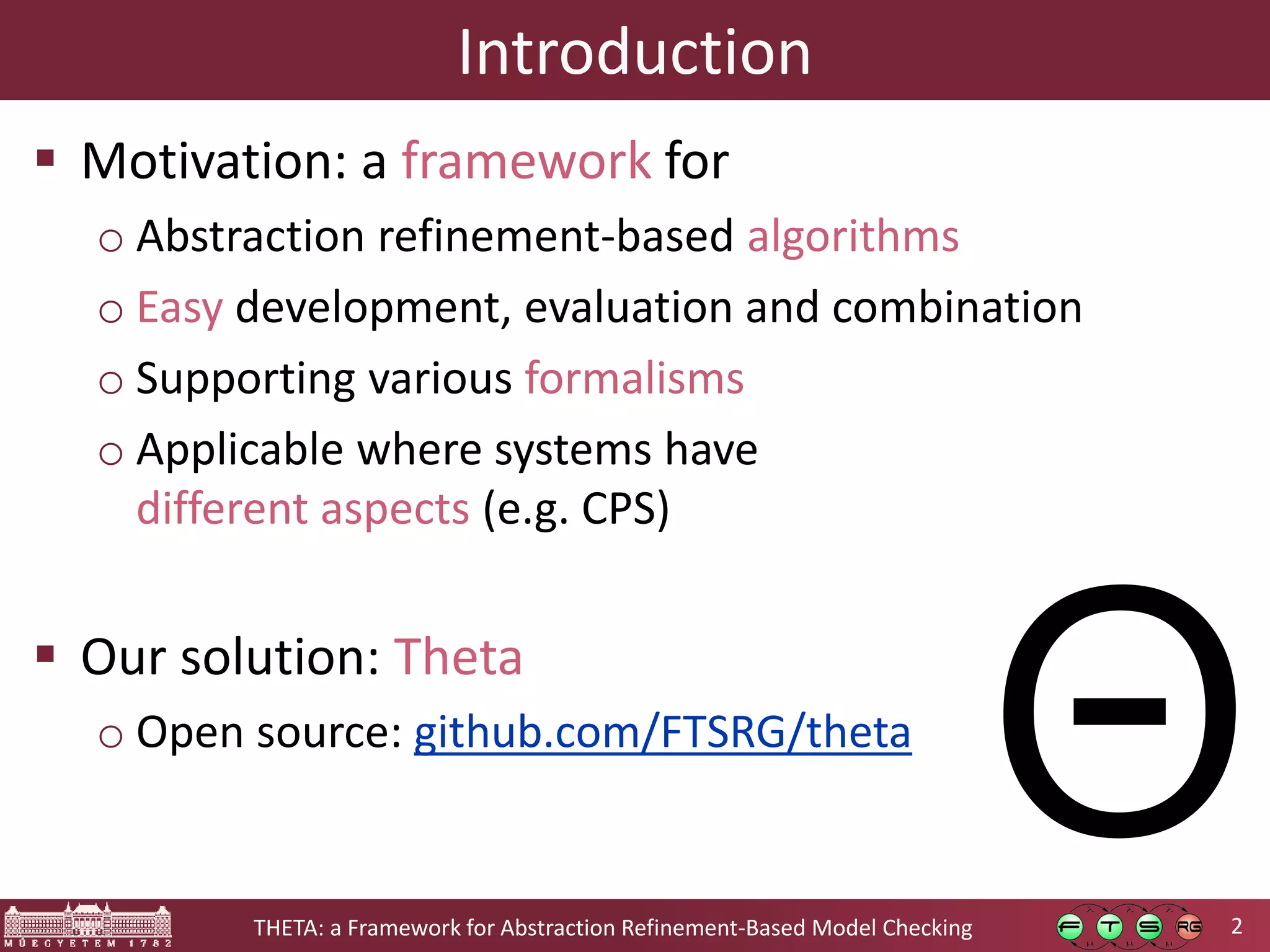
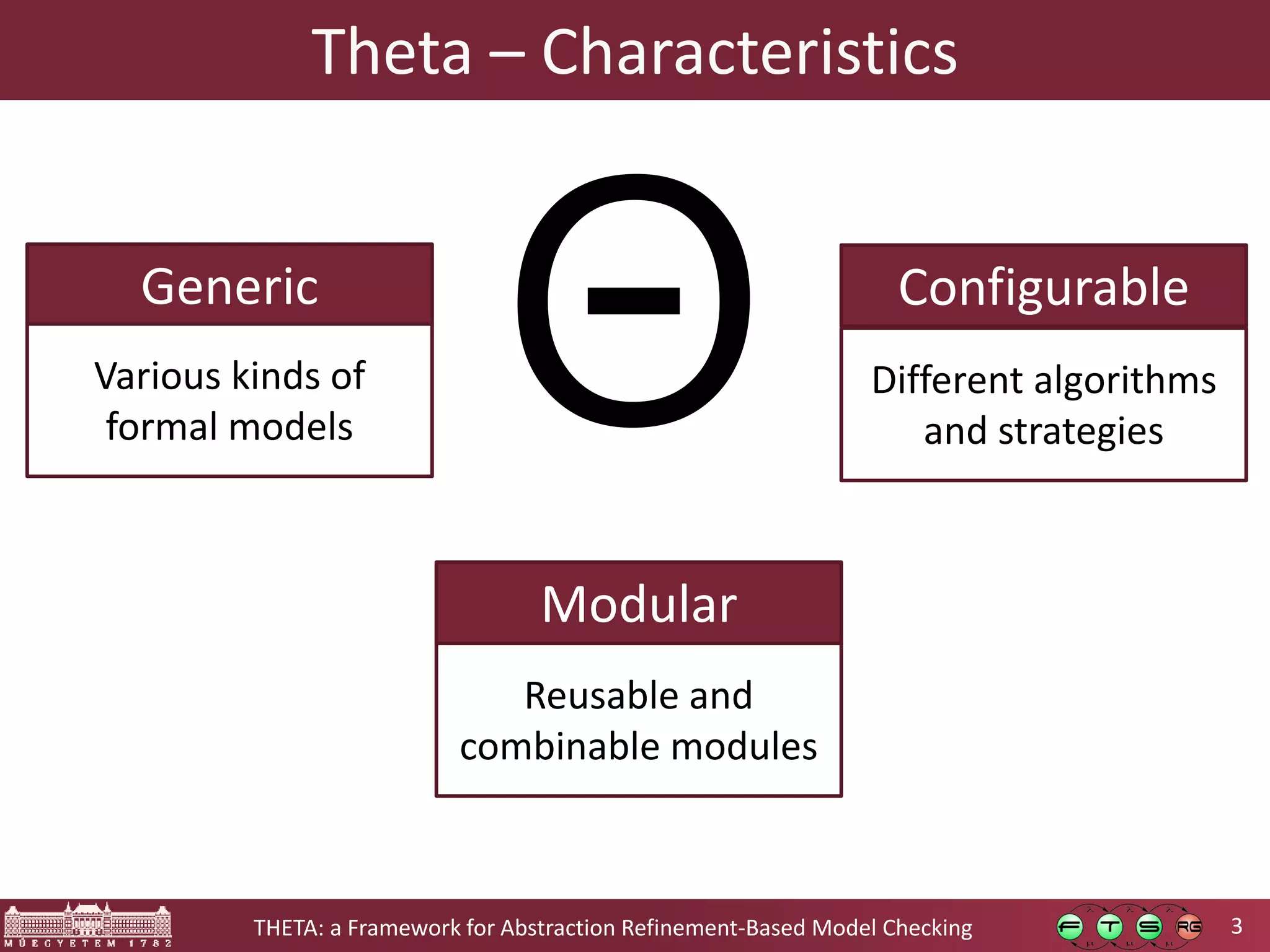
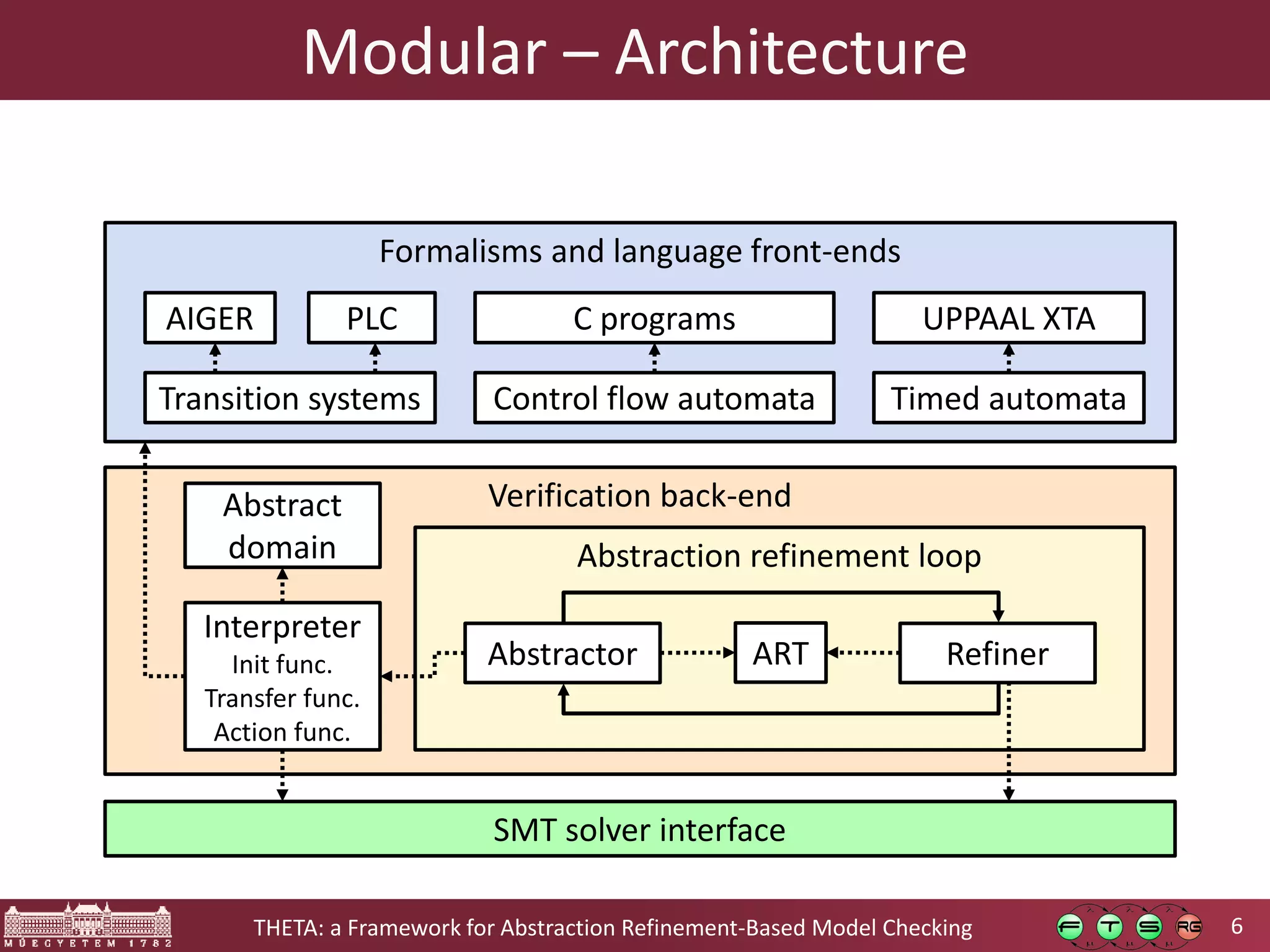
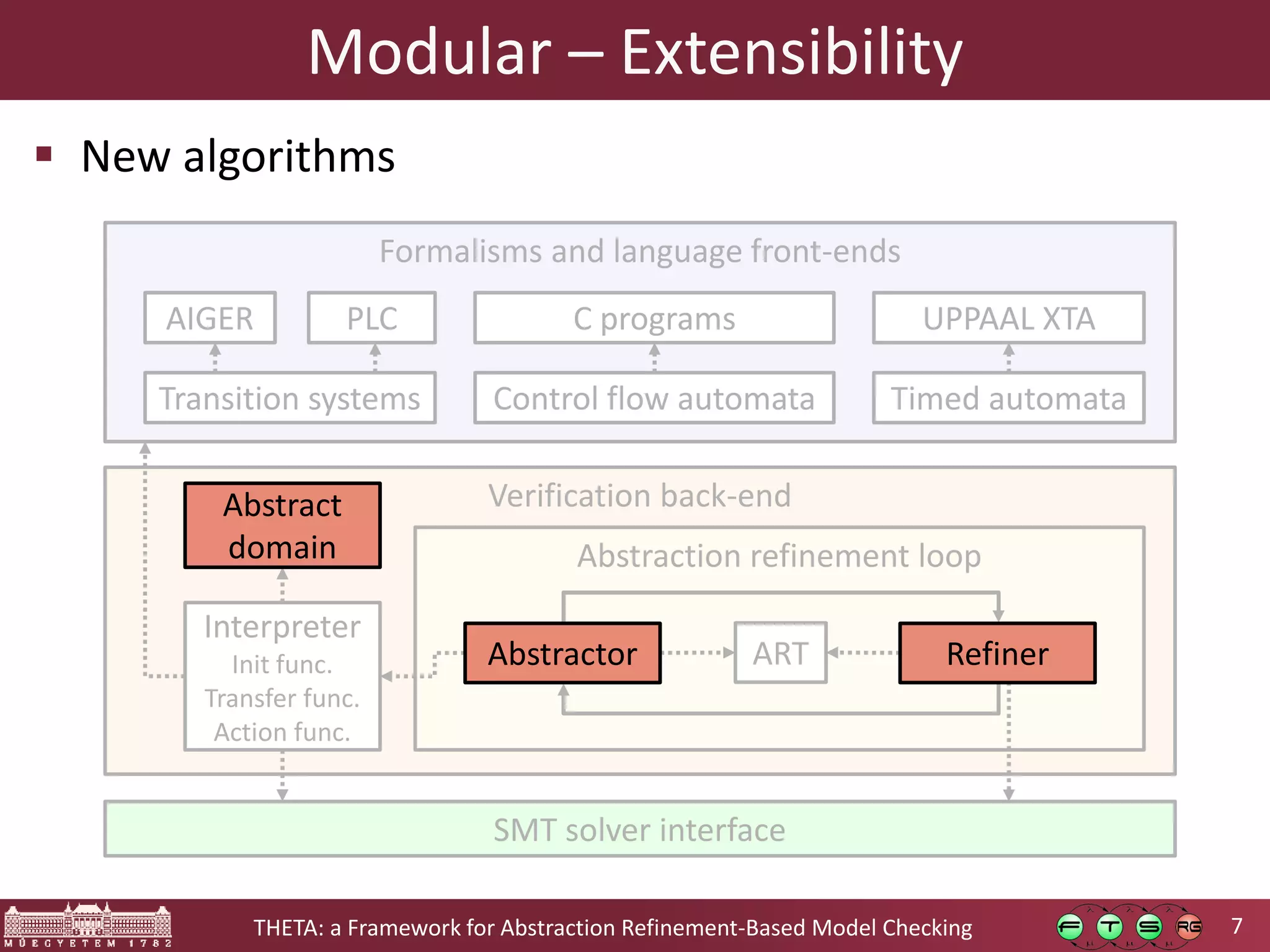
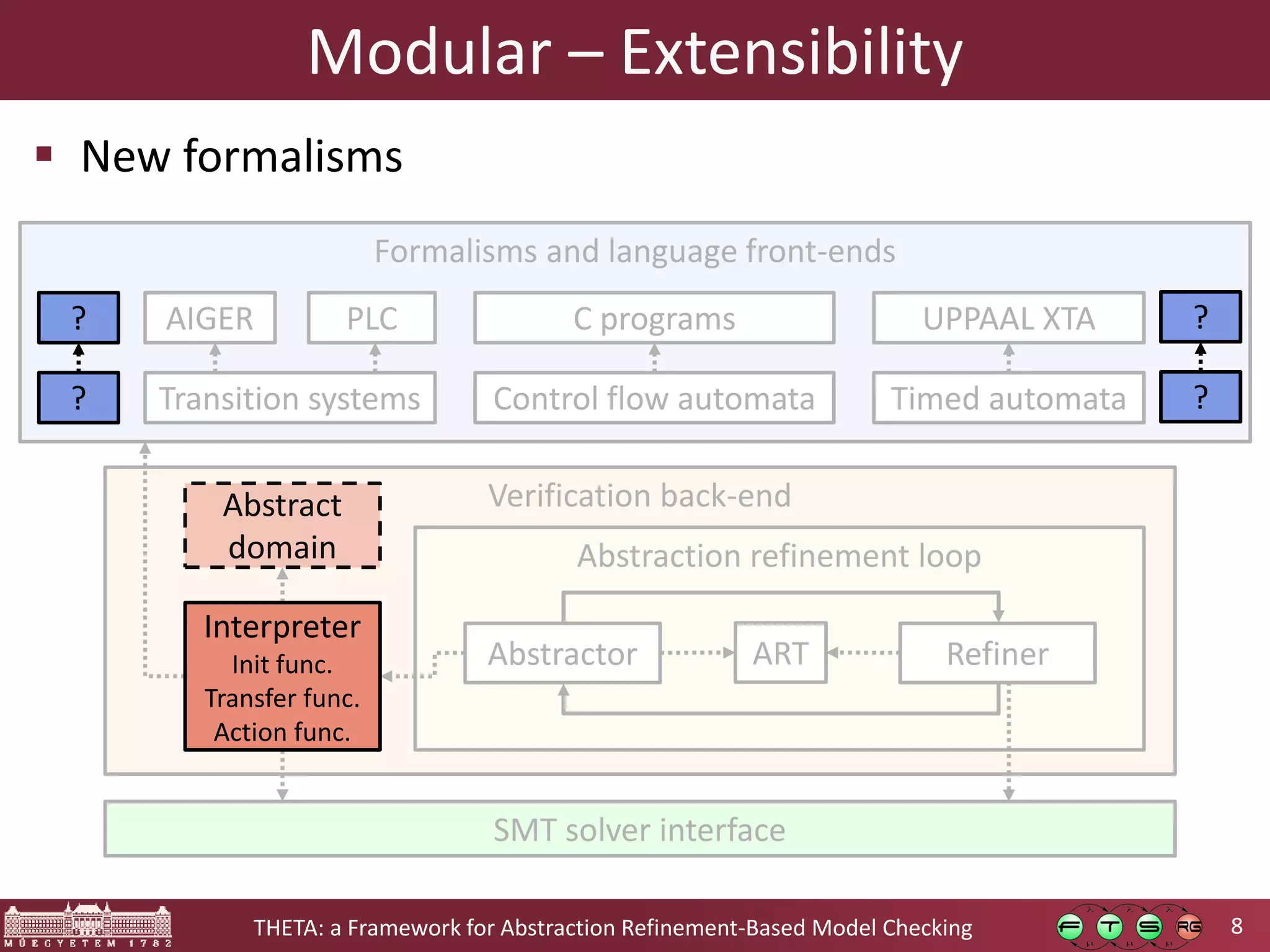
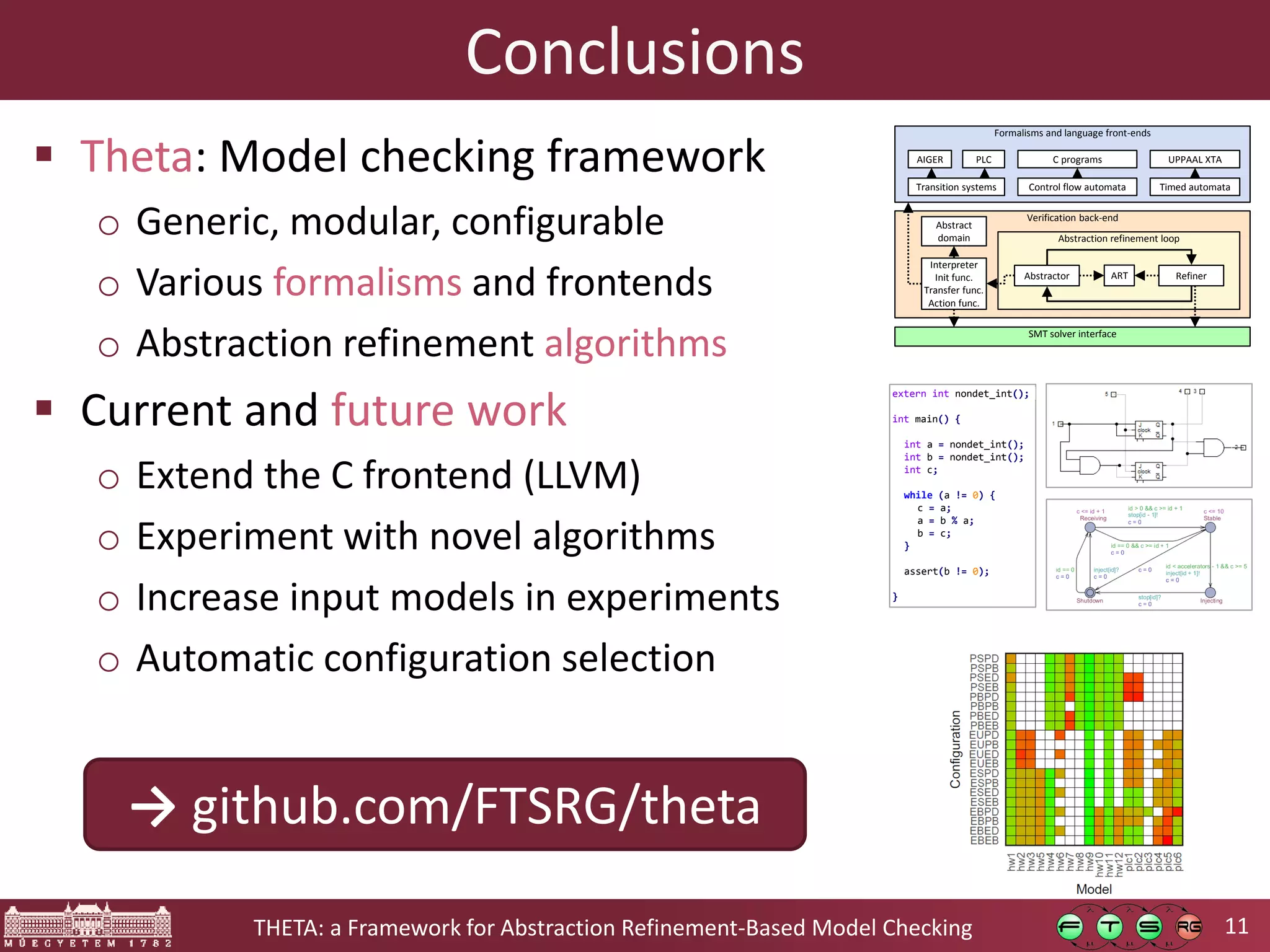
Theta is an open source framework for abstraction refinement-based model checking. It is generic, supporting various formalisms like symbolic transition systems, control flow automata, and timed automata. Theta is also modular, with reusable components that can be combined. It is configurable, allowing different abstraction refinement algorithms and strategies to be used. The goal of Theta is to facilitate the development, evaluation, and combination of abstraction refinement approaches for formal verification.
![4THETA: a Framework for Abstraction Refinement-Based Model Checking Generic – Formalisms Symbolic transition systems o Low level formalism o Based on SMT formulas Control flow automata o Programs as graphs o Edges annotated with statements Timed automata o Clock variables o Operations over clocks Support for new formalisms o Reusable components, e.g. expressions I := x = 0 Ʌ y = 0 T := x' = y + 1 Ʌ y’ = 2 * y x := 0 [x ≥ 5] [x < 5]x := x + 1 t := 0 t > 3 t ≤ 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fmcad2017theta-171005120945/75/Theta-a-Framework-for-Abstraction-Refinement-Based-Model-Checking-4-2048.jpg)
![5THETA: a Framework for Abstraction Refinement-Based Model Checking Generic – Language frontends Symbolic transition systems [FORTE’16] o AIGER format o Intermediate language for PLCs Control flow automata [VPT’17] o Subset of C o Size reduction techniques Timed automata [FORMATS’17] o UPPAAL XTA extern int nondet_int(); int main() { int a = nondet_int(); int b = nondet_int(); int c; while (a != 0) { c = a; a = b % a; b = c; } assert(b != 0); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fmcad2017theta-171005120945/75/Theta-a-Framework-for-Abstraction-Refinement-Based-Model-Checking-5-2048.jpg)
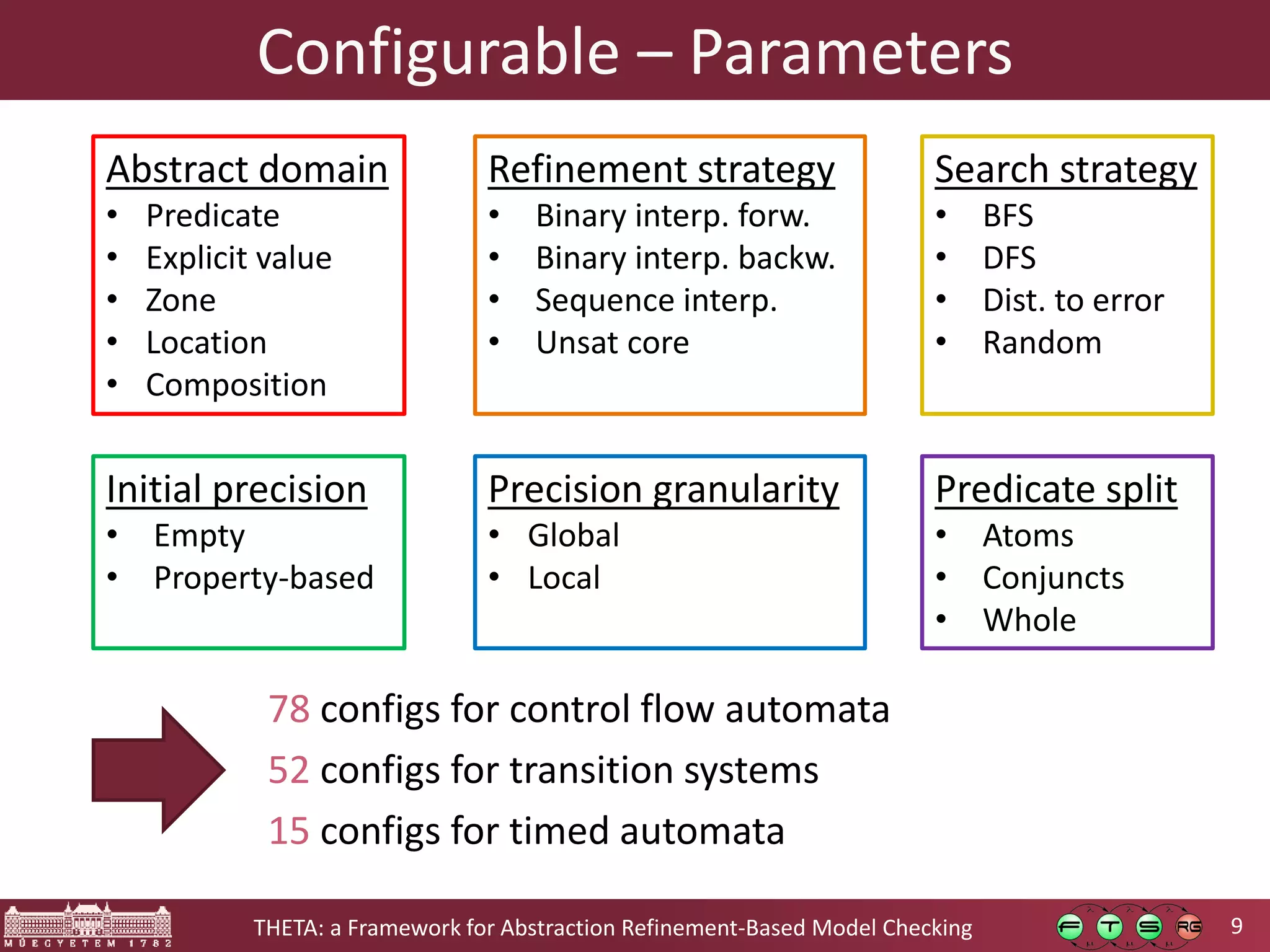
![10THETA: a Framework for Abstraction Refinement-Based Model Checking Configurable – Use Cases Developing and evaluating new algorithms o Extending predicate abstraction with explicit values [FORTE’16] o Lazy reachability checking of timed automata [FORMATS’17] Diverse results support configurability HWMCC & PLC [MiniSym’17] SV-COMP [VPT’17] UPPAAL [FORMATS’17] Comparison of execution time in case of different analysis configurations on various models](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fmcad2017theta-171005120945/75/Theta-a-Framework-for-Abstraction-Refinement-Based-Model-Checking-10-2048.jpg)
![12THETA: a Framework for Abstraction Refinement-Based Model Checking References [FORTE’16] A Configurable CEGAR Framework with Interpolation-based Refinements. Hajdu, Á.; Tóth, T.; Vörös, A.; and Majzik, I. In Formal Techniques for Distributed Objects, Components and Systems, vol. 9688 of LNCS, pages 158--174. Springer, 2016. [MiniSym’17] Exploratory Analysis of the Performance of a Configurable CEGAR Framework. Hajdu, Á.; and Micskei, Z. In Proceedings of the 24th PhD Mini-Symposium, pages 34--37, 2017. Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department of Measurement and Information Systems [VPT’17] Towards Evaluating Size Reduction Techniques for Software Model Checking. Sallai, Gy.; Hajdu, Á.; Tóth, T.; and Micskei, Z. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Workshop on Verification and Program Transformation, vol. 253 of EPTCS, pages 75--91. Open Publishing Association, 2017. [FORMATS’17] Lazy Reachability Checking for Timed Automata using Interpolants. Tóth, T.; and Majzik, I. In Formal Modelling and Analysis of Timed Systems, vol. 10419 of LNCS, pages 264--280. Springer, 2017.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fmcad2017theta-171005120945/75/Theta-a-Framework-for-Abstraction-Refinement-Based-Model-Checking-12-2048.jpg)