, web, and desktop platforms using the Dart programming language. It discusses Flutter's advantages such as hot reload, a rich collection of customizable widgets, and efficient testing processes, while also mentioning its disadvantages like limited access to SDK libraries and the need for developers to learn Dart. The document outlines the architecture of Flutter, explaining its framework, engine, and embedder components, along with the anatomy of a Flutter app.