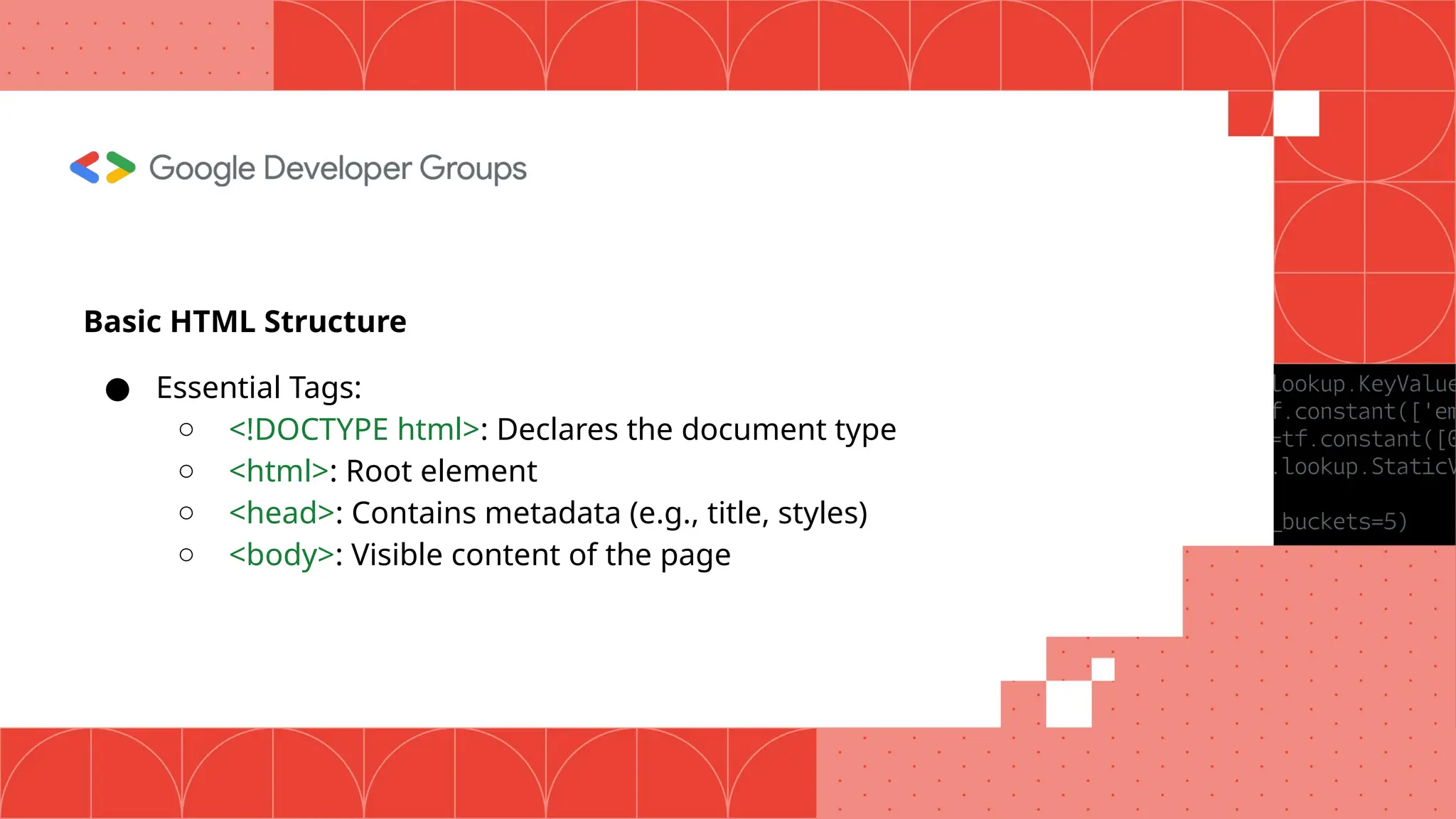
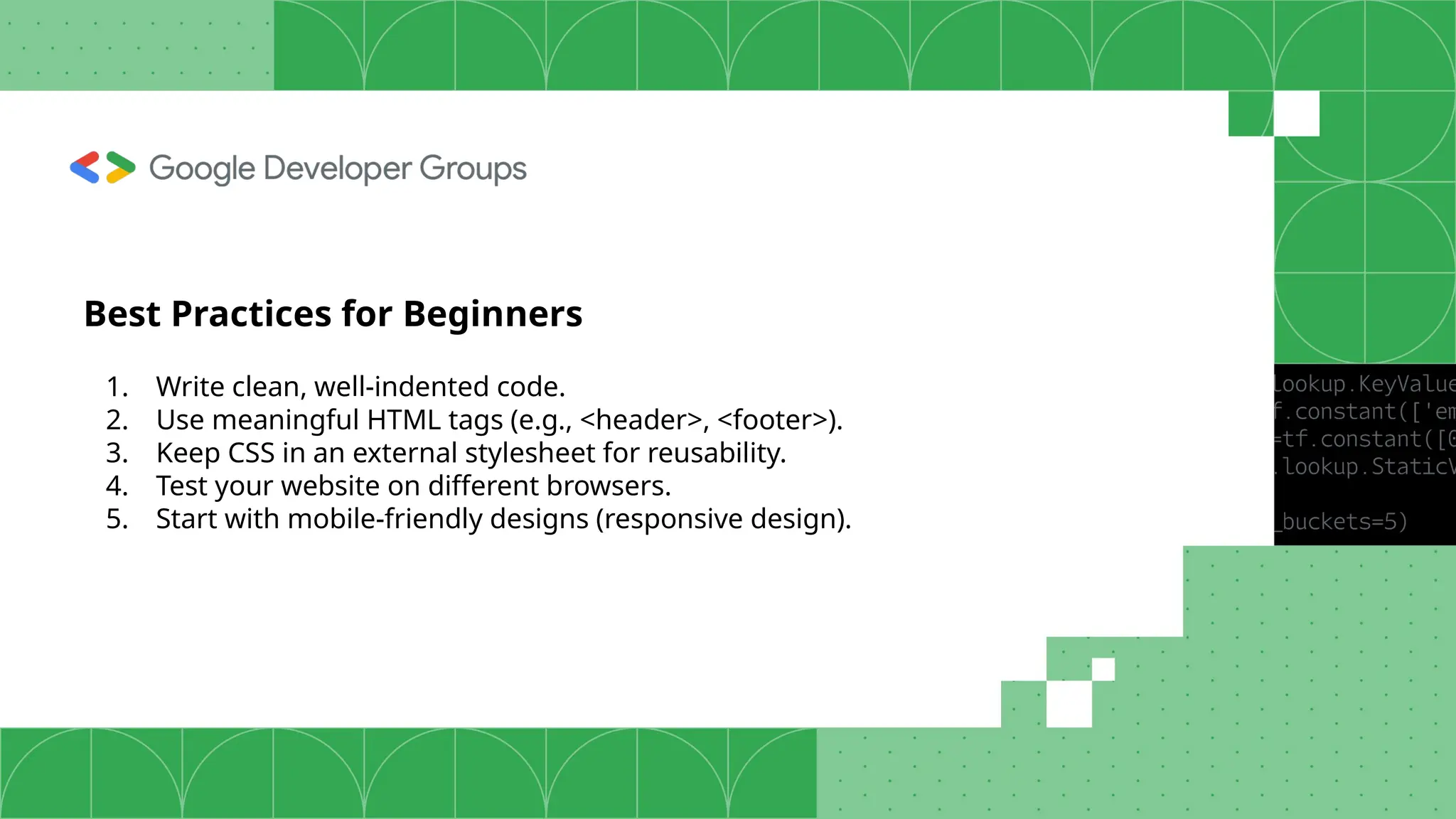
The document outlines the basics of web development, including the distinction between frontend and backend technologies, and the roles of HTML and CSS in creating web pages. Key elements include the structure of HTML, the styling capabilities of CSS, and tools for development and testing. It encourages beginners to start with small projects and provides best practices for writing clean and effective code.