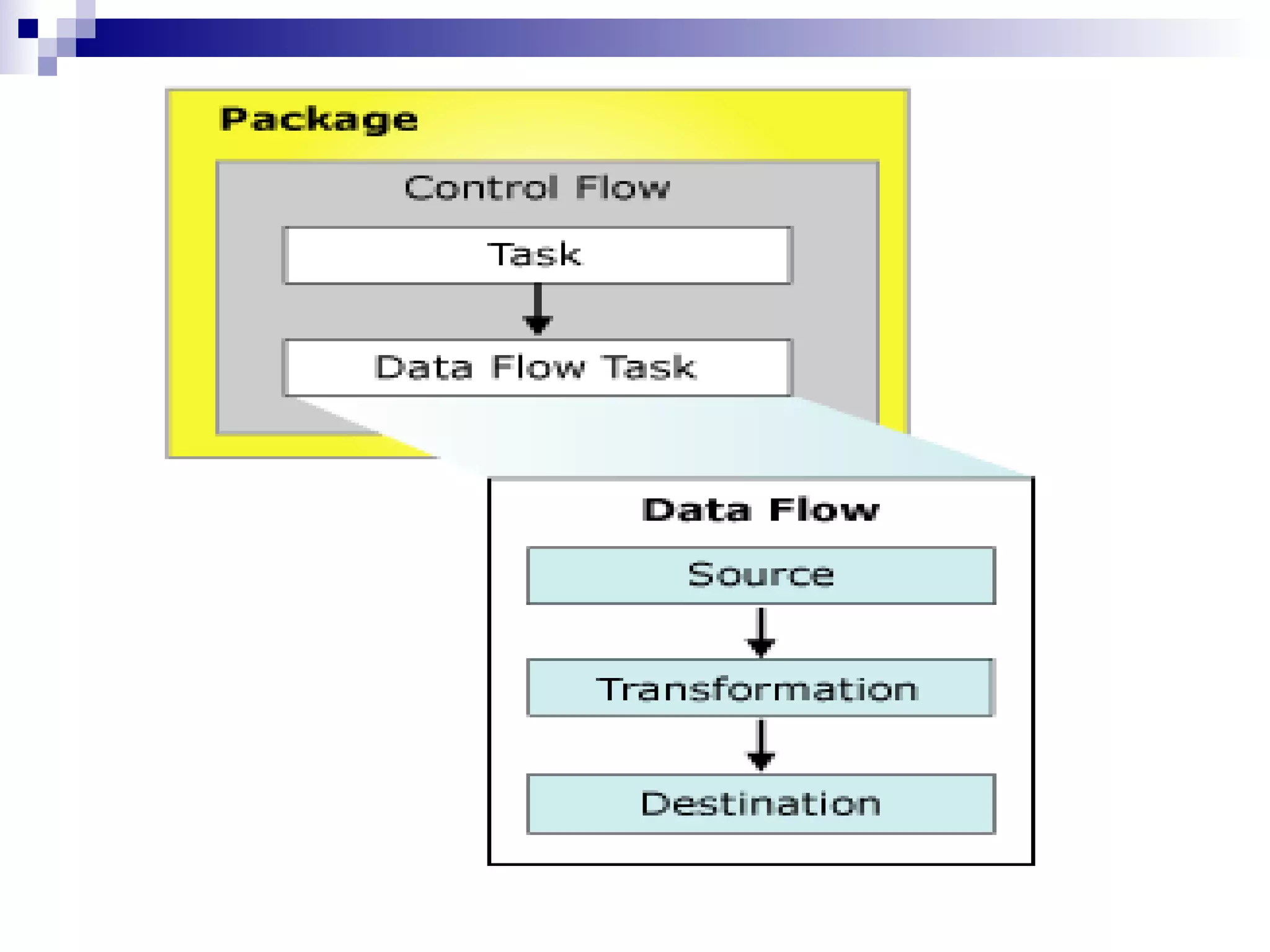
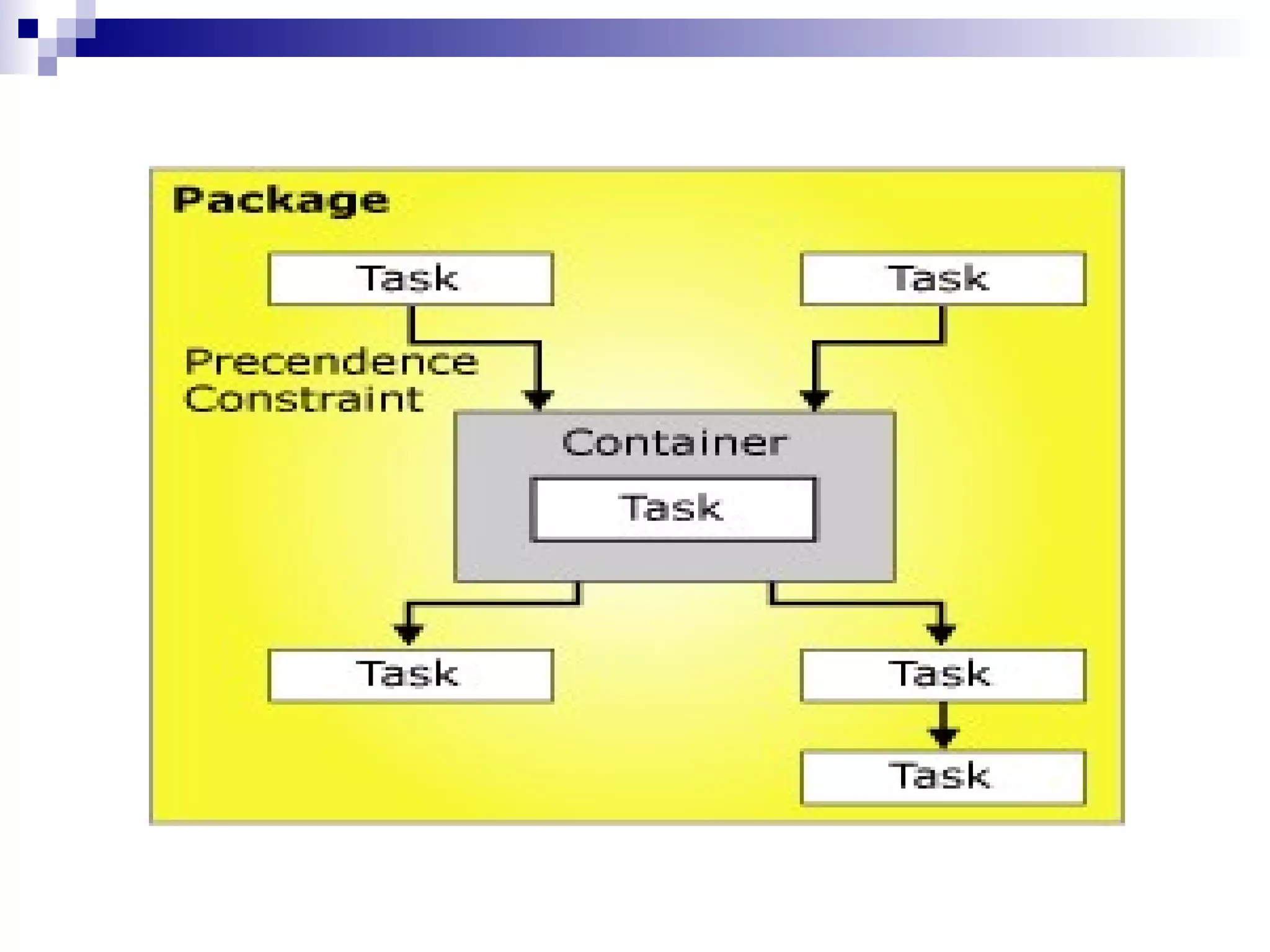
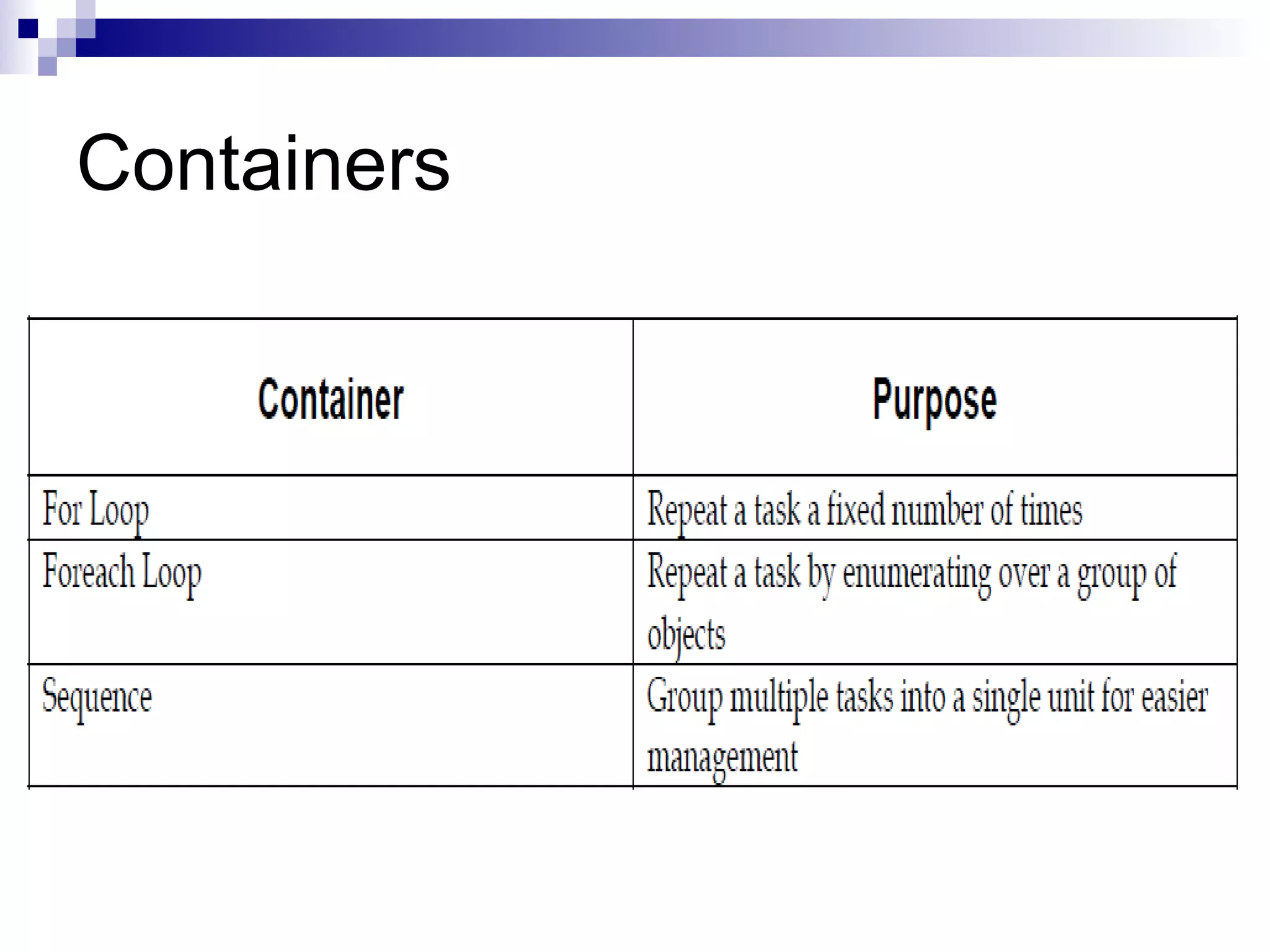
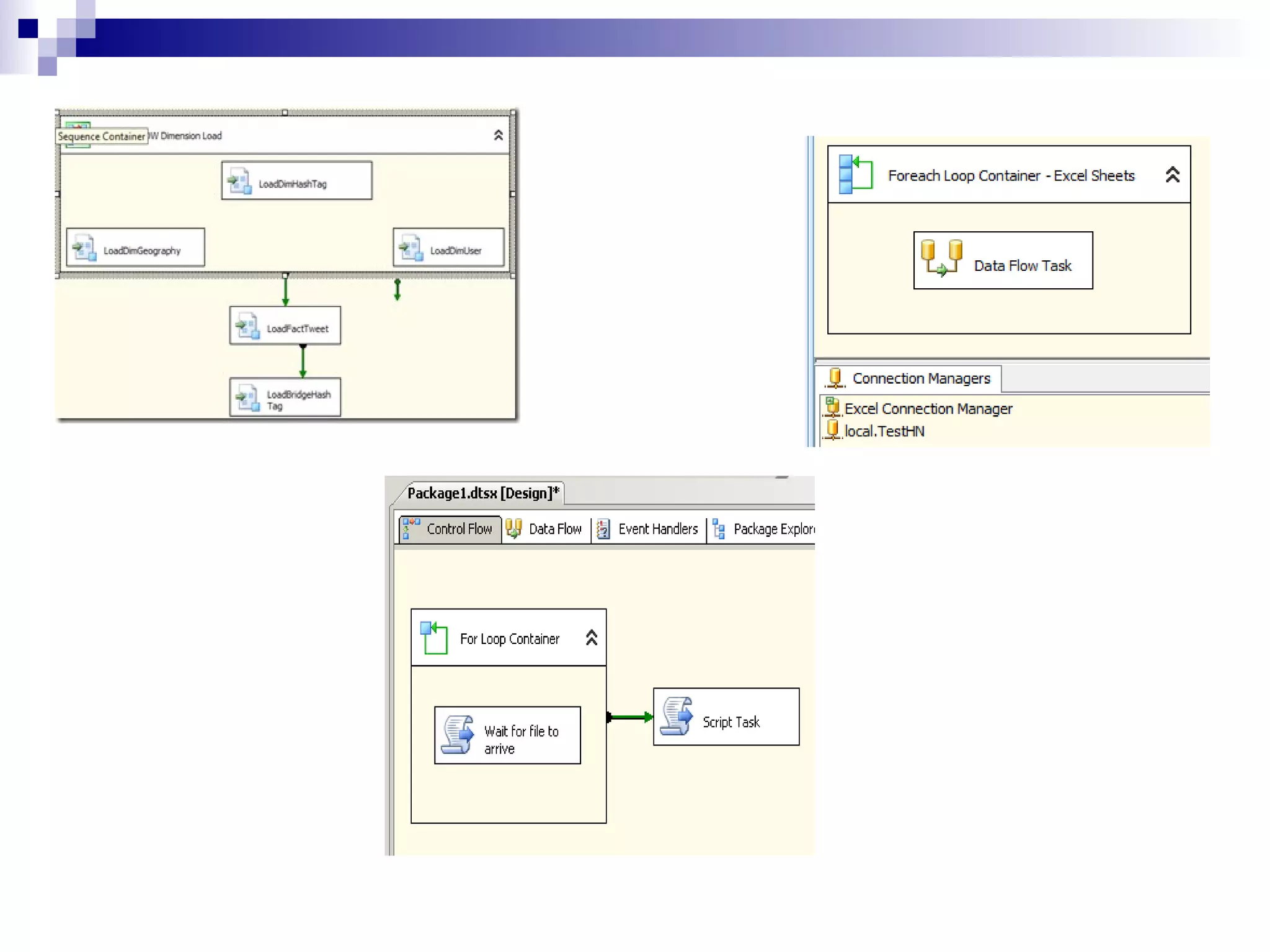
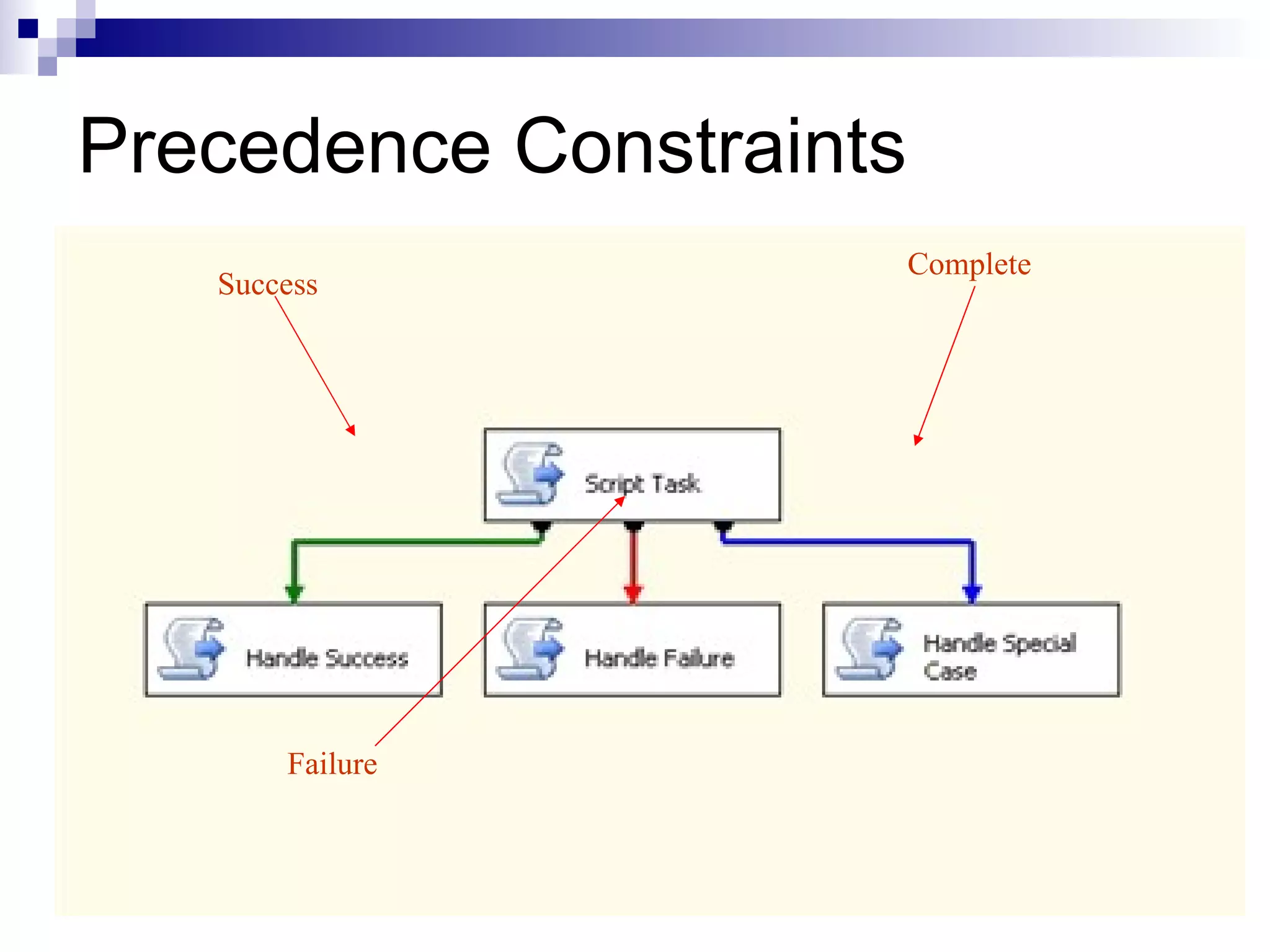
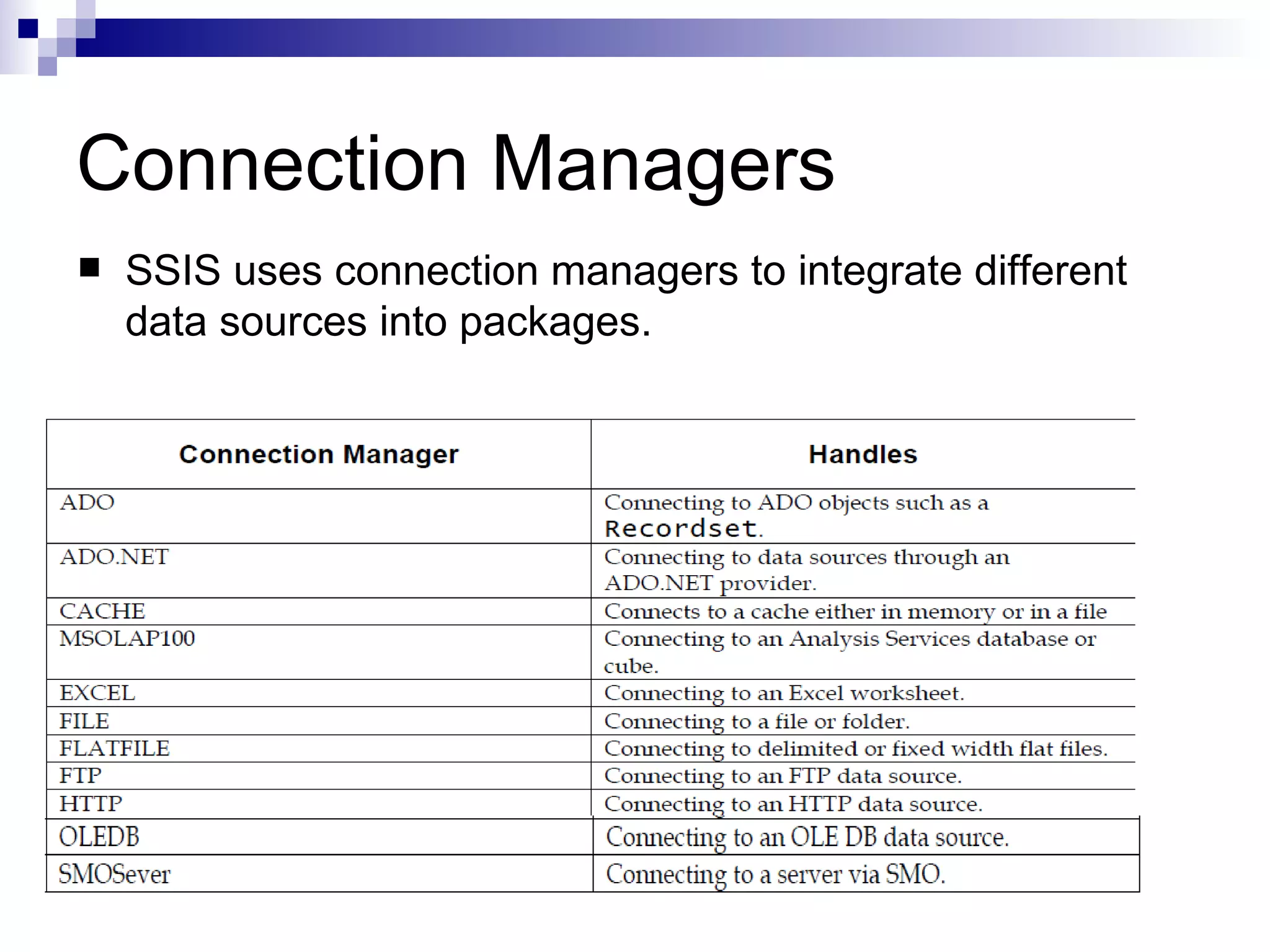
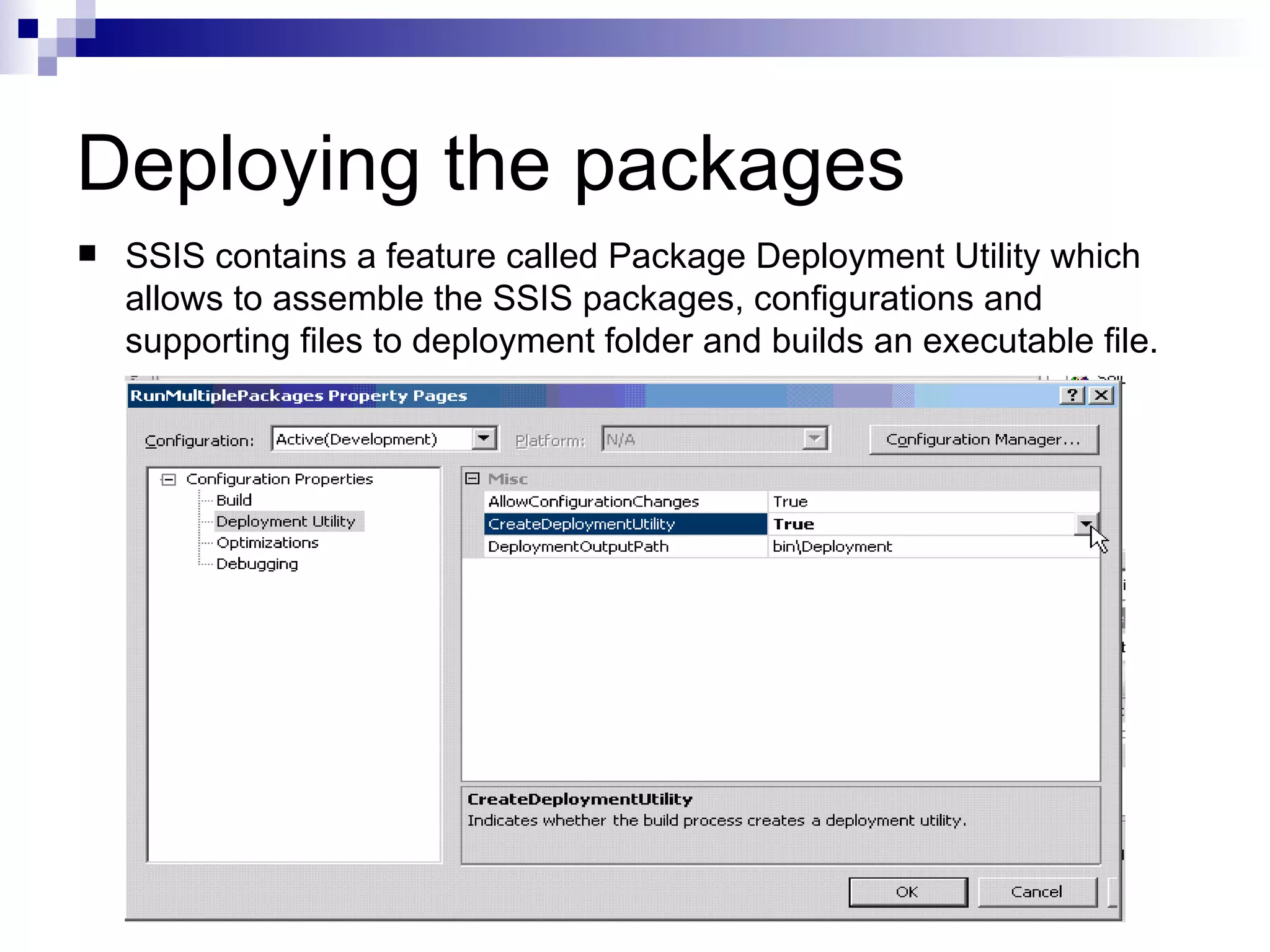
SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) is a platform for building extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) packages and other data integration tasks. SSIS packages contain graphical tasks and workflows that can be developed using Visual Studio tools and debugged. Packages integrate various data sources, handle data flows between sources and destinations with transformations, and include features for logging, error handling, restarting failed executions, and configuring variables and parameters.