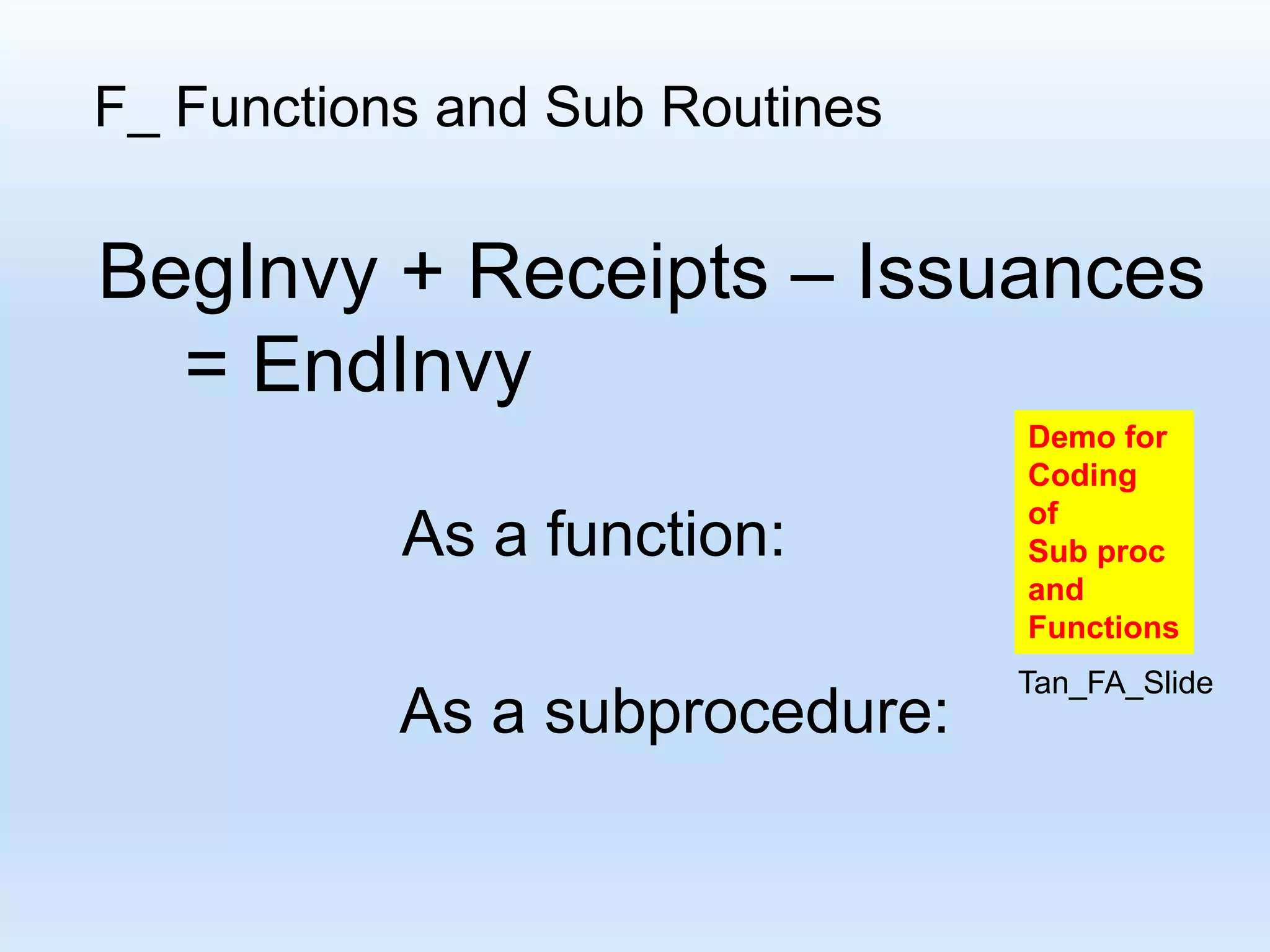
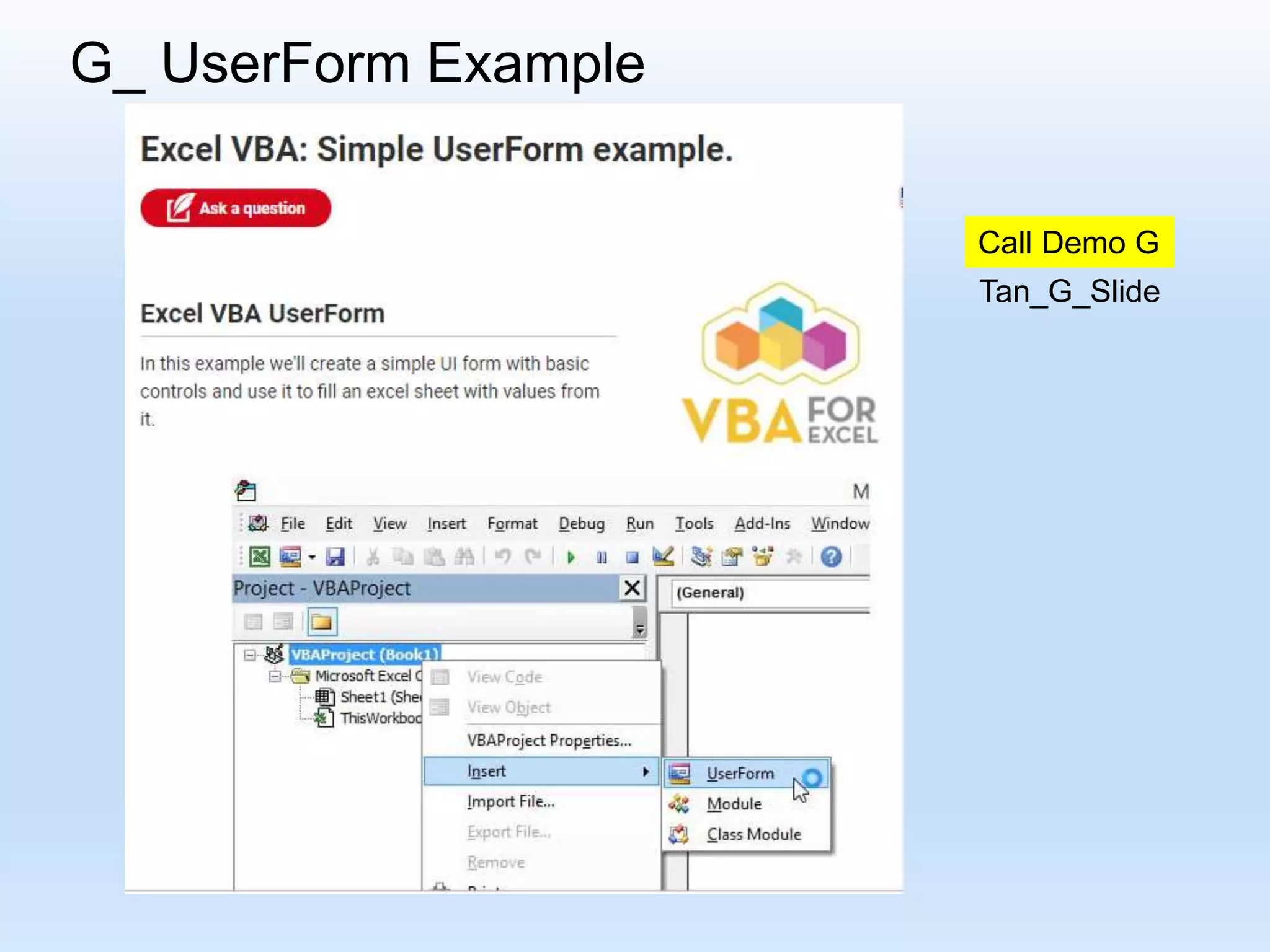
This document provides an introduction to using Excel VBA and macros for logistics and supply chain management. It outlines topics like why VBA is important given Excel's widespread use, what VBA is, how to start with VBA, recording macros, running macros, functions and subroutines, and using user forms. Examples are provided for coding procedures and functions to automate tasks like filling cells, reading cell values, and preparing reports.











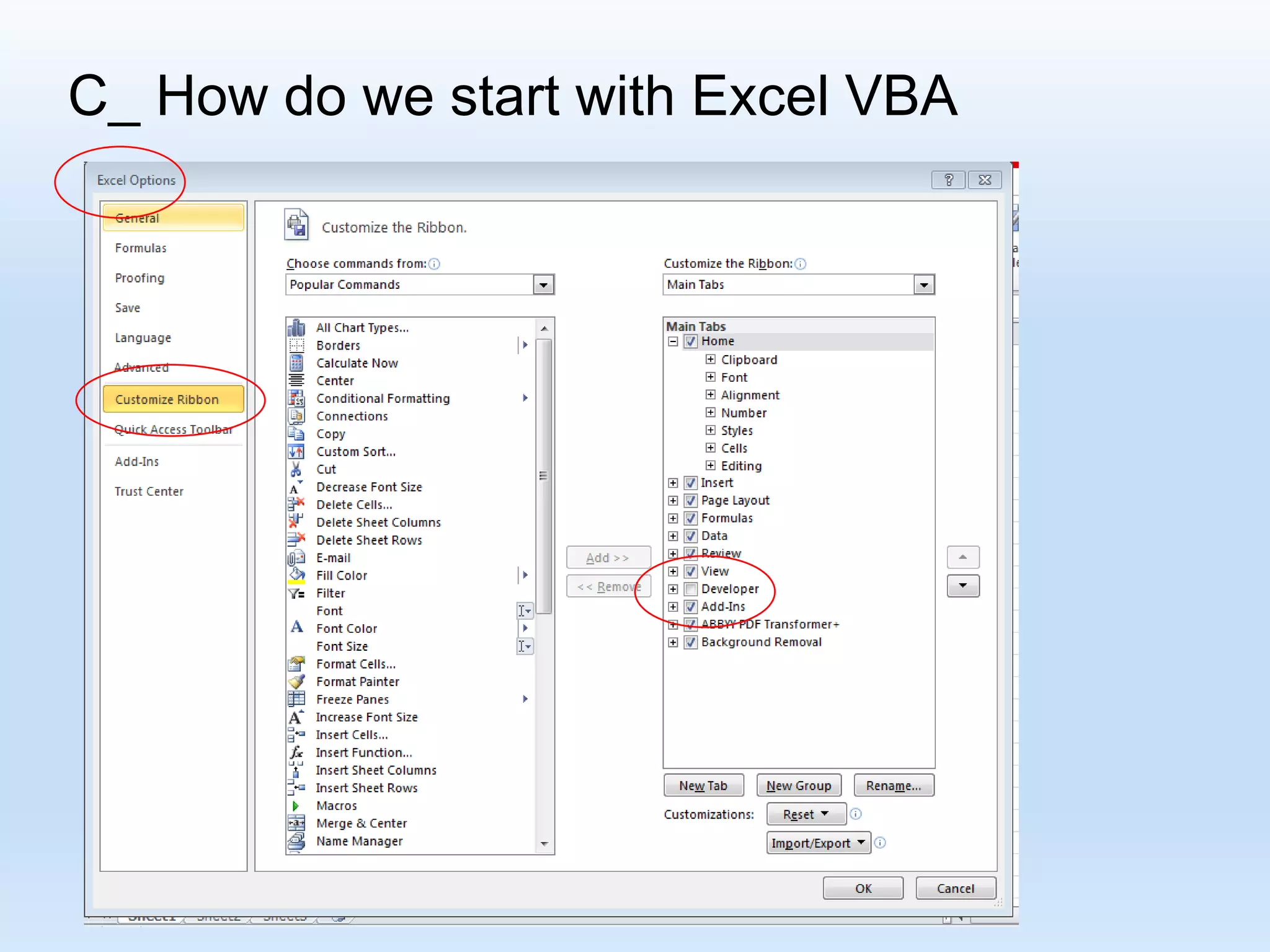
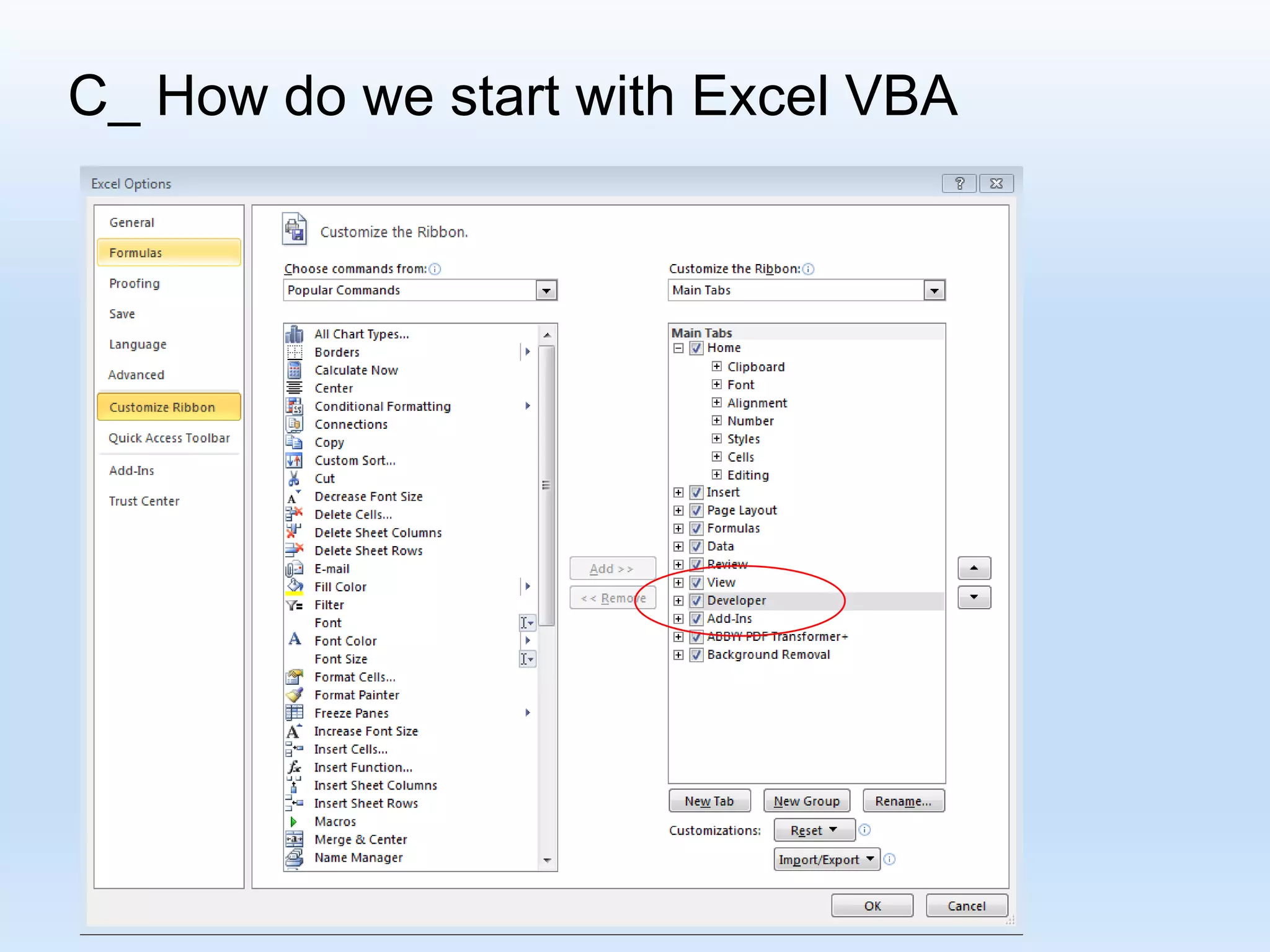
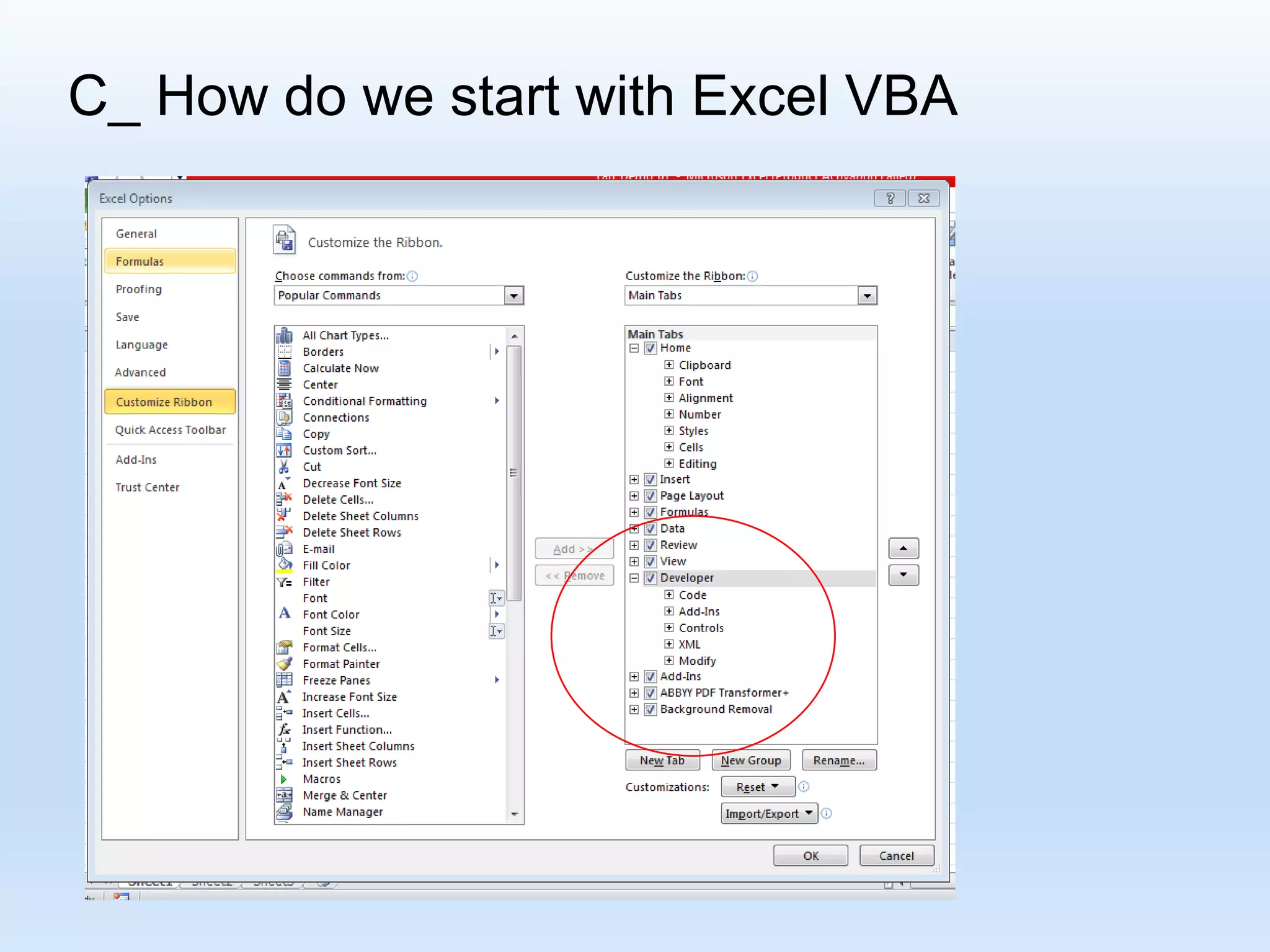
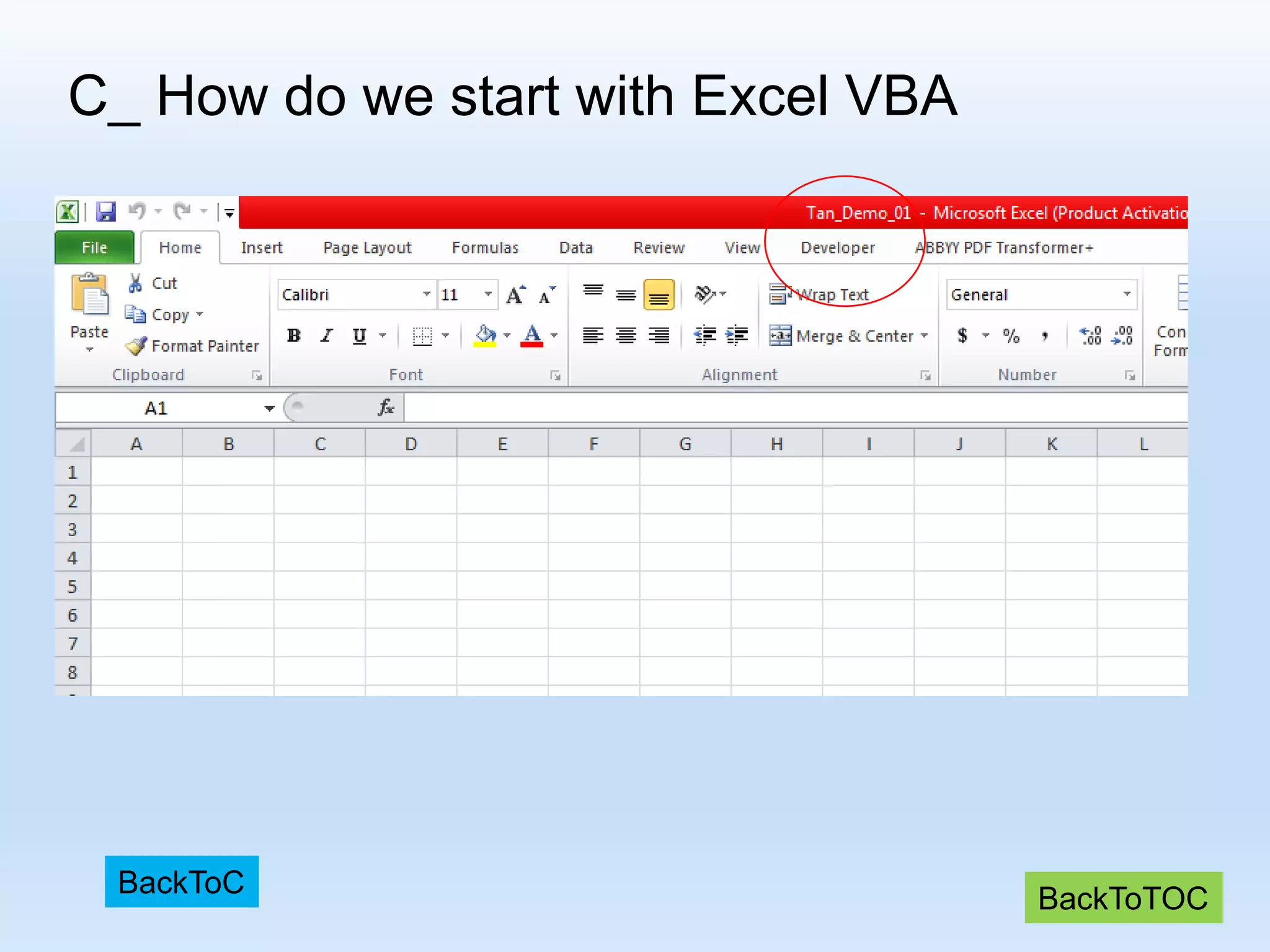



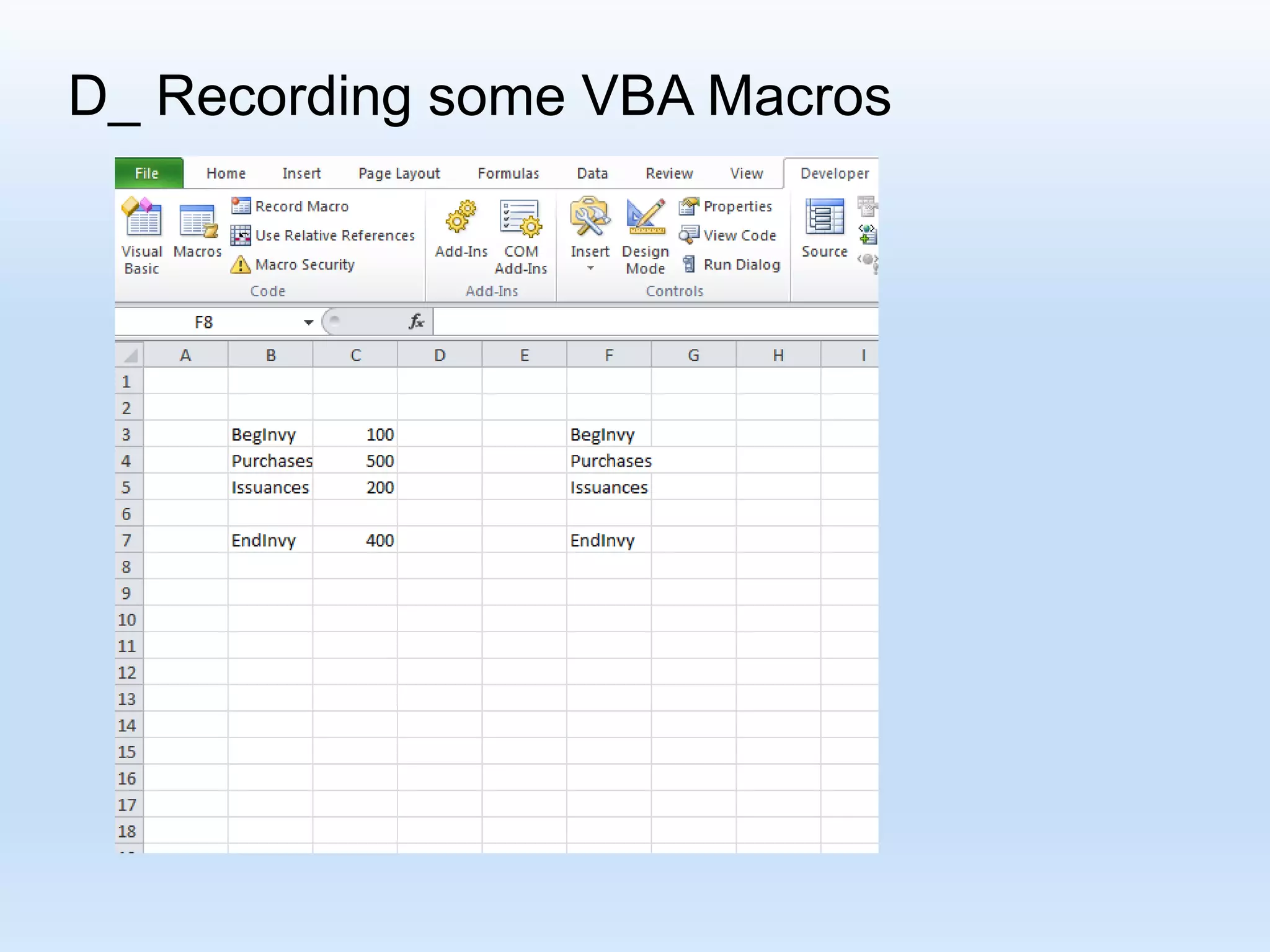
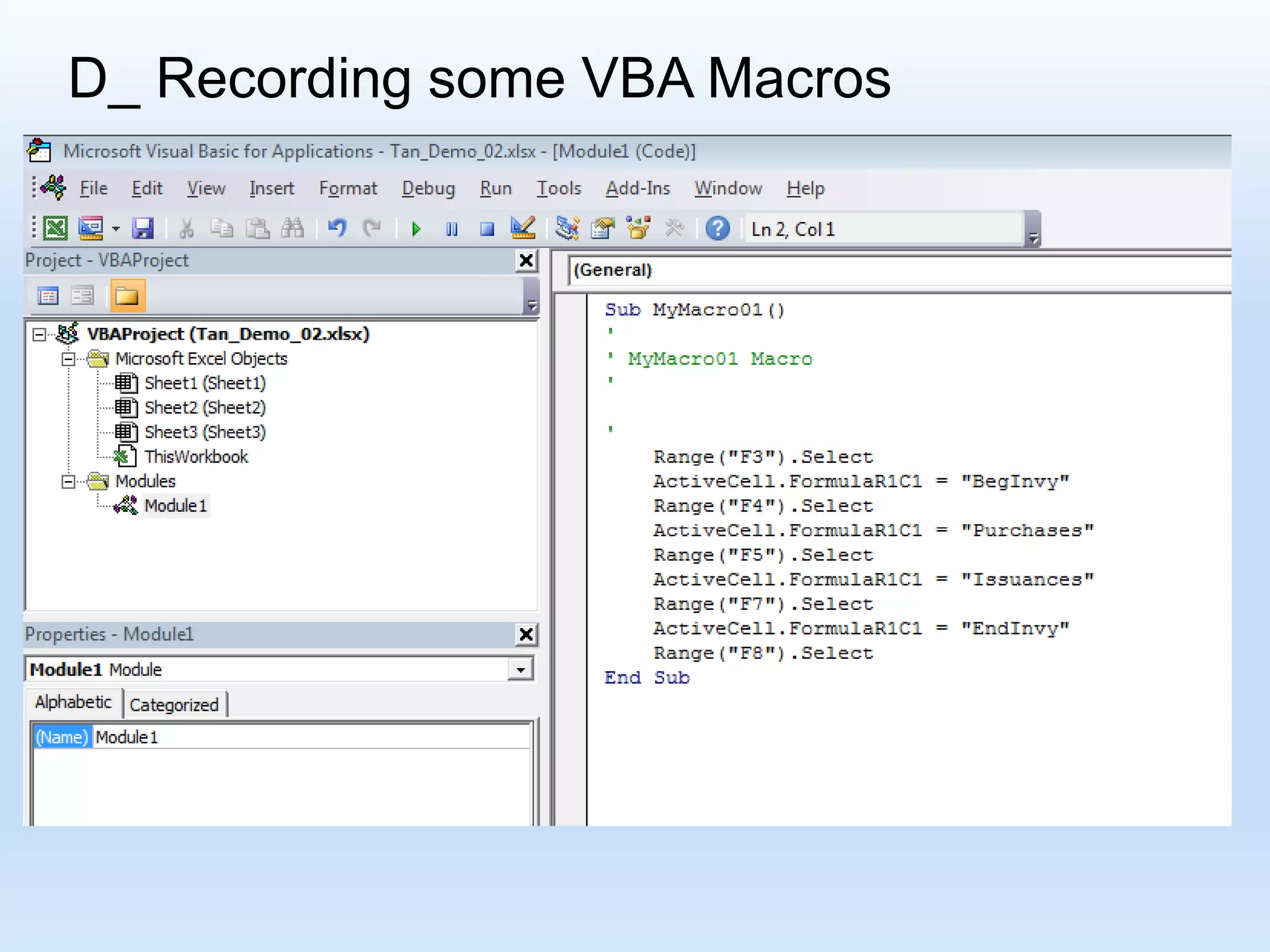


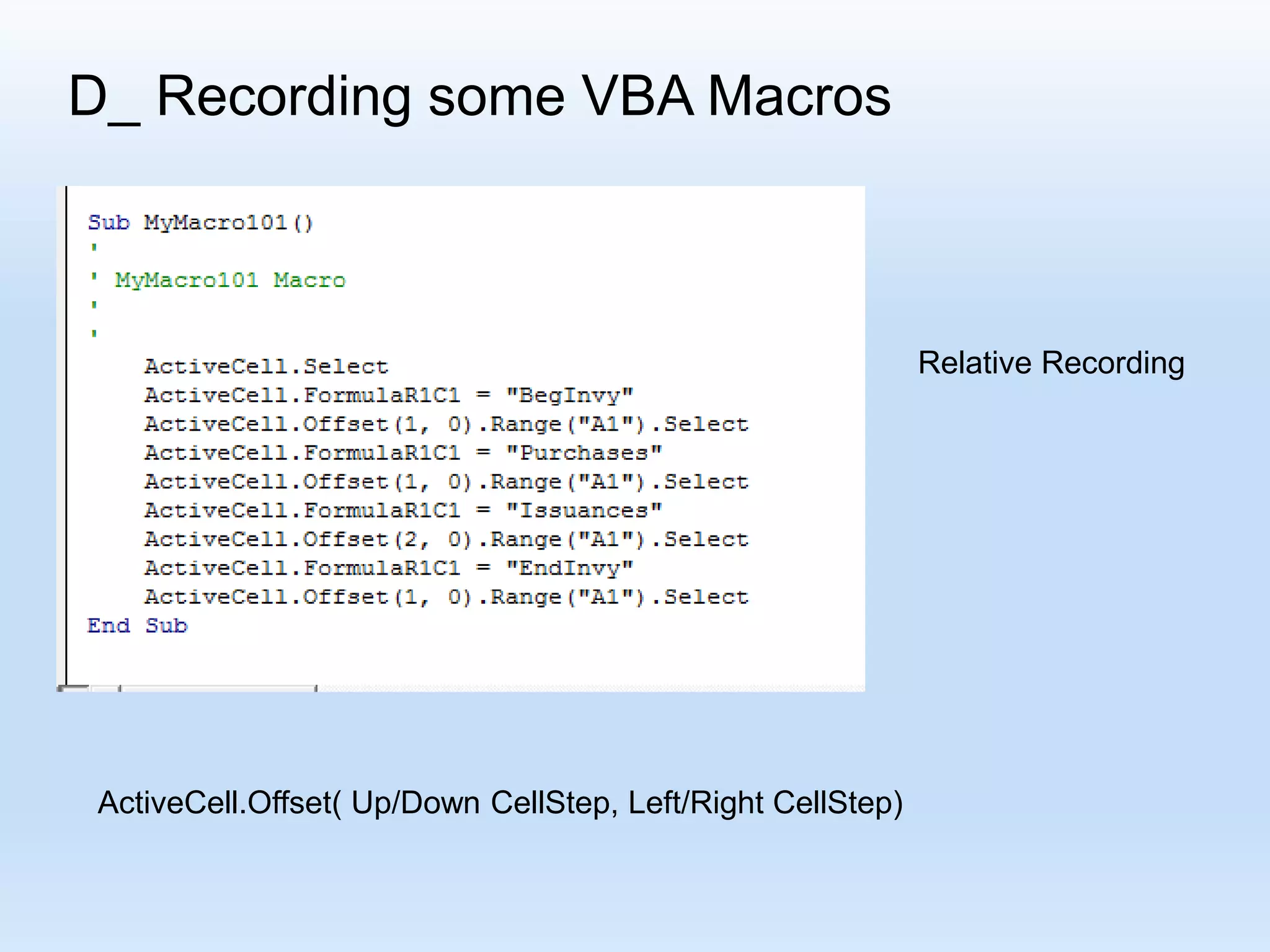
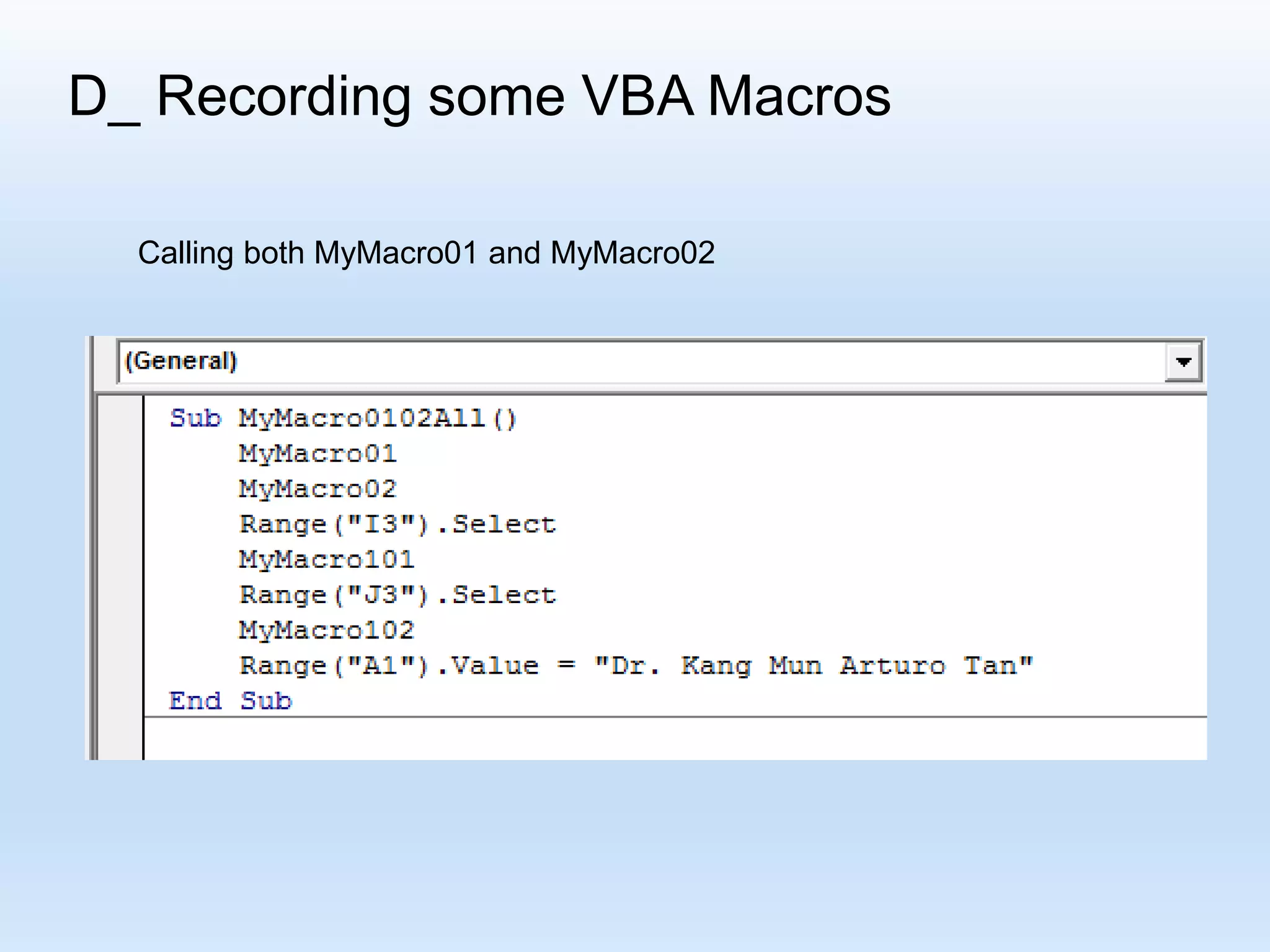
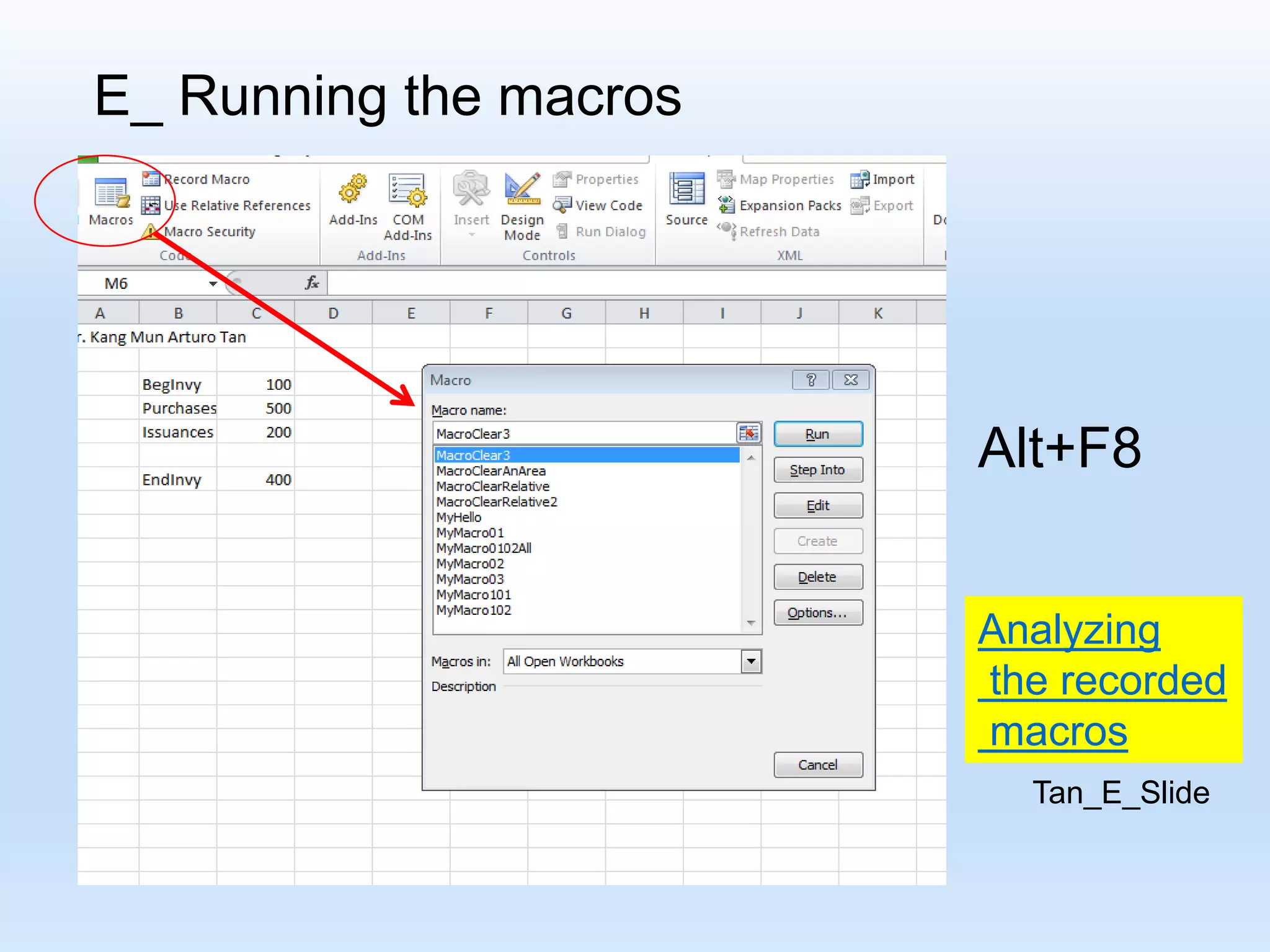
![D_ Recording some VBA Macros R[ Up/Down CellDistance] C[Left/Right CellDistance] Focusing on the formula: “R[-4] C + R[-3] C - R[-2] C “](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tanmacroslidespresentation-190125062613/75/Introduction-to-Excel-VBA-Macros-25-2048.jpg)