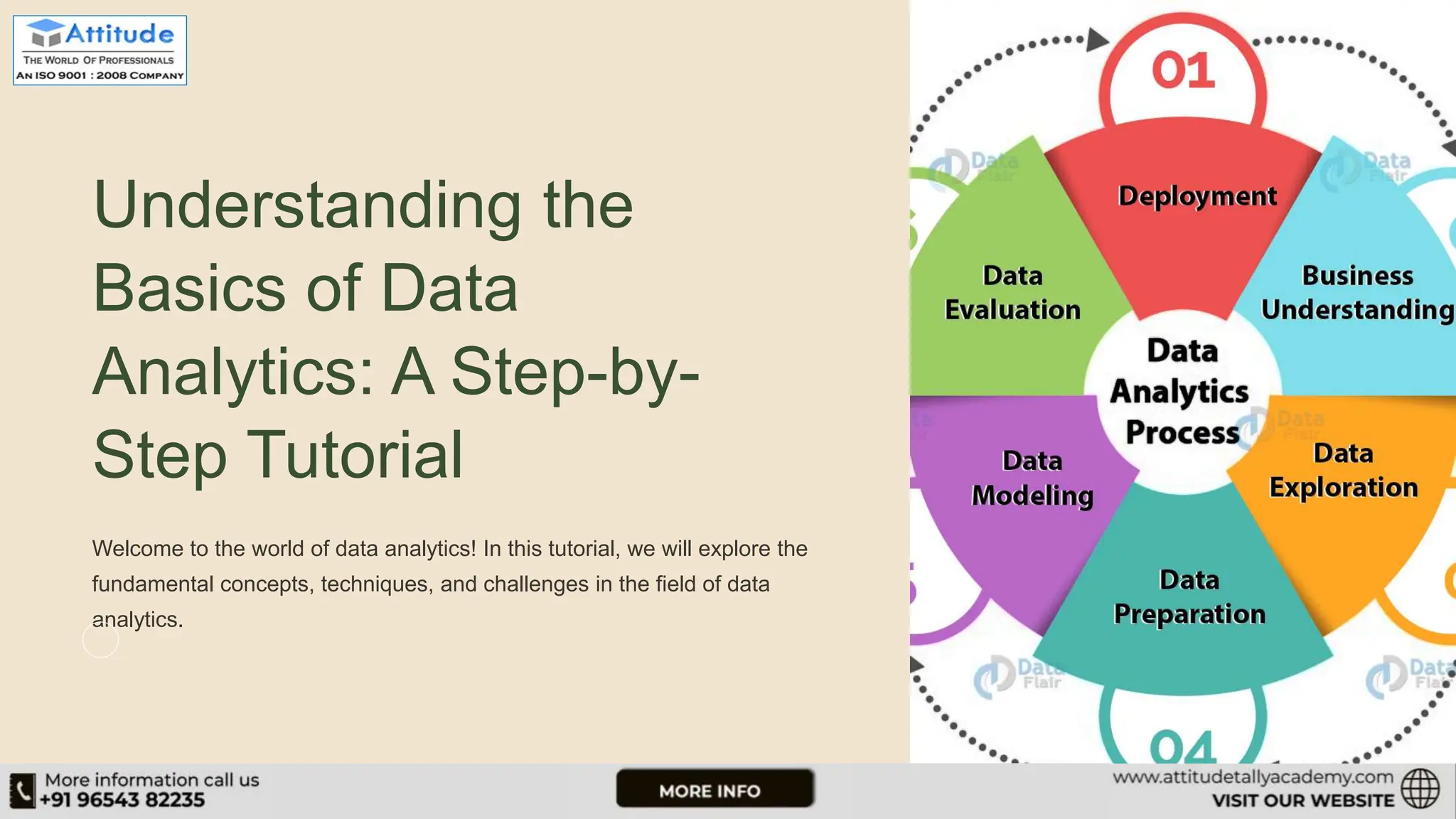
This document is a comprehensive tutorial on data analytics, covering its definitions, processes, and techniques. It outlines the importance of data analytics for decision-making and the key concepts including descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics. Additionally, it highlights challenges in the field, such as data privacy and ethical considerations, and emphasizes the necessity of continuous learning and available resources for further education.