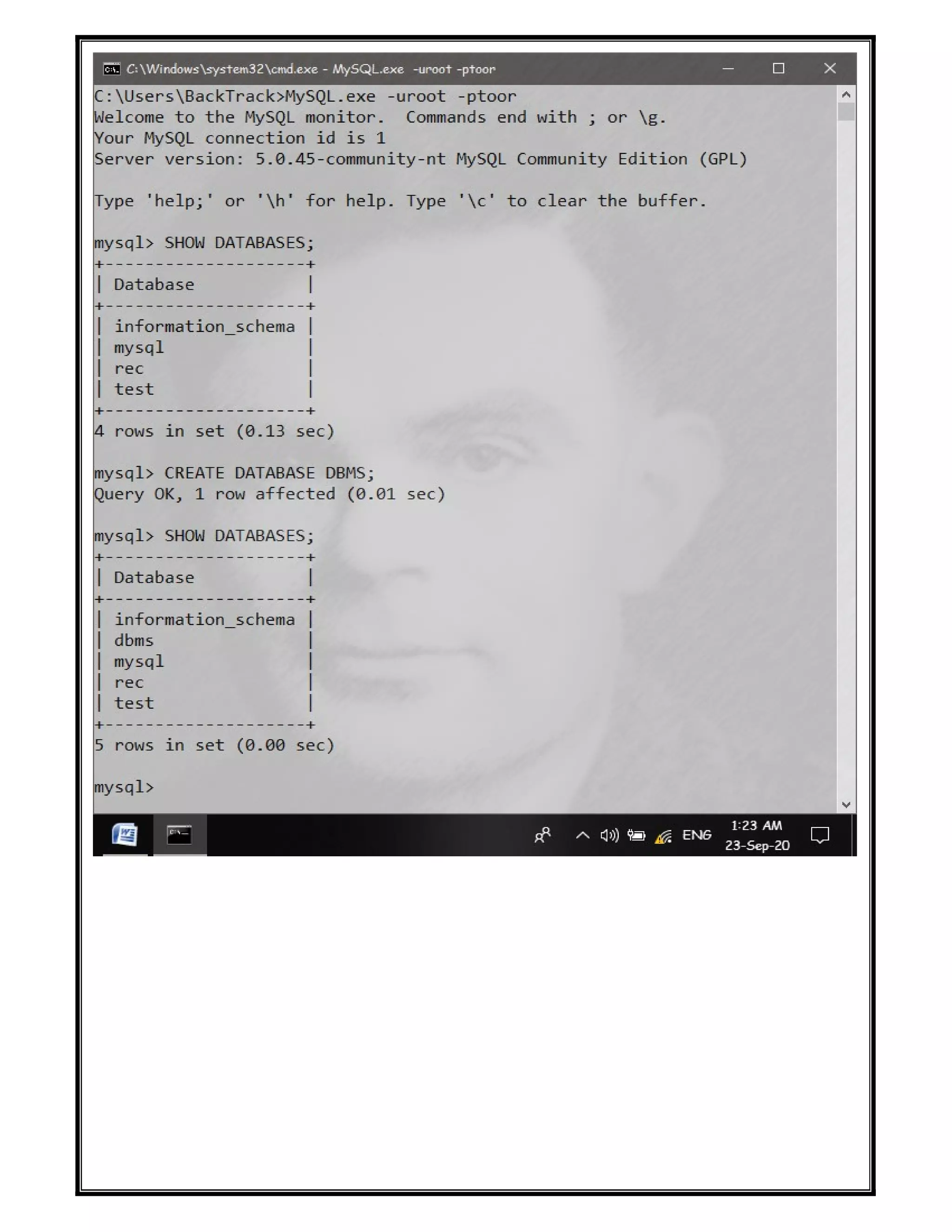
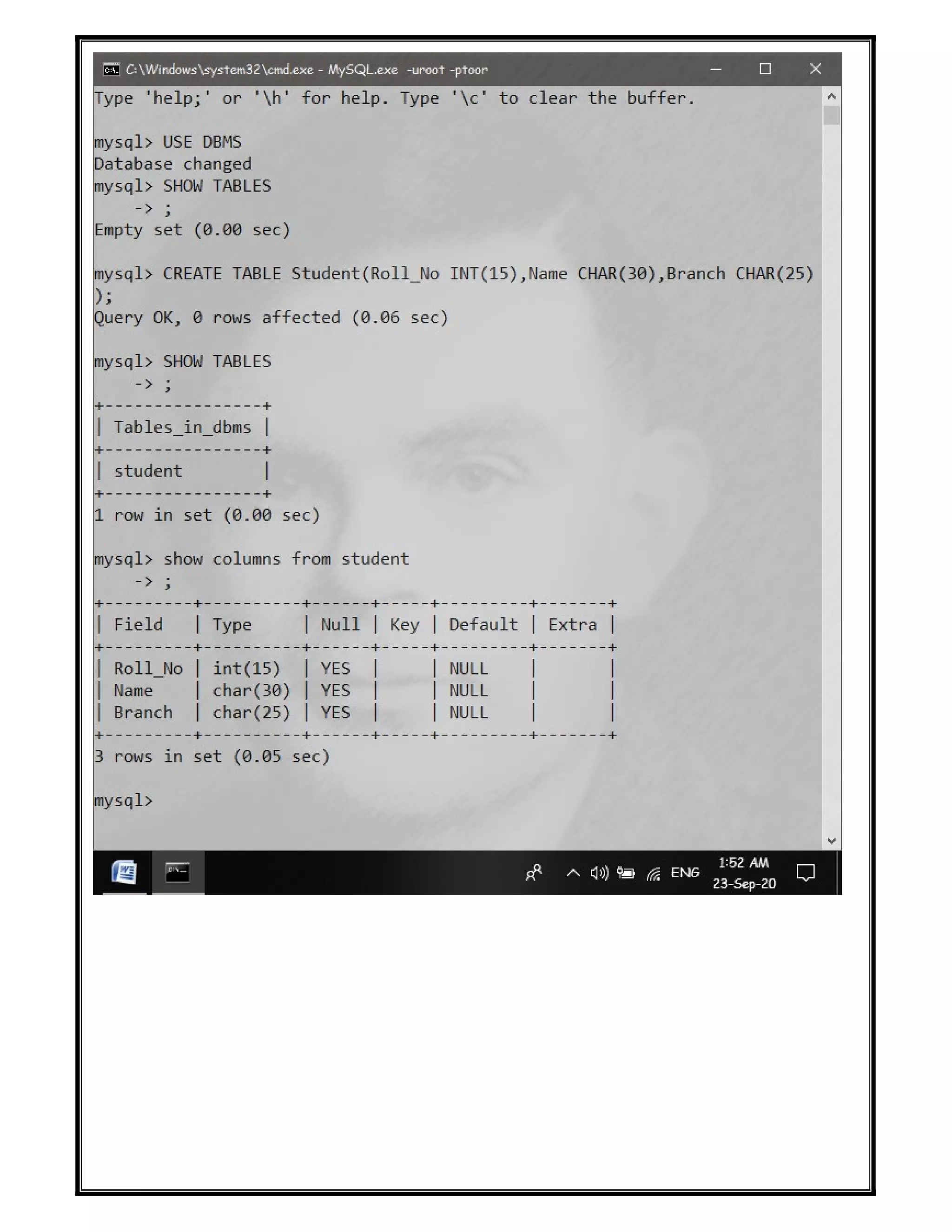
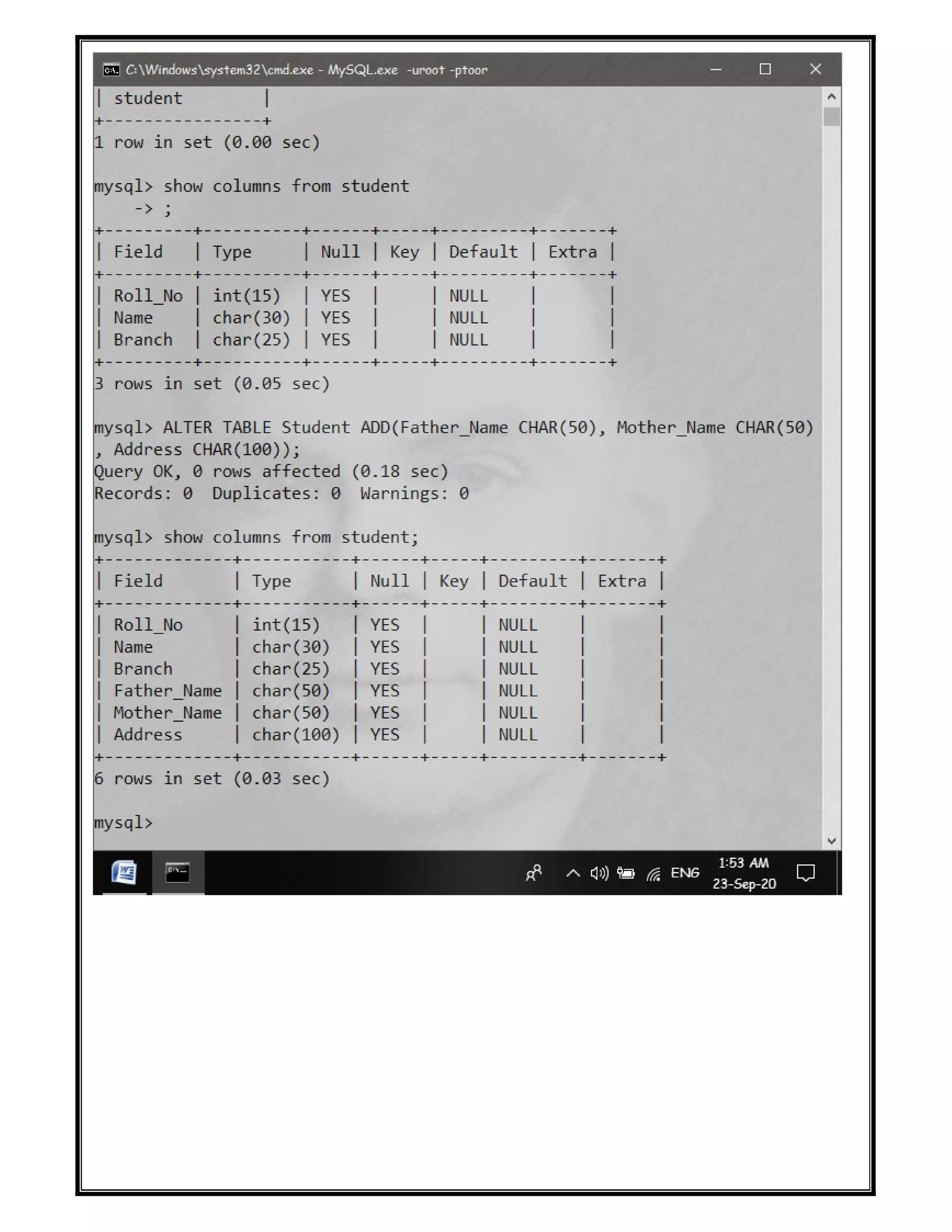
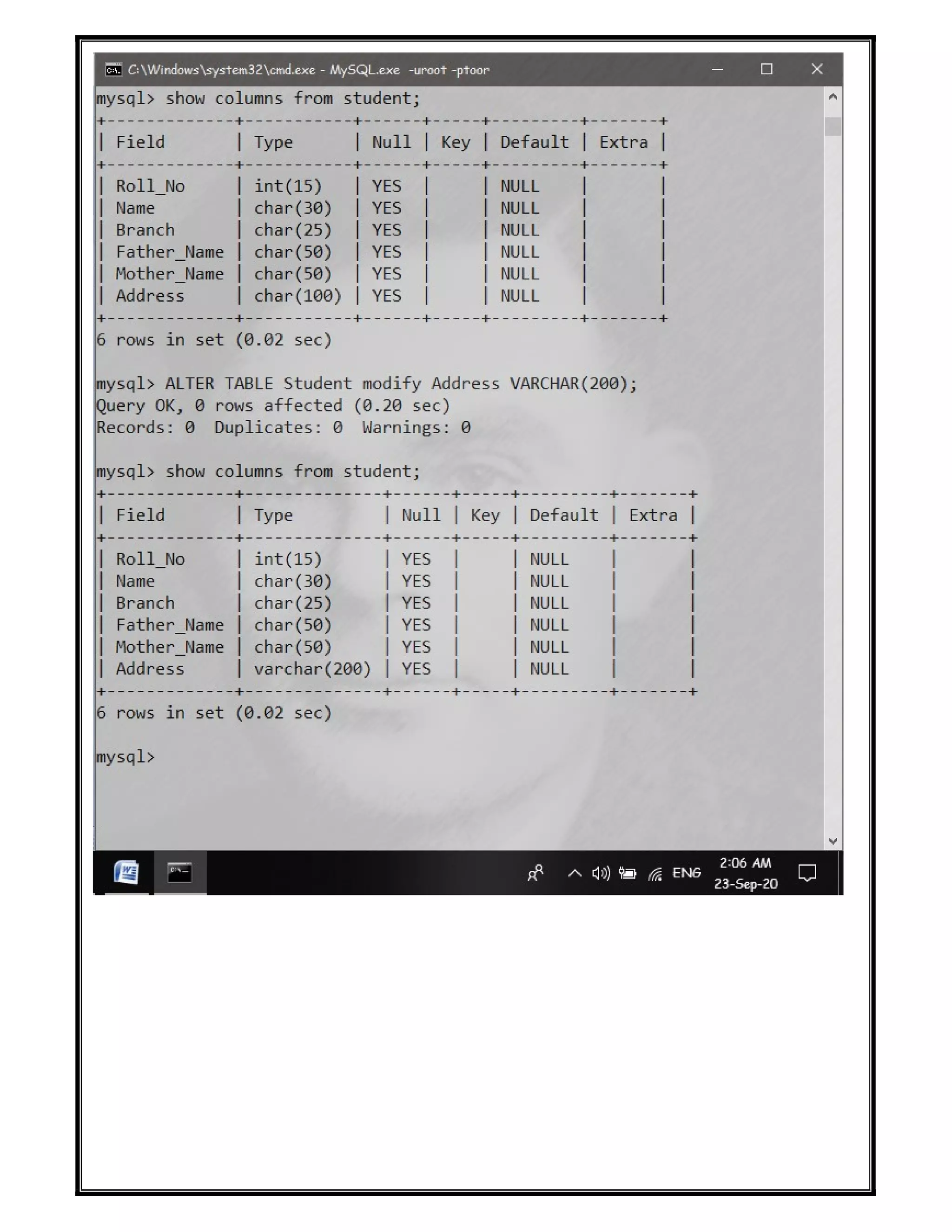
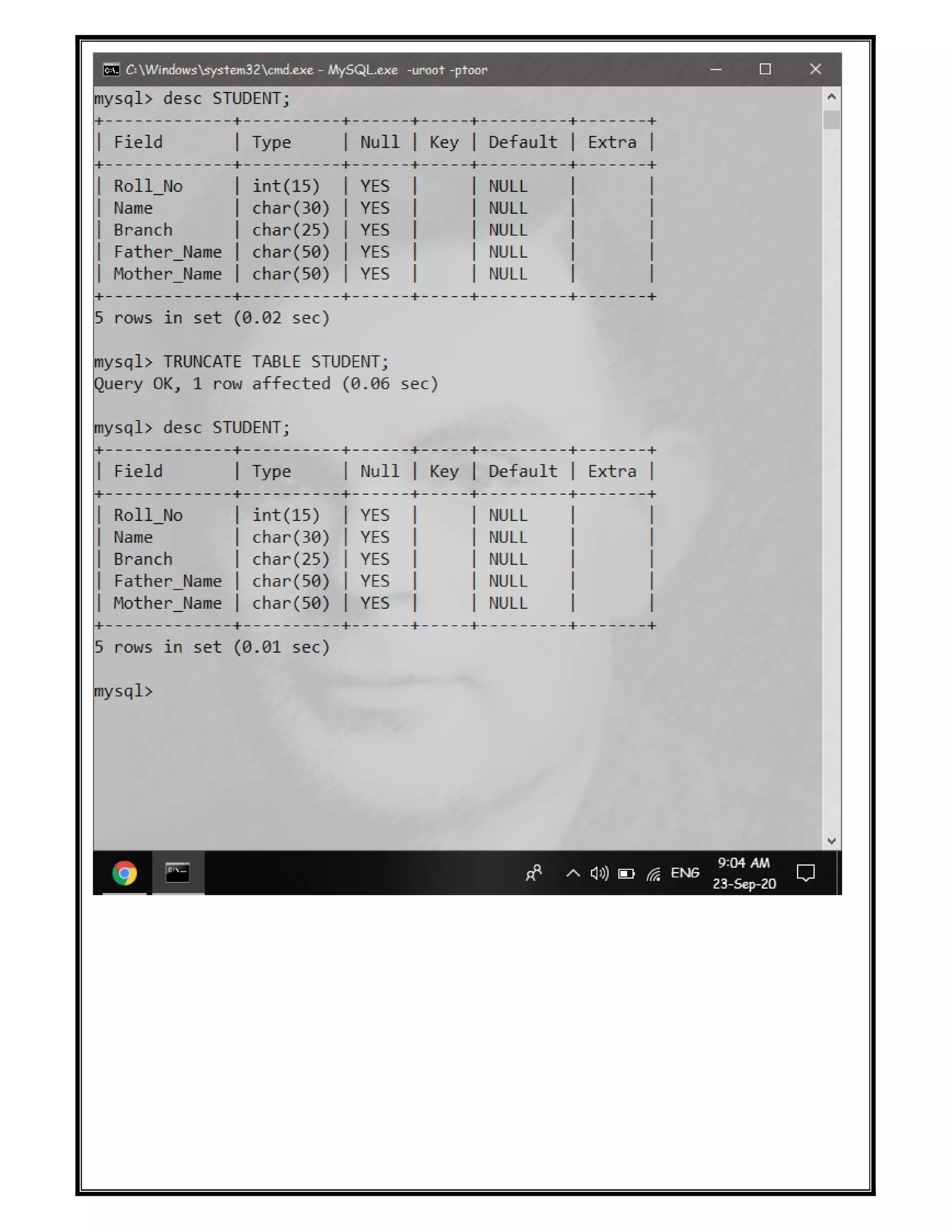
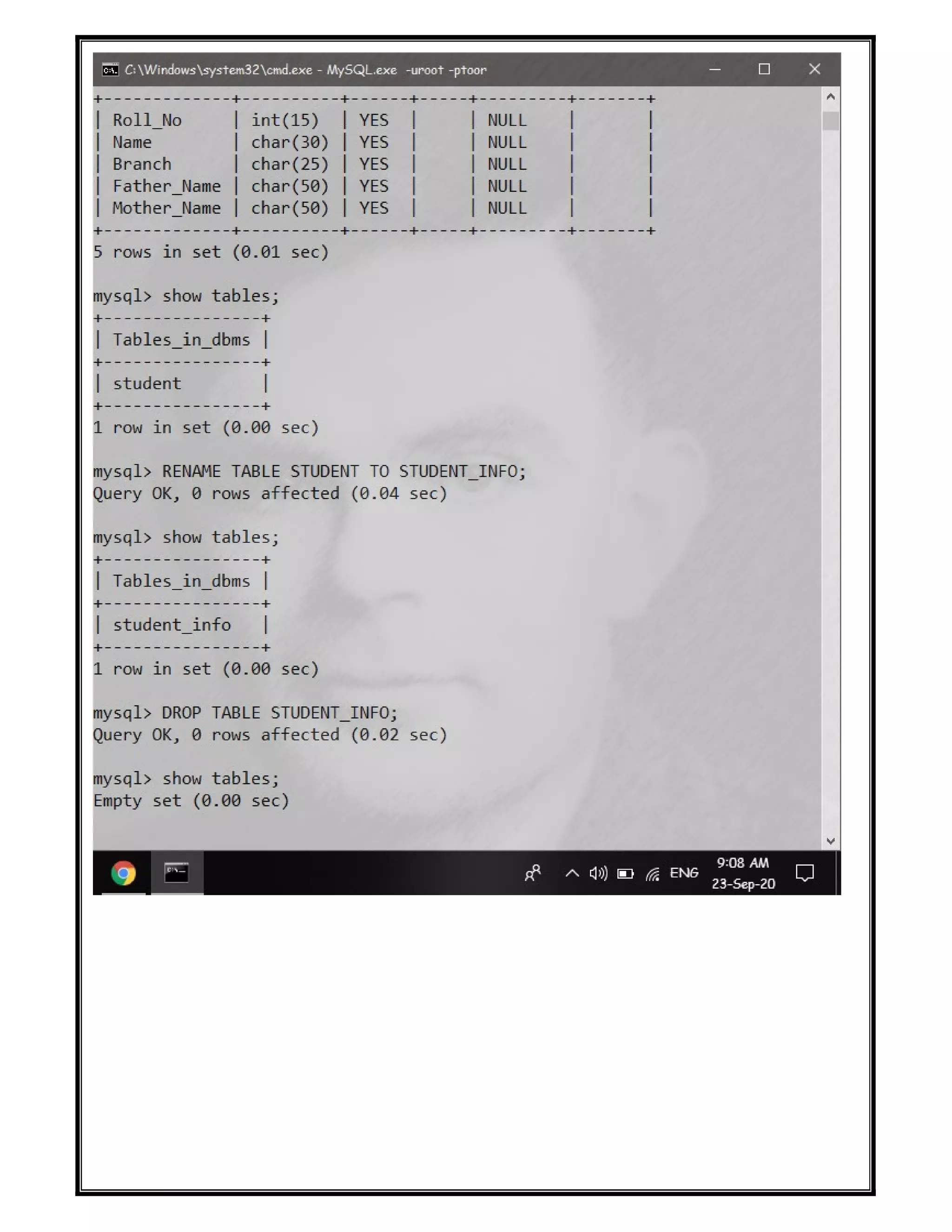
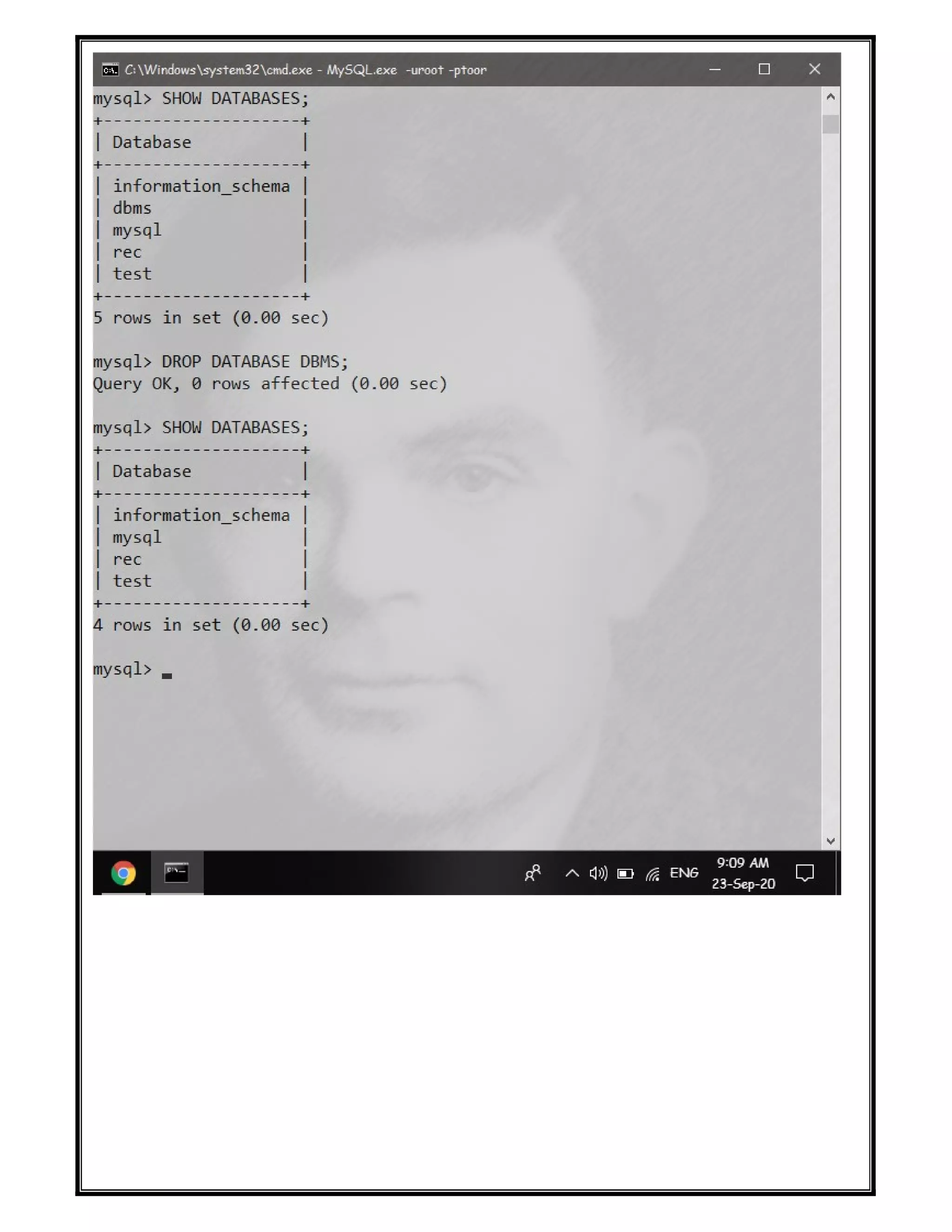
The document discusses various SQL DDL commands: - CREATE command is used to create databases and tables. CREATE DATABASE creates a database and CREATE TABLE defines columns and data types. - ALTER command modifies table structures by adding/dropping columns or changing column properties. - TRUNCATE quickly empties a table without deleting the structure. - RENAME sets a new name for an existing table. - DROP completely removes a table or database, deleting the structure and all data.