Here are solutions to the exercises: 1. Write a program that reverses a string: ```java import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter a string: "); String input = scanner.nextLine(); String reversed = ""; for (int i = input.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { reversed += input.charAt(i); } System.out.println("Reversed string: " + reversed); } } ``` 2. Write a program to







![JAVA.LANG.STRING • String objects are like arrays of characters (char[]) • Have fixed length (String.length()) • Elements can be accessed by index • Using charAt() method • The index is in the range 0...length()-1 String s = "Hello!"; int len = s.length(); // len = 6 char ch = s.charAt(1); // ch = 'e„` index = 0 1 2 3 4 5 s.charAt(index) = H e l l o !](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringandstringmanipulation-130307033146-phpapp01/75/String-and-string-manipulation-x-9-2048.jpg)
![STRINGS – FIRST EXAMPLE String s = “Hidaya Institute of Science & Tchnology."; System.out.printf("s = "%s"%n", s); System.out.printf("s.length() = %d%n", s.length()); for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { System.out.printf("s[%d] = %c%n", i, s.charAt(i)); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringandstringmanipulation-130307033146-phpapp01/75/String-and-string-manipulation-x-10-2048.jpg)





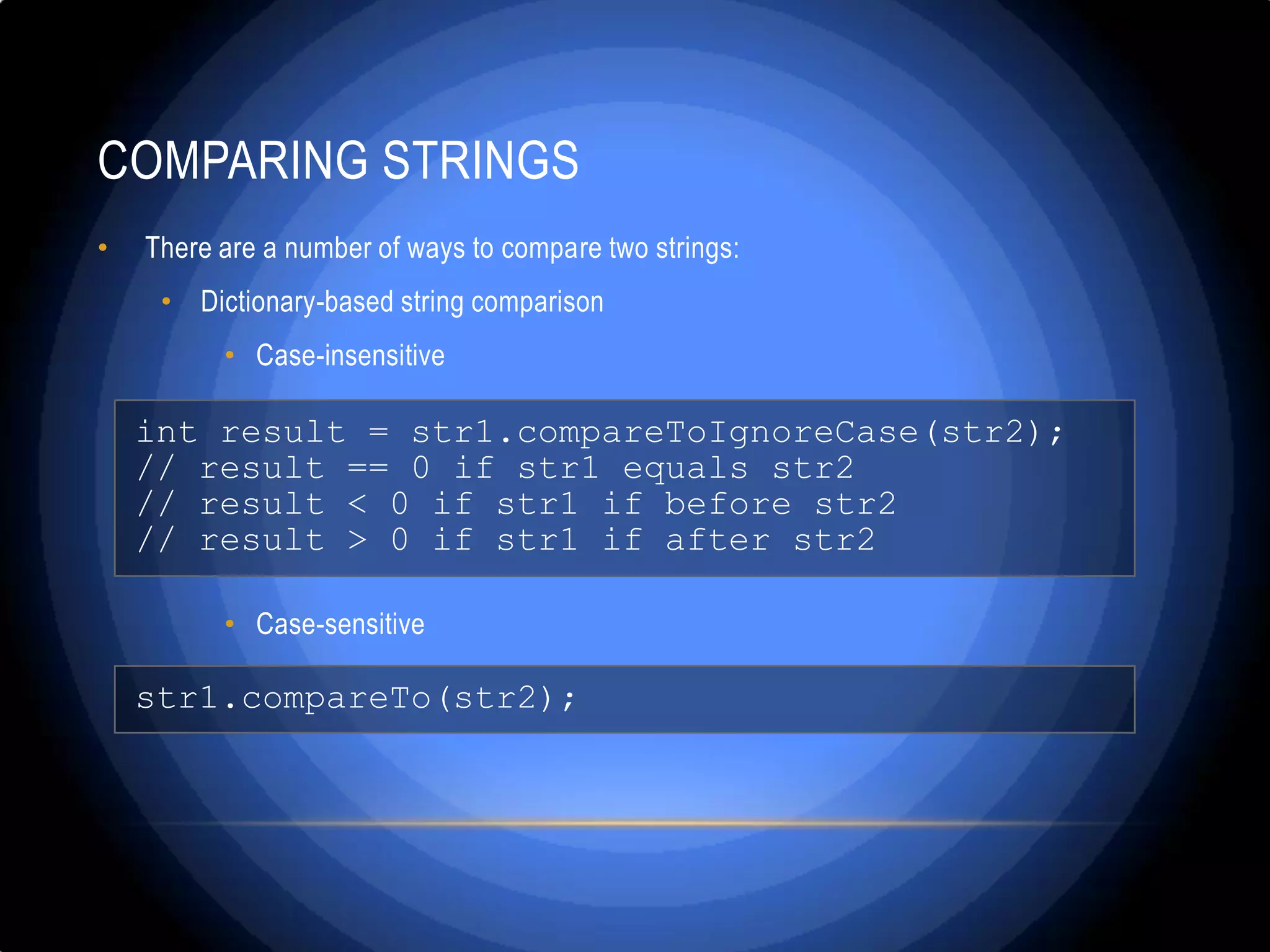
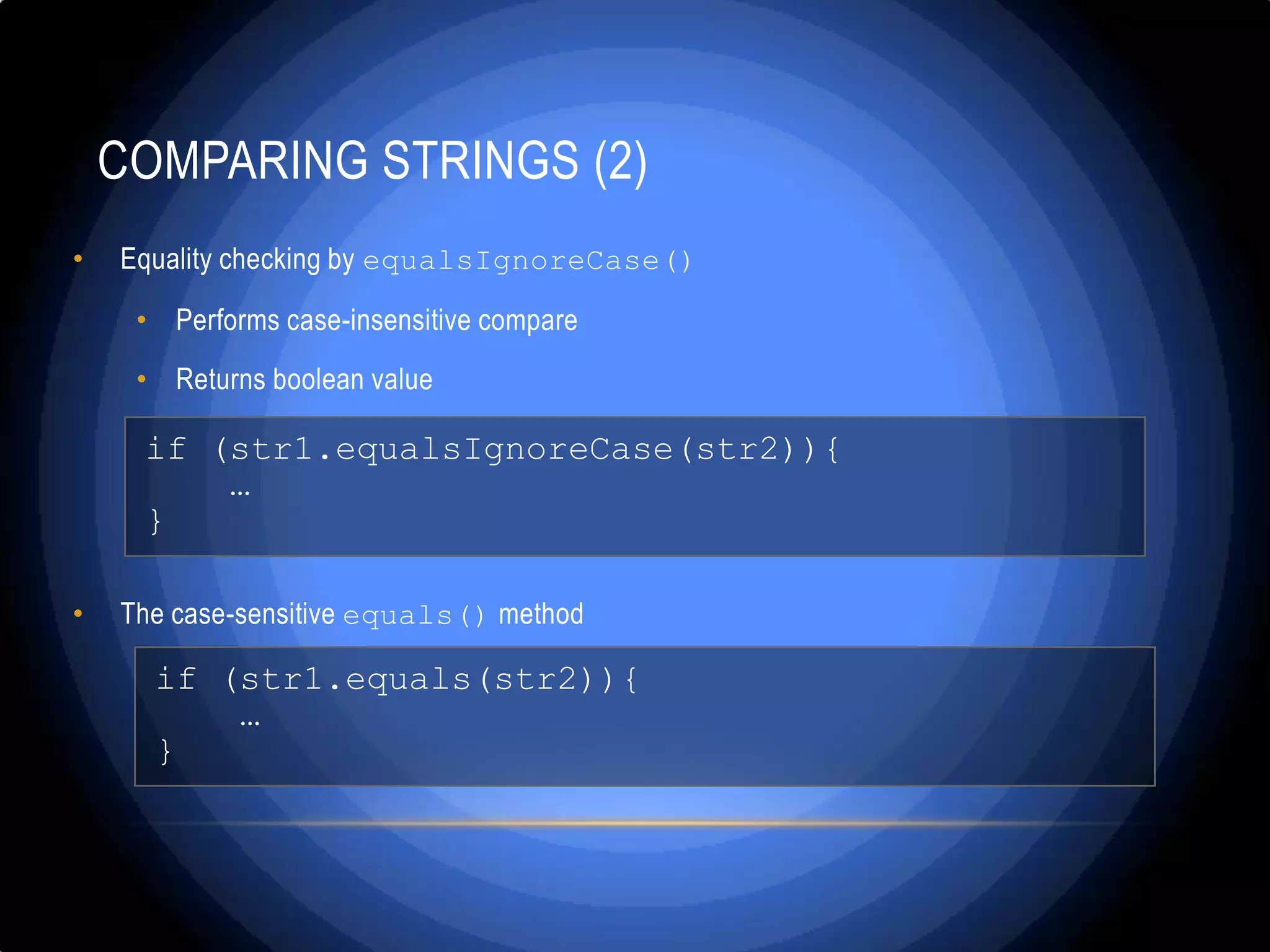

![COMPARING STRINGS – EXAMPLE • Finding the first in a lexicographical order string from a given list of strings String[] towns = {"Jamshoro", "hyderabad", "Qasimabad","Latifabad", "Kotri", "Heerabad"}; String firstTown = towns[0]; for (int i=1; i<towns.length; i++) { String currentTown = towns[i]; if (currentTown.compareTo(firstTown) < 0) { firstTown = currentTown; } } System.out.println("First town: " + firstTown);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringandstringmanipulation-130307033146-phpapp01/75/String-and-string-manipulation-x-21-2048.jpg)







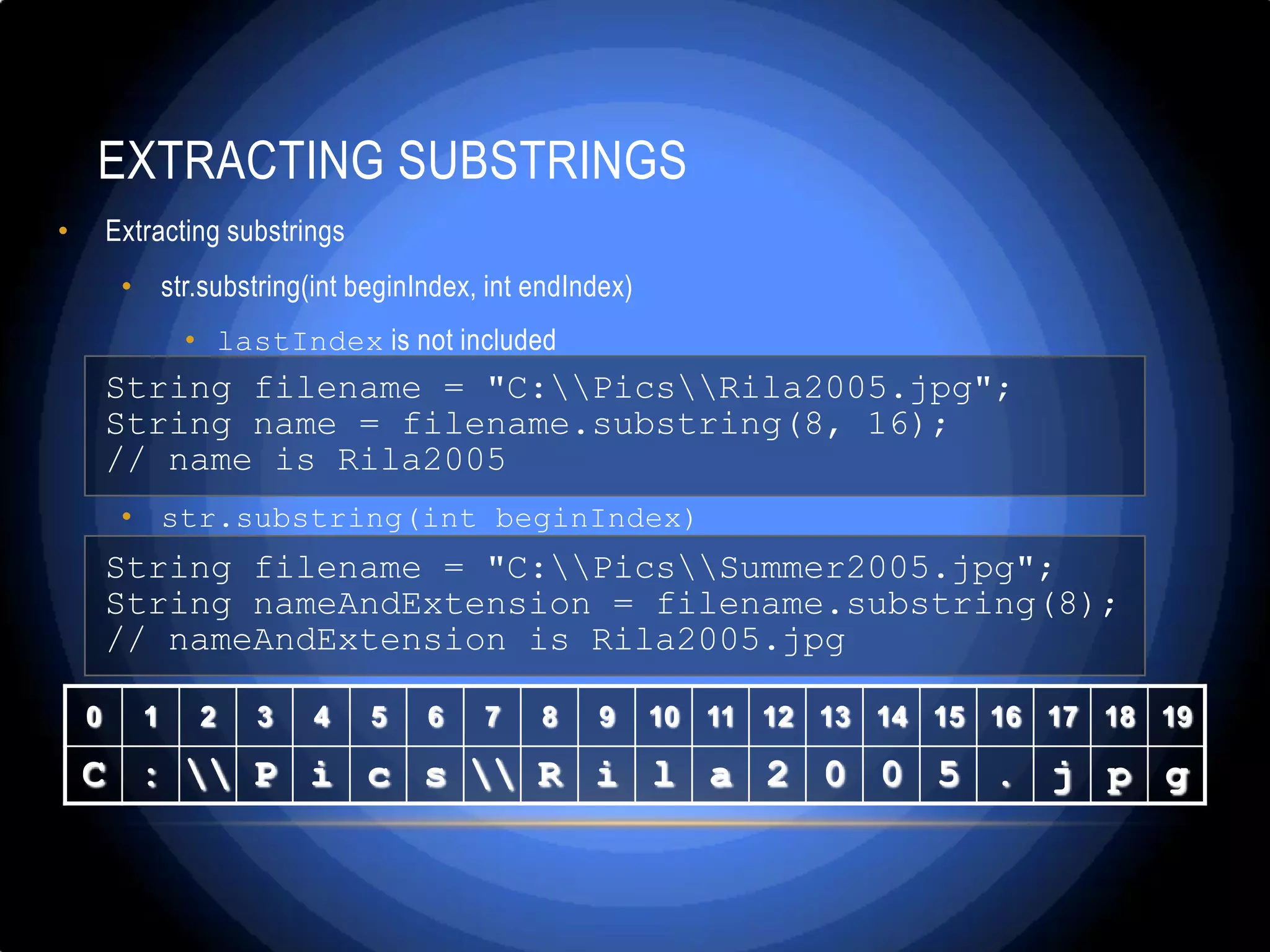

![SPLITTING STRINGS • To split a string by given separator(s) use the following method: String[] split(String regex) • String regex – String with special format • We can list the character which we want to use for separator in square brackets […] String[] parts = "Ivan; Petar,Gosho".split("[;,]"); // this wil separate the stirng into three parts // "Ivan", " Petar" and "Gosho"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringandstringmanipulation-130307033146-phpapp01/75/String-and-string-manipulation-x-31-2048.jpg)
![SPLITTING STRINGS - EXAMPLE String listOfBeers = "Amstel, Zagorka, Tuborg, Becks."; String[] beers = listOfBeers.split("[ ,.]"); System.out.println("Available beers are:"); for (String beer : beers) { if (!"".equalsIgnoreCase(beer)) { System.out.println(beer); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringandstringmanipulation-130307033146-phpapp01/75/String-and-string-manipulation-x-32-2048.jpg)


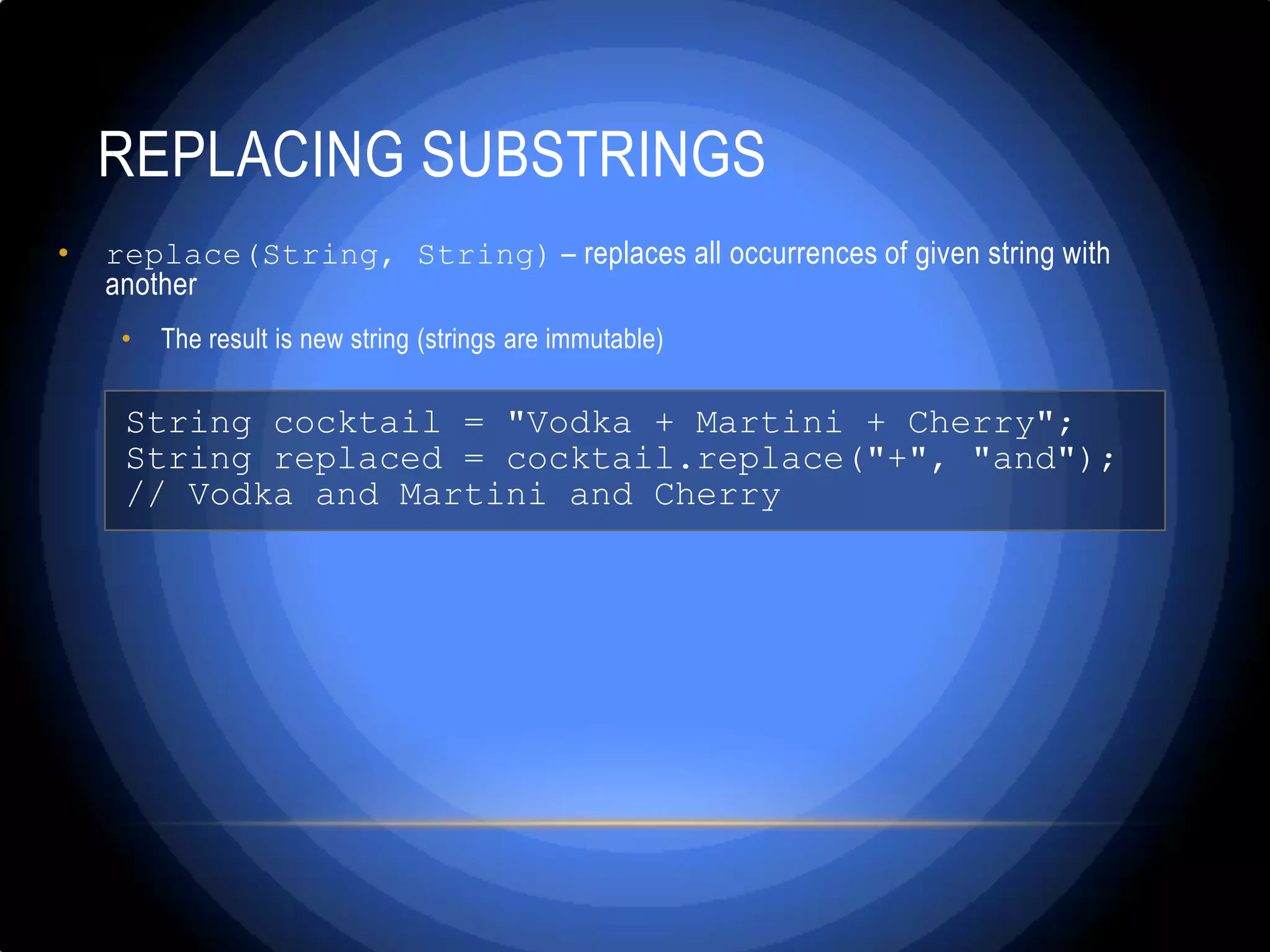
















![ Write a program that parses an URL address given in the format: [protocol]://[server]/[resource] and extracts from it the [protocol], [server] and [resource] elements. For example from the URL http://www.devbg.org/forum/index.php following information should be extracted: [protocol] = "http", [server] = "www.devbg.org", [resource] = "/forum/index.php "](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringandstringmanipulation-130307033146-phpapp01/75/String-and-string-manipulation-x-56-2048.jpg)